Unmasking Anxiety: The Role of Nightmares in Uncovering and Addressing Underlying Fears
Have you ever experienced a nightmare that left you feeling shaken and filled with a sense of unease? Nightmares are not merely random occurrences during sleep; they can be powerful windows into our deepest fears and anxieties. In this article, we will delve into the nature of nightmares, exploring their definition and common themes. We will also gain an understanding of anxiety and its various manifestations. By uncovering the link between nightmares and anxiety, we can begin to address and conquer our underlying fears. Through recognizing nightmares as signals, analyzing them using effective techniques, and seeking professional help when needed, we can alleviate the grip anxiety has on our lives. Join us as we delve into the mysterious realm of nightmares and uncover the profound role they play in unmasking anxiety.
The Nature of Nightmares

Nightmares are intense and distressing dreams that evoke a strong emotional response, typically followed by feelings of fear, terror, or anxiety upon awakening. These vivid and often unsettling dreams usually occur during the REM (rapid eye movement) stage of sleep, which is when the brain is highly active and dreams are most likely to be experienced. Unlike regular dreams, nightmares can leave a lasting impact on an individual, disrupting their sleep patterns and causing significant distress. It is important to note that not all dreams that evoke negative emotions are considered nightmares; rather, the intensity and emotional response differentiate nightmares from regular dreams.
Nightmares can vary in content and imagery, but there are several common themes and patterns that tend to emerge. These themes often revolve around feelings of helplessness, threat, danger, or being chased. Nightmares may feature scenarios such as falling from great heights, being pursued by a menacing figure, or finding oneself in a life-threatening situation. Additionally, recurring nightmares, where the same or similar themes are experienced repeatedly, are not uncommon. These repetitive nightmares often serve as potent indicators of underlying fears and anxieties that need to be addressed.
While nightmares and bad dreams share some similarities, they are distinct experiences. Bad dreams are typically less intense and intense emotionally than nightmares and may not always cause significant distress upon waking. They might involve less threatening situations or evoke milder negative emotions. Nightmares, on the other hand, can be more vivid, terrifying, and disruptive to one’s sleep and mental well-being. It is important to distinguish between the two, as the intensity and frequency of nightmares can be indicative of deeper psychological issues that need to be explored and addressed properly.
By understanding the definition of nightmares, recognizing common themes and patterns, and differentiating nightmares from bad dreams, we can begin to unravel the complexities of these intriguing and sometimes distressing dream experiences. Next, we will delve into the topic of anxiety and its various manifestations, paving the way to uncover the link between nightmares and anxiety.
1. Definition of Nightmares
Nightmares can be defined as vivid and disturbing dreams that provoke intense feelings of fear, terror, or anxiety upon awakening. These dreams are characterized by their ability to elicit strong emotional reactions and can often leave individuals feeling unsettled and shaken. The content of nightmares can vary widely, ranging from being chased or attacked to experiencing a life-threatening situation. It is important to note that nightmares are not mere figments of imagination; they are an expression of our subconscious mind processing emotions, fears, and anxieties. Nightmares often occur during the REM (rapid eye movement) stage of sleep, which is when dreams are most vivid and emotionally charged. It is through the exploration and analysis of nightmares that we can uncover deeper psychological issues and address underlying fears that may contribute to anxiety. Understanding the definition of nightmares is crucial in recognizing their significance and the role they play in unmasking anxiety. To learn more about how trauma can contribute to anxiety-related nightmares, you can read our article on trauma-induced anxiety nightmares.
2. Common Themes and Patterns
When exploring the common themes and patterns in nightmares, it becomes evident that certain motifs frequently recur across individuals. These themes often tap into primal fears and evoke strong emotional responses. Here are some of the most prevalent nightmare themes:
1. Falling: Many people experience nightmares where they are falling from great heights, unable to regain control. These dreams often reflect a sense of vulnerability, powerlessness, or a fear of losing control in waking life. The sensation of falling in a dream can be incredibly intense and may cause a sudden jolt upon awakening.
2. Being chased: Being pursued by a menacing figure or an unknown threat is a common nightmare theme. The fear of being chased symbolizes a sense of vulnerability, the need to escape or confront something, or a fear of being caught or exposed. These dreams often reflect underlying anxieties and a feeling of being overwhelmed in daily life.
