The Mystery of False Awakening Dreams: Unveiling the Enigma
Have you ever woken up from what seemed like reality, only to discover it was actually just another dream? These perplexing experiences, known as false awakening dreams, continue to confound scientists and sleep experts alike. False awakening dreams mimic the sensation of waking up, complete with vivid details and familiar surroundings, only to realize later that it was all an illusion. In this article, we will delve into the science behind false awakening dreams, unraveling the mystery behind their occurrence, the psychology behind them, the role of sleep stages, their differences from nightmares, scientific theories explaining them, and techniques to distinguish them. Brace yourself for a journey into the fascinating world of the unconscious mind and the puzzling realm of false awakening dreams.
What are False Awakening Dreams?

False awakening dreams are a perplexing phenomenon that involve the vivid perception of waking up, only for the dreamer to realize later that they are still immersed within the realm of dreams. These dreams often mimic reality with remarkable detail, encompassing familiar surroundings, daily routines, and even interacting with people or objects that appear entirely lifelike. The line between wakefulness and dreams becomes blurred, leaving individuals questioning their own perception of reality. False awakening dreams can be disorienting and confusing, as they challenge our basic understanding of what it means to be awake. They can occur during any stage of sleep and are most commonly reported during the morning hours when individuals are more likely to transition between sleep and wakefulness. To gain a deeper understanding of false awakening dreams, it is essential to explore their definition, occurrence, prevalence, and the differences between false awakening dreams and lucid dreams, as well as their psychological implications. For more information on lucid dreaming, you can check out our previous article “Lucid Dreaming vs. False Awakening Dreams: Exploring the Difference”. If you are interested in the psychological perspective of false awakening dreams, take a look at our article “The Psycho Perspective of False Awakening Dreams: A Journey into the Unconscious Mind” and get ready to dive deeper into the intriguing world of false awakening dreams and their tales “Tales of False Awakening Dreams: Real-life Encounters with the Surreal”.
Definition
False awakening dreams can be defined as dreams in which individuals believe they have awakened from sleep, only to realize later that they are still in the midst of a dream. These dreams closely mimic reality, often including realistic settings, familiar faces, and everyday activities. The dreamer experiences a vivid and convincing sensation of waking up, complete with sensory details such as feeling the warmth of the bed, hearing familiar sounds, and even engaging in routine actions like getting out of bed or making breakfast. However, upon closer inspection or after experiencing unusual events, the dreamer gradually becomes aware that they are still dreaming. This realization can be accompanied by varying degrees of confusion and surprise, as the dreamer questions their perception of reality. False awakening dreams can leave individuals with a lingering sense of uncertainty and can lead to further dream scenarios or even a subsequent awakening. Whether they occur sporadically or frequently, these dreams offer a fascinating glimpse into the complex nature of human consciousness and the intricacies of our dream world.
Occurrence and Prevalence
False awakening dreams can occur in individuals of all ages and backgrounds. While the exact frequency of these dreams is challenging to determine, research suggests that they are relatively common. Various factors can influence the occurrence of false awakening dreams, including sleep patterns, lifestyle, stress levels, and overall sleep quality. Those who experience frequent or recurring lucid dreams may also be more prone to false awakening dreams. The prevalence of false awakening dreams highlights the intricacies of the human mind and the complexities of the dream state. As individuals become more aware of the concept of false awakening dreams, they are more likely to recognize the occurrence of these dreams in their own sleep experiences. The prevalence of false awakening dreams sheds light on the need for further research and exploration into the mechanisms and underlying factors contributing to their occurrence. Understanding the occurrence and prevalence of false awakening dreams is a crucial step in unraveling the mystery behind these intriguing phenomena.
