The impact of sleep deprivation on mental health is a subject that has perplexed researchers and health professionals for years. The link between a good night’s sleep and mental well-being is undeniable, yet sleep deprivation continues to be a prevalent issue in today’s fast-paced society. In this article, we will delve into the intricate connection between sleep deprivation and mental health, exploring the consequences it can have on various aspects of our well-being. From anxiety and depression to impaired cognitive performance and strained relationships, the effects of sleep deprivation are far-reaching. We will provide practical tips for improving sleep and discuss the importance of seeking professional help when necessary. So, grab a cup of tea, relax, and join us on this exploration of how sleep deprivation impacts our mental health.
The Importance of Sleep
Adequate sleep is often overlooked in our fast-paced society, yet it is crucial for our overall well-being. Sleep plays a vital role in physical and mental restoration, allowing our body to repair and rejuvenate. During sleep, our brain consolidates memories, processes emotions, and clears out toxins that accumulate throughout the day. It also contributes to the normal functioning of our brain and cognitive abilities, enhancing our concentration, attention, and creativity. Without enough sleep, our brain and body suffer, leading to a range of negative consequences in our daily lives. Lack of sleep can impair our decision-making, emotional stability, and even our physical health. Prioritizing quality sleep should be an essential part of our self-care routine. To learn more about the impact of sleep deprivation on mental health, read our article on the relationship between sleep disorders and chronic fatigue.
Physical and Mental Restoration
Quality sleep is essential for both physical and mental restoration. When we sleep, our body undergoes various restorative processes that help repair and rejuvenate different systems. The release of growth hormones during sleep aids in tissue repair and muscle growth, promoting physical recovery. Additionally, sleep allows our immune system to strengthen itself, making us more resilient to illnesses and infections. Mentally, sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation and emotional processing. During the REM (Rapid Eye Movement) stage of sleep, our brain processes and consolidates memories, transferring them from short-term memory to long-term memory storage. This consolidation process enhances our ability to recall and retain information. Sleep also plays a vital role in regulating our emotions and mood, allowing us to process and regulate our emotional experiences effectively. Without sufficient sleep, these restorative processes are disrupted, leading to physical fatigue, decreased cognitive abilities, and emotional instability. To learn more about different sleep disorders and their impact on physical and mental restoration, check out our article on narcolepsy symptoms and treatment.
Brain Functions and Cognitive Abilities
Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal brain functions and cognitive abilities. When we sleep, our brain undergoes various processes that are essential for mental health and overall well-being. One of these processes is memory consolidation, where information that is acquired during the day is encoded and stored for later retrieval. During deep sleep, the brain strengthens synaptic connections, allowing for better memory formation and retention. Research has shown that individuals who experience sleep deprivation often have difficulty with focusing, attention, and concentration, making it harder to learn and retain new information. Sleep deprivation affects our cognitive flexibility, which refers to our ability to adapt and switch between different tasks or thoughts efficiently.
In addition to memory and cognitive flexibility, sleep also plays a vital role in emotional regulation and decision-making. A lack of sleep can lead to a heightened emotional response, making it challenging to regulate our emotions effectively. This can result in increased irritability, mood swings, and a decreased ability to manage stress. Sleep deprivation can impair our judgment and decision-making abilities. Studies have shown that individuals who are sleep-deprived are more likely to make impulsive decisions and have difficulty evaluating options critically.
To understand more about sleep-related phenomena, such as sleep paralysis, its causes, symptoms, and coping strategies, you can refer to our comprehensive article on sleep paralysis. Proper sleep hygiene and sufficient rest are crucial for maintaining optimal brain functions and cognitive abilities, which in turn contribute to our mental well-being and overall productivity.
