Sleeping is an essential part of our daily routine, allowing our bodies and minds to rest and rejuvenate. However, for many individuals, sleep disorders can disrupt this process, leading to a cascade of negative effects. One such effect is the increased likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Nightmares not only disrupt a person’s sleep, but they can also cause distress and anxiety upon waking. In this article, we will delve into the intriguing connection between sleep disorders and nightmares, exploring the different types of sleep disorders, the role of sleep in dreaming, and how sleep disorders can influence the frequency and intensity of nightmares. By understanding this connection, we can gain insights into managing both sleep disorders and nightmares to improve overall sleep quality and well-being.
The Basics of Sleep Disorders
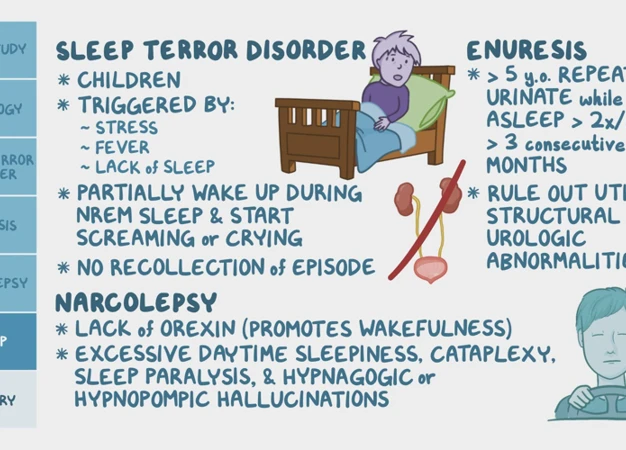
Sleep disorders encompass a range of conditions that affect the quality, timing, and pattern of sleep. These disorders can have a profound impact on an individual’s overall well-being. One common type of sleep disorder is insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Sleep apnea is another prevalent sleep disorder, where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. Restless leg syndrome involves uncomfortable sensations in the legs, leading to an urge to move them, often disrupting sleep. Other sleep disorders include narcolepsy, sleepwalking, and REM sleep behavior disorder.
Sleep disorders can arise from various factors, including underlying medical conditions, such as respiratory or neurological disorders, or lifestyle factors like excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption. Stress, anxiety, and poor sleep hygiene can also contribute to the development of sleep disorders. The symptoms of sleep disorders can vary, from excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue to restless or interrupted sleep. Additionally, these disorders can have a detrimental impact on a person’s mental health, cognitive functioning, and overall quality of life.
It is essential to seek medical evaluation and diagnosis if you suspect you may be experiencing a sleep disorder. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment plan. Treatment for sleep disorders may involve lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, practicing good sleep hygiene, and avoiding stimulants. In some cases, medication or therapy may be prescribed to manage symptoms and improve sleep quality. By understanding the basics of sleep disorders, individuals can take necessary steps to address these conditions and improve their sleep patterns and overall well-being.
Types of Sleep Disorders
There are several types of sleep disorders that can disrupt the normal sleep patterns of individuals. Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep and can be either acute or chronic. Sleep apnea is a condition where the airway becomes blocked during sleep, leading to pauses in breathing and subsequent awakenings. Restless leg syndrome causes uncomfortable sensations in the legs, leading to a strong urge to move them, which can disrupt sleep. Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden episodes of sleep. Sleepwalking, or somnambulism, is a disorder where individuals engage in complex behaviors while asleep, often unaware of their actions. REM sleep behavior disorder involves acting out vivid and often intense dreams during the REM stage of sleep, leading to potential injury or harm. These are just a few examples of sleep disorders that can severely impact the quality of sleep and overall well-being of individuals. Identifying the specific type of sleep disorder is crucial for designing an appropriate treatment plan and regaining control over one’s sleep patterns.
