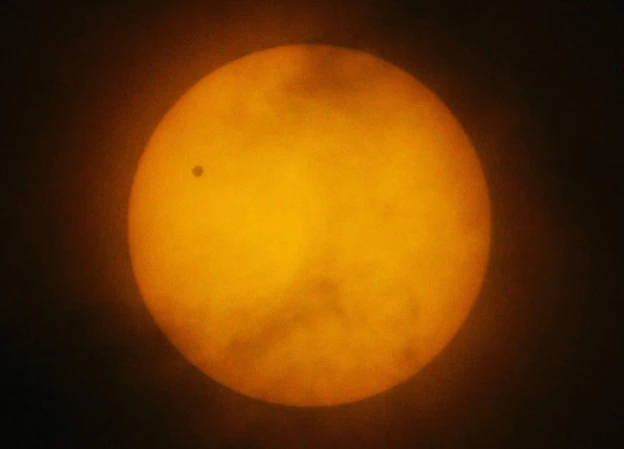
The world is full of extraordinary celestial phenomena that leave us in awe and wonder. One such phenomenon is the Transit of Venus, a rare event that captures the attention and curiosity of astronomers and sky watchers alike. This celestial spectacle occurs when Venus passes directly between the Earth and the Sun, creating a mesmerizing silhouette against the backdrop of the fiery star. The Transit of Venus has a rich historical significance and has played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the universe. In this article, we will delve into the historical significance, the science behind the event, the best ways to observe it, and the future transits that astronomy enthusiasts can look forward to. So, grab your telescopes and prepare to be captivated by the celestial dance of the Transit of Venus.
What is the Transit of Venus?

The Transit of Venus is a captivating celestial event that occurs when the planet Venus passes directly between the Earth and the Sun. This rare phenomenon can only be observed when Venus is at its inferior conjunction, which is when it is closest to the Earth. During the transit, Venus appears as a small black dot traversing across the Sun’s surface. This happens because, from our perspective on Earth, Venus is aligning with both the Sun and our planet. The transit is a result of the geometry of the solar system, with Venus’s orbit positioned in such a way that it periodically crosses the line between the Earth and the Sun. This alignment can last anywhere from a few hours to several minutes. It is crucial to note that observing the Transit of Venus should only be done with proper equipment and precautions to avoid any damage to the eyes from direct sunlight. This phenomenon provides astronomers and scientists with a unique opportunity to study the planet Venus, as well as gain insights into planetary atmospheres and the dynamics of our solar system. The Transit of Venus holds historical significance and has also played a crucial role in the advancement of scientific study and astronomical calculations.
Historical Significance

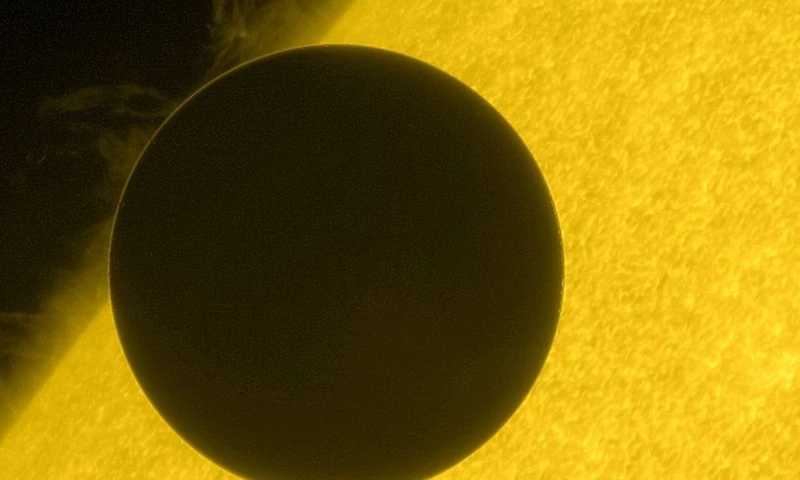
The Transit of Venus holds a significant place in history as it has served as a pivotal moment in the development of astronomy and scientific exploration. Early observations of the transit provided crucial data for astronomers to calculate the scale of the solar system. In the 17th and 18th centuries, astronomers such as Johannes Kepler and Edmond Halley realized that by observing the transit from different locations on Earth at the same time, they could accurately measure the distance between the Earth and the Sun, known as the astronomical unit (AU). This allowed for the first estimation of the scale of our solar system. The transit also played a role in the exploration of the unknown, such as Captain James Cook’s voyage to Tahiti in 1769 to observe the Transit of Venus. This expedition aimed to measure the distance between the Earth and the Sun and resulted in the creation of the first precise measurements of the solar system. The historical significance of the Transit of Venus cannot be understated as it has paved the way for advancements in scientific study and has contributed to our understanding of the universe.
