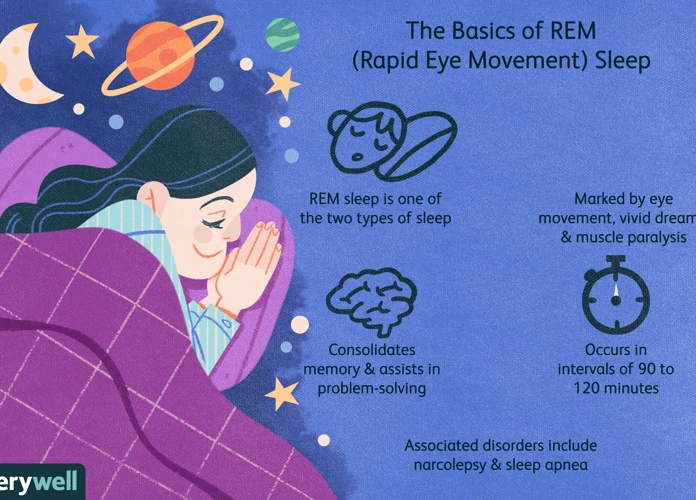
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep, leading to disrupted sleep patterns and decreased oxygen levels in the body. While the physical effects of sleep apnea are well-documented, its impact on dreaming during REM sleep is less understood. REM sleep is the stage of sleep associated with vivid dreaming, and individuals with sleep apnea may experience altered dream perception, interrupted dream sequences, and reduced dream recall. This article aims to explore the effects of sleep apnea on REM sleep dreaming and the factors contributing to these dream-related issues. Additionally, it will provide methods to improve dreaming during REM sleep in individuals with sleep apnea.
Understanding Sleep Apnea

Sleep apnea is a perplexing sleep disorder that can have significant impacts on an individual’s overall health and well-being. This condition is characterized by repetitive pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep, which can result in disrupted sleep patterns and decreased oxygen levels in the body. These pauses in breathing can be caused by various factors, such as the relaxation of throat muscles or obstructions in the airway. Understanding the causes of sleep apnea is crucial in developing effective treatment strategies and managing its effects on sleep. Some common causes of sleep apnea include obesity, genetic predisposition, and anatomical abnormalities in the airway. It is also important to note that sleep apnea can be a contributing factor to other sleep disorders, such as sleepwalking and parasomnias. If left untreated, sleep apnea can lead to a range of health complications, including cardiovascular problems and daytime fatigue. It is essential for individuals who suspect they may have sleep apnea to seek medical intervention and explore appropriate treatment options. For more information on the link between sleep apnea and nightmares, you can refer to this informative article: .
Definition and Causes
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. These pauses, known as apneas, can last for a few seconds to a few minutes and can occur numerous times throughout the night. The two main types of sleep apnea are obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA).
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when there is a blockage or obstruction in the airway, usually caused by the relaxation of throat muscles during sleep. This obstruction can limit or completely halt the airflow, leading to apneas and disruptions in breathing. On the other hand, central sleep apnea is caused by a failure of the brain to signal the muscles responsible for breathing. This lack of communication results in the absence of breathing efforts during sleep.
While the exact causes of sleep apnea can vary, certain risk factors can contribute to its development. Obesity is a significant risk factor for sleep apnea, as excess weight can lead to the narrowing of the airway. Other factors such as smoking, anatomical abnormalities in the nose and throat, family history of sleep apnea, and certain medical conditions like diabetes and hypertension can also increase the likelihood of developing sleep apnea.
It is crucial to recognize the symptoms of sleep apnea, which may include loud snoring, excessive daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and restless sleep. If left untreated, sleep apnea can have severe consequences on an individual’s overall health, including an increased risk of cardiovascular problems, stroke, and even depression.
To learn more about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sleep apnea, you can refer to this detailed resource: .
Types of Sleep Apnea
There are three primary types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea, central sleep apnea, and complex sleep apnea syndrome.
1. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common form of sleep apnea. It occurs when the muscles in the back of the throat fail to keep the airway open during sleep, leading to repeated breathing pauses. OSA is often associated with loud snoring and daytime drowsiness. It can be caused by factors such as obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, or anatomical abnormalities in the throat or airway. The treatment for OSA can range from lifestyle changes, weight loss, to CPAP therapy and even surgery in severe cases.
