Have you ever experienced the bizarre sensation of being aware that you’re dreaming while still in the midst of a dream? This phenomenon, known as lucid dreaming, has fascinated and perplexed scientists and dream enthusiasts alike for centuries. The scientific community has been exploring the neurological processes behind this fascinating phenomenon in an effort to uncover the secrets of the dreaming mind. In this article, we delve into the intricate workings of the brain during lucid dreaming, uncovering the role of the pre-frontal cortex, the connection to REM sleep, and the influence of neurotransmitters like dopamine and acetylcholine. Join us as we navigate the vast landscape of the dreaming mind and unlock the science behind lucid dreaming.
Understanding Lucid Dreaming

Lucid dreaming is a captivating state of consciousness that occurs when a person becomes aware that they are dreaming while still in the midst of a dream. It is a unique and intriguing experience that allows individuals to have control and agency within their dreams. Lucid dreaming opens up a world of possibilities, where the boundaries of reality are no longer constraints. In this altered state of consciousness, individuals can manipulate the dream scenario, fly through the sky, explore imaginary landscapes, or interact with entities from the dream world. This phenomenon has been the subject of fascination throughout history, with cultures and traditions across the globe incorporating it into their practices. The practice of lucid dream maintenance can be utilized as a tool for self-discovery, personal growth, and even managing nightmares and sleep disorders. While the concept of lucid dreaming may seem fantastical and mystical, scientific research has shed light on the neurological processes behind this phenomenon, allowing us to delve deeper into the mechanics of the dreaming mind.
What is Lucid Dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is a fascinating phenomenon that occurs when an individual becomes aware that they are dreaming while still in the midst of a dream. This state of consciousness allows individuals to have a sense of control and awareness within their dreams, blurring the line between reality and the dream world. Lucid dreaming can be characterized by various indicators such as the ability to think logically, make decisions, and even engage in deliberate actions within the dream. It is estimated that approximately 55% of people have experienced at least one lucid dream in their lifetime. During a lucid dream, individuals may possess a remarkable ability to manipulate the dream environment, engage with dream characters, and explore imaginative scenarios. It offers an extraordinary platform for creativity, self-exploration, and personal growth. Lucid dreaming can be facilitated through various techniques, such as reality testing, keeping a dream journal, or practicing mindfulness. Additionally, lucid dream maintenance practices can be employed to prolong the lucid dream state, allowing individuals to further explore and engage with their dreams.
The Benefits of Lucid Dreaming
Lucid dreaming offers a plethora of benefits that extend beyond the realm of ordinary dreaming. One of the key advantages of lucid dreaming is the ability to actively engage and manipulate the dream environment. This empowers individuals to overcome fears, practice new skills, and unlock their creative potential. For example, athletes can utilize lucid dreaming to visualize and enhance their performance, improving muscle memory and refining techniques even while they sleep. Lucid dreaming also provides a unique platform for self-exploration and introspection. By consciously venturing into the inner depths of their subconscious minds, individuals can gain valuable insights, resolve emotional conflicts, and promote personal growth and healing. Lucid dreaming can be a source of joy and adventure, offering a sense of escapism and boundless possibilities. Engaging in lucid dreaming can also augment sleep quality and overall well-being, as it encourages a sense of empowerment and control over one’s dreamscape. Whether for personal growth, creativity, or simply experiencing a thrilling alternate reality, the benefits of lucid dreaming are undeniably intriguing and captivating.
The Science Behind Lucid Dreaming

Lucid dreaming is not simply a random occurrence; there is actual science behind it. To understand the science behind lucid dreaming, we need to explore the neurological processes that take place in the brain during this extraordinary state of consciousness. One key player in lucid dreaming is the pre-frontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making, self-awareness, and self-control. Studies have shown that this area of the brain becomes highly active during lucid dreaming, contributing to the individual’s enhanced level of consciousness and ability to exert control over their dreams. Another essential component is the connection between lucid dreaming and REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep. During REM sleep, the brain is highly active, and dreams are known to occur. Neurologically, lucid dreaming is believed to happen when the brain transitions smoothly between REM sleep and wakefulness, blurring the line between the two states. One intriguing hypothesis is related to the involvement of neurotransmitters like dopamine and acetylcholine. These chemicals play a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle and are thought to play a part in facilitating lucid dreaming. While the exact mechanisms are still being studied, the interaction between these neurotransmitters is believed to influence the likelihood and frequency of lucid dreaming experiences. Understanding the science behind lucid dreaming provides us with valuable insights into the inner workings of the dreaming mind and paves the way for further exploration of this fascinating phenomenon.
