Have you ever found yourself wandering through the mysterious realm of dreams, fully aware that you are actually dreaming? This phenomenon, known as lucid dreaming, has captivated the curiosity of many. But what happens when the world of dreams intersects with the reality of sleep disorders? In this article, we will delve into the intriguing relationship between lucid dreaming and sleep disorders, exploring the impact of these disorders on the frequency and control of lucid dreams, as well as the potential benefits and risks that lucid dreaming may hold for those experiencing sleep disorders. We will also discuss strategies for managing sleep disorders while maintaining the ability to engage in lucid dreaming. So, get ready to embark on a journey through the depths of slumber and consciousness as we unravel the fascinating connection between lucid dreaming and sleep disorders.
Definition of Lucid Dreaming

Lucid dreaming is a unique state of consciousness where a person becomes aware that they are dreaming while still being immersed in the dream world. It is often described as a bridge between the sleeping mind and waking consciousness, allowing individuals to have a sense of control over their dreams. In a lucid dream, the dreamer can actively participate in and manipulate the dream narrative, characters, and environment. This heightened level of awareness enables the dreamer to engage in experiences that may not be possible in the waking world, such as flying or interacting with imaginary beings. Lucid dreaming can be a thrilling and transformative experience for those who are able to achieve it. It offers a fascinating window into the capabilities of the human mind and opens up a realm of exploration and self-discovery. To learn more about the potential benefits and techniques for inducing lucid dreams, check out our article on inducing lucid dreams.
Common Sleep Disorders

There are several common sleep disorders that can disrupt the normal sleep patterns and quality of life for individuals. One such disorder is insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non-restorative sleep. It can lead to daytime fatigue, irritability, and impaired cognitive function. Another sleep disorder is narcolepsy, a neurological condition where individuals experience excessive daytime sleepiness and uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep. These sudden sleep attacks can occur at any time, even during activities like eating or talking. Additionally, sleep apnea is a disorder that involves the repeated interruption of breathing during sleep, leading to frequent awakenings and poor sleep quality. This can result in excessive daytime sleepiness and increased risk of cardiovascular problems. Understanding these common sleep disorders is crucial in recognizing their impact on sleep patterns and, subsequently, their potential influence on the occurrence and experience of lucid dreams. To gain further insight into the relationship between sleep disorders and lucid dreaming, read our article on the lucid dreaming experience.
Insomnia
Insomnia, a common sleep disorder, can significantly impact one’s ability to experience lucid dreaming. It is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or both, leading to inadequate rest and daytime fatigue. Insomnia creates a restless state of mind that is often characterized by racing thoughts, anxiety, and an inability to relax. These symptoms can make it challenging to achieve the mental clarity needed for lucid dreaming. Additionally, individuals with insomnia may find it difficult to maintain the level of focus and concentration required to recognize the dream state while they are asleep. The disrupted sleep patterns caused by insomnia may reduce the overall frequency of lucid dreaming experiences. However, it is worth noting that some individuals with insomnia may still experience occasional lucid dreams despite their sleep difficulties. To delve deeper into how lucid dreaming plays a role in problem-solving and decision making, you can read our article on the role of lucid dreaming in problem-solving and decision making.
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. People with narcolepsy often experience excessive daytime sleepiness and have sudden, uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep or experiencing a strong urge to sleep. These episodes, known as sleep attacks, can occur at any time during the day and can last from a few seconds to several minutes. Along with excessive daytime sleepiness, individuals with narcolepsy may also experience other symptoms such as cataplexy, which is a sudden loss of muscle tone often triggered by emotions like laughter or excitement. Sleep paralysis, hallucinations, and disrupted nighttime sleep are also common in individuals with narcolepsy. The impact of narcolepsy on lucid dreaming varies among individuals. While some people with narcolepsy may have more opportunities for lucid dreaming due to disrupted sleep patterns, others may find it challenging to maintain a stable sleep state that is conducive to lucid dreaming. It is important for individuals with narcolepsy to work closely with healthcare professionals to manage their symptoms and explore techniques, such as improving sleep hygiene and practicing lucid dreaming techniques, to enhance their overall sleep quality and potentially increase the likelihood of lucid dreaming experiences.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep. These interruptions, known as apneas, occur when the muscles in the throat fail to keep the airway open, leading to brief pauses in breathing. These pauses can last for a few seconds to a minute and can occur multiple times throughout the night. Sleep apnea can be categorized into three types: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), and complex sleep apnea syndrome (CSAS). OSA, the most prevalent form, is caused by a physical obstruction of the airway, while CSA is a result of the brain’s failure to send appropriate signals to the muscles responsible for breathing. CSAS is a combination of both OSA and CSA.