3. Teeth falling out: Dreams where teeth crumble, fall out, or are pulled out are frequently reported nightmares. This theme can be associated with feelings of inadequacy, loss of power or control, or concerns about appearance and self-image. Such dreams may also indicate underlying anxiety about communication and expressing oneself effectively.
4. Being trapped: Nightmares featuring situations where individuals feel trapped, enclosed, or unable to escape are common. These dreams often reflect feelings of being stifled, restrained, or overwhelmed by life circumstances. The sense of confinement may symbolize a need for freedom or a desire to break free from real or perceived limitations.
5. Being unprepared: Nightmares in which individuals find themselves unprepared for exams, presentations, or important events tap into common anxieties about performance, competence, and judgment. These dreams often reveal insecurities and a fear of failure or public humiliation.
It is important to remember that the interpretation of nightmare themes is highly subjective, and each individual may have unique personal associations and fears connected to these universal motifs. By identifying and reflecting on the recurring themes in nightmares, individuals can gain insights into their deepest anxieties and fears. In the next section, we will explore the distinction between nightmares and bad dreams further and discuss the link between nightmares and anxiety, paving the way for addressing and managing anxiety-related nightmares. For tips on managing anxiety nightmares, refer to this article.
3. Nightmares vs. Bad Dreams
Nightmares and bad dreams may seem similar at first glance, but they have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Here are some key differences between the two:
1. Intensity and Emotional Impact: Nightmares are typically more intense and emotionally distressing than bad dreams. They evoke a stronger sense of fear, terror, or anxiety upon awakening. Bad dreams, on the other hand, may involve milder negative emotions or less threatening situations.
2. Disruption of Sleep: Nightmares have a greater tendency to disrupt sleep, causing the individual to wake up feeling disturbed and potentially making it difficult to fall back asleep. Bad dreams may not necessarily cause significant sleep disturbances or interfere with the individual’s ability to resume sleep.
3. Content and Imagery: Nightmares often feature themes of helplessness, danger, threat, or being chased. They may involve vivid and terrifying scenarios, such as falling from great heights or being pursued by a menacing figure. Bad dreams, on the other hand, may involve less threatening situations or evoke milder negative emotions.
4. Frequency and Recurrence: Nightmares can occur sporadically, but they can also become recurring, with the same or similar themes experienced repeatedly. This repetition can be a significant indicator of underlying fears and anxieties that need to be addressed. Bad dreams, on the other hand, may not occur as frequently or persistently.
It is important to recognize the distinction between nightmares and bad dreams, as the intensity and frequency of nightmares can be indicative of deeper psychological issues. Coping strategies for managing anxiety and nightmares can be valuable in addressing the underlying fears and anxieties associated with nightmares. By understanding the differences between nightmares and bad dreams, individuals can navigate these dream experiences more effectively and seek appropriate support to alleviate distress.
Understanding Anxiety

Anxiety is a complex and multifaceted emotional state that affects people in different ways. It is a normal and natural response to stress or perceived threats, but when anxiety becomes excessive or chronic, it can significantly impact one’s overall well-being. Understanding anxiety involves recognizing its various facets and how it manifests in different individuals.
There are several types of anxiety disorders, each with its unique characteristics and symptoms. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is marked by excessive worry and fear about everyday situations. Panic Disorder involves recurrent and unexpected panic attacks, which are sudden episodes of intense fear accompanied by physical symptoms like a rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Social Anxiety Disorder is characterized by an intense fear of social interactions and situations, while Specific Phobias involve irrational and intense fears of specific objects or situations, such as heights or spiders.
The manifestations of anxiety can vary widely. Physical symptoms may include restlessness, muscle tension, headaches, stomachaches, or fatigue. Emotionally, anxiety can cause irritability, a sense of impending doom, or feelings of being constantly on edge. Cognitive symptoms may manifest as racing thoughts, difficulty concentrating, or excessive worry. Behavioral changes can include avoidance of certain situations or activities, seeking reassurance, or engaging in repetitive behaviors as a way to cope with anxiety.
