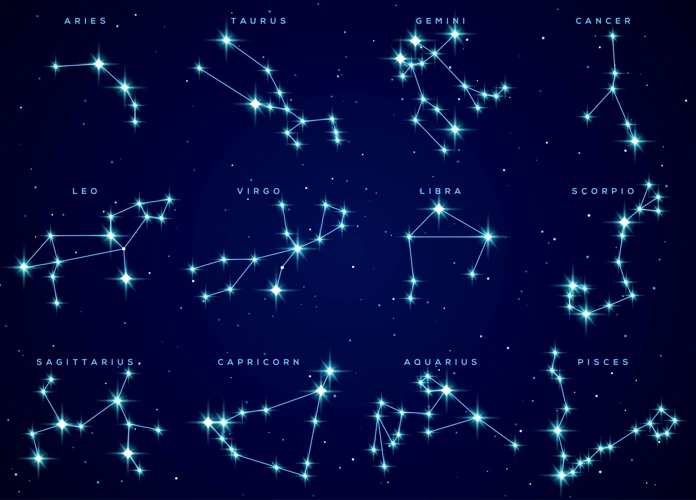
The wonders of the night sky have captivated humans for centuries, sparking both curiosity and imagination. Among the celestial phenomena that have intrigued us the most are the zodiac constellations. These patterns of stars, believed to influence our lives and personalities, have a rich history rooted in ancient mythology and astrology. But what exactly is the science behind these constellations? How do they align with the movement of celestial bodies and what do astronomers have to say about them? In this article, we will explore the origins of zodiac constellations, their astrological significance, scientific studies surrounding them, and even delve into the debunking of astrological claims. So, sit back, stargazers, as we embark on a journey to unravel the fascinating science behind the zodiac constellations.
The Origins of Zodiac Constellations
The origins of zodiac constellations can be traced back to ancient mythology and astrology, where they held significant cultural and spiritual meanings. In ancient Mesopotamia, the Babylonians were the first known civilization to develop a zodiac system around the 5th century BCE. They divided the sky into twelve equal parts, each corresponding to a specific constellation. This system was later adopted and expanded upon by the Greeks, who assigned the twelve zodiac signs their names and symbolisms that we recognize today. However, it is important to note that the concept of zodiac constellations predates these civilizations, as they were inspired by even older cultures and their astronomical observations. Ancient cultures like the Egyptians, Chinese, and Mayans also had their own versions of zodiac constellations, each with their own unique interpretations and celestial symbols. To delve deeper into the lesser-known zodiac constellations across different cultures, you can explore our article on lesser-known zodiac constellations. Understanding the historical context of zodiac constellations helps us appreciate their significance and the diverse perspectives that have shaped their interpretations over time. To learn more about the specific zodiac constellations and their historical significance, you can refer to our article on historical zodiac constellations.
Ancient Mythology and Astrology
Ancient mythology and astrology played a crucial role in the development and interpretation of zodiac constellations. In many ancient cultures, the celestial bodies were believed to have a direct influence on human affairs and personalities. The Babylonians, for example, believed that the position of the stars at the time of a person’s birth determined their destiny. This gave rise to the concept of astrology, where the zodiac constellations became a tool for understanding and predicting human behavior. Each zodiac sign was associated with specific characteristics and traits based on the mythology and symbolism associated with its respective constellation. For instance, Aries was linked to courage and leadership, while Taurus represented strength and determination. The Greeks further expanded upon these associations, associating zodiac signs with their pantheon of gods and goddesses. The rich tapestry of ancient mythology intertwined with astrology has shaped our understanding of zodiac constellations. To explore how different cultures interpreted these celestial patterns, you can refer to our article on zodiac constellations in various cultures.
Important Historical Astronomers
When exploring the history of zodiac constellations, it is impossible to ignore the contributions of important historical astronomers who have shaped our understanding of the night sky. These individuals made groundbreaking discoveries and observations that laid the foundation for our knowledge of the zodiac constellations. Here are a few notable astronomers and their contributions:
1. Claudius Ptolemy: Ptolemy, a Greek-Roman astronomer who lived in the 2nd century CE, is known for his work “Almagest.” In this influential text, Ptolemy presented a geocentric model of the universe, which placed the Earth at the center and described the motion of celestial bodies, including zodiac constellations.
