Trauma can leave a lasting impact on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being, often manifesting in various ways. One of the most common and unsettling manifestations of trauma is recurring nightmares. These vivid and distressing dreams can disrupt sleep, cause intense fear, and even interfere with daily functioning. Understanding how trauma can manifest in recurring nightmares is crucial for both individuals who have experienced trauma and those who aim to support and assist them. In this article, we will explore the definition of trauma, the role it plays in recurring nightmares, the impact of these nightmares on sleep and daily life, and strategies for healing and coping.
Understanding Trauma

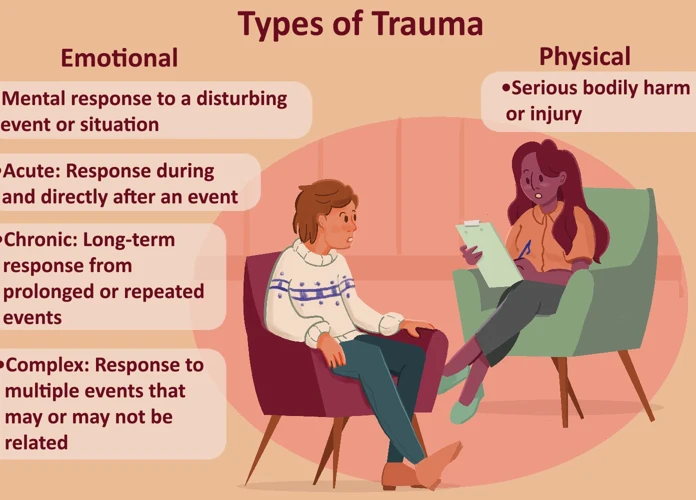
Trauma is a complex and multifaceted experience that can have profound effects on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being. Defined as a response to a distressing or life-threatening event, trauma can leave lasting imprints on the brain and significantly disrupt a person’s sense of safety, self, and perception of the world. There are various types of trauma, including but not limited to physical abuse, sexual assault, natural disasters, and war experiences. Each type of trauma can have its own unique psychological consequences, but they all share a common thread of deep distress and overwhelming emotional impact. When it comes to the brain, trauma can disrupt neural pathways and impair cognitive functions. The brain’s intricate network of synapses, neurotransmitters, and regions responsible for regulating emotions can all be significantly affected by a traumatic event. This profound impact on the brain’s functioning helps to explain why trauma can have such far-reaching and long-lasting effects on an individual’s mental health. For a more in-depth analysis on how trauma can impact dreams, you can explore our article on trauma dream analysis. Understanding trauma is essential for recognizing its influence on recurring nightmares and taking steps towards healing and recovery.
Definition of trauma
Definition of trauma: Trauma can be defined as a psychological and emotional response to a distressing or life-threatening event. It goes beyond the realm of typical human experience and overwhelms an individual’s ability to cope. Traumatic events can vary widely and include experiences such as physical or sexual abuse, accidents, natural disasters, combat, or witnessing violence. What distinguishes trauma from a regular stressful event is the profound and lasting impact it has on a person’s physical, emotional, and cognitive well-being. Trauma can shatter an individual’s sense of safety, trust, and belief in the world as a predictable and secure place. It can lead to a range of symptoms including anxiety, depression, intrusive thoughts, hypervigilance, avoidance, and nightmares. Understanding the definition of trauma is crucial in order to recognize its effects on recurring nightmares and seek appropriate support and treatment. If you’re looking for tips on managing nightmares, you can refer to our comprehensive guide on nightmare management tips. If you’re interested in exploring how trauma specifically relates to nightmares associated with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), you may find our article on PTSD nightmares informative.
Types of trauma
When it comes to trauma, there are various types that individuals may experience. Here are some common types of trauma:
- Acute trauma: This type of trauma refers to a single traumatic event that occurs within a short period. Examples include car accidents, natural disasters, or physical assaults.
- Chronic trauma: Chronic trauma involves repeated exposure to traumatic events over an extended period, such as ongoing physical or sexual abuse, domestic violence, or living in a war zone.
- Complex trauma: Complex trauma typically occurs during childhood and involves chronic and multiple traumatic experiences within a caregiving relationship, such as neglect, emotional abuse, or witnessing domestic violence.
- Secondary trauma: Also known as vicarious trauma, secondary trauma refers to the emotional toll experienced by individuals who witness or hear about traumatic events happening to others, such as first responders, healthcare professionals, or therapists.
- Developmental trauma: Developmental trauma occurs when a person experiences chronic trauma during critical periods of growth and development. This can have long-lasting effects on their emotional, cognitive, and social development.
Each type of trauma carries its own unique challenges and impacts on an individual’s well-being. It is essential to recognize and understand the various types of trauma to provide appropriate support and treatment for those who have experienced them.
