Trauma has a profound impact on our mental and emotional well-being, often leaving lasting scars that manifest in various ways. One such manifestation is recurring nightmares, which can be intensely distressing and disruptive to our daily lives. Understanding the relationship between past trauma and these haunting dreams is crucial for finding effective coping strategies. In this article, we will explore the role of past trauma in recurring nightmares, examining common types of trauma, how trauma manifests in nightmares, factors that influence their occurrence, the effects of recurring nightmares on well-being, and methods for coping with trauma-related nightmares. Discovering the connections between trauma and nightmares is a crucial step towards healing and restoring a sense of peace and tranquility in our lives.
The Relationship between Trauma and Nightmares
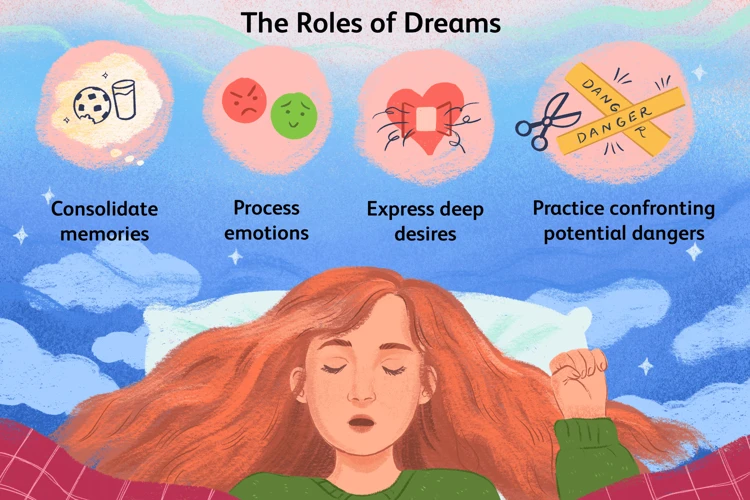
The Relationship between Trauma and Nightmares:
– Trauma and nightmares are closely intertwined, with traumatic experiences often leading to the occurrence of recurrent and distressing dreams during sleep. When individuals undergo trauma, it can leave a lasting impact on their psychological well-being, causing their mind to replay and process the distressing events during sleep. This link between trauma and nightmares can be attributed to various factors, such as the brain’s attempt to process and integrate the traumatic memories, as well as the emotional distress associated with the traumatic event.
– Research has shown that individuals who have experienced trauma are more likely to report nightmares compared to those who haven’t. Traumatic events can include a wide range of experiences, from physical or sexual abuse to accidents, natural disasters, or witnessing violent events. These events can deeply affect the individual’s sense of safety and security, initiating a cascade of emotional and psychological reactions that can manifest in the form of nightmares.
– Nightmares related to trauma often involve vivid, distressing, and realistic reenactments of the traumatic event(s). The content of these nightmares may vary depending on the type of trauma experienced, but common themes include threat to personal safety, helplessness, fear, and intense emotions associated with the traumatic event. These nightmares can be recurring, intrusive, and may disrupt sleep patterns, leading to further distress and impairment in daily functioning.
– It’s important to note that not everyone who experiences trauma will develop recurrent nightmares. The relationship between trauma and nightmares is complex, influenced by various factors such as individual resilience, coping mechanisms, and the presence of underlying mental health conditions like post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Understanding these factors is crucial in determining why some individuals are more prone to trauma-related nightmares than others. By addressing these underlying factors, individuals can work towards reducing the frequency and intensity of their nightmares, improving their overall well-being.
– The relationship between trauma and nightmares is not limited to a one-way causality. Nightmares can also act as a trigger for heightened anxiety, fear, and distress, impacting an individual’s daily life and exacerbating existing trauma-related symptoms. This bidirectional relationship between nightmares and trauma highlights the importance of addressing both aspects during therapy and developing comprehensive treatment strategies.
Related Resources:
– To learn more about the link between nightmares and sleep disorders, read our article: “Unraveling the Link Between Nightmares and Sleep Disorders”.
– Discover how nightmares can be associated with anxiety disorders in our comprehensive guide: “Nightmares and Anxiety Disorders: Exploring the Connection”.
– For a deeper understanding of the symbolism in nightmares, check out our article: “Exploring the Symbolism in Nightmares”.
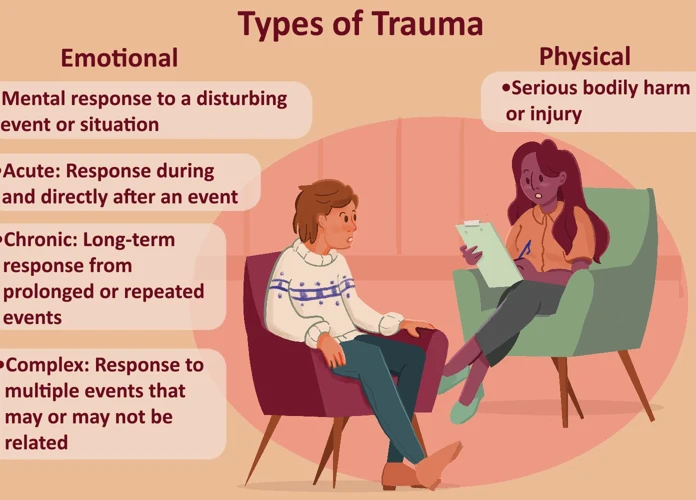
Common Types of Trauma Leading to Recurring Nightmares

Common Types of Trauma Leading to Recurring Nightmares:
Childhood Abuse: Childhood abuse, including physical, sexual, or emotional abuse, can have long-lasting effects on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being. Survivors of childhood abuse often experience recurring nightmares that depict the traumatic events, as their minds attempt to process and make sense of the distressing experiences they endured.
Accidents and Near-Death Experiences: Trauma resulting from accidents, such as car crashes or near-death experiences, can leave a lasting impact on an individual’s psyche. These traumatic events can trigger recurring nightmares, where the individual relives the fear, helplessness, and intense emotions associated with the accident or near-death experience.
War and Combat Trauma: Military personnel who have served in warzones or experienced combat often suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and recurrent nightmares. These nightmares can involve vivid and distressing depictions of the traumatic events witnessed or directly experienced during their time in service.
Natural Disasters: Survivors of natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, or floods, may develop recurring nightmares related to the event. These nightmares may involve the reliving of the chaos, fear, and devastation caused by the disaster, as the mind tries to process the traumatic experience.
Witnessing Violent Events: Individuals who have witnessed violent acts, such as assaults, robberies, or acts of terrorism, may experience recurring nightmares reflecting the traumatic events they witnessed. These nightmares can be highly distressing and may portray the intense fear, helplessness, and distress associated with the witnessed violence.
