Have you ever woken up in a cold sweat, heart pounding, after experiencing a vivid and disturbing dream? Nightmares can be incredibly distressing, leaving us feeling scared, confused, and even questioning our own sanity. But what exactly are nightmares, and why do they occur? In this article, we will delve into the depths of the human mind to explore the psychology behind nightmares. We will examine the nature of nightmares, their possible causes, the symbolism hidden within our dreams, the impact they can have on our mental health, and most importantly, we will provide practical strategies to cope and find relief from these unsettling nighttime experiences. So if you’re ready to unravel the mysteries of your darkest dreams, let’s embark on this journey together.
The Nature of Nightmares

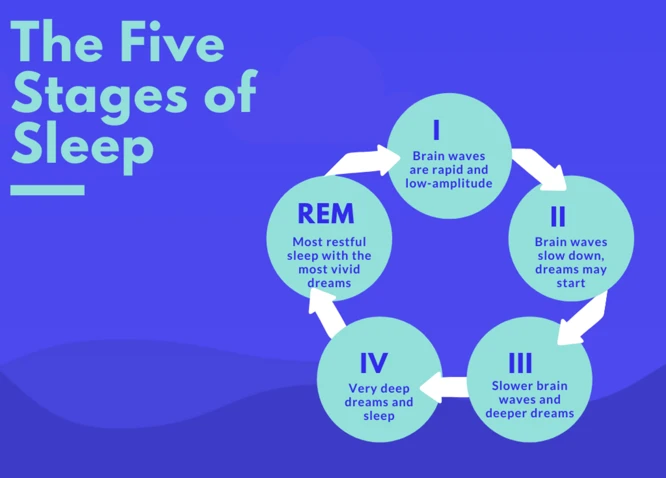
Nightmares are unsettling dreams that can leave us feeling terrified, anxious, and shaken to our core. They often occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, which is when our brains are most active and dreams are most vivid. Unlike regular dreams, which can be fantastical or nonsensical, nightmares tend to be intense and disturbing in nature. They can involve vivid images of danger, threat, or personal harm, and may elicit strong emotions such as fear, helplessness, or despair. Nightmares can vary in length and frequency, with some individuals experiencing them occasionally while others suffer from recurrent or chronic nightmares. Some individuals can recall the details of their nightmares with vivid clarity, while others may only remember the intense emotions they felt upon waking. Nightmares can have a profound impact on our quality of sleep and overall well-being, often leaving us feeling fatigued, anxious, and on edge during the day. It is important to note that nightmares are a natural and common occurrence across all age groups, from childhood through adulthood. However, the significance and interpretation of nightmares can vary depending on cultural and personal beliefs. Understanding the nature of nightmares is the first step toward unraveling their psychological intricacies and finding effective coping strategies to manage them.
Definition and Characteristics
Nightmares can be defined as highly distressing and vivid dreams that evoke intense emotions such as fear, horror, or anxiety. These dreams often contain elements that are threatening, dangerous, or traumatic in nature. Unlike regular dreams, nightmares can leave a lasting impression upon waking, with individuals able to recall the details of the dream, including specific images, scenarios, and emotions. The characteristics of nightmares can vary from person to person, but some common features include a sense of helplessness or being trapped, a feeling of impending doom, and themes of being chased, attacked, or experiencing a life-threatening situation. Nightmares can also be accompanied by physical manifestations such as sweating, rapid heart rate, or even waking up in a state of distress. It’s important to note that nightmares are different from night terrors, which are characterized by sudden, intense episodes of fear or terror during sleep that typically occur in children. While nightmares can be unsettling, they are a normal part of the sleep cycle and most individuals experience them at some point in their lives. However, when nightmares become frequent or significantly disrupt daily functioning, it may be an indication of an underlying issue or trauma that may require professional intervention. It’s important to seek support and guidance if nightmares persist and cause significant distress. If you’re interested in learning more about nightmares in the context of trauma, you can refer to our article on nightmares and trauma.
