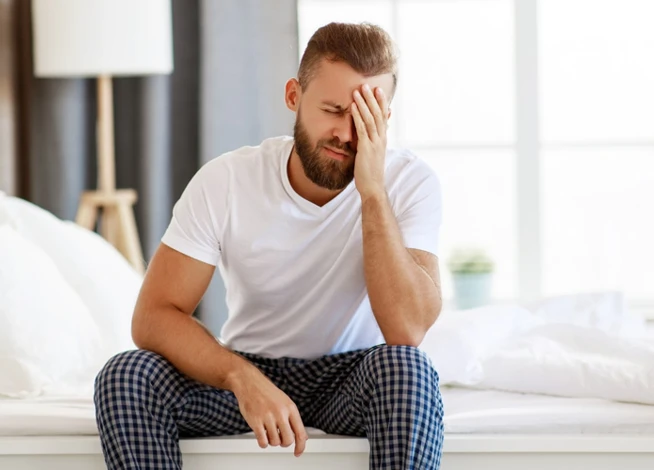
Despite being commonly associated with children, bedwetting in adults is a prevalent condition that affects a significant number of individuals, leading to embarrassment, shame, and a diminished quality of life. It is essential to understand the psychological and physical factors that contribute to adult bedwetting in order to effectively address and manage this condition. By exploring the psychological factors like anxiety, stress, depression, trauma, and psychological disorders, as well as the physical factors such as bladder dysfunction, sleep disorders, and medication side effects, we can gain a deeper understanding of adult bedwetting and develop strategies to support those who experience it. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the psychological components behind adult bedwetting and offer insights into treatment options, coping strategies, and debunking common misconceptions surrounding this condition.
The Prevalence of Adult Bedwetting

Adult bedwetting, also known as nocturnal enuresis, is often considered a taboo subject, making it difficult to determine the exact prevalence. However, studies suggest that this condition affects a significant number of adults worldwide. According to the International Continence Society, approximately 2% of adults struggle with bedwetting. That may seem like a small percentage, but when we consider the global population, it translates to millions of individuals facing this challenge. It’s important to note that these figures likely underestimate the true prevalence since many adults feel ashamed and hesitant to seek help for their bedwetting issues. Adult bedwetting can occur in people of all genders and ages, and it’s crucial to recognize that it is not a deliberate act or a sign of immaturity. Understanding the prevalence of adult bedwetting is the first step towards breaking the stigma associated with this condition, encouraging individuals to seek support, and promoting awareness in healthcare settings and communities.
Psychological Factors Contributing to Adult Bedwetting

Adult bedwetting can often be attributed to various psychological factors that contribute to the condition. Anxiety and stress play a significant role in adult bedwetting, as they can disrupt the normal functioning of the bladder and increase the frequency of nighttime urination. The fear of wetting the bed can create a vicious cycle, where the anxiety about bedwetting leads to bedwetting itself. Depression and trauma can also impact adult bedwetting, as feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and past traumatic experiences can disrupt the normal sleep patterns and bladder control. Additionally, certain psychological disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) can contribute to bedwetting in adults. It’s important to address these psychological factors through therapy, counseling, and developing coping strategies to effectively manage and treat adult bedwetting. Seeking professional help and diagnosis is crucial in understanding the root causes of bedwetting and tailoring appropriate treatment plans to address the psychological aspects associated with this condition.
Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress play a significant role in adult bedwetting. The pressures and demands of daily life can lead to heightened levels of anxiety and stress, which, in turn, can affect bladder control during sleep. When individuals experience anxiety or stress, the body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol, that can increase the production of urine and lead to more frequent trips to the bathroom. In some cases, the fear of bedwetting itself can contribute to anxiety, creating a cycle where anxiety exacerbates bedwetting, and bedwetting increases anxiety. This cycle can be overwhelming and contribute to a sense of shame and embarrassment. It is important for individuals experiencing bedwetting to address and manage their anxiety and stress levels. Techniques such as stress-reduction exercises, therapy, and engaging in activities that promote relaxation can all be beneficial in reducing anxiety and creating a calmer state of mind. Additionally, making certain dietary changes, such as avoiding certain foods and beverages that can exacerbate anxiety, may also help manage bedwetting in individuals who experience it alongside anxiety and stress.
