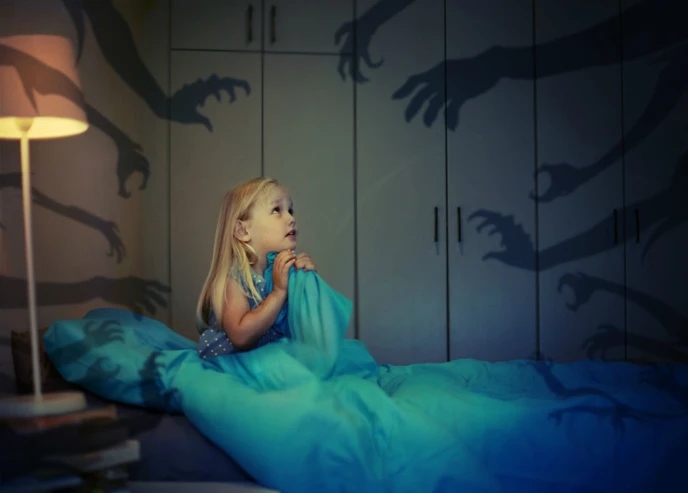
Unraveling the Connection Between Trauma and Nightmares: Decoding the Hidden Messages of Dreams
For many individuals who have experienced trauma, the haunting presence of nightmares can be a distressing and bewildering experience. These vivid and often terrifying dreams can leave individuals feeling unsettled, anxious, and unable to find peace during sleep. In this article, we delve into the intricate connection between trauma and nightmares, aiming to shed light on the hidden messages that dreams hold. By unraveling the symbolic language of dreams, understanding the brain’s processing of trauma during sleep, and exploring therapeutic interventions, we hope to provide insights and guidance for those seeking to heal from trauma and find solace in their dreams. Join us on this captivating journey as we unveil the mysteries that lie within the realm of trauma-related nightmares.
The Nature of Trauma
Trauma is a complex and deeply distressing experience that can have profound effects on an individual’s psychological and emotional well-being. It refers to a distressing event or series of events that overwhelms a person’s ability to cope, leaving them feeling helpless and threatened. Trauma can manifest in various forms and its impact may vary from person to person. Here are some key points about the nature of trauma:
Definition and Types of Trauma: Trauma can be categorized into different types based on the nature of the event. These can include acute trauma, such as accidents or natural disasters, or chronic trauma, such as ongoing abuse or war experiences. Trauma can also be categorized as interpersonal trauma, which involves harm caused by another person, or non-interpersonal trauma, which involves events like accidents or disasters.
Impact of Trauma on the Mind: Trauma can profoundly affect the mind, leading to a range of psychological and emotional effects. Many trauma survivors experience symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), such as intrusive thoughts, hypervigilance, and emotional numbing. These symptoms can create significant distress and disrupt various aspects of life, including sleep.
Trauma has a deep resonance within the psyche, often giving rise to intense dreams and nightmares while asleep. Nightmares serve as an unconscious expression of the trauma experience, allowing the mind to process and make sense of the overwhelming emotions and memories. Understanding the connection between trauma and nightmares is crucial for unraveling the hidden messages within dreams and embarking on a journey of healing.
Let us now explore the intricacies of nightmares and their connection to trauma to gain deeper insights into this fascinating realm.
Definition and Types of Trauma
Definition and Types of Trauma: Trauma can encompass a wide range of distressing events that have a profound impact on an individual’s well-being. Here are some key aspects to understand about the definition and types of trauma:
– Acute Trauma: Acute trauma refers to a single traumatic event that occurs within a short period, such as a car accident, natural disaster, or assault. It is often characterized by a sudden and intense sense of fear, helplessness, or horror.
– Chronic Trauma: Chronic trauma involves repeated exposure to distressing events or ongoing traumatic situations, such as experiencing domestic violence, prolonged abuse, or being exposed to war or conflict. This prolonged exposure can lead to cumulative psychological and emotional effects.
– Interpersonal Trauma: Interpersonal trauma refers to trauma that is caused by another person or group of individuals. This can include physical or sexual abuse, intimate partner violence, bullying, or any form of violence perpetrated by others.
– Non-Interpersonal Trauma: Non-interpersonal trauma encompasses traumatic events that are not directly related to the actions of another person. Examples can include accidents, natural disasters, serious injuries, medical trauma, or witnessing traumatic events.