Effects of trauma on the brain
The effects of trauma on the brain are significant and wide-ranging. Trauma can disrupt the normal functioning of the brain, impacting various areas and processes. Here are some key effects of trauma on the brain:
1. Hypervigilance: Trauma can lead to a heightened state of hypervigilance, where an individual is constantly on high alert, anticipating potential threats or danger. This response is mediated by the amygdala, a part of the brain responsible for processing emotions and detecting threats.
2. Hyperarousal: The brain’s stress response system may become overactive in individuals who have experienced trauma. This results in symptoms such as irritability, difficulty sleeping, and an exaggerated startle response. The stress hormone cortisol is also often dysregulated, leading to chronically elevated levels.
3. Impaired memory: Trauma can affect both short-term and long-term memory processes. During traumatic events, the brain may prioritize survival over encoding details, leading to fragmented or incomplete memories of the event. Additionally, traumatic memories can become intrusive and difficult to control, causing distress and interfering with daily functioning.
4. Altered brain structures: Trauma has been found to impact the structure and function of various brain regions. The prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for executive functions such as decision-making and emotional regulation, may become dysregulated, leading to difficulties in these areas. The hippocampus, involved in memory processing, can also be affected, contributing to memory impairments.
5. Changes in neural connectivity: Trauma can disrupt neural connections within the brain, affecting communication between different regions. This can lead to difficulties in processing and regulating emotions, as well as impairments in cognitive functioning.
It is important to note that the effects of trauma on the brain are not static and can vary between individuals. The brain has a remarkable capacity for plasticity, meaning it can adapt and change over time. Seeking professional help and engaging in trauma-informed therapies can support the brain’s healing process and help individuals regain a sense of safety and well-being.
Recurring Nightmares: An Overview

Recurring nightmares are a distressing sleep phenomenon characterized by repeated and frequent occurrences of intensely disturbing dreams. These nightmares often involve vivid and realistic scenarios that evoke fear, helplessness, or intense emotional distress. While occasional nightmares are relatively common, recurring nightmares can be more persistent and have a significant impact on an individual’s well-being. Common themes and characteristics of recurring nightmares can vary widely, including but not limited to scenarios involving danger, physical harm, being chased or attacked, falling, or being trapped. The content of these nightmares often reflects the individual’s fears, anxieties, or traumatic experiences. The repetitive nature of these dreams can be exhausting, leading to sleep disturbances and a constant state of unease. If you are seeking tips on managing nightmares, you can refer to our article on nightmare management tips. Understanding the nature of recurring nightmares is vital for addressing their underlying causes and finding effective coping strategies.
Definition of recurring nightmares
When discussing the topic of recurring nightmares, it is important to understand their definition and characteristics. Recurring nightmares are unpleasant dreams that occur frequently, often repeating similar themes or content. Unlike ordinary nightmares that may occur occasionally, recurring nightmares can persist over an extended period, causing distress and disrupting sleep patterns. These nightmares tend to recur with a certain frequency, sometimes even happening multiple times in a week. They are typically vivid, intense, and can evoke strong emotions such as fear, anxiety, or helplessness. The content of recurring nightmares may vary widely, ranging from reliving a traumatic event to experiencing surreal or fantastical situations. Some common themes in recurring nightmares include being chased, falling, being trapped, or feeling physically threatened. These nightmares often leave individuals feeling disturbed and can have a significant impact on their overall well-being.
Common themes and characteristics
When it comes to recurring nightmares, there are common themes and characteristics that often emerge. These themes can vary depending on the individual’s unique experiences and the specific nature of their trauma. One common theme is re-experiencing the traumatic event itself. People may find themselves reliving the details of the event, feeling a sense of helplessness and fear all over again. This can manifest as vivid and terrifying nightmares, where the trauma is replayed repeatedly. Another theme is a feeling of helplessness and vulnerability. Individuals may find themselves in situations where they are unable to escape or defend themselves, reflecting the powerlessness they may have felt during the traumatic event. Additionally, the theme of escape and survival often emerges in recurring nightmares. These dreams may involve attempts to flee from danger or find a way to survive the traumatic situation. These recurring themes and characteristics are manifestations of the deep emotional impact that trauma can have on an individual’s psyche. It is important to acknowledge and address these themes in order to understand and work through the trauma-related nightmares.