Prevalence and Symptoms
The prevalence of sleep disorders is more common than one might imagine, affecting a significant portion of the population. Insomnia, for example, is estimated to affect around 30% of adults at some point in their lives. Sleep apnea, characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep, is also prevalent and is estimated to affect up to 20% of adults. Restless leg syndrome, with its uncomfortable sensations in the legs, affects approximately 10% of adults. These numbers highlight the widespread impact of sleep disorders on individuals’ lives.
The symptoms of sleep disorders can vary depending on the specific condition. For insomnia, individuals may experience difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early. This can lead to daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and reduced cognitive function. Sleep apnea symptoms include loud snoring, gasping for air during sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness. Restless leg syndrome is characterized by unpleasant sensations in the legs, often accompanied by an irresistible urge to move them, which can disrupt sleep and lead to daytime fatigue.
It’s important to recognize the symptoms of sleep disorders as they can significantly impact an individual’s daily life, making it difficult to function at work or school and increasing the risk of accidents. If you suspect you may have a sleep disorder, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options. Treating sleep disorders not only alleviates the symptoms but can also help prevent potential complications associated with inadequate sleep. For more information on the impact of sleep disorders, you can read our article on uncovering the impact of trauma on nightmares.
Effects on Sleep Quality
Sleep disorders can have a significant impact on sleep quality, leading to a range of negative effects. One of the primary consequences is sleep deprivation, which occurs when an individual does not get enough sleep to meet their body’s needs. Sleep deprivation can result in daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, and reduced cognitive functioning. Individuals with sleep disorders may also experience fragmented sleep, where their sleep is frequently interrupted and they struggle to maintain continuous periods of rest. This can lead to a disrupted sleep cycle, preventing individuals from experiencing the necessary stages of sleep for optimal rest and restoration.
Sleep disorders can contribute to an increase in sleep latency, which refers to the time it takes to fall asleep. Insomnia, for example, often involves difficulties initiating sleep, causing individuals to spend prolonged periods lying awake in bed. This not only reduces the overall duration of sleep but also creates frustration and anxiety surrounding bedtime. Sleep disorders can also result in sleep fragmentation, causing individuals to wake up multiple times during the night. These awakenings disrupt the natural sleep cycle, leading to a decrease in the amount of time spent in deep, restorative sleep stages such as REM sleep.
The impact of sleep disorders on sleep quality cannot be underestimated. When sleep is disrupted or insufficient, the body and mind are unable to recharge effectively, leading to a range of negative consequences. Addressing sleep disorders and improving sleep quality is essential for overall health and well-being. By seeking appropriate treatment and implementing strategies to manage sleep disorders, individuals can work towards restoring healthy sleep patterns and improving their overall quality of life. (Source: investigating-stress-nightmares)
The Role of Sleep in Dreaming

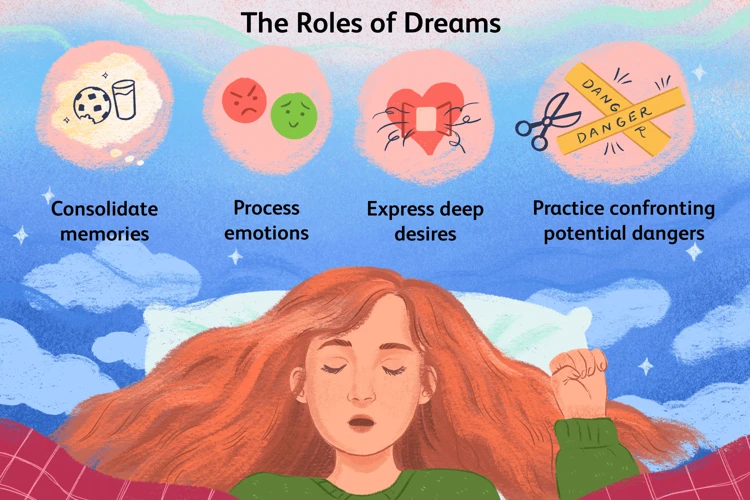
Sleep is not just a period of rest for our bodies; it also plays a crucial role in the realm of dreaming. Dreams occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, which occurs multiple times throughout the night. During REM sleep, our brains become highly active, and vivid dreams can unfold. This stage is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and temporary paralysis of the voluntary muscles, preventing us from acting out our dreams. The significance of dreaming is still not entirely understood, but it is believed to play a role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, and creativity.