2. Central sleep apnea (CSA) is less common and occurs when the brain fails to send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing while sleeping. Unlike OSA, CSA is not caused by a physical obstruction in the airway. Instead, it is typically associated with underlying medical conditions such as heart failure, stroke, or brainstem damage. Treatment for CSA often involves addressing the underlying cause while utilizing positive airway pressure therapy.
3. Complex sleep apnea syndrome (CompSAS) is a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea. It is also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea. CompSAS occurs when a person who initially had only OSA later develops central sleep apnea after starting treatment with positive airway pressure therapy, such as CPAP. The exact cause of CompSAS is not well understood, but it is believed to result from a complex interaction between the airway and the brain’s respiratory control center. Treatment for CompSAS may involve adjusting CPAP settings or exploring alternative therapies. For individuals with sleep apnea who also experience sleepwalking and parasomnias, understanding the role of sleep apnea in these conditions can be crucial—more information can be found in the relevant article: .
Signs and Symptoms
1. Loud and Excessive Snoring:
Snoring is a common symptom of sleep apnea, particularly the obstructive type. It is characterized by loud, frequent, and disruptive snoring, often accompanied by choking or gasping sounds during sleep.
2. Excessive Daytime Sleepiness:
One of the prominent signs of sleep apnea is excessive daytime sleepiness. Individuals with sleep apnea often feel drowsy and fatigued throughout the day, regardless of the amount of sleep they get at night. This excessive sleepiness can significantly impact their daily functioning, leading to difficulties in concentration, memory problems, and decreased productivity.
3. Witnessed Pauses in Breathing:
Another telltale sign of sleep apnea is when someone notices the individual experiencing pauses in their breathing while asleep. This may be observed by a bed partner or family member who witnesses the individual momentarily stop breathing during the night, followed by a sudden gasp or choking sound as they resume breathing.
4. Morning Headaches:
Morning headaches are commonly reported by individuals with sleep apnea. These headaches are often described as throbbing and may be accompanied by a feeling of pressure or heaviness in the head. Morning headaches can persist throughout the day and significantly impact quality of life.
5. Irritability and Mood Changes:
Sleep apnea can lead to irritability, mood swings, and emotional instability. The interrupted and fragmented sleep caused by sleep apnea can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to irritability, increased stress, and difficulty regulating emotions.
6. Dry Mouth and Sore Throat:
Individuals with sleep apnea may wake up with a dry mouth and sore throat due to breathing through the mouth and the airway being partially blocked during sleep. This can cause discomfort and may lead to additional issues such as bad breath.
It is important to note that while these signs and symptoms can indicate the presence of sleep apnea, a proper diagnosis can only be made by a healthcare professional specializing in sleep medicine. If you or a loved one experience these symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention for a proper evaluation and potential treatment.
Effects of Sleep Apnea on REM Sleep
Sleep apnea can have significant effects on REM sleep, the stage of sleep associated with vivid dreaming. One of the key effects is altered dream perception, where individuals with sleep apnea may experience distorted or unusual dream content. This can be attributed to the disrupted sleep patterns and decreased oxygen levels during apnea episodes. Additionally, sleep apnea can lead to interrupted dream sequences, causing a fragmented and inconsistent dream narrative. As a result, individuals may struggle to engage in continuous and cohesive dreaming during REM sleep. Sleep apnea can result in reduced dream recall, making it difficult for individuals to remember and recall their dreams upon waking. These effects on REM sleep dreaming can contribute to a decrease in the quality of sleep and may impact overall cognitive well-being.
Altered Dream Perception
– Individuals with sleep apnea may experience altered dream perception during REM sleep. This altered perception can manifest in various ways, including changes in dream content, emotions, and sensory experiences.
– Dreams may become distorted or fragmented, making it challenging to understand or remember their narratives. This alteration in dream perception can lead to confusion and a sense of disconnection from the dream world.
– The emotions portrayed in dreams may also be affected, with individuals reporting heightened levels of fear, anxiety, or sadness in their dream experiences.
– Sensory experiences in dreams, such as colors, sounds, and smells, may be altered or diminished. Dreams may appear duller or less vibrant, and sounds or smells may be less vivid or clear.
– Altered dream perception can impact an individual’s overall sleep quality and can contribute to feelings of restlessness and dissatisfaction upon waking up.