Sleep apnea can have various repercussions on the quality of sleep and overall health of an individual. The interruptions in breathing can cause frequent awakenings or shallower sleep, leading to excessive daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. Sleep apnea has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular conditions, such as hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. The relationship between sleep apnea and lucid dreaming is not well-researched, but it is plausible that the disruptions in breathing could potentially interfere with the continuity of sleep, making it more challenging for individuals with sleep apnea to achieve lucid dreams. However, it is important to note that each individual may experience sleep apnea and its impact on sleep and dreaming differently. Seeking effective treatment for sleep apnea, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, can help alleviate the symptoms of the disorder and potentially improve sleep quality and the ability to engage in lucid dreaming.
Impact of Sleep Disorders on Lucid Dreaming
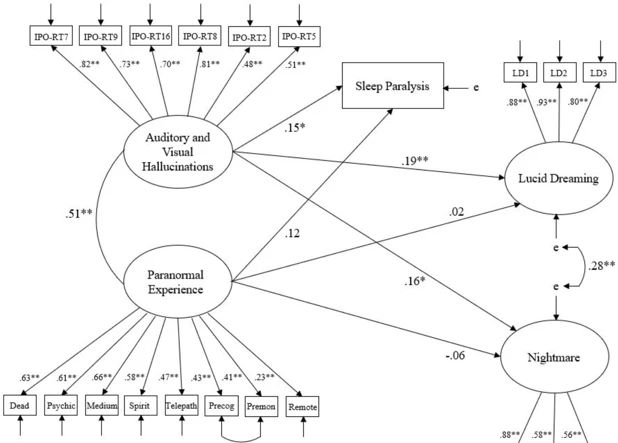
Sleep disorders can have a significant impact on the experience of lucid dreaming. Let’s explore some of the ways in which sleep disorders can influence various aspects of lucid dreaming:
- Lucid Dreaming Frequency: Sleep disorders such as insomnia, narcolepsy, and sleep apnea can disrupt the sleep cycle, making it more difficult to enter the REM stage of sleep where dreams, including lucid dreams, occur most frequently. The fragmented sleep patterns and decreased REM sleep can decrease the likelihood of experiencing lucid dreams.
- Dream Control and Clarity: Sleep disorders can affect the overall quality of sleep, leading to a decrease in dream control and lucidity. Fatigue, sleep deprivation, and irregular sleep patterns can make it harder to maintain awareness and control within the dream state, resulting in less vivid and less controllable lucid dreams.
- Recurring Lucid Dreams: Some sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy, may cause an increased frequency of lucid dreaming. In narcolepsy, the boundary between waking and dreaming states can become blurred, leading to an overlap where individuals may experience lucid dreams more frequently.
Understanding how sleep disorders impact lucid dreaming can help individuals with sleep disorders better manage their sleep patterns and maximize the potential for lucid dreaming experiences.
