Have you ever found yourself waking up with a sense of déjà vu, as if you’ve lived through the same dream over and over again? Recurring dreams are a fascinating phenomenon that have intrigued and puzzled us for years. These dreams, which repeat themselves in similar patterns or themes, can often leave us wondering why they happen and what they mean. In this article, we will delve into the science behind recurring dreams, exploring various theories that attempt to explain their occurrence. From psychological and neurological perspectives to spiritual and parapsychological beliefs, we will uncover the possible reasons behind these repetitive nocturnal experiences. Additionally, we will examine the role of recurring dreams in emotional processing and their connection to REM sleep. Join us on this journey as we unravel the secrets behind this enigmatic aspect of our dream world.
What are Recurring Dreams?
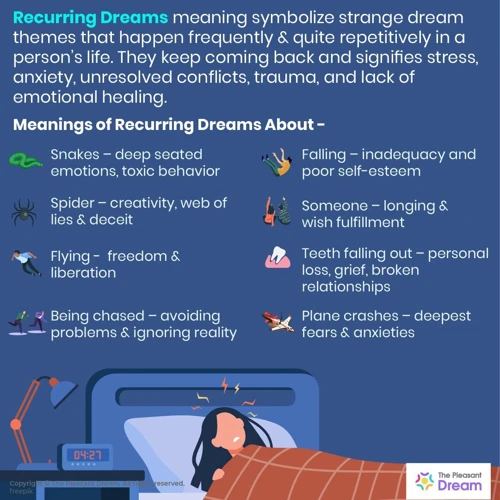
Recurring dreams are a fascinating aspect of the human dreaming experience. These dreams, which often repeat themselves with similar themes or patterns, can leave individuals feeling curious and sometimes even perplexed. The definition of recurring dreams encompasses the idea that they involve the repetition of specific dream scenarios or content. Unlike regular dreams that may be forgotten or rarely experienced again, recurring dreams tend to recur frequently and can persist over a long period. While research is ongoing to understand the common themes in recurring dreams, some common examples include being chased, falling, or being unprepared for an exam. These dreams may vary in content and intensity from person to person, but they often evoke intense emotions and can be highly memorable. Understanding the significance and frequency of recurring dreams is crucial in unraveling their mysterious nature and potential symbolism. The analysis of such dreams can offer valuable insight into an individual’s subconscious mind and can serve as a powerful tool for self-reflection. By exploring the intriguing world of recurring dreams, we can gain a deeper understanding of their origins and significance in our lives.
Definition of Recurring Dreams
The definition of recurring dreams refers to a type of dream experience characterized by the repetition of specific dream scenarios or content. These dreams differ from ordinary dreams in that they occur with frequency and persist over time. Recurring dreams may involve similar themes, symbols, or situations that reoccur across multiple dream episodes. The content of these dreams can vary widely from person to person, but some common themes include being chased, falling, or being unprepared for an important event. These dreams tend to be vivid and memorable, often evoking strong emotions such as fear, anxiety, or curiosity. The repetitiveness of recurring dreams sets them apart and raises questions about their underlying meaning and significance. Exploring the patterns and symbolism within these dreams can offer valuable insights into the subconscious mind and provide a window into our inner thoughts, feelings, and desires.
Common Themes in Recurring Dreams
When it comes to recurring dreams, there are several common themes that tend to reappear in people’s dream experiences. One prevalent theme is the sensation of falling. Many individuals report having recurring dreams where they are plummeting from great heights, often accompanied by a feeling of fear or unease. Another frequently encountered theme is being chased. In these dreams, the dreamer is pursued by an unknown entity or person, creating a sense of urgency and anxiety. Dreams involving teeth are also quite common. People often report dreams where their teeth are falling out, breaking, or crumbling, which can be associated with feelings of vulnerability or loss of control. Another recurring theme is being unprepared for an exam or an important event. These dreams reflect the fear of being judged or evaluated. Additionally, dreams featuring death or encounters with deceased loved ones may occur repeatedly, potentially indicating unresolved grief or the need for closure. It is important to remember that while these themes are common, the specific meanings behind them can vary from person to person. Exploring the symbolism and personal associations of these recurring dream themes can provide valuable insights into an individual’s subconscious mind.