Depression and Trauma
Depression and trauma are two psychological factors that have been found to contribute to adult bedwetting. Individuals who experience depression may have disrupted sleep patterns, which can increase the likelihood of bedwetting. Additionally, depression can lead to feelings of hopelessness and low self-esteem, further exacerbating the emotional distress caused by bedwetting episodes. Trauma, such as physical or sexual abuse, can also play a role in adult bedwetting. The experience of trauma can lead to anxiety, stress, and an increased sensitivity to certain triggers, making bedwetting more likely to occur. Trauma survivors may carry feelings of shame and guilt associated with their past experiences, which can intensify emotional reactions to bedwetting incidents. It is important for individuals with depression or a history of trauma to seek professional help and support to address these underlying psychological factors that contribute to adult bedwetting. Therapy, counseling, and support groups can provide valuable tools and resources for healing and managing the impact of depression and trauma on bedwetting.
Psychological Disorders
Psychological disorders can play a significant role in adult bedwetting, contributing to its occurrence and persistence. Conditions such as anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) have been associated with an increased risk of bedwetting in adults. Anxiety disorders can cause intense worry, fear, and excessive tension, which can disrupt the normal bladder control mechanisms. Individuals with PTSD, who have experienced traumatic events, may also be at higher risk for bedwetting due to heightened arousal and stress reactions. Additionally, OCD, characterized by intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors, can interfere with the regulation of bladder function. These psychological disorders can create a vicious cycle, as bedwetting further exacerbates the distress and psychological burden experienced by individuals. Seeking professional help and addressing the underlying psychological conditions are crucial steps in the management of adult bedwetting. Psychological therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), may be recommended to address the root causes of the bedwetting and help individuals develop coping strategies. Integrating holistic approaches, like relaxation techniques and stress management, can also be beneficial in reducing the impact of psychological disorders on bedwetting. It’s important to understand that bedwetting is not a result of personal failure or weakness; rather, it is a complex interaction of various factors that require a comprehensive approach to treatment and support.
Physical Factors Related to Adult Bedwetting

Physical factors can also play a significant role in adult bedwetting. One common factor is bladder dysfunction, where the bladder fails to empty properly or stores urine in small amounts, leading to involuntary leakage during sleep. Conditions such as urinary tract infections, bladder stones, and bladder muscle problems can contribute to bladder dysfunction. Additionally, certain sleep disorders like sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome can disrupt the sleep cycle and affect bladder control during the night. It’s important to note that some medications, such as those used to treat high blood pressure or psychiatric disorders, can also have side effects that contribute to adult bedwetting. Understanding and addressing these physical factors can help individuals find appropriate treatment and management options for their bedwetting condition. For more information on the connection between sleep disorders and bedwetting, please refer to /sleep-disorders-bedwetting-connection/.
Bladder Dysfunction
Bladder dysfunction is one of the physical factors that can contribute to adult bedwetting. The bladder plays a crucial role in storing and eliminating urine, but in individuals with bladder dysfunction, this process becomes disrupted. One common cause is an overactive bladder (OAB), where the bladder muscles contract involuntarily, causing a sudden urge to urinate. This can lead to bedwetting if the individual is unable to wake up in time to use the bathroom. Another form of bladder dysfunction is called detrusor underactivity, where the bladder muscles are weak and unable to empty the bladder effectively. This can result in incomplete emptying and increased urine production, leading to bedwetting episodes during sleep.
Additionally, bladder dysfunction can be caused by anatomical abnormalities, such as a small bladder capacity or an abnormally shaped bladder. Conditions like urinary tract infections (UTIs), bladder stones, or bladder tumors can also contribute to bladder dysfunction and adult bedwetting. In some cases, neurological conditions affecting the nerves that control the bladder, such as multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injuries, can disrupt normal bladder function.
