Have you ever wished you could control your dreams? Imagine being able to fly, travel to exotic locations, or even meet your favorite celebrities, all within the confines of your own mind. Well, it turns out that this is possible through a phenomenon known as lucid dreaming. Lucid dreaming refers to the state of being aware that you are dreaming while you are in the dream itself. It is a fascinating concept that has captivated scientists and dream enthusiasts for centuries. In this article, we will delve into the science behind lucid dreaming and explore its history, the role of the brain, various techniques to induce lucidity, its benefits, and potential applications in a therapeutic and scientific context. Get ready to embark on a journey through the realms of the mind where anything is possible.
What is Lucid Dreaming?

Defined as a phenomenon where a person becomes aware that they are dreaming while still in the dream state, lucid dreaming opens up a world of endless possibilities within the confines of one’s own mind. It is a unique state of consciousness that allows individuals to actively participate and manipulate their dreams with complete awareness. When lucid dreaming occurs, the dreamer gains control over their actions, experiences heightened senses, and can even make decisions that impact the dream’s course. The concept of lucid dreaming has fascinated humans for centuries, with historical references dating back thousands of years. Lucid dreaming provides a platform for individuals to explore their deepest fantasies, test their limits, and unleash their creativity. It offers a unique opportunity to connect with the subconscious mind and tap into a realm where the ordinary rules of reality no longer apply. Whether it is flying through the skies, visiting exotic locations, or even meeting fictional characters, lucid dreaming allows individuals to turn their wildest dreams into reality – or rather, a reality within the dream itself. For those interested in delving deeper into the subject, understanding the symbolism in lucid dreams or exploring techniques for lucid dream induction can provide further insights into this fascinating realm. Additionally, learning about famous lucid dreamers’ experiences can offer inspiration for those starting their own journey into the world of lucid dreaming.
Definition and Explanation
Definition and Explanation: Lucid dreaming is a unique state of consciousness where an individual becomes aware that they are dreaming while still within the dream itself. This state allows individuals to have control over their dream experiences and actively participate in them. When lucid dreaming occurs, the dreamer is able to recognize the dream as a construct of their own mind, separate from waking reality. This awareness grants them the ability to manipulate their dream environment, characters, and events. Lucid dreaming can range from subtle awareness to a fully immersive experience where the dreamer feels fully awake and conscious within the dream world. While the exact mechanisms behind lucid dreaming are not yet fully understood, it is believed to occur during the Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep stage, which is characterized by increased brain activity and vivid dreaming. Lucid dreaming offers a unique opportunity for self-exploration, creativity, and personal growth as individuals can confront fears, test boundaries, and engage in experiences that may not be possible in the waking world. It is a fascinating phenomenon that has intrigued researchers and dream enthusiasts for centuries, and continues to be a subject of scientific study and exploration.
The History of Lucid Dreaming
The history of lucid dreaming is as old as human civilization itself, with references to this phenomenon found in various ancient cultures around the world. The practice of lucid dreaming can be traced back to as early as 1000 BCE in the teachings of Hinduism and Buddhism, where it was known as “dream yoga” or “yoga of the dream state.” In these traditions, lucid dreaming was seen as a means of spiritual exploration and self-realization. Similarly, ancient Egyptian culture valued the significance of dreams and believed that they could serve as portals to communicate with the divine. The Egyptians even had specific dream temples where individuals would go to seek spiritual guidance through their dreams. In Greek philosophy, figures like Aristotle and Plato recognized the potential significance of dreams and their connection to the subconscious mind. However, it wasn’t until the 19th and 20th centuries that scientific interest in lucid dreaming emerged. The term “lucid dreaming” itself was coined by Frederik van Eeden, a Dutch psychiatrist, in the early 20th century. Since then, researchers such as Stephen LaBerge have conducted extensive scientific studies on lucid dreaming, further advancing our understanding of this extraordinary phenomenon. Today, lucid dreaming continues to captivate the curiosity of psychologists, neuroscientists, and dream enthusiasts alike, contributing to a growing body of knowledge about the potential of the human mind.