Theories Explaining Recurring Dreams
There are several theories explaining recurring dreams from various perspectives. From a psychological standpoint, some theories propose that recurring dreams are a reflection of unresolved conflicts or unresolved emotions in our waking lives. These dreams may serve as a way for our subconscious mind to process and navigate through these unresolved issues. Another psychological theory suggests that recurring dreams may be linked to particular life events or traumas that have left a significant impact on an individual’s psyche. These dreams may be a means of revisiting and attempting to work through the emotions associated with these events. Neurologically, some theories suggest that recurring dreams might occur due to heightened brain activity in certain regions during sleep. These patterns of brain activity may lead to the replaying of specific dream content. From a spiritual or parapsychological perspective, some theories propose that recurring dreams could be messages or insights from the spiritual realm. These dreams may carry symbolic meanings or offer guidance on a deeper level. While these theories provide potential explanations, the true nature and causes of recurring dreams are still subject to ongoing research and exploration.
Psychological Theories
Psychological theories provide valuable insights into the phenomenon of recurring dreams. One theory suggests that recurring dreams may be a result of unresolved emotions or psychological conflicts. These dreams could serve as a mechanism for the unconscious mind to process and work through unresolved issues. In therapy, recurring dreams are often explored as a way to uncover underlying psychological tensions and facilitate healing. Another psychological theory proposes that recurring dreams could be a form of emotional rehearsal. Similar to how we practice certain skills in our waking lives, our dreams could serve as a practice ground for dealing with emotional challenges. This theory suggests that recurring dreams may help individuals prepare emotionally for real-life situations they anticipate or fear. By exploring these psychological theories, we can gain a deeper understanding of the potential functions and meanings behind recurring dreams.
Neurological Theories
Neurological theories provide another perspective on the phenomenon of recurring dreams. These theories suggest that the occurrence of recurring dreams may be attributed to the brain’s natural processes during sleep. One neurological theory proposes that recurring dreams are a result of neural pathways being reinforced and strengthened in the brain. According to this theory, when certain memories or experiences are repeatedly activated during REM sleep, the brain forms stronger connections related to those experiences. This can lead to the repetition of specific dream content, as these strengthened connections make it more likely for the same neural patterns to be activated again. Another neurological theory suggests that the brain’s attempts to consolidate memories during sleep may contribute to recurring dreams. During REM sleep, the brain engages in memory consolidation processes, where it organizes and stores information from the day. This theory posits that if certain memories or experiences are particularly emotionally charged or significant, the brain may prioritize their consolidation, leading to the repetition of related content in dreams. These neurological theories offer valuable insights into the potential underlying mechanisms behind recurring dreams and highlight the intricate relationship between the brain’s processes during sleep and the content of our dreams.
Spiritual/Parapsychological Theories
Spiritual and parapsychological theories offer another perspective on the phenomenon of recurring dreams. These theories suggest that recurring dreams may have a spiritual or supernatural significance. According to these beliefs, recurring dreams could be messages from the spiritual realm or reflections of past lives. Some people believe that these dreams are an indication of unresolved issues or karma from previous incarnations that need to be addressed. Additionally, parapsychologists propose that recurring dreams could be a result of psychic abilities or a connection to the collective unconscious. They suggest that these dreams may contain hidden symbols or messages that can only be deciphered through spiritual or psychic interpretations. While these theories may lack scientific evidence or consensus, they provide an alternative explanation for the mysterious nature of recurring dreams. Exploring these spiritual and parapsychological perspectives adds a layer of intrigue to the ongoing quest to understand the origin and purpose of recurring dreams. Whether one accepts these theories or not, they contribute to the rich tapestry of ideas surrounding the enigmatic realm of dreams.