1. Early Observations
Early observations of the Transit of Venus date back centuries and have contributed significantly to our understanding of the solar system. The first recorded observation of a transit occurred in 1639, by English astronomer Jeremiah Horrocks. Using a homemade telescope, Horrocks meticulously observed the transit and accurately calculated the size of Venus and its distance from the Earth. His observations marked the beginning of a new era in astronomical study. Later, in the 18th century, the renowned astronomer Edmond Halley proposed using the transit to measure the distance between the Earth and the Sun, known as the astronomical unit (AU). This idea sparked significant interest among astronomers, leading to the organization of worldwide expeditions to observe and record transits. The 1769 transit was particularly notable, as it involved expeditions to remote locations such as Tahiti and Newfoundland. These pioneering observations helped refine the calculation of the AU and paved the way for future scientific discoveries. The early observations of the Transit of Venus were crucial in advancing our knowledge of the solar system and laid the foundation for further exploration and scientific study.
[Click here to learn more about the secrets of Saturn’s rings unveiled.](/secrets-saturn-rings-unveiled/)
2. Scientific Study
The Transit of Venus has played a crucial role in scientific study and has contributed significantly to our understanding of the solar system. When Venus passes between the Earth and the Sun, it creates a unique opportunity for astronomers and researchers to study the planet’s atmosphere. By observing the transit, scientists can analyze the light passing through Venus’ atmosphere and gather valuable data about its composition. This information helps scientists gain insights into the planet’s temperature, pressure, and chemical makeup. One notable study enabled by the Transit of Venus involved the search for dark matter in the universe. Dark matter is a mysterious substance that makes up a significant portion of the universe’s mass but cannot be directly observed. Researchers used the transit to analyze the bending of light as it passed through Venus’ atmosphere, which provided valuable clues about the presence and distribution of dark matter. This study opened up new avenues of research and furthered our understanding of the elusive dark matter. Additionally, the Transit of Venus has been utilized to study distant stars and their properties. For example, during the transit, scientists can measure the brightness variations of distant stars such as Betelgeuse. These measurements help astronomers understand the complexities of stellar evolution and provide insights into the life cycles of massive stars. The scientific study of the Transit of Venus continues to contribute to our knowledge of the universe and its various phenomena.
3. Captain Cook’s Expedition
Captain Cook’s expedition during the Transit of Venus is a significant event in the history of astronomical observation. In the late 18th century, the British Royal Society organized an ambitious mission led by Captain James Cook to observe the transit in order to calculate the size of the solar system. Cook and his crew sailed to the remote island of Tahiti in the Pacific Ocean, where they set up an observation site to carefully record the timing and duration of the transit. This data was crucial for scientists to make accurate measurements and calculations of the distance between the Earth and the Sun, known as the astronomical unit. Cook’s expedition was a remarkable feat of navigation and planning, and it provided valuable observations that contributed to our understanding of the solar system. The success of this expedition not only advanced scientific knowledge but also marked a milestone in maritime exploration. The significance of Captain Cook’s expedition during the Transit of Venus cannot be overstated, and it stands as a testament to humanity’s relentless curiosity and quest for knowledge about the universe we inhabit.
How Often Does the Transit of Venus Occur?