The Brain and Lucid Dreaming
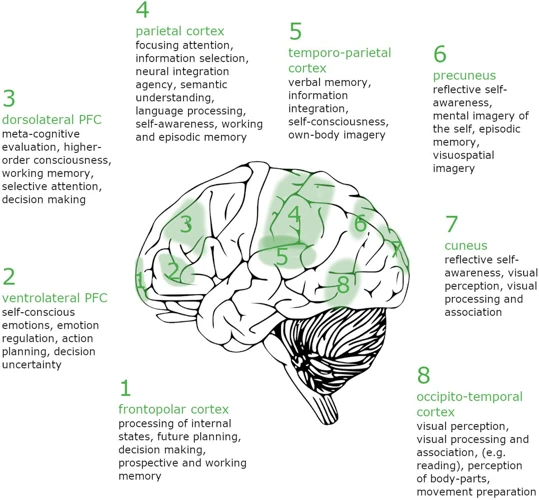
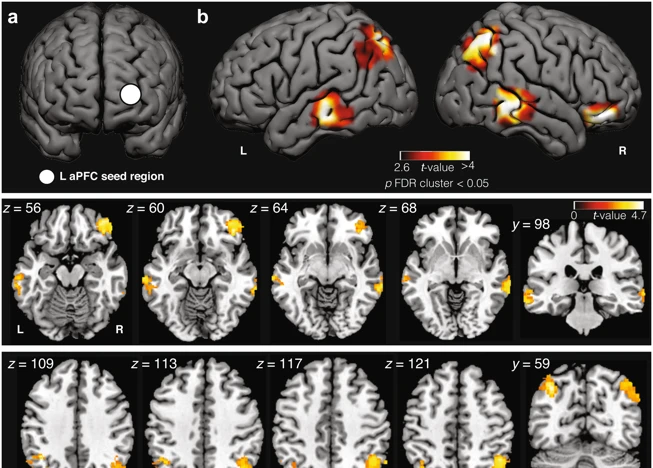
Exploring the relationship between the brain and lucid dreaming reveals fascinating insights into the mechanisms behind this phenomenon. The brain plays a crucial role in the creation and experience of dreams, including lucid dreams. During sleep, the brain undergoes various stages, one of which is Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, where most dreaming occurs. Research suggests that the prefrontal cortex, a region of the brain associated with decision-making and self-awareness, plays a significant role in lucid dreaming. This area becomes more active during lucid dreams, allowing individuals to gain awareness and control within the dream state. Neuroimaging studies have also shown increased activation in regions such as the parietal cortex and temporal gyrus during lucid dreaming. These findings suggest that a combination of neural activity and connectivity patterns contribute to the unique experience of lucidity. Understanding the brain’s involvement in lucid dreaming can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of consciousness, self-perception, and the boundaries between the waking and dreaming states. Additionally, further research into the neural correlates of lucid dreaming may shed light on how consciousness is constructed and experienced in general, both during sleep and wakefulness.
The Role of the Brain in Dreams
The brain plays a crucial role in the generation and experience of dreams, including lucid dreams. Throughout history, researchers have tried to unravel the mysteries of the brain’s involvement in the dream state. Dreams are complex mental experiences that occur during sleep and are believed to be a product of the brain’s activity. Various regions of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus, have been implicated in the formation of dreams. The prefrontal cortex, responsible for higher cognitive functions, is particularly active during lucid dreaming. This activation allows for heightened self-awareness and conscious control over dream events. The amygdala, known for processing emotions, influences the emotional intensity of dreams, while the hippocampus contributes to memory consolidation, influencing dream content. These brain regions work together in a intricate dance, shaping the narrative and emotional aspects of dreams. Neurotransmitters such as serotonin and acetylcholine also play a role in modulating the dream state. During rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, which is closely associated with dreaming, the brain experiences increased activity, resembling waking consciousness. This neuroactivity during REM sleep is believed to contribute to the vividness and realism of dreams. Understanding the intricate interplay between different brain regions and neurotransmitters is essential for comprehending the nature of dreams, including the phenomenon of lucid dreaming.
REM Sleep and Lucid Dreaming
REM sleep (Rapid Eye Movement) plays a crucial role in the occurrence of lucid dreaming. During REM sleep, our brain activity becomes similar to that of wakefulness, and vivid dreams commonly occur. This stage of sleep is characterized by rapid eye movements, irregular breathing, and temporary paralysis of voluntary muscles. The majority of lucid dreams occur during REM sleep, although it is possible to have lucid dreams during other sleep stages as well.