The Psychology Behind False Awakening Dreams

Understanding the psychology behind false awakening dreams requires an exploration of the intricate workings of the mind during sleep. One key aspect is the brain mechanisms involved in dream production. Research suggests that false awakening dreams occur during the REM (Rapid Eye Movement) stage of sleep, which is characterized by heightened brain activity and vivid dreaming. During this stage, the brain generates complex narratives and scenarios, often fueled by the emotions and experiences of the individual. False awakening dreams may be a result of the brain attempting to create a seamless transition between dreaming and waking states. Additionally, the existence of lucid dreams, where individuals become aware that they are dreaming while still in the dream, sheds light on the potential relation to false awakening dreams. In lucid dreams, individuals may falsely believe they have woken up and are functioning in reality, when in fact, they are still within the dream state. This overlap between lucid dreams and false awakening dreams suggests that a level of subconscious processing and self-awareness is at play. The mind may create the illusion of awakening as a way to test and challenge one’s understanding of reality. By examining the intricate workings of the mind during sleep and its interplay with consciousness, we can unravel the psychology behind false awakening dreams and gain insight into their mysterious nature.
Brain Mechanisms
Understanding the brain mechanisms behind false awakening dreams can provide insights into why these experiences occur. While the exact neural processes are still being explored, there are several theories that shed light on this intriguing phenomenon.
1. Activation of the Prefrontal Cortex: The prefrontal cortex, a region of the brain associated with higher cognitive functions, plays a crucial role in distinguishing between dream and reality. During false awakening dreams, this area may fail to inhibit the dream-like elements, leading to a seamless blending of dream content with the perception of wakefulness.
2. Disruption in Sensory Processing: In normal waking states, sensory information flows seamlessly, allowing us to perceive and interact with the external world. However, during false awakening dreams, there can be a disruption in sensory processing, resulting in a distorted perception of reality. This disruption may be caused by alterations in the brain’s sensory processing centers, such as the thalamus.
3. Involvement of the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex: The ventromedial prefrontal cortex is responsible for self-referential processes, including self-awareness and introspection. It has been suggested that this region may play a role in differentiating between dreams and reality. Dysfunction or hyperactivity in this area during sleep may contribute to the confusion experienced during false awakening dreams.
4. Activation of the Limbic System: The limbic system, involved in emotional processing, memory, and motivation, is also implicated in the occurrence of false awakening dreams. Emotional experiences within dreams can be intensely vivid, mimicking real-life situations and evoking strong emotional responses.
These brain mechanisms provide a glimpse into the intricate processes underlying false awakening dreams. However, it is important to note that further research is needed to fully comprehend the complexity of these mechanisms and their interplay with other factors like sleep stages and conscious awareness. By unraveling the mysteries of the brain, we may gain a deeper understanding of false awakening dreams and the enigmatic nature of human consciousness.
Existence of Lucid Dreams
Lucid dreams, a related phenomenon to false awakening dreams, are dreams in which the dreamer becomes aware that they are dreaming while still immersed in the dream state. Unlike regular dreams where individuals passively experience events, in lucid dreams, they gain a sense of consciousness and control within the dream world. This heightened awareness allows dreamers to manipulate the dream environment, interact with dream characters, and even alter the dream narrative. Lucid dreams can range from fleeting moments of awareness to fully immersive and prolonged experiences. While false awakening dreams may have a similar appearance to lucid dreams, it is important to note that false awakenings specifically involve the illusion of waking up within the dream. This key distinction sets false awakening dreams apart from lucid dreams. The existence of lucid dreams has been well-documented and studied by researchers in the field of sleep and dreaming. Scientific studies using neuroimaging techniques have confirmed that lucid dreaming involves increased activity in areas of the brain associated with self-awareness and cognitive control. Lucid dreaming offers a fascinating glimpse into the capabilities of the human mind during sleep, providing insights into the relationship between consciousness and the dream state.
Subconscious Processing
When it comes to understanding false awakening dreams, one crucial aspect to consider is subconscious processing. During these dreams, the mind is actively engaged in processing information and creating a narrative that closely resembles waking reality. The subconscious mind plays a significant role in shaping the details and events experienced within the dream. It is responsible for recreating familiar environments, people, and situations, often based on memories and experiences stored deep within our subconscious. Subconscious processing allows the dreamer to perceive the dream as reality, with intricate details that can be indistinguishable from waking life. This process can be likened to the brain’s ability to construct a comprehensive virtual reality experience within the confines of our own minds. The subconscious mind acts as an artist, painting a vivid tapestry of sights, sounds, and emotions that seamlessly blend into the dream world. It is important to note that subconscious processing during false awakening dreams is not limited to visual stimuli alone. It encompasses a multisensory experience, involving touch, taste, smell, and even emotions, making the dream world feel incredibly real. The role of subconscious processing in false awakening dreams highlights the intricacies of the dreaming mind and its remarkable ability to create immersive worlds within the realm of sleep.