– It is important to note that altered dream perception in sleep apnea is likely due to the physiological changes and disruptions that occur during REM sleep. The interruptions in breathing and decreased oxygen levels can affect the brain’s functioning during this stage, leading to changes in dream perception.
– By addressing and effectively treating sleep apnea, individuals may experience improvements in their dream perception, leading to more vivid, memorable, and fulfilling dream experiences during REM sleep.
Interrupted Dream Sequences
Interrupted dream sequences are a common phenomenon experienced by individuals with sleep apnea during the REM sleep stage. REM sleep is the phase of sleep associated with the most intense and vivid dreaming. However, in the case of sleep apnea, the frequent pauses in breathing can disrupt the normal progression of REM sleep and cause interruptions in the dream sequence. This interruption can result in fragmented dreams or the inability to fully engage in a continuous dream narrative. As a result, individuals with sleep apnea may struggle to experience cohesive and immersive dreams during REM sleep. The interruption of dream sequences can be attributed to the underlying physiological disturbances caused by sleep apnea, such as the decreased oxygen supply to the brain and the brief awakenings that occur as the body attempts to restore normal breathing. These interruptions not only affect the quality of sleep but also impact the overall dreaming experience. Individuals with sleep apnea may find that their dreams are disjointed, incomplete, or lacking in narrative coherence. These interruptions can be frustrating and leave individuals feeling unsatisfied or unfulfilled in their dream experiences. Seeking effective treatment for sleep apnea can not only improve overall sleep quality but also enhance the continuity and depth of dream sequences during REM sleep.
Reduced Dream Recall
Reduced dream recall is a significant effect of sleep apnea on REM sleep. REM sleep is the stage of sleep characterized by vivid dreaming, but individuals with sleep apnea often struggle to recall their dreams upon waking up. This phenomenon can be attributed to the disrupted sleep patterns caused by sleep apnea. When the breathing pauses or becomes shallow during sleep, it triggers brief awakenings, although the person may not fully regain consciousness. These awakenings can disrupt the normal progression of sleep cycles, including the REM stage, where dreams typically occur. As a result, individuals with sleep apnea may experience a decrease in the overall frequency and intensity of their dream recall. This can be frustrating for those who enjoy remembering their dreams or want to analyze them for personal or therapeutic reasons. It is important to note that while reduced dream recall is a common experience for individuals with sleep apnea, it does not necessarily imply a decrease in the occurrence of dreams themselves. The dreams may still be happening, but the lack of recall can make them seem less vivid or even non-existent. Taking steps to effectively manage sleep apnea through appropriate treatment methods can help improve dream recall and the overall quality of REM sleep.
Factors Contributing to Dream-Related Issues in Sleep Apnea
Several factors contribute to dream-related issues in individuals with sleep apnea. One significant factor is the lack of oxygen supply to the brain during apnea episodes. As breathing pauses or becomes shallow, the levels of oxygen in the body decrease, leading to a condition called hypoxia. This lack of oxygen can impact the brain’s ability to generate or perceive dreams during REM sleep. Another factor is sleep fragmentation, which is a common occurrence in sleep apnea. Frequent awakenings disrupt the normal sleep architecture, including the cycles of REM sleep where dreaming predominantly occurs. As a result, dream sequences may be interrupted or fragmented, diminishing the overall dream experience. Additionally, sleep apnea can lead to dysregulated sleep architecture, meaning that the normal patterns of sleep stages, including REM sleep, are disrupted. This disruption can further affect the quality and frequency of dreaming. Understanding these factors can help researchers and clinicians develop strategies to improve dream-related issues in individuals with sleep apnea.
Lack of Oxygen Supply to the Brain
Lack of Oxygen Supply to the Brain can have significant implications for individuals with sleep apnea. During episodes of apnea, the airway becomes partially or completely blocked, resulting in reduced airflow to the lungs. This leads to a drop in oxygen levels in the blood, known as hypoxemia. The brain, being a highly oxygen-dependent organ, is particularly affected by this lack of oxygen supply. When the brain’s oxygen levels decrease, it can lead to various cognitive and physiological effects. In terms of dreaming during REM sleep, the lack of oxygen can disrupt the normal functioning of the brain regions responsible for dream perception and memory consolidation. This can result in altered dream perception, where dreams may become less vivid or more fragmented. Additionally, the reduced oxygen supply can lead to a state of hypoxia, which may cause the brain to generate abnormal dream experiences. The lack of oxygen supply to the brain in sleep apnea can contribute to dream-related issues, impacting the quality and coherence of dreams. To improve oxygen supply to the brain and consequently enhance dreaming during REM sleep, individuals with sleep apnea should seek appropriate treatment methods, such as CPAP therapy or lifestyle modifications.