The Role of Dreams and Nightmares in Psychology
Understanding the role of dreams and nightmares in psychology is crucial for unraveling the complexities of the human mind. Dreams, including nightmares, have long fascinated psychologists and researchers, as they offer a window into the unconscious and the inner workings of our psyche. One prominent theory is that dreams, including nightmares, serve as a way for our mind to process and work through emotions, experiences, and conflicts that we may not be consciously aware of. According to Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic theory, dreams, including nightmares, represent the fulfillment of unconscious desires and wishes. He believed that nightmares could be a manifestation of repressed emotions or unresolved conflicts. Carl Jung, a renowned psychologist, introduced the concept of dream symbolism and believed that dreams, including nightmares, provide insights into our collective unconscious and universal archetypes. More modern theories suggest that dreams, including nightmares, help regulate emotions, consolidate memories, and simulate threatening situations to prepare us for real-life challenges. Studying and analyzing dreams and nightmares can provide valuable insights into an individual’s mental and emotional state, as well as potential psychological issues or unresolved traumas that may require therapeutic intervention. Understanding the role of dreams and nightmares in psychology allows us to delve deeper into the human psyche and gain a better understanding of ourselves and our experiences. So, whether you are curious about the underlying meaning of your own nightmares or interested in exploring their significance in others, delving into the realm of dreams and nightmares is a fascinating journey of self-discovery and psychological exploration. (Source: Nightmares in Children: Causes and Solutions)
Common Themes in Nightmares
Common themes in nightmares often revolve around universally distressing experiences and fears. These themes can vary from person to person, but several recurring motifs emerge in nightmares across different cultures and age groups. One common theme is being chased or pursued by a menacing figure or unknown entity. This can symbolize a feeling of being overwhelmed, pursued by past traumas, or constantly on the run from unresolved issues. Another prevalent theme is falling or being trapped, which signifies a sense of loss of control, fear of failure, or being trapped in a difficult situation. Nightmares may also feature themes of death, injury, or harm to oneself or loved ones, reflecting deep-seated anxieties about mortality and the preservation of life. Other common nightmares include experiencing supernatural or paranormal phenomena, such as monsters, ghosts, or vampires, which may symbolize our fear of the unknown or our own inner demons. Additionally, many nightmares contain themes of being unprepared for a significant event or being embarrassed or humiliated in public, reflecting our deep-seated insecurities and fear of judgment. By identifying these common themes, we can gain insight into the underlying psychological fears and anxieties that our nightmares may be trying to communicate to us. Understanding these themes can help us explore their personal significance and potentially find ways to address and resolve the issues causing distress during sleep. For individuals seeking to gain control over their nightmares, techniques such as /lucid-dreaming-control-nightmares/ may offer a means to actively engage with and influence the content of their dreams.
Causes of Nightmares

Nightmares can have various causes, and they often serve as reflections of our emotional and psychological states. One of the key factors that contribute to nightmares is emotional distress. When we experience heightened emotions such as fear, anxiety, sadness, or anger during our waking hours, these intense feelings can manifest in our dreams as nightmares. Additionally, traumatic experiences and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can play a significant role in the occurrence of nightmares. Individuals who have experienced trauma may relive their traumatic events through nightmares, which can lead to further distress and sleep disturbances.
Stress and anxiety are also common culprits behind nightmares. When our stress levels are high, whether due to work pressures, relationship issues, or other life challenges, our dreams may become more vivid and unsettling. Substance abuse, such as alcohol or drug use, can also contribute to nightmares. These substances can disrupt our sleep patterns and affect the quality of our dreams.
It’s worth noting that certain medications, particularly those that influence the central nervous system, can potentially trigger nightmares as a side effect. This includes medications used for the treatment of depression, anxiety, and even some blood pressure medications. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect that your nightmares are linked to a medication you are taking.
While these are some common causes of nightmares, it’s essential to recognize that each individual may have their unique triggers. Exploring the underlying causes of your nightmares may require self-reflection, therapy, or even medical intervention. By identifying and addressing the root causes, you can begin to take steps toward finding relief and improving the quality of your sleep.
Emotional and Psychological Factors
Emotional and psychological factors play a significant role in the occurrence of nightmares. Our emotions and mental state can influence the content and intensity of our dreams, leading to the development of nightmares. Here are some key factors that contribute to nightmares:
1. Anxiety and Stress: High levels of anxiety and stress can disrupt the brain’s normal sleep patterns, making us more prone to experiencing nightmares. Stressful life events, such as work pressures, relationship problems, or financial difficulties, can trigger nightmares as our subconscious mind tries to process and deal with the emotional turmoil.