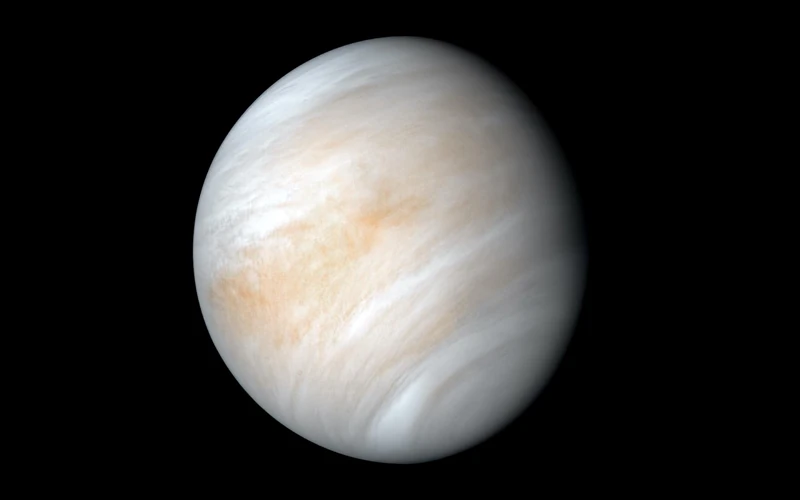

The Transit of Venus is a relatively rare celestial phenomenon that occurs in pairs separated by eight years. These pairs of transits are then separated by either 105 or 121 years. For example, if a transit occurs in one year, the next pair of transits will happen either 105 or 121 years later. This unique pattern is due to the alignment of Earth, Venus, and the Sun, which causes the transits to follow a specific cycle. The last pair of transits occurred in 2004 and 2012, and the next pair is predicted to happen in 2117 and 2125. This long interval between occurrences makes witnessing a transit of Venus a truly rare event in a person’s lifetime. The infrequency of the transits adds to their allure and sense of wonder, making them highly anticipated by astronomers and enthusiasts alike. It is worth noting that these transits have played a significant role in historical astronomical discoveries and continue to contribute to our understanding of the universe and planetary dynamics.
How Does It Happen?
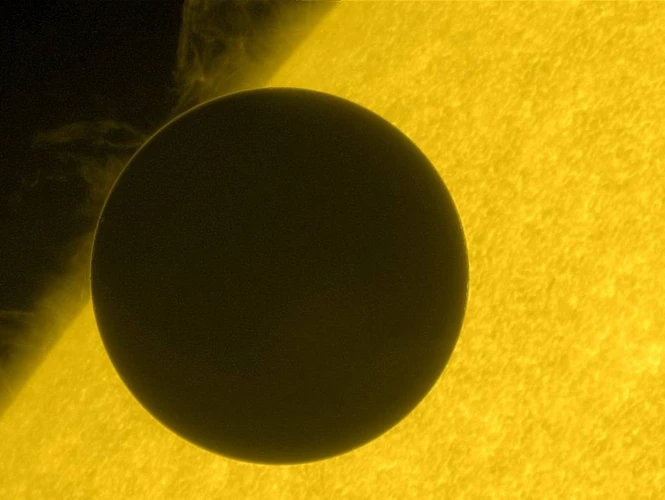
The occurrence of the Transit of Venus is a fascinating celestial phenomenon that is due to the relative positions of Venus, Earth, and the Sun in their respective orbits. As Venus orbits the Sun, it occasionally aligns with Earth in such a way that it passes between us and the Sun. This alignment occurs when Venus is at its inferior conjunction, which is the point in its orbit where it is closest to Earth. When this happens, Venus appears as a small black dot crossing the face of the Sun. The main reason for this phenomenon is the difference in orbital planes between Venus and Earth. While both planets orbit the Sun, their orbits are at a slight angle to each other. As a result, the Sun, Venus, and Earth only align in a way that allows for a Transit of Venus to occur approximately every 243 years. These transits occur in pairs, eight years apart, separated by over a century. The last pair occurred in 2004 and 2012. Understanding the mechanics of how the Transit of Venus happens has not only provided invaluable insights into the workings of our solar system but also contributed to the development of precise astronomical calculations and measurements. It is through such observations that scientists have been able to determine fundamental factors like the distance between the Earth and the Sun, known as the Astronomical Unit (AU), which plays a crucial role in our understanding of the cosmos.
Observing the Transit

Observing the Transit of Venus is an exciting endeavor for astronomy enthusiasts. To safely view this rare celestial event, specific equipment and precautions must be taken. One of the essential pieces of equipment is a solar filter, which helps protect the eyes from the intense brightness of the Sun. Specialized solar viewing glasses or telescopes with solar filters are recommended. It is crucial never to view the Sun directly without proper protection, as it can cause severe eye damage. Additionally, finding the best viewing spot is crucial for optimal visibility. Clear skies are essential, so checking the weather forecast is a good idea. Urban areas with tall buildings and trees can obstruct the view, so finding an open location with an unobstructed view of the horizon is ideal. Some popular locations for observing the Transit of Venus include open fields, hills, or even astronomical observatories. By following safety measures and choosing the right equipment, observers can witness this awe-inspiring celestial phenomenon and marvel at the wonders of our solar system.