The link between anxiety and nightmares is significant. Anxiety can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares, as heightened stress levels and emotional turmoil during wakefulness can manifest in vivid and distressing dreams during sleep. Nightmares may serve as symbolic expressions of underlying fears and anxieties, providing valuable insights into the individual’s psychological state.
Understanding anxiety requires a comprehensive exploration of its different forms and how it affects individuals physically, emotionally, cognitively, and behaviorally. By gaining insights into the nature of anxiety, we can then explore its connection to nightmares and begin to uncover strategies for addressing and managing anxiety-related nightmares. Next, we will delve into the role of dreams in processing emotions and how nightmares can be manifestations of anxiety.
1. Overview of Anxiety
1. Overview of Anxiety
Anxiety is a natural emotional response to potential threats or perceived dangers. It is a normal part of life and can even be helpful in certain situations, as it heightens our senses and prepares us to react. However, when anxiety becomes excessive, persistent, and disrupts daily functioning, it may indicate the presence of an anxiety disorder. Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive and uncontrollable worrying, irrational fears, and heightened physical and psychological symptoms of anxiety.
There are several types of anxiety disorders, each with its own specific features and symptoms. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is characterized by persistent and excessive worrying about various aspects of life, such as work, health, or relationships. Panic Disorder involves recurrent panic attacks – sudden and intense episodes of overwhelming fear and physical discomfort, often accompanied by a sense of impending doom. Social Anxiety Disorder, also known as social phobia, manifests as an intense fear of social situations and a constant worry about being judged or embarrassed.
Other anxiety disorders include Specific Phobias, which involve intense fear and avoidance of particular objects or situations; Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), characterized by intrusive and repetitive thoughts (obsessions) and the urge to perform certain rituals or behaviors (compulsions); and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), which occurs after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event and involves intrusive memories, nightmares, and heightened arousal.
The symptoms of anxiety can manifest in various ways, affecting both the mind and body. Common psychological symptoms include excessive worrying, restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances. Physical symptoms may include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, trembling, sweating, dizziness, and gastrointestinal issues. It is important to note that anxiety can significantly impact one’s quality of life, leading to avoidance behaviors, social isolation, and a decline in overall well-being.
Understanding the overview of anxiety provides crucial insights into the psychological and physiological aspects of this complex condition. In the next section, we will explore how anxiety can manifest, providing a deeper understanding of the connection between anxiety and nightmares.
2. Types of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders encompass a range of conditions characterized by excessive and persistent worry, fear, and apprehension. Understanding the different types of anxiety disorders can shed light on the underlying causes and symptoms associated with anxiety. One common type is generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), which involves excessive worry and tension about everyday situations. Individuals with GAD often find it challenging to control their worry, and it can interfere with their daily functioning. Social anxiety disorder (SAD) is another type of anxiety disorder characterized by intense fear and self-consciousness in social situations, leading individuals to avoid or endure such situations with extreme discomfort. Specific phobias are also a type of anxiety disorder, involving a severe and irrational fear of specific objects, animals, or situations. Panic disorder is characterized by recurring panic attacks, which are sudden and intense episodes of fear accompanied by physical symptoms such as a rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an anxiety disorder that can develop after a traumatic event, causing distressing symptoms such as intrusive memories, nightmares, and hypervigilance. Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is another anxiety disorder characterized by intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) aimed at reducing anxiety. Understanding the different types of anxiety disorders enables individuals to recognize and seek appropriate help for their specific condition. With the knowledge and awareness of coping strategies and professional support, individuals can navigate the complexities of anxiety disorders and find effective ways to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. For more information on coping strategies for anxiety and nightmares, refer to this helpful resource here.
3. How Anxiety Manifests
Anxiety can manifest in various ways, affecting individuals both mentally and physically. It is characterized by persistent feelings of unease, worry, and fear that can interfere with daily life. Here are three common manifestations of anxiety:
1. Cognitive Symptoms:
– Racing thoughts and excessive worrying
– Difficulty concentrating or finding it hard to make decisions
– Persistent feelings of dread or impending doom
– Intrusive thoughts or obsessive thinking
– Overthinking and catastrophizing situations
2. Emotional Symptoms:
– Feelings of restlessness or irritability
– Heightened sensitivity to criticism or rejection
– Intense fear or uneasiness
– Easily becoming overwhelmed or feeling on edge
– Mood swings and emotional instability
3. Physical Symptoms:
– Increased heart rate and palpitations
– Shortness of breath or difficulty catching one’s breath
– Muscle tension and headaches
– Upset stomach, digestive issues, or changes in appetite
– Fatigue or difficulty sleeping
It is important to note that everyone experiences anxiety differently, and individuals may exhibit a combination of these symptoms to varying degrees. Recognizing these manifestations helps to identify the presence of anxiety and provides a starting point for addressing and managing it effectively. In the next section, we will explore the intriguing role of nightmares in uncovering and shedding light on underlying fears related to anxiety.