2. Nicolaus Copernicus: Copernicus, a Polish astronomer from the 16th century, challenged the geocentric model proposed by Ptolemy. Instead, he proposed a heliocentric model, placing the Sun at the center of the solar system. Copernicus’ work revolutionized our understanding of celestial motion and had implications for the interpretation of zodiac constellations.
3. Johannes Kepler: Kepler, a German astronomer from the late 16th to early 17th century, is best known for his three laws of planetary motion. These laws provided a mathematical framework to explain the movement of planets and further enhanced our understanding of celestial bodies, including the zodiac constellations.
4. Galileo Galilei: Galileo, an Italian astronomer of the 17th century, made significant advancements in telescopic observations. He observed the phases of Venus, the moons of Jupiter, and the rings of Saturn, challenging the prevailing belief that all celestial bodies revolved around the Earth. Galileo’s observations contributed to our understanding of the physical characteristics of planets, further impacting our interpretation of zodiac constellations.
These astronomers, among others, played crucial roles in shaping our understanding of the night sky and the zodiac constellations we observe today. Their discoveries and theories paved the way for future astronomical research and continue to inspire scientists and stargazers alike.
The Zodiac Constellation Patterns
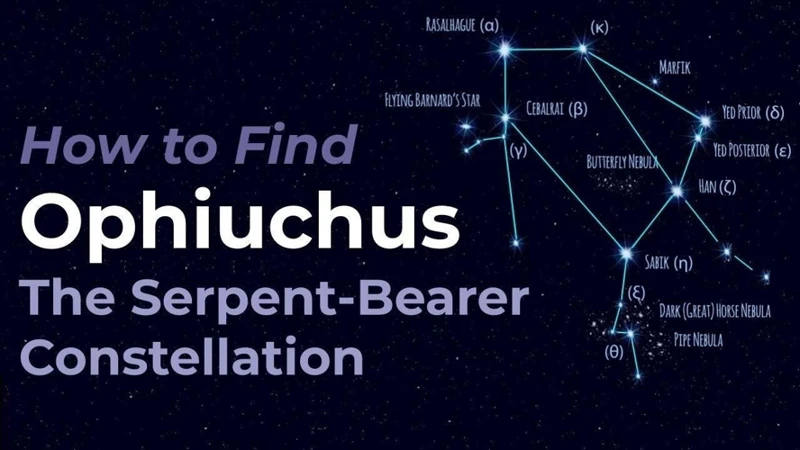
The Zodiac Constellation Patterns are a collection of twelve distinct constellations that form a belt around the celestial sphere. Each constellation represents one of the zodiac signs and follows a specific pattern based on their arrangement. The twelve zodiac signs are: Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. These patterns help astronomers and astrologers identify and locate the zodiac constellations in the night sky.
For example, Aries is known for its unique pattern of stars that resemble a ram. Taurus, on the other hand, is distinguished by the V-shaped star cluster known as the Pleiades. Gemini, the sign of the twins, consists of two bright stars, Castor and Pollux, which are easily spotted in the sky. Each zodiac constellation pattern has its own distinctive features and arrangement of stars, making them easily identifiable once you know what to look for.
To help stargazers and enthusiasts visualize the patterns of the zodiac constellations, astronomers have created various tools such as star charts and interactive apps. These resources provide detailed information about the positions, shapes, and relative distances of the stars within each constellation. By studying these patterns, astronomers can map the zodiac constellations more accurately and gain a deeper understanding of their celestial alignment.
Understanding the physical arrangement of the zodiac constellations also allows for a better comprehension of their formation and evolution. Star clusters, which are groups of stars that form and evolve together, play a crucial role in the creation of these constellations. The patterns formed by these clusters are influenced by factors such as the gravitational interactions between stars, their distances from each other, and their ages. By studying these star clusters and their formation, astronomers can further unravel the mysteries behind the intricate patterns of the zodiac constellations and gain insight into the larger picture of stellar evolution.
The zodiac constellation patterns represent the distinct arrangements of stars that form the twelve zodiac signs. Each pattern is unique and identifiable, providing astronomers and astrologers with valuable insights into celestial navigation and interpretation. By studying the physical characteristics and formation of these constellations, astronomers can deepen their understanding of the universe and its vast array of wonders.