Research suggests that lucidity in dreams is associated with increased activity in the prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain responsible for decision-making and self-awareness. This heightened activity during lucid dreaming is what enables individuals to realize they are dreaming and exert control over their dream experiences.
REM sleep and dreaming are intricately connected. When researchers studied the sleep patterns of individuals who frequently experienced lucid dreams, they found that these individuals tended to have increased REM sleep duration and density compared to those who rarely experienced lucid dreams. This suggests that there may be a correlation between the amount of REM sleep and the likelihood of experiencing lucid dreams.
A study conducted by German researchers found that individuals who were awakened during REM sleep were more likely to report having had a lucid dream compared to those who were awakened during non-REM sleep stages. This further supports the association between REM sleep and lucid dreaming.
Understanding the relationship between REM sleep and lucid dreaming can be invaluable in developing techniques for inducing lucidity and exploring the potential benefits of lucid dreaming. It highlights the importance of paying attention to our sleep cycles and maximizing opportunities for lucid dreaming by focusing on enhancing our REM sleep duration and quality.
Lucid Dreaming Techniques

When it comes to inducing lucid dreams, there are several techniques that individuals can practice to increase their chances of experiencing this state of awareness within their dreams. Here are a few popular techniques:
- Mnemonic Induction of Lucid Dreams (MILD): This technique involves setting an intention to become lucid in your dreams before you fall asleep. It requires repeated affirmations and mental rehearsal of your intention to recognize that you are dreaming. By focusing on the concept of lucidity and maintaining a strong desire to become aware during dreams, the MILD technique can help increase the likelihood of having lucid dreams.
- Reality Testing: Reality testing involves regularly questioning your reality throughout the day. By performing frequent reality checks, such as looking at your hands, checking the time, or trying to push your finger through your palm, you can create a habit of questioning whether you are dreaming or awake. This habit can then carry over into your dreams, increasing the chances of realizing that you are dreaming.
- Wake-Initiated Lucid Dream (WILD): The WILD technique involves transitioning directly from wakefulness to a state of lucid dreaming. It requires staying aware and conscious as your body falls asleep, while your mind remains alert. This technique often involves entering a state of sleep paralysis, maintaining focus, and allowing yourself to enter a lucid dream directly from the waking state. It can be a more advanced technique that requires practice and patience.
These techniques serve as stepping stones for individuals who wish to explore and experience lucid dreaming. However, it is important to note that the effectiveness of these techniques may vary from person to person. Experimenting with different techniques and finding what works best for you can significantly increase the likelihood of experiencing lucid dreams and unlocking the vast potential of your dream world.
Mnemonic Induction of Lucid Dreams (MILD)
One popular technique used to induce lucid dreams is the . Developed by psychophysiologist Dr. Stephen LaBerge, MILD involves setting intentions and using mnemonic cues to increase the chances of becoming lucid during dreaming. The technique is based on the idea that by repeating a specific phrase or affirmation before falling asleep, individuals can enhance their dream recall and raise their level of awareness within the dream state.
To practice MILD, follow these steps:
- Set your intention: Before going to bed, tell yourself, either out loud or mentally, that you will have a lucid dream. Be specific and focused on your intention.
- Create a mnemonic cue: Come up with a short phrase or sentence that reinforces your intention to become lucid. For example, you could say, “Next time I’m dreaming, I will remember that I am dreaming.”
- Visualize your dream: Close your eyes and imagine yourself in a recent dream or a specific scenario where you’d like to become lucid. Visualize yourself realizing that you are dreaming and engaging with the dream consciously.
- Repeat the affirmation: While visualizing, repeat your mnemonic cue repeatedly for a few minutes. Focus on the meaning and feeling behind the words.
- Relax and drift off to sleep: Allow yourself to relax and fall asleep while still holding the intention of becoming lucid in your dreams.
- Perform reality checks: Throughout the day, make it a habit to question your reality by performing reality checks. This will help train your mind to question whether you are dreaming or awake and increase the likelihood of becoming lucid during dreams.
