Nightmares and sleepwalking are two phenomena that have been perplexing humans for centuries. From the vivid and often terrifying dreams that leave us waking up in a cold sweat to the eerie episodes of walking and performing complex actions while still asleep, these experiences have fascinated and mystified researchers, psychologists, and the general public alike. In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of nightmares and sleepwalking and explore the role that nightmares play in sleepwalking episodes. We will examine the connection between these two phenomena, understand the underlying science, and discuss common nightmares associated with sleepwalking. Additionally, we will provide insights on managing nightmares and sleepwalking to ensure a good night’s sleep. So, put your mind at ease and join us on this journey of unraveling the mysteries behind nightmares and sleepwalking.
Nightmares: A Brief Overview

Nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that can cause intense emotional distress in individuals. They often involve frightening or unsettling scenarios, such as being chased, falling, or experiencing a life-threatening situation. During nightmares, individuals may awaken abruptly, sometimes with a racing heart, sweating, and a sense of fear or anxiety lingering. Nightmares typically occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, which is characterized by increased brain activity and vivid dreaming. While nightmares are a normal part of sleep, frequent or recurring nightmares can disrupt sleep quality and impact overall well-being. Some common themes in nightmares include being trapped, experiencing the loss of a loved one, or encountering supernatural creatures. Various factors contribute to the occurrence of nightmares, including underlying psychological issues, traumatic experiences, medications, and even certain sleep disorders. It is important to address and manage nightmares to ensure a restful and rejuvenating sleep.
Sleepwalking: A Brief Overview
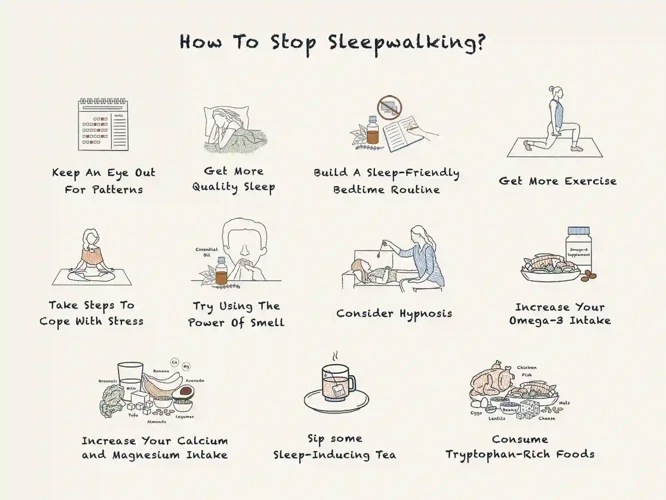
Sleepwalking, also known as somnambulism, is a sleep disorder that involves performing complex actions while still being asleep. It is more common in children than adults, but it can occur at any age. During sleepwalking episodes, individuals may sit up, walk around, talk, or even engage in activities such as preparing food or driving a car, all while remaining in a state of deep sleep. Sleepwalkers may have a blank expression on their face and appear unaware of their surroundings. These episodes typically occur during the deeper stages of sleep, known as slow-wave sleep. While the exact causes of sleepwalking are not fully understood, several factors can contribute to its occurrence. These include genetic predisposition, sleep deprivation, certain medications, stress, and underlying medical conditions. It is important to ensure the safety of sleepwalkers by removing any potential hazards in their sleep environment, such as sharp objects or obstacles that they could stumble upon. Taking appropriate safety measures can help prevent injuries and minimize the risks associated with sleepwalking.
The Relationship between Nightmares and Sleepwalking

The relationship between nightmares and sleepwalking is a complex one, with both phenomena often intersecting and influencing each other. While nightmares and sleepwalking are distinct experiences, they can be interconnected in several ways. Firstly, there is a connection between the two in terms of their occurrence during different stages of sleep. Nightmares are most commonly associated with the REM stage of sleep, where vivid dreaming takes place, while sleepwalking episodes typically happen during the deep non-REM stages of sleep. Despite these different stages, there are instances where nightmares can act as triggers for sleepwalking episodes. For example, individuals who have a particularly distressing nightmare may experience heightened arousal and become more prone to sleepwalking. On the other hand, nightmares can also manifest during sleepwalking episodes, with individuals reporting instances of vivid, disturbing dreams while they are still asleep and engaged in sleepwalking behaviors. This complex relationship highlights the intricate nature of sleep disorders and emphasizes the need for comprehensive management strategies to ensure sleep safety. (Reference: sleepwalking safety measures).