1. Equipment Needed
When it comes to observing the Transit of Venus, having the right equipment is essential for a safe and rewarding experience. Here are some key items you’ll need:
1. Solar Filter: Never observe the Sun directly without proper protection. A solar filter is a crucial component for safely viewing the Transit of Venus. It blocks harmful radiation and reduces the intense brightness of the Sun, allowing you to see the silhouette of Venus. Make sure to use a certified solar filter that fits securely over your telescope or binoculars.
2. Telescope or Binoculars: Having a telescope or binoculars with a suitable magnification will enhance your view of the transit. A telescope with a solar filter will provide a more detailed image, allowing you to observe Venus in greater clarity. Binoculars, when equipped with a solar filter, can also provide a good view of the transit.
3. Mount or Tripod: To keep your telescope or binoculars steady during the observation, using a mount or tripod is recommended. This will help minimize shaking or blurring, ensuring a clearer view of the transit.
4. Sun Finder: Locating the Sun can be challenging without the proper tools. A Sun finder is a helpful device that can assist you in aligning your telescope or binoculars accurately. It uses filters or mirrors to project an image of the Sun, making it easier to center your view.
5. Proper Attire: While not necessarily equipment, it’s important to dress appropriately for your observation. Wear protective clothing and a hat to shield yourself from the Sun’s intense heat and harmful rays. Sunglasses are not enough to protect your eyes, so make sure to rely on certified solar filters instead.
Remember, safety should always be a top priority when observing any solar event. Be cautious and follow proper guidelines to protect your eyes and equipment. Enjoy the awe-inspiring sight of the Transit of Venus with the appropriate equipment in hand.
2. Safety Measures
2. Safety Measures:
– Never look directly at the Sun during the Transit of Venus without proper eye protection. The Sun’s intense rays can cause permanent damage to your eyes, even during a partial or annular eclipse. To view the transit safely, use specialized solar filters or eclipse glasses that are designed to block harmful ultraviolet and infrared radiation. These filters should meet the ISO 12312-2 safety standard to ensure maximum protection.
– Another safe way to observe the transit is by using solar telescopes or binoculars equipped with solar filters. These filters attenuate the Sun’s brightness, allowing you to see Venus as a small black dot against the Sun’s disk. Always make sure to carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using such equipment to prevent any accidents or damage.
– If you don’t have access to specialized eclipse glasses or solar filters, you can indirectly observe the transit through a pinhole projector. Create a small hole on a piece of cardboard or paper and hold it up in sunlight, allowing the Sun’s image to project onto another surface. This method creates a safe and magnified view of the transit without any direct exposure to the Sun’s rays.
– Remember to educate and supervise children during the transit to ensure their safety. Encourage them to follow the same safety guidelines and emphasize the importance of never looking directly at the Sun without proper eye protection.
– Lastly, be mindful of the weather conditions during the transit. Overcast skies or cloudy weather may obstruct the view of the Sun and Venus. Ensure you have a clear line of sight to the Sun before attempting to observe the transit.
Following these safety measures will help you enjoy the Transit of Venus safely and protect your eyes from the Sun’s harmful radiation.
3. Finding the Best Viewing Spots
When it comes to observing the Transit of Venus, finding the best viewing spots is crucial for a memorable and clear experience. Here are some tips to help you find the perfect location:
1. Check the Weather: Before planning your viewing expedition, make sure to check the weather forecast for your area. Clear skies are essential for a successful observation, so choose a spot with the highest chance of clear weather.
2. Research Astronomical Organizations: Local astronomy clubs and organizations often organize special events and gatherings for observing celestial events like the Transit of Venus. These groups have experienced members who can guide you to the best viewing spots and provide insights on equipment and safety precautions. Check their websites or contact them for information on planned events.
3. Seek High Ground: Finding an elevated location away from city lights and obstructions is ideal for clear viewing. Mountains, hills, or even rooftop observatories can provide excellent vantage points to observe the transit without interference.
4. Consider Traveling: If you are determined to witness the Transit of Venus in all its glory, consider traveling to locations with a higher chance of optimal viewing conditions. Popular destinations for astronomical events include remote areas with minimal light pollution, like national parks or observatories.
5. Safety First: Remember to prioritize your safety during the observation. Never look directly at the Sun without proper eye protection. Utilize solar filters specifically designed for telescopes and binoculars to safeguard your eyes from harmful radiation.