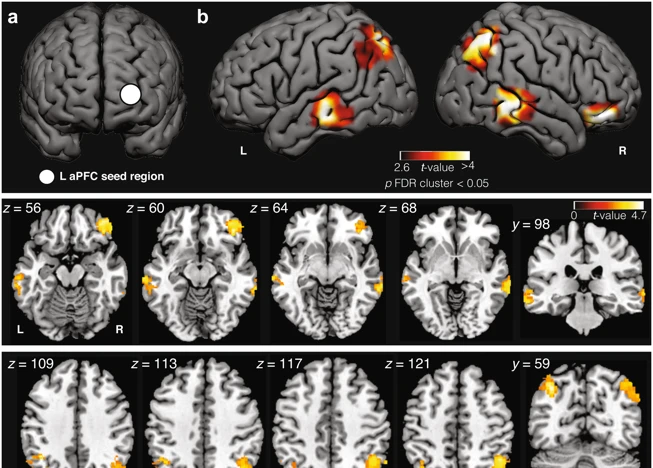
The Role of the Pre-Frontal Cortex
The pre-frontal cortex plays a significant role in lucid dreaming. This region of the brain, located in the frontal lobe, is responsible for executive functions such as decision-making, self-awareness, and working memory. During normal dreaming, the pre-frontal cortex is typically less active, resulting in a lack of self-awareness and rationality. However, during lucid dreaming, studies have shown that the pre-frontal cortex becomes highly activated. This increased activation allows individuals to maintain a sense of self-awareness and cognitive control while in the dream state. The pre-frontal cortex acts as a bridge between the dreaming mind and waking consciousness, enabling individuals to recognize the dream as a construct of their own imagination. This heightened activation of the pre-frontal cortex provides the foundation for individuals to exercise volitional control over their dream environment, enabling them to engage in various activities and manipulate the dream scenario. It is through the engagement of this region that individuals can experience the extraordinary phenomenon of lucid dreaming.
REM Sleep and its Connection to Lucid Dreaming
REM sleep (rapid eye movement sleep) plays a crucial role in the occurrence of lucid dreaming. REM sleep is a unique phase of the sleep cycle characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreaming. It is during this stage that most of our dreams take place, and it is also the stage where lucid dreams are most likely to occur. The connection between REM sleep and lucid dreaming lies in the activation of the pre-frontal cortex, the part of the brain responsible for decision-making, self-awareness, and logical reasoning. Studies have shown that the pre-frontal cortex is highly active during REM sleep and even more so during lucid dreaming. This increased activation allows individuals to become aware that they are dreaming and exert some level of control over the dream content. Additionally, the characteristic brainwave patterns observed during REM sleep, such as beta and gamma waves, have been linked to the cognitive processes associated with lucid dreaming. Understanding the intricate relationship between REM sleep and lucid dreaming sheds light on the neurological mechanisms that underlie this fascinating phenomenon.
The Dopamine and Acetylcholine Hypothesis
Within the scientific exploration of lucid dreaming, one of the key hypotheses that has emerged is the role of dopamine and acetylcholine in facilitating this phenomenon. The dopamine and acetylcholine hypothesis suggests that the levels and balance of these neurotransmitters play a crucial role in the occurrence of lucid dreams. Dopamine, known for its involvement in reward and motivation, is theorized to enhance the brain’s ability to recognize the dream state and maintain self-awareness during dreams. This theory is supported by studies that have found increased dopamine activity in the pre-frontal cortex during REM sleep, the stage of sleep where dreams predominantly occur. Acetylcholine, which is associated with memory and learning, is believed to enhance the brain’s ability to remember intentions and foster self-reflection within dreams. The interplay between dopamine and acetylcholine is thought to contribute to the overall cognitive processes involved in lucid dreaming, such as critical thinking, rational decision-making, and problem-solving. While research in this area is still ongoing, the dopamine and acetylcholine hypothesis provides valuable insights into the neural mechanisms that underlie the remarkable phenomenon of lucid dreaming.
