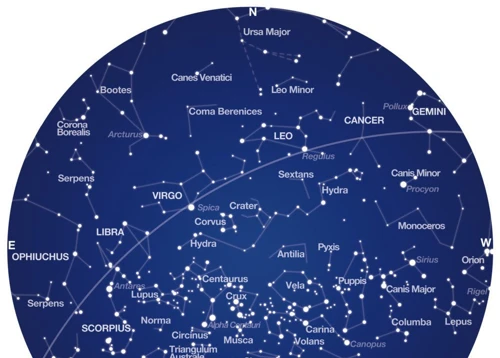
The night sky has always fascinated and captivated humans throughout history. It is a tapestry of celestial wonders, a canvas upon which ancient civilizations and modern astronomers have painted their stories and discoveries. In the Southern Hemisphere, the sky reveals a unique array of constellations, guiding sailors, astronomers, and dreamers alike. In this article, we will delve into the mysterious and enchanting world of the Southern Constellations, exploring their significance, uncovering lesser-known gems, and uncovering the historical and mythological tales that have shaped our understanding of the celestial sky down under. Join us on this celestial journey as we navigate the Southern Constellations and unravel their secrets.
The Importance of Constellations
Constellations hold immense importance in human history, culture, and scientific exploration. They have served as guides for ancient navigators, storytellers, and astronomers. The arrangement of stars in constellations provides a framework for understanding the night sky, enabling us to locate and identify celestial objects. Whether it’s the captivating mythological origins behind constellations or the stories they tell through the stars themselves, their significance permeates various aspects of human civilization. These patterns in the sky have played a pivotal role in astronomy, helping astronomers map and study the universe. From the ancients to the modern-day, constellations continue to inspire wonder and fuel our curiosity about the vastness of the cosmos. Their presence bridges the gap between our earthly existence and the infinite expanse above. To explore the mythological origins of constellations, you can read more here. For fascinating stories embedded within the stars, click here. And to understand the role of constellations in astronomy, click here.
1.1 An Overview of Constellations
An Overview of Constellations:
– Constellations are patterns of stars that form a recognizable shape or figure in the night sky. These celestial patterns have been observed, named, and studied by civilizations throughout history.
– There are 88 officially recognized constellations, each with its own unique arrangement of stars and mythology associated with it.
– The constellations are divided into two groups: northern constellations, visible from the Northern Hemisphere, and southern constellations, visible from the Southern Hemisphere.
– The stars within a constellation may not be physically connected to each other, but they appear close together when viewed from Earth due to their vast distances.
– Constellations act as a celestial roadmap, helping astronomers locate and identify stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects.
– Some famous constellations include Ursa Major (the Great Bear), Orion (the Hunter), and Cassiopeia (the Queen).
– Constellations have played a significant role in various cultures, serving as navigational aids, storytelling tools, and markers of the seasons.
– Astronomers often use constellations as a reference point for mapping and exploring the night sky.
– While some constellations are easily recognizable, others may require a trained eye or the use of star charts to identify and locate.
– Constellations are an integral part of our celestial landscape, connecting us to the wonders of the universe and inspiring curiosity and exploration.
1.2 Understanding the Southern Constellations
Understanding the Southern Constellations is a fascinating journey into the unique celestial sky of the Southern Hemisphere. Here, we will explore the key elements that make the Southern Constellations distinct and gain a deeper appreciation for their significance.
1. Location: The Southern Constellations can only be viewed from below the equator, making them exclusive to regions such as Australia, South America, and southern Africa. This positioning offers a different perspective of the night sky, with unfamiliar patterns and arrangements.
2. Southern Cross: One of the most iconic features of the Southern Constellations is the Southern Cross. Consisting of four main stars forming a cross-like shape, it has been widely used for navigation and symbolism throughout history.
3. Unique Constellations: The Southern Hemisphere hosts a plethora of unique constellations that are not visible from the Northern Hemisphere. Some prominent examples include Orion’s Belt in the South, Scorpius, and the Stinger.
4. Seasons: Just like in the Northern Hemisphere, the night sky in the Southern Hemisphere changes with the seasons. Understanding the movement of the constellations throughout the year allows for better observation and appreciation of their celestial dance.
5. Star Visibility: Due to the reduced light pollution in certain areas of the Southern Hemisphere, stargazing experiences can be exceptionally clear and immersive. The absence of obstructive city lights offers a fantastic opportunity to spot fainter stars and deep-sky objects.