Overview of the Twelve Zodiac Signs
The twelve zodiac signs, also known as the astrological signs, represent different personality traits and characteristics that are believed to be influenced by the positions of celestial bodies at the time of a person’s birth. Each zodiac sign is associated with a specific constellation and is said to govern a particular period of the year.
The first zodiac sign is Aries, represented by the Ram. As a fire sign, Aries individuals are often described as dynamic, ambitious, and passionate. They are natural-born leaders and tend to be assertive and courageous in their pursuits.
Taurus, the Bull, is an earth sign known for its groundedness and practicality. Taureans are typically reliable, patient, and enjoy the finer things in life. They have a strong sense of loyalty and are steadfast in their relationships and commitments.
Gemini, represented by the Twins, is an air sign associated with adaptability and versatility. Geminis are known for their quick wit, sociability, and intellectual curiosity. They thrive on communication and are excellent at multitasking.
Cancer, the Crab, is a water sign characterized by its nurturing and emotional nature. Cancers are deeply intuitive and empathetic individuals who value their close relationships and home life. They are typically nurturing, protective, and highly sensitive.
Leo, symbolized by the Lion, is a fire sign known for its confidence, warmth, and charisma. Leos are natural-born leaders and love being in the spotlight. They are often described as generous, creative, and fiercely loyal.
Virgo, represented by the Virgin, is an earth sign associated with practicality, detail-oriented thinking, and analytical skills. Virgos are often perfectionists and have a strong sense of responsibility. They are hardworking, reliable, and diligent.
Libra, the Scales, is an air sign known for its harmonious and fair-minded nature. Libras are diplomatic, cooperative, and strive for balance and equality in their relationships. They have a keen eye for beauty and enjoy aesthetics.
Scorpio, symbolized by the Scorpion, is a water sign associated with intensity, passion, and depth. Scorpios are known for their magnetic personalities and determination. They are often secretive, loyal, and have a strong sense of intuition.
Sagittarius, represented by the Archer, is a fire sign known for its adventurous and optimistic nature. Sagittarians are open-minded, freedom-loving individuals who have a thirst for knowledge and new experiences. They are often described as generous, philosophical, and idealistic.
Capricorn, the Goat, is an earth sign characterized by its practicality, discipline, and ambition. Capricorns are hardworking, responsible, and value tradition. They are typically goal-oriented and strive for success in their endeavors.
Aquarius, represented by the Water Bearer, is an air sign associated with individuality, innovation, and intellectualism. Aquarians are often described as forward-thinking, unconventional, and humanitarian. They value their independence and enjoy being part of a community.
Pisces, the Fish, is a water sign known for its empathetic, intuitive, and compassionate nature. Pisceans are often artistic, dreamy, and deeply connected to their emotions. They are adaptable and enjoy helping others.
Understanding the characteristics and symbolism associated with each zodiac sign can provide insights into our own personalities and help foster better understanding and communication in our relationships.
Star Clusters and Formation
When exploring star clusters and their formation, we gain insights into the structure and composition of the zodiac constellations. Star clusters are groups of stars that are gravitationally bound together, forming distinct patterns within constellations. There are two main types of star clusters: open clusters and globular clusters.
Open clusters, also known as galactic clusters, are relatively young and contain hundreds to thousands of stars. These clusters are formed when a large cloud of gas and dust collapses under its gravity, giving birth to new stars in the process. Over time, the gravitational forces between the stars cause the cluster to disperse and eventually dissolve into the general stellar population of the galaxy. The Pleiades, located in the constellation Taurus, is a famous example of an open cluster with its distinct grouping of bright stars.
Globular clusters, on the other hand, are much older and consist of hundreds of thousands to millions of stars. These clusters are spherical in shape and are found in the outer regions of galaxies. They are thought to have formed during the early stages of galaxy formation, with their stars tightly packed together due to the strong gravitational pull at the center of the cluster. The Hercules Cluster, found in the constellation Hercules, is a prominent globular cluster visible in the northern hemisphere.
The formation of star clusters is closely related to the formation of individual stars. Stars form from the gravitational collapse of dense regions within molecular clouds. As these regions collapse, they fragment into clumps, which eventually give rise to multiple stars. These stars are often born in close proximity to one another, leading to the formation of clusters.
