Embark on an awe-inspiring journey through the cosmos as we unravel the captivating relationship between stars and galaxies. In the vast expanse of space, these celestial entities dance harmoniously, shaping the very fabric of our universe. From the birth of stars within stellar nurseries to the explosive endings of supernovae, we delve into the intricate life cycle of these luminous beings. But stars are not alone in the cosmic ballet. Galaxies, the building blocks of the universe, come in various shapes and sizes, each possessing its own mesmerizing allure. As we explore the enigmatic beauty of spiral and elliptical galaxies, we also unveil the secrets of our very own home, the Milky Way. Prepare to be captivated by the peculiar cosmic relationships formed between stars and galaxies, and contemplate the future of our universe as we discuss the impending collision between the Milky Way and Andromeda. Join us on this extraordinary voyage of discovery into the wonders of the cosmos.
The Birth of Stars
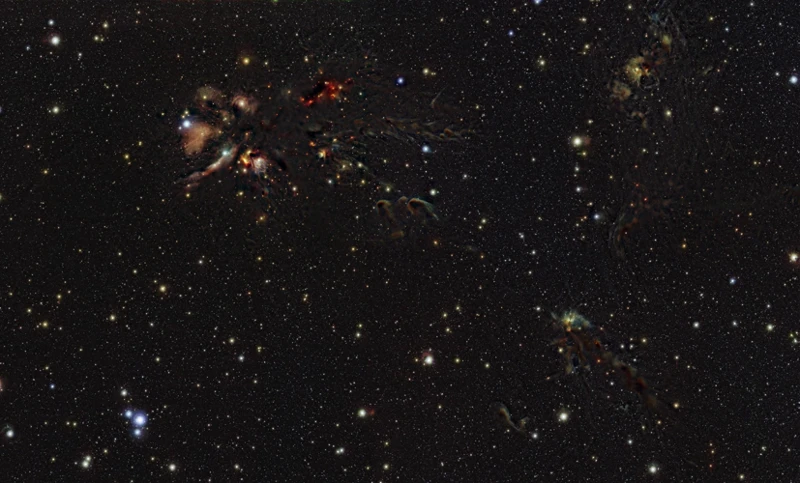

Within the vastness of space, the birth of stars is a truly remarkable phenomenon. It all begins within dense clouds of gas and dust known as nebulae, which serve as stellar nurseries. These nebulas, often illuminated by nearby stars, are breathtakingly beautiful and come in various forms such as the iconic Orion Nebula and the mesmerizing Eagle Nebula. As gravity causes the gas and dust to collapse inward, the protostar phase is initiated. This process can take millions of years as the swirling mass begins to heat up, eventually becoming hot enough for nuclear fusion to occur at its core, igniting the star. The birth of a star is a balance between gravity’s relentless pull inward and the pressure generated by the nuclear fusion process. It is a delicate harmony that sets the stage for the mesmerizing celestial dance we witness in the night sky. To learn more about the dazzling display of shooting stars that often accompanies the birth of stars, read our intriguing article on meteor showers and shooting stars.
Nebulae: Stellar Nurseries
Nebulae are celestial wonders that serve as the stellar nurseries where new stars are born. These vast clouds of gas and dust are scattered throughout the cosmos, captivating us with their ethereal beauty. Nebulae come in different types, each with its own distinct characteristics. The most common type is the emission nebula, which emits light of various colors as the gas within it interacts with nearby stars, creating stunning displays like the iconic Orion Nebula. Another type is the reflection nebula, which reflects the light of nearby stars, resulting in a beautiful blue glow. Dark nebulae, on the other hand, are dense clouds of gas and dust that block the light from the stars behind them, making them appear as dark patches against the backdrop of glowing nebulae. These cosmic structures are a testament to the intricate and complex processes occurring within our universe. To further explore the mysteries of the cosmos, check out our article on the thrilling hunt for dark matter, a substance that is believed to make up a significant portion of the universe’s mass.
