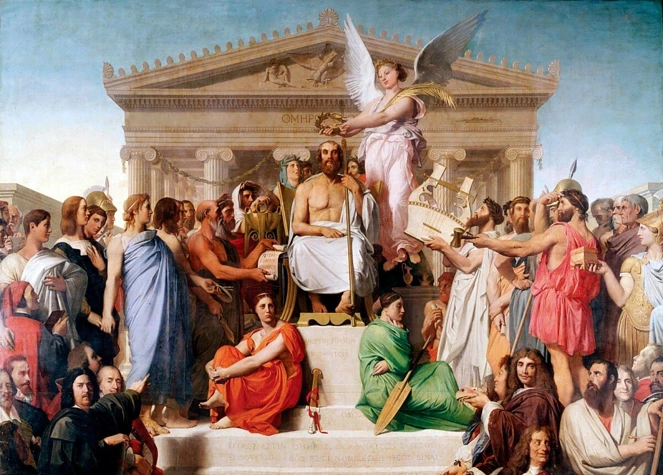
The Role of Mythology in Ancient Rituals and Festivals: Unraveling the Intricate Connection Between Myth and Tradition
Step back in time to the ancient world, where myth and ritual intertwined to create a tapestry of beliefs and practices. Mythology, with its captivating stories and larger-than-life figures, played a central role in shaping the rituals and festivals of ancient civilizations. In this article, we delve into the power of mythology and explore its significance in ancient societies. From the importance of mythical beliefs to the incorporation of mythological narratives in rituals, we uncover the profound impact that mythology had on the social, religious, and psychological fabric of ancient communities. Join us on this journey as we unravel the intricate connection between myth and tradition, shedding light on a fascinating era where gods and mortals coexisted.
The Power of Mythology
Mythology possesses an undeniable power, captivating and inspiring generations with its rich narratives and fantastical realms. The Importance of Mythical Beliefs lies in their ability to provide meaning and purpose to ancient civilizations. These myths were much more than mere stories; they were a source of collective wisdom and understanding, offering explanations for the mysteries of the natural world and the complexities of human existence. Whether it was the Greek pantheon with their tales of gods and heroes, the Egyptian Book of the Dead shedding light on the afterlife, or the roles of gods and goddesses in Norse mythology, these beliefs shaped the cultural identity and spiritual practices of entire societies. Exploring the origins and symbolism of Greek mythology, the concept of the afterlife in the Egyptian Book of the Dead, and the roles of gods and goddesses in Norse mythology, we begin to unravel the deeper layers of meaning embedded within these ancient belief systems.
Link: Origins and Symbolism in Greek Mythology
1. Importance of Mythical Beliefs
The importance of mythical beliefs in ancient societies cannot be overstated. These beliefs served as a foundation for understanding the world and one’s place in it. They provided a sense of meaning and purpose, offering explanations for natural phenomena, the creation of the universe, and the origins of humanity. Ancient Egyptian mythology, for example, famously depicted the journey of the soul in the afterlife, as described in the Egyptian Book of the Dead. People believed in the existence of an intricate underworld and a complex judgment process to determine one’s fate beyond death. In Norse mythology, the gods and goddesses played various roles in the world, representing different aspects of life and serving as symbols of human virtues and vices. These mythic narratives shaped the moral compass of ancient societies and influenced their daily lives and decision-making processes. They fostered a deep connection between individuals and their cultural heritage, promoting a sense of unity and shared identity. By embracing mythical beliefs, ancient civilizations found solace, guidance, and a sense of belonging that permeated the fabric of their existence.
2. Mythological Figures and Deities
When it comes to ancient rituals and festivals, Mythological Figures and Deities played a central role in shaping the beliefs and practices of ancient civilizations. These mythical beings were revered as powerful entities with supernatural abilities, serving as intermediaries between humans and the divine. Each culture had its own pantheon of gods and goddesses, such as the mighty Zeus and Athena in Greek mythology or the revered Ra and Osiris in Egyptian mythology. These mythological figures were not just characters in stories; they embodied the ideals and values cherished by their respective societies.
In Norse mythology, for example, gods and goddesses like Odin, Thor, and Freya held significant roles in shaping the world and the destiny of humans. Odin, the All-Father and chief deity, embodied wisdom and knowledge. Thor, the god of thunder, symbolized strength and protection, while Freya, the goddess of love and beauty, represented fertility and abundance.