The intricate patterns of zodiac constellations are shaped by the arrangement and distribution of these star clusters. By studying the dynamics of star cluster formation and evolution, astronomers can gain a deeper understanding of the celestial structures that make up our zodiac constellations, adding to the scientific knowledge behind their existence and significance.
Astrological Significance and Celestial Alignment
Astrological significance and celestial alignment play a crucial role in understanding the zodiac constellations. According to astrology, each zodiac sign represents certain personality traits and characteristics associated with individuals born under that sign. The alignment of celestial bodies, such as the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars, at the time of a person’s birth is believed to influence their personality and destiny. Astrologers refer to this alignment as a person’s natal chart or horoscope. The primary celestial alignment that the zodiac signs are based on is the ecliptic, which is the apparent path of the Sun across the sky throughout the year. The zodiac constellations lie along this path, and each sign is associated with a specific section of the ecliptic. The Sun’s position in a particular zodiac sign at the time of someone’s birth determines their Sun sign or their primary zodiac sign. However, it is important to note that celestial alignment does not only involve the Sun. The positions of other planets and the Moon in relation to the zodiac constellations are also taken into account for a more comprehensive astrological interpretation. Additionally, the precession of the equinoxes plays a role in celestial alignment. This is the gradual shift of the Earth’s rotation axis, causing the alignment of the equinoxes and solstices to slowly change over time. This phenomenon accounts for the slight discrepancy between the zodiac signs and the actual constellation positions in modern times. While the correlation between celestial alignment and astrological significance remains a subject of debate, many people find value and meaning in exploring their horoscopes and connecting with the ancient wisdom associated with the zodiac constellations.
The Ecliptic and the Sun’s Path
The Ecliptic is an imaginary circle in the sky that represents the apparent path of the Sun as seen from Earth. Also known as the Sun’s path, it is a crucial element in understanding the alignment of zodiac constellations. This path is set by the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, causing the Sun to appear to move through the zodiac constellations throughout the year. The Ecliptic is divided into twelve equal parts, each corresponding to one of the zodiac signs. As the Earth orbits the Sun, the Sun’s position relative to the zodiac constellations changes, marking the transition from one zodiac sign to another. This alignment plays a significant role in astrology, as individuals are believed to bear the traits and characteristics associated with the zodiac sign that the Sun was in at the time of their birth. This connection between the Ecliptic and the Sun’s path serves as a fundamental basis for understanding the astrological significance of zodiac constellations.
The Precession of the Equinoxes
The precession of the equinoxes is a fascinating phenomenon that plays a crucial role in understanding the alignment of zodiac constellations with the Earth’s axis and its effect on astrology. The Earth experiences a slow wobbling motion as it spins on its axis, causing its rotation axis to trace out a circular path over a period of approximately 26,000 years. This phenomenon is known as the precession of the equinoxes. It occurs due to the gravitational forces exerted by the Sun and the Moon on the Earth’s equatorial bulge. As a result of this precession, the positions of the equinoxes and solstices gradually shift relative to the backdrop of the zodiac constellations. Over the course of thousands of years, the zodiac constellations have shifted in relation to the solstices and equinoxes, giving rise to the concept of the “age of astrology.” This means that the zodiac sign that corresponds to a specific time of the year has slowly shifted as a result of the precession. For example, if you were born in April, your astrological sign would traditionally be Aries. However, due to the precession of the equinoxes, your sign may now correspond to Pisces. This phenomenon has been studied extensively by astronomers and is supported by scientific evidence. Understanding the precession of the equinoxes is crucial in addressing counterclaims and misconceptions in astrology, as it highlights the changing alignment of zodiac constellations over time.
Correspondence with the Seasons
Correspondence with the seasons is a fundamental aspect of the zodiac constellations. The zodiac signs align with specific times of the year, marking the changing seasons and reflecting the Earth’s journey around the Sun. Each zodiac sign is associated with a particular season, which influences the characteristics and traits ascribed to individuals born during that time. Here is an overview of the correspondence between the zodiac signs and the seasons:
1. Aries (March 21 – April 19): Aries corresponds with the spring season, symbolizing new beginnings, enthusiasm, and a surge of energy as nature comes back to life.
2. Taurus (April 20 – May 20): Taurus represents the stability and blossoming of spring, reflecting the grounding energy and steady growth observed during this season.
