Dreams have long captivated and mystified humankind. These enigmatic states of consciousness that occur during sleep often leave us wondering about their purpose and meaning. Why do we experience emotions in our dreams? What is the science behind it? In this article, we will delve into the intriguing realm of dream emotions, exploring their purpose, the role of the brain in generating them, the influence of REM sleep, the connection with emotional memories, and the significance of dream symbols. Prepare to embark on a journey through the fascinating world of dreams, where emotions take center stage and offer insight into our innermost thoughts and feelings.
The Purpose of Dreams

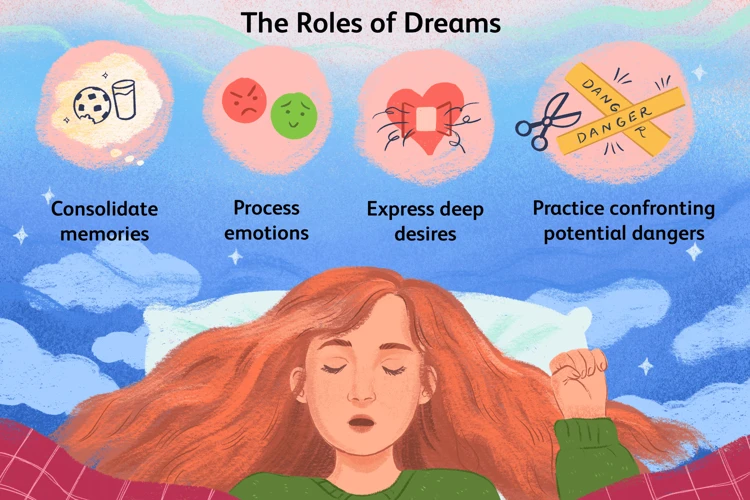
Dreams serve a multitude of purposes, and one of the most fascinating aspects is their ability to evoke emotions. Emotions experienced in dreams can range from joy and excitement to fear and sadness. The primary purpose of dreams is believed to be emotional processing and integration. During sleep, our brains work diligently to process and consolidate information from our waking lives. Dreams offer a safe space for the exploration and expression of emotions that we may not fully engage with during our waking hours. They provide an opportunity for the brain to sort through and make sense of complex emotional experiences, allowing us to process and integrate them into our overall emotional well-being. Research suggests that dreaming can help regulate emotions, making us more resilient and adaptive in our daily lives. Dreams provide a chance for personal growth and self-reflection, allowing us to gain insight into our subconscious desires, fears, and unresolved conflicts. By examining the emotions experienced in our dreams, we can gain valuable insights into our emotional landscape and identify areas for personal growth and development. So, while dreams may seem mysterious and nonsensical at times, they serve a crucial purpose in our emotional well-being and inner exploration. To learn more about the link between dreams and emotions, click here.
Dreams as Emotional Processing
Dreams play a crucial role in emotional processing by allowing us to explore and make sense of our complex emotions. While we may not always remember our dreams, they can have a profound impact on our emotional well-being. Dreams act as a sort of emotional laboratory where we can experience and process intense emotions without the constraints of reality. Through dreams, we can encounter situations and scenarios that may not be feasible in our waking lives, allowing us to safely confront and explore our emotions. For example, we may dream of confronting a fear or experiencing deep love and joy. These dream experiences provide an opportunity for our brains to process and integrate the associated emotions, helping us regulate and understand our emotional responses. Research suggests that dreams can even help us work through unresolved emotional issues and traumas, providing a means for emotional healing and growth. By allowing ourselves to engage with the emotions experienced in dreams, we can gain a deeper understanding of our inner selves and promote personal development. To explore more about the fascinating connection between dreams, emotions, and personal growth, click here.
Linking Dreams to Real-Life Experiences
Linking dreams to real-life experiences is a fascinating area of study that sheds light on the intricate relationship between our emotions and the events of our waking lives. Research suggests that dreams often draw upon our personal experiences, memories, and emotions, intertwining them in unique and symbolic ways. Dreams can serve as a mirror of our conscious reality, reflecting our thoughts, feelings, and unresolved conflicts. They provide a platform for our minds to make sense of our experiences, allowing for emotional processing and integration. By examining the emotions experienced in our dreams and connecting them to real-life situations, we can gain valuable insights into our subconscious mind and emotional landscape. Dreams can act as a subconscious guide, offering messages and symbols that facilitate our understanding of ourselves and our emotions. The emotional content of dreams can also assist in personal growth and self-reflection by highlighting areas that require attention or resolution. Exploring the relationship between dream emotions and real-life experiences can be a powerful tool for self-discovery and emotional healing. To learn more about how dreams and emotions contribute to personal growth, click here.