2. Traumatic Experiences: Individuals who have experienced trauma, such as physical or emotional abuse, accidents, or warfare, may be more susceptible to nightmares. These traumatic events can leave a lasting impact on our subconscious mind, manifesting as nightmares that reflect the distressing experiences.
3. Emotional Disturbances: Depression, grief, and other emotional disturbances can also contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. These disrupted emotions can surface in our dreams, creating unsettling and distressing scenarios that may reflect our inner struggles and unresolved issues.
4. Sleep Disorders: Certain sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or insomnia, can increase the likelihood of nightmares. Disruptions in the sleep cycle and quality of sleep can affect the brain’s ability to regulate dreams, leading to more frequent and vivid nightmares.
5. Personality Traits: Certain personality traits, such as being highly imaginative or sensitive, may make individuals more prone to nightmares. These traits can make individuals more receptive and empathetic, leading to heightened dream experiences.
It’s important to note that while emotional and psychological factors can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares, they do not necessarily indicate a mental health disorder. However, if nightmares persist and significantly impact daily functioning, it may be beneficial to seek professional guidance and support to address any underlying psychological issues.
Traumatic Experiences and PTSD
Traumatic experiences play a significant role in the development of nightmares, particularly in individuals with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). PTSD is a psychological condition that can occur after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event such as military combat, physical or sexual assault, natural disasters, or accidents. Nightmares are a hallmark symptom of PTSD, often involving the re-experiencing of the traumatic event during sleep. These nightmares can be incredibly vivid, realistic, and emotionally distressing, causing individuals to wake up in a state of panic or distress, with lingering feelings of fear and anxiety.
The content of nightmares in individuals with PTSD is often directly linked to the traumatic event they have experienced. For example, a war veteran may have nightmares depicting scenes of combat, while a survivor of assault may have nightmares reliving the traumatic incident. These nightmares serve as a way for the subconscious mind to process and integrate the traumatic experience. They can be seen as a form of “replay” or attempt to make sense of the overwhelming emotions and memories associated with the trauma.
It is important to note that not all individuals who experience a traumatic event develop PTSD or nightmares. The development of nightmares in the context of trauma is influenced by various factors, including the severity of the trauma, individual vulnerability, and the presence of other psychological or emotional factors. Additionally, the frequency and intensity of nightmares may vary among individuals with PTSD, with some experiencing them sporadically and others having recurrent or chronic nightmares that significantly disrupt their sleep and daily functioning.
Treatment approaches for addressing nightmares associated with trauma and PTSD often involve a combination of therapy and medication. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) are commonly used therapeutic techniques that can help individuals process and reduce the distressing effects of nightmares. Additionally, medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may be prescribed to alleviate anxiety and improve sleep quality.
It is crucial for individuals experiencing nightmares related to trauma and PTSD to seek professional help and support. Therapists and mental health professionals can provide guidance, validation, and effective interventions to help manage and reduce the impact of nightmares on overall well-being.
Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety play a significant role in the occurrence and intensity of nightmares. When we are under high levels of stress, our minds become preoccupied with worry, fear, and uncertainty. This heightened emotional and cognitive state can easily seep into our dreams, manifesting as nightmares during sleep. Stressors such as work pressure, relationship conflicts, financial difficulties, or major life changes can all contribute to increased levels of stress and subsequently lead to nightmares. Additionally, anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), can greatly influence the frequency and severity of nightmares. These conditions often involve intrusive thoughts, hypervigilance, and heightened arousal, which can continue to plague an individual even during sleep. The emotional intensity and vividness of nightmares can be particularly distressing for those already struggling with anxiety. It becomes a vicious cycle, where nightmares increase anxiety levels, which in turn creates a fertile ground for more nightmares. Addressing and managing stress and anxiety in our waking lives is crucial in reducing the occurrence of nightmares. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques can help calm the mind and promote more restful sleep. Seeking professional help from therapists or counselors specializing in anxiety disorders can also provide valuable tools and coping strategies to alleviate stress and anxiety, ultimately leading to a decrease in nightmare frequency and intensity.