The attributes and actions of these mythological figures were often portrayed in artwork and sculptures, allowing the ancient societies to connect with and honor these deities. Through rituals and festivals, people sought to appease and invoke the favor of these divine beings. These figures served as a source of inspiration and guidance, as well as a way to explain natural phenomena and human experiences.
Whether it was the powerful gods and goddesses of Greek and Norse mythologies or the diverse pantheon of Egyptian deities, mythological figures played a significant role in the religious and cultural practices of ancient societies. Each deity had their own unique attributes and dominions, offering a sense of order and purpose to the lives of the ancient people. Their stories and symbolism continue to fascinate us today, providing a window into the beliefs and imagination of our ancestors.
Link: Roles of Gods and Goddesses in Norse Mythology
Rituals and Festivals
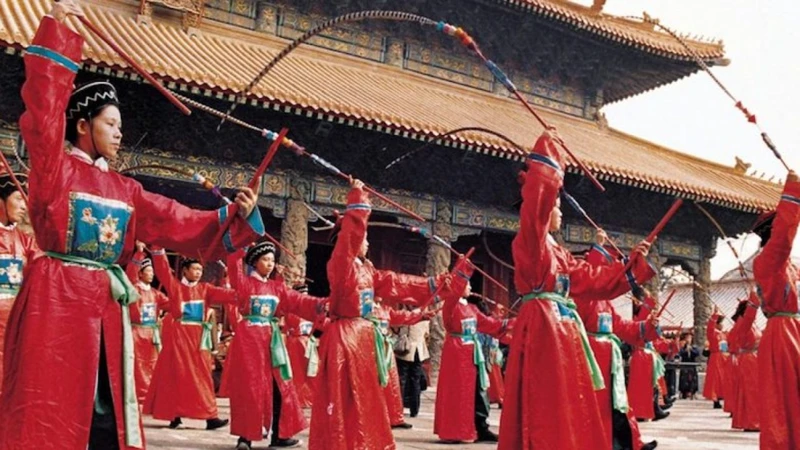

Rituals and festivals formed the heart of ancient communities, serving as a bridge between the mortal realm and the divine. These sacred ceremonies were infused with mythological narratives, which gave them a profound sense of meaning and purpose. From the incorporation of mythological narratives into ceremonies to the symbolism embedded within the rituals themselves, these practices were a reflection of the collective beliefs and values of a society. They fostered a sense of unity and cohesion, strengthening social bonds and reinforcing a shared cultural identity. These rituals and festivals often involved elaborate processions, music, dance, and feasting, creating a sense of joy and celebration. The ritualistic practices and offerings made during these events were believed to appease the gods, seek their favor, and ensure the prosperity and well-being of the community. Whether it was the stunning Persephone Festival in ancient Greece or the sacred rituals conducted during the Mayan New Year, these ceremonies were a vital part of ancient societies, connecting individuals to their mythological heritage and providing a conduit for spiritual and communal experiences.
1. Incorporation of Mythological Narratives
The incorporation of mythological narratives was a fundamental aspect of ancient rituals and festivals. Through storytelling and reenactments, myths and legends were brought to life, allowing individuals to connect with the divine and their cultural heritage. These narratives formed the basis for the rituals and ceremonies performed during these events, providing a sense of continuity and tradition. Mythological narratives not only entertained and educated, but they also served a deeper purpose. They conveyed important moral lessons, preserved historical accounts, and reinforced social values within the community. By weaving mythological stories into the fabric of rituals and festivals, ancient societies ensured the transmission of their cultural identity and beliefs to future generations. The myths acted as a bridge between the mortal world and the divine, allowing individuals to participate in the timeless stories of their gods and ancestors. This incorporation of mythological narratives added a layer of depth and meaning to the rituals and festivals, creating a powerful and immersive experience for all involved.
2. Symbolism in Rituals and Festivals
Symbolism in rituals and festivals played a crucial role in ancient civilizations, infusing these ceremonial practices with deeper meaning and significance. Symbolism was a language of its own, using visual representations, gestures, and objects to convey messages and evoke powerful emotions. Through intricate symbolism, rituals and festivals connected the mundane world with the divine, bridging the gap between mortals and gods. Each element of these rituals had a purpose, with symbolic actions and offerings representing abstract concepts and spiritual beliefs. For example, the use of fire in rituals symbolized purification and transformation, while the offering of flowers represented beauty, growth, and fertility. Additionally, certain colors held symbolic value, such as white symbolizing purity and red symbolizing power and vitality. By participating in these symbolic rituals and festivals, ancient communities sought to align themselves with the divine forces and harness their power for collective well-being and spiritual growth. Thus, symbolism not only added depth to these ancient traditions but also fostered a sense of awe, reverence, and connection to the spiritual realm.