3. Gemini (May 21 – June 20): Gemini captures the essence of early summer, characterized by curiosity, communication, and social interaction as the days grow longer.
4. Cancer (June 21 – July 22): Cancer aligns with the height of summer, signifying nurturing, emotional depth, and the sense of home and family.
5. Leo (July 23 – August 22): Leo corresponds with the peak of summer, depicting qualities such as creativity, courage, and leadership that are often associated with this vibrant and energetic season.
6. Virgo (August 23 – September 22): Virgo represents late summer and the transition to autumn, embodying practicality, attention to detail, and a focus on organization.
7. Libra (September 23 – October 22): Libra coincides with the autumn equinox, signifying balance, harmony, and the changing colors of nature as summer transitions into fall.
8. Scorpio (October 23 – November 21): Scorpio aligns with the deep transformation and introspection of autumn, encapsulating passion, intensity, and emotional depth.
9. Sagittarius (November 22 – December 21): Sagittarius corresponds with the beginning of winter, symbolizing exploration, adventure, and an expansive outlook as the days grow shorter.
10. Capricorn (December 22 – January 19): Capricorn represents the practicality and determination needed to endure the harshness of winter, reflecting ambition, discipline, and resilience.
11. Aquarius (January 20 – February 18): Aquarius aligns with mid-winter, embodying innovation, independence, and the forward-thinking mindset needed to navigate the colder months.
12. Pisces (February 19 – March 20): Pisces corresponds with the transition from winter to spring, symbolizing compassion, intuition, and the dreamy energy often associated with the changing of seasons.
Understanding the correspondence between zodiac signs and seasons allows us to explore the connection between celestial patterns and the cyclical nature of life on Earth. It highlights the interplay between astronomical observations, cultural interpretations, and our human experience of time and seasons.
Scientific Studies and Astronomical Research

Scientific studies and astronomical research have played a crucial role in deepening our understanding of zodiac constellations and their celestial counterparts. Astronomers have employed various techniques and tools to study these intricate patterns of stars. Astrometry, the branch of astronomy concerned with precise measurements of celestial objects, has been instrumental in cataloging the positions, motions, and distances of zodiac constellations. Through astrometry, scientists have been able to create detailed star maps and track the movements of individual stars within the constellations over time.
Another important aspect of scientific study is stellar evolution and classification. By analyzing the properties and spectra of stars within zodiac constellations, astronomers have been able to determine their ages, luminosities, and evolutionary stages. This information has shed light on how stars form and evolve within these constellations, helping us appreciate the dynamic nature of the cosmos.
Modern techniques and observations have also revolutionized the study of zodiac constellations. Advanced telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, have provided high-resolution images and data that allow astronomers to explore the intricate details of these celestial patterns. Additionally, space missions and satellites have allowed for observations from outside Earth’s atmosphere, reducing the impact of atmospheric interference and providing clearer views of zodiac constellations.
By combining scientific studies and astronomical research, astronomers continue to uncover new insights into the formation, composition, and dynamics of zodiac constellations. It is through these systematic investigations that our knowledge of the universe expands, enriching our understanding of the captivating beauty of the zodiac constellations.
Astrometry and Cataloging
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that focuses on the precise measurement and cataloging of celestial objects, including the zodiac constellations. Astronomers use astrometry to determine the coordinates, distances, motions, and other essential data of stars and other celestial bodies. Cataloging these objects allows astronomers to organize and classify them systematically, facilitating further study and observation. One notable catalog is the Hipparcos catalog, named after the European Space Agency’s Hipparcos satellite, which operated from 1989 to 1993. The Hipparcos catalog measured the positions, distances, and proper motions of nearly 120,000 stars, including those within the zodiac constellations. This catalog provided valuable data that contributed to our understanding of stellar evolution and the structure of the Milky Way galaxy. Another significant catalog is the Gaia mission, launched by the European Space Agency in 2013. Gaia aims to create a precise 3D map of our galaxy and has already cataloged over a billion stars, including those within the zodiac constellations. These catalogs, along with other astronomical surveys and databases, serve as invaluable resources for astronomers studying the zodiac constellations and their various properties. The meticulous work of astrometry and cataloging enables the scientific community to gain a deeper insight into the celestial phenomena that have captured our fascination for centuries.