Substance Abuse and Medications
Substance abuse and certain medications can also contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. Substance abuse, such as heavy alcohol consumption or drug use, can disrupt the natural sleep cycle and impact the quality of sleep. This disruption can increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Alcohol, in particular, is known to suppress REM sleep initially but then rebound during the second half of the night, leading to vivid and intense dreams, including nightmares. Similarly, certain medications, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and beta-blockers, have been associated with an increased risk of nightmares as a side effect. These medications can affect neurotransmitters and brain activity, potentially altering the content and intensity of dreams. It is important to note that not everyone who abuses substances or takes these medications will experience nightmares, but these factors can increase the likelihood. If you suspect that your nightmares are related to substance abuse or medication, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance and support. They can assess your situation, provide appropriate recommendations, and make adjustments to your treatment plan if necessary. By addressing the underlying substance abuse or adjusting medication dosage, it may be possible to alleviate the frequency or intensity of nightmares. It is important to prioritize your overall well-being and seek the necessary help to address any substance abuse issues or adverse effects from medications.
Understanding Dream Symbolism

Dreams are not always straightforward representations of our conscious thoughts and experiences; often, they are veiled in symbolism and metaphor. Understanding dream symbolism is key to unraveling the deeper meanings behind our dreams, including nightmares. There are various theories and approaches to interpreting dream symbolism, each providing unique insights into the unconscious mind.
1. Freudian Interpretation:
Sigmund Freud, the father of psychoanalysis, believed that dreams were the windows to the unconscious. He proposed that dreams were the manifestation of repressed desires and unfulfilled wishes. According to Freud, dream symbols represented latent content that needed to be decoded to reveal hidden desires or conflicts. For example, dreaming of snakes could symbolize sexual energy or hidden fears.
2. Jungian Analysis:
Carl Jung, a renowned Swiss psychiatrist, expanded on Freud’s theories and developed his own approach to dream analysis. Jung focused on the collective unconscious, which he believed contained archetypes or universal symbols shared by all humans. He suggested that dreams were a way for the unconscious to communicate important messages to the conscious mind. Jungian analysis involves exploring the personal and collective symbolism within dreams to gain a deeper understanding of one’s psyche.
3. Modern Symbolism Theories:
In addition to Freudian and Jungian theories, modern psychologists and dream researchers have developed their own interpretations of dream symbolism. These theories emphasize the individual’s unique experiences, personal associations, and cultural influences in understanding dream symbols. They encourage individuals to explore their own meanings and interpretations of dream symbols based on their personal context and experiences.
It is important to note that dream symbols can have different meanings for different individuals. For example, while fire may represent destruction and chaos for one person, it may symbolize passion and transformation for another. Keeping a dream journal and reflecting on personal associations can help uncover the symbolic meanings specific to individual dream experiences.
By understanding dream symbolism and exploring its various interpretations, we can delve deeper into the messages and meanings hidden within our dreams, providing valuable insights into our unconscious thoughts, emotions, and desires.
Freudian Interpretation
Freudian interpretation, developed by Sigmund Freud, is a psychoanalytic approach to understanding dream symbolism, including nightmares. According to Freud, dreams, including nightmares, serve as a window into the unconscious mind and allow hidden thoughts and desires to be expressed symbolically. In Freud’s view, nightmares often represented repressed emotions and unresolved conflicts from childhood or past experiences. He believed that these dreams contained latent content, which was the hidden meaning behind the dream, and manifest content, which was the symbolic representation of the latent content.
In the Freudian interpretation, nightmares were seen as a manifestation of unconscious desires, fears, and anxieties. For example, Freud theorized that nightmares involving falling from great heights could represent a fear of failure or loss of control in waking life. Similarly, nightmares involving being chased or attacked might symbolize repressed aggression or the fear of being pursued.
Freud believed that analyzing and interpreting the symbolism in nightmares could reveal underlying conflicts and help individuals gain insight into their unconscious desires and fears. This process, known as dream analysis, involved examining the elements and themes of the dream and exploring their possible connections to the individual’s personal experiences and emotions. By uncovering the hidden meanings of nightmares, Freud believed that individuals could achieve greater self-awareness and potentially resolve the unresolved conflicts that were contributing to their distressing dreams.
