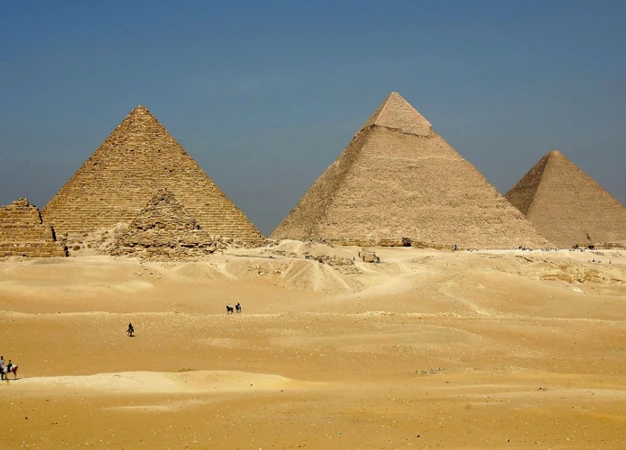
The Egyptian pyramids, a marvel of ancient civilization, have fascinated people for centuries. These ancient structures stand as a testament to the ingenuity and skill of the ancient Egyptians. Built over 4,000 years ago, the pyramids continue to captivate the imaginations of scholars and explorers alike. From their striking architecture to their mysterious purpose, the pyramids hold secrets waiting to be unraveled. In this article, we will delve into the significance of these iconic structures in ancient Egyptian society, exploring their religious, social, and economic importance. Additionally, we will discuss the enduring legacy of the pyramids and the ongoing mysteries that still surround them today. Join us on a journey through time as we explore the wonders of the Egyptian pyramids and their lasting impact on human history.
Background of Egyptian Pyramids

The background of Egyptian pyramids is rooted in the rich history and culture of ancient Egypt. The construction of these monumental structures began around 2700 BCE and continued for more than a thousand years. The pyramids were built as tombs to honor and house the pharaohs, who were considered divine rulers in Egyptian society. The earliest pyramid, the Step Pyramid of Djoser, was designed by the renowned architect Imhotep and marked a significant shift from traditional burial practices. The pyramids were initially made of mud bricks, but later evolved into the iconic limestone structures that we recognize today. The mastery of engineering and construction techniques allowed the ancient Egyptians to create pyramids that would endure for thousands of years. The pyramids were built with precise measurements and alignment, indicating the advanced knowledge of mathematics and astronomy possessed by the ancient Egyptians. The construction of these monumental structures required a large workforce and a highly organized society. Craftsmen, laborers, and overseers worked together to quarry stones, transport materials, and construct the pyramids. The scale of these projects is a testament to the power and resources of the ancient Egyptian civilization. The pyramids served not only as grand tombs but also as symbols of the pharaoh’s divine authority and their connection to the gods. The elaborate burial rituals and complex religious beliefs surrounding the afterlife played a central role in the construction and purpose of the pyramids. The pyramids were filled with treasures, offerings, and intricate decorations intended to assist the pharaoh in the journey to the afterlife. The intricate hieroglyphics carved on the walls provided instructions and prayers for the well-being of the deceased. The pyramids also served as a focal point for religious ceremonies and offerings to honor the pharaohs and invoke divine favor. The significance of the pyramids extends beyond their religious and cultural importance. These colossal structures were symbols of power and stability, showcasing the might and authority of the pharaohs and the Egyptian civilization as a whole. The pyramids were not only impressive architectural feats but also a demonstration of the wealth and resources of ancient Egypt. They served as a reminder to neighboring kingdoms of the power and grandeur of the pharaohs, reinforcing their status as divine rulers and deterring potential threats. The pyramids also played a crucial role in the economy of ancient Egypt. The construction and maintenance of these structures required a massive workforce and extensive resources, providing employment opportunities and stimulating economic activity. The pyramids attracted pilgrims and visitors from far and wide, contributing to the growth of trade and commerce in the region. The pyramids are a testament to the advanced civilization of ancient Egypt, providing valuable insights into their culture, beliefs, and technological prowess. By studying the pyramids, we can gain a deeper understanding of the achievements and legacy of this remarkable civilization. [internal link: /role-archaeology-understanding-prehistoric-humanity/]
Architecture and Construction

The architecture and construction of the Egyptian pyramids are feats of engineering marvel that have stood the test of time. These monumental structures were meticulously designed and constructed using advanced techniques for their era. The pyramids were typically built on the west bank of the Nile River, representing the realm of the dead in Egyptian mythology. The construction process involved several key steps. First, the site for the pyramid was carefully chosen, typically on a natural plateau or mound that provided a stable foundation. The workers would then level the ground and create a precise layout using ropes and measuring tools. The next step involved quarrying and transporting the massive stone blocks that would form the core structure of the pyramid. These stones were usually made of limestone, which was abundant in the surrounding areas. The blocks were cut into shape using copper tools and transported using sledges and ramps. The workers would carefully align and stack the blocks, gradually forming the pyramid’s shape layer by layer. To ensure stability, the stones were fitted tightly together using