Practicing MILD consistently and with dedication increases the chances of experiencing lucid dreams. It is worth noting that MILD may require some time and patience before achieving desired results. However, with persistence and a strong intention, this technique can serve as an effective tool for inducing lucid dreams.
Reality Testing
Reality testing is an essential technique used to distinguish between dreams and reality within the practice of lucid dreaming. Its purpose is to enhance one’s self-awareness and critical thinking skills to determine whether one is in a dream state or waking reality. By regularly performing reality tests throughout the day, individuals increase their chances of carrying out these tests while in a dream, leading to lucidity.
There are several common reality tests that individuals can incorporate into their daily routines. One popular method is the “finger through the palm” test, where the individual attempts to push their finger through their opposite palm. In a dream, the finger would likely pass through, as the dream world lacks the same physical constraints as waking reality.
Another common reality test involves examining the environment for inconsistencies or impossibilities. This can be done by looking at a digital clock or text, looking away, and then looking back to see if the numbers or words have changed. In a dream, text often changes or becomes unreadable.
Additionally, individuals can practice jumping and assessing gravity. In dreams, physics may not follow the same rules as in reality, so attempting to jump and seeing if one hovers or floats can indicate a dream state.
Reality testing can be recorded in a dream journal, noting any anomalies or inconsistencies experienced during dreams. Consistently reviewing and reflecting on these journal entries helps individuals recognize dream patterns and further increases their chances of achieving lucidity.
To maximize the effectiveness of reality testing, it is recommended to perform these tests multiple times throughout the day and to approach them with a genuine sense of curiosity and open-mindedness. With time and practice, reality testing becomes ingrained in one’s daily routine, making it more likely to carry over into dreams and facilitate lucid dreaming experiences.
Wake-Initiated Lucid Dream (WILD)
Wake-Initiated Lucid Dream (WILD) is a technique that involves transitioning directly from wakefulness to a lucid dream state, bypassing the typical process of falling asleep. It requires a high level of awareness and concentration. To achieve a WILD, one must find a balance between relaxation and maintaining mental clarity. Here is a step-by-step process to practice WILD:
1. Prepare for sleep: Find a comfortable position in your bed and create a peaceful sleep environment.
2. Relaxation: Begin by relaxing your body and focusing on your breath. Slowly inhale and exhale, allowing any tension to leave your body.
3. Entering hypnagogia: As you relax, you may begin to enter a state known as hypnagogia – the transitional phase between wakefulness and sleep. During this stage, you may experience visual or auditory hallucinations or even body sensations. Embrace these experiences without clinging to them, as they can serve as gateways to lucidity.
4. Sustain awareness: Maintain a level of consciousness as you enter hypnagogia. It is crucial to stay aware and observe these sensations without becoming too engaged or losing focus.
5. Visualization: While in the hypnagogic state, imagine yourself in a dream setting or a specific scenario. Visualize the details vividly, engaging all your senses. This step helps to strengthen the connection between wakefulness and dream state.
6. Enter the dream: With sustained awareness and strong visualization, you may begin to feel sensations of drifting or floating. At this point, allow yourself to transition fully into the dream state while maintaining lucidity. You may find yourself in a fully formed dream environment.
7. Stabilize the dream: Once in the dream state, take a moment to stabilize the dream by engaging your senses. Look around, touch objects, or focus on sound. This step helps to prolong the lucid experience.
8. Enjoy and explore: Now that you have successfully initiated a lucid dream through WILD, take advantage of the opportunities and possibilities it offers. Remember, you are in control, so have fun and explore the dream world to your heart’s content.
It is important to note that practicing WILD requires patience and persistence. It may take time and practice to achieve a successful wake-initiated lucid dream. Experiment with different techniques and find what works best for you. Keep a dream journal to track your progress and identify patterns in your dreams. With dedication and practice, Wake-Initiated Lucid Dreaming can become a doorway to incredible dream experiences and self-discovery.