The Role of Trauma in Recurring Nightmares

Trauma plays a significant role in the development and persistence of recurring nightmares. The psychological impact of trauma can permeate every aspect of an individual’s life, including their dreams. When someone experiences a traumatic event, the memory of that event often becomes fragmented and disorganized. These fragmented memories can then infiltrate their dreams, manifesting as vivid and distressing nightmares. Additionally, the repetition of traumatic themes in nightmares can serve as a coping mechanism for the individual, allowing them to process and attempt to make sense of the traumatic experience. It is important to recognize that the presence of recurring nightmares is not a sign of weakness, but rather a natural response to the trauma. Seeking professional help and implementing self-care practices, such as engaging in relaxation techniques or practicing good sleep hygiene, can help individuals navigate the role of trauma in recurring nightmares and begin the journey towards healing. For more tips on managing nightmares, you can visit our article on nightmare management tips.
Psychological impact of trauma
The psychological impact of trauma is profound and can have long-lasting effects on an individual’s mental health. Traumatic experiences can disrupt the way a person perceives themselves, others, and the world around them. Some common psychological effects of trauma include:
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Trauma can lead to the development of PTSD, a mental health condition characterized by intrusive memories, flashbacks, avoidance of triggers, negative thoughts and emotions, and hyperarousal. Individuals with PTSD often experience nightmares related to their traumatic experiences, which can contribute to the cycle of distress.
- Depression and anxiety: Trauma can increase the risk of developing depression and anxiety disorders. These mental health conditions can further exacerbate nightmares and contribute to a sense of ongoing fear, sadness, and worry.
- Emotional dysregulation: Trauma can disrupt the regulation of emotions, leading to intense and unpredictable emotional responses. This can manifest in nightmares as heightened fear, anger, or sadness during sleep.
- Hyperarousal and hypervigilance: Trauma can result in a constant state of heightened arousal and vigilance, where individuals are always on edge and anticipating potential danger. This state of hypervigilance can make it difficult to relax and sleep peacefully, increasing the likelihood of nightmares.
- Low self-esteem and self-blame: Trauma can negatively impact an individual’s self-worth and lead to self-blame or feelings of guilt and shame. These negative beliefs about oneself can contribute to the content of nightmares that often revolve around themes of helplessness and vulnerability.
- Sleep disturbances: Trauma can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to difficulties falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restful sleep. Nightmares can contribute to these sleep disturbances, creating a cycle of sleep deprivation and emotional distress.
The psychological impact of trauma can be overwhelming, and it is essential to seek professional help in processing and healing from these effects. Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), can be beneficial in addressing the psychological consequences of trauma and reducing the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares.
How trauma memories infiltrate dreams
Trauma memories have a profound and intricate way of infiltrating dreams, creating vivid and distressing scenarios that closely mirror the traumatic event. When a person experiences trauma, the memories associated with the event become deeply ingrained in their subconscious mind. These memories can be intrusive and invasive, often resurfacing during sleep in the form of nightmares. During the dreaming process, the brain relies heavily on memory retrieval and consolidation. Trauma memories, with their intense emotional charge, tend to take precedence over other memories, making them more likely to be incorporated into dreams. The brain’s attempt to process and make sense of the trauma creates a breeding ground for these memories to make their way into our dreams. The emotional impact of the trauma also plays a significant role in infiltrating dreams. The intense fear, helplessness, and distress associated with the traumatic event can seep into the dream content, causing the dreamer to relive and re-experience the emotions they felt during the actual event. This fusion of traumatic memories and heightened emotions creates a potent recipe for recurring nightmares. It is crucial to understand that these infiltrations are not a deliberate choice of the dreamer, but rather a reflection of the deep imprint left by the traumatic experience on their psyche.
Repetition as a coping mechanism
Repetition can serve as a coping mechanism for individuals who have experienced trauma and are plagued by recurring nightmares. When someone endures a traumatic event, their mind and body may struggle to process and make sense of the overwhelming emotions and sensations associated with the experience. As a result, the trauma memories often become fragmented and disorganized, making it difficult for the individual to fully grasp and integrate what happened. These fragmented memories can then infiltrate their dreams, contributing to the repetitive nature of nightmares.
The repetitive nature of these nightmares can be viewed as a way for the mind to attempt to make sense of the trauma and bring resolution to the unresolved emotions and memories. Through the repetition, the individual’s psyche may be striving to create a coherent narrative out of the fragmented memories, in an effort to process and heal from the trauma. By reliving the traumatic event in their nightmares, they may be subconsciously seeking a sense of control or mastery over the experience that eluded them in reality.
Repetition in nightmares can also serve as a form of desensitization. By repeatedly exposing themselves to the distressing images and emotions associated with the trauma, individuals may hope to gradually diminish the intensity of their emotional response. In a way, this repetition can act as a self-imposed exposure therapy, allowing the mind to gradually confront and process the traumatic experience in a controlled environment.