Lucid Dreaming Frequency
The frequency of lucid dreaming can be significantly influenced by the presence of sleep disorders. Sleep disorders such as insomnia, narcolepsy, and sleep apnea can disrupt the sleep cycle and interfere with the natural progression of sleep stages, including the REM (Rapid Eye Movement) stage where most dreams occur. As a result, individuals with sleep disorders may experience a decrease in the frequency of lucid dreams. Insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, can lead to sleep fragmentation and a reduction in REM sleep, making it more challenging to enter the lucid dreaming state. Narcolepsy, a neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden bouts of sleep, may also disrupt the normal sleep architecture and decrease the occurrence of lucid dreams. Additionally, sleep apnea, a condition where a person experiences pauses in breathing during sleep, can lead to frequent awakenings throughout the night, interrupting REM sleep and inhibiting lucid dreaming opportunities. It’s important to note that while sleep disorders may decrease the frequency of lucid dreaming, it doesn’t necessarily mean that individuals with these disorders are unable to experience lucid dreams altogether. With proper management and treatment of the underlying sleep disorder, it is possible to improve the chances of having lucid dreams.
Dream Control and Clarity
Dream control and clarity are two crucial aspects that come into play when exploring the relationship between lucid dreaming and sleep disorders. When individuals experience sleep disorders, such as insomnia or sleep apnea, it can impact their ability to achieve and maintain lucidity within their dreams.
Dream control refers to the extent to which individuals are able to influence and shape the events and elements of their dreams. In the context of lucid dreaming, dream control becomes even more significant as it allows individuals to actively manipulate their dream scenarios. However, sleep disorders can disrupt this control, making it more challenging for individuals to exert their desired influence on their dreams. For example, someone with insomnia may be more focused on trying to fall asleep rather than actively engaging in dream control techniques.
On the other hand, dream clarity pertains to the level of vividness and detail experienced within a dream. Lucid dreaming often involves a heightened sense of realism, where colors may be more vibrant, sounds more distinct, and textures more palpable. However, sleep disorders can diminish dream clarity, resulting in fragmented, blurry, or hazy dream experiences. This lack of clarity can hinder the overall lucidity and recall of the dream, making it difficult for individuals to fully engage with their dreams and exercise control.
It’s important to note that while sleep disorders can potentially impact dream control and clarity, there may also be instances where individuals with sleep disorders still experience lucid dreaming. The relationship between sleep disorders and lucid dreaming is complex and varies from person to person.
Maintaining optimal sleep health and managing sleep disorders can contribute to enhancing the quality of lucid dreaming experiences. By addressing underlying sleep issues, individuals may have a greater chance of achieving lucidity and experiencing heightened dream control and clarity.
Recurring Lucid Dreams
Recurring lucid dreams are a fascinating phenomenon in which individuals experience the same or similar lucid dreams on multiple occasions. These recurrent dreams can occur spontaneously or be triggered by specific cues or events in the dreamer’s life. One possible explanation for recurring lucid dreams is that the dreamer has developed a certain level of skill and control in lucid dreaming, allowing them to intentionally recreate the dream scenario. This can be particularly exciting for individuals who enjoy specific dream scenarios and wish to revisit them. Recurring lucid dreams also provide an opportunity for individuals to delve deeper into their dream world, explore different aspects of the dream environment, and gain a better understanding of their own subconscious mind. These dreams can serve as a platform for personal growth and self-reflection, as individuals often work through emotional or psychological issues within the safe confines of their dreams. For some, recurring lucid dreams may offer a sense of stability and familiarity in an otherwise unpredictable dream world. These dreams can be seen as an extraordinary gift, providing individuals with the chance to continuously engage in lucid exploration and enrichment of their inner dream realm.
Benefits and Risks of Lucid Dreaming in Sleep Disorders

Lucid dreaming, despite its enchanting allure, can have both benefits and risks when it comes to sleep disorders. On the one hand, lucid dreaming holds therapeutic potential for individuals with sleep disorders. It provides a creative outlet for exploring one’s dream world, reducing stress, and enhancing overall well-being. Additionally, lucid dreaming can serve as a form of problem-solving and decision-making, offering insights and solutions to real-life challenges. On the other hand, the practice of lucid dreaming can disrupt sleep patterns and exacerbate sleep disorders, leading to decreased sleep quality and daytime fatigue. It is important for individuals with sleep disorders to find a balance between engaging in lucid dreams and ensuring sufficient restorative sleep. Awareness of these potential benefits and risks is vital in order to make informed decisions and effectively manage the relationship between lucid dreaming and sleep disorders.