3. Ritualistic Practices and Offerings
Ritualistic practices and offerings were an integral part of ancient societies, deeply rooted in their mythological beliefs and traditions. These practices were performed with precision and reverence, aiming to establish a connection between the mortal and divine realms. One common ritualistic practice was the sacrifice, which involved offering animals, crops, or valuable objects to the gods or goddesses. This act symbolized an exchange between humans and the divine, with the hope of gaining favor or appeasing the deities. The choice of offerings varied depending on the specific mythology and purpose of the ritual. For example, in Greek mythology, various animals were commonly sacrificed, such as bulls, goats, and sheep. In Norse mythology, on the other hand, offerings often included mead, weapons, and precious items. These rituals were often accompanied by elaborate ceremonies, chants, dances, and prayers, creating a sacred atmosphere and involving the entire community in their observance. The meticulousness of these practices reflected the deep respect and belief in the power of the gods, as well as the desire to maintain harmony with the divine forces that governed their existence.
Impact on Ancient Societies
The impact of mythology on ancient societies was far-reaching and profound, permeating every aspect of their social, religious, and psychological realms. Social Cohesion and Identity were fostered through shared mythological narratives, providing a sense of belonging and unity among community members. These myths served as a common cultural heritage, reinforcing social bonds and establishing a collective identity. Mythology played a significant role in influencing and shaping religious and spiritual practices. Religious and Spiritual Significance influenced rituals, ceremonies, and offerings dedicated to the gods. Ancient communities sought divine favor and blessings through these practices, ensuring their spiritual well-being and protection. Lastly, the impact of mythology extended to the Psychological and Emotional Effects on individuals. The stories and legends intertwined with the human experience, offering solace, hope, and guidance during times of uncertainty, grief, or longing. The impact of mythology on ancient societies cannot be overstated, as it shaped their collective consciousness, moral values, and understanding of the world and its purpose.
1. Social Cohesion and Identity
Social cohesion and identity were profoundly influenced by mythology in ancient societies. Mythological narratives served as a powerful tool to unite communities by providing shared stories, traditions, and values. These myths created a sense of belonging and a collective identity among individuals who identified with the characters and events depicted in their cultural folklore. The stories of gods, heroes, and epic battles served as a common thread that connected people from different regions and backgrounds. They were shared, retold, and passed down through generations, strengthening the bonds within communities and fostering a sense of unity.
Mythology played a crucial role in constructing the societal hierarchy and reinforcing social norms. The tales of powerful gods and goddesses demonstrated the proper conduct and virtues that society valued. For example, the Greek myth of Prometheus emphasized the significance of defying the gods’ will and the consequences of disobedience. These myths were not only cautionary tales but also provided a moral compass for individuals to navigate their daily lives.
Rituals and festivals rooted in mythology provided a platform for collective participation and celebration, further enhancing social cohesion. Whether it was the lavish ceremonies dedicated to the Egyptian gods or the vibrant festivals honoring Greek deities, these communal events brought people together, fostering a sense of community and reinforcing shared beliefs and values.
Mythology played a significant role in shaping the social cohesion and identity of ancient societies. Through shared narratives, moral teachings, and collective rituals, mythology provided a framework that united individuals, reinforced societal norms, and fostered a sense of belonging and collective identity within communities.
2. Religious and Spiritual Significance
2. Religious and Spiritual Significance
The religious and spiritual significance of mythology in ancient rituals and festivals cannot be overstated. Mythology provided a framework for understanding the divine and the mysteries of the universe. It served as a bridge between the mortal realm and the realm of the gods, offering guidance and establishing a connection to the divine. Ancient societies believed in the existence of powerful deities who controlled various aspects of life, and through mythology, they created rituals and festivals to honor and appease these gods.
Religion played a central role in ancient societies, and mythology served as the backbone of religious practices. It dictated not only the ceremonies and rituals performed but also the moral and ethical codes followed by individuals and communities. The gods and goddesses represented ideals and values, and their stories served as moral lessons for the believers.