PTSD: Post-traumatic stress disorder is a common consequence of experiencing or witnessing trauma. Alongside other symptoms, individuals with PTSD often experience recurring nightmares related to the traumatic event(s) that trigger emotional distress and disrupt their sleep patterns.
It’s important to note that these are just some of the common types of trauma that can lead to recurring nightmares. Each individual’s experience of trauma is unique, and the specific content and themes of their nightmares may vary. Seeking professional help and support can provide valuable guidance and assistance to individuals struggling with trauma-related nightmares.
1. Childhood Abuse
1. Childhood Abuse:
Childhood abuse, whether it be physical, sexual, or emotional, can have a profound impact on an individual’s psychological well-being, often leading to recurring nightmares. The trauma experienced during childhood abuse can disrupt the development of a sense of safety and security, leaving lasting scars that can manifest in the form of nightmares later in life. These nightmares may involve vivid and distressing reenactments of the abusive events or symbolic representations of the fear, helplessness, and pain associated with the abuse.
The effects of childhood abuse on nightmares can be long-lasting, persisting well into adulthood if not addressed. The content of these nightmares can vary, but common themes include feelings of vulnerability, powerlessness, betrayal, and fear. Survivors of childhood abuse may also experience night terrors or sleep disturbances, further intensifying the impact on their sleep quality and overall well-being.
Childhood abuse-related nightmares can serve as a means for the subconscious mind to process and attempt to make sense of the traumatic experiences. These nightmares may continue until the underlying trauma is addressed and healing begins. Therapy, such as trauma-focused therapy, can help survivors of childhood abuse explore and process the trauma, working towards reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
It is important for individuals who have experienced childhood abuse to seek professional help to address the trauma and its impact on their mental health. By addressing the underlying trauma, survivors can work towards healing, improving their overall well-being, and reducing the occurrence of recurring nightmares.
Related Resources:
– To learn more about the effects of childhood abuse on mental health, check out our article: “The Lasting Effects of Childhood Abuse on Mental Health”.
– For information on how trauma-focused therapy can help survivors of childhood abuse, read our comprehensive guide: “Trauma-Focused Therapy for Childhood Abuse Survivors”.
2. Accidents and Near-Death Experiences
2. Accidents and Near-Death Experiences:
Accidents and near-death experiences can have a profound impact on an individual’s psyche, leading to the development of recurring nightmares. These traumatic events are often characterized by a sudden and unexpected threat to life, resulting in intense fear, helplessness, and a loss of control. The vivid and distressing nature of the experience can leave a lasting imprint on the individual’s subconscious mind, leading to the reemergence of the trauma during sleep.
Nightmares related to accidents and near-death experiences often involve vivid recollections of the traumatic incident. Individuals may find themselves reliving the event or being trapped in a recurring cycle of danger and desperation. They may experience intense emotions such as fear, panic, and a sense of impending doom. These nightmares can be accompanied by physical sensations like rapid heartbeat, sweating, and a feeling of being trapped or unable to escape.
The content of these nightmares may vary depending on the specifics of the accident or near-death experience. For example, someone who survived a car crash may have nightmares featuring graphic depictions of the collision, the sound of screeching tires, or the sight of mangled vehicles. Others who have experienced near-drowning incidents may have nightmares about being submerged underwater, gasping for air, or feeling trapped beneath the surface.
The occurrence and intensity of nightmares related to accidents and near-death experiences can be influenced by various factors. These include the individual’s proximity to death, the severity of the trauma, the presence of physical injuries, and the level of emotional distress associated with the event. Additionally, previous experiences with trauma or other psychological factors may contribute to the development of more intense and recurrent nightmares.
It’s crucial to recognize that these nightmares serve a purpose. They are the mind’s way of processing and attempting to make sense of the overwhelming and traumatic experience. Although they can be distressing, nightmares can also provide an opportunity for the individual to work through and cope with their feelings of fear and helplessness.
If individuals continue to experience nightmares related to accidents or near-death experiences, it may be beneficial to seek professional help. Therapists specializing in trauma can provide support, guidance, and specific techniques to address the underlying issues stemming from the trauma. Through therapy, individuals can learn healthy coping mechanisms, gain a greater understanding of their nightmares, and work towards reducing their frequency and intensity, ultimately improving their overall well-being.
By addressing the unresolved trauma and associated nightmares, individuals can begin the healing process, regain a sense of control, and work towards a peaceful and restorative sleep experience.
3. War and Combat Trauma
War and combat trauma is a specific type of trauma that can have a profound impact on the mental well-being of individuals and often contributes to recurring nightmares. The experiences of soldiers and individuals who have been involved in war or combat situations can be incredibly traumatic, leading to a range of psychological and emotional disturbances.
These traumatic events can include exposure to violence, witnessing the injury or death of comrades, the constant threat of harm, and the distressing nature of combat itself. The intensity of these experiences can deeply affect the individuals involved, causing deep-rooted psychological wounds that may manifest as recurring nightmares.
In the context of war and combat trauma, nightmares often involve vivid and realistic recreations of the traumatic events. These nightmares can be filled with the sounds, sights, and emotions experienced during combat, making them particularly distressing. They may feature themes such as being under attack, feeling helpless or unable to protect oneself, or being chased by enemy forces. The emotional intensity of the nightmare experience can be overwhelming, causing individuals to wake up feeling anxious, fearful, and emotionally drained.
For individuals who have experienced war and combat trauma, these nightmares can significantly impact their overall well-being. Nightmares can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to chronic sleep disturbances and sleep deprivation. This can result in daytime fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and impaired functioning in daily life. The ongoing presence of these nightmares can also contribute to the development or exacerbation of other mental health conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or anxiety disorders.
It is important to highlight that war and combat trauma affects individuals differently, and not everyone who has experienced these events will develop recurring nightmares. Factors such as individual resilience, coping mechanisms, and the presence of social support systems can all influence the likelihood and severity of nightmares following war and combat trauma.
Addressing war and combat trauma-related nightmares requires a multidimensional approach. Seeking professional help is crucial in the management and treatment of trauma-related nightmares. Therapies such as trauma-focused therapy and cognitive-behavioral techniques can aid in processing and integrating traumatic experiences, reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Additionally, relaxation and mindfulness techniques can promote better sleep hygiene, while creating a safe sleep environment can help individuals feel more secure and at ease during sleep.
War and combat trauma can leave a lasting impact on individuals, with recurring nightmares being a common manifestation of the psychological wounds inflicted. Understanding the specific challenges faced by those who have experienced war and combat trauma can guide efforts to provide effective support, treatment, and coping strategies for managing these nightmares and promoting overall well-being.
4. Natural Disasters
4. Natural Disasters:
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and tsunamis can have a profound impact on individuals who experience them. These traumatic events can lead to the development of recurring nightmares as the mind tries to process and make sense of the overwhelming emotions and fear associated with the disaster.