Uncovering the Link: Nightmares and Anxiety
Uncovering the Link: Nightmares and Anxiety
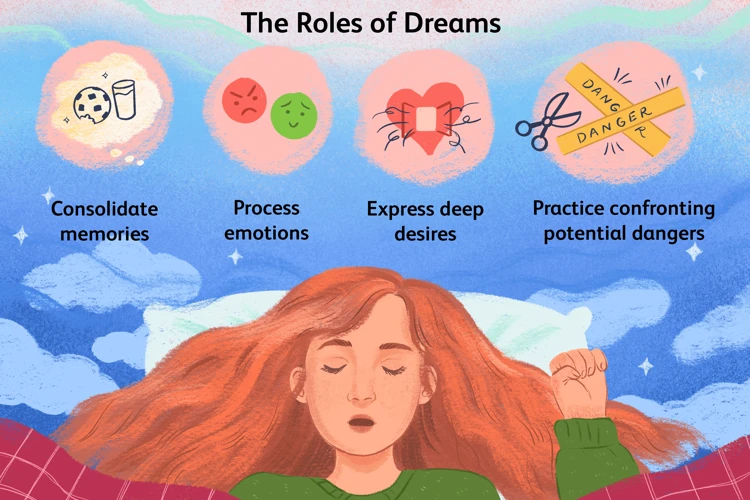
1. The Role of Dreams in Processing Emotions:
Dreams, including nightmares, serve a crucial role in processing and regulating our emotions. During sleep, our brains engage in a complex process of organizing and making sense of the events and emotions we experience while awake. Nightmares can be seen as a way for our subconscious minds to confront and process difficult emotions, particularly those related to anxiety. By presenting us with intense and fear-inducing scenarios, nightmares offer an opportunity for our minds to work through and gain insights into our deepest fears and worries.
2. Nightmares as Manifestations of Anxiety:
Anxiety and nightmares often go hand in hand. While anxiety can manifest in various ways, nightmares provide a distinct outlet for the expression of anxious thoughts and emotions. In individuals with anxiety disorders, nightmares may be more frequent and intense. These dreams can reflect the individual’s underlying fears, worries, and unresolved conflicts related to their anxiety. Nightmares act as a stage where anxieties can take center stage, allowing them to be processed and potentially addressed.
3. Common Anxiety Themes in Nightmares:
Nightmares linked to anxiety can exhibit common themes related to the specific fears and concerns of individuals experiencing anxiety. Some of these themes may include feelings of being trapped or suffocated, being chased or hunted, experiencing physical harm or danger, or facing social humiliation. These anxiety-driven themes often mirror the worries and anxieties that individuals struggle with in their waking lives. Recognizing these common anxiety themes in nightmares can provide valuable insights into the nature of one’s anxiety and help identify areas that require attention and support.
Understanding the link between nightmares and anxiety can be a key step in addressing and managing anxiety effectively. By recognizing the role of dreams in processing emotions, acknowledging nightmares as manifestations of anxiety, and identifying common anxiety themes in nightmares, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their own anxieties and begin to explore strategies for addressing them. In the next section, we will explore techniques for analyzing nightmares and how individuals can leverage them to address and alleviate their anxiety. (You can learn more about managing anxiety nightmares with helpful tips and coping strategies for anxiety nightmares to delve deeper into practical methods for dealing with nightmares related to anxiety.)
1. The Role of Dreams in Processing Emotions
Dreams play a significant role in processing and regulating our emotions. During sleep, our brains engage in a complex series of activities that involve consolidating memories, organizing thoughts, and processing emotional experiences. Dreams serve as a powerful mechanism for the brain to make sense of and integrate these emotions. They provide a safe space for exploring and expressing intense feelings that may be difficult to confront in waking life.