Whether you are an avid astronomer or simply in awe of the night sky, understanding the Southern Constellations opens up a world of cosmic wonders. By delving into their location, unique features, and visibility, you can develop a deeper connection with the intricacies of the celestial realm. So, let us embark on this celestial voyage and uncover the mysteries of the Southern Constellations.
Exploring the Southern Celestial Sky
Exploring the Southern Celestial Sky is a mesmerizing journey into a realm filled with unique wonders. One of the most recognizable and iconic constellations in the southern hemisphere is the Southern Cross. This famous constellation, also known as Crux, consists of four prominent stars that form a distinct cross shape. It serves as a navigation tool, guiding travelers and sailors in the Southern Hemisphere. Another remarkable sight in the southern sky is Orion’s Belt. Unlike its more familiar appearance in the northern hemisphere, Orion’s Belt can be seen in the southern sky during winter evenings, showcasing its three bright stars lined up in a straight row. The constellation Scorpius dominates the southern horizon during summer months. Its distinctive curved tail resembling a stinger provides a celestial spectacle. Gazing upon these southern constellations brings a sense of awe and reverence for the celestial beauty that exists above us. The Southern Celestial Sky is a treasure trove of discovery and a window into the mysteries of the universe.
2.1 The Southern Cross
The Southern Cross is one of the most iconic and recognizable constellations visible in the Southern Hemisphere. It is composed of four bright stars that form a distinctive cross shape in the night sky. These stars, named Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta Crucis, hold great cultural and historical significance to many southern civilizations. The Southern Cross is an essential navigational aid, particularly for sailors in the Southern Ocean who use it to determine their latitude and orientation. Astronomers also rely on the Southern Cross as a celestial marker for locating other constellations and objects in the night sky. This constellation has been a subject of fascination and inspiration for centuries, featuring prominently in artworks, literature, and indigenous mythologies. Observing the Southern Cross is a breathtaking experience, as it represents not only a celestial landmark but also a connection to the rich history and spirit of the southern regions.
2.2 Orion’s Belt in the South
Orion’s Belt is one of the most recognizable and prominent features in the night sky, and it can also be observed in the southern hemisphere. This celestial trio, consisting of three bright stars in the constellation of Orion, forms a distinctive line that stretches across the sky. Located near the celestial equator, Orion’s Belt is best viewed during the southern winter months.
In the southern hemisphere, Orion’s Belt appears lower in the sky compared to its position in the northern hemisphere. This means that observers in the south may see it closer to the horizon, adding an extra enchanting element to its presence. Its visibility depends on the time of year and the observer’s latitude, but generally, you can find Orion’s Belt in the southern sky during the winter months, such as June, July, and August.
Known as Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka, the three stars that make up Orion’s Belt are named after Arabic words. They are prominent enough to be easily identified, even amidst the other stars and constellations that decorate the southern celestial canvas. Draw an imaginary line through the belt from left to right (or right to left), and you can trace the sword of Orion, which contains the famous Orion Nebula (M42), a stunning emission nebula visible to the naked eye in a dark sky.
The presence of Orion’s Belt in the southern sky is a constant reminder of the interconnectedness of our globe, as it can be observed by stargazers on different continents. Its prominence has inspired countless cultures, including ancient civilizations who wove tales around it, and modern astronomers who continue to study its celestial wonders. Although the position and visibility may differ between the northern and southern hemispheres, the awe-inspiring beauty and significance of Orion’s Belt remain universal.
2.3 Scorpius and the Stinger
Scorpius, also known as the Scorpio constellation, is one of the most recognizable and magnificent constellations in the Southern Hemisphere. With its distinctive curved shape, it resembles the iconic image of a scorpion, complete with a pointed stinger. Let’s delve into the captivating features that make Scorpius a fascinating celestial sight.
1. Bright Stars: Scorpius is adorned with several bright stars, making it easily identifiable. The most prominent stars in Scorpius include Antares, a red supergiant star that signifies the heart of the scorpion, and Shaula, a blue-white star located at the tip of the scorpion’s stinger. These stars, along with others in the constellation, create a stunning visual spectacle.
2. The Stinger: One of the defining features of Scorpius is its stinger, represented by the stars at the end of the scorpion’s tail. The stinger is made up of Shaula (also known as Lambda Scorpii) and Lesath (also known as Upsilon Scorpii). These two stars, appearing close together, form an imaginary stinger and enhance the mythical allure of the constellation.
3. Mythological Connections: Scorpius has a rich mythology associated with it, dating back to ancient times. In Greek mythology, the constellation represents the scorpion that was sent by the goddess Hera to kill the hero Orion. It is said that during a hunt, Orion incurred the wrath of Artemis, and as a result, became locked in a fatal battle with the scorpion. The gods eventually placed both Orion and Scorpius in the sky as a testament to the tragic showdown.
