Have you ever wondered what it would be like to have complete control over your dreams? To be able to fly, explore ancient civilizations, or even meet fictional characters? These experiences can become a reality through the intriguing phenomenon known as lucid dreaming. Lucid dreaming allows individuals to become aware that they are dreaming while in the midst of a dream, providing them with the ability to actively participate and manipulate the dream plot. It is a fascinating topic that has captured the interest of scientists, psychologists, and individuals seeking to explore the depths of their minds. In this article, we will delve into the science behind lucid dreaming, uncovering the mysteries surrounding this phenomenon and exploring its potential applications. So, put on your dreamer’s cap, and let’s embark on an adventure into the realm of lucid dreaming.
The Basics of Lucid Dreaming

Lucid dreaming is a fascinating phenomenon that allows individuals to become conscious and aware within their dreams. This means that while dreaming, one can recognize that they are in fact in a dream state and actively engage with the dream environment. It is a state where the boundaries between imagination and reality become blurred, and the possibilities are limitless. One of the common techniques used to induce lucid dreams is reality checking. This involves regularly questioning the reality of one’s surroundings, looking for inconsistencies or anomalies that signal a dream state. By developing the habit of questioning reality, individuals increase their chances of achieving lucidity in their dreams. Another effective technique is keeping a dream journal, which involves recording dreams upon waking up. This practice helps to enhance dream recall and can also reveal recurring dream patterns, which can be used as cues for lucidity. Lucid dreaming opens up a world of exploration and adventure, allowing individuals to tap into their subconscious mind and uncover hidden depths within themselves. It can also have numerous benefits, such as enhancing creativity, improving problem-solving skills, and even contributing to spiritual growth. So, if you have ever wondered what it feels like to fly through the sky or have a conversation with your favorite fictional character, it’s time to dive into the realm of lucid dreaming and unlock the incredible possibilities that await.
1. Definition of Lucid Dreaming
Lucid dreaming, as the name suggests, refers to the state of being aware that one is dreaming while still in the midst of a dream. It is a unique phenomenon where individuals can experience a heightened level of consciousness within their dream state. In a lucid dream, the dreamer has the ability to recognize that their current experience is not happening in the physical world but is a product of their own imagination. This distinction between reality and the dream world is what sets lucid dreaming apart from regular dreaming. When lucidity is achieved, individuals can actively engage with the dream environment, manipulate the dream plot, and even exert control over their own actions within the dream. The level of lucidity can vary from a mild awareness to a fully immersive, vivid experience. Lucid dreaming has been a topic of interest and fascination for centuries, with accounts of lucid dreams dating back to ancient civilizations. In recent years, scientific research has shed light on the neural correlates and mechanisms underlying this phenomenon, providing a deeper understanding of what occurs in the brain during the lucid dreaming state. Lucid dreaming offers a gateway to explore the depths of our subconscious mind and tap into our imagination with full awareness. It opens up endless possibilities for self-exploration, creativity, and personal growth. Whether it’s using lucid dreaming as a tool for self-reflection, harnessing its therapeutic potential, or tapping into spiritual experiences, the definition and practice of lucid dreaming have captivated the curiosity of dreamers and researchers alike. To learn more about the benefits of lucid dreaming, click here.
2. History and Cultural Significance
The history of lucid dreaming stretches back thousands of years, with evidence of its practice found in ancient civilizations and across various cultures. One of the earliest recorded references to lucid dreaming can be traced back to the Hindu scriptures known as the Upanishads, which date back to around 500 BCE. These texts describe the concept of “svapna,” which refers to the state of lucid dreaming. Similarly, in Tibetan Buddhism, the practice of dream yoga involves training to become aware and in control during dreams. Indigenous cultures, such as the Aboriginal people of Australia and the Native American tribes, also have a long history of incorporating lucid dreaming into their spiritual practices. Lucid dreaming was recognized as a way to connect with ancestral spirits, gain wisdom, and receive guidance. In more recent times, the scientific study of lucid dreaming emerged in the 19th century with the work of Dutch psychiatrist Frederik van Eeden, who coined the term “lucid dream” in his 1913 paper. Since then, researchers such as Stephen LaBerge have made significant contributions to our understanding of lucid dreaming through experiments and studies. The cultural significance of lucid dreaming continues to evolve, with its practice being recognized not only for its entertainment value but also for its potential for personal growth and self-reflection. Individuals from various backgrounds are embracing lucid dreaming as a tool for exploring the depths of their psyche and gaining insights into their subconscious mind. Whether it is for spiritual growth, self-reflection, or simply the thrill of adventure, the history and cultural significance of lucid dreaming are testament to its enduring allure and relevance in today’s world. (Reference to lucid-dreaming-spiritual-growth)
3. Common Techniques to Induce Lucid Dreams
One of the keys to experiencing lucid dreams lies in utilizing various techniques that can help induce this remarkable state of awareness during sleep. Let’s explore some of the common techniques that have been found effective in triggering lucid dreams.