The Scientific Benefits of Lucid Dreaming

Lucid dreaming not only offers a thrilling and immersive experience, but it also holds several scientific benefits that have piqued the interest of researchers. Let’s explore some of these benefits below:
Enhancing Creativity and Problem-Solving:
During lucid dreaming, individuals have the ability to actively engage with their dreams and unleash their creativity. This can aid in enhancing creative thinking, as dreamers can explore new ideas, visuals, and concepts that may inspire artistic endeavors or problem-solving in the waking world. Lucid dreaming provides a unique space for brainstorming, experimenting, and generating innovative solutions to real-life challenges.
Rehearsing and Improving Skills:
One fascinating aspect of lucid dreaming is the opportunity to practice and improve skills while in the dream state. Research suggests that engaging in specific activities or scenarios in a lucid dream can translate into improved proficiency in those same activities in waking life. Athletes, musicians, and performers, for example, can use lucid dreaming to mentally rehearse their skills, leading to enhanced performance and muscle memory.
Overcoming Nightmares and PTSD:
Lucid dreaming can also be utilized as a therapeutic tool for individuals suffering from nightmares or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). By becoming aware during a nightmare, individuals can actively change the dream narrative or consciously wake themselves up, effectively interrupting the distressing experience. Lucid dreaming therapy has shown promising results in reducing the frequency and severity of nightmares, providing relief and improved sleep quality for those affected.
These scientific benefits of lucid dreaming demonstrate the potential impact and practical applications of this unique phenomenon. Whether it is nurturing creativity, honing skills, or providing relief from nightmares, lucid dreaming offers a captivating avenue for personal growth and exploration.
Enhancing Creativity and Problem-Solving
One of the scientific benefits associated with lucid dreaming is its potential to enhance creativity and problem-solving skills. When individuals engage in lucid dreaming, they have the unique opportunity to navigate and manipulate their dreamscape, actively shaping the dream narrative. This level of control allows for the exploration of unconventional ideas and scenarios that may not be easily feasible in waking life. Lucid dreaming offers a creative playground where individuals can experiment with new concepts, invent novel solutions, and explore different perspectives. It provides a safe environment to push boundaries and think outside the box without the fear of real-life consequences. By embracing the imaginative and unrestricted nature of dreams, individuals can tap into their subconscious mind and unleash their creative potential. Additionally, lucid dreaming can facilitate problem-solving by providing a platform to confront and resolve personal challenges and fears. Through the practice of lucid dreaming, individuals can confront difficult situations and develop strategies to overcome them, improving their critical thinking and adaptability skills. This process can be particularly beneficial for individuals seeking innovative solutions to real-life problems. The ability to actively participate in problem-solving scenarios within the dream world can enhance cognitive flexibility, allowing individuals to approach challenges from different angles and discover unique solutions. Lucid dreaming can serve as a valuable tool for enhancing both creativity and problem-solving skills, opening up new avenues for personal growth and intellectual exploration.
Rehearsing and Improving Skills
Rehearsing and improving skills is another remarkable benefit of lucid dreaming. When individuals have the ability to control their dreams, they can utilize this state to practice and hone their skills, both physical and mental. For instance, athletes can mentally rehearse their specific sport techniques, improving muscle memory and enhancing their performance in real life. Research has shown that practicing certain movements in a lucid dream can lead to improved motor skills in waking life. This phenomenon is known as “dream incorporation” and has been observed in various fields, including music, art, and even public speaking. Lucid dreamers can also engage in mental rehearsals for exams, presentations, or any other important events. They can visualize themselves successfully navigating through challenges, boosting their confidence and reducing anxiety. This rehearsal in a lucid dream state can be immensely helpful in building skills and overcoming obstacles. Lucid dreaming offers a safe space for exploring and experimenting with new ideas and techniques without the fear of failure or consequences. It allows individuals to push their boundaries, think creatively, and refine their abilities. Whether it is perfecting a dance routine, practicing a musical instrument, or even working on problem-solving skills, lucid dreaming provides a valuable opportunity to enhance and improve various aspects of one’s life.
