Imagine a world where you can explore vibrant landscapes, soar through the sky, and even meet your favorite celebrities—all from the comfort of your own mind. This intriguing phenomenon, known as spontaneous lucid dreaming, has fascinated individuals for centuries. But did you know that sleep parasomnias, a group of sleep disorders characterized by abnormal movements, behaviors, and experiences during sleep, may play a role in unlocking the ability to experience these vivid and immersive dreams? In this article, we will dive into the intricate relationship between sleep parasomnias and spontaneous lucid dreaming, exploring the different types of parasomnias that can influence dream experiences, the science behind how lucid dreaming occurs, techniques to achieve spontaneous lucid dreams, and the potential benefits and risks that accompany this unique dream state. Get ready to unlock the secrets of the dream world!
What are Sleep Parasomnias?

Sleep parasomnias refer to a group of sleep disorders characterized by abnormal movements, behaviors, and experiences that occur during sleep. These disorders disrupt the normal sleep cycle and can affect individuals of all ages. Sleep parasomnias can involve a wide range of activities, including sleepwalking, sleep talking, nightmares, REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD), sleep-related eating disorder (SRED), sleep paralysis, and even exploding head syndrome (EHS).
Sleepwalking, also known as somnambulism, is a common sleep parasomnia where individuals engage in complex behaviors while asleep. They may walk, talk, or even perform activities that are normally associated with wakefulness, all while in a sleep state. Sleep talking, on the other hand, involves talking or mumbling during sleep, often without the individual’s awareness.
Nightmares are intense and vivid dreams that cause feelings of fear, terror, or anxiety and can often awaken the individual from sleep. REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) is a parasomnia characterized by the acting out of dreams during the REM (rapid eye movement) stage of sleep, resulting in vocalizations, limb movements, and even potentially aggressive behaviors.
Sleep-related eating disorder (SRED) involves recurrent episodes of eating or drinking during sleep without the person’s awareness. This disorder can lead to nocturnal eating binges and even potential safety risks due to the consumption of inappropriate or harmful foods.
Sleep paralysis is a temporary inability to move or speak while falling asleep or upon awakening. This unsettling experience is often accompanied by vivid hallucinations and can be quite distressing for those who experience it.
Exploding head syndrome (EHS) is a sleep disorder characterized by the perception of loud noises, such as explosions or thunderclaps, during sleep onset or upon awakening. These noises are entirely imaginary and do not have an external source.
Understanding these various sleep parasomnias is crucial in exploring their potential connection to /aromatherapy-lucid-dreaming/ spontaneous lucid dreaming. By delving into the science behind sleep disorders and their impact on the dream state, we can unlock the secrets of the dream world and harness the power of lucid dreaming.
The Phenomenon of Lucid Dreaming

The phenomenon of lucid dreaming is a fascinating experience where individuals become aware that they are dreaming while still in the dream state. Unlike regular dreams, which often feel fleeting and uncontrollable, lucid dreams empower individuals with the ability to actively participate and manipulate their dream environment. This heightened state of awareness allows individuals to influence the narrative, characters, and even the laws of physics within their dreams.
During a lucid dream, individuals may find themselves flying, exploring fantastical landscapes, engaging in conversations with dream characters, or even testing their own limits and abilities. Lucid dreaming offers a unique opportunity to tap into the boundless potential of the subconscious mind and create extraordinary experiences that go beyond the limitations of reality.
The /the-science-behind-lucid-dreams/ science behind lucid dreaming is still a subject of ongoing research. However, it is believed that lucidity in dreams occurs when the prefrontal cortex, the area of the brain responsible for logic, decision-making, and self-awareness, becomes activated during the dream state. This activation allows individuals to recognize the dream as a construct of their own mind and gain control over their actions within the dream.
Achieving lucid dreaming can be a transformative experience for individuals, offering opportunities for personal growth, creativity, and even self-exploration. It can provide a platform for overcoming fears, practicing new skills, and indulging in fantasies that may not be possible in waking life.
While there are different techniques that can be employed to induce lucid dreams, such as reality checks, dream journaling, and meditation, the quest for lucidity often begins with improving general sleep quality and exploring the impact of various factors, such as /exploring-diet-lucid-dreaming/ diet and sleep patterns, on dream experiences. Understanding the mechanisms behind lucid dreaming and how it connects to sleep parasomnias can shed light on the potential interplay between these two phenomena, encouraging individuals to further explore and harness the power of their dream world.
The Relationship between Sleep Parasomnias and Lucid Dreaming
The relationship between sleep parasomnias and spontaneous lucid dreaming is a complex and intriguing one. While sleep parasomnias are typically considered disruptive and unwanted sleep disturbances, they can also provide a gateway to experiencing lucid dreams. Lucid dreaming is a phenomenon where the dreamer becomes aware that they are dreaming while still in the dream state. This awareness allows individuals to actively participate in and manipulate their dreams, giving them a sense of control and freedom within the dream world.
Studies have suggested that individuals with sleep disorders, such as sleepwalking, sleep talking, or nightmares, may have a higher propensity for experiencing spontaneous lucid dreams. The disrupted sleep patterns and unusual brain activity associated with these parasomnias may create a fertile environment for the occurrence of lucid dreams. Additionally, the vivid and often intense nature of sleep parasomnias may serve as a catalyst for triggering lucidity within the dream state.