In the case of natural disasters, nightmares may include vivid and disturbing scenes related to the specific event. Survivors may find themselves reliving the moment of the disaster, witnessing the destruction and chaos unfold, or experiencing the fear and helplessness they felt during the event. The intensity of these nightmares can be magnified by the individual’s personal experiences, the loss of loved ones, or the loss of their home and belongings.
Recurring nightmares following natural disasters can be particularly distressing because they often act as reminders of the trauma and serve as a constant reactivation of the individual’s stress response. This can lead to increased feelings of anxiety, hypervigilance, and a sense of impending doom, even when the danger has passed. The combination of the traumatic event itself and the subsequent nightmares can create a cycle of fear and distress that can significantly impact an individual’s psychological well-being.
In addition to the nightmare content related specifically to the natural disaster, survivors may also experience other dream elements related to ongoing stressors and challenges in the aftermath of the event. These dreams may involve themes such as displacement, loss, rebuilding, and the uncertainty of the future. The emotional intensity of these dreams can make it difficult for individuals to find restful sleep, further exacerbating the negative impact on their overall well-being.
It’s important to recognize that the effects of natural disasters on mental health, including recurring nightmares, can vary from person to person. Factors such as preexisting mental health conditions, prior trauma history, available support systems, and individual resilience can all influence the frequency and intensity of nightmares experienced. Seeking professional help and support from therapists, counselors, or support groups is essential for survivors of natural disasters to address their trauma, process their emotions, and find effective coping mechanisms to alleviate the impact of recurring nightmares on their quality of life.
5. Witnessing Violent Events
Witnessing Violent Events:
Witnessing violent events can have a profound and lasting impact on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being, often leading to recurring nightmares. Whether it’s experiencing violence firsthand or witnessing it as a bystander, the psychological repercussions can be significant. The vivid and distressing nature of these events can leave a lasting impression on the individual’s subconscious mind, causing nightmares that reflect the intense emotions and fear associated with what they witnessed.
When someone witnesses a violent event, it can trigger a range of emotional responses, such as fear, helplessness, and shock. These emotions become deeply ingrained in their memory and can resurface during sleep in the form of nightmares. The content of these nightmares may involve vivid reenactments of the violent event, showcasing the individual’s fear, vulnerability, and the chaos they witnessed. The nightmares can also incorporate symbolic representations of the violence, allowing the mind to process and make sense of the traumatic experience.
It is important to note that the impact of witnessing violent events can vary from person to person. Factors such as the proximity to the event, the level of perceived threat, and the individual’s psychological resilience all play a role in determining the intensity and frequency of nightmares. While some individuals may experience recurring nightmares immediately following the event, others may develop them weeks or even months later as the mind continues to process and integrate the traumatic memories.
Apart from the direct witnessing of violent events, individuals can also experience nightmares as a result of exposure to violent media, such as movies or news footage. The graphic and disturbing nature of such content can leave a lasting impression on the individual’s mind, triggering nightmares that mirror the violence and distress depicted in the media.
Addressing the impact of witnessing violent events and related nightmares often requires a multifaceted approach. Therapy, particularly trauma-focused therapy, can be immensely beneficial in helping individuals process and cope with the emotional fallout of their experiences. Techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) can aid in managing the distressing memories and reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Additionally, creating a safe and calming sleep environment and implementing relaxation techniques before bed can promote better sleep and alleviate some of the anxiety associated with these nightmares.
Witnessing violent events can leave deep emotional scars, and the nightmares that accompany them can further compound the distress. However, with proper support, therapy, and coping strategies, individuals can gradually find healing and see a reduction in the frequency and intensity of these recurring nightmares.
6. PTSD
PTSD, or post-traumatic stress disorder, is a mental health condition that can have a significant influence on the occurrence of recurring nightmares. Individuals who have experienced a traumatic event, such as military combat, physical or sexual assault, or a life-threatening accident, may develop symptoms of PTSD. These symptoms can include intrusive memories, flashbacks, avoidance of triggers related to the trauma, and emotional numbness.
PTSD-related nightmares are a common symptom of this disorder and can be particularly distressing. These nightmares often involve vivid and realistic reexperiencing of the traumatic event(s), bringing back intense emotions and sensations. The content of these nightmares may closely mirror the details and themes of the original trauma, reflecting the individual’s fears, anxieties, and unresolved emotions.
It is important to note that not all individuals with PTSD experience nightmares, but they are more prevalent among this population compared to those without PTSD. Nightmares in individuals with PTSD may be triggered by reminders of the trauma, such as certain sounds, smells, or situations, and can contribute to a heightened sense of anxiety and hypervigilance.
The recurring nature of PTSD-related nightmares can further exacerbate the symptoms of this disorder. These nightmares can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to sleep deprivation and exhaustion, which in turn can worsen other PTSD symptoms. The exhaustion resulting from chronic nightmares can impact an individual’s overall well-being, affecting their ability to function in daily life and increasing their vulnerability to other mental health conditions like depression and anxiety disorders.
Treating PTSD and addressing its associated nightmares often involves a multidimensional approach. Therapy techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) may be employed to help individuals process and reframe their traumatic experiences. Additionally, medication management, relaxation techniques, and sleep hygiene practices can also be beneficial in managing PTSD-related nightmares.
Related Resources:
– To dive deeper into the topic of PTSD and its impact on mental health, read our comprehensive article: “PTSD and Mental Health: Untangling the Connections”.
– Discover how trauma-focused therapy can effectively address PTSD and associated nightmares in our dedicated guide: “Trauma-Focused Therapy for PTSD and Nightmares”.
How Trauma Manifests in Nightmares
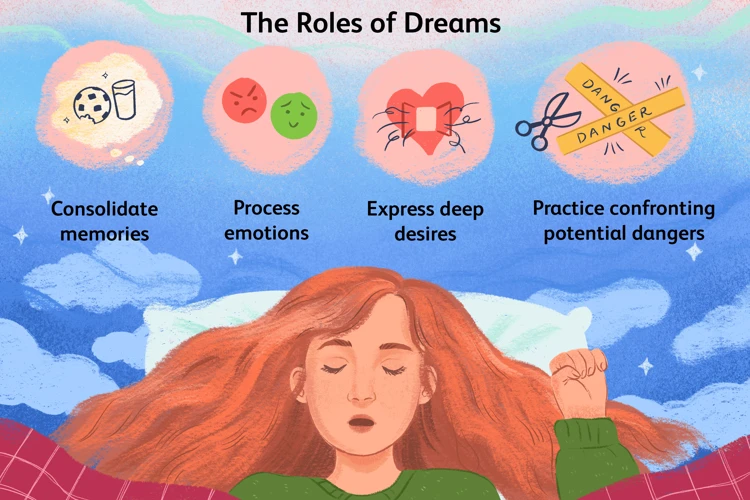
How Trauma Manifests in Nightmares:
– Trauma has a profound impact on our subconscious mind, and this is often reflected in the way it manifests in nightmares. When an individual has experienced trauma, their subconscious tries to process and make sense of the distressing events, leading to the creation of nightmares that are closely tied to the traumatic experiences. These nightmares may take different forms depending on the nature of the trauma, but they typically involve vivid and emotionally charged reenactments of the events.