Sleep Fragmentation
Sleep fragmentation refers to the frequent interruptions or disruptions in sleep that occur as a result of sleep apnea. During episodes of sleep apnea, the individual experiences pauses in breathing or periods of shallow breathing, which can lead to brief awakenings throughout the night. These awakenings may not always be fully conscious and are often too brief to be remembered upon awakening in the morning.
The fragmented sleep caused by sleep apnea has several effects on an individual’s sleep quality and overall well-being. Firstly, it prevents the individual from achieving deep, restorative sleep, particularly during the crucial REM (rapid eye movement) sleep stage. REM sleep is associated with the most vivid dreams and plays a vital role in memory consolidation and cognitive function. However, the interruptions caused by sleep apnea disrupt the natural progression of sleep stages, including REM sleep, leading to a fragmented and less restful night’s sleep.
Sleep fragmentation also affects the overall sleep architecture, which refers to the pattern and organization of different sleep stages throughout the night. In individuals with sleep apnea, the normal progression of sleep stages can be disrupted, with frequent transitions from deeper stages of sleep to lighter stages or even brief awakenings. This disruption can result in a decrease in the overall amount of time spent in deep, restorative sleep and REM sleep.
Additionally, sleep fragmentation can contribute to daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and cognitive impairment. The constant interruptions in sleep can leave individuals feeling tired and unrefreshed upon waking, leading to difficulties in concentration, memory problems, and decreased overall performance during waking hours.
It is important to address sleep fragmentation in individuals with sleep apnea to improve their overall sleep quality. Effective treatment of sleep apnea, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, can help alleviate the interrupted sleep patterns and promote a more restful and consolidated sleep. By addressing sleep fragmentation, individuals with sleep apnea can experience improved daytime functioning, enhanced cognitive abilities, and a better overall quality of life.
Dysregulated Sleep Architecture
Dysregulated sleep architecture is another factor that contributes to dream-related issues in individuals with sleep apnea. Sleep architecture refers to the organization and structure of different sleep stages throughout the night. In a normal sleep pattern, individuals experience a cyclical pattern of non-REM (NREM) sleep and REM sleep. However, in sleep apnea, this natural rhythm can be disrupted.
Sleep Fragmentation: One aspect of dysregulated sleep architecture in sleep apnea is sleep fragmentation. The frequent pauses in breathing and subsequent awakenings characteristic of sleep apnea can disrupt the normal progression of sleep stages. This fragmentation can result in a higher frequency of awakenings throughout the night, leading to a fragmented and interrupted sleep pattern. As a result, individuals with sleep apnea may have difficulty entering or maintaining REM sleep, which is the stage of sleep associated with dreaming.
Decreased REM Sleep: Dysregulated sleep architecture in sleep apnea can also lead to a decrease in the overall time spent in REM sleep. This reduction in REM sleep can have a direct impact on dreaming, as REM sleep is the stage during which dreams are most likely to occur. The interruptions and fragmentation of sleep caused by sleep apnea can disrupt the natural progression into REM sleep or cause it to be cut short, limiting the opportunities for dreaming.
Altered Sleep Stages: In addition to affecting REM sleep, sleep apnea can also impact the other stages of sleep. It can cause an increase in lighter stages of NREM sleep and a decrease in deep sleep stages. This alteration in sleep stages can further contribute to cognitive difficulties, daytime sleepiness, and potentially impact dream perception and recall.
The dysregulated sleep architecture observed in sleep apnea disrupts the natural progression of sleep stages, leading to sleep fragmentation, decreased REM sleep, and alterations in other stages of sleep. These disruptions can have a significant impact on dreaming and dream recall in individuals with sleep apnea.