The Brain and Dream Emotions

The experience of emotions in dreams is intricately connected to various regions and processes within the brain. Neurotransmitters play a crucial role in generating emotions, both in waking life and during dreams. Specifically, neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine are involved in regulating emotions and can influence the emotional content of dreams. The amygdala, a key structure in the brain responsible for processing emotions, also plays a significant role in dream emotions. It is activated during REM sleep, the stage of sleep where most dreaming occurs. The amygdala helps to generate and intensify emotions in dreams, leading to vivid emotional experiences while we sleep. On the other hand, the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for higher cognitive functions and emotional regulation, becomes less active during REM sleep, resulting in decreased control over emotional responses in dreams. This decreased regulation allows emotions to have a stronger impact on dream experiences. The interplay between these brain regions and neurotransmitters creates a rich and complex tapestry of emotions in our dreams. To learn more about how the brain influences dream emotions, click here.
Neurotransmitters and Emotions
Neurotransmitters play a crucial role in generating and regulating emotions both in our waking lives and in dreams. These chemical messengers transmit signals between nerve cells in the brain, influencing the intensity and duration of emotional experiences. One of the key neurotransmitters involved in emotions is serotonin. Serotonin modulates mood, happiness, and feelings of well-being, and its levels profoundly impact our dream experiences. Low serotonin levels can lead to more negative emotions in dreams, while higher levels contribute to positive and pleasant dream experiences. Another neurotransmitter, norepinephrine, is linked to stress and arousal. Increased norepinephrine activity can result in vivid and emotionally intense dreams, particularly during times of heightened stress or anxiety. GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, helps regulate the intensity of emotions by dampening down excessive neuronal activity. Its role in dreams is to prevent overwhelming emotional experiences during sleep. Understanding the interplay between neurotransmitters and emotions enhances our comprehension of the emotional content of dreams and the factors that influence their intensity and tone. To explore more about how dreams and emotions intertwine and contribute to personal growth, click here.
Impact of the Amygdala
The amygdala, a small almond-shaped structure deep within the brain, plays a significant role in the impact of emotions in dreams. This region is known for its involvement in the processing and regulation of emotions. During dream states, the amygdala becomes active, contributing to the experience of emotions within dreams. Its activation can trigger strong emotional responses, leading to the vividness and intensity of emotions experienced during dreaming. The amygdala processes emotional information and connects it with relevant memories and experiences. It helps link the emotional content of dreams to our real-life experiences, allowing us to make sense of and process our emotions more effectively. Additionally, the amygdala is responsible for activating the stress response in the brain, which can explain why dreams often evoke feelings of fear, anxiety, or stress. This emotional activation in the amygdala during dreaming provides valuable insights into our emotional landscape and can aid in personal growth and self-awareness. To learn more about the impact of the amygdala on emotions in dreams, click here.
The Role of the Prefrontal Cortex
The prefrontal cortex (PFC) plays a crucial role in the generation and regulation of emotions during dreams. This region of the brain is responsible for executive functions such as decision-making, planning, and emotional regulation. During REM sleep, when dreams primarily occur, the activity in the PFC is significantly reduced, leading to a decreased ability to regulate emotions. This can explain why emotions in dreams often feel intense and unfiltered compared to our waking experiences. Without the PFC’s usual control, the emotional centers of the brain, such as the amygdala, become more active, amplifying emotional responses during dreams. The PFC also interacts with other brain regions involved in memory and emotion processing, influencing the content and intensity of emotions experienced in dreams. Understanding the role of the PFC in dream emotions provides valuable insights into the neurological basis of our dream experiences and their impact on our emotional well-being. To further explore how dreams and emotions contribute to personal growth, click here.