Spirituality, on the other hand, delved deeper into the personal connection with the divine. Mythology provided individuals with a sense of purpose and meaning, allowing them to seek personal enlightenment and transcendence. Ancient rituals and festivals were not just social gatherings; they were spiritual experiences where individuals communed with the gods, sought divine guidance, and connected with their inner selves.
To highlight the religious and spiritual significance of mythology, let’s examine two examples from different ancient civilizations. In Ancient Greece, the Olympic Games were not just sporting events but also religious ceremonies held in honor of Zeus, the king of the gods. The games were believed to bring favor from the gods and unite the Greek city-states in peaceful competition.
Similarly, in ancient Egypt, the annual flooding of the Nile River was seen as a divine event controlled by the god Hapi. This natural phenomenon was celebrated through rituals and festivals, thanking the gods for their benevolence and ensuring a prosperous harvest season.
The religious and spiritual significance of mythology in ancient rituals and festivals encompassed the belief in higher powers, the performance of rituals to honor and connect with the divine, and the exploration of personal spirituality. Mythology provided ancient societies with a moral and ethical framework and served as a guiding force in their religious practices and spiritual journeys.
html table solution:
| Religious Significance | Mythology provided a framework for understanding the divine and the mysteries of the universe. |
| Ancient societies created rituals and festivals to honor and appease powerful deities. | |
| Mythology dictated religious ceremonies, rituals, and moral codes. | |
| Gods and goddesses represented ideals and values, and their stories served as moral lessons. | |
| Spiritual Significance | Mythology provided individuals with purpose and meaning. |
| Ancient rituals and festivals were spiritual experiences connecting individuals with the divine. | |
| Personal enlightenment and transcendence were sought through mythology. |
3. Psychological and Emotional Effects
The influence of mythology on ancient societies extended beyond the realm of social cohesion and religious significance. It also had a profound impact on the psychological and emotional well-being of individuals. The stories and archetypal figures found in myths were vehicles for exploring the depths of human experience and understanding the complexities of the human psyche. Mythology provided a framework for interpreting and navigating life’s challenges, offering individuals a sense of purpose, meaning, and guidance in their personal journeys.
One of the psychological effects of mythology was the sense of identity and belonging it instilled in individuals. By connecting themselves to the mythical narratives and characters, people felt a deeper connection to their ancestral roots and a greater sense of belonging within their communities. This connection to the past and shared ancestry fostered a sense of cultural pride and identity, strengthening social bonds and promoting unity among diverse individuals.
Beyond identity, mythology also played a role in emotional healing and catharsis. The mythical tales often depicted the struggles and triumphs of gods, heroes, and mortals, reflecting the universal human experience of joy, love, loss, and suffering. Through these stories, individuals found solace and a sense of catharsis as they witnessed their own emotions and struggles mirrored in the lives of mythical beings. The narratives served as a source of comfort, allowing individuals to process, understand, and cope with their own emotions and experiences.
Mythology provided a source of inspiration and motivation for individuals to overcome challenges and strive for personal growth. The heroes and heroines in mythological tales embodied virtues such as courage, resilience, and wisdom. Their journeys and trials served as powerful metaphors for the transformative potential within each person. By internalizing these ideals and drawing inspiration from mythical figures, individuals found the strength and determination to face their own obstacles and embark on their own heroic quests.
The psychological and emotional effects of mythology were far-reaching and profound. It provided individuals with a sense of identity and belonging, facilitated emotional healing and catharsis, and served as a wellspring of inspiration and motivation. The power of mythology to delve into the depths of the human psyche and offer guidance in navigating life’s challenges is a testament to its enduring significance in ancient societies.