One theory suggests that dreams act as a form of overnight therapy. By reimagining and replaying emotional experiences in our dreams, we are able to process and come to terms with them on a deeper level. This therapeutic process allows for the release of pent-up emotions and can lead to a sense of resolution and understanding. In this way, dreams serve as a natural mechanism for emotional healing and growth.
Dreams can also serve as a means of problem-solving and self-reflection. Sometimes, when faced with a particularly challenging situation or decision, our dream state provides a fresh perspective and new insights. This phenomenon is often referred to as “dream incubation,” where the subconscious mind actively works on unresolved issues and presents possible solutions or alternative viewpoints in dreams.
When it comes to anxiety, dreams play an integral role in helping us process and confront our fears. Anxiety is often rooted in underlying concerns and worries that may be difficult to identify and address consciously. However, our dreams have a way of bringing these fears to the surface, vividly illustrating our anxieties and allowing us to confront them in a controlled environment.
In the context of anxiety disorders, dreams frequently manifest as nightmares, characterized by intense feelings of fear, terror, and distress. These nightmares act as a mirror, reflecting the deep-seated fears and worries that contribute to anxiety. By exploring and analyzing these anxiety-themed dreams, we can gain valuable insights into the underlying factors contributing to our anxiety and begin to develop strategies for addressing and managing it effectively.
Understanding the role of dreams in processing emotions is crucial in grasping the significance of nightmares in uncovering and addressing underlying fears. By acknowledging the therapeutic nature of dreams and their ability to both process and confront emotions, we can start to unlock the potential of nightmares as valuable tools for self-exploration and growth. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the specific link between nightmares and anxiety, exploring their common themes and the implications they hold for addressing anxiety disorders.
2. Nightmares as Manifestations of Anxiety
Nightmares can serve as manifestations of anxiety, providing insight into the underlying fears and concerns that individuals may be experiencing. Anxiety is a psychological condition characterized by excessive worry, fear, and apprehension. It encompasses a broad range of disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder, among others. These anxiety disorders can impact various aspects of a person’s life, including sleep patterns and the occurrence of nightmares.
When anxiety becomes heightened, it can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and trigger nightmares. The emotional distress and recurring themes experienced in nightmares often mirror the anxieties present in an individual’s waking life. For example, someone who has a fear of failure may have nightmares about being unprepared for an exam or facing disastrous consequences at work. Similarly, individuals with social anxiety may have nightmares about embarrassing or humiliating situations in social settings.
Nightmares can act as direct expressions of anxiety, allowing individuals to process and confront their fears on a subconscious level. Through the intense emotions and vivid imagery experienced during nightmares, the mind attempts to work through and make sense of these anxieties. Analyzing the content and symbolism of nightmares can provide valuable insights into the specific fears and concerns that need to be addressed in the waking life.
It is important to note that not all nightmares are solely manifestations of anxiety. They can also arise from other factors such as trauma, stress, medication, and sleep disorders. However, when anxiety is a prevailing factor, nightmares often serve as a window into the fears and anxieties that individuals may be struggling with.
In the next section, we will explore common anxiety themes that frequently appear in nightmares. By understanding these recurring themes, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their own anxieties and take steps towards addressing and managing them more effectively.
3. Common Anxiety Themes in Nightmares
Common Anxiety Themes in Nightmares
Nightmares can often serve as a gateway into understanding and exploring our deepest anxieties and fears. While the specific content and imagery of nightmares may vary from person to person, there are several common anxiety themes that frequently emerge. These themes provide insight into the underlying anxieties we may be grappling with in our waking lives. Here are some examples of common anxiety themes in nightmares:
1. Being Chased or Hunted: This is a prevalent theme in nightmares and often symbolizes a feeling of being pursued or threatened in some way. It may reflect a fear of being unable to escape a certain situation or a sense of being overwhelmed by external pressures.
2. Falling or Losing Control: Dream scenarios involving falling, losing control, or experiencing a sense of powerlessness can indicate feelings of insecurity and a lack of control in our waking lives. These nightmares may signal deep-seated anxieties about failure, instability, or a fear of the unknown.