4. Observing Scorpius: The best time to observe Scorpius is during the southern hemisphere’s winter months when it is visible in the evening sky. The constellation reaches its highest point in the sky around midnight in the months of June and July. Its unique shape and bright stars make it a favorite target for stargazers and amateur astronomers.
Scorpius and its stinger add an element of intrigue and wonder to the tapestry of the Southern Celestial Sky. Its bright stars and distinct shape make it a celestial landmark worth exploring. So, when the winter nights come around, be sure to venture out and marvel at the captivating beauty of Scorpius and its iconic stinger.
Lesser-Known Southern Constellations
While many people are familiar with popular constellations like Orion or the Big Dipper, the Southern Hemisphere offers a wealth of lesser-known celestial gems waiting to be discovered. One such constellation is Centaurus, which features the famous Alpha Centauri system, the closest star system to our own. This constellation, resembling a centaur wielding a spear, is a prominent feature of the Southern Sky. Another intriguing constellation is Tucana, named after the colorful toucan bird. Tucana is home to the Small Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy visible to the naked eye. Finally, Crux Australis, also known as the Southern Cross, is a distinctive and iconic constellation representing the Southern Crown. These lesser-known constellations may not be as widely recognized as their northern counterparts, but they hold their own unique stories and wonders waiting to be explored in the southern celestial sky.
3.1 Centaurus and the Alpha Centauri System
Centaurus is one of the most prominent and fascinating constellations in the southern celestial sky. It is named after the mythological centaur, a creature combining elements of horse and human, known for its wisdom and strength. Within Centaurus lies the remarkable Alpha Centauri System, which consists of three stars: Alpha Centauri A, Alpha Centauri B, and Proxima Centauri. Alpha Centauri A and B form a binary star system, orbiting around a common center of mass. They are the closest stars to our solar system, located roughly 4.37 light-years away. Alpha Centauri A is the larger and brighter of the two, similar in size and type to our Sun, while Alpha Centauri B is a slightly smaller and cooler star. Proxima Centauri, on the other hand, is the closest individual star to our Sun, located just over 4.24 light-years away.
The Alpha Centauri System captured the imagination of astronomers and science fiction writers alike. It has been the subject of numerous scientific studies and speculation about the possibility of hosting habitable exoplanets. Proxima Centauri, in particular, has been of great interest due to the discovery of a potentially Earth-like planet orbiting around it, named Proxima Centauri b. This captivating celestial dance of multiple stars and the possibility of habitable worlds have fueled our fascination with the Centaurus constellation and the Alpha Centauri System.
Whether gazing at the stars or contemplating the mysteries of the universe, Centaurus and the Alpha Centauri System offer a mesmerizing spectacle in the southern celestial sky. Its presence serves as a reminder of the vastness and diversity of our cosmic neighborhood, urging us to delve further into the exploration of the unknown.
3.2 Tucana: The Toucan
Tucana, known as “The Toucan,” is a small but visually striking constellation in the southern celestial sphere. Its name and shape are derived from the vibrant and tropical bird found in South America. Tucana is predominantly visible from the Southern Hemisphere, particularly during the months of September and November. One of the notable features within this constellation is the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), a dwarf galaxy that can be seen with the naked eye. The SMC is located about 200,000 light-years away from Earth and provides astronomers with valuable insights into the study of stellar evolution and galactic dynamics. Tucana itself contains several other fascinating deep-sky objects such as the Tucana Dwarf Galaxy and the Tucana II Dwarf. These galaxies are of great interest to astronomers as they provide opportunities to study the early universe and contribute to our understanding of galaxy formation and evolution. With its distinctive shape and intriguing celestial objects, Tucana offers stargazers and astronomers an exciting glimpse into the mysteries of the cosmos. So, next time you find yourself under the southern skies, be sure to search for Tucana, the toucan-inspired constellation that holds a treasure trove of celestial wonders.
3.3 Crux Australis: The Southern Crown
Crux Australis, also known as the Southern Crown, is one of the most iconic and easily recognizable constellations in the Southern Hemisphere. This compact and distinct constellation resembles a cross, once used by sailors to navigate the southern seas. Here are some key details about Crux Australis:
1. Southern Hemisphere Symbolism: The Crux Australis holds significance in Australian and New Zealand cultures. It appears on their flags, representing their geographical location and historical ties to exploration and navigation.