Sleep Deprivation and Mental Health Disorders

The relationship between sleep deprivation and mental health disorders is a complex and concerning one. Sleep deprivation can contribute to the development and exacerbation of various mental health disorders, including anxiety and panic disorders, depression, and bipolar disorder. Individuals who consistently lack sufficient sleep are more prone to experiencing heightened levels of anxiety and panic attacks. Similarly, sleep deprivation is closely linked to depression, with studies showing that individuals with insomnia have a higher risk of developing depressive symptoms. Additionally, those affected by bipolar disorder often experience disrupted sleep patterns, with sleep deprivation potentially triggering manic episodes. Understanding the connection between sleep deprivation and these mental health disorders can help healthcare professionals develop comprehensive treatment plans that prioritize adequate sleep alongside other therapeutic interventions. To learn more about specific mental health disorders and their relationship with sleep, read our article on unraveling narcolepsy symptoms and treatment.
Anxiety and Panic Disorders
Anxiety and panic disorders are common mental health conditions that can be significantly impacted by sleep deprivation. Lack of sleep can exacerbate anxiety symptoms and increase the frequency and intensity of panic attacks. When we don’t get enough sleep, our brain becomes more susceptible to stressors, leading to heightened anxiety levels. Additionally, sleep deprivation impairs our ability to regulate emotions, making it harder to cope with anxious thoughts and feelings. This can create a vicious cycle, where anxiety keeps us awake at night, and in turn, sleep deprivation worsens our anxiety symptoms during the day. Research has shown a bidirectional relationship between sleep and anxiety disorders, with poor sleep quality and quantity contributing to the development and maintenance of anxiety. It is crucial to address sleep issues when managing anxiety, as improving sleep can significantly alleviate anxiety symptoms. If you want to learn more about sleep-related disorders and their impact on mental health, check out our comprehensive article on sleep paralysis: causes, symptoms, and coping strategies.
Depression
Depression is a serious mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities. Sleep deprivation is closely linked to the development and worsening of depression. When individuals struggle with depression, it can disrupt their ability to fall asleep or maintain a deep and restful sleep. This can lead to a vicious cycle, as sleep deprivation can exacerbate depressive symptoms and make it more challenging to recover from depression. Research suggests that individuals with insomnia, especially those with difficulty falling asleep, are at a higher risk of developing depression. Sleep disturbances can affect neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin, which plays a crucial role in regulating mood and emotions. The lack of quality sleep disrupts the delicate balance of these chemicals in the brain, contributing to depressive symptoms. Additionally, sleep deprivation can exacerbate feelings of fatigue, lack of energy, and a general inability to function, all of which are hallmarks of depression. Addressing sleep problems is crucial in the treatment and management of depression. It is important to seek professional help for both the depression and the sleep disturbances to break the cycle and improve overall mental health.
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as manic-depressive disorder, is a mental health condition characterized by extreme shifts in mood, energy, and activity levels. Sleep deprivation has a profound impact on individuals with bipolar disorder, exacerbating their symptoms and triggering episodes of mania or depression. Research suggests that sleep disturbances and irregular sleep patterns can act as triggers for manic episodes in individuals with bipolar disorder. Lack of sleep can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to an increase in activity levels, racing thoughts, impulsivity, and a decreased need for sleep. During manic episodes, individuals may feel invincible, engage in risky behaviors, and experience an inflated sense of self-worth. Conversely, sleep deprivation can also precipitate depressive episodes in individuals with bipolar disorder. Lack of sleep can intensify feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and fatigue, leading to a worsening of symptoms. It is crucial for individuals with bipolar disorder to prioritize good sleep hygiene and establish a consistent sleep routine to minimize the risk of triggering manic or depressive episodes. Seeking professional help is also essential for managing bipolar disorder and addressing any sleep-related issues that may arise.
Impact on Emotional Stability

Chronic sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on our emotional stability. Irritability and anger are common symptoms experienced by individuals who do not get enough sleep. The smallest inconveniences or stressors can trigger outbursts, making it challenging to regulate emotions effectively. Additionally, sleep deprivation can lead to mood swings, causing drastic shifts in emotions from joy to sadness to frustration within a short period. These emotional fluctuations can strain relationships and make it difficult to engage in social interactions. It is essential to address sleep deprivation to maintain emotional well-being and establish healthier relationships.