3. Being Trapped or Unable to Escape: Nightmares featuring a sense of confinement or being trapped can reflect a fear of being stuck in a suffocating situation or feeling unable to break free from constraints. This theme may be associated with anxieties about being trapped in a job, relationship, or other aspects of life.
4. Experiencing Physical Harm: Nightmares involving physical harm, injury, or violence can be unsettling and distressing. These dreams may symbolize a fear of harm, vulnerability, or feelings of inadequacy in being able to protect oneself or others.
5. Public Humiliation or Embarrassment: Dreams portraying situations of public humiliation, embarrassment, or being judged by others may reflect underlying social anxieties or self-esteem issues. These nightmares can be an indication of a fear of judgment, rejection, or a desire for acceptance.
6. Witnessing or Experiencing Disasters: Nightmares that involve witnessing or experiencing natural disasters, accidents, or catastrophes often tap into our primal fears of danger and survival. These dreams may be linked to anxieties about our own vulnerability and the unpredictability of life.
It is important to note that these common anxiety themes in nightmares are not exhaustive, and individual experiences may vary. Nightmares are highly personal, and their interpretation depends on the unique circumstances and emotions of each individual. By recognizing and analyzing these anxiety themes, we can gain valuable insights into our fears, enabling us to address them more effectively and promote emotional well-being.
Addressing Anxiety Through Nightmares
Addressing Anxiety Through Nightmares
Recognizing nightmares as signals is a crucial step in addressing and tackling anxiety. While nightmares can be distressing, they also serve as valuable messengers, offering us insights into our fears and concerns. Paying close attention to the emotions, themes, and imagery in our nightmares can provide important clues about the underlying anxieties we are grappling with. By keeping a dream journal and recording our nightmares, we can begin to identify recurring patterns or themes that point towards specific fears or triggers. This awareness helps us to better understand the root causes of our anxieties and provides a starting point for addressing them effectively.
Techniques for analyzing nightmares can provide us with further tools to address and manage our anxiety. One effective method is dream analysis, which involves exploring the symbolism and meaning behind the elements in our nightmares. This process can be done individually or with the guidance of a therapist who specializes in dream work. By unpacking the hidden messages and symbolism within our nightmares, we can gain deeper insights into our fears and anxieties. We can also unearth possible coping strategies or solutions that may assist us in overcoming these challenges.
Seeking professional help is essential for those struggling with anxiety and nightmares. A mental health professional, such as a therapist or psychologist, can provide valuable guidance and support in addressing the underlying causes of anxiety and nightmares. They can help us explore the deeper psychological issues that may be contributing to our anxiety and provide evidence-based strategies and treatments to manage it effectively. This may include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns, relaxation techniques, or exposure therapy to gradually confront and overcome specific fears or phobias.
Addressing anxiety through nightmares requires recognition, analysis, and support. By recognizing nightmares as signals, analyzing their themes and symbolism, and seeking professional help, we can begin to address and overcome the underlying fears and anxieties that contribute to our nightmares. It is through this process of self-reflection and intervention that we can actively work towards managing anxiety and improving our overall well-being.
1. Recognizing Nightmares as Signals
Sometimes, we may dismiss nightmares as mere products of an overactive imagination or a result of watching a scary movie before bed. However, it is crucial to recognize that nightmares can serve as powerful signals, offering valuable insights into our emotional and psychological well-being. By paying attention to the underlying messages, we can gain a deeper understanding of our fears and anxieties, enabling us to address them effectively.
One way to recognize nightmares as signals is to keep a dream journal. By recording our dreams upon waking, we can capture the details and emotions associated with the nightmare. This practice helps us identify recurring themes or patterns that may be tied to our subconscious fears. Writing down our nightmares also allows us to examine the events or situations within the dream that elicit strong emotional responses.
Another important aspect of recognizing nightmares as signals is acknowledging the emotional impact they have. Nightmares can leave us feeling anxious, frightened, or unsettled long after we wake up. It is crucial to honor these emotions and reflect on their possible connections to our waking life. Are there any current stressors or unresolved issues that could be linked to the content of the nightmare? By recognizing the emotional significance of our nightmares, we can begin to dissect and understand the underlying fears that they represent.