– One common way trauma manifests in nightmares is through the recurrence of the traumatic event itself. Individuals may find themselves reliving the trauma in their dreams, with details and emotions feeling just as intense as they did during the actual experience. This can be incredibly distressing, as it prolongs the emotional impact of the trauma, making it difficult for individuals to move forward and heal.
– Trauma can also give rise to nightmares that are symbolic in nature. Instead of directly reenacting the traumatic event, these nightmares may use symbols or metaphors to represent the underlying emotions and psychological impact of the trauma. For example, someone who has experienced physical abuse may have nightmares about being chased or attacked by an unidentified figure, representing their feelings of vulnerability and fear.
– The emotional intensity of trauma is often magnified in nightmares. The fear, helplessness, and other intense emotions associated with the traumatic event can come to the forefront during sleep, making nightmares feel incredibly real and frightening. Individuals may wake up from these nightmares feeling distressed, anxious, or even physically aroused due to the intense emotional response triggered by the dream.
– Additionally, trauma can lead to sleep disturbances that further contribute to the manifestation of nightmares. Sleep disruptions, such as insomnia or fragmented sleep, can increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. This may be due to heightened arousal, hyperarousal, or hypervigilance associated with trauma, which can make it difficult for individuals to relax and enter into a restful sleep state.
– It’s important to recognize that the manifestation of trauma in nightmares can vary from person to person. Each individual’s experience of trauma is unique, and their nightmares may reflect their own personal narrative and emotions related to the traumatic event. By understanding how trauma manifests in nightmares, individuals can gain insight into their subconscious processing, paving the way for healing and effective coping strategies.
Resources:
– Unraveling the connection between nightmares and sleep disorders: Learn more.
– Exploring the relationship between nightmares and anxiety disorders: Read more.
– Understanding the symbolism in nightmares: Discover more.
Factors that Influence Recurring Nightmares from Past Trauma

Various factors can influence the occurrence of recurring nightmares in individuals who have experienced past trauma. One significant factor is emotional triggers, where certain stimuli or situations evoke intense emotions associated with the traumatic event, thereby increasing the likelihood of nightmares. Unresolved guilt and shame also play a role, as these emotions can be deeply ingrained following trauma and may resurface in nightmares, perpetuating the cycle of distress. Additionally, hyperarousal and hypervigilance, common symptoms of trauma-related disorders, can heighten the arousal levels during sleep and contribute to the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Psychological defense mechanisms, such as repression or denial, can impact the processing of traumatic memories, leading to their manifestation in nightmares. Lastly, psychological conditioning and reinforcement can contribute to the persistence of trauma-related nightmares, where repeated nightmares can solidify the association between the traumatic event and the dream content, further perpetuating the cycle of distress. Understanding these factors is crucial in developing tailored treatment approaches to address the root causes of recurring nightmares and promote healing and recovery.
1. Emotional Triggers
1. Emotional Triggers:
Emotional triggers play a significant role in recurring nightmares stemming from past trauma. These triggers are specific experiences, thoughts, or stimuli that evoke intense emotional responses associated with the traumatic event. When exposed to these triggers, individuals may experience intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, and nightmares related to the trauma.
Emotional triggers can vary greatly depending on the individual and the nature of the trauma. For example, someone who has experienced childhood abuse may be triggered by certain smells, sounds, or physical touch that remind them of the traumatic event. Similarly, individuals who have survived accidents or near-death experiences may be triggered by situations that replicate the sense of danger or helplessness they experienced during the traumatic incident.
These triggers can set off a cascade of emotions, such as fear, anxiety, anger, or sadness, which directly influence the content and intensity of nightmares. The emotional intensity present in the traumatic memories can be reactivated during sleep, leading to vivid and distressing nightmares that often replicate the emotional distress felt during the actual event.
Understanding and identifying emotional triggers is crucial in effectively managing and reducing the occurrence of trauma-related nightmares. Through therapy and self-reflection, individuals can develop strategies to address and regulate their emotional responses to triggers. This can involve techniques such as cognitive restructuring, relaxation exercises, and grounding techniques to help manage the emotional distress associated with the triggers. By working through these emotional triggers, individuals can regain a sense of control over their nightmares and pave the way for healing and recovery.
2. Unresolved Guilt and Shame
Unresolved Guilt and Shame:
Guilt and shame are powerful emotions that can arise from traumatic experiences and contribute to the manifestation of recurring nightmares. When individuals go through a traumatic event, they may internalize feelings of guilt and shame, believing that they are somehow responsible for what happened or that they could have done something differently to prevent it. These unresolved feelings can become deeply ingrained and may surface during sleep in the form of nightmares.
One way in which unresolved guilt and shame can be expressed in nightmares is through scenarios where the individual is placed in situations where they feel powerless and at fault for the trauma. They may experience vivid dreams where they are unable to protect themselves or others, leading to a sense of overwhelming guilt. These nightmares may replay the events in different variations, intensifying the feelings of shame and self-blame.
The content of the nightmares may reflect the individual’s perceived moral shortcomings or failures associated with the traumatic experience. For instance, a survivor of a car accident may have nightmares where they are unable to save someone trapped in a burning vehicle, reinforcing their feelings of guilt and inadequacy.
Unresolved guilt and shame can keep individuals trapped in a cycle of self-blame, preventing them from fully processing and healing from the trauma. These intense emotions can contribute to the persistence of nightmares and present additional challenges in their resolution.
Addressing unresolved guilt and shame is a crucial aspect of therapy for trauma-related nightmares. By exploring and challenging these negative beliefs in a supportive therapeutic environment, individuals can begin to reframe their experiences and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Therapy techniques such as cognitive restructuring and self-compassion exercises can aid in alleviating guilt and shame, enabling individuals to gradually reduce the frequency and intensity of their nightmares.
It’s important to recognize that resolving unresolved guilt and shame takes time and patience. Working with a qualified therapist can provide the necessary guidance and support to navigate these complex emotions and facilitate the healing process.
3. Hyperarousal and Hypervigilance
Hyperarousal and hypervigilance are two key factors that contribute to the occurrence and intensity of recurring nightmares in individuals who have experienced trauma.