However, while repetition can provide a temporary sense of relief or control, it is important to note that it is not a substitute for professional therapeutic intervention. It is crucial for individuals experiencing trauma-based nightmares to seek support from mental health professionals who can provide guidance, tools, and treatments specifically tailored to their needs. Therapeutic interventions such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), and other trauma-focused therapies can help individuals address the underlying trauma and reduce the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares. Exploring coping strategies and self-care practices, such as relaxation techniques, maintaining a consistent sleep routine, and engaging in activities that promote a sense of safety and well-being, can also contribute to managing and minimizing the impact of these repetitive nightmares. So, while repetition may serve as a coping mechanism, it is essential to seek professional help to address the root causes of trauma and work towards healing and recovery.
Understanding Nightmares as a Form of Processing

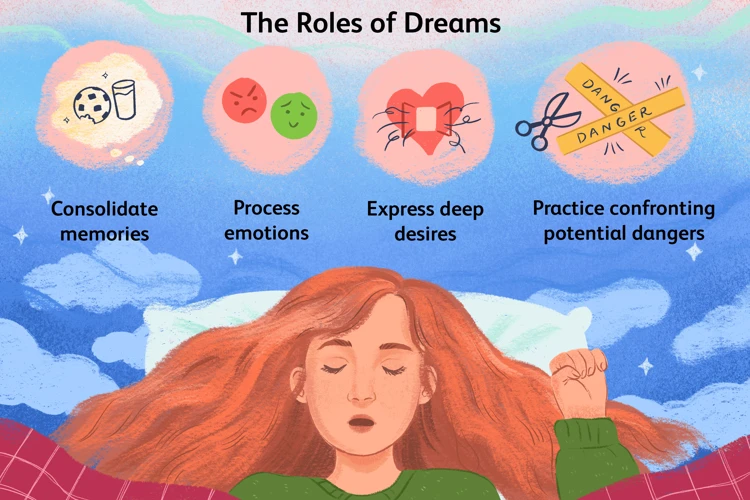
Nightmares, often characterized by intense fear, vivid imagery, and a sense of distress, can serve as a form of processing traumatic experiences. Dreams have long been recognized as a means for the brain to integrate and make sense of our daily experiences and emotions. When it comes to trauma, nightmares can be a way for individuals to confront and process the overwhelming emotions and memories associated with their traumatic event. During sleep, the brain continues to work through unresolved emotions and experiences, and this can result in the intrusion of trauma memories into dreams. In fact, research suggests that individuals who have experienced trauma are more likely to experience nightmares compared to those who haven’t. Nightmares can serve a vital function by allowing the individual to confront their fears, re-experience the trauma in a safe environment, and potentially find ways to cope and heal. To learn more about managing nightmares and developing effective coping strategies, you can explore our article on nightmare management tips. Understanding nightmares as a form of processing can help individuals find a sense of meaning and healing in their journey towards recovery.
Dreams as a means of processing trauma
Dreams serve as a powerful mechanism for the processing of trauma. They provide an avenue for the subconscious mind to make sense of and cope with traumatic experiences. When we sleep, our brain enters a state of heightened creative activity, allowing it to process, integrate, and make meaning out of the emotional and sensory information stored within our memories. During this time, the brain actively works to consolidate memories and emotions associated with trauma. Dreams can be seen as a way for the mind to replay and replayexperiences, enabling individuals to confront their fears, anxieties, and unresolved emotions that stem from the traumatic event. Through the symbolism and imagery presented in dreams, the mind attempts to make sense of the trauma by connecting fragmented memories and emotions. In doing so, it helps to create a more coherent narrative of the traumatic experience. This processing function of dreams is crucial in the healing process, as it allows individuals to gradually process and assimilate their trauma, leading to a sense of resolution and healing over time. For individuals who have experienced trauma, understanding the role of dreams as a means of processing trauma can provide insight into their nightmares and offer a path towards healing and recovery.
Intrusion of trauma memories during sleep
is a significant aspect of how trauma manifests in recurring nightmares. When an individual experiences a traumatic event, the associated memories can be stored in a fragmented and disorganized manner in the brain. During sleep, the brain attempts to process and consolidate these memories, but the fragmented nature of trauma memories can lead to their intrusion into dreams. These intrusive trauma memories can cause nightmares that vividly re-enact the traumatic event or contain elements and symbols that are closely linked to the trauma. As a result, individuals may find themselves reliving the distressing event during sleep, which can provoke intense fear, anxiety, and a sense of helplessness. This intrusion of trauma memories during sleep further reinforces the trauma’s hold on the individual’s subconscious mind and can contribute to the continuation of recurring nightmares. Understanding this intrusive nature of trauma memories during sleep is crucial in comprehending why recurring nightmares related to trauma occur and in developing effective therapeutic interventions to help individuals process and heal from their traumatic experiences.