It is important to note that not all individuals with sleep parasomnias will necessarily experience spontaneous lucid dreaming. Lucid dreaming is a highly individualized phenomenon, and its occurrence cannot be guaranteed. However, recognizing the potential correlation between sleep disorders and lucid dreaming opens up avenues for further research and exploration in the field of dream science.
By studying the relationship between sleep parasomnias and lucid dreaming, researchers hope to gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind these experiences. This knowledge can then be used to develop techniques and interventions to enhance dream control and improve the quality of sleep for individuals with sleep disorders. So, while sleep parasomnias may present challenges and disruptions in daily life, they also offer an intriguing window into the realm of lucid dreaming.
Types of Sleep Parasomnias Influencing Lucid Dreaming

Various types of sleep parasomnias can have an influence on spontaneous lucid dreaming. One such type is sleepwalking, where individuals engage in complex behaviors while asleep, potentially creating opportunities for lucidity within the dream state. Sleep talking, another sleep parasomnia, can also contribute to the occurrence of lucid dreams. Nightmares, which are intense and vivid dreams, can evoke a sense of fear, leading individuals to question the reality of their dreams and potentially triggering lucidity. REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD), characterized by the acting out of dreams during REM sleep, can provide opportunities for individuals to become aware that they are dreaming and exercise control over their dream experiences. Sleep-related eating disorder (SRED), sleep paralysis, and even the intriguing exploding head syndrome (EHS) may also play a role in facilitating or influencing spontaneous lucid dreaming. By understanding the different types of sleep parasomnias and their potential impact on dream experiences, individuals may be able to explore and enhance their ability to achieve lucidity in their dreams.
1. Sleepwalking
Sleepwalking, also known as somnambulism, is a fascinating sleep parasomnia characterized by complex behaviors during sleep. Here are some key points to understand about sleepwalking:
– Sleepwalking is more common in children, but it can also occur in adults.
– It usually happens during the deep stages of sleep, particularly during non-REM sleep.
– Sleepwalkers may engage in a variety of activities while asleep, such as walking, sitting up in bed, or even leaving the house.
– They typically have a blank expression, glassy eyes, and may be unresponsive to their environment.
– Episodes of sleepwalking can vary in duration, ranging from a few minutes to an hour or more.
– Sleepwalkers may perform routine activities, mix up words, or even speak gibberish.
– It is important to create a safe sleeping environment for sleepwalkers to prevent potential injuries.
– Sleep deprivation, stress, certain medications, and sleep disorders like sleep apnea can increase the likelihood of sleepwalking.
– Most sleepwalkers do not have any recollection of their sleepwalking episodes.
It is important to differentiate sleepwalking from other sleep disorders and seek professional medical advice if sleepwalking episodes are frequent, causing injuries, or interfering with daily life. Understanding sleepwalking and its connection to the phenomenon of spontaneous lucid dreaming can provide helpful insights into exploring the dream world and harnessing the power of conscious dreaming.
2. Sleep Talking
Sleep talking, also known as somniloquy, is a fascinating sleep parasomnia that involves talking or mumbling during sleep. This phenomenon typically occurs during non-REM sleep stages, particularly during the deeper stages of sleep. Sleep talking can range from simple and incoherent mumbling to full conversations and coherent sentences.
Symptoms: Sleep talking can vary in intensity and frequency among individuals. Some may experience occasional episodes, while others may talk in their sleep regularly. The content of sleep talking can also vary widely, ranging from random words and phrases to complete conversations that may or may not make sense.
Causes: The exact cause of sleep talking is not fully understood, but various factors have been associated with this sleep parasomnia. Stress, anxiety, sleep deprivation, certain medications, alcohol consumption, fever, and underlying sleep disorders such as sleep apnea and insomnia can contribute to sleep talking.
Impact: Sleep talking is usually harmless and rarely requires treatment. However, it can be disruptive to the sleep of both the person talking in their sleep and their sleeping partner. It is important to note that sleep talking is involuntary and that the individual is often unaware of their actions.
Tips for Managing Sleep Talking: While sleep talking may not be something you can completely control, there are some strategies that may help manage its impact:
1. Create a conducive sleep environment: Ensure your sleep environment is comfortable, quiet, and free from distractions to promote better sleep quality.
2. Establish a consistent sleep routine: Stick to a regular sleep schedule to encourage a more stable sleep pattern.
3. Manage stress: Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, to help reduce stress and anxiety levels before bed.
4. Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid potential triggers such as alcohol, caffeine, and certain medications that may contribute to sleep talking.
5. Consider seeing a sleep specialist: If sleep talking significantly impacts your quality of sleep or persists despite lifestyle changes, consulting a sleep specialist may be beneficial.
It’s interesting to note that individuals who experience sleep talking may also have a higher likelihood of experiencing /the-science-behind-lucid-dreams/ spontaneous lucid dreams. The relationship between sleep talking and lucid dreaming is still being explored, but further research may shed light on the connection between these two intriguing sleep phenomena.
3. Nightmares
Nightmares, one of the sleep parasomnias, are intense and vivid dreams that evoke feelings of fear, terror, or anxiety. They can occur during any stage of sleep, but they are most commonly associated with REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. Nightmares can be distressing and can often lead to disrupted sleep and difficulty in returning to sleep after awakening. These unsettling dreams may involve scenarios or themes that are threatening, dangerous, or traumatic.