Methods to Improve Dreaming during REM Sleep in Sleep Apnea
Developing methods to improve dreaming during REM sleep in individuals with sleep apnea is crucial for enhancing the overall sleep experience and quality of life. One effective approach is to undergo proper sleep apnea treatment. This may involve lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, quitting smoking, and avoiding alcohol and sedatives, which can exacerbate sleep apnea symptoms. Additionally, utilizing Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy can help maintain an open airway and ensure a steady flow of oxygen during sleep. CPAP machines work by delivering pressurized air through a mask worn over the nose or mouth, preventing airway collapse. Another important aspect is practicing good sleep hygiene, including maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and adopting relaxation techniques before bed. By incorporating these methods, individuals with sleep apnea can improve their REM sleep and enhance their dream experiences.
Effective Sleep Apnea Treatment
When it comes to treating sleep apnea, there are several options available that can help improve breathing during sleep and alleviate the negative effects on dreaming during REM sleep. It is important to note that the most appropriate treatment will depend on the severity and underlying cause of the sleep apnea. Here are some effective sleep apnea treatment options:
1. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy: CPAP therapy is considered the gold standard treatment for moderate to severe sleep apnea. It involves wearing a mask over the nose or mouth during sleep, which delivers a continuous stream of air pressure to keep the airway open. This helps prevent pauses in breathing and promotes uninterrupted sleep, allowing for more consistent dreaming during REM sleep. CPAP therapy can greatly improve the quality of sleep and reduce the symptoms associated with sleep apnea.
2. Oral Appliance Therapy: For some individuals, oral appliance therapy may be a suitable treatment option. This involves wearing a custom-fit mouthguard-like device that helps keep the airway open by repositioning the jaw or tongue. Oral appliances are typically recommended for individuals with mild to moderate sleep apnea or those who cannot tolerate CPAP therapy. While it may not completely eliminate the effects on dreaming during REM sleep, oral appliance therapy can significantly reduce the severity of sleep apnea and improve overall sleep quality.
3. Lifestyle Modifications: Making certain lifestyle changes can also contribute to the effective management of sleep apnea. For instance, maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can help reduce the severity of sleep apnea symptoms. Avoiding alcohol and sedatives, especially before bed, can also prevent further relaxation of throat muscles and decrease the chances of interrupted breathing during sleep. Additionally, establishing a regular sleep routine and optimizing sleep hygiene practices, such as ensuring a comfortable sleep environment and avoiding stimulating activities before bed, can promote better sleep quality.
4. Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address the underlying causes of sleep apnea. Surgical options may include removing excess tissues, repositioning the jaw, or correcting structural abnormalities in the airway. These procedures are typically recommended for individuals with severe sleep apnea who have not achieved adequate improvement with other treatment methods. However, it is important to note that surgical interventions are considered a last resort and are generally only pursued when other treatment options have been exhausted.
It is important for individuals with sleep apnea to consult with a medical professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their specific needs and circumstances. A multi-faceted approach that combines lifestyle modifications, therapy, and, if necessary, surgery, can effectively manage sleep apnea and improve the quality of sleep and dreaming during REM sleep.
Utilizing CPAP Therapy
Utilizing CPAP Therapy is a widely recommended treatment for individuals with sleep apnea. CPAP stands for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure, and it involves wearing a mask over the nose or mouth during sleep. The mask is attached to a machine that delivers a continuous stream of air pressure, which helps keep the airway open and prevents pauses in breathing. CPAP therapy effectively alleviates the symptoms of sleep apnea, including the disrupted sleep patterns and decreased oxygen levels. By ensuring a consistent flow of air, CPAP therapy helps maintain proper oxygenation of the body and reduces the occurrence of apnea episodes during sleep. This therapy not only improves the quality of sleep but also addresses the impact of sleep apnea on dreaming during REM sleep.
CPAP therapy can have beneficial effects on dream perception, interrupted dream sequences, and dream recall. As sleep apnea often disrupts the normal sleep cycle and impacts REM sleep, using CPAP therapy can restore a more regular sleep pattern, allowing individuals to experience more vivid dreams and improved dream recall. The continuous air pressure helps in maintaining a stable breathing pattern, reducing the number of apnea episodes that can interrupt dream sequences. With improved oxygenation and a stable sleep environment, individuals can have enhanced dream perception during REM sleep. It is important to note that the effectiveness of CPAP therapy may vary among individuals, and it may take some time to adjust to wearing the mask and finding the right air pressure settings. It is recommended to work closely with healthcare professionals to ensure proper usage and adherence to CPAP therapy.