1. Reality checks: Reality checks involve regularly questioning your waking reality throughout the day, which can then carry over into your dreams. By establishing a habit of questioning the nature of your surroundings, you increase the likelihood of becoming aware that you are dreaming when similar situations occur in your dream world. Some popular reality checks include attempting to read text or numbers, looking at a reflection, or trying to push your finger through your palm. When these reality checks fail in your dream, they can serve as a trigger for lucidity.
2. Mnemonic induction of lucid dreams (MILD): MILD is a technique developed by Dr. Stephen LaBerge, a prominent researcher in the field of lucid dreaming. It involves setting an intention to remember that you are dreaming before falling asleep. As you drift off, repeat a phrase such as “I will become aware that I am dreaming” in your mind. By focusing your thoughts and intentions on lucidity before sleep, you enhance the chances of achieving a lucid dream.
3. Wake back to bed (WBTB): The WBTB technique involves waking up from sleep after a few hours, staying awake for a short period, and then returning to sleep. During the wakeful period, engage in activities that promote wakefulness and alertness, such as reading about lucid dreaming or practicing relaxation techniques. This technique capitalizes on the fact that REM sleep, which is associated with vivid dreaming and higher chances of lucidity, occurs more frequently towards the morning. By interrupting your sleep and then going back to sleep, you can increase your chances of entering a lucid dream.
4. Lucid dreaming supplements: Another approach to inducing lucid dreams is by using certain supplements that have been reported to enhance dream recall and lucidity. One such supplement is galantamine, which is derived from a type of flower. Galantamine has been shown to increase acetylcholine levels in the brain, a neurotransmitter associated with lucid dreaming. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any supplements, as individual reactions may vary.
By incorporating these techniques into your routine and experimenting with what works best for you, you can significantly increase your chances of experiencing lucid dreams. It is essential to remember that patience and persistence are key in developing the skill of lucid dreaming. So, keep exploring, honing your awareness, and maintaining a curious mindset as you delve into the extraordinary world of lucid dreaming. (For further exploration on the topic of self-reflection in lucid dreams, check out our article on lucid dreaming and self-reflection).
The Neuroscience of Lucid Dreaming
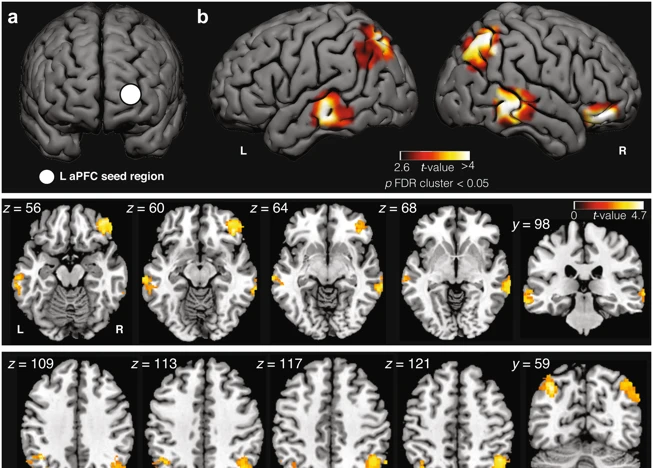
Understanding the neuroscience behind lucid dreaming offers valuable insights into how our brains navigate the complexities of dreaming. One key aspect is the role of the brain and its sleep stages. During REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, which is associated with dreaming, the brain experiences increased activity in the prefrontal cortex, the region responsible for conscious awareness and decision-making. EEG (Electroencephalography) studies have revealed distinct neural correlates of lucid dreaming, including heightened gamma wave activity and increased connectivity between different brain regions. Neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine and dopamine, also play a crucial role in facilitating lucidity within dreams. Studies have shown that drugs affecting these neurotransmitters can induce lucid dreams or increase the likelihood of experiencing them. Interestingly, there is a link between lucid dreaming and REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD), a condition where individuals physically act out their dreams. Research suggests that lucid dreaming may serve as a protective mechanism against this disorder by maintaining awareness and motor inhibition during REM sleep. Exploring the intricate workings of the brain during lucid dreaming brings us closer to unraveling the enigmatic nature of this phenomenon and its potential applications in fields such as psychology, neuroscience, and sleep medicine.