By taking these factors into consideration and planning ahead, you can ensure a memorable and successful observation of the Transit of Venus. So, pack your gear, find the ideal spot, and prepare to witness this celestial marvel firsthand.
Note: For more on the fascinating mysteries of the universe, you may be interested in exploring the concept of dark matter and its role in shaping our understanding of the cosmos, or the intriguing brightness variations of Betelgeuse, a well-known star in the constellation Orion.
Notable Transits of Venus
Throughout history, there have been several notable transits of Venus that have captured the attention of astronomers and the general public alike. One such significant event was the Transit of Venus in 1639, where Jeremiah Horrocks and William Crabtree made independent observations in England, marking it as the first recorded transit. Another remarkable transit took place in 1874 when the American astronomer Maria Mitchell led an all-women expedition to observe the event from different locations. Their observations helped refine the value of the Astronomical Unit and contributed to the field of solar parallax measurements. In more recent times, the Transit of Venus in 2004 drew global interest and provided valuable data for scientists studying exoplanets. These notable transits of Venus have not only advanced our understanding of the universe but have also served as historical milestones in the field of astronomy.
1. The Transit of 1639
The Transit of 1639 holds great significance in the history of astronomy. It was the first recorded observation of the transit of Venus, and it played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the solar system. The French astronomer, Pierre Gassendi, meticulously observed the transit and documented his findings. Gassendi’s observations helped confirm the theories proposed by Johannes Kepler and Nicolaus Copernicus regarding the heliocentric model of our solar system. By measuring the exact timing and duration of the transit, Gassendi provided valuable data that allowed astronomers to accurately calculate the distance between the Earth and the Sun. This, in turn, led to the development of the Astronomical Unit (AU), which is a fundamental unit of measurement used in astronomical calculations. The transit of 1639 marked a significant milestone in our understanding of the cosmos and paved the way for future scientific discoveries.
2. The Transit of 1874
The Transit of 1874 was a particularly significant event in the study of the celestial phenomenon. It was observed by numerous scientists and astronomers who were eager to gain a deeper understanding of the solar system. One of the most notable expeditions during this time was led by the British astronomer Sir Edward James Stone, who traveled to the island of Rodrigues in the Indian Ocean to observe the transit. Stone’s expedition was part of a broader international effort to collect data and measurements from various locations around the world to calculate the scale of the solar system. The 1874 transit proved crucial in providing valuable data that helped astronomers determine the distance between the Earth and the Sun, known as the Astronomical Unit (AU). By carefully observing and timing the transit from different vantage points, scientists were able to make highly accurate calculations, leading to a more precise measurement of the AU. This information was instrumental in furthering our understanding of the solar system’s scale and paved the way for advancements in space exploration and astronomical research. The Transit of 1874 marked a significant milestone in the history of scientific study and highlighted the importance of international collaboration in astronomical observations and discoveries.
3. The Transit of 2004
The Transit of Venus in 2004 was a highly anticipated event that garnered significant attention from astronomers and sky watchers around the world. It was the first transit visible from Earth since the year 1882. During this transit, Venus appeared as a small black dot crossing the face of the Sun, captivating observers with its rare and spectacular view. The 2004 transit occurred on June 8th and was visible from various parts of the globe, including Europe, Asia, and Africa. Astronomers and scientists seized this opportunity to study the event in detail, using advanced telescopes and equipment to capture images and measurements. By meticulously observing and analyzing the transit, scientists were able to refine their understanding of Venus’s atmosphere, as well as gain insights into the precise calculations of the astronomical unit (AU). The 2004 Transit of Venus served as a significant milestone in astronomical research and further fueled the curiosity and admiration for these celestial occurrences.
Scientific Importance
The Transit of Venus holds great scientific importance and has contributed to significant advancements in our understanding of the universe. Here are three key scientific aspects that make this celestial event particularly noteworthy:
1. Measuring the Astronomical Unit: One of the most significant contributions of the Transit of Venus is its role in measuring the distance between the Earth and the Sun, known as the Astronomical Unit (AU). By observing the transit from different locations on Earth, scientists can measure the time it takes for Venus to cross the sun’s disk. Using the principles of parallax, they can then calculate the distance between Earth and Venus, and subsequently determine the AU. This measurement is crucial for accurately determining the distances between celestial bodies in our solar system.