mortise and tenon joints. The outer layer of the pyramid was often clad in polished limestone or granite, giving the structure a smooth and majestic appearance. The construction process required an enormous workforce, including stonecutters, laborers, and overseers. The organization and coordination of such a massive construction project were a testament to the advanced planning and engineering skills of the ancient Egyptians. The size and scale of the pyramids varied in different periods of Egyptian history. The earlier pyramids, such as the Step Pyramid of Djoser, had a step-like structure with several tiers, while later pyramids, such as those at Giza, had smooth, sloping sides. The Great Pyramid of Giza, built for Pharaoh Khufu, is the largest and most famous of all the pyramids, standing at an impressive height of around 481 feet. The precision and accuracy of the pyramid’s construction are astounding, with each face aligning almost perfectly with the cardinal points of the compass. The pyramids are a testament to the architectural genius and mathematical knowledge of the ancient Egyptians. Surrounded by enigmatic mysteries, they continue to intrigue and captivate us to this day. [internal link: /enigma-easter-island-moai-statues/]
Purpose and Function
The purpose and function of the Egyptian pyramids extended beyond being grand tombs for the pharaohs. These iconic structures served multiple roles that were integral to the ancient Egyptian civilization. Firstly, the pyramids held great religious significance [internal link: /deciphering-inca-civilization/]. The ancient Egyptians believed in the afterlife and the immortality of the soul. The pyramids were designed as elaborate burial chambers intended to provide a comfortable and secure resting place for the pharaohs in their journey to the next life. The intricate hieroglyphics and decorations found inside the pyramids served as both a guide and a source of divine protection for the deceased ruler. Secondly, the pyramids were powerful symbols of the pharaoh’s political and divine authority. The construction of these massive structures showcased the wealth, resources, and mastery of the ancient Egyptians, instilling a sense of awe and fear among neighboring kingdoms. The pyramids served as a physical manifestation of the power and stability of the pharaoh, reinforcing their position as the link between the mortal world and the gods. Additionally, the pyramids played a pivotal role in the social and economic aspects of ancient Egyptian society. The construction and maintenance of the pyramids required an enormous workforce, providing employment opportunities and stimulating economic activity. The pyramids attracted pilgrims and visitors, contributing to the growth of trade and commerce in the region. The purpose and function of the Egyptian pyramids encompassed religious beliefs, political symbolism, and socioeconomic development, making them an integral part of the ancient Egyptian civilization.
Religious Significance
The religious significance of the Egyptian pyramids cannot be understated. In ancient Egyptian belief, the afterlife played a central role, and the pyramids were built to ensure a smooth transition for the pharaohs into the next world. The pyramid structure was considered a sacred symbol, representing the primordial mound from which the Egyptian creation myth originated. It was believed that the pharaoh, as the earthly embodiment of the gods, would ascend to join them in the heavens after death. The pyramids were believed to serve as a powerful conduit between the earthly realm and the divine realms, facilitating the pharaoh’s journey to the afterlife and their transformation into a god. The pyramids were carefully designed and adorned with intricate hieroglyphics, prayers, and spells to assist the pharaoh in this next phase of existence. These inscriptions included sacred texts such as the Pyramid Texts and the later Coffin Texts, which contained instructions, spells, and rituals for the deceased to navigate the challenges of the afterlife. The pharaoh’s burial chamber, hidden deep within the pyramid, was filled with treasures and offerings to sustain and appease the pharaoh on their eternal journey. The religious rituals performed at the pyramids were of utmost importance, ensuring that the gods were pleased and that the pharaoh would receive their divine favor in the afterlife. The pyramids were not only a physical monument but also a sacred space where the living could communicate with the gods and seek their blessings. Pilgrims and devotees would journey to the pyramids on special occasions to present offerings and pay their respects to the pharaohs, believing that their prayers would be heard and answered. The act of worshipping at the pyramids was seen as an act of reverence and devotion to the pharaohs, who were seen as powerful intermediaries between the earthly realm and the gods. The religious significance of the Egyptian pyramids continues to captivate scholars and researchers, shedding light on the profound spiritual beliefs and practices of ancient Egypt. The pyramids stand as a testament to the remarkable faith and devotion of the ancient Egyptians and their unwavering belief in the afterlife and the power of the pharaohs.