1. Hyperarousal: Hyperarousal refers to a state of heightened physiological and psychological activation, where the individual is constantly on high alert and experiences an increased level of arousal. This state is often a symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and is commonly associated with trauma-related nightmares.
– People experiencing hyperarousal may have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep due to a persistent sense of fear or anxiety. Additionally, they may experience an accelerated heart rate, rapid breathing, and increased muscle tension, making it challenging to relax and enter a deep sleep state.
– Hyperarousal can intensify nightmares by amplifying the emotional and visceral response to traumatic memories. The heightened state of arousal during sleep increases the likelihood of experiencing vivid and emotionally charged nightmares that closely mirror the traumatic event(s). These nightmares can increase the distress experienced during sleep, leading to frequent awakenings and a disrupted sleep pattern.
2. Hypervigilance: Hypervigilance is another common symptom of PTSD that can contribute to recurring nightmares. It refers to a state of constant alertness and heightened awareness of potential threats in the environment. Individuals who are hypervigilant may have difficulty letting their guard down, even during sleep, which can manifest in their dreams.
– Hypervigilance can lead to nightmares characterized by themes of danger, vulnerability, and the anticipation of harm. The individual may have dreams where they are constantly on edge, expecting danger from their surroundings or from specific triggers associated with their trauma. These nightmares can result in increased levels of fear, anxiety, and unease, further impacting the quality of sleep and overall well-being.
Addressing hyperarousal and hypervigilance is essential for managing trauma-related nightmares. Therapy techniques such as eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals regulate their arousal levels, reduce vigilance, and develop coping strategies to manage distressing dreams.
By working to reduce hyperarousal and hypervigilance, individuals can alleviate the intensity and frequency of their nightmares, allowing for a more restful and rejuvenating sleep experience.
4. Psychological Defense Mechanisms
4. Psychological Defense Mechanisms:
– Psychological defense mechanisms play a significant role in how individuals cope with trauma and, subsequently, how it manifests in nightmares. These defense mechanisms are unconscious strategies that the mind employs to protect itself from overwhelming emotional pain or anxiety. While defense mechanisms serve to shield us from distress, they can also influence the content and intensity of recurring nightmares related to past trauma.
– One of the commonly observed defense mechanisms associated with trauma-related nightmares is repression. Repression involves the unconscious blocking of traumatic memories and emotions, pushing them out of awareness. However, these repressed memories can resurface in dreams, as the unconscious mind attempts to process and release the repressed material. These dreams may contain fragmented or distorted elements of the trauma and can be intense and disturbing.
– Another defense mechanism relevant to trauma-related nightmares is displacement. Displacement occurs when the mind redirects intense emotions and impulses from their original source onto a less threatening target. This can manifest in nightmares as the traumatic content is symbolically represented or displaced onto other people, objects, or scenarios. The symbolism in these dreams can be abstract or metaphorical, making it vital to explore the underlying meaning to understand the connection to the trauma.
– Denial is another defense mechanism that can impact how trauma manifests in nightmares. Denial involves refusing to accept or acknowledge the reality of the traumatic event, often as a way to protect oneself from the associated pain. In nightmares, denial may manifest as distorted dream scenarios or themes that minimize or distort the severity of the trauma. This can make it challenging for individuals to recognize the connection between their nightmares and the underlying unresolved trauma.
– Regression is another defense mechanism that can influence the content of trauma-related nightmares. Regression involves reverting to an earlier, less mature stage of psychological development as a means of coping with emotional distress. In nightmares, regression may present as depictions of helplessness, vulnerability, or situations reminiscent of childhood. These dreams can be indicative of the individual’s unconscious desire for safety and protection in the face of trauma.
– Lastly, dissociation is a defense mechanism that can impact the experience of nightmares related to past trauma. Dissociation involves a disconnection from oneself or the environment, often as a response to overwhelming trauma. In nightmares, dissociation may be represented by a detachment from the dream scenario or a sense of observing the dream from outside oneself. This dissociative element can intensify the sense of terror or helplessness in the dream and contribute to sleep disturbances.
Understanding these psychological defense mechanisms is crucial in appreciating the complexities of trauma-related nightmares and their underlying causes. By identifying and addressing these defense mechanisms in therapy, individuals can gain insight into their nightmares and work towards healing the unresolved trauma. It is important to remember that these defense mechanisms are adaptive responses to distress, but seeking professional help can provide guidance in navigating their effects on recurring nightmares.
5. Psychological Conditioning and Reinforcement
5. Psychological Conditioning and Reinforcement:
– Psychological conditioning and reinforcement play a significant role in the development and maintenance of recurring nightmares stemming from past trauma. In many cases, nightmares associated with trauma can become a conditioned response to specific triggers or cues related to the traumatic event. This conditioning occurs when the brain forms associations between certain stimuli and the emotional and physiological responses that accompany the trauma.
– For example, if a person experienced a traumatic event in a particular location, such as a car accident, their brain may associate being in or near a car with the intense fear and distress experienced during the trauma. As a result, being in a car or seeing a car may act as a trigger for nightmares related to that traumatic event.
– The reinforcement of nightmares can perpetuate their recurrence. Nightmares often evoke strong emotions, such as fear, anxiety, and distress, which can lead to physiological responses like increased heart rate and sweating. These intense emotional and physiological reactions serve as reinforcement for the nightmares. The brain associates the nightmares with the release of adrenaline and the activation of the body’s stress response, reinforcing the occurrence of these distressing dreams.
– Additionally, the psychological reinforcement of nightmares can occur through the interpretation of dream content. Individuals who have experienced trauma may attribute deep meaning and significance to their nightmares, believing that the dreams are a representation of their unresolved fears, guilt, or trauma-related emotions. This interpretation and psychological reinforcement can contribute to the perpetuation of recurring nightmares as the individual’s mind continues to process and grapple with the unresolved trauma.
Examples of psychological conditioning and reinforcement in trauma-related nightmares:
1. A person who witnessed a violent incident in a crowded area, such as a shooting, may develop recurrent nightmares whenever they find themselves in crowded spaces.
2. An individual who survived a natural disaster, such as an earthquake, may experience recurring nightmares whenever they feel the slightest tremor or hear a loud noise resembling the initial earthquake.
3. Someone who experienced childhood abuse in their own bedroom may have nightmares linked to their trauma whenever they enter or attempt to sleep in a similar-looking bedroom.
Understanding the role of psychological conditioning and reinforcement in trauma-related nightmares is crucial in developing effective treatment approaches. By identifying and addressing these conditioning factors, individuals can work towards breaking the cycle of recurring nightmares and find relief from the distressing symptoms associated with their past trauma experiences.