It is important to note that Freud’s interpretation of nightmares has been widely debated and critiqued in modern psychology. While his ideas laid the groundwork for understanding dream symbolism, many contemporary psychologists and researchers have since developed alternative theories and approaches to dream interpretation. Nonetheless, Freud’s influence in the field of psychology continues to be significant, and his ideas still hold relevance in the study of nightmares and their deeper meanings.
Jungian Analysis
Jungian analysis, developed by renowned psychologist Carl Jung, offers a unique perspective on dream symbolism and interpretation, including nightmares. According to Jung, dreams are a manifestation of the unconscious mind and serve as a bridge between the personal and collective unconscious. In Jungian analysis, nightmares are seen as important messages from the unconscious, trying to communicate underlying emotions, conflicts, or unresolved issues. Jung believed that dreams, including nightmares, contain archetypal symbols that reflect universal human experiences and themes. These symbols can include common figures such as the shadow, the anima/animus, and the wise old man/woman. Jungian analysis suggests that exploring the meaning and symbolism within nightmares can provide valuable insights into our personal journey of individuation and self-discovery. To uncover the hidden messages within nightmares, Jungian therapists employ various techniques such as dream journaling, active imagination, and amplification. Dream journaling involves recording and reflecting on the details of the nightmare, noting any recurring symbols or themes. Active imagination involves actively engaging with the dream’s imagery and allowing the unconscious to speak through creative processes like drawing, painting, or writing. Amplification involves exploring the broader cultural and symbolic meanings behind the dream symbols. By delving into the realm of the unconscious through Jungian analysis, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their nightmares and use this knowledge for personal growth and psychological healing.
Modern Symbolism Theories
Modern Symbolism Theories offer alternative perspectives on the interpretation of dream symbols within nightmares. These theories reject the strict psychoanalytic approach of Freud and Jung and instead emphasize the subjective and individual nature of dream symbolism. One modern theory of dream symbolism suggests that dream images and symbols are influenced by personal experiences, cultural backgrounds, and even current events. According to this view, symbols in nightmares are unique to each individual and may not have universal meanings. For example, seeing a snake in a nightmare may evoke fear and anxiety for some, while for others it may represent transformation or healing. Another modern theory proposes that dream symbols are influenced by our daily experiences and emotions. It suggests that the subconscious mind uses familiar and recent events to construct dream scenarios. For instance, if someone recently experienced a stressful job interview, they may have a nightmare involving a hostile interviewer or a sense of being trapped in a daunting situation. These modern symbolism theories highlight the importance of personal context and interpretation when analyzing nightmares. They encourage individuals to explore their own associations and emotions connected to specific dream symbols rather than relying solely on predetermined interpretations. By paying attention to the unique symbolism within nightmares, individuals can gain deeper insight into their subconscious fears and concerns and potentially find ways to address them in their waking lives.
Impact on Mental Health
The impact of nightmares on mental health can be significant. Frequent nightmares can disrupt our sleep patterns and leave us feeling exhausted, irritable, and unable to concentrate throughout the day. They may contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health conditions such as anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Nightmares can trigger intense emotions and distressing memories, which can further contribute to feelings of anxiety and emotional instability. Additionally, the fear of experiencing nightmares can lead to sleep anxiety or avoidance behaviors, causing a cycle of sleep deprivation and worsening mental health. The content of nightmares can also reflect our subconscious fears and worries, providing insight into underlying psychological issues that may require professional attention. It is important to address the impact of nightmares on mental health and seek support from mental health professionals if needed. Strategies such as therapy, stress management techniques, and medication can be helpful in managing the distress associated with frequent nightmares and improving overall mental well-being. It is also advisable to create a calm and relaxing sleep environment, practice good sleep hygiene, and engage in self-care activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction. Taking proactive steps to address the impact of nightmares on mental health can be crucial in finding relief and improving overall quality of life.