Symbol of Power
Symbol of Power:
The Egyptian pyramids were more than just tombs; they also served as powerful symbols of the pharaoh’s divine authority and the might of the ancient Egyptian civilization. These imposing structures, with their massive size and precise construction, made a bold statement about the ruling pharaoh’s power and dominance. The pyramid’s shape, with its triangular sides converging to a single point, was believed to represent the sun’s rays descending to Earth and connecting the pharaoh with the gods. This belief reinforced the pharaoh’s position as a divine ruler and the intermediary between the mortal world and the realm of the gods. The pyramids’ grandeur and architectural magnificence showcased the pharaoh’s ability to mobilize vast resources and a skilled workforce to accomplish such monumental undertakings. The construction of pyramids required extensive planning, architectural finesse, and engineering expertise. The precision in aligning the pyramids with cardinal directions demonstrated the pharaoh’s command over nature and the cosmos. The pyramids were also adorned with intricate hieroglyphic inscriptions, documenting the pharaoh’s accomplishments, divine lineage, and connection to deities. These inscriptions further solidified the pharaoh’s status as a powerful ruler and amplified their legitimacy and influence. The visibility of the pyramids from miles away created a lasting visual impact on the Egyptian landscape, serving as a constant reminder of the pharaoh’s authority and the greatness of the civilization they led. The symbolism and architectural splendor of the pyramids ensured that the reign and legacy of the pharaoh would not be easily forgotten. Their construction required vast resources, including materials, labor, and organizational skills, which further highlighted the economic and administrative capabilities of the pharaoh and the state. As a result, the pyramids became not only a symbol of power but also a testament to the economic prosperity and stability of ancient Egypt. The monumental nature of the pyramids and their enduring presence laid the foundation for the widespread reverence and admiration that the pharaohs enjoyed during their rule. The pyramids were an integral part of the pharaoh’s assertion of authority, allowing them to establish their divine connection, solidify their leadership, and inspire awe and admiration among their subjects. [no need for html tags]
Importance to Ancient Egyptian Civilization

The pyramids held immense importance to ancient Egyptian civilization, serving as more than just grand tombs for the pharaohs. They played a central role in religious beliefs and the afterlife. Egyptians believed in the existence of an afterlife, and the pyramids were seen as vehicles to ensure a smooth transition for the pharaohs into the divine realm. These monumental structures were filled with treasures, offerings, and detailed decorations, all intended to assist the pharaohs on their journey. The pyramids became sacred places of worship, attracting pilgrims and visitors who brought offerings and conducted religious ceremonies. The pyramids symbolized the authority and power of the pharaohs, serving as a representation of stability and control. The construction and maintenance of the pyramids required extensive resources and a large workforce, stimulating economic activity and contributing to the overall prosperity of ancient Egypt. The pyramids were not only architectural marvels but also economic and religious centers, playing a vital role in shaping the ancient Egyptian society.
Religious Beliefs and Afterlife
In ancient Egyptian culture, religious beliefs and the concept of the afterlife played a central role in the construction and purpose of the pyramids. The Egyptians believed in the immortality of the soul and that life continued in the afterlife, hence the need to prepare for the journey beyond death. The pyramids were intricately designed tombs specifically created to ensure the safe passage of the pharaohs into the afterlife.
1. Mummification: The process of mummification was essential to preserve the body for the afterlife. This complex and sacred ritual involved removing internal organs, preserving them separately, and then embalming the body with oils and resins. The mummified body was intended to serve as a vessel for the soul to recognize and inhabit in the afterlife.