It is important for individuals experiencing bladder dysfunction and bedwetting to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and diagnosis. Treatment options for bladder dysfunction may include behavioral interventions, such as bladder training and pelvic floor exercises, medications to relax the bladder muscles, or surgical interventions in severe cases.
Understanding the role of bladder dysfunction in adult bedwetting is essential for individuals seeking solutions and healthcare providers offering appropriate interventions. Addressing the underlying causes of bladder dysfunction can significantly improve the management of adult bedwetting and enhance the overall quality of life for those affected.
Reference:
– Foods that may contribute to bedwetting
Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders can play a significant role in adult bedwetting. These disorders disrupt the normal sleep patterns and can impair the brain’s ability to recognize bladder signals during sleep. One common sleep disorder associated with adult bedwetting is sleep apnea. Sleep apnea causes interruptions in breathing during sleep, leading to fragmented sleep and increasing the chances of bedwetting episodes. Another sleep disorder that can contribute to bedwetting is insomnia. Insomnia affects sleep quality and can lead to frequent awakenings during the night, making it difficult to maintain bladder control. Additionally, conditions like sleepwalking and restless legs syndrome (RLS) can also disrupt sleep and increase the likelihood of bedwetting incidents. It is essential for individuals experiencing bedwetting to discuss their sleep patterns and any potential sleep disorders with a healthcare professional. Treating underlying sleep disorders can help improve sleep quality and reduce the incidence of bedwetting. To learn more about the connection between sleep disorders and bedwetting, visit our article on /sleep-disorders-bedwetting-connection/.
Medication Side Effects
Medications can play a significant role in managing various health conditions, but it’s important to recognize that they can also have unintended side effects, including adult bedwetting. Certain medications, such as sedatives, hypnotics, anti-anxiety drugs, and muscle relaxants, can interfere with bladder control and contribute to nocturnal enuresis. These medications may affect the muscles in the urinary tract or increase urine production, leading to an increased risk of bedwetting episodes during sleep.
Additionally, medications that impact the central nervous system, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antiepileptic drugs, can disrupt the normal communication between the brain and the bladder, further contributing to adult bedwetting. It’s essential for individuals taking these medications to be aware of the potential side effects and to consult with their healthcare provider if they experience bedwetting as a result of their medication regimen.
Managing medication side effects related to adult bedwetting requires a collaborative approach between the individual and their healthcare provider. It may involve adjusting the dosage, switching to an alternative medication with fewer urinary side effects, or incorporating additional strategies to manage bedwetting, such as bladder training exercises or the use of protective bedding. It’s crucial not to discontinue or alter medications without professional guidance, as this can have negative consequences for overall health and wellness.
For individuals taking medications that contribute to adult bedwetting, it’s essential to coordinate care between the prescribing healthcare provider and a healthcare professional who specializes in bedwetting management. They can work together to find a balance between effectively managing the primary health condition and minimizing the impact of medication side effects on urinary control.
Addressing medication side effects as a potential cause of adult bedwetting highlights the importance of a comprehensive approach to treatment and emphasizes the need for open communication with healthcare providers. By understanding the potential impact of medications on bladder control, individuals can take proactive steps to manage bedwetting and improve their overall quality of life.
For more information on managing bedwetting in teenagers, please refer to our article on managing bedwetting in teenagers.
The Impact on Mental Health and Quality of Life

The Impact on Mental Health and Quality of Life
Adult bedwetting can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental health and overall quality of life. The constant fear and embarrassment associated with bedwetting can lead to anxiety, stress, and feelings of shame and isolation. Many adults who experience bedwetting often avoid social situations, intimate relationships, and overnight stays at friends’ or relatives’ homes due to the fear of wetting the bed and potential judgment from others. This social withdrawal can result in feelings of loneliness and depression, further exacerbating the negative impact on mental well-being. Additionally, the disrupted sleep caused by bedwetting episodes can lead to fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and decreased productivity. The constant worry about wetting the bed can also interfere with a person’s ability to relax and enjoy a restful night’s sleep, creating a cycle of anxiety and sleep disturbance. The financial burden of continuously purchasing protective bedding and laundry costs can add to the stress and strain on an individual’s budget. It is important to recognize the psychological toll that adult bedwetting can have and to provide support and understanding to those affected. By addressing the psychological impact, individuals can begin to regain their confidence, improve their mental health, and enhance their overall quality of life.