1. The Role of the Brain and Sleep Stages
The role of the brain and sleep stages is crucial in understanding and exploring the science behind lucid dreaming. To comprehend this phenomenon, we must first delve into the intricate workings of our brain during different stages of sleep. The sleep cycle consists of four main stages: 1, 2, 3, and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. During stage 1, which marks the transition between wakefulness and sleep, brain activity slows down, and we experience alpha and theta waves. Stage 2 is characterized by the onset of periods of rhythmic brain wave activity, known as sleep spindles and K-complexes. Stage 3 is the deep sleep stage, also referred to as slow-wave sleep, as it is marked by the presence of slow delta waves. It is during REM sleep that lucid dreams are most likely to occur. While the REM stage is associated with vivid dreams, what sets lucid dreams apart is the activation of the prefrontal cortex, the region of the brain responsible for logical thinking and self-awareness. This activation allows individuals to become conscious within their dreams, enabling them to recognize that they are dreaming and exert control over the dream narrative. Understanding the role of the brain and the different sleep stages provides valuable insights into the mechanisms through which lucid dreaming occurs. It opens up avenues for further research and exploration into the fascinating intersection of consciousness and dreaming.
2. EEG Studies and Neural Correlates
EEG (Electroencephalography) studies have played a crucial role in unraveling the secrets of lucid dreaming and its neural correlates. These studies involve measuring the electrical activity of the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp. By examining the brainwave patterns during different stages of sleep and dreaming, researchers have been able to identify distinct markers associated with lucid dreaming. One significant finding is the increase in gamma wave activity during lucid dreaming states. Gamma waves are fast, high-frequency brainwaves associated with heightened cognitive processing and focused attention. This suggests that lucid dreaming involves an intensified state of consciousness, where the brain is highly engaged and focused. EEG studies have revealed unique patterns of brain activity in the frontal and prefrontal cortex areas during lucid dreams. These regions are associated with self-awareness, decision-making, and cognitive control. The activation of these areas indicates the involvement of higher-level cognitive processes during lucid dreaming. Additionally, studies have shown that the level of integration and communication between different brain regions, such as the frontoparietal network and the default mode network, may play a role in facilitating lucidity. These EEG studies provide valuable insights into the neural mechanisms underlying lucid dreaming and contribute to our understanding of the conscious experience within dreams.
3. Neurotransmitters and Lucidity
Neurotransmitters play a crucial role in the experience of lucid dreaming. These chemical messengers in the brain facilitate communication between neurons, influencing various aspects of our mental processes and experiences. When it comes to lucidity, two neurotransmitters are particularly relevant: acetylcholine and dopamine.
Acetylcholine: Acetylcholine is heavily involved in the regulation of the sleep-wake cycle and plays a significant role in promoting REM sleep, the stage of sleep where most dreaming occurs. Studies have found that acetylcholine levels are elevated during REM sleep, and the release of this neurotransmitter is associated with increased brain activity and the vividness of dreams. In lucid dreaming, it is believed that higher levels of acetylcholine contribute to greater awareness and conscious control within the dream state.
Dopamine: Dopamine is another neurotransmitter that influences lucid dreaming. It is associated with reward, motivation, and pleasure-related processes in the brain. Research suggests that dopamine levels are linked to the level of self-awareness and introspection during wakefulness. In the context of lucid dreaming, dopamine may play a role in enhancing self-awareness within dreams, allowing individuals to recognize the dream state and exert control over their dream experiences.
Both acetylcholine and dopamine are essential for the occurrence of lucid dreaming, but their precise interactions and mechanisms are still not fully understood. Scientists believe that a delicate balance of neurotransmitters and neural activity is required for the optimal conditions for lucidity.
It’s important to note that the levels and balance of neurotransmitters can vary among individuals, which may explain differences in the frequency and ease of achieving lucidity in dreams. Additionally, certain medications or substances that affect neurotransmitter levels, such as certain antidepressants or recreational drugs, may influence the occurrence of lucid dreaming.
Understanding the role of neurotransmitters in lucid dreaming provides valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of this phenomenon. Further research is needed to unravel the complex interactions between these chemicals and the brain to fully comprehend the science behind lucid dreaming.
4. Lucid Dreaming and REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
There is an intriguing connection between lucid dreaming and REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD), a parasomnia disorder characterized by the absence of normal muscle atonia during REM sleep, leading to the acting out of dreams. While lucid dreaming involves being aware and in control within a dream, individuals with RBD experience the opposite – they act out their dreams involuntarily. However, there have been fascinating cases where individuals with RBD have reported lucid dreaming experiences during episodes of REM sleep.
RBD is typically associated with disturbances in the brain circuits responsible for inhibiting muscle movement during REM sleep, which results in vivid, violent, and often dangerous dream enactments. Interestingly, some patients have reported instances where they were aware that they were dreaming and were able to influence the content or outcome of their dreams, similar to lucid dreaming.