Nightmares can vary in content and intensity, ranging from simple situations that evoke mild anxiety to elaborate scenarios that cause extreme fear and distress. Common themes in nightmares include being chased or attacked, experiencing a life-threatening situation, falling from great heights, or being trapped in a helpless situation. The emotions and sensations felt during nightmares may be so vivid that they can seem real, causing individuals to wake up in a state of panic or distress.
One theory suggests that nightmares may serve an evolutionary purpose by simulating potential threats and helping individuals prepare for challenging or dangerous situations in real life. Nightmares can act as a form of rehearsal, allowing the dreamer to practice responding to and coping with fear-inducing experiences. However, when nightmares become frequent or interfere with daily life, they can be indicative of an underlying psychological or emotional issue that may require professional assistance.
It is important to note that not all bad dreams can be classified as nightmares. Nightmares are typically more intense, causing significant distress upon awakening. If you are frequently experiencing distressing nightmares that disrupt your sleep or interfere with your quality of life, it may be beneficial to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or sleep specialist who can provide strategies and therapies to manage and reduce the frequency of nightmares.
By understanding the nature and characteristics of nightmares as a sleep parasomnia, we can better grasp their potential impact on the experience of spontaneous lucid dreaming. The relationship between nightmares and lucid dreaming is complex, as nightmares can both hinder and facilitate the occurrence of lucidity within dreams. Further exploration of this connection can provide valuable insights into how individuals can navigate and harness the power of their dreams.
4. REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD)
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD) is a sleep parasomnia that involves the acting out of dreams during the REM (rapid eye movement) stage of sleep. Typically, during REM sleep, our voluntary muscles are temporarily paralyzed, preventing us from physically acting out our dreams and potentially endangering ourselves or others. However, individuals with RBD do not experience this muscle paralysis, allowing them to physically manifest their dream content.
The symptoms of RBD can vary in severity and intensity. Some common signs include kicking, punching, shouting, or even jumping out of bed during sleep. These actions are a result of the individual physically acting out the events or actions taking place in their dreams.
RBD can pose risks not only to the individual experiencing it but also to their bed partner or those sharing the same sleeping environment. Due to the potential for injurious behaviors during sleep, it is important to create a safe sleep environment for individuals with RBD. This may involve padding the sleeping area with soft materials and removing any sharp or hazardous objects from the immediate vicinity.
The exact cause of RBD is not fully understood, but research suggests that neurological factors may play a role. RBD has been associated with certain neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. These disorders disrupt the normal functioning of the brain structures responsible for regulating sleep and muscle activity during REM sleep.
Diagnosing RBD often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, sleep studies, and medical history assessment. Treatments for RBD aim to reduce the frequency and intensity of the abnormal behaviors during sleep. Medications, such as clonazepam, may be prescribed to help suppress muscle activity during REM sleep and alleviate the symptoms of RBD.
Understanding the relationship between RBD and /the-science-behind-lucid-dreams/ spontaneous lucid dreaming can shed light on the potential connections between sleep disorders and lucid dreaming experiences. Further research is needed to explore how RBD and other sleep parasomnias may influence the occurrence and control of lucid dreams.
5. Sleep-Related Eating Disorder (SRED)
Sleep-Related Eating Disorder (SRED) is a type of sleep parasomnia characterized by episodes of eating or drinking while asleep, typically during the night. Individuals with SRED often have no memory of these episodes and may only become aware of their behavior upon discovering food or drink remnants in their bed or waking up with unexplained weight gain.
This disorder can have various manifestations. Some individuals may consume large amounts of food during sleep, including unhealthy and unusual food choices, while others may engage in repetitive eating behaviors like binge eating. SRED is more common in individuals with a history of other sleep disorders, such as sleepwalking or sleep apnea, and is often associated with stress or anxiety.
The exact causes of SRED are still not fully understood, but some factors that may contribute to its development include genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, and certain medications. Additionally, sleep deprivation and certain lifestyle factors, such as irregular sleep patterns or excessive alcohol consumption, can increase the likelihood of experiencing SRED episodes.
Managing SRED typically involves a multidisciplinary approach. A thorough evaluation by a sleep specialist is crucial to diagnose the disorder and rule out other sleep-related conditions. Treatment may include addressing any underlying sleep disorders, making lifestyle modifications to improve sleep hygiene, and implementing behavioral interventions to minimize nighttime eating behaviors. In some cases, medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or hypnotics may be prescribed to help regulate sleep and reduce the frequency of SRED episodes.
It is important for individuals with SRED to create a sleep-friendly environment by removing any easily accessible food from the bedroom and taking precautions to ensure their safety during sleep. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, such as sleep specialists, dietitians, or therapists, can also be beneficial in managing SRED and addressing any underlying psychological factors.
By understanding the complexities of sleep-related eating disorder and its impact on sleep and overall well-being, individuals can take steps towards better managing their condition and improving the quality of their sleep and overall health.
6. Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis is a fascinating sleep parasomnia that affects many individuals around the world. During sleep paralysis, a person is temporarily unable to move their body or speak, typically occurring when falling asleep or upon waking up. This phenomenon is often accompanied by intense hallucinations, which can be visual, auditory, or tactile in nature. The exact cause of sleep paralysis is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to the disruption of the normal transition between sleep stages.