Seeking Professional Help and Diagnosis
Seeking professional help and diagnosis is crucial for adults experiencing bedwetting. If you or someone you know is struggling with this condition, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional or a specialist in urology or urogynecology. They are trained to understand and address adult bedwetting and can provide guidance and support. During the diagnostic process, the healthcare provider will conduct a thorough assessment, which may include reviewing medical history, conducting physical examinations, and performing laboratory tests. These tests may involve analyzing urine samples, checking bladder capacity, or assessing any underlying medical conditions. Keep in mind that open and honest communication is essential during the diagnosis process, as it helps the healthcare professional understand your symptoms, concerns, and specific circumstances. Remember that seeking professional help for adult bedwetting is not a sign of weakness or embarrassment. It is a brave step towards improving your quality of life and finding effective treatment options tailored to your specific needs. If you’re unsure where to start, ask your primary care physician for a referral to a specialist.
Treatment Options for Adult Bedwetting

When it comes to treating adult bedwetting, there are several options available that can help individuals manage and even overcome this condition. Behavioral therapies, such as bladder training and fluid management, are commonly recommended as first-line treatments. These approaches aim to improve bladder control and develop healthy voiding habits. Additionally, medications may be prescribed to address underlying causes, such as an overactive bladder or hormonal imbalances. Anticholinergic drugs, desmopressin, and tricyclic antidepressants are among the medications often used. Complementary approaches, such as acupuncture or hypnosis, have also shown promise in some cases. It’s important to note that the effectiveness of treatment options can vary from person to person, so it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of action. With proper treatment and support, many adults with bedwetting can significantly improve their symptoms and regain control over their bladder function.
Behavioral Therapies
Behavioral therapies are a common and effective approach to treating adult bedwetting. These therapies aim to modify behavior and establish new habits that promote continence during sleep. Here are some behavioral therapies that may be recommended for adults experiencing bedwetting:
1. Bladder training: This technique involves gradually increasing the time between bathroom visits to help train the bladder to hold urine for longer periods. A healthcare professional may create a schedule to gradually extend the intervals between voiding, helping the individual develop better bladder control.
2. Motivational therapy: This therapy focuses on boosting motivation and self-esteem by setting achievable goals and providing positive reinforcement. It may involve rewards or praise for dry nights, which can help individuals stay committed to managing their bedwetting.
3. Fluid management: Regulating fluid intake, especially in the evening hours, can be helpful in reducing the frequency of bedwetting episodes. Limiting caffeine and alcohol consumption, which can irritate the bladder and increase urine production, is also recommended.
4. Bedtime routines: Establishing a consistent bedtime routine can signal to the body that it’s time for sleep and reduce the chances of bedwetting. Going to bed at the same time each night, practicing relaxation techniques, and emptying the bladder before sleep can all contribute to better nighttime continence.
5. Alarm therapy: Bedwetting alarms are devices that emit a sound or vibration when they detect moisture, waking the individual as soon as bedwetting occurs. Over time, this can help condition the person to wake up when they need to empty their bladder, eventually leading to dry nights.
It’s important to note that these therapies may require time and patience before significant improvements are seen. It’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional who can tailor the approach to individual needs and provide guidance and support throughout the process. The success of behavioral therapies often relies on the individual’s commitment, consistency, and willingness to implement the recommended strategies. They can be particularly effective when combined with other treatment approaches, such as medications or complementary therapies.