Irritability and Anger
One of the notable impacts of sleep deprivation on mental health is the exacerbation of irritability and anger. When we don’t get enough sleep, our emotional regulation becomes compromised, leading to heightened irritability and a shorter fuse. Even minor inconveniences or disruptions can trigger intense feelings of frustration or anger that would normally be manageable with sufficient rest. This heightened emotional reactivity can strain relationships and lead to conflicts in both personal and professional settings. Additionally, sustained irritability and anger can contribute to increased stress levels and negatively impact overall well-being. It is crucial to recognize the connection between sleep deprivation and emotional stability, and take steps to prioritize healthy sleep habits to prevent or alleviate these negative effects. For more information on sleep-related disorders and their impact on mental health, you can explore our article on sleep paralysis: causes, symptoms, and coping strategies.
Mood Swings
Mood swings are a common consequence of sleep deprivation, causing erratic and unpredictable changes in one’s emotional state. When we do not get enough sleep, our brain’s ability to regulate emotions is compromised. As a result, we may experience intense shifts in mood, ranging from irritability and frustration to sadness or even euphoria. These sudden changes can make it challenging to manage our emotions effectively, leading to conflicts in personal and professional relationships. Moreover, mood swings can amplify existing mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression, making it more challenging to cope with daily stressors. It is important to note that addressing sleep deprivation and establishing healthy sleep patterns can significantly improve mood stability. By prioritizing sleep hygiene and seeking professional help if needed, we can regain control over our emotions and experience a more balanced, positive mental state.
Impaired Cognitive Performance
The consequences of sleep deprivation extend beyond physical fatigue and impact our cognitive abilities as well. When we lack sufficient sleep, our cognitive performance is decreased and impaired. One of the key areas affected is our attention and concentration. Without proper rest, it becomes challenging to stay focused on tasks, leading to decreased productivity and efficiency. Moreover, memory impairment becomes a common occurrence, making it difficult to recall information and retain new knowledge. This cognitive fog can hinder our ability to learn, problem-solve, and make informed decisions. If you find yourself struggling with decreased attention and memory problems, it may be helpful to read our article on narcolepsy symptoms and treatment to explore more about sleep disorders that can contribute to impaired cognitive performance.
Decreased Attention and Concentration
Decreased attention and concentration are two significant consequences of sleep deprivation. When we don’t get enough sleep, our ability to focus becomes compromised. Our mind tends to wander, and we may find it difficult to stay engaged in tasks or conversations. We may also struggle to maintain our concentration on complex or demanding activities, leading to reduced productivity and performance levels. Sleep deprivation affects our cognitive processes, making it harder to process and retain information. This can have a detrimental impact on our academic or professional success.
In addition to affecting our ability to concentrate, sleep deprivation also impairs our attention span. We may become easily distracted by external stimuli or have trouble filtering out irrelevant information. This can make it challenging to prioritize tasks and make decisions. Simple tasks that require sustained attention, such as reading a book or completing paperwork, may take longer to accomplish due to frequent interruptions or a lack of focus.
Moreover, sustained sleep deprivation can lead to microsleep episodes, where we involuntarily fall asleep for a few seconds without realizing it. These brief lapses in attention can be dangerous, especially if they occur during activities that require our full engagement, such as driving or operating machinery.
To combat decreased attention and concentration caused by sleep deprivation, it is crucial to prioritize getting enough sleep each night. Establishing a consistent sleep routine, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques can all contribute to improving the quality and quantity of our sleep. By taking proactive steps to address sleep deprivation, we can enhance our attention and concentration levels, leading to improved overall performance and productivity in our daily lives.