This phenomenon raises questions about the underlying neural mechanisms of both lucid dreaming and RBD. Research suggests that lucid dreaming may involve increased activation in regions of the brain associated with self-awareness, decision-making, and metacognition. On the other hand, RBD is characterized by abnormal activation in structures related to motor control during sleep.
While lucid dreaming can be a voluntary and positive experience, individuals with RBD may have overwhelming and sometimes harmful dream enactments. It is essential for individuals experiencing RBD to seek professional medical help to manage and treat the disorder effectively.
Understanding the relationship between lucid dreaming and RBD not only provides insights into the complexities of sleep and dreaming but also sheds light on the potential overlap and differences in the neural processes underlying these two phenomena. Further research in this area could contribute to advancements in our understanding of sleep disorders and consciousness.
The Psychology of Lucid Dreaming
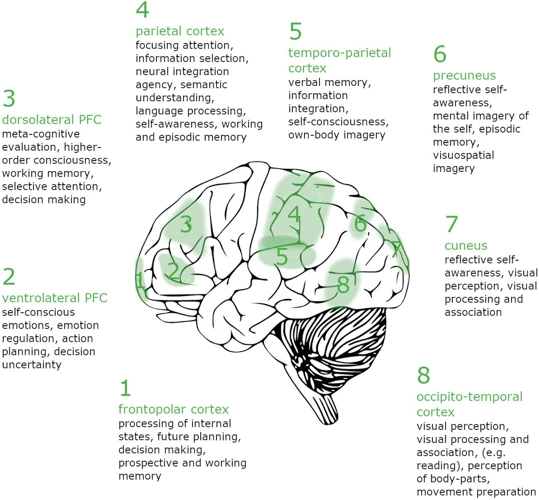
The intricacies of lucid dreaming go beyond the realm of neuroscience and delve into the fascinating field of psychology. Researchers have put forward various theories on dreaming and consciousness, seeking to understand the underlying mechanisms behind this phenomenon. One prominent theory suggests that lucid dreaming is linked to self-awareness. It is believed that the act of becoming aware within a dream reflects a higher level of consciousness and introspection. Lucid dreamers often report a heightened sense of control, agency, and even the ability to shape their dream narratives. This connection between lucid dreaming and self-awareness highlights the potential for personal growth and self-reflection within dream states. Additionally, lucid dreaming has been associated with improved emotional regulation and problem-solving abilities. By actively engaging with dreams and exploring the depths of our subconscious, we can gain insights into our emotions, fears, and desires. This can lead to a greater understanding of ourselves and contribute to psychological well-being. So, as we unravel the psychology of lucid dreaming, we uncover the endless possibilities for personal exploration and self-discovery that lie within the confines of our dreams.
1. Theories on Dreaming and Consciousness
Theories on dreaming and consciousness have long fascinated researchers and philosophers alike. One widely accepted theory is the activation-synthesis theory proposed by psychiatrist J. Allan Hobson and Robert McCarley in 1977. This theory suggests that dreams are a result of random neural firings in the brain stem, which are then interpreted and synthesized by the brain into a coherent narrative. According to this theory, dreams serve no specific purpose and are simply a byproduct of the brain’s activity during sleep.
Another prominent theory is the neurocognitive theory, which views dreaming as a cognitive process that serves several functions. This theory proposes that dreams are a unique form of consciousness that allows for the processing and integration of memories, emotions, and experiences. The neurocognitive theory suggests that dreams play a role in memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and problem-solving. Dreams are seen as a way for the brain to organize and make sense of information, thus contributing to an individual’s overall cognitive development.
On the other hand, psychoanalytic theories, particularly those put forth by Sigmund Freud, have a different perspective on dreaming. Freud believed that dreams are a manifestation of unconscious desires, conflicts, and wishes. He argued that the content of dreams represents symbolic representations of repressed thoughts and emotions. According to Freud’s psychoanalytic theory, dreams serve as a protective mechanism that allows individuals to safely express their forbidden desires and fears. Analyzing the symbolism and content of dreams can provide insight into an individual’s subconscious mind and help uncover underlying psychological issues.
Despite the variety of theories, the precise nature and purpose of dreaming and its connection to consciousness remains a subject of ongoing research and debate. While some theories focus on the neural and cognitive aspects of dreaming, others delve into the psychological and symbolic meanings behind dream content. Understanding these theories can provide valuable insights into the complex nature of the dreaming mind and its interface with consciousness.
2. The Connection Between Lucid Dreaming and Self-Awareness
One of the fascinating aspects of lucid dreaming is its connection to self-awareness. When we are engaged in a lucid dream, we have a unique opportunity to observe our own consciousness and explore the depths of our minds. This heightened state of awareness can have profound effects on our self-perception and understanding.