Stellar Evolution and Classification
Stellar evolution and classification play a crucial role in understanding the nature and characteristics of the stars within the zodiac constellations. Stars go through a series of stages during their lifetime, and their classification provides insights into their size, temperature, luminosity, and composition. The process of stellar evolution begins with the formation of a star from a cloud of gas and dust. Over time, gravity causes the cloud to collapse, forming a protostar. As the protostar continues to contract, its core temperature rises, triggering nuclear fusion and the birth of a main-sequence star. The star remains in this phase for the majority of its lifetime, where the balance between the inward pull of gravity and the outward pressure from nuclear fusion maintains its stability. The precise color and temperature of a star, which determines its classification, depend on its mass and its position on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. Classifications include main-sequence stars (such as our Sun), red giants, white dwarfs, and more. Understanding stellar evolution and classification helps astronomers make connections between the physical characteristics of stars and their placement within zodiac constellations. This knowledge enhances our understanding of how these celestial bodies impact our lives through astrological interpretations.
Modern Techniques and Observations
In the realm of astronomy, modern techniques and observations have played a crucial role in furthering our understanding of zodiac constellations. Technological advancements have enabled astronomers to gather more precise and detailed data about these celestial formations. One such technique is astrometry, the measurement of the positions and movements of celestial objects. Astrometry has allowed astronomers to create accurate catalogs of stars, including those that make up the zodiac constellations. These catalogs serve as references for researchers and aid in studying the evolution and characteristics of these stars.
Stellar evolution and classification have also contributed to our knowledge of zodiac constellations. By studying the life cycles of stars, astronomers can determine the type and age of the stars within the constellations. This information helps us understand the formation and development of the zodiac constellations, shedding light on their origins and structure.
Modern observations with advanced telescopes and instruments have allowed for detailed studies of zodiac constellations. Astronomers can analyze the properties of individual stars, such as their brightness, temperature, and composition. High-resolution imaging techniques reveal intricate details within the constellations, providing insights into their intricate patterns and formations.
Additionally, astronomical surveys and space missions have expanded our knowledge of zodiac constellations beyond what is visible from Earth. Missions like the Hubble Space Telescope and the Gaia mission have provided stunning images and precise measurements of stars within these constellations, offering a deeper understanding of their properties and interactions.
Modern techniques and observations continue to push the boundaries of our knowledge, unraveling the mysteries of zodiac constellations and contributing to the broader field of astronomy. With ongoing advancements, we can look forward to further discoveries and a deeper appreciation of these celestial wonders.
Debunking Astrological Claims
Debunking astrological claims requires a critical examination of the scientific validity behind the concept of astrology. While astrology is a popular belief system that suggests a relationship between celestial bodies and human affairs, it lacks empirical evidence and is considered a pseudoscience by the scientific community. One of the main reasons astrological claims are debunked is the disconnect between the science of astronomy and the subjective interpretations of astrology. Astronomers study the physical properties and movements of celestial objects, while astrologers make subjective predictions and interpretations based on these movements. Confirmation bias and the Barnum effect play a significant role in the perpetuation of astrological claims. Confirmation bias occurs when individuals seek out information that confirms their preconceived beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence. The Barnum effect, named after P.T. Barnum, refers to the tendency of people to accept general and vague statements as highly accurate descriptions of themselves. Astrology often relies on such generalized statements that can be interpreted in various ways, leading individuals to find personal meaning in them. These psychological factors contribute to the persistence of astrology’s popularity, despite its lack of scientific validity. It is important to approach astrological claims with skepticism and recognize the distinction between science and subjective beliefs.
The Disconnect between Science and Astrology
The disconnect between science and astrology arises from the fundamental differences in their approaches and principles. While science is based on empirical evidence, systematic observation, and rigorous experimentation, astrology relies on subjective interpretations, belief systems, and anecdotal experiences. Science follows the scientific method, which involves formulating hypotheses, conducting experiments, and analyzing data to draw conclusions. On the other hand, astrology relies on astrological charts, horoscopes, and the positions of celestial bodies at the time of birth to make claims about personality traits and future events. These astrological claims often lack scientific validity and have been debunked by various studies. Astrology tends to emphasize general statements that can apply to a wide range of individuals, leading to what is known as the Barnum Effect. This effect refers to the tendency of individuals to accept vague and general descriptions as accurate and personally meaningful. Confirmation bias also plays a role, with people seeking out information that confirms their beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence. Ultimately, astrology and science occupy different realms, with science focusing on objective data and astrology relying on subjective interpretations, making it difficult for them to reconcile their perspectives.