Effects of Frequent Nightmares
Frequent nightmares can have a significant impact on our mental and emotional well-being. The effects of these unsettling dreams can extend beyond the boundaries of our sleep, seeping into our waking lives. One of the most common consequences of frequent nightmares is sleep disturbance. Individuals who experience nightmares regularly often find themselves struggling to fall asleep or stay asleep due to the fear of experiencing another terrifying dream. This can lead to chronic sleep deprivation, fatigue, and impaired cognitive functioning during the day.
Frequent nightmares can greatly affect our emotional state. The intense emotions experienced during these dreams can linger long after waking, leaving us feeling anxious, stressed, or even traumatized. This emotional distress can negatively impact our overall mood, leading to irritability, depression, and a decreased quality of life. Additionally, recurrent nightmares can exacerbate existing mental health conditions such as anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and depression.
Nightmares can also have a profound impact on our physical health. The fear and stress experienced during these dreams can result in increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and rapid breathing, mimicking the physical response of a real-life threat. The repeated activation of our body’s stress response can have detrimental effects on our cardiovascular health, immune system, and overall physical well-being.
In addition to the immediate emotional and physical effects, frequent nightmares can also disrupt our long-term psychological development. For children, nightmares can be particularly distressing and can interfere with healthy cognitive and emotional development. They may experience difficulties with concentration, learning, and social interactions due to the persistent fear and anxiety caused by these dreams.
Recognizing and addressing the effects of frequent nightmares is crucial for our mental and physical well-being. Seeking professional help, such as therapy or counseling, can provide valuable support in managing and overcoming the impact of nightmares. By addressing the underlying causes and developing effective coping strategies, it is possible to mitigate the harmful effects and find relief from the distressing cycle of frequent nightmares.
Relationship with Mental Disorders
The relationship between nightmares and mental disorders is complex and multifaceted. While nightmares can be a symptom of an underlying mental health condition, they can also contribute to the development or exacerbation of certain disorders. Research has shown a strong correlation between nightmares and conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, depression, and even psychotic disorders.
Nightmares can be particularly prevalent in individuals with PTSD, as they often serve as a re-experiencing of traumatic events. These nightmares can be distressing and vivid, causing the individual to wake up in a state of heightened fear and anxiety. Nightmares can also contribute to the development of anxiety disorders, as the intense emotions experienced during the nightmares can spill over into waking life, leading to heightened levels of anxiety and distress.
Depression and nightmares can also have a bidirectional relationship. Nightmares can be a symptom of depression, with individuals experiencing disturbing and negative dreams that reflect their feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and despair. Additionally, recurring nightmares can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to sleep disturbances and an increased risk of developing or worsening symptoms of depression.
In the case of psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia, nightmares can be intertwined with hallucinations and delusions. These nightmares can be particularly vivid and disturbing, reflecting the individual’s altered perception of reality. The presence of nightmares in individuals with psychotic disorders can further contribute to their overall distress and impact their quality of life.
It is important to note that while nightmares can be associated with mental disorders, not everyone who experiences nightmares will develop a mental health condition. However, it is crucial to recognize the potential impact of nightmares on mental health and seek appropriate support and treatment when necessary.
If you’re interested in learning more about nightmares stemming from trauma, you can explore our article on nightmares and trauma.
Coping Strategies
Coping with nightmares can be challenging, but there are strategies and techniques that can help alleviate their impact on our mental well-being. Developing a consistent sleep routine is essential for promoting better sleep hygiene and reducing the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. This involves going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, creating a calming pre-sleep routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment. Additionally, journaling and dream analysis can be beneficial tools for understanding the underlying emotions and themes present in our nightmares. Keeping a dream journal by our bedside and writing down our dreams as soon as we wake up can help us gain insight into recurring patterns or triggers. With the help of a therapist or through personal introspection, we can analyze these dream entries for symbolic meaning and explore any unresolved emotions or conflicts that may be contributing to our nightmares. Another coping strategy is the practice of lucid dreaming, where individuals train themselves to become aware that they are dreaming, enabling them to take control and manipulate the content of their nightmares. This technique can empower individuals to confront their fears, rewrite the narrative of their nightmares, and transform them into more positive or neutral experiences. Additionally, seeking professional help from therapists specializing in trauma, anxiety, or sleep disorders can provide valuable support in managing and overcoming nightmares. Therapeutic approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) can help individuals reframe negative thought patterns, process traumatic experiences, and reduce the frequency and severity of nightmares. Remember, finding coping strategies that work for you may require some trial and error, and it’s important to be patient and persistent in your efforts to find relief from nightmares.