During an episode of sleep paralysis, individuals may experience a sense of pressure or heaviness on their chest, making it difficult to breathe. This can lead to feelings of panic or fear, as the person may be fully aware of their surroundings but unable to move or call for help. The hallucinations that occur during sleep paralysis can range from mild and subtle to vivid and terrifying. Some people report seeing shadowy figures, monsters, or even experiencing out-of-body sensations.
It is important to note that sleep paralysis is typically a harmless condition and is not considered to be a medical emergency. Episodes of sleep paralysis often resolve on their own within a few minutes, and they do not cause any long-term physical harm. However, the experience can be distressing and may disrupt an individual’s sleep patterns, leading to feelings of fatigue or daytime sleepiness.
To manage sleep paralysis and reduce the frequency of episodes, there are several strategies that can be helpful. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, practicing relaxation techniques before bed, and creating a comfortable sleep environment can all contribute to better sleep quality. Additionally, managing stress levels and avoiding substances that can interfere with sleep, such as caffeine and alcohol, may also be beneficial.
While sleep paralysis can be unsettling, it can also provide a unique opportunity for individuals to explore lucid dreaming techniques. Some people have successfully transitioned from sleep paralysis into lucid dreams by embracing the experience and using visualization or other mental techniques to navigate the dream state. This integration between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming offers a fascinating glimpse into the intricate relationship between sleep disorders and the unconscious mind, showcasing the vast potential of the human dream experience.
7. Exploding Head Syndrome (EHS)
Exploding Head Syndrome (EHS) is a fascinating and relatively uncommon sleep disorder that falls under the category of sleep parasomnias. Despite its alarming name, EHS does not involve any actual explosions or physical harm. Instead, individuals with EHS experience loud and sudden auditory sensations, such as explosions, gunshots, or thunderclaps, either as they are falling asleep or upon waking up.
During these episodes, individuals may feel a sense of intense fear or anxiety, although physical pain is not associated with EHS. The auditory hallucinations are entirely subjective and do not have an external source. They can be highly disruptive to the sleep-wake transition and may cause individuals to experience difficulty in falling asleep or fear going to sleep altogether.
While the exact cause of EHS remains unclear, researchers hypothesize that it may be related to /the-science-behind-lucid-dreams/ abnormalities in the brain’s auditory system. It has been suggested that the brain mistakenly amplifies internal neural activity meant to occur during sleep, resulting in the perception of loud noises. Factors such as stress, sleep deprivation, and changes in sleep patterns may contribute to the occurrence of EHS episodes.
It is important to note that individuals experiencing EHS should seek medical evaluation to rule out any underlying medical conditions or medications that could be contributing to the symptoms. Although EHS can be disruptive and distressing, it is generally considered a benign condition and does not cause long-term harm.
As we continue to explore the relationship between sleep parasomnias and spontaneous lucid dreaming, understanding the unique experiences associated with EHS provides valuable insight into the intricate world of sleep disorders and their potential impact on dream states.
The Science Behind Spontaneous Lucid Dreaming
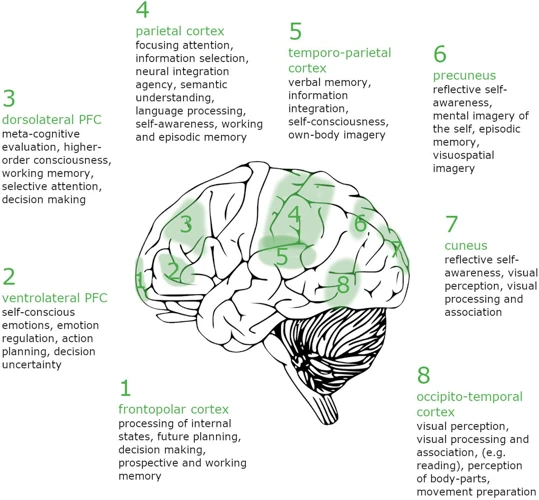
Spontaneous lucid dreaming is a fascinating phenomenon that occurs when a person becomes aware that they are dreaming while still within the dream itself. The science behind spontaneous lucid dreaming revolves around the understanding of different brain states during sleep.
During sleep, our brain goes through various stages, including non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Lucid dreaming primarily occurs during REM sleep, which is associated with increased brain activity, vivid dreams, and muscle atonia (temporary paralysis).
Neuroscientific research suggests that spontaneous lucid dreaming is linked to increased activation in regions of the brain associated with self-awareness, such as the prefrontal cortex. This activation allows individuals to recognize the dream state and gain control over their actions and decisions within the dream.
One theory proposes that spontaneous lucid dreaming may be facilitated by an optimal balance between two neurotransmitters: acetylcholine and dopamine. Acetylcholine is involved in REM sleep, while dopamine is associated with reward and motivation. The interplay between these neurotransmitters may contribute to the ability to recognize and manipulate the dream world.
Other factors that may influence the likelihood of spontaneous lucid dreaming include sleep quality, dream recall abilities, and overall psychological well-being. Improved sleep hygiene, regular dream journaling, and mindfulness practices can potentially enhance the chances of experiencing spontaneous lucid dreams.
Understanding the scientific mechanisms behind spontaneous lucid dreaming offers valuable insights into how to better navigate and control our dream experiences. By exploring the relationship between sleep parasomnias and lucid dreaming, we can further unravel the mysteries of the dream world and leverage this unique state of consciousness for personal growth and exploration.