Confirmation Bias and Barnum Effect
Confirmation bias and the Barnum effect are two psychological phenomena that play a significant role in the belief and interpretation of astrology. Confirmation bias refers to our tendency to search for, interpret, and remember information in a way that confirms our preexisting beliefs or expectations. In the context of astrology, this means that individuals are more likely to seek out information that aligns with their zodiac sign and interpret it as accurate, while disregarding or overlooking contradictory evidence. The Barnum effect, named after the famous showman P.T. Barnum, is the tendency to believe generalized statements or personality descriptions that are vague and can apply to a wide range of individuals. Astrology often provides broad and ambiguous personality traits for each zodiac sign, which individuals may find relatable due to the Barnum effect. This allows people to perceive the information as highly personalized, even though it could apply to many others as well. Both confirmation bias and the Barnum effect contribute to the continued belief in astrological claims despite the lack of scientific evidence supporting them. It is essential to recognize these cognitive biases and approach astrology with a critical mindset. By understanding these psychological phenomena, we can better evaluate and question the validity of astrological claims.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the science behind the zodiac constellations reveals a fascinating intersection of ancient mythology, astrology, and astronomical research. The origins of these constellations can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Babylonians and Greeks, who sought to understand and interpret the celestial movements. Over time, the zodiac constellations became intertwined with cultural beliefs, shaping the astrological significance we associate with each sign today. However, it is important to differentiate between the science of astronomy and the pseudoscience of astrology. While astronomers continue to study and catalog the stars, the connection between zodiac constellations and personal traits remains unverified by scientific evidence. Astrology is often criticized for its confirmation bias and the Barnum Effect, where general statements are interpreted as personal insights. Nevertheless, the allure of the zodiac constellations and their impact on popular culture persist. Whether you are a believer or a skeptic, the science behind the zodiac constellations invites us to marvel at the vastness of the universe and the intricate patterns it presents.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of zodiac constellations in astrology?
Zodiac constellations are believed to influence our personalities and have a profound impact on our lives. Astrologers associate each zodiac sign with specific traits, characteristics, and even future events.
How were the zodiac constellations named?
The zodiac constellations were named by the ancient Greeks, who associated them with various mythological figures and symbols. These names and symbols have been passed down through generations.
Do zodiac signs align with the real positions of the constellations?
Not entirely. While zodiac signs share names with constellations, they do not precisely align with their current positions in the sky. This is due to the phenomenon known as the precession of the equinoxes.
What is the precession of the equinoxes?
The precession of the equinoxes is a gradual shift in the orientation of Earth’s axis, causing the position of the equinoxes and solstices to change over time. This shift affects the alignment of zodiac constellations with the seasons.
Are zodiac constellations the same across different cultures?
No, different cultures have their own versions of zodiac constellations. While there are similarities, each culture has its own unique interpretations and celestial symbols associated with the zodiac.
How do astronomers study and catalog zodiac constellations?
Astronomers use astrometry, a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements and calculations, to study and catalog the positions, movements, and characteristics of stars within the zodiac constellations.
Do zodiac constellations play a role in modern astronomy?
While zodiac constellations have historical and cultural significance, modern astronomy focuses more on studying the individual stars, galaxies, and celestial objects within these constellations, rather than their astrological interpretations.
Do scientific studies support the claims made in astrology?
No, scientific studies have not been able to establish a direct correlation between zodiac constellations and human personalities, future events, or life outcomes. Astrology is considered a pseudoscience by the scientific community.
What is confirmation bias and how does it relate to astrology?
Confirmation bias is the tendency to interpret information in a way that confirms our preexisting beliefs or biases. In the context of astrology, people may selectively focus on aspects that align with their zodiac sign while ignoring contradictory evidence.
What is the Barnum effect and how does it relate to astrology?
The Barnum effect, also known as the Forer effect, refers to the tendency of individuals to believe general, vague, and highly positive descriptions as accurate personal assessments. Astrology often uses generalized statements that can apply to a wide range of individuals, leading people to believe in their accuracy.