Neurological Processes in Lucid Dreaming
1. Increased Activation of the Pre-Frontal Cortex: One of the key areas of the brain involved in lucid dreaming is the pre-frontal cortex (PFC). Studies have shown that during lucid dreaming, there is a significant increase in PFC activity compared to regular dreaming or wakefulness. The PFC is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as decision-making, self-awareness, and working memory. This heightened activation allows individuals to have greater control and awareness within their dreams.
2. Seamless Interplay Between Brain Regions: Lucid dreaming involves a unique interplay between different brain regions. Research has shown that during lucid dreaming, there is increased connectivity and communication between the PFC, parietal cortex, and other regions associated with sensory processing and self-referential thinking. This synchronized activity allows for the integration of sensory information from the dream world and the generation of conscious awareness.
3. Enhanced Self-Awareness and Metacognition: Lucid dreaming is characterized by a heightened sense of self-awareness and metacognition, which is the ability to think about one’s own thoughts. This enhanced self-awareness enables individuals to recognize the dream state and distinguish it from waking reality. It also facilitates the ability to reflect on and manipulate the dream environment consciously.
4. Neurochemical Modulation During Lucid Dreaming: Various neurotransmitters play a role in the modulation of brain activity during lucid dreaming. One hypothesis suggests that an increase in dopamine levels may contribute to the experience of lucidity, as dopamine is involved in reward processing and attention. Additionally, acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter associated with wakefulness and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, is also believed to play a role in promoting lucid dreaming.
The intricate neurological processes involved in lucid dreaming provide insights into the mechanisms behind this unique cognitive phenomenon. The increased activation of the PFC, seamless interplay between brain regions, enhanced self-awareness, and neurochemical modulation all contribute to the vivid and conscious experience of lucid dreaming. Understanding these processes can help researchers uncover the mysteries of the dreaming mind and potentially develop techniques to induce lucidity and explore its various benefits further.
Increased Activation of the Pre-Frontal Cortex
One of the key neurological processes underlying lucid dreaming is the increased activation of the pre-frontal cortex. This region of the brain, located just behind the forehead, is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as decision-making, self-awareness, and working memory. During a normal dream, the pre-frontal cortex is typically deactivated, leading to a lack of critical thinking and self-awareness. However, in a lucid dream, this area of the brain becomes highly active, allowing individuals to possess a heightened sense of awareness and control within the dream state. The increased activation of the pre-frontal cortex enables individuals to recognize inconsistencies or anomalies within the dream, triggering the realization that they are, in fact, dreaming. This awareness then grants them the ability to manipulate and shape the dream’s narrative and environment. Several studies utilizing brain imaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), have demonstrated the significant role that the pre-frontal cortex plays in the phenomenon of lucid dreaming. Understanding the increased activation of the pre-frontal cortex provides valuable insights into the mechanism behind lucid dreaming and its impact on consciousness and cognition.
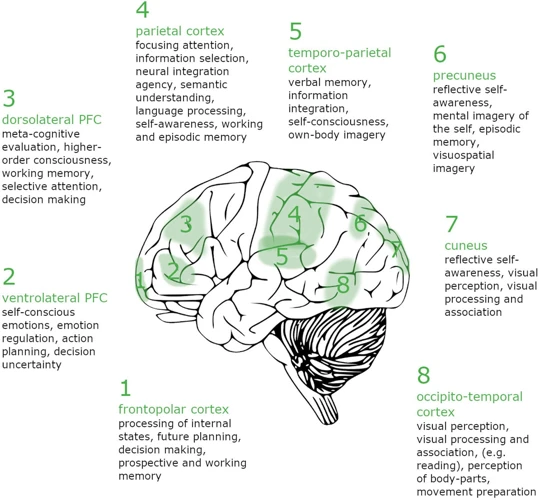
Seamless Interplay Between Brain Regions
During a lucid dream, there is a fascinating interplay between different regions of the brain, facilitating a seamless flow of neural activity. This interplay involves various brain regions working in harmony to create and maintain the lucid dreaming experience.