Overcoming Nightmares and PTSD
Nightmares and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can be debilitating and have a significant impact on an individual’s well-being. However, lucid dreaming has shown promise in helping people overcome these distressing experiences. One of the significant benefits of lucid dreaming is that it allows individuals to confront their fears and traumas within the safe confines of a dream. By becoming aware and taking control of the dream, individuals can change the dream’s narrative, confront their fears head-on, or even transform the nightmare into a more positive experience. In the context of PTSD, lucid dreaming can provide a sense of empowerment and control over recurring nightmares associated with traumatic events. With practice, individuals can learn techniques to recognize when they are dreaming during a nightmare and subsequently take control of the dream to transform it into a more positive or less distressing experience. Lucid dreaming also offers an opportunity for individuals to process and work through their emotions related to the traumatic event. Through a process known as dream re-scripting, individuals can actively modify the dream scenario to foster healing and resolution. This technique involves rehearsing alternative outcomes or engaging in self-soothing actions within the dream, which can have a therapeutic effect on the individual’s waking life. While more research is needed in this area, the potential for lucid dreaming to help individuals overcome nightmares and manage the symptoms of PTSD is an exciting prospect that continues to be explored by researchers and clinicians alike.
Applications of Lucid Dreaming Research
The research conducted on lucid dreaming has yielded valuable insights into its potential applications in various fields. One significant area where lucid dreaming research shows promise is in therapeutic applications. Lucid dreaming can be used as a tool for treating nightmares and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). By practicing lucid dreaming techniques, individuals can gain control over their dreams and actively change the content or confront their fears, leading to a reduction in the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Lucid dreaming therapy can also help individuals with PTSD by allowing them to reprocess traumatic events within the safety of the dream world, facilitating healing and mitigation of associated symptoms.
Another exciting application of lucid dreaming research lies in exploring consciousness and neuroscience. Lucid dreaming offers a unique opportunity to study the relationship between dreaming and waking consciousness, as well as the functioning of the brain during lucid dreaming states. Scientists can use brain imaging techniques to examine neural activity patterns during lucid dreaming, providing valuable insights into the neural mechanisms underlying this phenomenon. This research contributes to a deeper understanding of consciousness itself, as well as the nature of dreams and their connection to the brain’s functioning.
Lucid dreaming research has the potential to enhance virtual reality experiences. By combining the principles of lucid dreaming with virtual reality technology, it may be possible to create immersive experiences where individuals can fully engage their senses and actively control their virtual environments. This application has implications for fields such as gaming, education, and therapy, opening up exciting possibilities for interactive and personalized experiences.
The research conducted on lucid dreaming has unveiled promising applications in the realms of therapy, consciousness exploration, and virtual reality. The therapeutic use of lucid dreaming can help individuals overcome nightmares and trauma, while the study of lucid dreaming allows for a deeper understanding of consciousness and the brain. Additionally, the integration of lucid dreaming with virtual reality technology opens up new avenues for immersive and interactive experiences. As research in this field continues to evolve, we can expect to uncover even more exciting and practical applications of lucid dreaming.
Therapeutic Applications
Therapeutic applications of lucid dreaming have garnered significant attention in recent years. One area of focus is the potential use of lucid dreaming as a tool for psychotherapy. By entering a lucid dream state, individuals have the opportunity to confront and work through emotional or psychological issues in a controlled and safe environment. This can be particularly beneficial for those dealing with trauma or recurring nightmares. Through lucid dreaming, individuals can actively rewrite the narrative of their dreams, facing their fears head-on, and finding resolution or closure. Studies have shown that lucid dreaming can be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares, providing relief for individuals suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other anxiety-related conditions. Additionally, lucid dreaming has been explored as a technique for pain management. By utilizing the power of the mind, individuals can alter their perception of pain while in a lucid dream, potentially reducing the need for medication. Lucid dreaming can also be used for personal growth and self-improvement. By practicing specific techniques, individuals can enhance their problem-solving abilities, boost creativity, and gain insights into their own subconscious mind. The therapeutic applications of lucid dreaming offer a promising avenue for mental health treatment and self-exploration.