The Role of REM Sleep
REM sleep, or Rapid Eye Movement sleep, plays a crucial role in the generation and experience of emotions during dreams. During REM sleep, our brain activity becomes more similar to that of wakefulness, and this is when dreams predominantly occur. It is during REM sleep that emotional memories are replayed and consolidated. The activation of the amygdala, a key brain region involved in emotional processing, is heightened during REM sleep. The amygdala is responsible for processing emotional stimuli and generating emotional responses. It is believed that this increased amygdala activity during REM sleep contributes to the vividness and intensity of emotions experienced in dreams. Additionally, the prefrontal cortex, known for its role in emotional regulation and decision-making, exhibits decreased activity during REM sleep. This reduction in prefrontal cortex activity may explain why emotions in dreams can sometimes be more intense and unregulated compared to waking life. The combination of heightened amygdala activity and decreased prefrontal cortex activity during REM sleep creates an optimal environment for emotional experiences to unfold. To learn more about the impact of REM sleep on emotions and personal growth, click here.
REM and Emotional Relevance
During Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, a stage of sleep characterized by vivid dreaming, emotions play a significant role. REM sleep is closely associated with emotional relevance in dreams. Studies have shown that there is a correlation between the intensity of emotions experienced in dreams and the activation of certain brain regions during REM sleep. The amygdala, a region of the brain involved in processing emotions, becomes particularly active during this stage. This activation may help explain why emotions in dreams can feel so intense and vivid. Additionally, the prefrontal cortex, responsible for regulating emotions, may exhibit decreased activity during REM sleep, leading to reduced emotional control and increased emotional expression. As a result, emotions experienced during REM sleep tend to be more uninhibited and less influenced by rational thought. This state of heightened emotional arousal during REM sleep allows for the consolidation and integration of emotional experiences, contributing to our overall emotional well-being. To learn more about how dreams and emotions are linked, check out this article.
Emotion Regulation during REM Sleep
During REM sleep, our brains engage in intricate processes to regulate emotions experienced in dreams. REM, or Rapid Eye Movement, is the stage of sleep where dreams occur most vividly. It is during this stage that the brain becomes highly active, similar to the awake state. One theory suggests that REM sleep provides a mechanism for emotional regulation and resilience. During REM sleep, the brain is believed to simulate emotional scenarios, allowing us to experience and process emotions in a safe environment. This process helps in the regulation of intense emotions and reduces the emotional charge associated with certain memories and experiences. Research has shown that the areas of the brain responsible for emotional processing, such as the amygdala, are highly active during REM sleep. This heightened activity allows for the integration and adaptation of emotional information, making it easier to cope with challenging or distressing emotions in waking life. The emotional regulation that occurs during REM sleep serves as a form of emotional therapy, helping us navigate and come to terms with difficult experiences. Understanding this intricate process of emotion regulation during REM sleep can offer valuable insights into our emotional well-being and personal growth. To learn more about the link between dreams, emotions, and personal growth, click here.
Emotional Memories and Dreaming

When it comes to the fascinating connection between dreams and emotions, one important aspect to consider is the role of emotional memories. Our dreams often incorporate and revisit emotional experiences from our waking lives, providing a platform for the processing and consolidation of these memories. Research suggests that during REM sleep, the stage of sleep where most dreaming occurs, the brain actively replays and strengthens emotional memories. This process helps to solidify and integrate these memories into our long-term memory storage. By reliving and re-experiencing these emotions in our dreams, our brains are essentially rehearsing and reinforcing the neural pathways associated with these memories, making them more accessible and understandable to us. Dreaming also offers an opportunity for the reprocessing and resolution of traumatic events or emotional conflicts. Through the intricate interplay of various brain regions during sleep, including the hippocampus and amygdala, emotional memories are revisited, allowing for potential emotional healing and resolution. This phenomenon highlights the intricate relationship between emotional memories and dreaming, and the crucial role that dreams play in our cognitive and emotional processing. To learn more about the link between dreams, emotions, and personal growth, click here.