The Role of Sleep Stages
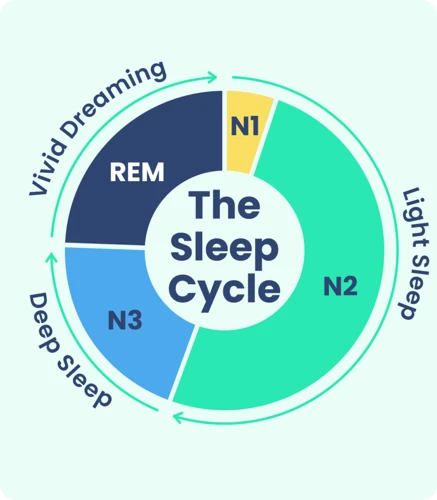
Understanding the different stages of sleep is crucial in unraveling the mystery behind false awakening dreams. Sleep consists of several distinct stages that cycle throughout the night. The two main types of sleep are Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep and Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep. REM sleep is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreaming. This is the stage where false awakening dreams predominantly occur. During REM sleep, the brain becomes highly active, and the body goes into a state of temporary paralysis to prevent acting out dreams. It is in this stage that false awakening dreams often manifest, blending the dreamer’s perception of reality with the dream world. On the other hand, NREM sleep can be further divided into three stages: N1, N2, and N3. N1 is the transitional stage between wakefulness and sleep, while N2 is a deeper stage of sleep where the brain begins to produce sleep spindles – brief bursts of higher-frequency brain waves. N3, also known as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep, is the stage where the body undergoes physical restoration and repair. False awakening dreams are less likely to occur during NREM sleep due to the absence of vivid dreaming. By understanding the role of sleep stages, we can gain insight into why false awakening dreams primarily occur during REM sleep and shed light on the mechanisms that govern these mysterious experiences.
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep is a crucial stage of the sleep cycle closely associated with dreaming, including false awakening dreams. During REM sleep, the brain exhibits highly active and intense neuronal activity, similar to that of wakefulness. This stage is characterized by rapid eye movements, hence the name, along with heightened brain activity, increased heart rate, and irregular breathing patterns. REM sleep typically occurs multiple times throughout the night, with each REM period becoming longer as the night progresses. It is during REM sleep that dreams, including false awakening dreams, are most likely to occur. The exact mechanisms behind REM sleep and dreaming are still not fully understood, but it is believed that the brain regions responsible for emotional processing, memory consolidation, and imagination play significant roles. The release of certain neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, serotonin, and dopamine, is also thought to contribute to the occurrence and vividness of dreams during REM sleep. Interestingly, REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) is a condition where individuals physically act out their dreams due to a lack of muscle paralysis during this stage. This suggests a strong link between REM sleep and the immersive nature of dreams, including false awakening dreams.
Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep (NREM)
Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep (NREM) is one of the two main stages of sleep, alongside Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep. NREM sleep is characterized by a lack of rapid eye movement, hence its name. It is further divided into three distinct stages: N1, N2, and N3.
N1 stage: This initial stage of NREM sleep is a transitional phase between wakefulness and sleep. During this phase, brain waves become slower and irregular, and muscle activity begins to decrease. Individuals in N1 may experience fleeting thoughts or dream-like sensations, often referred to as hypnagogic hallucinations.
N2 stage: The N2 stage is a deeper state of NREM sleep. In this stage, the brain continues to exhibit slower brain waves, along with intermittent bursts of rapid brain activity called sleep spindles. These sleep spindles help in the consolidation and processing of memories. It is also during the N2 stage that the body begins to relax further, heart rate slows down, and body temperature decreases.