Understanding the different types of trauma is essential in recognizing the diverse experiences individuals may have endured. It helps to validate their emotions and experiences and guides therapeutic approaches toward healing. By acknowledging the specific type of trauma that individuals have faced, professionals can tailor interventions to address their unique needs. If you’re interested in learning more about overcoming nightmares related to trauma, you can explore the use of lucid dreaming as a powerful tool for healing.
Impact of Trauma on the Mind
The impact of trauma on the mind can be profound and far-reaching. Traumatic experiences can have a lasting effect on an individual’s psychological and emotional well-being. Here are some key insights into the impact of trauma on the mind:
1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Trauma can trigger the development of PTSD, a mental health condition characterized by intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, and nightmares related to the traumatic event. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s ability to function in daily life and often lead to persistent feelings of fear, anxiety, and hypervigilance.
2. Emotional Dysregulation: Trauma can disrupt the normal regulation of emotions, leading to intense and unpredictable emotional responses. Individuals may experience heightened sensitivity, irritability, or emotional numbness as a result. This emotional dysregulation can also contribute to the intensity and frequency of nightmares.
3. Fragmented Memory: Traumatic experiences can disrupt the normal functioning of memory processes. Memories of the trauma may be fragmented or disjointed, making it challenging to process and integrate the experience. This fragmentation can manifest in dreams as recurring themes or symbols, reflecting the disjointed nature of the traumatic memories.
4. Hyperarousal and Hypervigilance: Trauma survivors often experience a heightened state of arousal and hypervigilance, constantly on guard for potential threats. This hyperarousal can impact sleep quality, contributing to the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
5. Impact of Medication and Substance Abuse: In some cases, individuals may turn to medication or substance abuse as a way to cope with the emotional distress caused by trauma. However, certain medications and substances can have an impact on dream patterns and may contribute to the occurrence of vivid and disturbing nightmares. Seeking proper treatment and guidance, such as therapy, can be crucial in addressing these issues and finding healthier coping mechanisms.
Nightmares: An Unconscious Expression
Nightmares, often characterized by vivid, disturbing, and emotionally intense dreams, serve as an unconscious expression of our inner psyche. They can be particularly prominent in individuals who have experienced trauma. Here are some key points about nightmares as an unconscious expression:
What Are Nightmares? Nightmares are distressing dreams that evoke strong negative emotions such as fear, anxiety, and terror. They often disrupt sleep, leaving individuals feeling unsettled and distressed upon awakening. Nightmares can be highly detailed, with vivid imagery, and may involve threatening or traumatic situations. They differ from regular dreams by their ability to evoke a strong emotional response, often causing individuals to wake up with a racing heart and a sense of relief that it was just a dream.
Common Themes in Trauma-Related Nightmares: Trauma-related nightmares tend to revolve around the themes and elements associated with the traumatic event. For example, individuals who have experienced physical violence may have nightmares involving being chased or attacked. Those who have undergone emotional trauma may experience nightmares centered around feelings of abandonment or betrayal. These nightmares can serve as a reflection of the unresolved emotions, fears, and memories related to the trauma.
In order to decipher the messages hidden within nightmares, it is essential to delve into the symbolism and interpretation of dream content. By exploring the symbols and themes present in nightmares, we can gain insights into the unconscious mind’s attempt to process traumatic experiences and provide healing.
It is important to note that nightmares are not limited to adults; children can also experience distressing dreams. Understanding and addressing nightmares in children is vital for their emotional well-being and overall development. If your child is experiencing frequent nightmares, it is crucial to seek appropriate support and guidance to help them process their emotions and ensure a restful night’s sleep. Learn more about how to help children cope with nightmares and promote their emotional resilience.
Now that we have explored the nature of nightmares as an unconscious expression, let’s unravel the dream messages hidden within and understand their connection to trauma on a deeper level.
What Are Nightmares?
Nightmares are intense and vivid dreams that evoke strong feelings of fear, terror, and distress. They often wake the dreamer abruptly, leaving them feeling unsettled and anxious. These dreams can be highly detailed and may involve themes or scenarios that reflect the individual’s deepest fears or unresolved emotions.