2. Book of the Dead: The Book of the Dead, a collection of spells and rituals, played a crucial role in guiding the deceased through the perilous journey in the afterlife. These texts were often inscribed on the walls of the pyramids, providing the deceased with instructions and prayers to protect them from evil spirits and ensure a successful transition.
3. Solar symbolism: The pyramids were often aligned with specific astronomical phenomena, particularly the sun. The Egyptians believed that the sun god Ra played a significant role in the afterlife, guiding the souls of the deceased. The design and positioning of the pyramids aimed to establish a connection between the pharaohs and Ra, ensuring their eternal journey under the sun’s blessings.
4. Offerings and rituals: The pyramids served as places of worship and offerings to the pharaohs. Priests would conduct rituals to honor the deceased, leaving food, drink, and other offerings to sustain them in the afterlife. These ceremonies were believed to maintain the pharaoh’s well-being and maintain a positive relationship between the living and the dead.
5. Belief in the ka: The ka, a vital aspect of Egyptian spirituality, was a spiritual double that resided within the body and continued to live on after death. It was essential to provide the ka with a physical and spiritual home in the form of the pyramids. The lavish decorations and treasures within the pyramids were meant to cater to the ka’s needs and ensure its comfort in the afterlife.
The religious beliefs surrounding the pyramids played a profound role in shaping ancient Egyptian society. The construction and maintenance of these grand structures required the devotion and resources of the entire civilization. The pyramids symbolized not only the divine status of the pharaohs but also the Egyptian people’s unwavering commitment to honoring and preserving their religion and the afterlife.
Social and Economic Impact
The Egyptian pyramids had a profound social and economic impact on ancient Egyptian society. These monumental structures served not only as religious and burial sites but also played a crucial role in shaping the social dynamics and economic prosperity of the civilization.
1. Symbol of Power and Authority:
The pyramids served as symbols of the pharaoh’s power and authority, representing the divine connection between the ruler and the gods. The construction of these grand structures was a demonstration of the pharaoh’s wealth and ability to command vast resources. The pyramids solidified the pharaoh’s position as the supreme leader and provided a sense of stability and order in society.
2. Economic Stimulus:
The construction and maintenance of the pyramids required a massive workforce and extensive resources, leading to the growth of various industries and economic activities. Architectural and engineering specialists were employed to design and oversee the construction process, while laborers and artisans were hired to quarry stones, transport materials, and create intricate decorations. This massive undertaking boosted employment opportunities and stimulated economic growth in ancient Egypt.
3. Trade and Commerce:
The pyramids attracted pilgrims, visitors, and traders from different parts of the region. The influx of people brought about a growth in trade and commerce, as goods and resources were exchanged for offerings and supplies needed for the pyramid complex. Local merchants and craftsmen prospered from the demand for supplies, food, and services, creating a network of economic activity around the pyramids.
4. Taxation and Wealth Redistribution:
The construction of the pyramids necessitated a strong central government and an organized taxation system. Taxes were levied on individuals and regions to fund the construction projects, ensuring a steady flow of resources for the pyramids. The redistribution of wealth through taxation allowed the pharaoh to maintain control and finance other economic projects, such as irrigation systems and public infrastructure.
5. Religion and Social Cohesion:
The religious beliefs associated with the pyramids played a crucial role in maintaining social cohesion and order. The construction and maintenance of these sacred structures required the collective effort of various social classes, from peasants to skilled craftsmen. The pyramid projects fostered a sense of communal identity, as people worked together in service of a common goal related to their religious beliefs.
6. Cultural Identity and National Pride:
The pyramids became iconic symbols of ancient Egyptian civilization and a source of national pride. The grandeur and scale of these structures showcased the achievements and glory of the pharaohs, reinforcing the unique cultural identity of the Egyptians. The pyramids served as a reminder of the greatness of their civilization and instilled a sense of pride and unity among the Egyptians.
The social and economic impact of the Egyptian pyramids cannot be understated. These structures shaped the social hierarchy, stimulated economic growth, and played a significant role in the cultural and religious fabric of ancient Egyptian society. The legacy of the pyramids has endured through the centuries, continuing to inspire and awe people from all over the world.