During a lucid dream, we become aware that we are dreaming while still in the dream itself. This realization allows us to step back from the narrative of the dream and observe it from a detached perspective. We can witness our thoughts, emotions, and actions within the dream, giving us insight into our subconscious mind.
This self-awareness within a dream can extend beyond the dream itself and impact our waking life as well. By regularly practicing lucid dreaming, individuals may develop a greater sense of self-awareness in their everyday experiences. They become more attuned to their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, resulting in a deeper understanding of themselves.
Additionally, lucid dreaming can provide a unique platform for self-reflection and personal growth. When we are aware within a dream, we have the opportunity to confront and work through our fears, anxieties, and unresolved issues. We can engage in conversations with dream characters, explore symbolic representations, and gain insights that can be applied to our waking lives.
The connection between lucid dreaming and self-awareness also extends to the exploration of identity and self-perception. In a lucid dream, individuals can experiment with different versions of themselves, exploring aspects they may be curious about or wish to develop. This exploration can lead to a greater understanding of one’s own identity and a sense of empowerment in one’s waking life.
Lucid dreaming provides a unique window into our own consciousness and self-perception. It allows us to observe and explore our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors within a dream, leading to greater self-awareness in both our dream and waking states. This heightened self-awareness has the potential to contribute to personal growth, self-reflection, and a deeper understanding of ourselves.
3. Improved Emotional Regulation and Problem Solving
Lucid dreaming goes beyond just being a thrilling adventure; it also offers potential benefits in emotional regulation and problem-solving. When we are in a lucid dream state, we have the unique ability to engage with and manipulate the dream environment consciously. This gives us an opportunity to explore and confront our emotions and fears in a safe and controlled setting. By consciously navigating challenging dream scenarios, we can gain insights into our emotional responses and learn to regulate them more effectively. This practice can be particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle with anxiety, phobias, or recurring nightmares. Lucid dreaming also provides a platform for problem-solving. Since the dream world is created by our own minds, we can use it as a playground to experiment with different solutions and perspectives. By actively engaging in problem-solving within our dreams, we can enhance our creativity and develop innovative approaches to real-life challenges. Additionally, overcoming obstacles and finding solutions in lucid dreams can boost our confidence and problem-solving skills in waking life. Lucid dreaming not only offers exciting experiences but can also contribute to personal growth and development through improved emotional regulation and problem-solving abilities.
Benefits and Applications of Lucid Dreaming

Lucid dreaming not only offers exciting and memorable experiences but also holds numerous benefits and applications. One of its therapeutic potentials lies in mental health, as it can be used to combat nightmares, phobias, and recurring traumatic dreams. By becoming aware within the dream, individuals can confront their fears and anxieties in a safe and controlled environment. Additionally, lucid dreaming can enhance creativity and skill development. Artists and musicians, for example, can use lucid dreaming to explore new ideas, gain inspiration, and practice their craft. Lucid dreaming has the potential to provide individuals with spiritual and transcendent experiences. It allows for self-reflection and the exploration of one’s inner self, leading to personal growth and a deeper understanding of one’s beliefs and values. Lucid dreaming opens up a vast array of possibilities for personal development, creativity, and self-exploration that can greatly enrich our waking lives.
1. Therapeutic Potential in Mental Health
The therapeutic potential of lucid dreaming in the field of mental health is a topic that has garnered significant attention in recent years. Researchers have been exploring how lucid dreaming can be utilized as a tool to aid in the treatment of various mental health conditions. One area of focus is post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Lucid dreaming offers individuals with PTSD the opportunity to revisit and confront traumatic experiences within the safety of a dream environment. This can allow them to gain a sense of control, process emotions, and potentially reduce the intensity of their PTSD symptoms.
Additionally, lucid dreaming has shown promise in the treatment of nightmares. Nightmares are a common symptom of conditions such as anxiety, depression, and PTSD. By becoming aware that they are dreaming during a nightmare, individuals can actively change the dream narrative and transform a terrifying experience into something more positive or empowering. This technique, known as lucid dream therapy, has been found to significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares, leading to improved sleep quality and overall psychological well-being.
Lucid dreaming has the potential to enhance mindfulness and promote self-reflection, which are integral components of many therapeutic approaches. In a lucid dream, individuals have the opportunity to explore their subconscious mind, confront fears, and gain insights into their emotions and thought patterns. This self-exploration can contribute to personal growth, increased self-awareness, and improved emotional regulation.
It is important to note that while lucid dreaming may hold promise as a therapeutic tool, it should be approached with caution and under the guidance of a trained professional. As with any intervention, individual differences and specific circumstances must be taken into consideration. Nonetheless, the growing body of research suggests that lucid dreaming has the potential to play a valuable role in the field of mental health by providing individuals with unique opportunities for emotional healing, self-exploration, and personal transformation.