Maintaining a Sleep Routine
Maintaining a consistent sleep routine is crucial for managing and potentially reducing the occurrence of nightmares. An erratic sleep schedule can disrupt the balance of our sleep cycles and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Here are some key strategies for establishing and maintaining a healthy sleep routine:
1. Set a regular bedtime: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock and promotes a more consistent sleep pattern.
2. Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Engage in calming activities leading up to bedtime to signal to your body that it’s time to unwind. This may include taking a warm bath, practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation, or reading a book.
3. Create a sleep-conducive environment: Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature. Use earplugs, an eye mask, or a white noise machine if necessary.
4. Avoid stimulating activities before bed: Limit exposure to electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers, as the blue light emitted from these devices can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.
5. Avoid caffeine and heavy meals close to bedtime: Stimulants like caffeine can disrupt sleep, so it’s best to avoid consuming them in the evening. Additionally, refrain from eating heavy meals too close to bedtime as this can cause discomfort and indigestion.
6. Exercise regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can promote better sleep. However, it’s important to avoid vigorous exercise too close to bedtime, as this can increase alertness and make it harder to fall asleep.
7. Manage stress levels: High levels of stress and anxiety can contribute to the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Incorporate stress-management techniques into your routine such as practicing mindfulness, engaging in hobbies, or seeking support from a therapist.
By implementing these sleep routine strategies, you can create a more conducive environment for restful sleep and potentially reduce the occurrence of nightmares. Remember, establishing a sleep routine takes time and patience, so be consistent and give your body time to adjust.
Journaling and Dream Analysis
Journaling and dream analysis can be powerful tools for gaining insight into the underlying emotions and themes present in our nightmares. By recording our dreams in a journal, we create a space to reflect on and analyze the content of our nightmares. Here are some strategies to effectively utilize journaling and dream analysis:
1. **Keep a Dream Journal**: Start by keeping a dedicated journal or notebook by your bedside. As soon as you wake up from a nightmare, take a few moments to jot down any details you can remember. Write down the vivid images, the emotions you experienced, and any specific symbols or themes that stood out to you. Capturing the essence of your nightmare in writing can help you process the experience more effectively.
2. **Reflect on Patterns and Triggers**: Regularly review your dream journal to identify any recurring patterns or triggers in your nightmares. Look for common symbols, themes, or emotions that appear across multiple nightmares. Pay attention to any external factors, such as certain events, stressors, or changes in your life, that may have contributed to the frequency or intensity of your nightmares.
3. **Explore Symbolism and Personal Meaning**: Engage in reflective writing exercises to delve deeper into the symbolic meaning behind your nightmares. Ask yourself questions like, “What could this symbol represent in my life?” or “Does this dream mirror any unresolved issues or fears?” Analyze the emotions you felt during the nightmare and try to connect them to your waking life experiences. This process of self-reflection can provide valuable insights into your subconscious mind.
4. **Seek Professional Help**: If you find it challenging to interpret your nightmares on your own, consider seeking the guidance of a therapist or psychologist who specializes in dream analysis. They can provide a more objective perspective and help you navigate the hidden meanings behind your nightmares.
By engaging in journaling and dream analysis, you can develop a deeper understanding of the psychological factors that contribute to your nightmares. These tools can empower you to confront and process your emotions, helping you find resolution and relief from the distressing impact of your nightmares.