Protostars: The Formation Process
During the fascinating formation process of protostars, gravity plays a central role in bringing together the gas and dust within stellar nurseries. As the dense cloud collapses inward, it begins to rotate, forming a flattened disk of material known as an accretion disk. This disk acts as a reservoir, continuously feeding the growing protostar with matter. As the material spirals inwards due to gravity, it gains momentum, forming a hot, rotating core at the center of the disk. This core, known as a protostellar core, becomes increasingly dense and hot as the matter continues to accrete. As the temperature rises, the core emits infrared radiation, marking the presence of a developing protostar. The process of protostar formation is still not fully understood, and scientists are continually studying the intricate dynamics of these cosmic nurseries. To explore another phenomenon affected by gravitational forces, read our captivating article on the impact of planetary alignment on Earth’s tides.
The Life Cycle of Stars
As stars take center stage in the cosmic theater, they navigate through a distinct life cycle, each stage characterized by its own unique characteristics and behaviors. The first stage, known as the Main Sequence Stars, represents the longest and most stable period of a star’s life. During this phase, stars, fueled by the fusion of hydrogen into helium within their cores, emit a consistent amount of energy. This equilibrium between gravity pulling inward and radiation pushing outward allows them to maintain a harmonious balance for millions or even billions of years. However, this stellar serenity is not eternal. Eventually, the hydrogen fuel depletes and stars begin to undergo dramatic transformations. For massive stars, this leads to a dazzling and explosive outcome known as a Supernova. A supernova is a cataclysmic event where the star releases an enormous amount of energy, briefly outshining an entire galaxy. This monumental explosion scatters heavy elements across the cosmos, providing the building blocks for future generations of stars and planets. To delve deeper into the thrilling world of supernovae and their significance, check out our informative article on the subject. With each supernova, the cycle of life and death continues, perpetuating the cosmic dance of stars.
Main Sequence Stars: The Stellar Prime
Main sequence stars are the stellar powerhouses that dominate the majority of a star’s life. These stars, including our very own Sun, are in a stable state known as the stellar prime. They generate energy through nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms fuse together to form helium, releasing an incredible amount of energy in the process. This energy radiates outwards, creating the intense light and heat that we see and feel. Main sequence stars come in various sizes, from the smallest red dwarfs to the massive blue giants. Each size class has distinct characteristics, such as differing lifespans and energy outputs. The size of a main sequence star is determined by its mass, with larger stars burning brighter and hotter than their smaller counterparts. As stars age within the main sequence, they gradually exhaust their hydrogen fuel, leading to changes in their physical properties. These changes can result in a star expanding into a red giant or even undergoing a cataclysmic supernova explosion. To comprehend the intricate life stages of stars beyond the main sequence, stay tuned for our upcoming articles on stellar evolution and the thrilling hunt for dark matter, a mysterious substance that continues to perplex scientists around the world.
Supernovae: The Explosive Endings
Supernovae, the explosive endings of stars, are among the most cataclysmic events in the universe. These extraordinary events occur when massive stars reach the end of their life cycles. It is during this phase that the core of the star collapses, triggering a massive explosion. This explosion releases an immense amount of energy, outshining entire galaxies for a brief period of time. The remnants of a supernova can form various celestial objects, including neutron stars or even black holes. Supernovae play a crucial role in the universe as they disperse heavy elements, such as carbon and iron, into space, which are then used as building blocks for new stars and planets. The energy and shockwaves generated by supernovae can trigger the formation of new stars in neighboring regions. Studying these explosive events helps scientists gain insights into the life cycles of stars, the creation of elements, and the evolution of galaxies. To unravel the thrill of hunting for some of the universe’s most elusive mysteries, check out our article on the thrilling hunt for dark matter.