1. The Connection
The connection between nightmares and sleepwalking is a fascinating area of study. While not all individuals who experience nightmares also sleepwalk, there is a notable overlap between the two phenomena. Research suggests that both nightmares and sleepwalking stem from disruptions in the sleep cycle and abnormalities in the brain’s functioning. Studies have shown that individuals who frequently experience nightmares are more likely to engage in sleepwalking episodes. This could be because nightmares may disrupt the normal sleep patterns, leading to increased arousal during sleep and a higher likelihood of sleepwalking. Both nightmares and sleepwalking have been linked to underlying psychological factors and stress. It is believed that individuals who are more prone to anxiety or trauma may be more susceptible to both nightmares and sleepwalking. Understanding the connection between nightmares and sleepwalking can help shed light on the complex nature of these experiences and assist in developing strategies to manage and treat them effectively. For more information on the causes and triggers of sleepwalking, refer to our article “Causes and Triggers of Sleepwalking”.
2. Nightmares as Triggers
Nightmares can act as triggers for sleepwalking episodes, where individuals engage in complex behaviors while still asleep. When someone experiences a particularly distressing or emotionally charged nightmare, it can disrupt their sleep cycle and lead to transitions between sleep stages. This disturbance in the sleep pattern can trigger sleepwalking. The connection between nightmares and sleepwalking lies in the impact they have on the brain’s arousal system. Nightmares activate the amygdala, which is responsible for processing emotions, resulting in an increase in heart rate and arousal levels. These heightened levels of arousal can cause individuals to partially wake up during their sleep, entering a state of sleepwalking. The emotions and fears experienced in the nightmare can manifest as physical movements and actions while still in a sleep state. It is important to note that not all nightmares will result in sleepwalking episodes, as individual susceptibility to sleepwalking varies. However, the emotional intensity and content of nightmares can increase the likelihood of sleepwalking episodes occurring. Understanding this connection between nightmares and sleepwalking can help individuals take appropriate measures to manage both phenomena and ensure a safe and restful sleep. For more information on the relationship between sleepwalking and other sleep disorders, you can read our article on the sleepwalking and lucid dreaming connection.
3. Nightmares as Manifestations
Nightmares can sometimes serve as manifestations or symbolic representations of underlying emotions, fears, or unresolved conflicts. They can be a way for the subconscious mind to express and process deep-seated anxieties that may not be readily apparent in waking life. For example, a person who has repressed feelings of guilt or shame may experience recurring nightmares involving feelings of being chased or attacked. These nightmares could be seen as a manifestation of their inner turmoil and the need to confront and resolve those emotions. Similarly, individuals who have experienced trauma or stressful events may have nightmares that replay aspects of those experiences, allowing their subconscious to work through the associated emotions and memories. By examining the themes and symbolism present in nightmares, individuals may gain valuable insights into their own psychological and emotional states. This awareness can be the first step towards addressing and working through the underlying issues that may be contributing to recurring nightmares. It is important to note that interpreting nightmares can be complex, and the assistance of a qualified mental health professional may be beneficial in understanding their deeper meaning. Understanding nightmares as manifestations can lead to personal growth, self-reflection, and ultimately, improved psychological well-being.
Understanding the Science behind Nightmares and Sleepwalking
Understanding the science behind nightmares and sleepwalking is crucial in unraveling the mysteries of these phenomena. Nightmares often occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, a phase characterized by heightened brain activity and vivid dreaming. During this stage, the amygdala, a part of the brain responsible for emotional processing, becomes hyperactive, leading to the intense emotions experienced in nightmares. Additionally, disruptions in the neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. Sleepwalking, on the other hand, is a sleep disorder that occurs during deep non-REM sleep. It is believed to result from an imbalance between the sleep-wake systems in the brain, leading to an impaired ability to transition between sleep stages. Factors such as genetics, stress, and sleep deprivation can also influence the occurrence of sleepwalking episodes. By understanding the intricate workings of the brain and the various factors at play, we can gain insights into how nightmares and sleepwalking are intertwined and develop strategies to manage and prevent them effectively.