Nightmares are a normal part of dreaming and can occur in people of all ages. However, when nightmares are frequent, recurring, and significantly impact one’s quality of life, they may be indicative of underlying trauma or psychological distress. In the context of trauma, nightmares can be particularly distressing, as they can vividly replay traumatic events or symbolize the internal struggles and unresolved emotions related to the trauma experience.
Nightmares may include common themes such as being chased, experiencing danger or harm, or feelings of helplessness. They can evoke vivid imagery, sound, and physical sensations, immersing the dreamer in a realm of intense emotions. These dreams often represent the mind’s attempt to process and make sense of the trauma, serving as a medium for emotional release and healing.
Understanding the nature of nightmares is essential in decoding the hidden messages they hold within the realm of trauma. By delving deeper into the symbolism and patterns within nightmares, we can begin to unravel the unconscious expressions of trauma and embark on a journey toward healing and resolution.
Common Themes in Trauma-Related Nightmares
Common Themes in Trauma-Related Nightmares:
Trauma-related nightmares often contain recurring themes and images that reflect the individual’s traumatic experiences and the emotional impact they have had. These nightmares can be intense, vivid, and emotionally distressing. While the specific content of nightmares varies from person to person, there are some common themes that frequently emerge:
1. Reliving the Traumatic Event: Trauma survivors often find themselves reliving the traumatic event in their nightmares. They may experience flashbacks or vivid reenactments of the event, sometimes with slight variations or symbolic representations.
2. Threatening Situations and Helplessness: Nightmares may depict the person being pursued, trapped, or threatened by an unseen force or a specific perpetrator. These dreams can evoke feelings of fear, helplessness, and vulnerability, mirroring the emotions experienced during the traumatic event.
3. Loss and Abandonment: Many trauma-related nightmares involve themes of loss, abandonment, or separation. These dreams may portray the loss of loved ones, a sense of isolation, or being left behind, reflecting the emotional impact of trauma on relationships and a fear of being alone.
4. Symbolic Representations: Trauma-related nightmares often contain symbolisms and metaphors that represent the person’s psychological struggles and unresolved emotions. These symbols can be personal and subjective to the individual, but may also have common archetypal meanings.
Understanding these common themes in trauma-related nightmares can provide valuable insights into the underlying emotions and experiences that the individual is grappling with. It allows for a deeper exploration of the hidden messages held within these dreams, empowering individuals to unravel their trauma and begin the healing process. Seeking professional help and support is crucial for those who are struggling with trauma-related nightmares, as it can provide guidance and strategies to address and integrate these experiences in a safe and supportive manner.
Unraveling the Dream Messages

Symbolism and Interpretation: Dreams often communicate through symbols that represent underlying emotions, experiences, and conflicts. When it comes to trauma-related nightmares, understanding the symbolic language becomes even more important. Symbolism in dreams can be highly personal, making it crucial to explore the specific meaning for each individual. For example, a recurring nightmare about being trapped in a confined space may symbolize feelings of suffocation or a sense of powerlessness associated with the trauma.
Recognizing Trauma Triggers in Dreams: Trauma triggers are stimuli that remind individuals of their traumatic experience and can evoke intense emotional and physiological responses. In dreams, these triggers may manifest as recurring themes or situations that closely resemble the traumatic event. It is essential to pay attention to these triggers in order to identify and address the underlying trauma. For instance, a person who experienced a car accident may have nightmare scenarios involving car crashes or being trapped in a vehicle.
By analyzing the symbols and triggers present in trauma-related nightmares, individuals can begin to piece together the hidden messages their dreams are conveying. Engaging in self-reflection, journaling, or working with a therapist can provide valuable insights into the meaning of these dreams. Understanding these messages can be a significant step towards healing and resolution.
If you want to learn more about the impact of medication and substance abuse on dreams and nightmares, you can explore our comprehensive guide on this topic. Understanding the interplay between substances and dreams can provide additional insight into the connection between trauma and nightmares.
Symbolism and Interpretation
Dreams, including nightmares, often communicate through symbols and imagery, providing a rich tapestry of hidden meanings and messages. Symbolism and interpretation play a crucial role in unraveling the significance of these dreams in the context of trauma. Here are some key points to consider:
Symbolism in Dreams: Dreams use symbolism as a way to convey complex emotions and experiences. Symbols can be personal, cultural, or archetypal in nature. Personal symbols may reflect individual experiences and memories related to the trauma, while cultural symbols draw from shared experiences and societal influences. Archetypal symbols are universal symbols that evoke deep collective meanings, such as water representing emotions or a cave symbolizing the unconscious mind.