Galaxies: The Building Blocks of the Universe
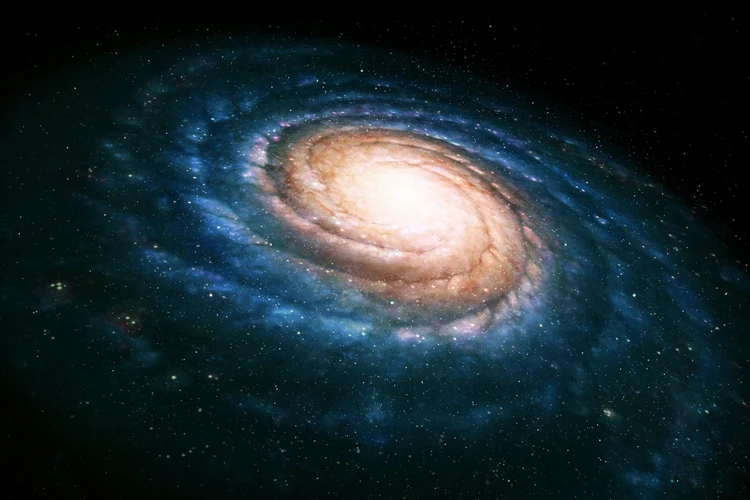

When we gaze up at the night sky, the beauty and vastness we behold are a result of the intricate dance of galaxies, which act as the building blocks of the universe. There are various types of galaxies, each possessing its own unique characteristics and allure. One such type is the spiral galaxy. These cosmic beauties exhibit swirling arms extending from a central core, adorned with bright clusters of stars and interstellar dust. Examples of spiral galaxies include the majestic Andromeda Galaxy and our very own Milky Way. Their graceful spiral arms captivate the imagination and inspire awe in the depths of space. On the other hand, elliptical galaxies showcase a different form of beauty. They lack the distinct spiral structure and instead appear as smooth, symmetrical ellipsoids. The stars within elliptical galaxies are densely packed, giving rise to stunning displays of stellar eclipses. To explore the captivating nature of dark matter and its role in the formation of galaxies, check out our thrilling article on the hunt for dark matter. Understanding the intricate nature of galaxies allows us to unravel the mysteries of our vast universe and appreciate the boundless wonders it holds.
Spiral Galaxies: Whirling Cosmic Beauties
Spiral galaxies are truly captivating cosmic wonders that grace the expanses of the universe. These galactic structures are characterized by their whirling arms that radiate outwards from a central nucleus. The arms are made up of billions of stars, dust, and gas, all swirling together in a graceful dance. One of the most famous examples is the Andromeda Galaxy, a stunning spiral galaxy that is visible to the naked eye on a clear, dark night. The arms of spiral galaxies contain a wealth of celestial treasures, including young, bright stars that illuminate the interstellar medium with their brilliance. These galaxies are a testament to the immense power of gravity, as it shapes the stars and pulls them into their spiral patterns. The intricate and beautiful structures of spiral galaxies have captivated astronomers for centuries, inspiring awe and curiosity about the vastness and complexity of our universe.
Elliptical Galaxies: The Majesty of the Eclipses
Elliptical galaxies, with their majestic and enigmatic nature, stand as celestial marvels in the cosmos. These galaxies, named for their elliptical shape, differ greatly from spiral galaxies in their structure and characteristics. Where spiral galaxies possess distinct arms and a central bulge, the beauty of elliptical galaxies lies in their smooth and symmetric appearance. Unlike spiral galaxies that are hubs of vibrant star formation, elliptical galaxies are home to aging and dying stars, making them a unique spectacle to behold. Within these galaxies, stars move along random orbits, creating a mesmerizing dance full of fascinating eclipses. The collisions and interactions between stars within elliptical galaxies often result in intricate shadow patterns, further enhancing the allure of these cosmic wonders. These celestial light shows within elliptical galaxies captivate astronomers and stargazers alike. To dive deeper into the thrilling mysteries of the universe, explore our article on the thrilling hunt for dark matter and expand your understanding of the cosmos.