Medications
can be a valuable treatment option for adults with bedwetting, especially when there are underlying medical conditions causing the issue. When behavioral therapies alone are not effective or practical, medications may help reduce or eliminate bedwetting episodes. One commonly prescribed medication is desmopressin, which is a synthetic hormone that mimics the effects of antidiuretic hormone (ADH). Desmopressin works by reducing the amount of urine produced during the night, allowing individuals to maintain bladder control. Another medication option is anticholinergic drugs, such as oxybutynin, which help relax the bladder muscles and increase bladder capacity. These medications can be prescribed by a healthcare professional after a thorough evaluation of the individual’s medical history and the potential benefits and risks of the medication. It’s important to note that medication should always be used under medical supervision, and regular follow-ups are necessary to monitor the effectiveness and any possible side effects. It’s also worth mentioning that medications may not provide a long-term solution and may need to be combined with other treatment approaches or lifestyle modifications to achieve optimal results.
Complementary Approaches
Complementary approaches can be valuable in the treatment of adult bedwetting, especially when used in combination with traditional therapies. These approaches focus on alternative or holistic methods that aim to address the underlying causes or contribute to the management of bedwetting symptoms. One such approach is acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Acupuncture is thought to stimulate the nervous system, releasing neurochemicals that promote relaxation and potentially improve bladder control. Another alternative therapy is hypnotherapy, which utilizes relaxation techniques and suggestive therapy to access the subconscious mind and reframe patterns of behavior. Through hypnosis, individuals may gain better control over their bladder function during sleep. Additionally, herbal remedies, such as botanical extracts and natural supplements, have been explored for their potential benefits in managing bedwetting. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any herbal remedies, as they can interact with medications or have adverse effects. While complementary approaches can be promising, it’s crucial to approach them with caution and always seek guidance from a qualified healthcare practitioner. These approaches should be seen as adjunctive therapies that complement the primary treatment plan, which may include behavioral techniques and medications.
Coping Strategies for Adults with Bedwetting

Living with adult bedwetting can be challenging, but there are coping strategies that can help individuals manage the condition and improve their quality of life. One effective strategy is managing stress and anxiety, as these psychological factors can contribute to bedwetting episodes. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or participating in hobbies can help alleviate anxiety and promote relaxation. Additionally, using protective bedding, such as waterproof mattress covers or absorbent bed pads, can provide peace of mind and protect the mattress. Seeking support from support groups or individual counseling can also be beneficial in navigating the emotional impact of bedwetting. Through these coping strategies, adults with bedwetting can gain a sense of control and find ways to minimize the impact of bedwetting on their daily lives.
Managing Stress and Anxiety
When it comes to managing stress and anxiety related to adult bedwetting, there are several strategies that can be beneficial in reducing the frequency or severity of incidents. Here are some approaches to consider:
1. Therapy and Counseling: Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can provide individuals with a safe space to discuss their feelings, fears, and concerns surrounding their bedwetting. Therapy can help identify triggers, develop coping mechanisms, and manage stress levels effectively.
2. Relaxation Techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga, can help reduce overall stress and anxiety levels. These techniques can be incorporated into a daily routine or used in moments of heightened stress or anxiety.
3. Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can have a positive impact on managing stress and anxiety. Engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, and minimizing the consumption of caffeine and alcohol can contribute to overall well-being.
4. Social Support: Sharing experiences and concerns with trusted friends, family members, or support groups can provide a sense of understanding, validation, and emotional support. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can help alleviate stress and anxiety associated with bedwetting.
5. Self-Care: Engaging in self-care activities that promote relaxation and well-being can significantly reduce stress levels. This can include activities such as taking a warm bath, practicing mindfulness, listening to calming music, or engaging in hobbies and interests that bring joy and relaxation.
Remember that managing stress and anxiety takes time and patience. It is essential to find strategies that work best for each individual’s unique needs. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance and recommendations based on the specific situation.