Link: The Egyptian Book of the Dead and the Concept of the Afterlife
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of mythology in ancient rituals and festivals cannot be overstated. Throughout history, mythology has served as a powerful force, shaping the beliefs, rituals, and traditions of ancient societies. It provided a framework for understanding the world, offering answers to fundamental questions and defining the cultural identity of these civilizations. Mythological figures and deities were not simply characters in stories; they held profound significance and played an active role in the lives of people. The incorporation of mythological narratives in rituals and festivals added depth and meaning to these practices, reinforcing social bonds and connecting individuals with their spiritual heritage. Symbolism played a crucial role in these ancient ceremonies, as objects and rituals were imbued with deeper meanings and associations. Whether it was offering sacrifices to appease the gods, reenacting mythical events, or invoking the supernatural powers of deities, rituals served as a bridge between the mortal and divine realms, fostering a sense of awe and reverence. The impact of these mythological rituals extended beyond the spiritual realm; they created a sense of social cohesion and collective identity within ancient communities. Through shared belief systems and participation in rituals, individuals formed connections and fostered a sense of belonging. Moreover, these rituals had profound psychological and emotional effects on participants, providing a sense of purpose and meaning in life. The enduring influence of mythology can still be observed in various forms today, as ancient stories continue to inspire literature, art, and popular culture. By studying the role of mythology in ancient rituals and festivals, we gain insights into the depths of human imagination and the universal quest for understanding our place in the world.
Overall, the legacy of mythology in ancient rituals and festivals is one of wonder, fascination, and a profound appreciation for the power of storytelling. It reminds us of the enduring human need for connection, meaning, and a desire to make sense of the world around us.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How did mythology shape the rituals and festivals of ancient civilizations?
Mythology played a fundamental role in shaping rituals and festivals in ancient civilizations by providing the narratives, symbolism, and belief systems that formed the basis of these practices. Mythological stories and figures often served as the inspiration for rituals and festivals, creating a connection between the divine and the mortal realms.
2. What is the significance of incorporating mythological narratives in rituals?
Incorporating mythological narratives in rituals adds a layer of meaning and symbolism to the practices. These narratives not only bring to life the stories of gods, heroes, and mythical beings but also allow participants to connect with and embody the qualities and attributes represented by these figures.
3. How did symbolism play a role in ancient rituals and festivals?
Symbolism was integral to ancient rituals and festivals as it conveyed deeper meanings and invoked spiritual or sacred qualities. Symbols, whether in the form of objects, gestures, or actions, represented concepts, ideals, and the mystical forces associated with the mythology, enhancing the transformative and transformative power of the rituals.
4. What were some common ritualistic practices and offerings in ancient societies?
Common ritualistic practices in ancient societies included prayers, chants, dances, and purification rituals. Offerings such as food, drink, flowers, or precious items were made as a gesture of devotion or gratitude to the deities. Sacrifices, both animal and symbolic, were also prevalent in various cultures.
5. How did mythology contribute to social cohesion and identity in ancient societies?
Mythology provided a shared framework of beliefs, stories, and values that fostered social cohesion and a sense of collective identity in ancient societies. It created a common mythology, shared rituals, and a shared understanding of the world, serving as a unifying force amidst diverse communities.
6. What was the religious and spiritual significance of mythology in ancient civilizations?
Mythology held immense religious and spiritual significance in ancient civilizations. It served as the basis for religious practices, rituals, and the worship of deities. It provided moral and ethical guidance, offered explanations for the creation of the world, and explored the nature of good and evil, ultimately shaping the spiritual beliefs and practices of the people.
7. How did mythology impact the psychological and emotional well-being of individuals in ancient societies?
Mythology had a profound impact on the psychological and emotional well-being of individuals in ancient societies. Mythical stories and figures served as archetypes, offering guidance, inspiration, and a sense of purpose. They provided a framework for understanding and navigating life’s challenges, offering solace, hope, and a sense of connectedness to something greater than oneself.
8. Was mythology limited to religious practices, or did it influence other aspects of ancient societies?
While mythology had a significant influence on religious practices, it also extended its reach to other aspects of ancient societies. Mythical themes were often depicted in art, architecture, literature, and even political systems. They shaped cultural norms, social structures, and the worldview of the people.
9. Were there regional variations in the mythology and rituals of ancient civilizations?
Absolutely! There were numerous regional variations in the mythology and rituals of ancient civilizations. Different cultures and geographical locations gave rise to unique mythological narratives, deities, and ritualistic practices. While certain overarching themes may have been present, each civilization had its own distinct myths and rituals that reflected their specific beliefs and traditions.
10. Can we still see the influence of ancient mythology in contemporary rituals and festivals?
Absolutely! The influence of ancient mythology can still be seen in contemporary rituals and festivals across the globe. Many cultural traditions, religious ceremonies, and even popular celebrations draw inspiration from ancient mythological narratives, employing symbols, stories, and customs that have been passed down through generations, maintaining a connection to our ancient past.