Link between nightmares and emotional regulation
Nightmares can have a profound impact on emotional regulation, as they often elicit intense and distressing emotions during sleep. These powerful emotions can linger upon waking, influencing an individual’s emotional state and ability to regulate their feelings throughout the day. Research has shown that individuals who experience recurring nightmares often display difficulties in emotional regulation, such as difficulty managing stress, heightened emotional reactivity, and lower overall emotional resilience. The nightmares themselves serve as a catalyst for emotional dysregulation, triggering a cascade of negative emotions and physiological responses.
During nightmares, individuals may experience intense fear, anxiety, sadness, anger, or a combination of these emotions. The vivid and realistic nature of nightmares can make it challenging for the brain to distinguish between the dream world and reality, prolonging the emotional impact upon waking. This heightened emotional arousal can spill over into waking hours, making it more difficult for individuals to effectively regulate and manage their emotions in response to daily stressors.
Nightmares can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to sleep deprivation and fatigue. These physical consequences can further contribute to emotional dysregulation, as sleep deprivation has been linked to increased irritability, mood swings, and difficulty coping with stress. The combination of ongoing nightmares, emotional dysregulation, and sleep disturbances creates a vicious cycle that can lead to a significant deterioration in mental and emotional well-being.
Recognizing the link between nightmares and emotional regulation is crucial for individuals working towards healing and managing the impact of trauma. Developing strategies to improve emotional regulation, such as practicing mindfulness, engaging in therapy, and seeking support from mental health professionals, can be instrumental in breaking the cycle and promoting emotional well-being. For more tips and techniques on managing nightmares and improving emotional regulation, you can refer to our article on nightmare management tips.
Common Themes in Trauma-based Nightmares

Trauma-based nightmares often revolve around common themes that reflect the emotional and psychological impact of the traumatic event. These recurring dreams serve as a means of reliving and processing the trauma, often in a fragmented and distorted manner. One common theme in trauma-based nightmares is the re-experiencing of the traumatic event. This can involve vivid and distressing images, sounds, and sensations that mimic the original trauma. Another prevalent theme is a sense of helplessness and vulnerability, where the dreamer feels powerless in the face of danger or threat. Escape and survival is another recurring theme, often reflecting the individual’s desire to escape the trauma or overcome the challenges associated with it. These common themes not only reflect the intense emotions tied to the trauma but also provide insights into the individual’s subconscious attempts to process and cope with the experience. Understanding the common themes in trauma-based nightmares can guide therapists and individuals in their healing journey and facilitate deeper exploration and analysis.
Re-experiencing the traumatic event
When it comes to trauma-based nightmares, one common theme is the re-experiencing of the traumatic event itself. These nightmares can vividly recreate the sights, sounds, and emotions associated with the initial trauma. Individuals may find themselves reliving distressing moments, feeling as though they are back in the traumatic situation once again. These nightmares can be incredibly distressing and overwhelming, causing intense fear, anxiety, and even physical sensations similar to those experienced during the actual event. The re-experiencing of the traumatic event in nightmares often serves as a painful reminder of the unresolved emotions and memories related to the trauma. It is important to note that these nightmares are not a form of reliving the event for pleasure or nostalgia, but rather a manifestation of the ongoing psychological impact of the trauma. Processing and making sense of the traumatic event is a crucial step in the healing journey, and these nightmares can be a way for the subconscious to attempt to integrate and understand the experience. Seek professional help such as trauma-focused therapy in order to address and manage these recurring nightmares effectively.
Helplessness and vulnerability
Helplessness and Vulnerability
When trauma is experienced, it can often leave individuals feeling a profound sense of helplessness and vulnerability. The nightmares that arise from these feelings often reflect the same themes, amplifying the distress experienced during waking hours. In these nightmares, individuals may find themselves in situations where they are unable to defend or protect themselves. They may feel trapped, powerless, or at the mercy of a threatening force. The fear and anxiety associated with these dreams can be overwhelming, as they vividly reenact the emotions felt during the traumatic event. The sense of vulnerability and helplessness can be magnified in these nightmares, intensifying the emotional impact on the individual. It is important to recognize that these nightmares are a manifestation of the trauma and not a reflection of weakness or personal shortcomings. Understanding the connection between helplessness, vulnerability, and trauma-based nightmares can assist individuals in processing their experiences and seeking appropriate support and therapy.