One significant area involved in this process is the prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions, decision-making, and self-awareness. Studies have shown that the prefrontal cortex exhibits increased activation during lucid dreaming, leading to enhanced cognitive abilities and metacognition. This heightened activation enables individuals to have a clear sense of self, awareness of their surroundings, and the ability to make consciously guided choices within the dream.
Another essential region involved in the seamless interplay is the temporoparietal junction (TPJ), responsible for self-other distinction and perspective-taking. The TPJ plays a crucial role in distinguishing between the self and the world, allowing individuals to have a sense of agency and control over the dream environment. The interplay between the prefrontal cortex and the TPJ contributes to the enhanced self-awareness experienced during lucid dreaming.
Studies have indicated that the parietal cortex and the occipito-temporal cortex also play a role in the seamless interplay during lucid dreaming. The parietal cortex is responsible for spatial awareness, while the occipito-temporal cortex is involved in processing visual information. The coordination between these regions allows for the creation and visualization of vivid dream scenarios, enhancing the immersive nature of the lucid dreaming experience.
The hippocampus and the amygdala are two additional brain regions that contribute to the seamless interplay during lucid dreaming. The hippocampus, known for its role in memory consolidation, helps in the integration of past experiences, creating a coherent narrative within the dream. The amygdala, involved in emotion regulation, influences the emotional content and intensity of the dream.
The seamless interplay between these various brain regions during lucid dreaming showcases the complexity and intricacy of the neural processes involved in this phenomenon. By unraveling the mechanisms behind this interplay, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the neuroscience of lucid dreaming and how it relates to the wider functioning of the brain.
Enhanced Self-Awareness and Metacognition
One of the remarkable aspects of lucid dreaming is the heightened level of self-awareness and metacognition that individuals experience within their dreams. During a lucid dream, individuals have the ability to recognize that they are dreaming, which brings about a profound sense of self-realization. This enhanced self-awareness allows dreamers to actively engage in self-reflection and introspection, exploring their thoughts, emotions, and actions within the dream world.
Metacognition, which refers to the awareness and understanding of one’s own thinking processes, is also enhanced during lucid dreaming. Dreamers are able to reflect on their mental state, analyze their decision-making, and consciously manipulate their thoughts and behaviors within the dream. This unique cognitive ability is a result of the increased activation of the pre-frontal cortex, the region responsible for executive functions such as self-awareness, decision-making, and metacognition.
During lucid dreaming, individuals can intentionally engage in tasks that require higher cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving or creative thinking. They can experiment with various scenarios, test out different approaches, and observe the outcomes of their actions, all within the boundaries of their lucid dream.
To understand the impact of enhanced self-awareness and metacognition during lucid dreaming, researchers have conducted studies using neuroimaging techniques. These studies have revealed that the pre-frontal cortex, along with other regions involved in self-reflection and introspection, exhibit increased neural activity during lucid dreaming. This heightened activation contributes to the heightened sense of self-awareness and metacognition experienced by individuals.
Lucid dreaming provides a unique opportunity for individuals to explore and enhance their self-awareness and metacognition. With the ability to recognize and manipulate their dreams, dreamers can engage in introspection, problem-solving, and creative thinking within the confines of their dreaming mind. This phenomenon offers a fascinating window into the depths of human consciousness and highlights the intricate neurological processes that govern our dreaming experiences.
Neurochemical Modulation During Lucid Dreaming
During the state of lucid dreaming, the brain undergoes fascinating neurochemical modulation that contributes to the unique qualities of this phenomenon. Neurochemicals, such as dopamine and acetylcholine, play a crucial role in shaping the experience of lucid dreaming. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with reward and motivation, has been found to have an impact on the occurrence and intensity of lucid dreams. Research suggests that increased levels of dopamine in the brain can enhance the clarity and vividness of dreams, making them more likely to be experienced as lucid dreams. On the other hand, acetylcholine, another neurotransmitter involved in REM sleep and dreaming, is believed to play a role in maintaining the state of lucidity during dreaming. Studies have shown that higher acetylcholine levels are associated with increased self-awareness and control within dreams. The interplay between these neurochemicals, along with other factors such as the activation of the pre-frontal cortex, contributes to the unique and immersive experience of lucid dreaming. By understanding the neurochemical modulation during lucid dreaming, researchers are uncovering the intricate mechanisms of the brain that allow for this extraordinary phenomenon to occur.