N3 stage: The N3 stage is the deepest stage of NREM sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS). It is characterized by slow, high-amplitude brain waves known as delta waves. During this stage, the body reaches its most relaxed state, and it becomes more challenging to awaken someone. This stage is crucial for physical restoration and growth, as it promotes tissue repair, muscle development, and the release of essential hormones. It is also believed to play a vital role in memory consolidation and learning.
NREM sleep plays a fundamental role in the restoration of the body and mind. It is during these stages that essential bodily functions are regulated, memories are consolidated, and the brain undergoes important processes for overall well-being. NREM sleep works in conjunction with REM sleep to form the complete sleep cycle, allowing us to experience a restorative and rejuvenating night’s sleep.
False Awakening Dreams vs. Nightmares

False awakening dreams and nightmares, while both falling under the umbrella of dream experiences, differ in various aspects, including their content and emotional impact. Here, we will explore the distinguishing features between these two phenomena.
Content: False awakening dreams typically involve the dreamer’s everyday life experiences and routines. The dreamer may go through their morning routine, interact with familiar people, or even perform mundane tasks. In contrast, nightmares often involve disturbing themes, frightening scenarios, and intense emotions, such as being chased or experiencing a threat. The content of false awakening dreams tends to mirror reality, while nightmares deviate into more distressing and often surreal territories.
Emotion: False awakening dreams are generally neutral or even positive in emotional tone. The dreamer may feel a sense of routine and normalcy, as they are led to believe they have woken up in their familiar surroundings. In contrast, nightmares are characterized by intense fear, anxiety, and distress. Nightmares can leave the dreamer feeling deeply unsettled, scared, and even wake them up in a state of panic.
Interplay with Sleep Disorders: False awakening dreams can occur independently or in conjunction with other sleep disorders, such as sleep paralysis or insomnia. They are not necessarily indicative of an underlying sleep disorder themselves. On the other hand, nightmares are often associated with conditions like post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and may be more commonly experienced by individuals with a history of trauma or anxiety.
Understanding the differences between false awakening dreams and nightmares can help individuals make sense of their dream experiences and provide insights into the underlying psychological processes. Whether it’s an eerie and unsettling false awakening dream or a heart-pounding nightmare, dreams continue to intrigue and perplex us as we strive to unlock the secrets of our subconscious minds.
Differences in Content and Emotion
False awakening dreams and nightmares are two distinct experiences with notable differences in content and emotion. In false awakening dreams, the dreamer often finds themselves in their usual sleeping environment, believing they have awakened, and engaging in mundane activities such as getting ready for the day or having breakfast. The content of false awakening dreams closely resembles the waking state, with familiar settings and routines. However, the emotion experienced during false awakening dreams can range from neutral to mildly unsettling, as individuals may feel a sense of confusion or frustration upon realizing they are still dreaming. On the other hand, nightmares typically involve intense fear, anxiety, or distressing emotions, and they often contain explicit threats, vividly terrifying scenarios, or disturbing imagery. Nightmares tend to deviate from the everyday reality, presenting the dreamer with surreal or nightmarish situations that evoke strong emotional reactions. While false awakening dreams can momentarily deceive the dreamer into believing they have woken up, nightmares often jolt the dreamer out of sleep due to the sheer intensity of the emotions they elicit. Thus, the differences in content and emotion between false awakening dreams and nightmares contribute to distinct psychological experiences during sleep.
Interplay with Sleep Disorders
Interplay with Sleep Disorders
False awakening dreams are not only intriguing in their own right but also have a significant interplay with sleep disorders. These dreams can occur in individuals with various sleep disorders, further complicating their experiences and affecting their overall sleep quality. One sleep disorder that often intersects with false awakening dreams is insomnia. Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to daytime impairment. The relentless cycle of insomnia can heighten the occurrence of false awakening dreams as individuals may awaken frequently throughout the night, increasing the chances of experiencing these puzzling dreams.
Another sleep disorder linked to false awakening dreams is sleep apnea. Sleep apnea involves episodes of interrupted breathing during sleep, leading to significant sleep fragmentation. The recurrent awakenings caused by sleep apnea can provide fertile ground for false awakening dreams to flourish. Individuals with sleep apnea may find themselves continuously awakening throughout the night and may mistake these awakenings as actual wakefulness when, in reality, they are still in the realm of dreams.