2. Creativity Enhancement and Skill Development
Lucid dreaming has shown promising potential when it comes to enhancing creativity and skill development. When we are in a lucid dream, we have the ability to manipulate the dream environment in any way we desire. This creative freedom allows us to explore new concepts, ideas, and scenarios that we may not have considered before. We can engage in activities such as painting, playing music, practicing a sport, or even learning a new language, all within the depths of our dreams. This immersive experience provides a unique platform for skill development and practice. Research has shown that practicing a skill in a lucid dream can lead to tangible improvements in real life. For example, if you want to improve your basketball skills, you can visualize and practice shooting hoops in your lucid dreams, reinforcing the neural pathways associated with that skill. When you wake up, you may find that your actual basketball performance has improved. Lucid dreaming can help overcome creative blocks and stimulate out-of-the-box thinking. The imaginative nature of these dreams allows us to explore unusual scenarios, generate innovative ideas, and make connections between seemingly unrelated concepts. This boosts our creativity and problem-solving abilities in waking life. Whether you are an artist, musician, athlete, or simply want to enhance your creative thinking, lucid dreaming can be a valuable tool for unlocking your creative potential and honing your skills. So, next time you find yourself in a lucid dream, don’t hesitate to use it as a canvas for exploration, growth, and creative expression.
3. Spiritual and Transcendent Experiences
3. Spiritual and Transcendent Experiences
One of the most intriguing aspects of lucid dreaming is its potential for spiritual and transcendent experiences. For many individuals, lucid dreams provide a unique platform to explore their spirituality, connect with the divine, and experience a higher level of consciousness.
During a lucid dream, the dreamer has the opportunity to engage with their inner self, accessing deep levels of introspection and self-reflection. This can lead to profound insights and a heightened sense of self-awareness. Some people report encountering spiritual entities or guides within their lucid dreams, which they believe to be manifestations of their subconscious or higher realms of consciousness.
Lucid dreaming can also be seen as a tool for exploring various spiritual traditions and practices. Some individuals use lucid dreams to engage in meditation, visualizations, or other spiritual exercises. These experiences can provide a sense of connection to a greater spiritual reality and a deepening of personal beliefs.
Additionally, lucid dreams offer a unique space for individuals to explore concepts of life, death, and the afterlife. Some people view lucid dreaming as a glimpse into the nature of existence beyond the physical realm. They may use these experiences to gain insights into the nature of consciousness, the soul, or the interconnectedness of all beings.
Transcendent experiences can be profound and life-changing. They often involve a sense of interconnectedness with the universe, a feeling of profound bliss and joy, or a profound sense of peace and oneness. Lucid dreaming can provide a safe and controlled environment to access these transcendent states of consciousness, allowing individuals to explore and deepen their spiritual beliefs and experiences.
It is important to note that the interpretation and significance of spiritual and transcendent experiences in lucid dreaming are highly subjective and can vary greatly from person to person. Each individual brings their own beliefs, experiences, and understanding to these experiences, and the meaning derived from them is deeply personal.
Lucid dreaming offers a unique pathway to spiritual and transcendent experiences. Whether seeking to connect with one’s inner self, explore spiritual practices, or gain insights into the nature of existence, lucid dreaming provides a platform for individuals to delve into the depths of consciousness and potentially encounter profound and transformative experiences.
Practical Tips for Lucid Dreaming
When it comes to lucid dreaming, there are practical tips and techniques that can increase your chances of experiencing these extraordinary dreams. One effective method is reality checking and reality testing. By regularly questioning the reality of your surroundings throughout the day, you will develop the habit of doing the same in your dreams, increasing the likelihood of becoming lucid. Keeping a dream journal is another invaluable tool. By recording your dreams immediately upon waking, you improve your dream recall and can identify recurring themes or patterns that may serve as cues for lucidity. Additionally, there are supplements available that can potentially enhance lucid dreaming experiences. Substances like galantamine and choline have been reported to increase the likelihood of attaining lucidity and dream vividness. Utilizing advanced technology, such as lucid dreaming devices, can also aid in achieving lucidity. These devices often use techniques like detecting rapid eye movement (REM) sleep patterns to provide cues or stimulation during dreams. With these practical tips and techniques, you can embark on a journey into the world of lucid dreaming and explore the vast realms of your own imagination.
1. Reality Checking and Reality Testing
Reality checking and reality testing are fundamental techniques used in the practice of lucid dreaming. The core principle behind reality checking is to question the reality of one’s surroundings and determine whether one is in a dream or in waking life. By establishing a habit of regularly questioning the nature of reality, individuals increase their chances of becoming aware within their dreams. There are various methods of reality checking that can be incorporated into one’s daily routine. Some popular techniques include looking at written words or clocks, examining one’s hands, or attempting to push a finger through the palm of the opposite hand. These actions are rooted in the idea that the dream state often presents inconsistencies or unusual elements that can serve as triggers for lucidity.