Using Protective Bedding
Using protective bedding can be an effective strategy for managing adult bedwetting and reducing the impact on sleep quality and daily life. Investing in waterproof mattress protectors, mattress pads, and absorbent bed sheets can help prevent damage to the mattress and bedding, as well as minimize discomfort caused by wetness. These specialized bedding products are designed to be waterproof and can provide a barrier between the individual and any potential leaks, keeping the mattress dry and preventing odors. It’s important to choose high-quality, durable materials that are easy to clean and maintain. Look for bedding that is specifically designed for urinary incontinence and offers features such as moisture-wicking properties and odor control. Additionally, using disposable or washable bed pads or absorbent underwear can provide an extra layer of protection and give peace of mind. Having protective bedding in place can alleviate anxiety and allow individuals to sleep more soundly, knowing that any accidents can be easily managed.
Support Groups and Counseling
Support groups and counseling can be invaluable resources for adults dealing with bedwetting. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide a sense of validation, comfort, and a safe space to share struggles and triumphs. Support groups, whether in-person or online, offer individuals the opportunity to exchange coping strategies, discuss treatment options, and gain emotional support from individuals who understand the challenges of adult bedwetting. These groups may also provide access to expert advice from healthcare professionals who specialize in this area.
Counseling, including individual therapy or couples/family counseling, can help individuals address the emotional impact of bedwetting and develop strategies to manage stress, anxiety, shame, or low self-esteem. Therapists can assist in reframing negative beliefs and thoughts around bedwetting, improving self-acceptance, and enhancing overall well-being. Additionally, counseling can aid individuals who have experienced trauma or have underlying psychological conditions that contribute to bedwetting. By addressing these underlying factors, individuals can work towards healing and reducing the impact of bedwetting on their mental health and overall quality of life. Support groups and counseling offer a vital support system, promoting resilience, empowerment, and a sense of belonging for adults living with bedwetting.
Living with Adult Bedwetting: Tips and Advice

Living with adult bedwetting can be challenging, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can effectively manage this condition and improve their quality of life. Here are some tips and advice to consider:
1. Managing Stress and Anxiety: Since stress and anxiety can contribute to adult bedwetting, it’s essential to find healthy coping mechanisms. Engaging in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress levels and promote better sleep hygiene.
2. Using Protective Bedding: Investing in waterproof mattress covers, mattress pads, and absorbent undergarments can provide peace of mind and help manage any nighttime accidents effectively. These products can protect bedding and make cleanup easier, reducing feelings of embarrassment and frustration.
3. Support Groups and Counseling: Connecting with others who share similar experiences through support groups or counseling can be highly beneficial. Sharing stories, tips, and advice can provide emotional support and reassurance, helping individuals feel less isolated and more empowered to manage their bedwetting condition.
4. Creating a Supportive Environment: It’s important to have open and understanding communication with loved ones about adult bedwetting. Creating a supportive and empathetic environment ensures that individuals feel safe discussing their challenges and seeking the help they need.
5. Developing a Nighttime Routine: Establishing a consistent nighttime routine can be helpful in managing adult bedwetting. This may include limiting fluid intake before bedtime, going to the bathroom before sleep, and incorporating relaxation techniques to promote better sleep quality.
It’s crucial to remember that living with adult bedwetting is not a reflection of one’s character or personal hygiene. Seeking professional help, embracing coping strategies, and creating a supportive network are key steps towards effectively managing and overcoming the challenges associated with adult bedwetting.
Creating a Supportive Environment
When it comes to managing adult bedwetting, creating a supportive environment plays a crucial role. A supportive environment can help individuals experiencing bedwetting feel understood, accepted, and encouraged to seek appropriate treatment and support. Here are some strategies for creating a supportive environment:
1. Open Communication: Establish open and non-judgmental communication channels with the individual. Encourage them to express their feelings, concerns, and experiences without fear of embarrassment or criticism.
2. Normalize the Experience: Help the individual understand that adult bedwetting is a relatively common condition and reassure them that they are not alone. Share relevant resources, stories of others who have successfully managed bedwetting, and provide accurate information to alleviate shame and isolation.