1. The Role of the Brain
The brain plays a crucial role in both nightmares and sleepwalking episodes. When it comes to nightmares, certain regions of the brain are involved in the generation and processing of these intense dreams. The amygdala, which is responsible for processing emotions and fear responses, may become hyperactive during REM sleep, leading to the creation of vivid and frightening dream experiences. The hippocampus, involved in memory consolidation, can also contribute to the content of nightmares by recalling past traumas or distressing events. Additionally, there is evidence to suggest that irregularities in the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for logical thinking and decision-making, may influence the occurrence of nightmares. Dysfunction in this region could result in an impaired ability to differentiate between dreams and reality, leading to heightened emotional responses during nightmares.
In the case of sleepwalking, the brain’s involvement is equally significant. Sleepwalking, also known as somnambulism, often occurs during the deepest stages of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. During this time, the brain is not fully awake, and certain parts, such as the prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions and control, may still remain in a sleep-like state. This can result in a dissociation between the brain’s wakefulness and the body’s actions. The brain’s motor control centers continue to function, allowing individuals to move and perform complex activities, such as walking or even driving, while remaining in a sleep state. This unique state of consciousness during sleepwalking can cause individuals to engage in bizarre behaviors without awareness or recollection upon awakening.
Understanding the intricate workings of the brain during nightmares and sleepwalking is crucial in comprehending the mechanisms behind these phenomena. Further research and studies continue to shed light on the complex interplay between brain activity, sleep stages, and the occurrence of nightmares and sleepwalking episodes.
2. Neurological Factors at Play
Neurological factors play a significant role in the occurrence of nightmares and sleepwalking episodes. The brain is responsible for regulating sleep and dream cycles, and any disruptions or abnormalities in its functioning can contribute to these phenomena. One key neurological factor that influences nightmares and sleepwalking is an imbalance in neurotransmitters, chemicals in the brain that transmit signals between nerve cells. Imbalances in neurotransmitters such as serotonin and norepinephrine have been linked to an increased likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Additionally, abnormalities in the brain regions responsible for sleep regulation, such as the amygdala and hippocampus, can also contribute to the occurrence of nightmares and sleepwalking. These regions are involved in processing emotions, memories, and fear responses, which can influence the content of dreams and the manifestation of sleepwalking behaviors. Disruptions in the overall sleep structure, such as fragmented or irregular sleep patterns, can further exacerbate the likelihood of experiencing nightmares and sleepwalking episodes. Understanding the neurological factors at play is crucial in developing effective strategies for managing and preventing these sleep disturbances.
3. The Influence of Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety have a profound influence on both nightmares and sleepwalking episodes. When individuals experience high levels of stress and anxiety, it can disrupt their sleep patterns and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Stress triggers the release of cortisol, the stress hormone, which can interfere with the normal sleep cycle and lead to fragmented and restless sleep. This disruption in sleep can make individuals more susceptible to nightmares. The content of nightmares is often reflective of a person’s emotional state, and stress and anxiety can manifest in the form of terrifying and distressing dream scenarios.
Stress and anxiety can also contribute to sleepwalking episodes. Sleepwalking is often triggered by factors that disrupt the normal sleep architecture, and stress is a common factor. When individuals are under stress, their sleep quality can be compromised, leading to increased chances of sleepwalking. The heightened arousal levels associated with stress can disrupt the transition between different stages of sleep, causing an imbalance in the brain activity that regulates sleep and wakefulness. This imbalance can result in sleepwalking behavior during the deepest stages of sleep.
It is important to address and manage stress and anxiety to minimize the occurrence of nightmares and sleepwalking episodes. Adopting relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga, can help reduce stress levels and promote better sleep. Engaging in regular physical exercise can also help alleviate stress and promote overall well-being. Additionally, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can be beneficial in managing and reducing stress and anxiety levels. By addressing these underlying factors, individuals can improve their sleep quality and reduce the frequency of nightmares and sleepwalking episodes.