Methods to Induce Lucid Dreams
Methods to induce lucid dreams have been developed and refined over the years, offering individuals a variety of techniques to enhance their chances of experiencing this unique state of consciousness. These methods can be employed by both avid dreamers and those new to the concept of lucid dreaming. One popular technique is reality testing. This involves regularly questioning one’s waking reality by performing reality checks throughout the day, such as asking, “Am I dreaming?” and performing simple actions like trying to push a finger through the palm of the opposite hand. By habitually carrying out reality tests, individuals increase their awareness and may carry this habit into their dreams, leading to critical self-reflection and eventually lucidity within the dream state. Another method is the wake-back-to-bed technique. This involves waking up after a few hours of sleep, staying awake for a short period, and then returning to sleep with the intention of entering a lucid dream. This practice takes advantage of the higher likelihood of entering the REM stage, where dreams occur. Additionally, there are lucid dreaming supplements available that can potentially increase the chances of having lucid dreams. Substances such as galantamine and choline have been reported to enhance dream vividness and recall, promoting the occurrence of lucidity. It is worth noting that while these methods have proven effective for many individuals, results vary, and consistent practice is paramount. By incorporating these techniques into one’s routine, individuals can increase their potential to experience the extraordinary world of lucid dreaming.
Reality Testing
Reality testing is a fundamental technique used to induce and enhance lucid dreaming experiences. Reality testing involves regularly questioning the nature of reality during waking hours, with the hope that this habit will carry over into the dream state. This technique takes advantage of a common phenomenon in dreams where the dreamer accepts the dream world as real without question. By performing reality checks throughout the day, such as looking at a clock or reading text multiple times, individuals train their minds to be more aware of their surroundings and question whether they are in a dream. This practice creates a habit that can carry over into dreams, leading to increased chances of becoming lucid. The theory behind reality testing is that by consistently questioning reality during wakefulness, the habit will transfer to the dream state, prompting individuals to question the authenticity of their dreams. This heightened awareness can trigger the realization that one is in a dream, unlocking the ability to become lucid and consciously navigate the dream world. Additionally, reality testing helps individuals identify dream signs, which are recurring themes or elements that frequently appear in their dreams. By recognizing these dream signs, individuals can further enhance their ability to achieve lucidity and take control of their dreams. So, if you’re looking to delve into the fascinating realm of lucid dreaming, incorporating reality testing into your daily routine is a crucial step toward unlocking the mysteries of the dreaming mind.
Wake-Back-to-Bed Technique
The Wake-Back-to-Bed (WBTB) technique is a popular method used to induce lucid dreams. It involves setting an alarm to wake up during the later part of the sleep cycle, typically around 4-6 hours after falling asleep. After waking up, individuals stay awake for a short period, usually around 15-30 minutes, before returning to bed with the intention of entering a lucid dream state.
The Wake-Back-to-Bed technique capitalizes on the natural sleep cycle and the increased likelihood of entering a REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep stage during the later part of the night. By disrupting sleep and then returning to bed, individuals can take advantage of this REM rebound effect and increase the chances of experiencing a lucid dream.
During the brief period of wakefulness, individuals can engage in activities that promote wakeful awareness and focus. This can include reading about lucid dreaming, journaling dreams, or practicing reality-testing techniques. Reality-testing involves questioning the nature of reality throughout the day, and this habit can carry over into dreams, enhancing the chances of becoming lucid.
The Wake-Back-to-Bed technique can be combined with other methods, such as using lucid dreaming supplements, to further enhance the likelihood of having a lucid dream. It is important to note that consistency and practice are key when using this technique, as it may take time for individuals to become proficient at inducing lucid dreams through this method.
The Wake-Back-to-Bed technique is a strategy used to increase the probability of experiencing lucid dreams. By waking up during the later part of the sleep cycle and staying awake for a short period before returning to bed, individuals can take advantage of the REM rebound effect and enhance their chances of entering a lucid dream state. Combining this technique with other practices, such as reality-testing, can further enhance the effectiveness of inducing lucid dreams.