Interpretation of Dreams: Interpreting dreams requires a careful and individualized approach. The same symbol can have different meanings for different people, depending on their personal experiences and associations. It is essential to consider the dreamer’s unique context and emotions when attempting to interpret a dream related to trauma. Working with a therapist or dream expert experienced in trauma can provide valuable guidance in deciphering the symbolism and gaining deeper insights into the hidden messages of the dream.
It is important to approach dream interpretation with sensitivity and curiosity, acknowledging that dreams are highly subjective and can be influenced by individual perspectives. While dream symbolism can offer valuable insights, it is crucial to recognize that it is not an exact science and that multiple interpretations may coexist. The process of interpreting dreams allows individuals to explore their subconscious landscapes, gaining a deeper understanding of their trauma experiences, and facilitating healing and growth.
Recognizing Trauma Triggers in Dreams
Our dreams have a unique way of reflecting our innermost thoughts and emotions, providing a window into the unconscious mind. When it comes to trauma, dreams can serve as a conduit for unresolved emotions and memories, offering valuable insights into the triggers that continue to affect us. Recognizing trauma triggers in dreams is an important step towards understanding and healing from past traumatic experiences.
One of the key aspects of recognizing trauma triggers in dreams is paying attention to the emotional intensity within the dream. Trauma-related nightmares are often characterized by intense fear, helplessness, and a sense of being overwhelmed. These emotions may be accompanied by specific themes or symbols that are closely tied to the traumatic event.
Symbolism plays a significant role in decoding the messages within trauma-related dreams. For example, a person who has experienced a car accident might dream of being trapped in a vehicle or constantly reliving the moment of impact. These symbols can serve as powerful indicators of the underlying trauma and its impact on the individual’s psyche.
It is also important to consider the physiological and emotional reactions that occur upon waking from a trauma-related dream. Waking up in a state of fear, anxiety, or with a racing heartbeat can be an indication that the dream has tapped into unresolved trauma. These reactions may persist even after waking, influencing the individual’s mood and overall well-being.
Recognizing trauma triggers in dreams requires a willingness to delve into the depths of one’s own experiences and emotions. It may be helpful to keep a dream journal, recording details of the dreams, emotions felt, and any patterns that emerge over time. This can aid in identifying recurring themes and symbols that are linked to the trauma.
By recognizing trauma triggers in dreams, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the impact of past experiences on their current state of being. This awareness opens the door to healing and seeking appropriate support and therapeutic interventions to process and resolve the trauma.
The Brain’s Processing of Trauma during Sleep
During sleep, the brain engages in a complex process of consolidating and integrating memories, including those associated with traumatic experiences. This process primarily occurs during Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, the stage of sleep when vivid dreams commonly occur. Understanding the brain’s processing of trauma during sleep can provide valuable insights into the connection between trauma and nightmares. Here are a few key points to consider:
REM Sleep and Memory Consolidation: REM sleep plays a critical role in consolidating memories, particularly emotional memories. It is believed that during REM sleep, the brain selectively processes and stores emotional memories, including traumatic experiences. This process helps the brain to make sense of and integrate these memories into a person’s overall memory system.
Reprocessing Traumatic Experiences in Dreams: Research suggests that during REM sleep, the brain may attempt to reprocess and make sense of the traumatic experiences through dreams. These dreams often contain vivid and emotionally charged scenarios that mirror the elements of the trauma. The purpose of such dreams is thought to be the brain’s attempt to process and integrate the emotions and memories associated with the trauma in a safe and controlled environment.
By examining the brain’s processing of trauma during sleep, we gain a deeper understanding of why nightmares related to trauma occur and how they may contribute to the healing process. In the next section, we will explore approaches to decoding and interpreting the symbolic language of dreams to unravel the hidden messages they hold.
REM Sleep and Memory Consolidation
REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep is a crucial stage of the sleep cycle that plays a significant role in memory consolidation and overall cognitive functioning. During REM sleep, the brain becomes highly active, and vivid dreaming occurs. Here’s a closer look at the connection between REM sleep and memory consolidation:
1. Activation of the Hippocampus: The hippocampus, a region of the brain involved in memory processing, plays a vital role during REM sleep. It helps to consolidate and integrate new information, transferring it from short-term to long-term memory storage.