Discussing our nightmares with trusted individuals can provide valuable insights and support. Sharing our experiences with a partner, friend, or therapist allows us to gain different perspectives and interpretations. Sometimes an external viewpoint can shed light on subconscious fears or triggers that we may not have considered.
Recognizing nightmares as signals requires us to view them as more than just scary dreams. They offer a window into our inner world, providing clues to our anxieties and fears. By keeping a dream journal, exploring the emotional impact, and seeking outside perspectives, we can unlock the hidden messages within our nightmares and embark on a journey of self-discovery and healing. In the next section, we will delve into techniques for analyzing nightmares, further aiding us in our quest to address anxiety and its manifestations.
2. Techniques for Analyzing Nightmares
When it comes to analyzing nightmares and understanding their underlying meanings, several techniques can be helpful in unraveling their symbolism.
1. Keep a dream journal: One effective technique is to keep a dream journal next to your bed and write down your nightmares immediately upon waking. Record as many details as possible, including emotions, visuals, and any key symbols or events. This will help you identify recurring themes or patterns in your nightmares over time.
2. Reflect on personal associations: Take some time to reflect on the symbols, events, and emotions present in your nightmares. Consider what these elements may represent to you personally. For example, if you frequently dream of being chased, ask yourself what or whom you feel pursued by in your waking life. This reflection can provide insight into hidden fears or unresolved issues.
3. Seek input from others: Sharing your nightmares with trusted friends or family members can offer fresh perspectives and interpretations. Sometimes, an outside perspective can shed light on aspects of your dreams that you may not have considered.
4. Explore dream analysis resources: There are various resources available, such as books and online guides, that delve into the interpretation of dreams and nightmares. These resources can provide frameworks and insights that may resonate with your experiences. However, it is essential to remember that dream interpretation is subjective, and the meaning of symbols can vary from person to person.
5. Consider professional assistance: If your nightmares persist, significantly distress you, or interfere with your daily functioning, it may be beneficial to consult a mental health professional, such as a therapist or psychologist, who specializes in dream analysis. They can provide guidance, support, and a deeper understanding of the underlying causes of your nightmares.
Remember that analyzing nightmares is a process that requires patience and self-reflection. It’s important to approach this exploration with an open and curious mindset. By using these techniques, you can begin to decode the messages your nightmares may hold and gain valuable insights into your fears, emotions, and subconscious thoughts.
3. Seeking Professional Help
Seeking professional help is a crucial step in addressing anxiety-related nightmares and the underlying fears they represent. While self-analysis and personal coping mechanisms can be effective for some individuals, there are cases where the guidance and expertise of a trained professional are necessary for lasting relief. Here are some considerations and options when seeking professional help for anxiety-related nightmares:
1. Therapists: Psychotherapists, specifically those specializing in anxiety disorders and dream analysis, can help individuals explore the deeper meaning and triggers behind their nightmares. Therapists may use techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, or psychodynamic therapy to address anxiety and its manifestations. Working closely with a therapist allows for a safe environment to process emotions, discuss fears, and identify strategies for managing anxiety-related nightmares.
2. Sleep Specialists: If nightmares significantly disrupt sleep patterns and quality of life, consulting with a sleep specialist may be beneficial. These professionals can conduct assessments to determine if there are any underlying sleep disorders contributing to the nightmares. They may recommend specific sleep hygiene practices or prescribe medications to alleviate nightmares and promote better sleep overall.
3. Support Groups: Engaging in support groups and counseling sessions with others who have experienced similar anxiety-related nightmares can provide a sense of community and validation. These groups can offer a space for sharing experiences, coping mechanisms, and emotional support. Support groups can be found through local mental health organizations or online platforms.
4. Holistic Practitioners: Some individuals find relief through alternative approaches such as acupuncture, mindfulness practices, or herbal remedies. While not scientifically proven to directly address nightmares or anxiety disorders, these holistic practices may help alleviate stress and promote relaxation, contributing to a more peaceful sleep environment.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate avenue for seeking professional help. They can provide guidance, recommend suitable professionals, and help create a personalized plan for addressing anxiety-related nightmares. Remember, seeking professional help is a sign of strength and a proactive step towards regaining control over one’s mental well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the nature of nightmares is a multifaceted and fascinating subject. Nightmares serve as windows into our deepest fears and anxieties, allowing us to confront and address underlying issues that may be contributing to our distress. By understanding the definition of nightmares and recognizing common themes and patterns, we can gain insight into the messages that our subconscious mind is trying to convey. Moreover, we have explored the link between nightmares and anxiety, understanding how nightmares can be manifestations of our anxious thoughts and emotions. Recognizing nightmares as signals and analyzing them using effective techniques can provide us with valuable information for personal growth and healing.