Common Signs and Symptoms

Common signs and symptoms of sleep parasomnias can vary depending on the specific disorder. However, there are some general indicators that may suggest the presence of a parasomnia. One of the most noticeable signs is unusual behaviors or movements during sleep. For example, sleepwalking involves getting out of bed and walking around while still asleep, while sleep talking can manifest as talking, mumbling, or making nonsensical sounds during sleep.
Disrupted sleep patterns are also often observed in individuals with sleep parasomnias. These disruptions can range from frequent awakenings during the night to experiencing excessive daytime sleepiness. Nightmares, a type of parasomnia, can cause individuals to wake up suddenly and feel fearful, anxious, or unsettled.
Physical symptoms may also accompany certain parasomnias. In REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD), individuals may exhibit vigorous and often violent movements while acting out their dreams. Sleep paralysis, on the other hand, may lead to a temporary inability to move or speak upon awakening, along with the presence of hallucinations.
Lastly, emotional distress is common among individuals with sleep parasomnias. Sleep disorders can result in feelings of fear, stress, and embarrassment. These emotional experiences can arise from the disruptive nature of parasomnias and the impact they have on daily life and overall well-being.
Recognizing these common signs and symptoms is essential for identifying the presence of sleep parasomnias and seeking appropriate treatment. By understanding the manifestation of these disorders, individuals can take steps towards managing their symptoms and improving the quality of their sleep and overall health.
Techniques to Achieve Spontaneous Lucid Dreaming

Spontaneous lucid dreaming, the ability to become aware and conscious within a dream, can be an awe-inspiring experience. While it may seem like a purely random occurrence, there are techniques and practices that can increase the likelihood of experiencing spontaneous lucid dreams. Here are some effective techniques to achieve this unique dream state:
1. Reality Checks: Perform reality checks throughout the day to question whether you are dreaming or awake. This habit will carry over into your dreams, increasing the chances of recognizing when you are dreaming. Some common reality checks include trying to push your finger through your palm or looking at a digital clock and then looking away and back again to see if the numbers change.
2. Keep a Dream Journal: Keep a journal by your bedside and record your dreams immediately upon waking up. This practice helps improve dream recall and makes it easier to recognize dream patterns, themes, and signs of being in a dream state.
3. Meditation: Regular meditation can enhance self-awareness and mental clarity, which are beneficial for lucid dreaming. Meditation can also help improve focus and relaxation, creating an optimal state of mind for entering the dream world with lucidity.
4. Wake-Back-to-Bed (WBTB) Technique: Set an alarm to wake yourself up after about 4-6 hours of sleep. Stay awake for a short period and engage in activities like reading about lucid dreaming, practicing relaxation techniques, or doing light stretching. Then, go back to sleep with the intention of lucid dreaming. This technique capitalizes on the brain’s increased propensity for entering the REM sleep stage during the later stages of sleep, increasing the chances of experiencing lucidity.
5. Wake-Induced Lucid Dreaming (WILD): This technique involves staying consciously aware while transitioning from wakefulness to a dream state. It requires focus, relaxation, and the ability to maintain awareness as the body falls asleep. WILD is a more advanced technique and may require practice and patience to master.
Remember that achieving spontaneous lucid dreaming requires persistence and dedication. It’s essential to experiment with different techniques and find what works best for you. With practice and a willingness to explore the depths of your dreams, you can unlock the powerful potential of spontaneous lucidity.
How Sleep Parasomnias Can Facilitate Spontaneous Lucid Dreaming
Sleep parasomnias can actually facilitate the occurrence of spontaneous lucid dreaming. Lucid dreaming is a phenomenon where the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming while still immersed in the dream itself. This heightened state of consciousness allows individuals to actively participate and manipulate the dream experience.
One of the ways sleep parasomnias can contribute to spontaneous lucid dreaming is through the disruption of the normal sleep cycle. Sleep disorders like sleepwalking and sleep talking can serve as potential triggers for lucidity. When individuals experience these parasomnias, their sleep patterns are often altered, resulting in sleep fragmentation or disruption. These disruptions can increase the chances of becoming partially awake during the dream state, thus providing an opportunity for lucidity to occur.
Certain sleep disorders, such as RBD and sleep paralysis, can directly influence the content and vividness of dreams. In the case of RBD, where individuals physically act out their dreams, the intense and realistic experiences can trigger lucid awareness. Similarly, sleep paralysis, with its hallucinatory nature, can create a sense of familiarity and abnormality within dreams, leading to the realization that one is dreaming.
Additionally, the fear and anxiety associated with nightmares can act as a catalyst for achieving lucidity. Nightmares often evoke strong emotional reactions, prompting individuals to question the reality of the dream and potentially realize that they are dreaming. This realization can then allow them to take control and transform the nightmare into a more positive or empowering experience.
While sleep parasomnias may initially seem disruptive or undesirable, they can actually serve as gateways to spontaneous lucid dreaming. By understanding and embracing the potential connection between sleep disorders and lucidity, individuals can learn to use sleep parasomnias as opportunities to unlock the power of their dreams and explore the limitless possibilities of the dream world.