2. Emotional Memory Processing: REM sleep is particularly influential in the processing of emotional memories. Traumatic experiences often have a profound emotional impact, and REM sleep allows the brain to process and integrate these emotional components of trauma-related memories.
3. Memory Reconsolidation: During REM sleep, memories undergo a process called reconsolidation. This process involves the recalling and reactivation of stored memories, followed by their reintegration into the memory network. This reconsolidation process can be significant for individuals who have experienced trauma, as it provides an opportunity for the brain to reprocess and potentially alleviate the distressing aspects of traumatic memories.
4. Dream Incorporation: Dreams during REM sleep can incorporate fragments of both recent and past memories, including traumatic experiences. These dream scenarios often provide a platform for the brain to process and make sense of the traumatic events, aiding in the emotional integration and healing process.
Understanding the role of REM sleep in memory consolidation can provide insights into the connection between trauma and nightmares. The processing and integration of traumatic memories during REM sleep may give rise to vivid and emotionally charged nightmares. Recognizing this relationship can be helpful in deciphering the hidden messages within these dreams and fostering healing and resolution.
Reprocessing Traumatic Experiences in Dreams
Dreams provide a unique opportunity for the brain to reprocess and integrate traumatic experiences. During Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, which is the phase of sleep associated with vivid dreaming, the brain actively engages in memory consolidation and emotional processing. This process plays a crucial role in helping individuals make sense of and come to terms with their trauma. Here are some key points to consider about the reprocessing of traumatic experiences in dreams:
Symbolic Representation: Dreams often employ symbolism and metaphorical language to represent traumatic experiences. These symbols can manifest as recurring themes, specific images, or even abstract representations of the trauma. By examining these symbolic elements, individuals can gain insight into the hidden meanings and emotions associated with their trauma.
Emotional Catharsis: Traumatic experiences are often accompanied by intense emotions that may be repressed or difficult to express in waking life. In dreams, these suppressed emotions can be safely explored and released, allowing the dreamer to experience a form of emotional catharsis. This cathartic process helps individuals process and release pent-up emotions associated with their trauma, contributing to their healing journey.
Integration and Meaning-Making: Dreams play a crucial role in integrating fragmented memories and emotions related to trauma. Through the symbolism and narrative structure of dreams, the brain actively works to make sense of the traumatic experience, ultimately aiding in the individual’s journey towards understanding and meaning-making.
It is important to note that reprocessing traumatic experiences in dreams may not always be a linear or straightforward process. Some dreams may be distressing or intense, while others may provide moments of insight and resolution. The interpretation and understanding of these dreams should be approached with compassion and support. By working with mental health professionals experienced in trauma and dreamwork, individuals can navigate the complex landscape of their dreams to promote healing and resolution.
Healing from Trauma through Dreamwork

Healing from Trauma through Dreamwork:
Dreams have long been recognized as a powerful tool for healing and self-exploration, and this holds true for individuals who have experienced trauma. Through the practice of dreamwork, individuals can gain valuable insights and facilitate the healing process. Here are two approaches that can be beneficial for healing from trauma through dreamwork:
Therapeutic Approaches to Decode Dream Messages: One therapeutic approach for working with dreams is to decode the symbolic messages they contain. Dreams often use symbols and metaphors to communicate deeply rooted emotions and unresolved experiences related to trauma. Jungian analysis and other methods of dream interpretation can help individuals explore the hidden meanings behind their dreams and gain a deeper understanding of their trauma. This process of decoding can offer validation, insight, and a sense of empowerment to survivors.
Lucid Dreaming for Trauma Resolution: Lucid dreaming, a state in which individuals are aware that they are dreaming and can actively participate in the dream, can be another powerful tool for healing trauma. In a lucid dream, individuals have the opportunity to confront and resolve traumatic experiences on their own terms. They can change the dream narrative, practice coping strategies, or even visualize resolution and healing. Research suggests that lucid dreaming can reduce the emotional distress associated with trauma and provide a sense of empowerment and control over one’s own healing journey.