2. The Search for Exoplanets: The study of transits, like the Transit of Venus, has provided valuable insights into the search for exoplanets. When a planet passes in front of its host star, it causes a slight dimming of the star’s light, known as a transit. By analyzing the timing and characteristics of these transits, scientists can detect and study exoplanets, including their size, orbit, and even composition. The Transit of Venus has helped refine the techniques used to detect exoplanets and has paved the way for the discovery and understanding of other planetary systems beyond our own.
3. Studying Planetary Atmospheres: During the Transit of Venus, sunlight passes through Venus’s atmosphere before reaching Earth. By analyzing this sunlight, astronomers can gain valuable insights into the composition and properties of Venus’s atmosphere. They can detect various gases, such as carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide, as well as study the temperature, pressure, and chemical composition of the planet’s atmosphere. This information is crucial for understanding not only Venus but also for comparing and contrasting it with other planets in our solar system.
The Transit of Venus thus holds immense scientific importance, contributing to our knowledge of astronomical distances, the search for exoplanets, and the study of planetary atmospheres. With each occurrence of this rare celestial event, scientists are given new opportunities to expand our understanding of the universe and its many wonders.
1. Measuring the Astronomical Unit
One of the significant scientific contributions of the Transit of Venus is its role in measuring the astronomical unit. The astronomical unit (AU) is a fundamental unit of measurement in astronomy, representing the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. During the Transit of Venus, astronomers can use a technique known as parallax to determine the distance between the Earth and the Sun more accurately.
The parallax method involves observing the transit from two different locations on Earth, ideally on opposite sides of the planet. By precisely measuring the time it takes for Venus to cross the Sun’s disk from each location, astronomers can calculate the parallax angle. This angle is a result of the different viewing perspectives from the two observing points.
Using the parallax angle, along with the known distance between the two observing points on Earth, astronomers can use simple trigonometric formulas to estimate the distance between the Earth and the Sun. This crucial measurement allows for a more precise determination of the AU.
Notably, the transit events of 1761 and 1769 played a vital role in refining the measurement of the AU. Scientists from around the world undertook expeditions to various locations to observe the transits and gather data. These measurements, combined with meticulous calculations, brought astronomers closer to determining the accurate value of the AU.
Understanding the precise value of the AU has numerous practical applications in astronomy. It serves as a vital reference point for measuring distances within our solar system and beyond, such as determining the distances to other planets, asteroids, and even stars. Accurate AU measurement has led to important discoveries and advancements in various areas of astrophysics, including the study of exoplanets and the search for habitable worlds beyond our solar system.
2. The Search for Exoplanets
The Transit of Venus has also been instrumental in the search for exoplanets, which are planets that exist outside of our solar system. One of the key methods used to detect exoplanets is the transit method, which relies on observing the dimming of a star’s brightness when a planet passes in front of it during its orbit. This technique is based on the same principle as the Transit of Venus, where the planet Venus blocks a small portion of the Sun’s light as it passes between the Earth and the Sun. By studying transits of Venus and understanding the characteristics of these events, astronomers have gained valuable insights into how to identify and study exoplanets using the transit method. The transit method has proven to be a powerful tool in discovering and characterizing thousands of exoplanets to date. By studying the size, mass, and composition of these planets, astronomers can gain a better understanding of the diversity of planetary systems beyond our own. The Transit of Venus has therefore contributed significantly to our knowledge of the vast array of exoplanets that exist in the universe.
3. Studying Planetary Atmospheres
Studying planetary atmospheres is another important aspect of the Transit of Venus. During the transit, scientists have the unique opportunity to observe the faint ring of light that surrounds Venus, known as the planet’s atmosphere. By carefully analyzing the passage of Venus across the face of the Sun, researchers can gather valuable data about the composition and properties of Venus’s atmosphere. This information helps scientists better understand the complex processes occurring within planetary atmospheres, such as the greenhouse effect and the presence of various gases. Additionally, studying Venus’s atmosphere during the transit can provide insights into the similarities and differences between our neighboring planet’s atmosphere and Earth’s atmosphere. This knowledge is crucial in our quest to understand the conditions necessary for the existence and sustainability of life on other planets. The Transit of Venus thus serves as a gateway for scientists to delve deeper into the mysteries of planetary atmospheres and unravel the complexities of our cosmic neighbors.