Lucid Dreaming Supplements
When it comes to exploring methods to induce lucid dreams, lucid dreaming supplements have gained attention in recent years. These supplements are designed to enhance dream recall, promote vivid dreams, and increase the chances of experiencing lucidity. While scientific research on these supplements is limited, anecdotal reports from individuals who have used them suggest promising results. One popular supplement is Galantamine, a natural extract that acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, increasing the levels of acetylcholine in the brain. Acetylcholine plays a crucial role in promoting REM sleep and may enhance the likelihood of lucid dreaming. Another supplement is 5-HTP, a precursor to serotonin that is involved in regulating sleep patterns. Some users claim that taking 5-HTP before bed enhances dream vividness and recall. Melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep and wakefulness, is also popular among lucid dreaming enthusiasts. It can be taken as a supplement to promote better sleep and potentially increase the chances of having lucid dreams. It is important to note that while these supplements may have potential benefits for lucid dreaming, they should be used responsibly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. As with any supplement or substance, individual experiences may vary, and it is essential to prioritize overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lucid dreaming provides a fascinating glimpse into the inner workings of the human mind and consciousness. Through the exploration of the neurological processes involved in lucid dreaming, we have discovered the significant role of the pre-frontal cortex, the connection to REM sleep, and the influence of neurotransmitters like dopamine and acetylcholine. The increased activation of the pre-frontal cortex during lucid dreaming allows for enhanced self-awareness and metacognition, leading to a seamless interplay between different brain regions. Neurochemical modulation further contributes to the unique experience of lucid dreaming. These findings have not only deepened our understanding of the science behind lucid dreaming but also opened doors to potential methods to induce and enhance lucid dreaming experiences. Techniques such as reality testing and the wake-back-to-bed method have shown promise in increasing the likelihood of experiencing lucid dreams. Additionally, various supplements may aid in promoting lucid dreaming by modulating neurotransmitter levels in the brain. As our understanding of lucid dreaming continues to evolve, it offers exciting prospects for personal growth, creative exploration, and even potential therapeutic applications. Lucid dreaming truly showcases the incredible capabilities of our complex brain and invites us to further delve into the realm of the dreaming mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
How common is lucid dreaming?
The prevalence of lucid dreaming varies among individuals, but studies suggest that about 55% of people have experienced at least one lucid dream in their lifetime.
Can anyone learn to have lucid dreams?
Yes, with practice and techniques, most individuals can learn to have lucid dreams. It requires consistent effort and dedication to develop the ability to become aware within dreams.
Are there any benefits to lucid dreaming?
Absolutely! Lucid dreaming offers a range of benefits. It can be used for creative problem-solving, overcoming fears and phobias, practicing skills, and exploring one’s imagination and inner world.
Does lucid dreaming affect sleep quality?
Lucid dreaming does not generally affect overall sleep quality. However, individuals who frequently have intense lucid dreams may experience increased levels of mental arousal, which can affect sleep patterns.
Are there any risks associated with lucid dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is considered safe for most individuals. However, some people may experience sleep disruptions or have difficulty distinguishing between dreams and reality, which can lead to confusion.
Can lucid dreaming be used to treat nightmares?
Yes, lucid dreaming can be a valuable tool for managing nightmares. By becoming aware within a dream, individuals can consciously change the dream scenario, confront their fears, and gain control over the outcome.
Can lucid dreaming be used to enhance creativity?
Absolutely! Lucid dreaming provides a platform for exploring and harnessing creativity. Individuals can engage in artistic pursuits within their dreams, generate new ideas, and gain inspiration for various creative endeavors.
What is the relationship between lucid dreaming and astral projection?
Astral projection is a debated and controversial concept. Some individuals believe that lucid dreaming and astral projection are related, while others see them as distinct experiences. While lucid dreaming involves being aware within a dream, astral projection is believed to involve an out-of-body experience.
Can lucid dreaming be induced naturally without techniques?
While some individuals may experience spontaneous lucid dreams without any techniques, most people benefit from practicing specific techniques and exercises to increase their likelihood of having lucid dreams.
Are there any supplements that can aid in lucid dreaming?
There are certain supplements that are believed to enhance the likelihood of having lucid dreams. Some popular ones include vitamin B6, galantamine, and melatonin. However, it is important to research and consult with a healthcare professional before trying any supplements.