Effects of Recurring Nightmares on Well-being

Effects of Recurring Nightmares on Well-being:
Recurring nightmares can have significant impacts on an individual’s overall well-being, affecting various aspects of their life. Here are some of the effects that these distressing dreams can have:
1. Sleep Disturbances: Recurring nightmares can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to poor sleep quality and reduced overall sleep duration. This can result in daytime fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and decreased cognitive functioning.
2. Psychological Distress: The intense emotions and vivid imagery experienced during recurring nightmares can cause significant psychological distress. Individuals may experience heightened anxiety, fear, and a sense of helplessness, which can extend beyond the dream itself and impact their waking life.
3. Emotional Instability: The emotional intensity of nightmares can leave individuals feeling emotionally drained and more susceptible to mood swings. They may experience heightened sensitivity, irritability, and difficulty regulating their emotions.
4. Increased Stress and Anxiety: Recurring nightmares can contribute to elevated levels of stress and anxiety, both during sleep and in waking hours. The fear of experiencing another distressing dream can create a sense of anticipation and anxiety, affecting daily functioning and overall well-being.
5. Impaired Quality of Life: The combined effects of disrupted sleep, psychological distress, and increased stress can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. They may experience difficulties in personal relationships, work performance, and overall enjoyment of daily activities.
6. Avoidance Behaviors: In an attempt to prevent the recurrence of nightmares, individuals may develop avoidance behaviors, such as avoiding certain triggers or altering their sleep routine. These behaviors can further limit their engagement in activities and hinder their ability to fully participate in life.
7. Negative Impact on Mental Health: For individuals already dealing with trauma-related symptoms or pre-existing mental health conditions, recurring nightmares can worsen these symptoms. They may experience an exacerbation of anxiety, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), requiring additional support and treatment.
It’s important to recognize the detrimental effects that recurring nightmares can have on an individual’s well-being. Seeking professional help and implementing appropriate coping strategies can play a crucial role in addressing these effects and improving overall psychological and emotional health.
Methods for Coping with Trauma-related Nightmares
Methods for Coping with Trauma-related Nightmares:
When it comes to coping with trauma-related nightmares, there are various strategies that can help individuals find relief and regain control over their sleep and emotional well-being. Here are some effective coping methods to consider:
1. Seek Professional Help: Consulting with a mental health professional who specializes in trauma can provide invaluable guidance and support in navigating the impact of trauma-related nightmares.
2. Trauma-focused Therapy: Therapeutic approaches like Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) or Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) can help individuals process and heal from traumatic experiences, reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
3. Cognitive Behavioral Techniques: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) techniques, such as imagery rehearsal therapy, can assist individuals in reshaping their nightmares by altering the content or narrative to create a more positive outcome, ultimately reducing the distress they cause.
4. Relaxation and Mindfulness Techniques: Engaging in relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or mindfulness meditation can help calm the mind and promote better sleep, reducing the occurrence of nightmares.
5. Establishing a Bedtime Routine: Establishing a consistent bedtime routine, including relaxation activities, avoiding stimulating substances like caffeine or electronics before bed, and creating a calming environment, can contribute to better sleep quality and minimize the likelihood of nightmares.
6. Creating a Safe Sleep Environment: Creating a safe and comfortable sleep environment, such as using calming scents, having a supportive mattress and pillow, and ensuring adequate lighting and temperature, can promote a sense of safety and security, reducing the likelihood of disturbing nightmares.
By incorporating these coping methods into their routine, individuals can take proactive steps towards coping with trauma-related nightmares, improving overall sleep quality, and fostering emotional healing and well-being. Consulting with a mental health professional can provide personalized guidance and support throughout the journey of recovery.
1. Seek Professional Help
1. Seek Professional Help:
When dealing with trauma-related nightmares, seeking professional help is an essential step towards finding relief and healing. Mental health professionals, such as therapists, counselors, or psychologists, have the expertise and knowledge to provide the necessary support and guidance in addressing trauma and its associated nightmares.
A qualified professional can create a safe and supportive environment where individuals can openly discuss their experiences, fears, and concerns. Through therapy sessions, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the root causes of their nightmares and how trauma has impacted their lives. Therapists can also help individuals develop coping strategies to manage the distressing emotions and triggers associated with trauma-related nightmares.
A therapist may utilize various therapeutic approaches, such as trauma-focused therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), depending on the individual’s specific needs and therapeutic goals. These evidence-based techniques aim to address trauma’s impact on the brain, emotions, and behaviors, helping individuals process the traumatic memories and reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
In addition to professional therapy, psychiatrists can offer medical interventions to manage any underlying mental health conditions, such as PTSD or anxiety disorders, which may be contributing to the nightmares. They can prescribe medications when appropriate, which can help reduce anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances commonly associated with trauma-related nightmares.
It’s important to recognize that seeking professional help is not a sign of weakness but a brave and proactive step towards healing. Trauma and its effects can be complex and deeply ingrained, and the guidance of a trained professional can provide the necessary tools and support for individuals to navigate their journey towards recovery.
Remember, therapy is a collaborative process, and finding the right therapist and approach that resonates with you is crucial. Take the time to research and seek recommendations, ensuring that the therapist has experience and expertise in trauma treatment. With professional help, individuals can gain valuable insights, develop coping strategies, and work towards reclaiming their sense of well-being and tranquility.
2. Trauma-focused Therapy
2. Trauma-focused Therapy:
Trauma-focused therapy is an evidence-based therapeutic approach aimed at addressing the impact of traumatic experiences on an individual’s mental health and well-being. This specialized form of therapy focuses on helping individuals process and heal from their traumatic experiences, ultimately reducing the distressing symptoms, including nightmares, associated with those experiences. Here are some key aspects of trauma-focused therapy:
– Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT): CPT is a widely used trauma-focused therapy that focuses on challenging and reframing negative thoughts and beliefs related to the traumatic event(s). Through CPT, individuals are guided to examine their thoughts and understand how these thoughts contribute to their distressing emotions and behaviors. By modifying and replacing maladaptive cognitions, individuals can effectively reduce the emotional and psychological impact of the trauma, which may indirectly alleviate the frequency and intensity of their nightmares.
– Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR is a therapeutic technique that utilizes eye movements, taps, or sounds to stimulate bilateral brain activity. This process helps individuals reprocess traumatic memories in a controlled and safe environment, allowing for the integration of these memories and the associated emotions into a healthier and less distressing narrative. EMDR has shown promising results in reducing the distressing symptoms of trauma, including nightmares.
– Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy is often utilized in trauma-focused therapy to gradually expose individuals to the feared stimuli or traumatic memories in a safe and controlled manner. The goal is to reduce the emotional intensity and distress associated with these memories over time. By repeatedly confronting the traumatic memories within a therapeutic setting, individuals can often experience a decrease in the frequency and intensity of their nightmares, as the emotional charge associated with the traumatic event(s) diminishes.