Therapeutic Potential
The therapeutic potential of lucid dreaming in the context of sleep disorders is a fascinating area of study. Research suggests that lucid dreaming may offer various benefits for individuals experiencing sleep disorders.
1. Overcoming Nightmare Disorders: Nightmare disorders, such as nightmares associated with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or anxiety disorders, can greatly disrupt sleep and lead to distress. Lucid dreaming provides an opportunity for individuals to actively confront and change the content of their nightmares, transforming them into less threatening or more positive scenarios. This can help alleviate the distress associated with recurring nightmares and improve overall sleep quality.
2. Improving Sleep Quality: Sleep disorders often result in fragmented or poor-quality sleep. Lucid dreaming can act as a form of cognitive therapy during sleep, promoting relaxation, reducing anxiety, and enhancing sleep quality. Engaging in lucid dreaming techniques, such as guided imagery or visualization, can contribute to a more restful sleep experience.
3. Enhancing Emotional Resilience: Sleep disorders are often accompanied by emotional challenges. Lucid dreaming offers an opportunity for individuals to explore and resolve emotional conflicts within the dream state. This process can facilitate emotional healing, personal growth, and increased self-awareness. By working through emotional issues in a lucid dream, individuals may experience a sense of empowerment and develop greater emotional resilience.
4. Promoting Creative Problem-solving: Lucid dreaming can serve as a platform for creative problem-solving and decision-making. During a lucid dream, individuals can intentionally confront and work through real-life challenges, brainstorm creative solutions, and practice new skills. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals dealing with sleep-related cognitive impairments, allowing them to enhance cognitive functioning and explore innovative approaches to problem-solving.
The therapeutic potential of lucid dreaming within the realm of sleep disorders is still being explored, but its ability to provide a unique and immersive therapeutic experience holds promise. If you’re interested in learning more about the role of lucid dreaming in problem-solving and decision-making, check out our article on the role of lucid dreaming in problem solving.
Disturbance of Sleep Patterns
Disturbances in sleep patterns can be a significant concern for individuals who engage in lucid dreaming, particularly when they already struggle with sleep disorders. Lucid dreaming requires a delicate balance between the states of wakefulness and sleep, and disruptions to the natural sleep cycle can impede the ability to achieve and sustain lucid dreams. Sleep disorders such as insomnia, narcolepsy, and sleep apnea can all contribute to these disruptions.
Insomnia is characterized by difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to inadequate rest and daytime fatigue. Insomniacs may find it challenging to enter the necessary state of deep sleep where lucid dreams are more likely to occur. The sleep fragmentation caused by insomnia may disrupt the continuity of dreams and the ability to maintain awareness in a dream.
Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. Individuals with narcolepsy often experience excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden episodes of falling asleep. While lucid dreams can occur during these daytime naps, they may be brief and less vivid. Additionally, the disrupted sleep patterns associated with narcolepsy can make it difficult for individuals to achieve lucid dreaming during their nighttime sleep.
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, leading to fragmented sleep and daytime sleepiness. The repeated awakenings and interruptions in breathing can disrupt the necessary stages of sleep for lucid dreaming. The fatigue and drowsiness caused by sleep apnea may decrease the likelihood of achieving lucidity in dreams.
It is essential for individuals with sleep disorders to establish healthy sleep hygiene practices and manage their condition effectively to support their overall sleep quality and increase the chances of experiencing lucid dreams. Addressing and seeking treatment for the underlying sleep disorder can help improve sleep patterns and increase the potential for lucid dreaming.
Managing Sleep Disorders and Lucid Dreaming
Managing sleep disorders while maintaining the ability to engage in lucid dreaming requires a holistic approach that addresses both the underlying sleep issues and the practice of lucid dreaming. One of the key strategies is to prioritize sleep hygiene. This involves adopting healthy sleep habits, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime. Additionally, incorporating specific lucid dreaming techniques can help individuals with sleep disorders reap the benefits of lucid dreaming. Techniques like reality checks, dream journaling, and visualization exercises can enhance dream recall and increase the likelihood of experiencing lucid dreams. In some cases, behavioral and medical interventions may be necessary to address sleep disorders more directly. This can include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia, medication for certain sleep disorders, or seeking professional help from sleep specialists. By combining these approaches, individuals can actively manage their sleep disorders while still experiencing the potential benefits of lucid dreaming.