Dreams as Emotional Processing

Dreams play a significant role in emotional processing and can provide a unique platform for dealing with unresolved emotions. Unresolved emotions can often linger in our subconscious mind, affecting our thoughts and behavior in our waking lives. However, during sleep, our brains have the opportunity to process and integrate these emotions in the form of dreams. Dreams serve as a means of emotional release, allowing us to confront and explore our deepest fears, anxieties, and desires. This emotional processing can lead to a sense of catharsis and provide a sense of relief upon waking. Dreams act as a form of emotional rehearsal, allowing us to experience and practice dealing with challenging emotional situations in a safe and controlled environment. By confronting and working through these emotions in our dreams, we may be better equipped to handle similar situations in our waking lives. It is important to acknowledge the role of dreams as a powerful tool for emotional processing and to embrace the valuable insights they provide. Through further exploration, we can unlock the intricate connection between our dreams and our emotional well-being.
Role of Unresolved Emotions
The role of unresolved emotions in recurring dreams is a significant aspect to explore. Dreams serve as a pathway for the subconscious mind to process and integrate emotions, experiences, and conflicts. When emotions are left unresolved or unaddressed in waking life, they can manifest in dreams in the form of recurring motifs and scenarios. These dreams act as a means of highlighting and emphasizing the unresolved emotional issues that may require attention. The role of unresolved emotions in recurring dreams can range from unresolved trauma, unexpressed feelings, or unresolved conflicts in relationships. For example, someone who has experienced a traumatic event may continue to have recurring dreams related to that event until they process and heal from it. Similarly, if someone is struggling with unexpressed anger or grief, it may manifest in their dreams as recurring themes associated with those emotions. By acknowledging and addressing these unresolved emotions, individuals can potentially find closure, release emotional burdens, and gain a sense of resolution in their dreams and waking life. Understanding the role of unresolved emotions in recurring dreams can provide valuable insights into our emotional well-being and guide us towards personal growth and healing.
Dreams as Emotional Rehearsal
Dreams serve as a fascinating realm where our emotions can be explored and processed, and one theory explaining recurring dreams is that they function as emotional rehearsals. This role of unresolved emotions suggests that recurring dreams provide an opportunity for our minds to revisit and process unresolved emotional experiences or conflicts that we may not have adequately dealt with in our waking lives. These dreams often bring forward intense feelings and emotions connected to past events or relationships. By replaying these scenarios in our dreams, our subconscious mind may be attempting to make sense of these emotions and find resolution or closure. This emotional rehearsing can offer a safe space to explore and confront our feelings, allowing us to gain a deeper understanding of ourselves and our relationships. It is also possible that these dreams serve as a way for our mind to prepare for future emotional challenges, allowing us to practice and rehearse our responses to certain situations. While the exact mechanisms behind dreams as emotional rehearsals are still the subject of ongoing research, it is clear that they play a significant role in our emotional processing and growth.
REM Sleep and Dream Rehearsal
REM sleep, also known as Rapid Eye Movement sleep, plays a significant role in the occurrence and rehearsal of dreams. During REM sleep, our brain activity resembles that of wakefulness, and it is during this stage that dreams are most likely to occur. Research suggests that REM sleep and memory consolidation are closely intertwined. It is believed that the brain uses this stage of sleep to process and consolidate information from the day, including emotional experiences. This process could explain why recurring dreams often involve unresolved emotions or themes related to significant life events. Furthermore, REM sleep and problem solving have been linked, suggesting that the mind may use this state to rehearse and explore potential solutions to real-life challenges. Dreams can serve as a safe environment for the brain to simulate different scenarios and test various outcomes. This hypothesis aligns with the notion that recurring dreams may represent a form of rehearsal, allowing individuals to confront and process complex emotions or situations. The intricate relationship between REM sleep and dream content is still being explored, but it offers insights into why recurring dreams can have such a profound impact on our subconscious minds.