Dreams can take various forms and encompass a wide range of experiences, from mundane scenarios to fantastical adventures. They often incorporate random fragments of our daily experiences, thoughts, emotions, and memories. Dreams can be a reflection of our subconscious mind and can provide insights into our thoughts, fears, desires, and unresolved conflicts. They allow us to process and integrate information from our waking lives in a unique and sometimes symbolic way. While some dreams may be pleasant and enjoyable, others can be unsettling or even terrifying.
It is important to note that not all dreams are considered nightmares. Nightmares are distressing and intense dreams that often awaken us abruptly, leaving us feeling frightened, anxious, or disturbed. The causes of nightmares can be complex and multifaceted, encompassing psychological, physiological, and environmental factors. Exploring the psychological causes of nightmares can provide valuable insights into understanding and managing these distressing dream experiences (internal link)/exploring-psychological-causes-nightmares/.
Sleep and dreaming are interconnected phenomena that have a profound impact on our mental and emotional well-being. By understanding the role of sleep in dreaming, we can appreciate the significance of a good night’s sleep and gain insights into the potential causes and effects of nightmares.
The Stages of Sleep
The stages of sleep refer to the distinct phases that our bodies go through during the sleep cycle. There are typically four stages of sleep, each serving a different purpose in the restoration and rejuvenation of the body and mind.
1. Stage 1 – This is the transition phase between wakefulness and sleep. During this stage, the brain produces alpha and theta waves, and the muscles begin to relax. It is relatively easy to be awakened during this stage, and people may experience a dream-like state or brief hallucinations.
2. Stage 2 – In this stage, our brain waves slow down, and our body temperature drops. This is a deeper sleep than stage 1, and it accounts for the majority of our sleep cycle. Our heart rate and breathing also become more regular during this stage.
3. Stage 3 – This is the first stage of deep sleep. Also known as slow-wave sleep or delta sleep, this stage is characterized by very slow brain waves called delta waves. It is during this stage that our body repairs and regenerates tissue, boosts our immune system, and strengthens our memory.
4. REM Sleep – REM stands for Rapid Eye Movement, which is an indicator of intense brain activity during this stage. It is during REM sleep that most dreaming occurs. Our brain waves during REM sleep are similar to those when we are awake, and our eyes move rapidly. While our brain is active, the muscles in our limbs are temporarily paralyzed, preventing us from acting out our dreams and ensuring our safety during sleep.
These stages of sleep cycle through several times throughout the night, with each cycle lasting approximately 90-120 minutes. Understanding the stages of sleep helps us comprehend how our sleep patterns and dreams are influenced by different factors, including sleep disorders, which we will explore further in this article.
The Relationship between Sleep and Dreams
The relationship between sleep and dreams is a fascinating area of study that has intrigued scientists, psychologists, and philosophers for centuries. To understand this connection, it is crucial to delve into the stages of sleep. Sleep is divided into two main categories: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
1. NREM Sleep:
– Stage 1: This is the transitional stage between wakefulness and sleep. It is a brief period characterized by theta waves and is typically the lightest stage of sleep.
– Stage 2: In this stage, the brain produces sleep spindles and K-complexes. These patterns help protect sleep from external disturbances.
– Stage 3: Also known as slow-wave sleep or deep sleep, this stage is characterized by the production of delta waves. It is during this stage that the body’s physical restoration and rejuvenation occur.
2. REM Sleep:
– REM sleep is the stage where most dreaming occurs. It is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreaming experiences. During REM sleep, our voluntary muscles are temporarily paralyzed, preventing us from acting out our dreams.