Memory Impairment
Memory impairment is a significant consequence of sleep deprivation, affecting both short-term and long-term memory processes. When we sleep, our brain goes through various stages, including the important consolidation stage where memories are strengthened and stored. However, lack of sleep disrupts this crucial process, leading to difficulties in remembering and retaining information. In the short term, sleep deprivation can result in forgetfulness, making it challenging to recall recent events, details, or even simple tasks. Long-term memory retrieval and formation can also be severely impacted, making it harder to retain new information and learn effectively. Sleep deprivation not only impairs memory consolidation but also affects the ability to concentrate and encode information properly. These memory impairments can have detrimental effects on academic, professional, and personal life, as well as overall cognitive functioning. To delve deeper into the fascinating world of sleep disorders and their impact on memory, check out our comprehensive article on unraveling narcolepsy: symptoms and treatment.
Influence on Decision-making and Judgment

Sleep deprivation can significantly impair our decision-making and judgment abilities. When we are sleep-deprived, our cognitive functions become compromised, making it challenging to think clearly and make rational choices. Impulsive behavior becomes more prevalent as sleep deprivation decreases our ability to weigh the consequences of our actions. We may find ourselves acting on immediate gratification rather than considering long-term consequences. Additionally, poor problem-solving abilities become apparent when we lack adequate sleep. Our ability to think critically and find effective solutions diminishes, leading to suboptimal decisions in both personal and professional settings. It is crucial to recognize the impact that sleep deprivation has on our cognitive capabilities and prioritize quality sleep to ensure optimal decision-making and judgment.
Impulsive Behavior
Impulsive behavior is a significant consequence of sleep deprivation that can have detrimental effects on one’s mental health. When we lack sufficient sleep, our brain’s ability to regulate impulses and make rational decisions becomes compromised. This can lead to impulsive actions and poor judgment, as our inhibitions are lowered. Sleep-deprived individuals may engage in impulsive behaviors such as excessive spending, gambling, or engaging in risky activities without fully considering the consequences. Additionally, sleep deprivation can impair the brain’s reward system, making impulsive behaviors more appealing and satisfying in the moment. This cycle can become self-perpetuating, as impulsive actions can lead to negative outcomes, causing stress and further disrupting sleep patterns. To mitigate the impact of sleep deprivation on impulsive behavior, it is crucial to prioritize adequate sleep and establish healthy sleep habits. Implementing relaxation techniques, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and seeking professional help if necessary can all contribute to better sleep and reduce impulsive tendencies.
Poor Problem-solving Abilities
Poor problem-solving abilities are one of the cognitive impairments that can arise from sleep deprivation. When we lack sufficient sleep, our cognitive functions are compromised, making it difficult for us to think critically and find effective solutions to problems. Sleep deprivation impairs our ability to analyze situations, evaluate options, and make logical decisions, resulting in a decrease in problem-solving skills. This can have a significant impact on various aspects of our lives, from work to personal relationships. We may struggle to come up with innovative ideas, fail to see alternative perspectives, or make impulsive decisions without considering the consequences. To illustrate the effect of sleep deprivation on problem-solving abilities, let’s consider the following scenarios:
1. Work-related Challenges: Sleep-deprived individuals may find it challenging to address complex tasks or navigate unexpected challenges in the workplace. They may struggle to generate effective strategies, troubleshoot issues, or adapt to changing circumstances. This can lead to decreased productivity, increased stress levels, and potential conflicts with colleagues.
2. Interpersonal Conflicts: In personal relationships, poor problem-solving abilities resulting from sleep deprivation can strain communication and create misunderstandings. Sleep-deprived individuals may struggle to communicate their needs effectively or find compromises in conflicts. This can lead to unresolved issues, resentment, and deterioration in relationships over time.
3. Everyday Decision-making: From minor decisions like what to eat for breakfast to more significant choices like financial planning, poor problem-solving abilities can impact our daily lives. Sleep-deprived individuals may become overwhelmed by simple decisions, exhibit indecisiveness, or make impulsive choices without considering long-term consequences.