– Skills Building: Trauma-focused therapy often involves teaching individuals skills to manage their distress and regulate their emotions. These skills may include relaxation techniques, grounding exercises, mindfulness practices, and stress management strategies. By equipping individuals with these coping mechanisms, they can learn to effectively manage their emotional triggers and reduce the distress that may contribute to nightmares.
– Individualized Treatment: Since every individual’s experience of trauma is unique, trauma-focused therapy emphasizes the importance of tailoring the treatment to fit the specific needs and goals of the individual. Therapists collaborate with the individual to identify their specific trauma-related triggers and work together to develop coping strategies and techniques that address their unique experiences and symptoms.
Using trauma-focused therapy as part of an overall treatment plan can help individuals address the underlying trauma and develop healthier coping mechanisms. By specifically targeting the impact of trauma on an individual’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, trauma-focused therapy can significantly reduce the occurrence and severity of trauma-related nightmares, allowing individuals to heal and reclaim control over their lives.
3. Cognitive Behavioral Techniques
3. Cognitive Behavioral Techniques:
Cognitive Behavioral Techniques can be highly effective in addressing and managing trauma-related nightmares. These evidence-based therapeutic approaches aim to identify and modify negative thought patterns, beliefs, and behaviors that contribute to the occurrence and maintenance of nightmares. Let’s explore some of the key cognitive behavioral techniques that can help individuals cope with trauma-related nightmares:
1. Cognitive Restructuring: Cognitive restructuring involves challenging and restructuring negative thought patterns and beliefs associated with the traumatic event(s) and nightmares. By working with a therapist or using self-help techniques, individuals can learn to identify irrational or unhelpful thoughts and replace them with more rational and adaptive ones. This process helps to reduce the distress and emotional reactivity associated with nightmares, creating a sense of control and empowerment.
2. Imagery Rehearsal Therapy (IRT): IRT is a technique specifically designed to address nightmares. It involves imagining and mentally rehearsing an alternative, more positive outcome for the recurring nightmare. By repeatedly rehearsing the new scenario during wakefulness, individuals can transfer the revised dream content to their actual dreams during sleep. This technique aims to reduce the emotional intensity and distress associated with the nightmares and promote more restful sleep.
3. Relaxation Techniques: Various relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery, can be helpful in managing the anxiety and arousal levels associated with trauma-related nightmares. These techniques promote relaxation and mindfulness, helping to reduce stress and create a calm and conducive sleep environment.
4. Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy involves gradually and safely exposing individuals to the thoughts, images, and situations associated with the traumatic event(s) in a controlled therapeutic setting. By confronting and processing these distressing experiences, individuals can learn to reduce their fear and anxiety response, ultimately leading to a decrease in trauma-related nightmares.
5. Sleep Hygiene Education: Sleep hygiene refers to adopting healthy sleep habits and routines that promote quality sleep. Educating individuals about the importance of a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing sleep environment can contribute to better sleep quality and a reduction in the occurrence of nightmares.
6. Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): MBSR techniques, such as meditation and body awareness exercises, can help individuals cultivate present-moment awareness and acceptance of their thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can develop a non-judgmental and compassionate attitude towards their nightmares, reducing the distress and impact they have on their overall well-being.
Employing cognitive behavioral techniques under the guidance of a trained therapist can provide individuals with effective tools and strategies to manage and cope with trauma-related nightmares. These techniques empower individuals to take an active role in their healing journey, fostering resilience and promoting better sleep and overall psychological well-being.
4. Relaxation and Mindfulness Techniques
Relaxation and mindfulness techniques can be highly effective in coping with trauma-related nightmares. These techniques aim to promote a sense of calm, reduce anxiety, and improve sleep quality. Here are some relaxation and mindfulness techniques that can help individuals manage their nightmares:
1. Deep Breathing: Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing, can help activate the body’s relaxation response. By focusing on slow, deep breaths and consciously relaxing the body with each exhale, individuals can decrease physiological arousal and promote a sense of tranquility before bedtime.
2. Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This technique involves systematically tensing and then releasing different muscle groups in the body. By gradually releasing tension from head to toe, individuals can promote physical relaxation and reduce overall muscle tension, making it easier to fall asleep without the interference of nightmares.
3. Guided Imagery: Guided imagery involves visualizing calming and peaceful scenes to redirect attention away from distressing thoughts or memories. This technique can be especially helpful in creating a mental escape from trauma-related nightmares. Listening to guided imagery recordings or creating personalized imagery can induce a sense of relaxation and promote restful sleep.
4. Mindfulness Meditation: Mindfulness meditation encourages individuals to observe their thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations non-judgmentally, in the present moment. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can cultivate a greater sense of self-awareness and develop the ability to observe their nightmares without becoming overwhelmed by them. Regular mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress and improve overall sleep quality.
5. Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a sleep routine and following good sleep hygiene practices can improve the overall sleep environment and promote restful sleep. This includes creating a calm and relaxing bedroom environment, avoiding stimulating activities before bed, and maintaining a consistent sleep-wake schedule. Consistency in sleep patterns can minimize sleep disturbances, including nightmares.
6. Relaxation Techniques: Various relaxation techniques, such as listening to calming music, taking warm baths, or engaging in light stretching exercises, can help individuals unwind and prepare for sleep. Experimenting with different relaxation techniques can help individuals find what works best for them in terms of reducing stress and anxiety before bedtime.
It’s important to remember that finding the right relaxation and mindfulness techniques may require some trial and error. What works for one individual may not work for another. It’s advisable to seek guidance from a mental health professional who specializes in trauma therapy to explore and customize the relaxation techniques that will be most effective for addressing trauma-related nightmares. By incorporating these techniques into a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can gradually reduce the frequency and intensity of their nightmares, promoting better overall well-being.
5. Establishing a Bedtime Routine
5. Establishing a Bedtime Routine:
Establishing a bedtime routine can play a significant role in reducing trauma-related nightmares and improving overall sleep quality. A consistent routine helps signal to the brain and body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep, promoting a sense of relaxation and calmness before bedtime. Here are some key strategies to consider when establishing a bedtime routine:
1. Set a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock, improving the quality and duration of your sleep.
2. Create a Relaxing Environment: Make your bedroom a peaceful sanctuary by minimizing distractions and creating a conducive atmosphere for sleep. Keep the room cool, dark, and quiet. Consider using earplugs, eye masks, or white noise machines to block out any disruptive stimuli.
3. Practice Relaxation Techniques: Engage in relaxation techniques before bed to promote a sense of calmness and reduce stress. These techniques can include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery. Find what works best for you and incorporate it into your routine.
4. Avoid Stimulation Before Bed: Limit exposure to screens, such as smartphones, tablets, and computers, at least an hour before bedtime. The blue light emitted by these devices can interfere with your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Instead, engage in calming activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or engaging in light stretching.