Sleep Hygiene
Sleep hygiene refers to a set of habits and practices that promote good sleep quality and quantity. When it comes to managing sleep disorders and enhancing the potential for lucid dreaming, maintaining proper sleep hygiene is essential. Here are some key aspects of sleep hygiene that can positively influence both sleep disorders and lucid dreaming:
1. Consistent Sleep Schedule: Establishing a regular sleep schedule helps regulate the body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep. Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
2. Create a Restful Environment: Make your sleeping environment conducive to sleep. Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. Consider using earplugs, eye masks, or white noise machines to block any disruptive sounds or light.
3. Avoid Stimulating Substances: Limit or avoid the consumption of stimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, especially close to bedtime. These substances can interfere with the quality of your sleep and may disrupt the ability to have lucid dreams.
4. Establish a Bedtime Routine: Engage in relaxing activities before bed to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This could include reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing.
5. Limit Electronic Devices: The blue light emitted by electronic devices can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that promotes sleep. Avoid using smartphones, tablets, and computers at least an hour before bed to improve sleep quality.
By practicing good sleep hygiene, you can create an optimal sleep environment that supports both restful sleep and the potential for lucid dreaming. These habits can significantly improve the overall quality of your sleep and enhance your dream experiences. So, prioritize sleep hygiene as part of your journey towards managing sleep disorders and exploring the world of lucid dreaming.
Lucid Dreaming Techniques
Lucid dreaming techniques are various strategies and practices that individuals can employ to increase their chances of experiencing lucid dreams. These techniques aim to enhance dream awareness and improve the ability to recognize when one is within the dream state. One popular technique is reality testing, which involves regularly questioning one’s reality throughout the day. By performing reality checks, such as looking at a clock or reading a piece of text and then looking away and back again, individuals can train themselves to do the same in their dreams. In a dream, the text or clock may appear distorted or change, signaling that one is indeed in a dream. Another technique is keeping a dream journal, where individuals record their dreams upon waking up. This practice helps to improve dream recall and allows for the identification of common dream themes or patterns that can later serve as cues for lucidity. Other techniques include mnemonic induction of lucid dreams (MILD), where individuals repeat affirmations about becoming lucid in the dream state before falling asleep, and wake-induced lucid dreaming (WILD), where individuals maintain awareness as they transition from being awake to falling asleep. It is important to note that not all techniques work for everyone, and it may take time and practice to find the method that suits an individual’s unique sleeping and dreaming patterns.
Behavioral and Medical Interventions
When it comes to managing sleep disorders and their potential impact on lucid dreaming, a combination of behavioral and medical interventions can be employed. These interventions aim to improve sleep quality and regulate sleep patterns, ultimately reducing the symptoms of sleep disorders and creating an environment more conducive to lucid dreaming.
Behavioral interventions:
- Sleep hygiene: Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing the sleep environment are important aspects of sleep hygiene. By practicing good sleep hygiene, individuals with sleep disorders can improve their overall sleep quality, making it easier to attain lucid dreaming states.
- Stress reduction techniques: Stress and anxiety can negatively affect both sleep quality and the frequency of lucid dreaming. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and journaling can help reduce stress levels and promote relaxation, potentially enhancing the likelihood of lucid dreaming experiences.
- Lucid dreaming techniques: Various techniques can be utilized to increase the chances of having lucid dreams. These include reality checks (such as questioning reality throughout the day), dream journaling (recording dreams regularly), and visualization exercises (imagining oneself becoming lucid during a dream).