Addressing sleep deprivation and improving sleep quality can help enhance problem-solving abilities. Establishing a consistent sleep routine, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and implementing relaxation techniques, as discussed in our article, can contribute to a better night’s rest and improve cognitive functions. It is essential to prioritize sleep as an integral part of maintaining optimal cognitive performance and problem-solving skills.
Physical Health Consequences

The consequences of sleep deprivation extend beyond mental health and also have a significant impact on our physical well-being. Chronic sleep deprivation increases the risk of developing various chronic conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and obesity. Lack of sleep disrupts important physiological processes, such as hormone regulation and immune function, which can contribute to the development of these conditions. Additionally, inadequate sleep has been linked to weight gain and obesity. When we are sleep-deprived, our body craves high-calorie, sugary foods, and we often have an impaired ability to regulate our appetite. This combination can lead to unhealthy eating habits and weight gain over time. It is essential to recognize the connection between sleep and physical health and prioritize sufficient sleep as part of a healthy lifestyle. To learn more about sleep-related disorders and their impact on physical health, check out our article on narcolepsy symptoms and treatment.
Increased Risk of Chronic Conditions
Chronic conditions refer to long-term health conditions that require ongoing medical attention and management. Sleep deprivation has been found to increase the risk of developing chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity. Lack of sleep can have a negative impact on our body’s regulation of hormones and metabolism, leading to imbalances that contribute to the development of these conditions. For example, sleep deprivation has been linked to higher levels of cortisol, a stress hormone that can increase blood pressure and promote inflammation in the body. Inadequate sleep can disrupt the balance of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels, potentially leading to insulin resistance and the development of diabetes. Additionally, sleep deprivation has been associated with weight gain and obesity due to the impact on appetite-regulating hormones, such as leptin and ghrelin. These hormonal imbalances can increase hunger and cravings for unhealthy foods, leading to excess calorie intake and weight gain. Prioritizing sufficient and quality sleep is essential in reducing the risk of chronic conditions and maintaining overall health and well-being.
Weight Gain and Obesity
Weight gain and obesity are significant consequences of sleep deprivation that can have a detrimental impact on physical health. When we don’t get enough sleep, it disrupts the balance of hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism. One key hormone affected is ghrelin, which stimulates appetite, causing an increase in hunger. At the same time, lack of sleep decreases the production of leptin, the hormone responsible for signaling fullness and satiety. As a result, individuals who are sleep-deprived may experience intense cravings for high-calorie, sugary, and fatty foods, leading to overeating and weight gain. In addition, sleep deprivation can impair insulin sensitivity and disrupt glucose metabolism, increasing the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Studies have shown a consistent association between inadequate sleep and obesity, with sleep-deprived individuals being more likely to have a higher body mass index (BMI) and an increased risk of becoming obese over time. To prevent weight gain and obesity, it is essential to prioritize quality sleep and make lifestyle changes that promote healthy sleep habits.
Impact on Relationships and Social Interactions

Sleep deprivation not only affects our physical and mental well-being but also has a significant impact on our relationships and social interactions. Difficulty with communication is a common consequence of sleep deprivation. When we are sleep deprived, we may struggle to find the right words, have trouble focusing on conversations, or experience a decreased ability to empathize with others. This can lead to misunderstandings, frustration, and strained personal relationships. Additionally, sleep deprivation can result in heightened irritability and mood swings, making it challenging to maintain harmonious interactions with loved ones and colleagues. Constant fatigue can also limit our social engagement and participation, as we may lack the energy and motivation to participate in social activities. It’s essential to prioritize sleep and ensure that we are well-rested to nurture our relationships and enjoy fulfilling social interactions.