The relationship between sleep and dreams lies in the fact that dreams primarily occur during REM sleep. Dreams often reflect our thoughts, emotions, and experiences from our waking lives. They can be vivid, emotional, and sometimes bizarre or fragmented. Dreams serve several functions, including memory consolidation, emotional processing, and problem-solving. Research suggests that dreams can provide insights into our unconscious thoughts and desires.
Understanding the relationship between sleep and dreams is essential, as disruptions in sleep can impact the quality and frequency of dreaming. Sleep disorders, such as insomnia or sleep apnea, may interfere with REM sleep, leading to a decrease in dream recall or altered dream experiences. Additionally, medications or substances that affect the sleep cycle can also influence dreaming patterns.
By exploring the different stages of sleep and their relationship to dreams, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the human mind and its connection to the mysterious world of dreams.
Understanding Nightmares

Nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that can cause intense fear, anxiety, or terror during sleep. They are often characterized by a narrative structure, involving threats to personal safety or well-being. These dreams can be incredibly vivid and feel very real, making it difficult for the dreamer to distinguish between the dream world and reality. Nightmares primarily occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, which is the period associated with vivid dreaming.
Nightmares can be triggered by a variety of factors, including psychological and emotional stressors. Traumatic experiences, such as accidents or abuse, can also contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. Anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) are frequently linked to a higher frequency of nightmares. Additionally, individuals who have experienced significant life changes, such as the loss of a loved one, may also be more prone to nightmares.
While nightmares are a normal part of the dreaming experience for most individuals, recurrent and distressing nightmares can greatly impact one’s quality of life. They can lead to sleep disturbances, resulting in chronic sleep deprivation and emotional distress. Frequent nightmares may also contribute to the development of anxiety disorders and insomnia.
To manage and address nightmares, various strategies can be employed. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and meditation, can help reduce anxiety levels before bedtime, potentially decreasing the occurrence of nightmares. Creating a calming sleep environment, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and engaging in regular exercise can also promote better sleep hygiene and minimize the likelihood of nightmares. Additionally, seeking therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for nightmares (CBT-N), can be an effective approach for managing and reducing the frequency of nightmares. By understanding the nature of nightmares and implementing strategies for prevention and management, individuals can regain control over their sleep and overall well-being.
Definition and Characteristics
Nightmares, which are a type of dream that can cause intense fear, anxiety, or distress, can significantly disrupt an individual’s sleep and overall well-being. They are often vivid and tend to occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep. Nightmares often involve themes of danger, helplessness, or threat, and they can be accompanied by physical symptoms such as sweating, increased heart rate, and difficulty breathing. These distressing dreams can awaken individuals from their sleep, leaving them feeling afraid and shaken. Nightmares are often recalled in detail upon waking, and the emotions associated with the dream can linger throughout the day, impacting a person’s mood and daily functioning.
It is important to note that nightmares differ from night terrors, which are episodes of sudden arousal accompanied by intense fear or terror. Night terrors typically occur during non-REM sleep and are more common in children.
The frequency and intensity of nightmares can vary from person to person. While occasional nightmares are considered normal, frequent and recurring nightmares may indicate an underlying sleep disorder or other psychological factors. Understanding the definition and characteristics of nightmares can help individuals recognize and address them effectively, seeking appropriate support and treatment if necessary. By addressing the root causes of nightmares, individuals can work towards achieving better sleep quality and overall well-being.