Narcolepsy, a neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and irregular sleep-wake cycles, can also intertwine with false awakening dreams. Narcolepsy disrupts the boundaries between wakefulness and sleep, making it more challenging for individuals to differentiate between dreams and reality. As a result, false awakening dreams can become entangled within the complex tapestry of narcolepsy, further blurring the line between waking life and the dreaming world.
In addition to these sleep disorders, other conditions such as restless leg syndrome and sleepwalking have also been associated with false awakening dreams. Restless leg syndrome causes uncomfortable sensations in the legs, leading to an irresistible urge to move them, often disrupting sleep. Sleepwalking, on the other hand, involves complex behaviors performed during sleep, usually during the deeper stages of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. These disorders can influence the occurrence and content of false awakening dreams, adding another layer of complexity to the understanding of these enigmatic experiences.
The interplay between false awakening dreams and sleep disorders highlights the intricate relationship between the dream world and the disturbances in the sleep-wake cycle. Understanding the connections between these phenomena can not only shed light on sleep disorders but also provide valuable insights into the nature and mechanisms of false awakening dreams.
Scientific Theories Explaining False Awakening Dreams

Scientific theories aim to unravel the mystery behind false awakening dreams and provide insights into their underlying mechanisms. Two prominent theories have been proposed to explain these enigmatic experiences: the Activation-Synthesis Theory and the Continual-Activation Theory.
The Activation-Synthesis Theory suggests that false awakening dreams occur due to random and spontaneous brain activity during sleep. According to this theory, the brain’s cortex tries to make sense of these random signals by creating a narrative that resembles waking reality. In essence, the brain synthesizes a cohesive story from fragmented and unrelated neural impulses. This interpretation explains why false awakening dreams often contain elements from the dreamer’s immediate physical environment or recent experiences.
On the other hand, the Continual-Activation Theory proposes that false awakening dreams result from the ongoing activation of the brain’s sleep systems. Unlike the Activation-Synthesis Theory, which emphasizes the role of random brain activity, this theory posits that the brain remains partially in a sleep state during false awakening dreams. The sleep systems responsible for motor inhibition and sensory filtering don’t fully disengage, leading to an altered perception of reality. This theory is supported by studies showing that individuals experiencing false awakening dreams exhibit characteristics typically associated with sleep, such as decreased motor control and reduced critical thinking.
Both theories highlight the intricate interplay between brain activity and consciousness during sleep, shedding light on how false awakening dreams can occur. However, it’s important to note that the exact mechanisms underlying these dreams are still not fully understood, and further research is needed to unravel their complexities. As scientists continue to investigate the subject, these theories provide a framework for understanding the intriguing phenomenon of false awakening dreams.
Activation-Synthesis Theory
The Activation-Synthesis Theory is a prominent scientific theory that aims to explain the occurrence of dreams, including false awakening dreams. According to this theory, dreams are a result of random neural activity in the brain during sleep. The theory suggests that the brainstem sends random signals to the cerebral cortex, which is responsible for higher-level cognitive functions and interpretation of sensory information. These signals are then synthesized by the brain, creating a coherent story or narrative that we experience as dreams. In the case of false awakening dreams, the brain might generate a narrative that involves waking up in familiar surroundings, leading to the illusion of actually being awake.
The Activation-Synthesis Theory challenges the traditional view that dreams have deep psychological meanings. Instead, the theory proposes that dreams are a byproduct of the brain’s attempt to make sense of random neural activity. This theory is supported by research findings that demonstrate the unpredictable and nonsensical nature of dreams. While some dreams may contain elements and symbols that can be interpreted, the Activation-Synthesis Theory suggests that these interpretations are merely constructs of the waking mind attempting to give meaning to the unconscious processes of the brain.
It is important to note that the Activation-Synthesis Theory is just one of several theories proposed to explain the nature of dreams. Another theory that complements the Activation-Synthesis Theory is the Continual-Activation Theory, which suggests that dreaming serves a critical role in memory consolidation and emotional processing. These theories together contribute to our understanding of the complex and multifaceted nature of dreams, including false awakening dreams.