Common Nightmares Associated with Sleepwalking Episodes

Common nightmares associated with sleepwalking episodes can vary greatly, but they often involve themes of danger, fear, and threat. One recurring nightmare scenario is being pursued or chased by an unknown entity or dangerous figure. In this type of nightmare, individuals may feel a sense of urgency and panic, as if their life is in imminent danger. Another common nightmare theme is falling from a great height, which can induce intense feelings of fear and vulnerability. Sleepwalkers may act out these nightmares by attempting to escape their perceived threat, resulting in hazardous behaviors such as climbing or jumping off elevated surfaces. Nightmares that involve being trapped or unable to move, known as sleep paralysis, are also associated with sleepwalking episodes. In these nightmares, individuals may feel immobilized, helpless, and unable to call for help. Sleepwalkers experiencing this type of nightmare may exhibit restless and agitated movements or attempts to break free from their perceived confinement. It is important to note that not all nightmares will lead to sleepwalking episodes, but when they do, they can significantly heighten the dangers and risks associated with sleepwalking.
How to Manage Nightmares and Sleepwalking
Managing nightmares and sleepwalking can help improve sleep quality and address the underlying causes. One effective way to manage nightmares is to establish healthy sleep habits. This includes following a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment. Implementing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can also help alleviate nightmares. Another important aspect is reducing stress and anxiety in daily life. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing relaxation techniques, and seeking support from loved ones or a therapist can all be beneficial. If nightmares and sleepwalking persist and significantly impact daily life, it may be necessary to seek professional help. Sleep specialists, therapists, or psychologists can provide specialized guidance and treatment options tailored to individual needs. By taking proactive steps and seeking appropriate support, individuals can effectively manage nightmares and sleepwalking, ultimately promoting a more peaceful and restorative sleep experience.
1. Establishing Healthy Sleep Habits
Establishing healthy sleep habits is crucial for managing both nightmares and sleepwalking episodes. Here are some key practices that can promote better sleep:
1. Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock and promotes a more regular sleep pattern.
2. Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in relaxing activities before bed, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing gentle stretching or meditation. This will signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
3. Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Make sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet, as these conditions are conducive to good sleep. Consider using earplugs, eye masks, or a white noise machine if necessary.
4. Avoid Stimulants: Limit your intake of caffeine and nicotine, as they can interfere with sleep. Also, avoid consuming heavy meals and exercising vigorously close to bedtime, as these can disrupt your ability to fall asleep.
5. Establish a Relaxing Pre-Sleep Ritual: Engaging in calming activities before bed can help relax your mind and prepare it for sleep. This can include reading a book, practicing deep breathing exercises, or listening to soothing music.
6. Limit Screen Time: Avoid screens, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, in the hour leading up to bedtime. The blue light emitted by these devices can interfere with your body’s production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.
By incorporating these healthy sleep habits into your routine, you can create an environment conducive to restful sleep and decrease the likelihood of experiencing nightmares and sleepwalking episodes. Remember, consistency and patience are key when establishing new sleep habits, so give yourself time to adjust and stick to a routine.
2. Reducing Stress and Anxiety
Reducing stress and anxiety plays a crucial role in managing nightmares and sleepwalking episodes. High levels of stress and anxiety can trigger and exacerbate these phenomena. Here are some effective strategies for reducing stress and anxiety:
1. Practice relaxation techniques: Engage in activities that promote relaxation, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or meditation. These techniques can help calm the mind and reduce stress.
2. Exercise regularly: Physical activity has been proven to reduce stress and anxiety. Incorporate regular exercise into your routine, whether it’s going for a walk, practicing yoga, or participating in a favorite sport.
3. Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, get enough sleep, and avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption. Taking care of your physical health can have a positive impact on your mental well-being.
4. Engage in stress-reducing activities: Find activities that help you relax and unwind, such as reading, listening to music, taking a bath, or spending time in nature. These activities can help redirect your focus and alleviate stress.
5. Seek social support: Share your feelings and concerns with friends, family, or a support group. Talking about your worries can provide emotional relief and help you gain a new perspective.
6. Consider therapy: If stress and anxiety persist and significantly impact your daily life, consider seeking professional help. Therapy can provide valuable coping mechanisms and strategies to manage stress and anxiety effectively.
By implementing these stress-reducing techniques, you can create a more peaceful and relaxed mindset, which can ultimately contribute to a reduction in nightmares and sleepwalking episodes. Remember, taking steps to reduce stress and anxiety is essential for promoting overall well-being and achieving a better quality of sleep.