Legacy and Continuing Mysteries
The legacy of the Egyptian pyramids extends far beyond the ancient civilization that built them. These magnificent structures have captivated the world for centuries and continue to be a source of wonder and fascination. One of the most well-known and enduring legacies is the Giza Plateau, home to the Great Pyramid of Giza, the largest of all the pyramids. This iconic site attracts millions of tourists each year, who marvel at its immense size and architectural precision. Alongside the pyramids stands the enigmatic Great Sphinx, a massive statue with the body of a lion and the head of a pharaoh. The purpose and meaning behind the Sphinx continue to spark debate and speculation, adding to the mystique surrounding these ancient monuments. Despite countless studies and research, many mysteries surrounding the pyramids remain unsolved. From the construction techniques utilized to the precise alignment with astronomical phenomena, there is still much we do not fully understand. The process of building the pyramids, the role of mathematics and engineering, and the purpose of intricate burial rituals continue to elude scholars and researchers. The pyramids remain a testament to the greatness of the ancient Egyptian civilization, but also serve as a constant reminder of the enigmas waiting to be unraveled.
Giza Plateau and Great Sphinx
The Giza Plateau and the Great Sphinx are two iconic landmarks that are intricately connected to the Egyptian pyramids. Located on the outskirts of modern-day Cairo, the Giza Plateau is home to three of the most famous pyramids in Egypt: the Pyramid of Khufu (also known as the Great Pyramid), the Pyramid of Khafre, and the Pyramid of Menkaure. These pyramids were constructed during the Old Kingdom period and remain as awe-inspiring symbols of Egyptian civilization. The Giza Plateau served as the necropolis for the pharaohs of the Fourth Dynasty, who wanted their eternal resting place to be in close proximity to the sacred site of the Great Sphinx. The Great Sphinx, a massive limestone statue with the body of a lion and the head of a pharaoh, stands tall in front of the pyramids. Believed to represent the pharaoh Khafre, the Sphinx is an enigmatic and mysterious figure that has mesmerized countless generations. The purpose of the Sphinx remains a subject of debate and speculation among historians and archaeologists. Some theories suggest that it was built as a guardian figure, protecting the pyramids and their pharaohs from any potential threats. Others propose that it held a religious significance, symbolizing the divine authority of the pharaohs. The Sphinx has also played a role in ancient Egyptian mythology and folklore, with stories and legends surrounding its creation and purpose. Regardless of its exact function, the Sphinx adds to the aura of majesty and mystery that surrounds the Giza Plateau. Today, the Giza Plateau and the Great Sphinx continue to be popular attractions, drawing tourists and scholars alike. The site provides a glimpse into the remarkable achievements of the ancient Egyptians and offers visitors a chance to marvel at the architectural wonders that have withstood the test of time. Exploring the Giza Plateau and standing before the Great Sphinx is a captivating experience that allows us to connect with the past and appreciate the ingenuity and artistry of this ancient civilization.
Unsolved Secrets of Pyramids
The pyramids of Egypt have always been shrouded in mystery, leaving behind a trail of unsolved secrets that continue to intrigue researchers and historians. Despite extensive research and study, many aspects of the pyramids remain unexplained, sparking debates and speculation. Here are some of the intriguing unresolved mysteries surrounding these ancient structures.
1. Alignment with Constellations: One puzzling aspect is the precise alignment of the pyramids with celestial bodies. The Great Pyramid of Giza, for example, aligns almost perfectly with the constellation Orion. This alignment has led some theorists to suggest an advanced knowledge of astronomy by the ancient Egyptians or even extraterrestrial influence.
2. Construction Techniques: The construction methods employed in building the pyramids still baffle experts. How were massive stone blocks, some weighing several tons, quarried, transported, and precisely fitted together without the aid of modern machinery? Theories range from the use of ramps, sleds, and levers to more unconventional ideas involving advanced technologies or assistance from unknown civilizations.
3. Purpose of Hidden Chambers: Hidden chambers within the pyramids have posed numerous questions over the years. The purpose and function of these chambers, such as the Queen’s Chamber and the mysterious void recently discovered within the Great Pyramid, remain a subject of debate. Were they intended for the pharaoh’s use in the afterlife, for ceremonial rituals, or for some other unknown purpose?