Potential Causes of Nightmares
Nightmares can be unsettling and disruptive, leaving individuals feeling shaken and anxious upon waking. Understanding the potential causes of nightmares can provide valuable insights into managing and preventing these distressing experiences. One potential cause of nightmares is the impact of trauma. Traumatic experiences, such as accidents, abuse, or witnessing a distressing event, can trigger nightmares as the mind processes and relives the traumatic memory during sleep. Stress is another significant factor that can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. High levels of stress, whether from work, relationships, or other life events, can lead to heightened brain activity during sleep, increasing the likelihood of vivid and intense dreams, including nightmares. Psychological factors can also play a role in the development of nightmares. Conditions such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have been associated with an increased occurrence of nightmares. Sleep disorders, such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless leg syndrome, can disrupt the sleep cycle, leading to fragmented and poor-quality sleep. This can contribute to an increased likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Medications, including certain antidepressants and antihistamines, have also been known to cause nightmares as a side effect. It is important to note that everyone’s individual experiences and triggers for nightmares can vary. Identifying the potential causes specific to an individual can aid in developing personalized strategies to manage and reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
How Sleep Disorders Influence Nightmares
Sleep disorders can have a significant impact on the occurrence and intensity of nightmares. Individuals with sleep disorders are more likely to experience nightmares compared to those without these conditions. One sleep disorder that is closely associated with nightmares is sleep apnea. Sleep apnea disrupts the normal breathing pattern during sleep, leading to frequent awakenings and fragmented sleep. These interruptions in sleep can trigger vivid and distressing nightmares.
Another sleep disorder that influences nightmares is insomnia. Insomniacs often struggle with falling asleep or staying asleep, which can lead to sleep deprivation and increased REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. REM sleep is the stage of sleep when most dreaming occurs. Sleep deprivation and increased REM sleep can result in a higher frequency of nightmares.
Conditions like narcolepsy and restless leg syndrome can also contribute to nightmares. Narcolepsy is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and can lead to hallucinations and fragmented sleep, which can trigger nightmares. Restless leg syndrome causes discomfort in the legs, leading to leg movements and sleep disruptions, which can also impact the content and frequency of nightmares.
Sleep disorders can also exacerbate pre-existing psychological conditions that are associated with nightmares. For example, individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) often suffer from nightmares related to their traumatic experiences. The presence of a sleep disorder, such as insomnia or sleep apnea, can intensify the occurrence of these nightmares.
In addition to the direct effect on nightmare frequency, sleep disorders can also contribute to the emotional intensity of nightmares. Sleep disturbances can increase anxiety levels, emotional arousal, and the occurrence of negative emotions during sleep, which can manifest as more vivid and disturbing nightmares.
Understanding the link between sleep disorders and nightmares is essential for effective treatment. By managing the underlying sleep disorder, individuals can potentially reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Treatment options for sleep disorders vary depending on the specific condition but may involve lifestyle modifications, medication, or therapy. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan for addressing both the sleep disorder and the associated nightmares.
Sleep Disorders Associated with Nightmares
There are several sleep disorders that have been found to be associated with nightmares. One such disorder is post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), which can cause vivid and distressing nightmares related to past traumatic events. These nightmares can disrupt sleep and contribute to increased feelings of fear and anxiety. Another sleep disorder commonly linked to nightmares is REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD), where individuals physically act out their dreams during the REM sleep stage. This can lead to violent or aggressive behaviors during sleep and potentially result in injury. Sleep apnea, a disorder characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, has also been associated with an increased frequency of nightmares. The intermittent awakenings caused by sleep apnea can trigger vivid dreaming, potentially leading to nightmares. Finally, individuals with insomnia may experience nightmares due to the disruption in their sleep patterns and increased arousal during the night. Understanding the sleep disorders associated with nightmares is crucial in addressing and managing both the underlying sleep disorder and the distressing nightmares that accompany them.
Impact on Nightmare Frequency and Intensity
Sleep disorders have a significant impact on the frequency and intensity of nightmares. When individuals experience disruptions in their sleep patterns or quality, the likelihood of experiencing nightmares increases. Research has shown that individuals with sleep disorders such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and narcolepsy are more prone to nightmares compared to those without these disorders.
Insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, has been found to be associated with an increased frequency of nightmares. The fragmented sleep experienced by individuals with insomnia can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to more vivid and intense dreams, including nightmares. Sleep apnea, characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, also contributes to the occurrence of nightmares. The interruptions in breathing can cause brief awakenings and fragmented sleep, leading to more frequent and vivid nightmares. Narcolepsy, a disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden bouts of sleep, has also been linked to an increased occurrence of nightmares.