Escape and survival
Escape and survival are recurring themes in nightmares that are rooted in trauma. When individuals experience traumatic events, the overwhelming emotions of fear, helplessness, and vulnerability often persist in their subconscious minds. In nightmares, these emotions manifest in vivid scenarios where the individual feels trapped or hunted, desperately trying to escape a threatening situation. The dreamer may find themselves running through dark forests, being chased by unknown figures, or trapped in confined spaces. The intensity of these nightmares reflects the deep-seated desire for self-preservation and the longing to break free from the memories and emotional burdens associated with the traumatic event. The sense of urgency and the instinctual drive to survive often permeate these dreams, leaving the dreamer feeling exhausted and emotionally drained upon waking. It is important to note that these nightmares can vary in their specific details and settings depending on the individual’s personal experiences and the nature of their trauma. However, the overarching theme of escape and survival remains a constant and powerful presence in trauma-based nightmares.
Impact on Sleep and Daily Functioning
Experiencing recurring nightmares as a result of trauma can have a profound impact on an individual’s sleep and daily functioning. These distressing dreams can cause sleep disturbances, leading to insomnia and disrupted sleep patterns. The fear and anxiety experienced during nightmares can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, leaving individuals feeling exhausted and drained during the day. As a result, concentration and productivity can suffer, leading to impaired performance at work or school. The emotional and cognitive effects of recurring nightmares can also spill over into waking hours, triggering feelings of irritability, sadness, and anxiety. This, in turn, can strain relationships and make it challenging to engage in daily activities. It’s important to address the impact of trauma-based nightmares on sleep and daily functioning in order to prioritize self-care and seek appropriate support and treatment. For tips on managing nightmares, you can refer to our article on nightmare management tips.
Sleep disturbances and insomnia
Sleep disturbances and insomnia are common consequences of trauma-based nightmares. Individuals who experience recurring nightmares often find it challenging to achieve restful sleep and may experience insomnia. The distressing and vivid nature of these nightmares can make it difficult for individuals to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night. As a result, they may frequently wake up feeling tired and unrested. The fear and anxiety provoked by trauma-based nightmares can also lead to physiological responses such as increased heart rate, sweating, and hypervigilance, further disrupting sleep patterns. Insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or both, can contribute to a vicious cycle, as the lack of quality sleep exacerbates the emotional distress associated with trauma. This can lead to increased anxiety and arousal, perpetuating the recurrence of nightmares and creating a detrimental impact on overall well-being. For tips and strategies on managing sleep disturbances and improving the quality of sleep, refer to our article on nightmare management tips.
Emotional and cognitive effects during waking hours
Emotional and Cognitive Effects During Waking Hours
The impact of recurring nightmares goes beyond sleep disturbances and can have significant consequences on an individual’s emotional well-being and cognitive functioning during their waking hours. These effects can vary from person to person, but many individuals who experience trauma-based nightmares report experiencing heightened levels of emotional distress and psychological symptoms throughout the day.
Emotional Effects: Trauma-based nightmares can evoke intense emotions such as fear, sadness, anger, and helplessness. These emotional responses can linger long after waking up, making it challenging for individuals to regulate their emotions effectively. They may experience heightened anxiety, irritability, and mood swings, which can impact their relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life. It is not uncommon for individuals with trauma-based nightmares to constantly feel on edge or to have intrusive thoughts related to their traumatic experiences.
Cognitive Effects: The cognitive effects of trauma-based nightmares can impair various aspects of an individual’s cognitive functioning. One common cognitive impact is difficulty concentrating and focusing on daily tasks. The intrusive nature of traumatic memories that arise during nightmares can make it challenging for individuals to stay present and engaged in their activities. Additionally, nightmares can disrupt memory consolidation and retrieval processes, making it harder to recall information or experiences accurately.
Social and Interpersonal Effects: The emotional and cognitive consequences of trauma-based nightmares can also impact an individual’s social interactions and relationships. Persistent emotional distress and cognitive impairments can lead to social withdrawal, isolation, and difficulties in forming or maintaining relationships. It can be challenging for individuals to fully engage in social activities or connect with others when their mental and emotional resources are depleted by the ongoing effects of nightmares.
It is essential for individuals experiencing these emotional and cognitive effects to seek support and professional help. Therapeutic interventions such as trauma-focused therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) have shown effectiveness in addressing the emotional and cognitive consequences of trauma-based nightmares. Implementing self-care practices, such as journaling, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques, can also be beneficial in managing the emotional and cognitive effects throughout the day. Seeking professional help and taking proactive steps towards healing can bring relief and improve overall well-being.