Transits of Other Planets

The Transit of Venus is not the only transit phenomenon that occurs in our solar system. In fact, transits can also be observed for other planets, providing valuable opportunities for scientific study and astronomical observations. One notable example is the Transit of Mercury, which is similar to the Transit of Venus but involves the planet Mercury passing between the Earth and the Sun. However, due to its smaller size, Mercury appears as an even smaller dot compared to Venus during its transit. Transits of other planets, such as Mars or Jupiter, are much rarer and occur even less frequently than the Transit of Venus. The study of these transits allows astronomers to gather data on the planets’ atmospheres, their orbital characteristics, and even search for signs of exoplanets. While the Transit of Venus may be the most famous and well-known transit, it is important to acknowledge and explore the transits of other planets, which provide unique insights into the workings of our solar system and beyond.
Future Transits
Future Transits of Venus offer exciting opportunities for astronomers and sky watchers to witness this rare celestial event. After a Transit of Venus occurs, a new cycle begins, signaling when the next transits will take place. These future transits are highly anticipated as they allow scientists to continue their research and exploration of Venus and its position in our solar system. The next pair of transits will occur in the 22nd century, with the first one expected in 2117, followed by the second in 2125. These events will be observed by future generations, offering them the chance to marvel at the beauty and scientific significance of the Transit of Venus. However, it’s important to note that transits of Venus are relatively rare, with over a century passing between each pair. Because of their infrequency, it’s crucial to plan and prepare well in advance to ensure that you don’t miss out on the opportunity to witness this breathtaking celestial occurrence. So mark your calendars and make sure to share this information with future astronomers and enthusiasts, as they will have a chance to marvel at the Transit of Venus firsthand in the years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Transit of Venus is a truly rare and awe-inspiring celestial phenomenon. This event, where Venus passes between the Earth and the Sun, has captivated astronomers and sky watchers throughout history. Not only does the Transit of Venus have a rich historical significance, but it also holds great scientific importance. From early observations to Captain Cook’s expedition, the transit has provided invaluable data for scientific study. With the advancements in technology, we now have the tools to observe and document the transit in detail, allowing us to further our understanding of the universe. The Transit of Venus has also played a crucial role in measuring the astronomical unit, searching for exoplanets, and studying planetary atmospheres. As we look to the future, there will be more opportunities to witness and study the transit, providing even more insights into the workings of our solar system. So, whether you’re an astronomy enthusiast or just someone who appreciates the wonders of the universe, be sure to mark your calendars for the next Transit of Venus and witness this extraordinary event for yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How often does the Transit of Venus occur?
The Transit of Venus occurs in pairs, with each pair separated by eight years. After that, there is a gap of over a century before the next pair of transits occurs.
2. Can anyone see the Transit of Venus?
Yes, the Transit of Venus can be observed from various parts of the world, depending on the alignment of the Sun, Earth, and Venus. However, it is important to use proper equipment and take safety measures to protect your eyes during observation.
3. What equipment do I need to observe the Transit of Venus?
To safely observe the Transit of Venus, you will need a telescope with a solar filter or special eclipse glasses. These protective tools allow you to view the event without harming your eyes.
4. Why is the Transit of Venus historically significant?
The Transit of Venus has historical significance as it played a crucial role in early attempts to calculate the distance from the Earth to the Sun. These calculations, known as the “astronomical unit,” helped scientists determine the scale of the solar system.
5. Did Captain Cook observe the Transit of Venus?
Yes, Captain James Cook embarked on a groundbreaking expedition to observe the Transit of Venus in 1769. The observations made during this expedition helped refine our understanding of the solar system.
6. What scientific studies can be conducted during a Transit of Venus?
The transit provides scientists with an opportunity to study the atmospheres and properties of both Venus and Earth. It also allows for the measurement of the intensity of sunlight passing through the different layers of Venus’s atmosphere.
7. Can the Transit of Venus be used to discover exoplanets?
Yes, the transit method utilized during the observation of the Transit of Venus is similar to the technique used in the discovery of exoplanets. By analyzing the slight dimming of a star’s light as a planet passes in front of it, astronomers can infer the presence of exoplanets.
8. How long does the Transit of Venus last?
The duration of the Transit of Venus varies, but it typically lasts for several hours. The duration can depend on various factors, including the position and speed of Venus in its orbit.
9. When was the most recent Transit of Venus?
The most recent Transit of Venus took place on June 5-6, 2012. It was widely observed and celebrated by astronomers around the world.
10. When is the next Transit of Venus expected?
The next Transit of Venus is expected to occur on December 10-11, 2117. It will be an eagerly awaited event for future generations of astronomers and sky watchers.