The intensity of nightmares can also be influenced by sleep disorders. Individuals with sleep disorders often experience poor sleep quality, which can amplify the emotional intensity and content of nightmares. The lack of restorative sleep can lead to increased emotional reactivity and distress, leading to more intense and vivid nightmares. Additionally, the disruption of sleep stages, such as the rapid eye movement (REM) stage, can affect the content and intensity of nightmares. Nightmares often occur during REM sleep, and any disturbances in this stage can lead to more frequent and intense nightmares.
It is important to note that the relationship between sleep disorders and nightmares is complex and multifaceted. While sleep disorders can increase the likelihood of nightmares, nightmares can also exacerbate sleep disorders, creating a vicious cycle. Addressing and managing sleep disorders through appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes can help reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares, ultimately improving sleep quality and overall well-being.
Contributing Factors
There are several contributing factors that can influence the relationship between sleep disorders and nightmares. Firstly, psychological factors play a significant role. Conditions such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have been linked to both sleep disorders and nightmares. Traumatic experiences, such as accidents or abuse, can result in the development of sleep disorders and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Additionally, high levels of stress and emotional distress can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to the occurrence of nightmares.
Secondly, lifestyle factors can also have an impact. Substance abuse, including alcohol and drug use, can disrupt normal sleep patterns and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Poor sleep hygiene, such as irregular sleep schedules, exposure to electronic devices before bed, and a disruptive sleep environment, can also contribute to sleep disorders and nightmares.
Physical health conditions can also contribute to the development of both sleep disorders and nightmares. Chronic pain, respiratory disorders, and neurological conditions can disrupt sleep and increase the risk of nightmares. Medications used to treat various health conditions may also affect sleep patterns and contribute to the occurrence of nightmares as a side effect.
Lastly, environmental factors can play a part. Exposure to traumatic events, violence, or highly distressing content in movies or TV shows can increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Additionally, disruptions to sleep patterns caused by factors such as shift work or travel across time zones can contribute to the development of sleep disorders and nightmares.
It is important to recognize and address these contributing factors when managing sleep disorders and nightmares. By addressing underlying psychological issues, making necessary lifestyle changes, managing physical health conditions, and creating a supportive sleep environment, individuals can improve their sleep quality and reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
Managing Sleep Disorders and Nightmares
Managing sleep disorders and nightmares requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on both addressing the underlying sleep disorder and finding strategies to reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. When it comes to sleep disorders, seeking professional guidance is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Depending on the specific sleep disorder, treatment options may include lifestyle changes, medication, therapy, or a combination of these approaches.
For insomnia, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can help improve sleep quality. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) is also an effective treatment option that aims to identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors related to sleep.
Sleep apnea may require the use of a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine, which helps keep the airways open during sleep. Weight management and positional therapy may also be recommended to alleviate symptoms.
For nightmares, various strategies can be employed. One approach is image rehearsal therapy (IRT), where individuals are encouraged to visualize and mentally rewrite their nightmares into more positive or less threatening scenarios. This technique helps reduce the emotional impact of nightmares and can lead to fewer disturbing dreams.
Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques before bed, such as deep breathing or meditation, can help promote a more peaceful sleep environment. Creating a comfortable and calming sleep environment, free from distractions, can also contribute to a better night’s sleep.
It’s important to address any underlying psychological issues contributing to both sleep disorders and nightmares. Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or trauma-focused therapy, can be beneficial in processing and resolving psychological factors that may be influencing sleep disturbances.
Managing sleep disorders and nightmares involves a multi-faceted approach that targets the specific sleep disorder and implements strategies to alleviate nightmare frequency. Seeking professional help, implementing lifestyle changes, and exploring therapy options can all contribute to improved sleep quality and a reduction in nightmares. By addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of sleep disorders and nightmares, individuals can strive for better sleep and an improved overall quality of life.
Treatment Options for Sleep Disorders
Treatment options for sleep disorders depend on the specific type and underlying cause of the disorder. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and guidance on the most suitable treatment approach.