2. Brightest Star: The brightest star in Crux Australis is Acrux, also known as Alpha Crucis. Acrux is a multi-star system located around 321 light-years away from Earth. It is famous for its blue-white hue and ranks as the twelfth-brightest star in the night sky.
3. The Coalsack Nebula: A striking feature within Crux Australis is the Coalsack Nebula. This dark nebula appears as a prominent dark patch near the brightest stars of the constellation. It is a dense cloud of dust and gas that obscures the background stars, creating a contrasting visual element.
4. Cultural Significance: Crux Australis holds cultural significance to the indigenous people of Australia and Maori people of New Zealand. Aboriginal Australians see the dark spaces within the shape of the Southern Cross as an emu in the sky, while the Maori people associate it with the anchor of the explorer Maui’s canoe.
5. Stargazing Tips: To locate Crux Australis, look southward in the Southern Hemisphere’s night sky. It is most visible during the southern winter, around May to July. The constellation is circumpolar, meaning it can be seen year-round in southern latitudes.
Exploring the beauty and symbolism of Crux Australis, also known as the Southern Crown, offers stargazers a unique connection to the rich history and culture of the Southern Hemisphere. Whether navigating the vast oceans or unraveling celestial myths, this constellation continues to inspire awe and wonder in those who gaze upon the southern skies.
Historical Significance of Southern Constellations
The Southern Constellations have rich historical significance, offering a glimpse into the ancient astronomy and mythology of different cultures. Southern Celestial Navigators, such as Polynesian sailors and Aboriginal people of Australia, used these constellations as a celestial roadmap for their voyages across vast oceans. These constellations held practical importance, aiding in navigation and ensuring safe passage. Additionally, the Southern Constellations carry deep cultural significance. In Aboriginal and Maori mythology, celestial stories are interwoven with the landscape and traditional knowledge, portraying narratives of creation, heroes, and the interconnectedness of all things. By exploring the historical significance of Southern Constellations, we gain a greater understanding of the diverse cultural perspectives and the timeless human quest to comprehend the mysteries of the universe.
4.1 Southern Celestial Navigators
Southern Celestial Navigators have long relied on the southern constellations for guidance and orientation in the vast expanse of the southern hemisphere. These skilled navigators, such as early Polynesian seafarers and European explorers, understood the importance of studying the stars to navigate the southern oceans. The Southern Cross, with its distinctive shape, served as a crucial navigational tool, helping sailors determine their latitude and direction. By aligning the pointers of the Southern Cross with the south celestial pole, seafarers could establish a reliable southward reference. Additionally, other constellations such as Orion, Scorpius, and Centaurus played their part in aiding navigation, offering reference points and indicating seasonal changes. The art of celestial navigation in the southern hemisphere has been mastered by these skilled individuals, and their expertise and understanding of the southern constellations have contributed significantly to the exploration and mapping of the Earth’s southern regions. Today, while modern navigation systems have largely replaced celestial navigation, the legacy of the Southern Celestial Navigators lives on, reminding us of the rich history and accomplishments of those who relied on the stars to navigate the vast southern seas.
4.2 Aboriginal and Maori Mythology
Aboriginal and Maori mythology is rich with stories that explain the origins and meanings behind the Southern Constellations. In Aboriginal mythology, the celestial sky is seen as a reflection of the earthly realm, with constellations representing important figures and landmarks. For example, the constellation Orion represents the hunter, while the Pleiades constellation is associated with a group of women. The dreaming stories passed down through generations explain the creation of these constellations and their significance in Aboriginal culture.
Similarly, in Maori mythology, the celestial sky holds great importance. The Maori people refer to the Milky Way as “Te Ikaroa,” which means “the long fish” or “the pathway of spirits.” They believe it guides the spirits of the deceased to their final resting place. The constellation Scorpius holds special significance and is often associated with the demigod Maui. According to mythology, Maui’s fishhook caught the sun, causing him to have great power and influence.
Through these mythological tales, the Aboriginal and Maori cultures have preserved their connection to the celestial world, passing down knowledge and stories across generations. These stories not only provide insight into ancient beliefs but also serve as a reminder of the cultural richness and spiritual depth of the Southern Constellations.
Stargazing Tips for Southern Hemisphere
Stargazing in the Southern Hemisphere offers a unique and awe-inspiring experience. To make the most of this celestial adventure, here are some tips to enhance your stargazing journey:
1. Choose the right time: The best time for stargazing in the Southern Hemisphere is during the winter months when the nights are longer, darker, and the sky is clearer. Check the weather forecast and look for nights with minimal cloud cover to maximize your chances of observing the stars.