3. Empathy and Understanding: Show empathy towards the individual and understand the impact bedwetting can have on their emotional well-being. Avoid blaming or shaming them, as it can worsen feelings of embarrassment and self-esteem issues.
4. Encourage Professional Help: Support the individual in seeking professional help from healthcare providers who specialize in adult bedwetting. Encourage them to ask questions, voice concerns, and actively participate in their treatment plan.
5. Supportive Bedding: Help the individual find suitable bedding options, such as waterproof mattress protectors or absorbent pads, to manage the practical aspects of bedwetting. This can reduce the stress of potential accidents and make cleanup easier.
Creating a supportive environment is crucial in promoting understanding, acceptance, and emotional well-being for individuals with adult bedwetting. Remember, supporting someone with bedwetting requires empathy, patience, and a willingness to educate oneself about the condition. By offering a safe and supportive space, you can contribute significantly to their overall journey towards managing and overcoming bedwetting challenges.
/managing-bedwetting-teenagers/
Developing a Nighttime Routine
Developing a nighttime routine can be beneficial for adults dealing with bedwetting, as it helps create a conducive environment for better sleep and reduces the chances of accidents during the night. Here are some steps to consider when establishing a nighttime routine for managing bedwetting:
1. Consistent Bedtime: Set a regular bedtime to regulate your sleep cycle and encourage a more predictable bladder pattern. Going to bed at the same time every night can train your body to anticipate when it needs to empty the bladder before sleep.
2. Limit Fluid Intake: Be mindful of your fluid intake, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime. While it’s essential to stay hydrated, reducing the intake of fluids in the evening can minimize the likelihood of needing to urinate during the night.
3. Empty the Bladder: Make it a habit to empty your bladder right before getting into bed. This can help reduce the amount of urine in the bladder and decrease the chances of bedwetting incidents during the night.
4. Protective Bedding: Consider using /foods-and-bedwetting/protective bedding such as waterproof mattress covers or absorbent bed pads. These can provide an extra layer of protection and make cleanup easier in case of accidents.
5. Toilet Alarms: If bedwetting persists, using a toilet alarm system can be helpful. These devices emit a sound or vibration at the first sign of moisture, alerting the individual to wake up and use the bathroom. Over time, the alarm can condition the brain to respond to the sensation of a full bladder and prevent bedwetting incidents.
6. Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate relaxation techniques into your nighttime routine to help manage stress and anxiety, which can contribute to bedwetting. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or gentle stretching can help promote a calm and peaceful sleep environment.
Remember, developing a nighttime routine takes time and patience. It’s important to stick with the routine consistently to see the best results. If bedwetting persists despite implementing a routine, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.
Communicating with Loved Ones
When dealing with adult bedwetting, open and honest communication with loved ones can provide much-needed support and understanding. Here are some strategies to enhance communication in such situations:
1. Choose the right time and place: Find a quiet and comfortable environment where both parties can talk openly without interruptions or distractions. It is crucial to select a time when everyone is relaxed and in a receptive state of mind.
2. Use “I” statements: When expressing feelings or concerns, use “I” statements to avoid sounding accusatory. For example, saying “I feel embarrassed when I wet the bed” encourages empathy and understanding rather than placing blame.
3. Normalize the conversation: Let loved ones know that adult bedwetting is a common condition and not a result of laziness or lack of effort. Educate them about the various causes and treatments, emphasizing that support is essential.
4. Encourage questions and listening: Encourage loved ones to ask questions and actively listen to their concerns. Be patient and understanding, recognizing that they may have their own worries or misconceptions.
5. Offer reassurance: Reassure loved ones that bedwetting is a manageable condition. Share any progress made and discuss treatment options being pursued. It may also be helpful to mention success stories of individuals who have overcome bedwetting.
6. Provide resources: Share reliable resources, such as articles, support groups, or blogs, where loved ones can learn more about adult bedwetting and connect with others who have similar experiences. This can help them gain a better understanding and find ways to provide support.