For insomnia, non-medical interventions are often recommended as the first line of treatment. This may involve implementing good sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities and substances before bedtime. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is a highly effective therapeutic approach that focuses on addressing negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to sleep difficulties.
In cases where non-medical interventions are insufficient, medications may be prescribed. These can include over-the-counter sleep aids, such as antihistamines, or prescription medications like benzodiazepines or non-benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotics. However, it is essential to use these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional and be aware of potential side effects and dependency risks.
Sleep apnea treatment options often involve lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and smoking cessation, which can help reduce symptoms. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy is a common treatment for moderate to severe sleep apnea. It involves wearing a mask over the nose or mouth during sleep, which delivers a continuous flow of air to keep the airways open. Other treatment options may include oral appliances or surgery, depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition.
Restless leg syndrome can be managed by identifying and avoiding triggers such as certain medications or caffeine. Regular exercise, massage, and applying heat or cold to the affected areas can provide relief. In more severe cases, medication therapy may be necessary to alleviate symptoms.
Narcolepsy treatment may involve a combination of medications to manage excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden loss of muscle tone (cataplexy). Stimulant medications, such as modafinil or amphetamines, can help promote wakefulness, while antidepressants are often prescribed to control cataplexy.
It is worth noting that treatment options should be tailored to the individual, considering their specific needs, medical history, and potential underlying conditions. Following the recommended treatment plan consistently and making necessary lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve sleep disorder symptoms and overall sleep quality.
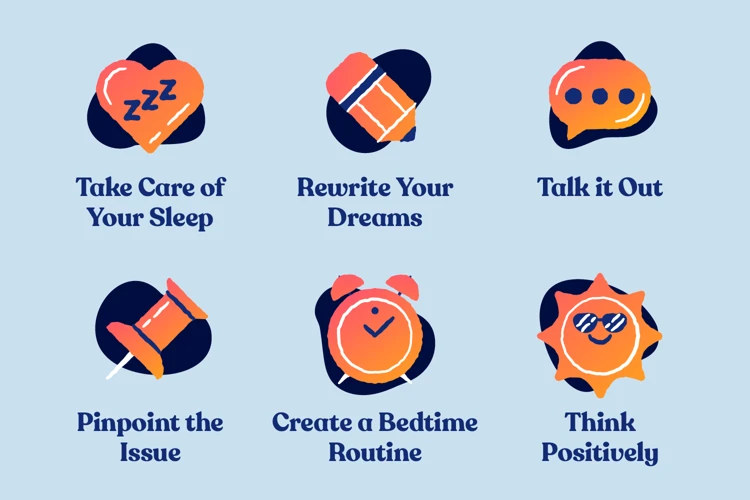
Strategies for Reducing Nightmares
Strategies for Reducing Nightmares:
1. Implement Relaxation Techniques: Engaging in relaxation techniques before bed can help calm the mind and reduce the occurrence of nightmares. Practices such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation can promote a sense of calmness and reduce anxiety before sleep.
2. Create a Soothing Bedtime Routine: Establishing a consistent bedtime routine can signal to the body and mind that it is time to unwind and prepare for sleep. Including activities that promote relaxation, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or listening to calming music, can help create a peaceful environment conducive to restful sleep.
3. Maintain a Sleep-Conducive Environment: Creating a comfortable sleep environment can play a significant role in reducing nightmares. Ensure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs, or white noise machines to minimize external disruptions that may trigger nightmares.
4. Keep a Dream Journal: Keeping a dream journal next to your bed allows you to jot down any vivid or troubling dreams immediately upon waking. This practice can help to bring awareness to recurring themes or triggers and may assist in identifying patterns or potential root causes of nightmares.
5. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): CBT-I is a therapeutic approach that targets sleep disturbances and associated negative thoughts and behaviors. This type of therapy can help individuals develop coping strategies for managing nightmares, improve sleep quality, and reduce anxiety around sleep.
6. Aromatherapy: Certain scents, such as lavender or chamomile, are known for their calming properties. Incorporating essential oils, either diffused or applied topically (following proper dilution), can help promote relaxation and potentially reduce nightmares.