The Milky Way and Beyond
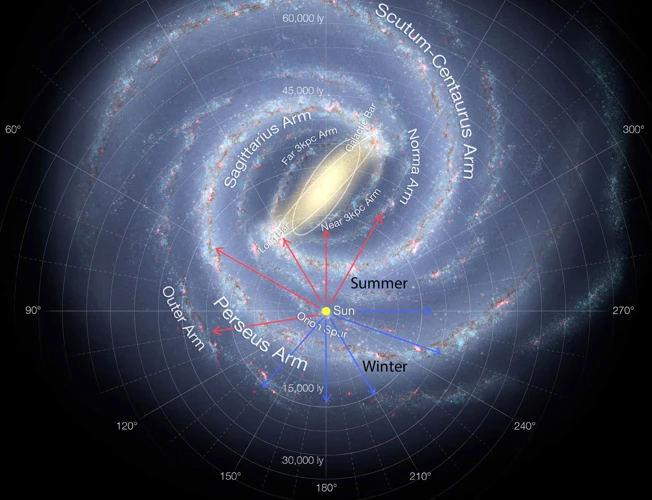
The Milky Way, our home galaxy, is a captivating sight in the night sky. It stretches across vast distances, boasting billions of stars, nebulae, and other celestial wonders. With its spiral shape, the Milky Way is a member of the grand family of spiral galaxies. These magnificent cosmic beauties showcase arms that elegantly curve outward, adorned with clusters of stars, gas, and dust. On the other hand, we have elliptical galaxies, which possess a more majestic and elliptical shape, resembling a giant celestial eclipse. They are a testament to the immense diversity of galaxies that exist throughout the universe, each possessing its own unique characteristics and allure. Beyond the bounds of the Milky Way and its neighboring galaxies lies a vast expanse of space holding countless mysteries still waiting to be discovered. Scientists and astronomers dedicatedly explore this realm, using powerful telescopes and innovative technologies in their quest to unravel the secrets of the cosmos. To find out more about the thrilling hunt for dark matter and its implications for our understanding of the universe, check out our article on the thrilling hunt for dark matter. The exploration of the Milky Way and beyond continues to captivate our imaginations and broaden our horizons as we witness the extraordinary marvels that exist in the far reaches of space.
Our Home: The Milky Way Galaxy
Nestled among the vast expanse of the cosmos, our home – the Milky Way Galaxy – is a mesmerizing sight to behold. Spanning approximately 100,000 light-years in diameter, the Milky Way is a colossal spiral galaxy, characterized by its distinct spiral arms and a luminous bulge at its center. These stunning arms, adorned with countless stars, gas, and dust, gracefully wind their way around the galactic center. As we journey through the Milky Way, we encounter various stellar phenomena, such as nebulae that serve as stellar nurseries, bringing forth new generations of stars. There are also remarkable celestial objects like supernovae – explosive endings of massive stars that release an extraordinary amount of energy and can be seen from immense distances. The elegant dance of stars within the Milky Way creates a breathtaking tapestry of light and wonder. To explore other captivating mysteries of the cosmos, such as the thrilling hunt for dark matter, be sure to check out our article on the subject.
Galactic Clusters: The Marvelous Migrations
Galactic clusters, with their marvelous migrations, are awe-inspiring assemblages of numerous galaxies bound together by gravity. These clusters are found throughout the vast expanse of the universe and come in two main types: open clusters and globular clusters. Open clusters, like the famous Pleiades in the constellation of Taurus, are relatively young and contain a few dozen to a few thousand stars. They are held together loosely and tend to disintegrate over time as their member stars drift apart due to gravitational forces. On the other hand, globular clusters are densely packed, spherical collections of ancient stars that contain hundreds of thousands to millions of stars. These clusters are found in the halos of galaxies, such as the Milky Way, and are some of the oldest objects in the universe. One extraordinary example is Omega Centauri, a globular cluster that boasts an estimated 10 million stars within its gravitational embrace. As these clusters migrate through the galactic landscape, they interact with other clusters and galaxies, triggering breathtaking celestial phenomena such as gravitational interactions and tidal disruptions. The dynamics and migrations of galactic clusters paint a vivid picture of the evolving nature of our universe. To further explore the mysteries of the cosmos, you may be interested in our article on the thrilling hunt for dark matter, which plays a crucial role in the formation and dynamics of galactic clusters (click here to read more).
Peculiar Cosmic Relationships
The cosmos is a realm of peculiar cosmic relationships, where stars and galaxies interact in fascinating ways. One such interaction is the gravitational tango between stars and galaxies. As stars orbit within galaxies, their paths can be influenced by the gravitational pull of nearby celestial bodies. This can lead to intricate dances, as stars weave intricate patterns in the fabric of space and time. Another captivating relationship is the role of black holes in galaxy formation. These incredibly dense objects have such immense gravity that they can devour surrounding material, including stars, and shape the structure and dynamics of galaxies. The interplay between stars and galaxies is a cosmic symphony of gravitational forces and celestial interactions that continues to astound astronomers. To delve deeper into the thrilling hunt for dark matter and its implications for the universe, check out our article on the captivating quest for dark matter.