Benefits and Potential Risks of Lucid Dreaming

Lucid dreaming, the ability to be aware and in control within a dream, offers a myriad of benefits that can enhance our waking life. One of the primary advantages is the opportunity for self-exploration and personal growth. Lucid dreaming provides a platform to confront fears, practice new skills, and experiment with different scenarios in a safe and controlled environment. It can also boost creativity, as individuals can tap into a realm of limitless possibilities and imagination.
Beyond personal development, lucid dreaming can have practical applications. For example, it can be used to improve problem-solving abilities, as individuals can consciously work through challenges and generate innovative solutions in their dreams. Lucid dreaming has also been explored in therapy, where it can be utilized as a form of virtual reality exposure therapy for individuals with phobias, PTSD, and other mental health conditions.
However, while lucid dreaming has a host of benefits, it is important to acknowledge the potential risks that come with this practice. One possible risk is sleep disruption. Constantly focusing on lucid dreaming and attempting to control dreams can lead to fragmented sleep patterns and overall sleep disturbances. This can result in daytime drowsiness and decreased cognitive performance.
Another risk is the potential for confusion between dreams and reality. Spending too much time engrossed in lucid dreaming can blur the line between the dream world and waking life, making it difficult to differentiate between the two. This can lead to confusion, disorientation, and potential issues in functioning socially and professionally.
Lastly, some individuals may experience parasomnias during lucid dreaming. While not necessarily exclusive to lucid dreaming, sleep-related behaviors such as sleepwalking, sleep talking, or night terrors may manifest during these experiences, potentially causing harm or injury to oneself or others.
It is essential for anyone engaging in lucid dreaming to approach it with caution and moderation, maintaining a balance between dream exploration and maintaining a healthy sleep routine. By being aware of both the benefits and possible risks, individuals can make informed decisions and fully embrace the potential of lucid dreaming while prioritizing their overall well-being.
FAQs about Sleep Parasomnias and Spontaneous Lucid Dreaming
1. Can Sleep Parasomnias Cause Nightmares?
Sleep parasomnias, such as sleepwalking and REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD), can indeed lead to nightmares. During sleepwalking episodes, individuals may experience vivid and intense dreams that can be frightening or trigger feelings of fear and anxiety upon awakening. Similarly, RBD involves acting out dreams, which can sometimes involve nightmares. However, it is important to note that not all sleep parasomnias directly cause nightmares, and the frequency and intensity of nightmares may vary among individuals with these disorders.
2. Can Someone with Sleep Parasomnias Experience Spontaneous Lucid Dreaming?
Yes, individuals with sleep parasomnias can experience spontaneous lucid dreaming. In fact, the disruption of the normal sleep cycle caused by sleep parasomnias may increase the likelihood of entering a lucid dream state. Lucid dreaming involves being aware that you are dreaming while still in the dream, and it can occur naturally or be induced through various techniques. The unique experiences and altered states of consciousness associated with sleep disorders may provide fertile ground for the emergence of spontaneous lucid dreams.
3. Are Sleep Parasomnias Dangerous during Lucid Dreaming?
While sleep parasomnias themselves can present certain risks and challenges, they do not necessarily make lucid dreaming inherently dangerous. Sleepwalking, for example, can pose physical risks if the individual engages in potentially harmful activities while asleep. However, in the context of lucid dreaming, the dreamer has a greater level of consciousness and control, which can help mitigate potential dangers. It is important for individuals with sleep parasomnias to understand how their specific sleep disorder may impact their dream experiences and take appropriate precautions to ensure their safety.
4. Is Spontaneous Lucid Dreaming Controllable?
Spontaneous lucid dreaming, by its very nature, may occur without conscious effort or control. However, there are techniques and practices that can increase the likelihood of experiencing spontaneous lucid dreams. These include reality testing, keeping a dream journal, practicing mindfulness and meditation, and incorporating visualization exercises into one’s routine. While the timing and frequency of spontaneous lucid dreams may be unpredictable, these techniques can help individuals develop greater awareness and become more adept at recognizing and navigating the dream state.
5. How Can Sleep Parasomnias Be Managed for Better Dream Control?
Managing sleep parasomnias with the goal of enhancing dream control can involve various strategies. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, practicing good sleep hygiene, and creating a safe and comfortable sleep environment can help minimize sleep disruptions and promote overall sleep quality. Additionally, working with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist can provide valuable guidance and treatment options tailored to specific sleep disorders. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, medication, and relaxation exercises may be recommended to address sleep parasomnias and improve overall dream control.
Understanding the relationship between sleep parasomnias and spontaneous lucid dreaming can shed light on the fascinating connections between sleep disorders and the dream world. By exploring frequently asked questions in this regard, individuals can gain insights into the potential causes, risks, and management strategies associated with both sleep disorders and lucid dreaming.
1. Can Sleep Parasomnias Cause Nightmares?
The relationship between sleep parasomnias and nightmares is a complex one. While sleep parasomnias are a group of sleep disorders characterized by abnormal behaviors during sleep, nightmares are intense, disturbing dreams that can cause fear, anxiety, and even awaken the individual from sleep. Although sleep parasomnias themselves may not directly cause nightmares, they can potentially contribute to the occurrence or severity of nightmares.