Difficulty with Communication
Difficulty with communication is a common consequence of sleep deprivation. When we are sleep-deprived, our cognitive functions, including language processing and verbal fluency, can be impaired. This can make it challenging to express ourselves clearly and effectively. We may find it harder to find the right words, organize our thoughts, or maintain coherent conversations. Sleep deprivation can affect our non-verbal communication skills, such as body language and facial expressions. We may appear more distant, less engaged, or have difficulty conveying our emotions accurately. This can lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and frustration in our interactions with others. It is important to note that difficulty with communication due to sleep deprivation can have a negative impact on personal and professional relationships. To mitigate these effects, it is crucial to prioritize sufficient and quality sleep. Creating a sleep-friendly environment and implementing relaxation techniques can help improve sleep, leading to better communication skills and enhanced social interactions.
Strained Personal Relationships
Strained personal relationships are one of the detrimental effects of sleep deprivation on mental health. When we consistently lack proper sleep, it can lead to irritability, mood swings, and difficulty regulating our emotions. These factors can put a significant strain on our interactions with others, especially those closest to us. Our irritability and short temper may cause us to lash out at loved ones over minor issues, leading to unnecessary conflicts and misunderstandings. Sleep deprivation can also hinder our ability to communicate effectively, as we may struggle to express ourselves clearly or listen attentively to others. This breakdown in communication can create a sense of distance and disconnect in personal relationships, exacerbating existing tensions and potentially damaging the bond between individuals. Over time, strained personal relationships can contribute to feelings of loneliness, isolation, and decreased overall satisfaction in life. It is important to recognize the role that sleep deprivation plays in these relationship dynamics and take steps to prioritize our sleep in order to nurture healthier and more fulfilling connections with those we care about.
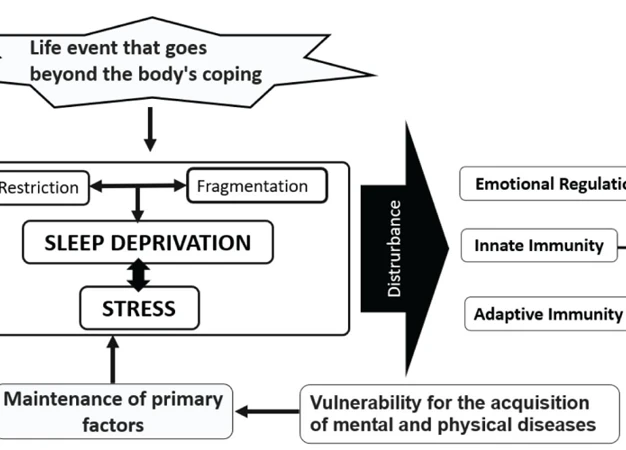
The Cycle of Sleep Deprivation and Mental Health
Sleep deprivation and mental health create a vicious cycle that can be difficult to break. The cycle begins with sleep deprivation, which can be caused by various factors such as work demands, lifestyle choices, or underlying sleep disorders. When we don’t get enough restful sleep, it directly impacts our mental health. Sleep deprivation can lead to increased stress levels and heightened anxiety, making it harder for us to relax and fall asleep. This, in turn, perpetuates the cycle by further disrupting our sleep patterns.
As the cycle continues, the effects of sleep deprivation on mental health become more pronounced. Chronic sleep deprivation can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health disorders such as depression and bipolar disorder. It disrupts the delicate balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, affecting our mood, emotional stability, and cognitive functioning.
Sleep deprivation impairs our ability to cope with stress and regulate our emotions effectively. When we are sleep-deprived, we are more likely to experience irritability, mood swings, and difficulty managing our emotions. This can strain our relationships and lead to social isolation, exacerbating feelings of anxiety and depression.
The cycle of sleep deprivation and mental health is detrimental to our overall well-being. It is crucial to address both aspects to break free from this cycle. By prioritizing sleep and implementing healthy sleep habits, we can improve our mental health and, in turn, improve our sleep. Seeking professional help, such as therapy or medication, may also be necessary for those struggling with chronic sleep deprivation and mental health issues.
The cycle of sleep deprivation and mental health is a complex and interconnected issue. Lack of sleep negatively impacts our mental health, exacerbating existing conditions and potentially leading to the development of new ones. Breaking this cycle requires a holistic approach that addresses both sleep deprivation and mental health concerns.