Continual-Activation Theory
Continual-Activation Theory is one of the scientific theories that attempts to explain the occurrence of false awakening dreams. According to this theory, false awakening dreams are a result of an incomplete transition between sleep and wakefulness. The brain goes through cycles of activation and deactivation during sleep, and it is believed that during false awakening dreams, there is a failure in the deactivation process. In other words, the brain continues to activate the areas responsible for generating dreams while the regions responsible for wakefulness remain partially active.
This theory suggests that during false awakening dreams, the brain creates a dream scenario based on the information available in memory and the surrounding environment. It is proposed that the activation of certain brain areas, such as the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for logical reasoning and self-awareness, is suppressed or inhibited during these dreams. This inhibition of self-awareness explains why individuals typically accept their dream reality without questioning its authenticity.
The continual-activation theory suggests that false awakening dreams may be linked to increased arousal during sleep, possibly due to external stimuli or internal factors such as stress or anxiety. This heightened arousal may disrupt the normal sleep-wake transition, leading to these vivid and deceptive dream experiences. While more research is needed to fully understand the intricacies of the continual-activation theory and its specific mechanisms, it provides valuable insights into the complex nature of false awakening dreams and highlights the intricate interplay between brain activity, consciousness, and sleep.
How to Distinguish False Awakening Dreams
- Mindfulness: Practicing mindfulness can help in distinguishing false awakening dreams from reality. By cultivating a habit of being present in the moment throughout the day, you are more likely to develop a similar habit in your dreams. When you question your reality during a dream, you are more likely to realize that you are in a false awakening dream.
- Reality Testing Techniques: Engaging in reality testing techniques can assist in distinguishing between waking life and false awakening dreams. These techniques involve performing quick reality checks, such as attempting to read a sentence twice or looking at a digital clock to see if the numbers change. In a false awakening dream, these reality checks may produce inconsistent or nonsensical results, indicating that you are still within the realm of dreams.
- Journaling: Keeping a dream journal can provide valuable insights into your dream patterns and help you identify recurring false awakening dreams. By recording your dreams upon waking, you’ll have a repository of experiences to reflect upon and analyze for common themes or occurrences that might indicate a false awakening.
- Reality Anchors: Setting up reality anchors in your waking life can carry over into your dreams and serve as reminders to question your reality. These anchors can be objects, behaviors, or specific rituals that you consciously incorporate into your daily routine. For example, glancing at a specific symbol or performing a certain action every time you enter a new room can help trigger a similar response in your dreams, prompting a reality check.
- Lucid Dreaming Techniques: Since false awakening dreams often occur during the transition between sleep and wakefulness, employing techniques to induce lucid dreaming can increase your likelihood of recognizing and controlling false awakening dreams. Techniques such as reality testing, maintaining dream awareness, and practicing visualizations or affirmations before bed can enhance your ability to become lucid within these dreams.
By employing these strategies and techniques, you can develop a heightened sense of self-awareness and better discern false awakening dreams from reality. Remember that practice and consistency are key, as it may take time to establish these habits and train your mind to question the nature of your experiences.
Mindfulness and Reality Testing Techniques
When it comes to discerning whether you are experiencing a false awakening dream or reality, practicing mindfulness and employing reality testing techniques can be highly useful. Mindfulness involves maintaining a heightened awareness and attentiveness to the present moment. By cultivating mindfulness in your everyday life, you can develop a habit of questioning your surroundings and mental states, which can spill over into your dream experiences. Here are some reality testing techniques to help you differentiate between a false awakening dream and reality:
1. Performing reality checks: Throughout the day, make it a habit to perform reality checks to verify if you are awake or dreaming. This can include actions such as trying to push fingers through the palm of your hand or reading a sentence, looking away, and then reading it again to see if the text changes. By ingraining this practice in your waking life, you are more likely to perform these reality checks during a dream and realize you are in a false awakening.
2. Maintaining a dream journal: Keeping a dream journal by your bedside allows you to record your dreams immediately upon waking. This practice not only helps improve dream recall but also enables you to identify patterns or recurring elements in your dreams. By becoming more familiar with your dream content, you are better equipped to recognize when you are in a false awakening.