By integrating dreamwork into the healing process, individuals can tap into the subconscious realm of dreams to gain insights, process emotions, and find resolution. It is important to note that while dreamwork can be a beneficial adjunct to therapy, it is not a substitute for professional treatment. Individuals seeking healing from trauma through dreamwork are encouraged to work with trained therapists or counselors who specialize in trauma and dream analysis.
In the next section, we will discuss the support and treatment options available for individuals experiencing trauma-related nightmares, emphasizing the importance of seeking professional help and providing practical tips for reducing nightmares.
Therapeutic Approaches to Decode Dream Messages
Decoding dream messages can provide valuable insights into the unconscious mind and help individuals process their trauma on a deeper level. Various therapeutic approaches can assist in unraveling the symbolism and hidden meanings within dreams. Here are some effective methods used to decode dream messages:
1. Dream Analysis: Psychotherapists often employ dream analysis as a fundamental tool to explore the unconscious mind. By examining the symbolism, themes, and emotions present in dreams, therapists can help individuals uncover the underlying messages and connections to their trauma. This process involves exploring personal associations, metaphors, and archetypal symbols embedded within the dream narrative.
2. Journaling and Reflection: Keeping a dream journal allows individuals to record dreams upon awakening. Reviewing and reflecting on dream content over time can help identify common themes, recurring symbols, and patterns associated with trauma. Journaling provides individuals with an opportunity to gain a deeper understanding of their dreams and uncover the hidden messages they convey.
3. Trauma-Focused Therapy: Therapeutic approaches specifically tailored for trauma, such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) or Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), can be utilized to decode dream messages. These therapies aim to process traumatic memories and beliefs, helping individuals integrate their trauma experiences and reduce the distressing impact on their dreams.
4. Group Therapy: Participating in group therapy or support groups can provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals to share their dreams related to trauma. Group members can offer perspectives and insights that may shed light on the hidden meanings within dreams, offering a collective space for decoding and understanding dream messages.
It is important to note that decoding dream messages is a deeply personal and subjective process. Engaging with a trained therapist or counselor who specializes in trauma and dream work can greatly enhance the effectiveness of these therapeutic approaches. Through these methods, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their dreams, find meaning in their trauma-related nightmares, and embark on a path towards healing and resolution.
Lucid Dreaming for Trauma Resolution
Lucid dreaming is an intriguing phenomenon that holds potential as a therapeutic tool for trauma resolution. In a lucid dream, the dreamer becomes aware that they are dreaming while still in the dream state. This awareness grants a unique level of control and conscious participation within the dream narrative. Here are some key points about the use of lucid dreaming for trauma resolution:
1. Empowerment and Emotional Regulation: Lucid dreaming can provide trauma survivors with a sense of empowerment and control. By recognizing the dream state, individuals can actively engage with the traumatic content and consciously change the dream’s course. This ability allows for the exploration and processing of traumatic memories at a manageable pace, promoting emotional regulation and a sense of agency.
2. Re-scripting Traumatic Experiences: Lucid dreaming offers an opportunity to re-script or re-envision traumatic experiences within the dream. Trauma survivors can create alternative outcomes or modify the dream narrative to reduce distress and empower themselves. This process can help individuals reclaim a sense of personal power and reshape their perception of the traumatic event.
3. Creating a Safe Dream Environment: In a lucid dream, individuals can also actively create a safe and supportive dream environment. This safe space serves as a foundation for processing and working through traumatic memories. By cultivating a secure dream setting, trauma survivors can enhance their sense of safety and facilitate the healing process.
4. Integration and Symbolic Exploration: Lucid dreaming allows trauma survivors to explore the symbolic language of their dreams in a conscious and intentional manner. By interacting with dream symbols and engaging in dialogue with dream figures, individuals can gain deeper insights into the meaning and messages behind their nightmares. This process can aid in the integration of fragmented aspects of the self and promote healing.
While lucid dreaming shows promise as a tool for trauma resolution, it is important to note that it may not be suitable for everyone. It requires practice, patience, and a strong foundation of coping skills. Additionally, it is crucial to approach lucid dreaming within a supportive and therapeutic framework. Seeking guidance from a qualified mental health professional who specializes in trauma is essential to ensure safe and effective utilization of lucid dreaming techniques for trauma resolution.