Consolidation of Emotional Experiences
When it comes to the consolidation of emotional experiences, dreams play a significant role. During sleep, our brains engage in a process that involves integrating and storing emotional memories. One theory suggests that dreams act as a mechanism for consolidating these emotional experiences, helping us to make sense of and process intense feelings. Research has shown that memories with emotional significance tend to be more resilient and vivid, and the same applies to emotional memories encoded during dreams. As we sleep, the brain reactivates and reprocesses these emotional memories, allowing for their consolidation and integration into our long-term memory storage. This process helps us better understand and cope with emotional events that have occurred in our lives. Dreams offer us a unique opportunity to revisit and reevaluate these emotional experiences from a new perspective, facilitating emotional growth and resilience. By examining the emotions experienced in our dreams, we can gain insight into the unresolved emotions and conflicts that may be impacting our daily lives. Understanding the consolidation of emotional experiences in dreams can provide valuable insight into our past, present, and future emotional well-being. To learn more about the link between dreams, emotions, and personal growth, click here.
Processing Traumatic Events
Processing traumatic events is a crucial aspect of emotional healing, and dreams play a significant role in this process. During sleep, our brains have the opportunity to process and make sense of distressing experiences, allowing us to emotionally integrate and cope with trauma. Dreams provide a unique avenue for the brain to work through the intense emotions and memories associated with trauma, often in a symbolic or metaphorical manner. Through the creation of dream narratives, our minds attempt to reprocess and reframe traumatic events, aiding in emotional healing and resolution. Research has shown that individuals who have experienced trauma may have more emotionally intense dreams compared to those without trauma. These dreams can serve as a way for the brain to work through and process the underlying emotions tied to the traumatic experience. They may also help individuals confront and process their fears, anxieties, and unresolved emotions related to the trauma. While the content and emotions experienced in these dreams can be challenging, they provide an opportunity for the subconscious mind to work through and ultimately integrate the trauma into one’s overall emotional well-being. Understanding the role of dreams in processing traumatic events can assist individuals in their healing journey and promote emotional resilience. To learn more about the link between dreams, emotions, and personal growth, click here.
Understanding Dream Symbols and Emotions
Understanding dream symbols and emotions is key to unraveling the deeper meaning behind our dreams. Dreams often present themselves in symbolic form, using various images, scenarios, and emotions to convey messages from our subconscious mind. Interpreting dream symbols and recognizing the emotions associated with them can provide valuable insights into our innermost thoughts, feelings, and desires. Some common dream symbols and their associated emotions include:
– Falling: Symbolizing a loss of control or insecurity, often accompanied by fear or anxiety.
– Flying: Representing a sense of freedom, empowerment, or success, evoking joy and excitement.
– Being chased: Indicating feelings of fear, vulnerability, or avoidance of a particular issue or situation.
– Water: Reflecting emotions and the subconscious mind’s depths, ranging from calmness to turbulence, depending on the state of the water.
– Death: Symbolizing transformation, change, or the end of a particular phase in life, which can evoke a wide range of emotions, including grief or liberation.
It’s important to note that the interpretation of dream symbols and emotions is subjective and can vary from individual to individual. Personal experiences, cultural background, and individual beliefs all play a role in shaping the meaning behind dream symbols. Keeping a dream journal and reflecting on the emotions experienced during dreams can help in identifying recurring patterns and gaining a deeper understanding of their significance. By exploring dream symbols and emotions, we can gain valuable insights into our subconscious mind and uncover hidden aspects of ourselves. To learn more about common emotions and symbols in dreams, click here.
Freudian Interpretation and Emotional Context
One of the most influential figures in the study of dreams and emotions is Sigmund Freud. Freud believed that dreams were a window into our unconscious mind and that they held significant psychological meaning. According to Freudian interpretation, dreams are symbolic representations of our repressed desires, fears, and unresolved conflicts. The emotional context of dreams, therefore, becomes a crucial factor in understanding their meaning. Freud suggested that emotions experienced in dreams are a reflection of our internal conflicts and desires. For example, feeling anxious or fearful in a dream may signify unresolved fears or anxieties in our waking life. Likewise, experiencing joy or pleasure in a dream could represent our hidden desires or longings. Freudian analysis emphasizes the importance of delving into the emotional content of dreams to uncover their underlying psychological significance. By examining the emotions that arise in our dreams, we can gain valuable insights into our subconscious mind and uncover hidden aspects of ourselves that may be influencing our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. To explore further how dreams can provide insight into our emotional landscape and contribute to personal growth, click here.