5. Create a Wind-Down Ritual: Develop a series of activities that help you transition from the busyness of the day to a relaxed state before sleep. This can include listening to soothing music, practicing mindfulness or meditation, journaling, or gentle stretching exercises. Experiment with different activities to find what helps you unwind and prepare for sleep.
6. Avoid Stimulating Food and Beverages: Limit or avoid consuming caffeinated drinks, such as coffee or energy drinks, especially in the evening. Additionally, avoid heavy meals close to bedtime, as digestion can interfere with sleep. Instead, opt for a light snack if you feel hungry.
Remember, consistency is key when establishing a bedtime routine. Be patient and give yourself time to adjust to the new schedule and activities. The goal is to create a relaxing ritual that helps signal to your body and mind that it’s time to leave the stresses of the day behind and prepare for a restful night’s sleep.
6. Creating a Safe Sleep Environment
Creating a Safe Sleep Environment:
Creating a safe sleep environment is crucial for individuals who experience trauma-related nightmares. By ensuring a soothing and secure atmosphere, individuals can promote a sense of calm and relaxation that can aid in reducing the occurrence and intensity of nightmares. Here are some tips for creating a safe sleep environment:
1. Comfortable Bedding: Use comfortable and cozy bedding, including a supportive mattress and soft pillows, that enhances physical comfort during sleep.
2. Darkness and Noise Reduction: Minimize external stimuli that may disrupt sleep, such as excessive light or noise. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine to create a quiet and dark sleeping environment.
3. Temperature Control: Maintain a comfortable temperature in the bedroom to promote uninterrupted sleep. A cool and well-ventilated room can contribute to a more restful sleep experience.
4. Safe and Secure Space: Ensure that the sleep environment feels safe and secure. This can be achieved by using nightlights in the hallway or bathroom, removing any potential hazards or clutter from the bedroom, and having a reliable lock on the door for added peace of mind.
5. Calming Scent: Incorporate calming scents, such as lavender or chamomile, through essential oils, sprays, or scented candles. These fragrances are known for their relaxing properties and can help create a soothing atmosphere conducive to peaceful sleep.
6. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Before going to bed, engage in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation. These practices can help alleviate anxiety and promote a more relaxed state before sleep.
7. Digital Detox: Minimize exposure to electronic devices, especially before bedtime. The blue light emitted by screens can disrupt the sleep-wake cycle, making it harder to fall asleep and increasing the likelihood of nightmares. Create a technology-free zone in the bedroom to encourage digital detox before sleep.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can create an environment that promotes relaxation, safety, and a sense of peace. Remember, creating a safe sleep environment is just one aspect of managing trauma-related nightmares. It’s essential to seek professional help and explore therapy options to address the underlying trauma and develop effective coping mechanisms.
Conclusion
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the relationship between past trauma and recurring nightmares is a complex and significant phenomenon. Traumatic events can leave a lasting impact on our psychological well-being, often manifesting in distressing dreams during sleep. The content of these nightmares can vary depending on the type of trauma experienced, but they commonly involve themes of threat, fear, and helplessness associated with the traumatic event.
Understanding the connection between trauma and nightmares is crucial for developing effective coping strategies. Factors such as emotional triggers, unresolved guilt and shame, hyperarousal, psychological defense mechanisms, and psychological conditioning can influence the occurrence of recurring nightmares. These nightmares can have harmful effects on overall well-being, exacerbating existing trauma-related symptoms and affecting daily functioning.
Fortunately, there are methods available to cope with trauma-related nightmares. Seeking professional help and engaging in trauma-focused therapy can provide valuable support and guidance. Cognitive behavioral techniques, relaxation, and mindfulness exercises can help individuals better manage their nightmares. Establishing a bedtime routine and creating a safe sleep environment can also contribute to reducing the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares.
By addressing past trauma and the resulting nightmares, individuals can work towards healing and finding a sense of peace and tranquility in their lives. It is essential to remember that each person’s journey is unique, and finding the most effective treatment approach may require patience and persistence.
In conclusion, by recognizing and understanding the role of past trauma in recurring nightmares, individuals can take significant steps towards reclaiming their sleep, reducing distress, and restoring their overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can past trauma really cause recurring nightmares?
Yes, past trauma can indeed cause recurring nightmares. Traumatic experiences can leave a lasting impact on our psyche, leading to the manifestation of distressing and vivid dreams during sleep.
2. Are nightmares a common symptom of trauma?
Yes, nightmares are a common symptom of trauma. They can be a way for the brain to process and integrate the traumatic memories and emotions associated with the traumatic event.
3. Do all individuals who experience trauma develop recurring nightmares?
No, not everyone who experiences trauma will develop recurring nightmares. The occurrence of nightmares can vary based on individual factors such as resilience, coping mechanisms, and the presence of underlying mental health conditions.
4. Can recurring nightmares worsen the effects of trauma?
Yes, recurring nightmares can exacerbate the effects of trauma. They can act as triggers for heightened anxiety, fear, and distress, impacting an individual’s daily life and overall well-being.
5. Can therapy help in managing trauma-related nightmares?
Yes, therapy can be instrumental in managing trauma-related nightmares. Trauma-focused therapy, cognitive-behavioral techniques, and relaxation strategies are among the therapeutic approaches that can help individuals cope with and reduce the frequency of nightmares.
6. How do emotional triggers influence recurring nightmares?
Emotional triggers can significantly influence recurring nightmares. These triggers may be stimuli or reminders that are associated with the traumatic event, often evoking intense emotions and increasing the likelihood of nightmares.
7. Are unresolved guilt and shame factors in the occurrence of trauma-related nightmares?
Yes, unresolved feelings of guilt and shame can contribute to the occurrence of trauma-related nightmares. These complex emotions can surface during sleep, leading to distressing dream content and the repetition of guilt-ridden or shameful scenarios.
8. What role does hyperarousal play in trauma-related nightmares?
Hyperarousal, a heightened state of physiological and psychological activation, can contribute to the occurrence of trauma-related nightmares. It can disrupt sleep patterns and make individuals more susceptible to experiencing intense and distressing dreams.
9. Are there any psychological defense mechanisms at play in trauma-related nightmares?
Yes, psychological defense mechanisms can be at play in trauma-related nightmares. The mind may utilize defense mechanisms such as repression, regression, or displacement to protect itself from the overwhelming emotions associated with the trauma, which can then manifest in the form of nightmares.
10. Can establishing a bedtime routine help reduce the frequency of trauma-related nightmares?
Yes, establishing a consistent bedtime routine can be beneficial in reducing the frequency of trauma-related nightmares. A relaxing routine before sleep can create a sense of safety and calmness, promoting better sleep quality and potentially decreasing the occurrence of distressing dreams.