Support and Treatment for Trauma-Related Nightmares
Trauma-related nightmares can be incredibly distressing and disruptive to one’s sleep and overall well-being. Fortunately, there are various forms of support and treatment available to help individuals cope with and reduce the frequency and intensity of these nightmares. Here are some key aspects to consider when seeking support and treatment for trauma-related nightmares:
Seeking Professional Help: It is highly recommended to seek the assistance of a mental health professional, such as a therapist or counselor, who specializes in trauma and dream therapy. These professionals can provide a safe and supportive space for individuals to explore and process their trauma-related nightmares. They can offer evidence-based therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), or dream work, tailored to address the specific needs of each individual.
Practical Tips for Reducing Nightmares: In addition to professional help, there are practical steps that individuals can take to reduce the occurrence and impact of trauma-related nightmares. These may include establishing a calming bedtime routine, creating a sleep-friendly environment, practicing relaxation techniques, and engaging in stress-reduction activities during the day. It can also be helpful to avoid stimulating or distressing content before bed, such as violent movies or news stories.
Lucid Dreaming for Trauma Resolution: Lucid dreaming, a practice where individuals become aware that they are dreaming while in the dream state, can be a powerful tool for resolving trauma-related nightmares and gaining control over the dream narrative. By learning and practicing lucid dreaming techniques, individuals can actively engage with their dreams, confront and process traumatic content, and even guide the dream towards a more positive resolution. [Link to our article on lucid dreaming as a tool to overcome nightmares]
Remember, the journey to healing from trauma-related nightmares may require patience, self-compassion, and a multidimensional approach. With the right support and treatment, it is possible to find relief and restore a sense of peace and well-being during sleep.
Seeking Professional Help
Seeking Professional Help:
When dealing with trauma-related nightmares, it is essential to recognize the importance of seeking professional help. Trauma can have a profound and lasting impact on an individual’s mental health, and the guidance of a trained professional can be invaluable in the healing process. Here are some key aspects to consider when seeking professional help for trauma-related nightmares:
1. Therapists or Counselors: A therapist or counselor specializing in trauma can provide a safe and supportive space to explore and process the trauma experiences underlying the nightmares. They can employ various evidence-based therapeutic approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), or somatic experiencing to address the underlying trauma and help in managing nightmares.
2. Support Groups: Joining a support group specifically focused on trauma and nightmares can be immensely beneficial. These groups provide a sense of community, validation, and understanding from individuals who have gone through similar experiences. Sharing experiences, emotions, and coping strategies in a supportive environment can be empowering and aid in the healing process.
3. Psychiatrists: In certain cases, psychiatrists may be involved in the treatment of trauma-related nightmares. They can prescribe medications if deemed necessary to address symptoms such as anxiety, depression, or sleep disturbances that may be exacerbated by nightmares. However, medication should always be used in conjunction with therapy and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
4. Integrated Treatment: Integrated treatment approaches that combine therapy, medications, and complementary interventions can be effective for addressing trauma-related nightmares. These approaches take into account the individual’s unique needs and work towards holistic healing and recovery.
Remember, seeking professional help is a sign of strength and a crucial step towards finding relief from trauma-related nightmares. It provides the opportunity to work through the underlying trauma, gain insights, learn coping mechanisms, and ultimately live a more fulfilling and peaceful life.
Practical Tips for Reducing Nightmares
There are various practical tips and strategies that can help individuals reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. By incorporating these techniques into their daily routine, trauma survivors can empower themselves to regain control over their sleep and find relief from distressing dreams. Here are some practical tips for reducing nightmares:
1. Establish a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Creating a soothing bedtime routine can signal to the brain that it’s time to unwind and prepare for sleep. Engaging in activities like reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and meditation can promote a sense of calmness and reduce nighttime anxiety.
2. Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Making your sleep environment comfortable and conducive to relaxation can contribute to better sleep quality. Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. Ensure that your mattress and pillows provide proper support. Remove any electronic distractions that could disrupt your sleep.
3. Develop Stress-Management Techniques: Implementing stress-management techniques during the day can help reduce anxiety and prevent the buildup of stress that can trigger nightmares. This can include practicing mindfulness, engaging in regular physical exercise, or seeking support from a therapist or support group.
4. Limit Exposure to Trauma Triggers: If certain situations, images, or media content act as triggers for nightmares, it may be helpful to limit exposure to these stimuli. This could involve avoiding violent movies or news stories, setting boundaries in relationships, or seeking professional help to address specific triggers.