Remember, effective communication is a two-way street. Encourage loved ones to share their thoughts and concerns as well. Building a supportive and understanding network can significantly improve the emotional well-being of individuals dealing with adult bedwetting.
Bedwetting Myths and Misconceptions
Bedwetting in adults is a complex condition that is often shrouded in myths and misconceptions. It is important to debunk these misunderstandings to promote understanding and empathy for those experiencing adult bedwetting. One common myth is that bedwetting is a deliberate act or a result of laziness or lack of motivation. This belief is completely false. Bedwetting is a medical condition that can have various underlying causes, including physical and psychological factors. Another misconception is that bedwetting only affects children and will resolve with age. However, adult bedwetting is a real and persistent problem for many individuals. Additionally, some people believe that drinking fluids before bed causes bedwetting. While it is wise to limit fluid intake before bedtime, excessive fluid consumption is not the sole cause of adult bedwetting. It is essential to understand that bedwetting is not a character flaw or a result of personal negligence. Individuals experiencing this condition deserve empathy, support, and access to appropriate medical interventions. By dispelling these myths, we can create a more supportive environment for those affected by adult bedwetting and help break the stigma surrounding it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the psychological factors behind adult bedwetting is crucial in order to provide effective support and treatment for individuals experiencing this condition. Psychological factors such as anxiety, stress, depression, trauma, and psychological disorders can contribute to adult bedwetting, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, physical factors like bladder dysfunction, sleep disorders, and medication side effects should be considered in the evaluation process. Adult bedwetting can have a significant impact on mental health and quality of life, leading to feelings of embarrassment, shame, and social isolation. Seeking professional help and diagnosis is essential for developing an individualized treatment plan. Treatment options for adult bedwetting may include behavioral therapies, medications, and complementary approaches. Coping strategies such as managing stress and anxiety, using protective bedding, and participating in support groups or counseling can also be beneficial. It is important to foster a supportive environment for individuals with adult bedwetting, communicate openly, and debunk myths and misconceptions surrounding this condition. With the right strategies and support, adults with bedwetting can manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQs about Adult Bedwetting
1. Can adults develop bedwetting even if they were dry as children?
Yes, adult bedwetting can occur even in individuals who were dry as children. It can be caused by various factors, including physical and psychological issues.
2. Is bedwetting in adults always a result of a medical problem?
Not necessarily. While adult bedwetting can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, it can also be influenced by psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and trauma.
3. Does bedwetting in adults affect men and women equally?
Yes, bedwetting can affect individuals of all genders equally. It is not limited to any specific gender.
4. Can adult bedwetting be treated effectively?
Yes, adult bedwetting can be treated effectively through various treatment approaches, including behavioral therapies, medications, and complementary treatments. Seeking professional help is crucial in finding the most suitable treatment plan.
5. Is stress a common cause of adult bedwetting?
Yes, stress and anxiety can contribute to adult bedwetting. Stress can affect bladder control and disrupt normal sleep patterns, leading to episodes of bedwetting.
6. Can certain medications cause adult bedwetting?
Yes, certain medications, such as diuretics or medications used to manage psychiatric conditions, may have the side effect of increased urine production, leading to bedwetting in some individuals.
7. Can changing dietary habits help with adult bedwetting?
While there is no specific diet proven to cure adult bedwetting, avoiding caffeine and alcohol consumption, especially in the evening, can help reduce nighttime urine production and improve bladder control.
8. Is adult bedwetting a sign of a mental health disorder?
Adult bedwetting is not a standalone mental health disorder. However, it can be associated with psychological issues like depression, anxiety, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
9. Can bedwetting in adults affect their relationships?
Bedwetting in adults may put a strain on relationships due to feelings of embarrassment and shame. It is essential for individuals experiencing bedwetting to have open conversations with their loved ones and seek support.
10. Is bedwetting common among older adults?
While bedwetting is more prevalent in children and young adults, it can still occur in older adults. Aging-related factors, such as bladder control issues or certain medical conditions, can contribute to bedwetting in older individuals.