Impaired concentration and productivity
Impaired concentration and productivity are common consequences of recurring nightmares resulting from trauma. When individuals experience disturbed sleep due to these nightmares, it can lead to daytime fatigue and difficulty focusing on tasks. The persistent fear and anxiety caused by the nightmares can also contribute to increased distractibility and reduced productivity. Those suffering from trauma-related nightmares may find it challenging to stay engaged and complete their work or daily responsibilities. The constant intrusion of traumatic memories and disturbing imagery during sleep can leave individuals feeling mentally drained and emotionally overwhelmed during waking hours. This can further hinder their ability to concentrate, effectively problem-solve, and perform at their optimal level. Seeking therapeutic interventions, such as trauma-focused therapy, can be crucial in addressing these concentration and productivity challenges and improving overall daily functioning. Additionally, adopting self-care practices like establishing a consistent sleep routine, practicing relaxation techniques, and seeking support from loved ones can help mitigate the negative impact of impaired concentration and productivity caused by trauma-related nightmares. For more tips on managing nightmares, you can refer to our article on nightmare management tips.
Healing and Coping Strategies
Healing from trauma and finding effective coping strategies is a crucial step towards reclaiming a sense of safety and well-being. There are various therapeutic interventions available for individuals who have experienced trauma, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and trauma-focused psychotherapy. These approaches aim to help individuals process and integrate their traumatic experiences in a safe and supportive environment. Seeking professional help is essential in navigating the complex emotions and memories associated with trauma and recurring nightmares. Additionally, self-care practices can play a significant role in managing nightmares and promoting overall well-being. Engaging in relaxation techniques like deep breathing and mindfulness can help reduce anxiety and improve sleep quality. Creating a soothing bedtime routine and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can also contribute to a more restful night’s sleep. Finally, seeking support from loved ones, joining support groups, and exploring creative outlets can provide additional avenues for expression and healing. Remember, healing from trauma is a unique journey, and it is important to find what strategies work best for individual needs. For more tips on managing nightmares, you can refer to our article on nightmare management tips.
Therapeutic interventions for trauma
Therapeutic interventions for trauma play a crucial role in helping individuals heal and recover from the profound effects of trauma. The field of trauma therapy has evolved significantly over the years, offering a range of evidence-based approaches to address the unique needs and experiences of trauma survivors. One commonly used approach is trauma-focused therapy, which aims to address the specific traumatic event and its associated symptoms and distress. This can include modalities such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy, Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT), and Prolonged Exposure Therapy (PE). These therapies help individuals process and make sense of their traumatic experiences in a safe and supportive environment. Additionally, somatic therapies, such as Somatic Experiencing and Sensorimotor Psychotherapy, focus on the mind-body connection and help individuals release and regulate trauma-related tension and bodily sensations. Group therapy and support groups provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, gain support, and foster a sense of community. It’s essential to note that seeking professional help from a trained therapist is crucial when dealing with trauma. Therapists have the expertise to guide individuals through the healing process, tailor interventions to their specific needs, and provide support every step of the way. Self-care practices, such as mindfulness, grounding techniques, and creative outlets, can also be helpful in managing trauma symptoms and promoting healing. Ultimately, therapeutic interventions for trauma offer individuals the support, tools, and guidance needed to navigate their healing journey and find a path towards resilience and recovery.
Importance of seeking professional help
The importance of seeking professional help cannot be overstated when it comes to addressing the impact of trauma-related nightmares. Professional therapists and counselors specializing in trauma can provide invaluable support, guidance, and expertise in navigating the healing process. Here are some key reasons why seeking professional help is crucial:
1. Expertise and understanding: Trauma therapists have extensive knowledge and understanding of the psychological and emotional effects of trauma. They can offer a safe space to explore and process traumatic experiences, providing validation and insight into the unique challenges associated with trauma-related nightmares.
2. Evidence-based interventions: Professionals are trained in evidence-based therapeutic interventions specifically designed to help individuals cope with trauma and its manifestations in nightmares. They can tailor treatment plans to address individual needs, utilizing techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and exposure therapy.
3. Safe and supportive environment: One of the most crucial aspects of seeking professional help is finding a safe and supportive therapeutic environment. Trauma therapists create a confidential space where individuals can feel comfortable expressing their emotions, fears, and experiences without judgment. This therapeutic relationship helps build trust and facilitates the healing process.
4. Coping strategies and skills: Professional therapists can teach individuals effective coping strategies and skills to manage and alleviate the distress caused by trauma-related nightmares. These strategies may include relaxation techniques, grounding exercises, imagery rehearsal therapy, and journaling.
5. Long-term support: Trauma healing is often a long and complex journey. Professional help provides ongoing support throughout this process, helping individuals navigate challenges, setbacks, and any other issues that may arise along the way.
Remember, seeking professional help is not a sign of weakness but a courageous step towards healing and reclaiming one’s well-being. If you or someone you know is struggling with trauma-related nightmares, reaching out to a qualified professional can make a significant difference in the recovery process.