REM Sleep and Memory Consolidation
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, plays a crucial role in memory consolidation. During this stage of sleep, our brain becomes highly active, and it is believed to be the phase in which memories are solidified and stored. Research has shown that the brain’s hippocampus and neocortex, regions responsible for memory processing, are particularly active during REM sleep. As we dream, our brain not only processes emotional experiences but also integrates newly acquired information into existing memory networks. This process helps to reinforce and strengthen memories, making them more resistant to forgetting. The connection between REM sleep and memory consolidation suggests that recurring dreams may serve as a means of reinforcing specific memories or experiences. It is possible that recurring dreams focus on unresolved emotions or unresolved conflicts, allowing the brain to repeatedly process and consolidate the associated memories. By revisiting these memories during REM sleep, the brain can further encode and consolidate them, contributing to the persistence of recurring dream themes and content. Understanding the role of REM sleep in memory consolidation can provide valuable insight into the potential mechanisms behind the occurrence of recurring dreams.
REM Sleep and Problem Solving
During REM sleep, when we experience vivid dreams, there is evidence to suggest that our brain is actively engaged in problem-solving activities. The relationship between REM sleep and problem solving has been studied extensively, and researchers have found that this stage of sleep is crucial for cognitive processing and creative thinking. One theory suggests that during REM sleep, our brain consolidates memories and processes information gathered throughout the day, which can lead to insights and solutions to complex problems. Studies have shown that individuals who engage in REM sleep have higher levels of creativity and are more likely to find innovative solutions to challenging tasks. Additionally, research has shown that sleep can enhance learning and improve overall cognitive performance. The process of dreaming during REM sleep helps to stimulate neural connections and strengthen memory recall. This phenomenon not only aids in problem-solving but also contributes to improving decision-making skills and critical thinking abilities. The connection between REM sleep and problem-solving highlights the importance of a good night’s sleep in promoting cognitive functioning and creative problem-solving abilities.
Repetitive Patterns and Dream Content
Repetitive patterns and dream content play a crucial role in recurring dreams. These dreams often feature recurring symbols or themes that can hold personal significance for the dreamer. Symbols and meanings in recurring dreams can vary widely and may be influenced by factors such as cultural background, personal experiences, and individual interpretation. It is essential to approach the interpretation of recurring dream symbols with an open mind, as the meanings can be highly subjective. To accurately interpret these symbols, it can be helpful to keep a dream journal and reflect upon the emotions and events associated with the recurring dreams. By identifying patterns and analyzing the repetitive dream patterns, individuals can gain insight into their subconscious mind and potentially uncover unresolved emotions or conflicts. A deeper understanding of these patterns can lead to personal growth and self-awareness. Interpreting recurring dream patterns requires careful observation and introspection, challenging the dreamer to explore their own emotions and experiences. By delving into the repetitive content of these dreams, individuals can begin to unravel the hidden messages and meanings that may be encoded within their unconscious psyche.
Symbols and Meanings in Recurring Dreams
Understanding the symbols and meanings in recurring dreams can provide valuable insights into our subconscious mind and inner emotions. Dreams are known to be a symbolic language, and recurring dreams often contain recurring symbols as well. These symbols may vary from person to person, but some common examples include water, vehicles, animals, or specific locations. It is important to note that the interpretation of these symbols can be subjective and personal, as they are influenced by individual experiences and emotions. For instance, water might represent emotions, transitions, or the unconscious mind, but its specific meaning in a recurring dream would depend on the context and the dreamer’s personal associations. Keeping a dream journal and noting down the symbols present in recurring dreams can help identify recurring patterns and themes, aiding in the interpretation process. Seeking the assistance of a dream analyst or therapist who specializes in dream interpretation can also provide useful insights. By delving deeper into the symbols and meanings in recurring dreams, we can unlock the hidden messages and unresolved emotions encoded within our dreamscape, ultimately assisting us in personal growth and self-discovery.