Although managing nightmares can be challenging, there are coping strategies and techniques available to help alleviate their impact on our lives. Seeking professional help from therapists or counselors with expertise in anxiety disorders and dream analysis can be beneficial in addressing the underlying issues that contribute to recurring nightmares. Additionally, implementing relaxation techniques, maintaining a consistent sleep routine, and practicing stress management can all contribute to better sleep and a reduction in nightmare frequency.
Ultimately, by unmasking the anxiety that lies beneath our nightmares, we can embark on a journey of self-discovery and healing. Through a combination of self-reflection, professional guidance, and implementing effective strategies, we can work towards alleviating anxiety and its manifestations in our dreams. In doing so, we can achieve a deeper sense of peace, improved sleep quality, and a greater understanding of our inner selves. So, embrace the power of nightmares, for within them lies the opportunity to uncover and address our underlying fears.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How often do nightmares occur?
Nightmares can occur from time to time for most people. However, the frequency of nightmares varies from person to person. Some individuals may experience nightmares sporadically, while others may have them more frequently, even multiple times a week.
2. Can nightmares be caused by external factors?
Yes, external factors can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. Stress, trauma, anxiety, medication side effects, substance abuse, sleep disorders, and even certain foods can trigger nightmares in susceptible individuals.
3. Are nightmares only experienced by children?
No, nightmares are not limited to children. While nightmares are more common in children, with up to 50% of children experiencing them at some point, adults can also have nightmares. In fact, nightmares can persist into adulthood and be a manifestation of underlying fears and anxieties.
4. Can nightmares be interpreted in a specific way?
Interpretation of nightmares varies depending on the individual and their personal experiences. While some believe that nightmares have symbolic meanings and may reflect unresolved emotions or subconscious fears, others view them as a result of random brain activity during sleep. Therapy or dream analysis may help uncover the potential significance of recurring nightmares.
5. Can nightmares be prevented?
While it is not always possible to prevent nightmares entirely, there are some strategies that may help reduce their frequency or severity. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a calm sleep environment, managing stress and anxiety, and avoiding certain triggers like heavy meals or stimulating substances close to bedtime can potentially decrease the occurrence of nightmares.
6. Are nightmares a sign of a mental health disorder?
Nightmares alone are not indicative of a mental health disorder. However, they can be a symptom or manifestation of an underlying condition such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, depression, or personality disorders. If nightmares are frequent or significantly impact daily functioning, it may be helpful to consult with a mental health professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
7. Can medications help in treating nightmares?
Medications may be prescribed in certain cases to help manage nightmares, especially when they are associated with specific conditions such as PTSD. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, or medications that suppress REM sleep cycles can be used to alleviate nightmares. However, medication should always be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional.
8. Can lucid dreaming techniques be used to control nightmares?
Lucid dreaming techniques, which involve becoming aware that one is dreaming while in the dream state, can potentially be used to gain some control over nightmares. By developing the ability to recognize that one is dreaming during a nightmare, individuals may be able to actively influence the dream’s outcome or wake themselves up, reducing the negative impact of the nightmare.
9. Do nightmares always have underlying fears or anxieties?
While nightmares often reflect underlying fears or anxieties, not all nightmares have a specific meaning or connection to one’s psychological state. Sometimes, nightmares can result from a combination of random brain activity and external stimuli. However, for individuals who experience recurrent nightmares, exploring the underlying fears and anxieties can be beneficial in addressing and resolving these issues.
10. Are there any positive aspects to having nightmares?
Although nightmares are generally seen as unpleasant experiences, they can serve a purpose in our psychological and emotional growth. Nightmares can provide valuable insights into our subconscious fears, allowing us to confront and address them. By exploring the themes and emotions in nightmares, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of themselves and potentially make positive changes in their lives.