7. Create a Safe and Comforting Atmosphere: If nightmares are a frequent occurrence, making efforts to create a safe and comforting atmosphere before bed can be beneficial. This might involve cuddling with a favorite blanket or using a weighted blanket, which can provide a sense of security and reduce anxiety.
8. Seek Professional Help: If nightmares persist despite trying self-help strategies, it is essential to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or sleep specialist. They can assist in further evaluation, provide tailored recommendations, and explore potential underlying causes that may be contributing to the nightmares.
By employing these strategies, individuals may experience a reduction in the frequency and intensity of nightmares, allowing for a more restful and peaceful night’s sleep.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sleep disorders can have a significant impact on the occurrence and intensity of nightmares. These disorders, such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless leg syndrome, disrupt the normal sleep patterns and can lead to an increased risk of experiencing nightmares. Nightmares are vivid, disturbing dreams that can cause distress and affect overall sleep quality. While the exact relationship between sleep disorders and nightmares is still being studied, it is clear that there is a strong connection.
Managing sleep disorders and reducing the frequency of nightmares requires a multi-faceted approach. Treatment options for sleep disorders may include lifestyle modifications, medication, and therapy, depending on the specific disorder and its underlying causes. Strategies for reducing nightmares involve techniques such as keeping a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and addressing any underlying psychological or emotional factors that may contribute to nightmares.
It is important for individuals who experience sleep disorders and nightmares to seek professional help and guidance to improve their sleep quality and overall well-being. By addressing and managing these sleep disruptions, individuals can experience better rest, reduced distress, and an improved quality of life. With the right strategies and support, it is possible to achieve a healthier and more peaceful sleep pattern free from the influence of sleep disorders and nightmares.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the most common symptoms of sleep disorders?
The symptoms of sleep disorders can vary, but common signs include difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, daytime sleepiness, fatigue, loud snoring, restless legs, and frequent awakening during the night.
2. Can sleep disorders be caused by underlying medical conditions?
Yes, sleep disorders can be caused by various underlying medical conditions, such as respiratory disorders like sleep apnea, neurological conditions, and even mental health disorders like depression and anxiety.
3. How does stress impact sleep disorders?
Stress can significantly contribute to the development and exacerbation of sleep disorders. Heightened stress levels can disrupt sleep patterns, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep.
4. Are there any lifestyle factors that can worsen sleep disorders?
Yes, certain lifestyle factors can worsen sleep disorders. Excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol, irregular sleep schedules, and exposure to electronic devices before bedtime can all negatively impact sleep quality.
5. Can sleep disorders affect mental health?
Yes, sleep disorders can have a significant impact on mental health. Poor sleep can contribute to the development of mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression, and it can also worsen existing mental health issues.
6. Is it necessary to consult a doctor for sleep disorders?
Yes, it is advisable to consult a doctor if you suspect you may have a sleep disorder. A healthcare professional can help assess your symptoms, diagnose the specific sleep disorder, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
7. How can sleep disorders be treated?
Treatment for sleep disorders can vary depending on the underlying cause. It may involve making lifestyle changes, practicing good sleep hygiene, using breathing devices for conditions like sleep apnea, or taking medication prescribed by a healthcare professional.
8. Can sleep disorders be managed without medication?
Yes, in some cases, sleep disorders can be managed without medication. Lifestyle modifications like maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and implementing relaxation techniques can help improve sleep quality.
9. Are there any natural remedies that can help with sleep disorders?
Some individuals find relief from sleep disorders by incorporating natural remedies such as herbal supplements like valerian root or chamomile tea, engaging in relaxation exercises like meditation or yoga, and practicing good sleep hygiene.
10. Can treating sleep disorders help alleviate nightmares?
Yes, effectively managing sleep disorders can positively influence the occurrence and intensity of nightmares. By improving overall sleep quality and reducing sleep disruptions, individuals may experience a decrease in nightmares.