5. Keep a Dream Journal: Keeping a dream journal can provide valuable insights into the content and patterns of your nightmares. Recording your dreams upon waking can help you identify recurring themes, symbols, or triggers. This can assist you in understanding the root causes of your nightmares and facilitate discussions with therapists or support groups.
6. Practice Imagery Rehearsal Therapy (IRT): IRT is a therapeutic technique that involves rewriting the endings of nightmares or creating positive imagery to overwrite distressing dream content. By visualizing a new and positive outcome for recurrent nightmares, individuals can gain a sense of empowerment and reduce the distress associated with the dream.
Remember, finding what works best for you may involve a trial-and-error process. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or therapist who can provide personalized guidance and support based on your specific needs and experiences. By incorporating these practical tips into your routine, you can take proactive steps towards reducing nightmares and improving your overall sleep quality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the connection between trauma and nightmares reveals a complex interplay between the mind, emotions, and memories. Nightmares serve as a potent expression of trauma, allowing the unconscious to process and confront deeply-rooted fears and experiences. Through symbolism and interpretation, individuals can uncover hidden messages within their dreams, providing valuable insights into their healing journey. Recognizing trauma triggers in dreams and utilizing therapeutic approaches like dreamwork and lucid dreaming can facilitate resolution and healing. It is important to seek professional help when dealing with trauma-related nightmares, as trained professionals can provide support and guidance tailored to individual needs. Practical tips like maintaining a consistent sleep routine, creating a calming bedtime routine, and practicing relaxation techniques can also help reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. By understanding and addressing the connection between trauma and nightmares, individuals can take steps towards healing, restoring a sense of safety, and finding peace within their dream world.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQs about the Connection Between Trauma and Nightmares
1. Can trauma cause nightmares?
Yes, trauma can trigger nightmares. The distressing experiences associated with trauma can leave a lasting impact on the mind, and nightmares often serve as a manifestation of the unconscious attempts to process and make sense of the trauma.
2. What are the common themes in trauma-related nightmares?
Trauma-related nightmares often revolve around themes such as reliving the traumatic event, feelings of fear, helplessness, or being chased. These themes can vary based on the specific nature of the trauma and the individual’s personal experiences.
3. Do nightmares have any symbolic meaning?
Yes, nightmares often contain symbolic meaning. The content of a nightmare can be seen as a metaphorical representation of the underlying emotional turmoil and unresolved experiences associated with the trauma.
4. Can nightmares be triggered by specific trauma-related cues?
Yes, specific cues related to the trauma can act as triggers for nightmares. These cues can include sights, sounds, smells, or situations that remind the individual of the traumatic event and activate the associated emotions and memories.
5. How does the brain process trauma during sleep?
During Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, which is the stage of sleep where most dreaming occurs, the brain processes and consolidates memories, including traumatic experiences. This process helps in integrating and understanding the trauma on a subconscious level.
6. Can nightmares help in the healing process of trauma?
Yes, nightmares can potentially aid in the healing process of trauma. They provide an avenue for the mind to process and release the intense emotions associated with the trauma, allowing for a gradual resolution and integration of the traumatic experiences.
7. How can dreams be decoded to understand their message?
Dreams can be decoded by analyzing the symbolism present within them. Symbols in dreams often represent deeper meanings and emotions. Keeping a dream journal, discussing dreams with a therapist, or utilizing dream interpretation techniques can help in decoding their messages.
8. What is lucid dreaming, and how can it assist in overcoming nightmares?
Lucid dreaming is a state of awareness during a dream where the individual becomes conscious that they are dreaming. By developing the skill of lucid dreaming, one can gain control over the dream narrative, allowing them to confront and change the course of nightmares, ultimately reducing their intensity and frequency.
9. When should someone seek professional help for trauma-related nightmares?
It is advisable to seek professional help if trauma-related nightmares significantly impact daily functioning, cause severe distress, or interfere with sleep and overall well-being. A mental health professional can provide guidance and support in navigating the healing process.
10. Are there practical tips to reduce the occurrence of trauma-related nightmares?
Yes, there are several practical strategies that can help reduce trauma-related nightmares. These may include maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, implementing relaxation techniques before bedtime, creating a soothing sleep environment, and incorporating stress-reduction practices into daily life.