3. Seeking Professional Help
Seeking professional help can be an important step in managing nightmares and sleepwalking episodes. Since these phenomena can be linked to underlying psychological or sleep-related disorders, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals who specialize in sleep disorders and mental health. A primary care physician or a sleep specialist can provide a comprehensive assessment of your sleep patterns, identify any potential disorders or underlying conditions, and recommend appropriate treatment approaches. This may include referral to a therapist or psychologist who can help address any psychological factors contributing to nightmares or sleepwalking. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has shown promise in treating nightmares and related sleep disorders. In CBT, individuals learn techniques to manage stress, anxiety, and emotional triggers that may contribute to nightmares. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms or treat an underlying condition. It is important to work collaboratively with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and goals. Remember, reaching out for professional help is a proactive step towards improving your sleep quality and overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of nightmares in sleepwalking episodes is a complex and fascinating subject. Nightmares can act as both triggers and manifestations of sleepwalking, creating a nuanced relationship between the two. Understanding the science behind nightmares and sleepwalking is crucial in comprehending their connection. The brain plays a significant role, with neurological factors and the influence of stress and anxiety contributing to the occurrence of both nightmares and sleepwalking. Identifying and managing common nightmares associated with sleepwalking can help individuals take steps towards better sleep hygiene and overall well-being. By establishing healthy sleep habits, reducing stress and anxiety, and seeking professional help when needed, individuals can effectively manage nightmares and sleepwalking. With further research and advancements in understanding these phenomena, we can continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding nightmares and sleepwalking, bringing relief to those affected. It is imperative that individuals prioritize their sleep health and take proactive measures to ensure safety and quality rest.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What causes nightmares?
Nightmares can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress and anxiety, traumatic experiences, medications, sleep disorders, and certain medical conditions. Understanding the underlying cause can help in managing and reducing the occurrence of nightmares.
2. Are nightmares a sign of a mental health disorder?
Nightmares alone are not necessarily indicative of a mental health disorder. However, frequent or distressing nightmares can be associated with conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and depression. If you are concerned about your nightmares, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional.
3. Can children have nightmares?
Yes, nightmares are common in children, especially during their early years. They can be triggered by normal fears and anxieties, as well as by changes in routine or exposure to scary or unfamiliar situations. Providing reassurance and a comforting bedtime routine can help alleviate children’s nightmares.
4. Can nightmares be prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent nightmares entirely, there are strategies that can help reduce their frequency and intensity. Establishing a relaxing bedtime routine, creating a calm sleeping environment, and managing stress and anxiety levels can all contribute to preventing nightmares.
5. Are nightmares the same as night terrors?
No, nightmares and night terrors are different phenomena. Nightmares occur during REM sleep and are often vivid and memorable upon waking. Night terrors, on the other hand, occur during non-REM sleep and are characterized by intense fear, screaming, and physical agitation, often with no memory of the episode upon waking.
6. Can medications cause nightmares?
Yes, certain medications can disrupt normal sleep patterns and increase the occurrence of nightmares. Medications such as antidepressants, beta-blockers, and some blood pressure medications may have this side effect. If you suspect that your medication is causing nightmares, consult with your doctor to explore alternative options.
7. How can I cope with nightmares?
There are several strategies that can help cope with nightmares. Engaging in relaxation techniques before bed, such as deep breathing exercises or mindfulness meditation, can aid in reducing stress and anxiety. Additionally, keeping a dream journal can help identify patterns or triggers, allowing for further exploration and understanding.
8. Are nightmares a sign of a sleep disorder?
While nightmares themselves are not classified as a sleep disorder, they can be associated with conditions such as nightmare disorder or sleep-related anxiety disorder. If you consistently experience distressing nightmares that significantly impact your sleep and daily functioning, it is advisable to consult with a sleep specialist for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
9. Can lucid dreaming influence nightmares?
Yes, lucid dreaming, which is the ability to become aware and control one’s dreams, can have an impact on nightmares. With practice, individuals can learn to recognize when they are dreaming and actively change the course of the dream, potentially turning a frightening nightmare into a more positive or neutral experience.
10. When should I seek professional help for nightmares?
If nightmares are causing significant distress, disrupting your sleep on a regular basis, or affecting your quality of life, it is advisable to seek professional help. A sleep specialist or mental health professional can help identify underlying causes, provide appropriate interventions, and support you in managing and overcoming your nightmares.