Exploring Consciousness and Neuroscience
Exploring consciousness and neuroscience is an exciting application of lucid dreaming research. Lucid dreaming provides a unique opportunity to study the intricacies of the brain and its connection to consciousness. Scientists and researchers are intrigued by the potential insights it can offer into the nature of perception, self-awareness, and the boundaries of human cognition. By studying the neural activity during lucid dreaming states, researchers aim to uncover the underlying mechanisms and processes that contribute to the phenomenon. Neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG), allow scientists to observe and analyze brain activity during lucid dreams, revealing patterns and changes that shed light on the relationship between brain function and conscious experience. Studying lucid dreaming can contribute to our understanding of altered states of consciousness, including those induced by meditation, psychedelic substances, or certain psychological conditions. It may also hold implications for the treatment of neurological disorders and psychiatric conditions related to consciousness disturbances. The exploration of consciousness and neuroscience through the window of lucid dreaming presents a fascinating opportunity for scientific advancement and a deeper understanding of what it means to be conscious.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lucid dreaming is a fascinating and captivating phenomenon that has intrigued scientists, researchers, and dream enthusiasts for centuries. It offers individuals the ability to consciously explore and manipulate their dreams, opening up a world of endless possibilities within the confines of the mind. Through various techniques such as mnemonic induction of lucid dreams (MILD), reality testing, and wake-initiated lucid dreaming (WILD), individuals can enhance their chances of experiencing lucidity during their dream state. The scientific benefits of lucid dreaming are vast and include enhancing creativity and problem-solving abilities, rehearsing and improving skills, as well as overcoming nightmares and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Furthermore, the applications of lucid dreaming research extend to therapeutic contexts, where it can be utilized for therapeutic purposes, and exploring consciousness and neuroscience, where it provides valuable insights into understanding the complexities of the human mind. Lucid dreaming truly offers a unique platform for self-discovery, personal growth, and expanding the boundaries of what we perceive as reality. So dive into the realm of lucid dreaming and unlock the infinite potential of your mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a regular dream and a lucid dream?
A regular dream is when you are unaware that you are dreaming and simply go along with the events unfolding in your mind. In contrast, a lucid dream is when you become conscious that you are in a dream while it is still happening. This awareness allows you to actively participate and control the dream’s content, making it a more immersive and interactive experience.
Can anyone learn to lucid dream?
Yes, with practice and dedication, anyone can learn to lucid dream. While some individuals may naturally experience lucid dreams more frequently, there are techniques and exercises that can significantly increase the likelihood of achieving lucidity during dreaming for anyone interested in exploring this phenomenon.
Are there any risks or dangers associated with lucid dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is generally considered safe and poses no significant risks or dangers. However, it is essential to maintain a healthy sleep schedule and not rely solely on lucid dreaming as a substitute for quality rest. Additionally, individuals may experience vivid or intense emotions during lucid dreams, which can be disturbing for some.
How long does a lucid dream typically last?
The duration of a lucid dream can vary greatly from person to person. Some individuals may have brief moments of lucidity within a regular dream, while others may experience prolonged and vivid lucid dreams that can last for several minutes or even longer.
Are there any specific techniques to induce lucid dreams?
Yes, there are various techniques that can increase your chances of having a lucid dream. Some popular methods include reality testing, where you question your surroundings to check if you are dreaming, and mnemonic induction of lucid dreams (MILD), which involves setting intentions and affirmations before sleep.
Can lucid dreaming be used for problem-solving or enhancing creativity?
Absolutely! Lucid dreaming has been used as a tool for problem-solving and enhancing creativity. Within the lucid dream state, individuals can explore different scenarios, find creative solutions, and gain new perspectives on real-life challenges.
Can lucid dreaming help with overcoming nightmares?
Yes, lucid dreaming can be helpful in overcoming nightmares. When you become aware that you are dreaming, you can take control of the dream and transform scary or unsettling experiences into more positive or neutral ones.
Is lucid dreaming connected to any spiritual or transcendental experiences?
Lucid dreaming can certainly intersect with spirituality and transcendental experiences for some individuals. Some people report having mystical or spiritual encounters within their lucid dreams, allowing them to explore the depths of their consciousness and connect with something greater than themselves.
Are there any therapeutic applications of lucid dreaming?
Yes, lucid dreaming has shown potential for therapeutic applications. It can be used as a tool for overcoming fears and traumas, reducing anxiety, improving self-confidence, and even aiding in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Can lucid dreaming be studied scientifically?
Yes, lucid dreaming is a subject of scientific research. Scientists use various methods, including brain imaging techniques, to study the brain activity associated with lucid dreaming. These studies contribute to a better understanding of the phenomenon and its potential applications.