Self-care practices for managing nightmares
Self-care practices are essential for managing nightmares and promoting overall well-being. These practices can provide comfort, relaxation, and a sense of control over one’s sleep experiences. Here are some self-care strategies to consider:
1. Establish a bedtime routine: Creating a consistent nighttime routine can signal to your body and mind that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. Engage in calming activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, practicing deep breathing exercises, or listening to soothing music.
2. Create a sleep-friendly environment: Make your bedroom a comfortable and peaceful space where you feel safe and relaxed. Keep the room cool, dark, and free from distractions. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine to minimize external stimuli.
3. Practice relaxation techniques: Relaxation exercises can help reduce anxiety and promote restful sleep. Incorporate techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, or meditation into your daily routine. These practices can help calm your mind and body before bedtime.
4. Implement stress management strategies: Stress can exacerbate nightmares, so it’s essential to find effective ways to manage stress during the day. Engage in activities that help you destress, such as exercise, yoga, journaling, or spending time in nature. Find healthy outlets for emotions and seek social support when needed.
5. Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol can contribute to better sleep quality. Regular exercise helps reduce stress and promotes a more restful sleep. Remember to establish a consistent sleep schedule and prioritize getting enough sleep each night.
6. Engage in creative outlets: Artistic and creative activities such as drawing, painting, writing, or playing music can help process emotions and provide a sense of release. These outlets allow for self-expression and can be cathartic for individuals experiencing trauma-related nightmares.
By incorporating these self-care practices into your daily routine and tailoring them to your individual needs, you can create a supportive environment for managing nightmares and improving overall sleep quality. Remember that self-care is a personal journey, and it may take time to find what works best for you.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recurring nightmares can be a distressing manifestation of trauma and can significantly impact an individual’s overall well-being. These vivid and unsettling dreams often serve as a reflection of the deep psychological impact of trauma and can disrupt both sleep and daily functioning. Understanding the relationship between trauma and nightmares is crucial for individuals who have experienced trauma and those who aim to support and assist them. Seeking professional help and engaging in therapeutic interventions can help individuals cope with the effects of trauma and manage their recurring nightmares. Additionally, practicing self-care strategies, such as relaxation techniques and maintaining a healthy sleep routine, can contribute to better sleep and improved emotional well-being. Remember that healing from trauma takes time and patience, and it is important to prioritize self-care and seek support from qualified professionals. Overall, with the right support and coping mechanisms in place, individuals can work towards healing, recovering, and finding peace beyond their recurring nightmares.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the definition of trauma?
Trauma is a psychological response to a distressing or overwhelming event that poses a threat to an individual’s physical or emotional well-being.
What are the different types of trauma?
There are various types of trauma, including acute trauma (one-time events), chronic trauma (repeated or prolonged events), and complex trauma (experiencing multiple traumas over a period of time).
How does trauma affect the brain?
Trauma can disrupt neural pathways in the brain, affecting areas responsible for emotional processing, memory, and the regulation of stress. This can lead to symptoms such as hyperarousal, flashbacks, and difficulty with emotional regulation.
What are recurring nightmares?
Recurring nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that repeat over time, often containing elements or themes related to a person’s traumatic experiences. These nightmares can cause significant distress and may interfere with sleep and daily functioning.
How does trauma contribute to recurring nightmares?
Trauma can infiltrate dreams due to the psychological impact it has on an individual. Traumatic memories and emotions can manifest in nightmares as the brain attempts to process and make sense of the traumatic experience.
Why do people experience repetitive nightmares as a coping mechanism?
Repetition in nightmares can serve as a way for the brain to try and process and integrate the traumatic experience. It can be a subconscious attempt to make sense of what happened and find a resolution.
How do nightmares help with the processing of trauma?
Nightmares can provide an opportunity for the brain to process and integrate traumatic memories and emotions. They allow individuals to confront and work through their fears and anxieties in a safe, controlled environment.
What are common themes in trauma-based nightmares?
Common themes in trauma-based nightmares include re-experiencing the traumatic event, feelings of helplessness and vulnerability, and themes of escape and survival.
How do recurring nightmares impact sleep and daily functioning?
Recurring nightmares can disrupt sleep, leading to sleep disturbances, insomnia, and increased fatigue. During waking hours, these nightmares can cause emotional distress, impaired concentration, and a decrease in overall productivity.
What coping strategies can help with managing trauma-based nightmares?
Seeking therapeutic interventions for trauma, such as trauma-focused therapy or EMDR, can be beneficial. Additionally, practicing self-care techniques, such as relaxation exercises, maintaining a regular sleep routine, and seeking support from loved ones, can also aid in managing trauma-based nightmares. For more tips on managing nightmares, you can refer to our article on nightmare management tips.