Medical interventions:
- Prescription medications: In some cases, individuals with sleep disorders may benefit from prescription medications to manage their symptoms. Medications such as hypnotics for insomnia, stimulants for narcolepsy, or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy for sleep apnea can help regulate sleep and improve overall sleep quality.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): CBT-I is a type of therapy that focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to insomnia. It can be an effective non-pharmacological treatment option for individuals with insomnia, addressing the underlying causes of the disorder and promoting better sleep.
- Alternative therapies: Complementary approaches, such as acupuncture, aromatherapy, or herbal supplements, may also be used as adjunct therapies for sleep disorders. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating these therapies, as their effectiveness and safety can vary.
By implementing a combination of these behavioral and medical interventions, individuals with sleep disorders can better manage their symptoms while still fostering the potential for lucid dreaming experiences. It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific sleep disorder and considers the individual’s overall health and well-being. Remember, finding the right balance between managing sleep disorders and exploring lucid dreaming can lead to a more harmonious and fulfilling sleep experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the relationship between lucid dreaming and sleep disorders is a complex and multifaceted one. While sleep disorders can impact the frequency and quality of lucid dreams, there are also potential benefits to be gained from engaging in lucid dreaming practices for individuals with sleep disorders. Lucid dreaming holds therapeutic potential, offering a means of exploring the subconscious mind and potentially addressing underlying psychological issues. However, it is important to be mindful of the potential disruption to sleep patterns that can occur with frequent lucid dreaming. Proper sleep hygiene and the incorporation of lucid dreaming techniques can help strike a balance between managing sleep disorders and exploring the realm of consciousness that lucid dreaming provides. It is advised that individuals with sleep disorders consult with healthcare professionals for guidance on managing their specific condition while pursuing lucid dreaming experiences. By combining the understanding of sleep disorders with the exploration of lucid dreaming, individuals can unlock the potential for self-discovery, creativity, and personal growth within the realms of their dreams.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can anyone experience lucid dreaming?
Yes, anyone has the potential to experience lucid dreaming. It is believed that with practice and certain techniques, individuals can increase their chances of having lucid dreams.
2. How can I increase the frequency of my lucid dreams?
There are several techniques that can help increase the frequency of lucid dreams. Some popular methods include reality checks, keeping a dream journal, and practicing visualization and reality affirmation techniques.
3. Are there any risks associated with lucid dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is considered safe. However, it is important to note that intense or frequent lucid dreaming experiences may disrupt normal sleep patterns and lead to sleep disturbances.
4. Can lucid dreaming help with problem-solving and decision making?
Yes, lucid dreaming has been found to have potential benefits in problem-solving and decision making. By engaging with dream scenarios consciously, individuals may gain insights and creative solutions to real-life challenges.
5. Can lucid dreaming be used for therapeutic purposes?
Yes, lucid dreaming has shown promise in therapeutic applications, such as overcoming nightmares, reducing anxiety, and addressing phobias. It can be used as a tool for self-exploration and personal growth.
6. Are there any techniques to prolong the duration of lucid dreams?
Yes, there are techniques that can help prolong the duration of lucid dreams. These include maintaining dream lucidity through stabilization techniques, such as spinning in the dream or rubbing hands together.
7. Can lucid dreaming improve dream recall?
Yes, practicing lucid dreaming techniques, such as keeping a dream journal and paying closer attention to dreams, can enhance dream recall abilities. This can lead to a more vivid and immersive dream experience.
8. Can lucid dreaming be used to explore creativity?
Absolutely! Lucid dreaming offers a unique platform to explore and tap into one’s creativity. By consciously shaping dream experiences, individuals can engage in limitless artistic expression and innovation.
9. Are there any specific foods or supplements that can enhance lucid dreaming?
While there is no definitive scientific evidence, some individuals claim that certain foods and supplements, such as vitamin B6, mugwort, and galantamine, may enhance the likelihood of lucid dreaming. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any supplements.
10. How can lucid dreaming impact sleep quality?
Lucid dreaming can have variable effects on sleep quality. While it can be an exciting and enjoyable experience, intense lucid dreaming may disrupt regular sleep patterns, potentially leading to sleep disturbances and decreased sleep efficiency.