Individual Variations in Emotional Dream Content
Individual variations in emotional dream content are a fascinating aspect of the dream experience. While there are common emotions that many people may experience in their dreams, such as fear, joy, or anger, the specific emotional content can vary significantly from person to person. One’s personal experiences, memories, and emotional history heavily influence the emotions that manifest in their dreams. For example, a person who has recently experienced a traumatic event may have dreams filled with fear, anxiety, and sadness, reflecting their emotional state and the need for processing and healing. On the other hand, someone who has recently fallen in love might have dreams brimming with joy, excitement, and passion. It is important to note that individual variations in emotional dream content are highly subjective and unique to each person’s internal world. The symbolism and meaning attached to different emotions within dreams can also vary based on culture, personal beliefs, and experiences. If you are interested in exploring the common emotions and symbols in dreams, you can find more information here. Ultimately, understanding and exploring the individual variations in emotional dream content can provide valuable insights into one’s psyche and emotional well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the science behind why we experience emotions in dreams is a fascinating and complex subject. Dreams serve an essential purpose in emotional processing, allowing our brains to integrate and make sense of the emotions we experience in our waking lives. During REM sleep, neurotransmitters and brain regions like the amygdala and prefrontal cortex play significant roles in generating and regulating dream emotions. These emotions are not only a result of our daily experiences but also contribute to the consolidation of emotional memories. Dreams provide a unique opportunity to process traumatic events and explore our inner emotional landscape. While there are common interpretations of dream symbols and emotions, individual variations exist, and it is essential to consider the personal context of each dream. Overall, understanding the science behind dream emotions can offer valuable insights into our subconscious thoughts, feelings, and personal growth. To delve deeper into the link between dreams, emotions, and personal growth, click here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do we experience emotions in dreams?
Our dreams serve as a reflection of our waking lives, and emotions are an integral part of our daily experiences. When we dream, our brain continues to process and make sense of these emotions, often amplifying or distorting them in the dream state.
Can dreams affect our mood upon waking up?
Absolutely! Dreams can have a profound impact on our mood upon waking up. If we have a dream filled with positive emotions, we may start our day feeling happy and uplifted. Conversely, a dream filled with negative emotions can leave us feeling unsettled or anxious.
Why are some dreams more emotionally intense than others?
The emotional intensity of dreams can vary depending on a range of factors, such as the significance of the waking-life experiences being processed, the level of emotional arousal during sleep, and individual differences in dream recall and emotional sensitivity.
Can we experience emotions in lucid dreams?
Absolutely! In lucid dreams, where the dreamer becomes aware that they are dreaming, emotions can be experienced just as vividly. The conscious control and awareness in lucid dreams may even intensify emotional experiences.
Do recurring dreams have a stronger emotional impact?
Recurring dreams, which are dreams that repeat over time, can indeed have a stronger emotional impact. The repetition of a particular dream theme or scenario may indicate unresolved emotional issues or important messages that need attention.
Can dream emotions provide insight into our subconscious mind?
Yes, dream emotions can offer valuable insights into our subconscious mind. They can reveal hidden desires, fears, and unresolved conflicts that may be influencing our thoughts, behaviors, and emotions in our waking lives.
What role do nightmares play in emotional processing?
Nightmares, while unpleasant, serve an important function in emotional processing. They often provide an opportunity for the mind to confront and process fears or traumas, helping us work through emotional challenges and promote psychological healing.
Can dreams help us process traumatic events?
Yes, dreams can play a significant role in processing traumatic events. They provide a safe space for the brain to revisit and work through emotional traumas, aiding in the integration and healing process.
Why do some dreams evoke strong nostalgic emotions?
Our dreams often draw upon our past experiences and memories. When nostalgic emotions arise in our dreams, it may be a reflection of the brain’s attempt to process and make sense of those memories, evoking feelings of sentimentality or longing.
How can we use dream emotions to enhance personal growth?
Awareness and reflection on dream emotions can offer valuable insights for personal growth. By paying attention to the emotions experienced in dreams, we can gain a deeper understanding of our inner world, uncover unresolved emotional issues, and work towards personal development and healing.