Sleepwalking and sleep talking, which are common sleep parasomnias, may involve vocalizations or physically acting out dreams. In some cases, these dreams can be vivid, frightening, or distressing, leading to the experience of nightmares. The actions and behaviors during sleepwalking or sleep talking can mimic the content of these intense dreams, exacerbating the fear or anxiety associated with the nightmare.
Additionally, sleep-related eating disorder (SRED) can also indirectly contribute to the development of nightmares. Consuming certain foods, especially those that are high in sugar or contain caffeine, close to bedtime can disrupt sleep patterns and increase the likelihood of nightmares. SRED episodes involving the consumption of inappropriate or harmful foods may further disrupt the sleep cycle and potentially lead to nightmares.
It’s important to note that not all individuals with sleep parasomnias will experience nightmares, and not all nightmares are related to sleep parasomnias. Nightmares can occur independently due to various factors such as stress, trauma, medications, or other sleep disorders. It is crucial to evaluate each individual’s specific situation and symptoms when exploring the relationship between sleep parasomnias and nightmares.
2. Can Someone with Sleep Parasomnias Experience Spontaneous Lucid Dreaming?
When it comes to the intriguing world of dreams, one may wonder if individuals with sleep parasomnias have the potential to experience spontaneous lucid dreaming. Lucid dreaming is the ability to become aware that one is dreaming while the dream is occurring, allowing for a sense of control and conscious participation in the dream scenario. In the case of individuals with sleep parasomnias, the experience of spontaneous lucid dreaming can vary.
Can someone with sleep parasomnias experience spontaneous lucid dreaming? The answer is not straightforward. The occurrence of spontaneous lucid dreaming in individuals with sleep parasomnias can depend on the specific parasomnia and the individual’s ability to maintain awareness during sleep.
In some cases, individuals with sleep parasomnias such as sleepwalking or REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) may have fragmented or disrupted sleep that can make it challenging to reach the REM stage of sleep, where most vivid dreaming occurs. This fragmentation may decrease the likelihood of experiencing spontaneous lucid dreaming.
However, there are instances where individuals with sleep parasomnias have reported experiencing lucidity within their dreams. This can occur when an individual with a parasomnia becomes aware that they are dreaming during an episode, leading to a brief period of lucidity within the dream. For example, someone who experiences sleepwalking may suddenly become conscious that they are in a dream state while sleepwalking, allowing them to have some level of control over their actions within the dream.
It is important to note that while some individuals with sleep parasomnias may experience spontaneous lucid dreaming, others may not. The occurrence and frequency of lucid dreaming can vary greatly from person to person, and additional factors such as sleep quality, overall sleep hygiene, and individual dream recall abilities can also influence the likelihood of experiencing spontaneous lucid dreaming.
While individuals with sleep parasomnias may have a chance of experiencing spontaneous lucid dreaming, the relationship between these sleep disorders and lucid dreaming is complex and nuanced. Further research is needed to fully understand the potential connections between sleep parasomnias and the occurrence of spontaneous lucid dreaming.
3. Are Sleep Parasomnias Dangerous during Lucid Dreaming?
Sleep parasomnias, such as sleepwalking, nightmares, and sleep-related eating disorder (SRED), can potentially pose risks during lucid dreaming. While lucid dreaming itself is generally considered safe, the presence of sleep parasomnias can complicate the dream experience and increase the potential for injury or harm.
For example, individuals who experience sleepwalking during lucid dreams may engage in physical activities that they wouldn’t normally attempt while awake. This can lead to accidents or injuries, especially if the dream scenario involves dangerous situations or environments. Sleepwalkers may wander into harm’s way or interact with objects or obstacles that could cause harm.
Nightmares, although not inherently dangerous, can be distressing and emotionally taxing during lucid dreaming. Intense and terrifying dream scenarios can trigger feelings of fear and anxiety, potentially causing a negative impact on the individual’s psychological well-being.
Sleep-related eating disorder (SRED) can also be problematic during lucid dreaming. Individuals experiencing SRED may engage in uncontrolled eating or drinking behaviors while asleep. This can lead to potential health risks, such as consuming unhealthful or inappropriate food items, overeating, or injuring oneself while preparing or consuming food.
It’s important to note that the level of risk associated with sleep parasomnias during lucid dreaming can vary from person to person. Some individuals may not experience any significant dangers, while others may be more prone to accidents or negative emotional experiences. It is advisable for individuals who experience sleep parasomnias and engage in lucid dreaming to take necessary precautions or seek guidance from a medical professional or sleep specialist to mitigate potential risks.
Understanding the potential hazards of sleep parasomnias during lucid dreaming can help individuals make informed decisions and take appropriate measures to ensure their safety and well-being during these extraordinary dream experiences.
4. Is Spontaneous Lucid Dreaming Controllable?
Spontaneous lucid dreaming raises the question of whether it is controllable. Lucid dreaming itself is a state of consciousness where the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming and can sometimes exert varying degrees of control over the dream content and their actions within the dream. However, the spontaneous nature of lucid dreaming means that it occurs unexpectedly and without prior intention or effort on the part of the dreamer.
While spontaneous lucid dreaming may not be directly controllable, there are techniques and practices that individuals can employ to increase the likelihood of experiencing lucidity during their dreams. These techniques include reality checks, keeping dream journals, practicing mindfulness, and engaging in certain induction methods like the Wake Back to Bed (WBTB) technique.