4. Preservation of Artifacts: Despite the passage of thousands of years, the pyramids have yielded remarkably preserved artifacts, including intricate hieroglyphics and paintings. The question remains: how did these delicate artworks survive the test of time, exposure to the elements, and potential looting?
5. The Pyramid’s Power Source: Some researchers propose that the pyramids held a unique power source or energy generator. They speculate that the shape, materials, and internal design of the pyramids could have served a practical purpose beyond their religious and funerary functions. However, concrete evidence has yet to be found to support these theories.
6. Construction Timeline and Techniques: Lastly, the sheer scale and speed of pyramid construction raise questions about the methods and tools used. How were these massive structures completed within the reigns of individual pharaohs? Did the ancient Egyptians possess a level of engineering knowledge and organizational capabilities that we have yet to fully comprehend?
These unsolved mysteries inspire ongoing investigations, with new discoveries and theories emerging regularly. The allure of the pyramids lies not only in their awe-inspiring beauty and historical significance but also in the enigmatic puzzles they present to humanity. Exploring these mysteries deepens our understanding of the ancient world and opens up possibilities for new perspectives and interpretations. The pyramids continue to stand as a testament to the remarkable achievements of the ancient Egyptians and remind us of the boundless wonders that await discovery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Egyptian pyramids stand as an indelible testament to the remarkable civilization that flourished in ancient Egypt. These monumental structures, built with precision and innovation, continue to captivate the world with their enigmatic beauty and historical significance. The background of the Egyptian pyramids reveals a rich tapestry of religious beliefs, cultural practices, and technological achievements. The pyramids served as sacred tombs for the pharaohs, showcasing their divine status and connecting them to the gods. Moreover, the pyramids were symbols of power and stability, reflecting the might of the pharaohs and the Egyptian civilization as a whole. Economically, the construction and maintenance of these structures stimulated trade and commerce, contributing to the growth of ancient Egypt. Today, the pyramids stand as a testament to the capabilities and ingenuity of ancient civilizations. Their enduring legacy and the mysteries that still surround them continue to pique the interest of researchers and explorers. By studying the pyramids, we gain invaluable insights into the religious beliefs, social structures, and architectural prowess of the ancient Egyptians. As we continue to uncover the hidden secrets of these majestic structures, we deepen our understanding of human history and our own place within it. The Egyptian pyramids truly remain one of the greatest wonders of the ancient world.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How many pyramids are there in Egypt?
There are over 100 known pyramids in Egypt, with the most famous ones located in the Giza Plateau near Cairo.
2. Who built the Egyptian pyramids?
The pyramids were built by skilled craftsmen and laborers under the command of pharaohs, who were considered divine rulers in ancient Egypt.
3. How long did it take to build a pyramid?
The construction of a pyramid could take several decades to complete, depending on its size and complexity.
4. What materials were used to build the pyramids?
The pyramids were primarily constructed using limestone, which was abundant in Egypt. The casing stones were often made of finer limestone or granite, giving the pyramids their distinctive appearance.
5. How were the pyramids aligned with the cardinal directions?
The ancient Egyptians were incredibly skilled astronomers and used astronomical observations to align the pyramids with the north-south axis. They used the Pole Star and other celestial markers to achieve this precision.
6. Why were the pyramids built in the shape of triangles?
The pyramid shape was symbolic of the mound that the ancient Egyptians believed emerged from the primordial waters and marked the beginning of creation. It represented the eternal and divine nature of the pharaoh.
7. Did all pharaohs have pyramids built for their burials?
No, not all pharaohs had pyramids built for their burials. The construction of pyramids was reserved for the Old and Middle Kingdoms, with later pharaohs preferring rock-cut tombs, such as the famous Valley of the Kings.
8. How were the massive stones transported to the pyramid construction sites?
The stones were transported using a combination of sledges and ramps. The sledges were pulled by a workforce using ropes and wooden sleds, while the ramps provided an inclined path for the ascent of heavy stones.
9. How were the pyramids protected from tomb robbers?
The pyramids were equipped with various security measures, such as false burial chambers and hidden passages, to confuse and deter potential thieves. Additionally, the pyramids were guarded by priests and soldiers.
10. Are there still undiscovered pyramids in Egypt?
It is possible that there are still undiscovered pyramids in Egypt. Ongoing archaeological research and new technology may reveal hidden structures and mysteries yet to be uncovered.