2. Find a dark location: Light pollution can significantly hinder your stargazing experience. To escape the bright city lights, head to a dark and remote location away from urban areas. National parks, rural areas, and even beaches can provide excellent stargazing spots.
3. Be patient and allow your eyes to adjust: When you arrive at your chosen stargazing spot, give your eyes time to adjust to the darkness. It takes around 20-30 minutes for your eyes to fully adapt to low-light conditions. Avoid looking at bright screens or using flashlights during this time.
4. Familiarize yourself with a star chart: Before embarking on your stargazing adventure, study a star chart or use a stargazing app to identify the Southern Hemisphere constellations and stars. This will help you navigate the sky and locate specific points of interest.
5. Use binoculars or a telescope: While stargazing with the naked eye can be a wonderful experience, using binoculars or a telescope can enhance your view and enable you to see more detail in celestial objects such as planets, galaxies, and star clusters.
6. Observe the Moon and planets: The Southern Hemisphere offers excellent views of the Moon and various planets such as Jupiter, Saturn, and Mars. Keep an eye on their positions and phases using a stargazing app, and take advantage of nights when they are visible.
7. Dress appropriately: Stargazing often involves spending long periods outside at night, so make sure to dress warmly and comfortable. Layer your clothing to adapt to changing temperatures and consider bringing blankets or sleeping bags for added coziness.
8. Capture the moment: If you have a camera with manual settings, try your hand at astrophotography to capture the beauty of the night sky. Use a tripod to keep your camera steady, adjust the exposure settings, and experiment with long exposure shots for stunning results.
Remember, stargazing is a peaceful and introspective activity, so take the time to relax, marvel at the vastness above, and let the wonders of the Southern Hemisphere’s night sky fill you with a sense of awe and wonder.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring the Southern Constellations unlocks a world of celestial wonders and cultural significance. From the iconic Southern Cross to the lesser-known gems like Centaurus and Tucana, the Southern Celestial Sky offers a unique perspective into the vastness of the cosmos. These constellations have guided navigators, inspired mythologies, and fascinated astronomers throughout history. By delving into the historical significance and mythological origins of the Southern Constellations, we gain a deeper understanding of humanity’s fascination with the stars above. Additionally, the tips for stargazing in the Southern Hemisphere help us navigate and appreciate the beauty of the night sky even more. So, grab a telescope or simply gaze up with nothing but your eyes and immerse yourself in the awe-inspiring celestial realms of the Southern Constellations. The wonders of the Southern Sky await your exploration!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How many constellations are there in the Southern Hemisphere?
In the Southern Hemisphere, there are a total of 88 officially recognized constellations.
2. Why are some constellations only visible in the Southern Hemisphere?
Constellations appear differently depending on the observer’s location on Earth. Some constellations, such as the Southern Cross, are only visible in the Southern Hemisphere due to their position in the night sky.
3. Can I see the Southern Cross from the Northern Hemisphere?
No, the Southern Cross is not visible from the Northern Hemisphere. It is a prominent constellation that can be observed in the Southern Hemisphere’s night sky.
4. Are the stars in constellations physically close to each other?
Stars in a constellation can vary significantly in distance from each other. While they appear grouped together from our perspective on Earth, many stars within a constellation may be at different distances from us.
5. How were constellations named?
Constellations were named by ancient civilizations based on their interpretation of the star patterns they observed. They often assigned names representing objects, animals, or mythological figures that the constellations resembled.
6. What is the brightest star in the Southern Hemisphere?
The brightest star in the Southern Hemisphere is Canopus, located in the constellation Carina. It is a prominent star and one of the brightest in the night sky.
7. Are there any constellations unique to the Southern Hemisphere?
Yes, there are several constellations that are exclusively visible in the Southern Hemisphere, including the Southern Cross, Centaurus, and Crux Australis.
8. Can I stargaze and see constellations in urban areas?
While light pollution in urban areas can make it more challenging to observe constellations, it is still possible to stargaze and see some brighter constellations. However, for optimal viewing conditions, it is recommended to venture away from city lights to darker, less populated areas.
9. What role did constellations play in ancient navigation?
Constellations served as crucial navigational tools for ancient civilizations. Sailors would use the positions of certain constellations, like the Southern Cross or Polaris in the northern hemisphere, to help determine their direction and navigate the open seas.
10. How have Aboriginal and Maori cultures incorporated constellations into their mythology?
Aboriginal and Maori cultures have rich mythologies intertwined with the constellations. They often have unique stories and interpretations for these celestial patterns, reflecting their deep connection to the land, sky, and ancestral traditions.