Interactions Between Stars and Galaxies
Interactions between stars and galaxies are a fascinating aspect of the cosmic tapestry. The gravitational forces exerted by galaxies can have a profound impact on the motion and formation of stars within them. Through various mechanisms, galaxies can influence the evolution of stars, leading to remarkable phenomena. One such interaction is known as tidal disruption, where a star strays too close to a massive galaxy’s gravitational pull. The immense tidal forces acting on the star can tear it apart, resulting in a luminous event called a tidal disruption event (TDE). Another intriguing interaction occurs when galaxies collide or merge. During these cosmic collisions, the gravitational forces between the stars and the galaxies cause intricate interactions and disturbances in their morphology. The stars within the merging galaxies can be flung into new orbits, creating chaotic patterns that eventually settle into a new stellar equilibrium. These interactions between stars and galaxies are vital in shaping the structures and dynamics of the universe. To delve deeper into the thrilling world of cosmic interactions, check out our article on the thrilling hunt for dark matter, as dark matter plays a crucial role in the gravitational dance between stars and galaxies.
The Role of Black Holes in Galaxy Formation
Black holes, enigmatic cosmic entities with immense gravitational pull, play a crucial role in the formation and evolution of galaxies. As matter spirals towards the black hole, it forms an accretion disk. The strong gravitational forces generated by the black hole cause this disk to release an incredible amount of energy in the form of quasars, which are among the brightest objects in the universe. This energy can have a profound impact on the surrounding galaxy, affecting its star formation rates and even inhibiting the growth of other black holes. Additionally, black holes have the ability to shape the structure of galaxies through processes like gravitational interactions. When galaxies collide or come in close proximity, the gravitational forces exerted by the black holes can cause material to be flung outwards, triggering intense starburst activity. Simultaneously, these interactions can also cause some of the gas and dust to be drawn towards the central region of the galaxy, fueling the growth of the central supermassive black hole. To learn more about the thrilling hunt for dark matter and its connection to our understanding of galaxy formation, check out our article on the thrilling hunt for dark matter. The complex interplay between black holes and their host galaxies continues to fascinate astronomers, revealing more about the birth and evolution of the universe itself.
The Future of Stars and Galaxies
As we ponder the future of stars and galaxies, one undeniable event looms on the cosmic horizon: the collision between our very own Milky Way and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy. This celestial tango is projected to take place in approximately 4 billion years, setting the stage for a dazzling display of cosmic fireworks. During this collision, the gravitational forces at play will cause the stars within both galaxies to be flung into new trajectories, disrupting their current dance and giving rise to an entirely new cosmic choreography. The merger of the Milky Way and Andromeda will ultimately lead to the formation of a new galaxy, aptly named Milkomeda, blending the unique characteristics of its predecessor galaxies. The fate of individual stars will vary as they either survive the merger intact, are ejected from the newly formed galaxy, or collide and merge with other stars. It is a spectacle that both captivates and reminds us of the constant evolution and grand nature of the universe. To explore further the potential implications of this collision on the universe’s fate and the thrilling hunt for dark matter, delve into our article on the thrilling hunt for dark matter.
The Collision of the Milky Way and Andromeda
In the vast cosmic dance, a breathtaking spectacle awaits us in the future – the collision of the Milky Way and the Andromeda galaxy. These two galactic giants, hurtling through space at incredible speeds, are being drawn towards each other by the irresistible force of gravity. While the collision is not imminent, it is predicted to occur in around 4 billion years, ushering in a cosmic event that will reshape both galaxies. As the galaxies approach, their gravity will intertwine, causing them to distort and stretch. Stars within each galaxy are unlikely to collide due to the vast distances between them, but the gravitational forces will disrupt their orbits, flinging them into new trajectories. This cosmic merger will create a mesmerizing display of swirling gas, dust, and star formations. As the galaxies continue to merge, they will eventually settle into a single, elliptical galaxy. Witnessing this cosmic collision will be a sight to behold, with astronomers in the future marveling at the intermingling of galactic structures. To delve into more thrilling cosmic phenomena, check out our article on the thrilling hunt for dark matter and its enigmatic presence in the universe.