Interpreting Recurring Dream Patterns
When it comes to interpreting recurring dream patterns, it is important to understand that each individual’s dreams are unique and personal to them. However, there are some general approaches that can help shed light on the meaning behind these recurring themes. One way to interpret these patterns is to pay attention to the emotions evoked during the dream. Are you feeling fear, anxiety, or joy? These emotions can provide valuable clues about underlying fears or desires in your waking life. Another technique is to analyze the symbols and imagery within the dreams. Symbols can vary in meaning depending on cultural backgrounds and personal experiences, so it’s essential to explore their significance in the context of your own life. Keeping a dream journal can be immensely helpful in identifying recurring symbols and patterns, allowing you to develop a deeper understanding over time. It can also be beneficial to seek guidance from a professional dream analyst or therapist who can provide insight and perspective on the recurring dreams. Ultimately, no one knows your dreams better than you do, so trust your intuition and explore the various layers of symbolism within your recurring dream patterns.
Managing Recurring Dreams
Managing recurring dreams can be a helpful approach for those seeking to gain control over their unconscious experiences. One effective method is to keep a dream journal, where individuals can record and analyze their dreams on a regular basis. This practice allows for journaling and self-reflection, providing an opportunity to identify patterns or symbols that may appear in recurring dreams. By examining these patterns, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying emotions and unresolved issues that may be causing the recurrence.
Another technique to manage recurring dreams is through the practice of lucid dreaming. Lucid dreaming involves becoming aware that one is dreaming while still in the dream state, thus allowing for a degree of control and manipulation of the dream content. Techniques such as reality testing and keeping a dream journal can help increase the likelihood of having lucid dreams. Once lucidity is achieved, individuals can actively alter the dream’s course or confront any recurring elements, potentially transforming the dream experience into a more positive or resolving outcome.
In addition to these methods, incorporating relaxation and stress-reduction techniques into one’s daily routine can also aid in managing recurring dreams. Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in calming activities before bedtime can help promote a more peaceful and restful sleep, reducing the occurrence of intense or distressing dreams.
It’s important to note that managing recurring dreams may require patience and perseverance, as each individual’s dream experiences and underlying issues are unique. Consulting a therapist or dream specialist may also be beneficial for those struggling with persistent or distressing recurring dreams. By actively working towards understanding and addressing the underlying emotions and unresolved issues, individuals can take steps towards achieving a healthier dream state and overall well-being.
Journaling and Self-Reflection
Journaling and self-reflection are valuable techniques that can assist individuals in understanding and interpreting their recurring dreams. Keeping a dream journal is a powerful way to record and analyze the details of these dreams. By documenting recurring dream experiences, dreamers can identify patterns, symbols, and emotions that consistently appear. Utilizing journaling as a tool allows individuals to reflect upon their dreams during wakefulness and gain a deeper understanding of their subconscious mind. When journaling about recurring dreams, it is important to note any changes or variations that may occur over time, as these can provide valuable insights into personal growth and the potential resolution of underlying conflicts. The act of self-reflection involves delving into the emotions, thoughts, and reactions evoked by recurring dreams. It encourages individuals to contemplate their own experiences, beliefs, and personal circumstances in order to make connections and understand the hidden messages within their dreams. By engaging in self-reflection, dreamers can explore the possible meanings and significance behind their recurring dreams, leading to enhanced self-awareness and personal development. The combination of journaling and self-reflection offers an effective approach for individuals to decode the symbolism and messages within their dreams, ultimately leading to a greater understanding of their own psyche.