Tips for Improving Sleep

Improving sleep quality is crucial for maintaining good mental health. Here are some practical tips for establishing healthier sleep habits:
1. Establishing a Consistent Routine: Set a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock.
2. Creating a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Make sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Use blackout curtains, earplugs, or white noise machines if needed. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillow.
3. Implementing Relaxation Techniques: Create a bedtime routine that includes relaxation activities, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing deep breathing exercises. Avoid stimulating activities or screens before bed.
4. Avoiding Stimulants: Limit or avoid caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, especially close to bedtime. These substances can interfere with your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep.
5. Eating Light and Healthy: Avoid heavy, spicy, or greasy meals before bed, as they can cause discomfort and disrupt sleep. Opt for a light snack if needed.
Remember, improving sleep takes time and consistency. Experiment with different strategies to find what works best for you. If you are struggling with chronic sleep issues, consider seeking help from a healthcare professional. For more information on sleep disorders and their treatment, check out our article on unraveling narcolepsy symptoms and treatment.
Establishing a Consistent Routine
Establishing a consistent routine plays a crucial role in improving sleep quality and combating sleep deprivation. By sticking to a regular sleep schedule, where you go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, you can train your body to become accustomed to a specific sleep pattern. This consistency allows your body’s internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm, to sync with your desired sleep-wake cycle. Creating a bedtime routine can also signal to your mind and body that it’s time to unwind and prepare for sleep. This routine can include relaxing activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing mindfulness exercises. Additionally, it’s important to avoid stimulating activities before bedtime such as using electronic devices or engaging in intense physical exercise, as these can interfere with the natural sleep process. By establishing a consistent routine, you can promote better sleep hygiene and improve your overall sleep quality.
Creating a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Creating a sleep-friendly environment is crucial for promoting better sleep and ensuring optimal rest. Here are some tips to transform your bedroom into a haven for sleep:
1. Keep it dark: Darkness signals to our brain that it’s time to sleep. Invest in blackout curtains or blinds to block out any external light sources that may disrupt your sleep. Remove electronic devices with bright displays from the bedroom to minimize artificial light.
2. Manage noise: Unwanted noises can disrupt your sleep. Consider using earplugs or a white noise machine to drown out disturbing sounds. If that’s not possible, try using a fan or gentle music to create a soothing background noise.
3. Control temperature: It’s important to maintain a comfortable temperature in your bedroom. Optimal sleeping conditions are typically cooler, around 60-67 degrees Fahrenheit (15-19 degrees Celsius). Experiment with different bedding and adjust your thermostat accordingly to find your ideal sleep temperature.
4. Choose a comfortable mattress and pillows: Your sleep environment should be a sanctuary of comfort. Invest in a mattress and pillows that align with your personal preferences and provide proper support for your body. This will help reduce discomfort and promote better sleep quality.
5. Declutter and organize: A clutter-free bedroom can promote a sense of calm and tranquility, making it easier to relax and unwind. Remove any unnecessary items from your bedroom and create a clean, organized space that promotes feelings of peace and serenity.
6. Create a routine: Establishing a bedtime routine can signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. Engage in calming activities such as reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation.
By implementing these strategies and creating a sleep-friendly environment, you can significantly enhance your sleep quality and improve your overall well-being.
If you want to explore more about sleep disorders and their effects, check out our article about narcolepsy symptoms and treatment.