Implications for the Universe’s Fate
As we contemplate the collision between the Milky Way and Andromeda, we can’t help but ponder the implications it holds for the fate of the universe. This cosmic event, slated to occur billions of years from now, offers a glimpse into the future evolution of galaxies. With the combined gravitational forces of these two massive structures, the collision will have a profound impact on their individual shapes and structures. The merger will likely lead to the creation of a new elliptical galaxy, altering the cosmic landscape as we know it. This monumental event raises intriguing questions about the destiny of our universe. Will it eventually succumb to a state of cosmic stagnation, with galaxies merging and resources depleting? Or will it continue to thrive and evolve, giving birth to new formations and phenomena that we have yet to comprehend? The collision of the Milky Way and Andromeda serves as a catalyst to explore these profound cosmic mysteries and to contemplate the immeasurable potential that lies within the vastness of space. To delve into more thrilling mysteries of the universe, don’t miss our article on the thrilling hunt for dark matter.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the relationship between stars and galaxies is a mesmerizing and intricate tapestry woven throughout the cosmos. From the birth of stars within stellar nurseries to the explosive supernovae that mark their endings, we have ventured into the captivating life cycle of these celestial entities. We have marveled at the beauty of spiral and elliptical galaxies, appreciating the unique features that make each one a cosmic masterpiece. Exploring our very own Milky Way, we have come to understand the immense expanse and complexity of our home galaxy. Pondering the peculiar cosmic relationships between stars and galaxies, we have contemplated the profound influence they have on each other’s evolution. As we look to the future, the collision of the Milky Way and Andromeda looms, raising questions about the fate of our universe. To delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos, such as the thrilling hunt for dark matter, be sure to read our intriguing article on this captivating subject. As we continue to explore and study the stars and galaxies, our knowledge and understanding of the universe expand, leaving us in perpetual wonderment at the marvels that lie beyond our reach.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How are stars formed?
Stars are formed within dense clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. Gravity causes these nebulae to collapse inward, leading to the formation of a protostar. Over time, the protostar heats up, eventually reaching a temperature at its core where nuclear fusion can occur, igniting the star.
2. What fuels a star’s energy?
A star’s energy is generated through the process of nuclear fusion. Within its core, hydrogen atoms fuse together to form helium, releasing an enormous amount of energy in the process. This energy is what powers a star and allows it to shine brightly.
3. How long does it take for a star to form?
The formation of a star can take millions of years. The protostar phase, where the collapsing mass begins to heat up, is particularly time-consuming. Once nuclear fusion initiates, the star enters the main sequence phase, which can last for billions of years.
4. What happens when a star runs out of fuel?
When a star exhausts its hydrogen fuel, its core contracts and heats up. This causes the outer layers of the star to expand, transforming the star into a red giant. Eventually, the star sheds its outer layers and forms a white dwarf, neutron star, or in the case of more massive stars, a supernova.
5. Are all stars the same size?
No, stars come in various sizes. They can range from smaller stars known as red dwarfs, which are less massive than our Sun, to massive stars that are many times larger than our Sun. The size of a star depends on its mass during its formation.
6. What is a stellar nursery?
A stellar nursery, also known as a nebula, is a region in space where stars are formed. These nurseries are composed of dense clouds of gas and dust that serve as the birthplace for new stars. Famous examples include the Orion Nebula and the Eagle Nebula.
7. How do stars die?
The fate of a star depends on its mass. Smaller stars, like our Sun, will eventually exhaust their fuel and transform into a white dwarf, gradually cooling over billions of years. More massive stars will undergo a supernova explosion, leaving behind either a neutron star or a black hole.
8. What are the different stages of a star’s life?
A star goes through several stages during its life cycle. These stages include the stellar nursery phase, protostar phase, main sequence phase (where most stars spend the majority of their lives), red giant phase, and, for more massive stars, the supernova phase, resulting in the formation of a neutron star or black hole.
9. How do stars influence galaxy formation?
Stars play a crucial role in galaxy formation. As stars are formed within nebulae, their gravitational pull can cause gas and dust to collapse, leading to the formation of galaxies. Additionally, the explosive endings of supernovae can trigger the formation of new stars and contribute to the enrichment of galactic material.
10. Can stars collide with each other?
While stars are incredibly far apart in the vastness of space, it is possible for them to collide under certain circumstances. However, these stellar collisions are relatively rare due to the vast distances between individual stars within galaxies and the vastness of the universe itself.