Lucid Dreaming Techniques
Lucid dreaming techniques can be a valuable tool for managing and even controlling recurring dreams. Lucid dreaming is the state of being aware that you are dreaming while still within the dream itself. This awareness allows individuals to actively participate in and manipulate the dream content, offering a sense of control over their recurring dreams. One popular technique for inducing lucid dreaming is reality testing. This involves performing regular reality checks throughout the day, such as looking at a clock or a written word, and asking yourself if you are dreaming. By incorporating this habit into your daily routine, you increase the likelihood of performing a reality check in your dreams, thus triggering lucidity. Another technique is known as mnemonic induction of lucid dreams (MILD), which involves focusing your mind on the intention to have a lucid dream while falling asleep. Visualization and creating a clear mental image of yourself becoming lucid in a dream can also be helpful. Other techniques such as wake-back-to-bed (WBTB) involve waking up in the middle of the night, staying awake for a short period, and then returning to sleep with the intention of having a lucid dream. Exploring and experimenting with these various lucid dreaming techniques can provide individuals with a new perspective on their recurring dreams, allowing them to actively engage and explore the subconscious landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recurring dreams continue to captivate our imagination and curiosity. From exploring various theories that attempt to explain their occurrence, such as psychological, neurological, and spiritual/parapsychological theories, to understanding the role of recurring dreams in emotional processing and memory consolidation, we have gained valuable insights into their significance. Recurring dreams can serve as a window into our subconscious minds, offering a glimpse into unresolved emotions and providing a platform for emotional rehearsal. Symbols and patterns within these dreams can hold deep meaning and can be interpreted to gain a better understanding of ourselves and our experiences. While managing recurring dreams can be challenging, techniques such as journaling and self-reflection, as well as lucid dreaming methods, can help individuals navigate these dreamscapes. It is important to remember that each individual’s experience with recurring dreams is unique, and interpretations may vary. By embracing the enigmatic nature of recurring dreams and delving into their depths, we embark on a journey of self-discovery and introspection, unlocking the profound potential of our dream world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes recurring dreams?
The exact causes of recurring dreams are still not fully understood. However, they can be attributed to various factors such as unresolved emotions, traumatic experiences, anxieties, or even certain medications.
Are recurring dreams common?
Yes, recurring dreams are relatively common. Studies have shown that around 60-75% of adults experience recurring dreams at some point in their lives.
Do recurring dreams have any significance?
Recurring dreams can hold significance and meaning for individuals. They often represent unresolved issues or emotions that the dreamer needs to confront or address in their waking life.
Can recurring dreams be changed or stopped?
While it may be challenging to completely stop recurring dreams, exploring their underlying meanings and addressing any related emotional issues can help reduce their frequency or change their content.
How can I interpret the symbols in my recurring dreams?
Interpreting the symbols in recurring dreams can be a personal and subjective process. It is helpful to keep a dream journal, reflect on the emotions and context of the dream, and explore any personal associations or connections to the symbols.
Can recurring dreams provide insights into our waking lives?
Yes, recurring dreams often serve as a window into our subconscious and can provide valuable insights into our waking lives. They may highlight areas of emotional conflict, unresolved issues, or hidden desires.
Can recurring dreams be therapeutic?
Recurring dreams can have a therapeutic effect as they provide an opportunity for individuals to explore and process unresolved emotions or conflicts. They can be seen as a form of emotional rehearsal or a way for the mind to work through unresolved issues.
Can lucid dreaming techniques help manage recurring dreams?
Yes, practicing lucid dreaming techniques can be beneficial in managing recurring dreams. Lucid dreaming allows individuals to become aware that they are dreaming and gives them some control over the dream’s content and outcome.
Do recurring dreams have any connection to REM sleep?
Yes, recurring dreams are closely linked to REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, which is the stage of sleep associated with vivid dreaming. During REM sleep, the brain is highly active, and it is believed that this activity plays a role in the occurrence and content of recurring dreams.
Can recurring dreams be a sign of a sleep disorder?
While recurring dreams themselves are not considered a sleep disorder, they can be associated with sleep disturbances such as insomnia, sleep apnea, or restless leg syndrome. If recurring dreams significantly disrupt sleep quality or cause distress, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation.