Reality checks involve questioning and testing the reality of one’s surroundings throughout the day, which can carry over into dreams and promote lucidity when the dreamer notices discrepancies or inconsistencies. Keeping a dream journal helps in remembering dream content, identifying patterns, and increasing self-awareness within dreams.
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation, can enhance overall awareness and consciousness, potentially leading to greater awareness within dreams as well. Techniques like the Wake Back to Bed (WBTB) involve setting an alarm to wake up during the night, staying awake for a short period, and then returning to sleep with the intention of inducing lucid dreams during the subsequent REM sleep stage.
While spontaneous lucid dreaming may not be controllable in the moment, these techniques can facilitate a higher likelihood of experiencing lucidity during dreams. By cultivating a state of awareness and actively engaging in practices that promote self-awareness within dreams, individuals can begin to explore and interact with their dream landscapes in more profound and intentional ways.
5. How Can Sleep Parasomnias Be Managed for Better Dream Control?
There are several strategies that can be employed to manage sleep parasomnias and enhance dream control. Here are some techniques that may be helpful in achieving better control over dreams:
1. Improving Sleep Hygiene: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a calm and comfortable sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques can help improve overall sleep quality and reduce the occurrence of sleep parasomnias.
2. Managing Stress: Since stress can exacerbate sleep disorders, it is important to find ways to manage stress levels. Engaging in activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help promote relaxation and improve sleep.
3. Creating a Bedtime Routine: Establishing a regular bedtime routine can signal to the body that it is time to relax and prepare for sleep. This can include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing gentle stretching exercises.
4. Maintaining a Dream Journal: Keeping a dream journal can help increase self-awareness during sleep and make it easier to identify patterns or triggers that may be contributing to sleep parasomnias. By recording dreams regularly, individuals can become more attuned to their dream experiences and potentially gain more control over them.
5. Implementing Lucid Dreaming Techniques: Lucid dreaming techniques, such as reality checks, visualization exercises, and mnemonic induction of lucid dreams (MILD), can be employed to increase the likelihood of becoming lucid during sleep. Lucid dreaming allows individuals to recognize when they are dreaming and potentially exercise more control over their dream experiences, including managing sleep parasomnias.
6. Seeking Professional Help: If sleep parasomnias significantly affect an individual’s daily life, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist. They can provide personalized guidance and recommend interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) or medication options if necessary.
Remember that managing sleep parasomnias for better dream control may require patience and experimentation. What works for one person may not work for another, so it’s important to find the strategies that best suit individual needs. With persistence and proper management, individuals can potentially achieve more control over their dreams and minimize the disruptive effects of sleep parasomnias.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the relationship between sleep parasomnias and spontaneous lucid dreaming opens up a fascinating realm of exploration. Sleep parasomnias, such as sleepwalking, sleep talking, nightmares, RBD, SRED, sleep paralysis, and EHS, can influence and even facilitate the occurrence of spontaneous lucid dreams. Understanding the science behind how these sleep disorders disrupt the sleep cycle and impact dream experiences can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of lucid dreaming.
While sleep parasomnias can be disruptive and potentially distressing for individuals, they also present an opportunity for those interested in experiencing spontaneous lucidity in their dreams. Techniques such as reality testing, keeping dream journals, and practicing meditation can enhance the ability to achieve lucidity during sleep.
However, it’s important to approach lucid dreaming with caution. While there are potential benefits, such as self-exploration, creativity, and problem-solving, there are also risks associated with intense and vivid dream experiences. It is essential to prioritize sleep hygiene, consult with a healthcare professional if experiencing severe sleep disturbances, and ensure a safe sleep environment.
In summary, the exploration of sleep parasomnias and spontaneous lucid dreaming provides a gateway to understanding the complexities of the human mind during sleep. By delving into the science, techniques, and potential risks of lucid dreaming, individuals can embark on a journey of self-discovery and unlock the vast potential of their dream world. Sweet dreams await those who dare to delve into the depths of their unconscious mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
6. Can Lucid Dreaming Help Alleviate the Symptoms of Sleep Parasomnias?
While lucid dreaming cannot cure sleep parasomnias, it may offer some relief by providing a sense of control and empowerment over the dream experience. Engaging in lucid dreaming techniques can also promote a more restful sleep, potentially reducing the frequency or intensity of sleep disorder episodes.
7. Are There any Medications Available to Treat Sleep Parasomnias?
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage specific sleep parasomnias. However, the type of medication prescribed will depend on the specific sleep disorder and its underlying causes. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
8. Can Lucid Dreaming Improve Overall Sleep Quality?
Lucid dreaming itself does not directly improve overall sleep quality. However, techniques used to induce lucid dreams, such as meditation and relaxation exercises, can promote deeper relaxation and potentially enhance the quality and duration of sleep.
9. Can Sleep Paralysis Lead to Lucid Dreaming?
Sleep paralysis can sometimes serve as a gateway to lucid dreaming. During sleep paralysis, individuals may become aware of the dream state and can then potentially enter a lucid dreaming experience. However, it is important to note that not all instances of sleep paralysis will lead to lucid dreaming.
10. Are There any Natural Remedies to Manage Sleep Parasomnias?
While natural remedies may provide some relief, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper guidance. Some natural remedies that have been explored in managing sleep parasomnias include relaxation techniques, /aromatherapy-lucid-dreaming/, and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule.