Reality testing goes hand in hand with reality checking and involves conducting assessments throughout the day to determine whether one is dreaming or awake. These tests aim to distinguish between the ordinary experiences of waking life and the surreal and fluid nature of dreams. One common reality testing method is the “pinch test,” where individuals attempt to pinch their nose shut and breathe. If successfully done in a dream, breathing is unaffected because the physical sensation of pinching the nose is absent. Additionally, flipping a light switch or trying to read a passage of text multiple times can reveal the unstable nature of dreams, where light levels may remain constant or text may change with each glance.
In order for reality checking and reality testing to be effective, they must be performed consistently, even during waking hours. By ingraining these habits into one’s routine, the likelihood of performing these checks within a dream increases, allowing individuals to become aware of and control their dreams. It’s worth noting that the success of these techniques can vary from person to person, and consistency and patience are key. With time and practice, reality checking and testing can become second nature, leading to a higher frequency of lucid dreams and an enhanced ability to explore and manipulate the dream world. So, don’t forget to question your reality and conduct reality tests throughout the day – you never know when you might discover yourself in a dream and unlock the realm of lucid dreaming.
2. Keeping a Dream Journal
Keeping a dream journal is an essential practice for anyone interested in exploring the world of lucid dreaming. It involves recording your dreams in a journal immediately upon waking up. This simple yet powerful technique enhances dream recall and helps you become more familiar with the patterns and themes within your dreams.
When starting a dream journal, keep it next to your bed along with a pen or pencil, ensuring easy access as soon as you wake up. As you wake up, take a few moments to lay still and reflect on your dreams, allowing the details to come back to you. Then, grab your journal and begin writing down everything you remember, no matter how fragmentary or unclear it may seem. It’s important to capture as much detail as possible, including emotions, characters, locations, and any significant events or symbols.
Organize your dream journal in a way that works best for you. You can use headings or categories to categorize different dreams or themes, making it easier to analyze and identify recurring patterns. Additionally, consider using bullet points or lists to capture key elements of each dream.
Keeping a dream journal not only helps with dream recall but also serves as a valuable tool for developing self-awareness and self-reflection. As you read through your journal, you may start noticing common themes, symbols, or emotions that appear in your dreams. This insight can provide valuable clues for achieving lucidity in future dreams.
Documenting your dreams allows you to revisit and reflect on them later, providing an opportunity for personal growth and understanding. You can gain insights into your subconscious thoughts, fears, desires, and aspirations. This introspection can lead to a deeper understanding of yourself and aid in other areas of your life beyond lucid dreaming.
Keeping a dream journal is an essential and fruitful practice for those interested in lucid dreaming. By recording your dreams, you enhance dream recall, identify patterns, and gain a deeper understanding of your inner thoughts and emotions. So, grab a journal, pen, and delve into the fascinating realm of dreams.
3. Utilizing Lucid Dreaming Supplements
Many individuals who are interested in exploring the world of lucid dreaming turn to supplements as a means to enhance their dream experiences. Lucid dreaming supplements are substances that are believed to promote lucidity and vividness in dreams. One popular supplement is melatonin, a hormone naturally produced by the body to regulate sleep-wake cycles. Taking melatonin before bed can potentially increase the likelihood of having lucid dreams. Another supplement is Galantamine, an alkaloid derived from certain plants, which has shown promise in enhancing dream recall and inducing lucidity. Galantamine works by increasing levels of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is involved in memory formation and cognitive processes. Additionally, there are certain herbs and plants that are believed to have dream-enhancing properties, such as Calea Zacatechichi, also known as the “dream herb,” and Mugwort. These herbs can be consumed in various forms, including teas or supplements. While utilizing supplements can potentially enhance lucid dreaming experiences, it is important to note that their effects can vary from individual to individual. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen. Supplements should be used in conjunction with other lucid dreaming techniques, such as reality checking and keeping a dream journal, for optimal results. With proper research and caution, lucid dreaming supplements can be a valuable tool in one’s lucid dreaming journey, allowing for deeper and more vivid dream experiences.