3. Developing a reality affirmation: Create a simple and memorable affirmation that you can repeat to yourself throughout the day, such as “Am I dreaming?” By consistently questioning your reality, this affirmation can carry over into your dream state, prompting you to question whether you are truly awake.
4. Engaging in meditation: Regular meditation practice can enhance your overall self-awareness and sharpen your ability to discern between different states of consciousness. By training your mind to observe thoughts, sensations, and emotions without attachment, you develop a greater sense of self-awareness that can extend into your dream experiences.
Remember, the key to successfully distinguishing false awakening dreams lies in cultivating a habit of critical self-reflection and maintaining an open state of inquiry. By incorporating mindfulness and reality testing techniques into your daily routine, you can increase your chances of recognizing and unraveling the enigma of false awakening dreams.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the phenomenon of false awakening dreams continues to mystify scientists and individuals alike. These dreams, which mimic waking reality with astonishing detail, blur the boundaries between dreams and waking life, leaving dreamers questioning their own perception of reality. The psychology behind false awakening dreams involves complex brain mechanisms, the existence of lucid dreams, and subconscious processing. False awakening dreams are closely intertwined with different sleep stages, particularly REM sleep and NREM sleep, each contributing to the unique characteristics of these dreams. While false awakening dreams share similarities with nightmares, they differ in terms of content and emotion, highlighting the subjective nature of dream experiences. Furthermore, false awakening dreams can be linked to various sleep disorders, further complicating their understanding. Scientists have proposed theories such as the activation-synthesis theory and the continual-activation theory to explain the occurrence of false awakening dreams, shedding light on the mechanisms that underlie these experiences. To distinguish false awakening dreams from reality, practicing mindfulness and reality testing techniques can be helpful. Overall, the enigma of false awakening dreams showcases the fascinating intricacies of the human mind, challenging our understanding of consciousness and perception. As we continue to unlock the mysteries of our dreams, false awakening dreams serve as a reminder of the vast and complex nature of our inner worlds.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQs About False Awakening Dreams:
1. Can false awakening dreams feel as real as waking life?
Yes, false awakening dreams can be incredibly vivid and realistic, making it difficult to distinguish them from actual wakefulness.
2. How often do false awakening dreams occur?
The frequency of false awakening dreams varies among individuals. Some may experience them occasionally, while others may have them more frequently.
3. Are false awakening dreams a type of lucid dreaming?
No, false awakening dreams and lucid dreams are distinct experiences. In lucid dreaming, individuals are aware they are dreaming and can actively engage in the dream. False awakening dreams, on the other hand, involve a false perception of waking up.
4. Can false awakening dreams be triggered by certain factors?
Yes, false awakening dreams can be influenced by various factors such as irregular sleep patterns, stress, anxiety, or even certain medications.
5. Can false awakening dreams be used for creative inspiration?
Absolutely! False awakening dreams can provide a rich source of imaginative material and inspiration for artistic endeavors, storytelling, and problem-solving.
6. Are false awakening dreams considered normal or abnormal?
False awakening dreams are considered a normal part of the dreaming experience. However, if they become distressing or severely impact sleep quality, it may be beneficial to seek guidance from a sleep specialist.
7. Is there any way to control or manipulate false awakening dreams?
With practice and mindfulness techniques such as reality testing, individuals may improve their ability to recognize false awakening dreams and potentially exert some control over the dream content.
8. Can false awakening dreams have any psychological significance?
False awakening dreams often reflect underlying emotions, anxieties, or unresolved issues. Analyzing these dreams can provide insights into the dreamer’s subconscious mind and facilitate self-reflection and personal growth.
9. Are false awakening dreams connected to sleep disorders?
While false awakening dreams themselves are not classified as sleep disorders, they can be associated with other sleep conditions such as insomnia, sleep apnea, or narcolepsy.
10. Are false awakening dreams more prevalent in certain age groups?
False awakening dreams can occur at any age, but they are more commonly reported among teenagers and young adults.