Implementing Relaxation Techniques
Implementing relaxation techniques can be incredibly beneficial for improving sleep quality and combating the effects of sleep deprivation on mental health. Engaging in relaxation techniques before bedtime can help calm the mind and prepare the body for sleep. One effective technique is progressive muscle relaxation, which involves systematically tensing and releasing different muscle groups to achieve a state of deep relaxation. Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing, can also induce a sense of calmness and reduce anxiety. Another popular technique is mindfulness meditation, which involves focusing one’s attention on the present moment and cultivating a non-judgmental awareness of thoughts and sensations. Practicing relaxation techniques consistently and incorporating them into a bedtime routine can signal to the body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. Additionally, incorporating other relaxing activities into your nighttime routine, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or listening to soothing music, can further enhance the relaxation response and promote better sleep. By prioritizing relaxation techniques, individuals can create a peaceful and conducive sleep environment, which supports optimal mental health.
Seeking Professional Help
When dealing with sleep deprivation and its impact on mental health, it is important to recognize the value of seeking professional help. Consulting with a healthcare professional who specializes in sleep disorders and mental well-being can provide valuable insights and guidance in addressing the underlying causes of sleep deprivation and its associated mental health issues. Professionals such as doctors, psychiatrists, psychologists, and sleep specialists can offer a range of treatment options tailored to individual needs. Medical interventions, such as medications or therapies, may be prescribed to address specific sleep disorders or mental health conditions. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBTI) is one such therapy that focuses on improving sleep habits and addressing the negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to insomnia. Additionally, therapy sessions with mental health professionals can help address the emotional and psychological aspects of sleep deprivation, offering coping strategies, stress management techniques, and tools for improving overall mental well-being. It is important to remember that everyone’s journey to better sleep and improved mental health is unique, and seeking professional help can provide the necessary guidance and support to navigate the challenges effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of sleep deprivation on mental health is undeniable. Poor sleep can lead to a wide range of mental health disorders, including anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorder. It affects our emotional stability, causing irritability, mood swings, and heightened stress levels. Sleep deprivation also impairs cognitive performance, diminishing attention, concentration, and memory. This can have a significant impact on our daily lives, affecting decision-making, problem-solving abilities, and judgment. Moreover, sustained sleep deprivation can result in various physical health consequences, such as an increased risk of chronic conditions and weight gain. It also strains relationships and social interactions, making communication difficult and personal relationships challenging to maintain. The cycle of sleep deprivation and mental health is deeply intertwined, as sleep disturbances often contribute to and exacerbate existing mental health issues. However, there are steps we can take to improve our sleep and protect our mental health. Establishing a consistent sleep routine, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and implementing relaxation techniques can all contribute to better sleep quality. When needed, seeking professional help is crucial in addressing and managing sleep disorders and their impact on mental health. By prioritizing and nurturing our sleep, we can enhance our mental well-being and overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How many hours of sleep do adults need for optimal mental health?
Most adults require around 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night to maintain optimal mental health.
2. Can sleep deprivation cause anxiety and panic disorders?
Yes, sleep deprivation can contribute to the development or exacerbation of anxiety and panic disorders.
3. Does sleep deprivation lead to weight gain and obesity?
Yes, research suggests that inadequate sleep can disrupt hormonal balance and increase the risk of weight gain and obesity.
4. How does sleep deprivation impact memory performance?
Sleep deprivation can impair memory consolidation and retrieval, leading to difficulties in learning and remembering information.
5. Can lack of sleep affect decision-making abilities?
Yes, sleep deprivation can negatively impact decision-making abilities, making individuals more impulsive and prone to poor judgment.
6. Is there a connection between sleep deprivation and strained personal relationships?
Yes, sleep deprivation can lead to irritability, mood swings, and difficulty with communication, which can strain personal relationships.
7. Can establishing a consistent sleep routine improve sleep quality?
Yes, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule helps regulate the body’s internal clock and can improve sleep quality.
8. What are some relaxation techniques that can promote better sleep?
Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, mediation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help prepare the body for sleep.
9. When should someone consider seeking professional help for sleep issues?
If sleep issues persist despite making lifestyle changes, or if they significantly impact daily functioning, it is advisable to seek professional help from a healthcare provider.
10. How can improving sleep positively impact overall mental well-being?
Improving sleep can enhance mood, cognitive performance, and emotional stability, leading to better overall mental well-being.