4. Lucid Dreaming Devices and Technology
Lucid dreaming devices and technology have become increasingly popular tools for those seeking to enhance their lucid dreaming experiences. These devices aim to assist in inducing and maintaining lucid dreams by providing external stimuli or cues during sleep. One such device is the lucid dreaming mask, also known as a dream mask or a reality-testing mask. These masks are worn during sleep and are equipped with sensors that detect Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, which is the stage of sleep where most dreaming occurs. When the mask detects REM sleep, it gently flashes LED lights or plays audio cues, such as beeps or recorded messages, to remind the dreamer that they are in a dream state. This can help trigger lucidity and increase the dreamer’s awareness within the dream. Another device worth mentioning is the lucid dreaming headband, which uses electroencephalography (EEG) technology to monitor brainwaves during sleep. By analyzing the brainwaves, the headband can detect when the dreamer is in a state of REM sleep and deliver gentle vibrations, as well as play sounds or lights, to promote lucidity. These devices are often accompanied by smartphone apps or software that allow users to customize their settings and track their progress in achieving lucid dreams. While lucid dreaming devices and technology can be helpful aids, it’s important to note that lucid dreaming can also be achieved without them through various techniques and practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lucid dreaming is a fascinating realm that holds immense potential for exploration and personal growth. Through the understanding of the science behind lucid dreaming, we have uncovered the intricacies of this phenomenon, from the basics of what lucid dreaming entails to the neuroscience and psychology behind it. We have explored the various techniques used to induce lucid dreams, such as reality checking and dream journaling, and discussed the benefits and applications of lucid dreaming, including its therapeutic potential, creativity enhancement, and spiritual experiences.
By delving into the world of lucid dreaming, individuals have the opportunity to tap into their subconscious mind, unlocking a vast playground where anything is possible. Lucid dreaming allows us to harness our creativity, problem-solving skills, and self-awareness, leading to personal development and greater understanding of ourselves.
It is essential to approach lucid dreaming with patience and practice, as it can take time to achieve lucidity regularly. However, with dedication and the implementation of various techniques, anyone can experience the wonder of lucid dreaming. Whether it be for personal growth, entertainment, or self-exploration, lucid dreaming offers a unique and captivating experience.
In conclusion, lucid dreaming is a fascinating phenomenon that bridges the gap between dreaming and waking life, offering individuals the ability to actively participate and shape their dreams. The potential for personal growth, creativity enhancement, and self-exploration make lucid dreaming a topic worth exploring. So, take the first step on the journey to lucid dreaming and unlock the mysteries of your subconscious mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can anyone learn to have lucid dreams?
Yes, anyone can learn to have lucid dreams with practice and patience. While some individuals may naturally experience lucid dreams more frequently, it is a skill that can be developed and improved upon with various techniques and strategies.
2. Are there any risks or side effects associated with lucid dreaming?
Generally, lucid dreaming is considered safe and does not have any negative side effects. However, it is important to maintain a healthy sleep schedule and not solely focus on lucid dreaming, as it could potentially disrupt regular sleeping patterns.
3. Can lucid dreaming be used to overcome nightmares or recurring bad dreams?
Yes, lucid dreaming can be a powerful tool for overcoming nightmares or recurring bad dreams. By becoming aware within the dream and realizing that it is not real, individuals can change the dream narrative or confront their fears, ultimately reducing the occurrence of such dreams.
4. How long does it take to achieve lucidity in a dream?
The time it takes to achieve lucidity in a dream can vary from person to person. It may take weeks or even months of practice before experiencing the first lucid dream. Consistency, patience, and using effective techniques can help speed up the process.
5. Can lucid dreaming improve real-life skills and performance?
Yes, some studies suggest that practicing skills in lucid dreams can enhance performance in real life. This is because the brain activates similar neural pathways during both dream visualization and waking practice, leading to improved skill acquisition and performance.
6. Is lucid dreaming the same as astral projection or out-of-body experiences?
No, lucid dreaming is a state of awareness within the dream while still being asleep. Astral projection and out-of-body experiences, on the other hand, involve the sensation of leaving the physical body and exploring the world beyond.
7. Can lucid dreaming be used for self-reflection and personal growth?
Absolutely. Lucid dreaming provides a unique opportunity for self-reflection and personal growth. By exploring dream landscapes and engaging with dream characters, individuals can gain insights into their subconscious mind and work on personal development.
8. How can lucid dreaming supplements aid in achieving lucidity?
Lucid dreaming supplements, such as galantamine or choline supplements, can potentially enhance dream recall and increase the likelihood of achieving lucidity. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using any supplements.
9. Are there certain sleep schedules or routines that can promote lucid dreaming?
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, practicing relaxation techniques before bed, and implementing reality checks throughout the day can help promote lucid dreaming. Additionally, waking up after a few hours of sleep and then going back to bed can increase the chances of experiencing lucid dreams.
10. Can lucid dreaming be used for spiritual growth and exploration?
Yes, lucid dreaming can be a powerful tool for spiritual growth and exploration. Some individuals have reported having transcendental experiences, connecting with higher consciousness, or engaging in deep meditation practices within their lucid dreams.