Practicing Sleep Hygiene
Practicing sleep hygiene is an essential aspect of managing sleep apnea and improving dreaming during REM sleep. Sleep hygiene refers to adopting healthy sleep habits and creating an optimal sleep environment that promotes quality sleep. Here are some key practices that can enhance sleep hygiene for individuals with sleep apnea:
1. Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Establishing a regular sleep schedule helps regulate the body’s internal clock and promotes a more consistent sleep pattern. Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
2. Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Ensure your sleep environment is conducive to quality sleep. Use a comfortable mattress and pillows that support your body. Keep the room cool, dark, and quiet to minimize disturbances.
3. Limit Stimulants and Avoid Napping: Stimulants like caffeine and nicotine can interfere with sleep. Avoid consuming these substances, especially close to bedtime. Additionally, try to avoid daytime napping, as it can disrupt the natural sleep-wake cycle.
4. Establish a Bedtime Routine: Engage in relaxing activities before bed to signal to your body that it’s time to sleep. This can include reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation.
5. Avoid Electronics Before Bed: The blue light emitted by electronic devices like smartphones and tablets can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep. Limit electronic device use at least an hour before bedtime.
6. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Regular exercise and a balanced diet can contribute to overall sleep quality. However, it is important to avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it may increase alertness and make it harder to fall asleep.
7. Use Sleep Aids Properly: If recommended by a healthcare professional, certain sleep aids may be used to assist with sleep. However, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and instructions to avoid dependency or adverse effects.
By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can improve your sleep hygiene, enhance sleep quality, and potentially experience better dreaming during REM sleep. Remember, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance and recommendations based on your specific condition and needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sleep apnea is a complex sleep disorder that can have significant effects on dreaming during REM sleep. Individuals with sleep apnea may experience altered dream perception, interrupted dream sequences, and reduced dream recall due to various factors, such as the lack of oxygen supply to the brain, sleep fragmentation, and dysregulated sleep architecture. These dream-related issues can contribute to a disrupted sleep experience and impact overall sleep quality. However, there are methods to improve dreaming during REM sleep in individuals with sleep apnea. Effective sleep apnea treatment, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, can help alleviate the symptoms of sleep apnea and improve sleep quality, including dreaming during REM sleep. It is also important for individuals to practice good sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants before bedtime. By addressing and managing sleep apnea effectively, individuals can enhance their dream experiences and promote overall sleep health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the definition of sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep.
What causes sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea can be caused by various factors, including obesity, genetic predisposition, and anatomical abnormalities in the airway.
Are there different types of sleep apnea?
Yes, there are different types of sleep apnea. The most common types are obstructive sleep apnea, central sleep apnea, and complex sleep apnea syndrome.
What are the signs and symptoms of sleep apnea?
Common signs and symptoms of sleep apnea include loud snoring, excessive daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, and difficulty concentrating.
How does sleep apnea affect dreaming during REM sleep?
Sleep apnea can have a significant impact on dreaming during REM sleep. It can cause altered dream perception, interrupted dream sequences, and reduced dream recall.
Why does sleep apnea affect dreaming during REM sleep?
Sleep apnea disrupts the normal sleep cycle and can lead to reduced oxygen supply to the brain, sleep fragmentation, and dysregulated sleep architecture, all of which can impact dreaming during REM sleep.
What is the role of oxygen supply in dreaming during REM sleep?
Oxygen supply plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy brain function during sleep, including dreaming during REM sleep. Lack of proper oxygen supply due to sleep apnea can affect the quality and perception of dreams.
What are effective treatments for sleep apnea?
Effective treatments for sleep apnea include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and exercise, positive airway pressure devices like CPAP machines, and in some cases, surgical interventions.
How can CPAP therapy improve dreaming during REM sleep?
CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) therapy helps to keep the airway open during sleep, ensuring an uninterrupted flow of oxygen. By improving breathing and oxygen levels, CPAP therapy can contribute to improved dreaming during REM sleep in individuals with sleep apnea.
What is the role of sleep hygiene in improving dreaming during REM sleep?
Practicing good sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants before bedtime, can help improve the quality of sleep and potentially enhance dreaming during REM sleep in individuals with sleep apnea.