Therapeutic Approaches and Techniques
Therapeutic approaches and techniques play a crucial role in helping individuals cope with and overcome the distress caused by nightmares. One commonly used therapeutic approach is cognitive-behavioral therapy for nightmares (CBT-N). This technique focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and beliefs associated with nightmares. CBT-N aims to replace these negative thoughts with more positive and adaptive ones, helping individuals gain a sense of control over their dreams. Another effective technique is image rehearsal therapy (IRT), which involves consciously rewriting the content of nightmares to create a more positive outcome. This technique allows individuals to repeatedly rehearse the new, less distressing dream scenarios in their minds, ultimately influencing their subconscious and reducing the occurrence of nightmares. Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) is another therapeutic approach that can be used to address nightmares stemming from traumatic experiences. EMDR combines the use of bilateral eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation with the processing of traumatic memories, helping individuals reprocess and reduce the emotional intensity associated with these experiences. Other relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can also be beneficial in managing nightmares. These techniques promote a state of relaxation and help individuals regulate their emotions and reduce anxiety, ultimately contributing to more restful sleep. Seeking the guidance of a qualified therapist or mental health professional is recommended when exploring therapeutic approaches and techniques for nightmares, as they can provide tailored strategies based on individual needs and circumstances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nightmares are not just random or meaningless dreams. They serve a purpose in our psychological landscape, providing a window into our subconscious mind and offering valuable insights into our fears, anxieties, and unresolved emotions. By understanding the nature of nightmares, we can begin to demystify their significance and learn to navigate the realm of our dreams with greater awareness and control. While nightmares can be distressing and disruptive to our sleep and mental well-being, there are coping strategies and therapeutic approaches available to help mitigate their effects. Maintaining a consistent sleep routine, practicing journaling and dream analysis, and seeking professional help through therapy are all valuable tools in managing and finding relief from nightmares. Remember, you are not alone in your nocturnal struggles, and there is hope for a peaceful and restorative sleep. Embrace the power of understanding the psychology behind nightmares, and embark on a journey of self-discovery and healing. Sweet dreams await!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do we have nightmares?
Nightmares can be caused by a variety of factors including stress, anxiety, trauma, medications, and sleep disorders. They may also serve as a way for our subconscious mind to process and work through emotional issues or unresolved conflicts.
2. Are nightmares the same as night terrors?
No, nightmares and night terrors are distinct experiences. Nightmares occur during REM sleep and can be vividly recalled upon waking. Night terrors, on the other hand, are episodes of intense fear or terror that occur during non-REM sleep and are often associated with sleepwalking or screaming, with minimal recollection of the event.
3. Can nightmares be a symptom of a mental health disorder?
Yes, frequent nightmares can sometimes be indicative of an underlying mental health condition such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, depression, or sleep disorders. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if nightmares significantly impact your daily life.
4. Is it possible to prevent nightmares?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent nightmares, there are steps you can take to reduce their occurrence. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a calming bedtime routine, managing stress, and avoiding certain triggers like late-night meals or stimulating activities before bed can help minimize the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
5. Can medications cause nightmares?
Yes, certain medications, such as antidepressants, beta-blockers, and some sleep aids, have been known to cause nightmares as a side effect. If you suspect that your nightmares are related to medication, it is recommended to speak with your healthcare provider to explore alternative options.
6. Do children experience nightmares more frequently?
Nightmares are common in childhood, particularly during periods of cognitive and emotional development. Children may have nightmares related to fears, anxieties, or imagination. Establishing a comforting bedtime routine and addressing any underlying concerns can help alleviate the frequency and intensity of nightmares in children.
7. Can lucid dreaming help control nightmares?
Yes, lucid dreaming, which is the ability to be aware and consciously control your dreams while you are asleep, can be a useful technique to manage nightmares. By practicing lucid dreaming techniques, individuals can actively change the dream narrative and transform the terrifying elements into more positive or controllable experiences.
8. Are recurring nightmares a cause for concern?
Recurring nightmares can be distressing and may indicate unresolved psychological issues or trauma. It is important to pay attention to the patterns, themes, and emotions associated with recurring nightmares. Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can provide valuable insights and support in addressing and resolving these repeating dreams.
9. Can nightmares be a result of trauma?
Yes, nightmares are often associated with trauma and can be a way for the mind to process distressing experiences. Nightmares related to trauma can be particularly intense and may be an indication of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Seeking help from a mental health professional who specializes in trauma can be beneficial in managing these nightmares.
10. How can I cope with nightmares?
There are various coping strategies that can help alleviate the distress caused by nightmares. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation, keeping a dream journal, and engaging in therapy or counseling can all be effective ways to cope with nightmares and reduce their impact on your overall well-being.