The mind is a mysterious realm that often holds hidden fears and anxieties. One such manifestation of these inner tumults is in the form of nightmares, the harbingers of unease that disrupt our precious moments of rest. Nightmares can have a profound impact on our sleep, leaving us feeling exhausted, anxious, and yearning for a reprieve. However, the relationship between nightmares, anxiety, and sleep disorders goes even deeper. Understanding this intricate connection can illuminate the causes and potential solutions for these unsettling nighttime experiences. So, let us embark on a journey to uncover the enigma of nightmares, explore the intricate dance between anxiety and sleep disorders, and discover how we can alleviate their grip on our restless minds.
The Impact of Nightmares on Sleep
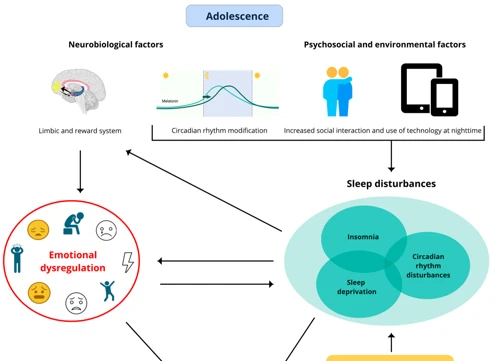
Nightmares have a profound impact on our sleep, disrupting its natural rhythm and leaving us feeling unsettled and anxious. These vivid and often distressing dreams can cause a range of disturbances, including increased nighttime awakenings, disturbed sleep patterns, and even insomnia. The negative effects of nightmares on sleep quality can further exacerbate anxiety and heighten feelings of unease, creating a vicious cycle that interferes with our overall well-being. Additionally, nightmares can be particularly distressing for individuals who have experienced trauma, as they may serve as reminders or reenactments of past traumatic events. Recognizing the impact of nightmares on sleep is crucial in understanding the importance of finding effective treatments to alleviate their occurrence and improve overall sleep health.
Definition and Characteristics of Nightmares
Nightmares can be defined as vivid and distressing dreams that occur during REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, which is a stage of sleep associated with heightened brain activity and intense dreaming. These nightmares often evoke strong emotions such as fear, terror, or anxiety, and are typically accompanied by a sense of threat or danger. The characteristics of nightmares can vary from person to person, but common elements include vivid imagery, intense emotional responses, and a sense of being trapped or unable to escape. Some individuals may experience recurring nightmares, where the same or similar themes and events occur repeatedly. It is important to note that nightmares are different from night terrors, which are episodes of abrupt awakening accompanied by intense fear and physical arousal. Understanding the definition and characteristics of nightmares is crucial in recognizing their impact on sleep and taking steps towards finding effective treatments, such as therapy, to alleviate their occurrence and improve overall sleep quality.
Types of Nightmares
There are various types of nightmares that can haunt our sleep, each with its own distinct characteristics and themes. Understanding these different types can provide insights into the underlying anxieties and fears that may be triggering them. One common type is anxiety nightmares, which are often associated with everyday worries and stressors. These nightmares typically reflect our concerns about work, relationships, or upcoming events, and they can leave us feeling anxious and unsettled even after waking up. Another type is recurring nightmares, which involve the repetitive occurrence of the same or similar dream themes. These nightmares can be particularly distressing, as they can make us feel trapped in a cycle of fear and unease every time we fall asleep. Nightmares can also be trauma-related, triggered by past traumatic experiences. These nightmares may reenact the trauma or incorporate elements of it, causing intense distress and anxiety. Additionally, parasomnia nightmares are characterized by unusual sleep behaviors, such as sleepwalking or night terrors, which can be incredibly disruptive and distressing. Exploring the different types of nightmares sheds light on the unique ways they impact our sleep and mental well-being, highlighting the importance of finding effective strategies to cope with and mitigate their effects. To further understand the impact of stress on nightmares, you can read our article on exploring the stress impact on nightmares.
Anxiety and Sleep Disorders

Anxiety and sleep disorders often go hand in hand, creating a complex and intertwined relationship that can significantly impact our well-being. Anxiety disorders encompass a range of conditions, such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder, characterized by persistent feelings of worry, fear, and apprehension. These anxiety disorders can directly contribute to the development of various sleep disorders, including insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless leg syndrome. The constant state of heightened arousal and racing thoughts experienced by individuals with anxiety can make it difficult to relax and fall asleep. Conversely, the lack of quality sleep caused by these sleep disorders can exacerbate anxiety symptoms. This intricate connection between anxiety and sleep disorders underscores the importance of addressing both issues simultaneously to improve overall mental health and sleep quality.
Understanding Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by intense and excessive worry, fear, and unease. These disorders can significantly impact a person’s daily life and overall well-being. Individuals with anxiety disorders often experience a range of symptoms, including restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances. There are several types of anxiety disorders, each with its own distinct features. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) involves persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life, while Panic Disorder is characterized by recurrent panic attacks accompanied by intense physical symptoms. Social Anxiety Disorder revolves around an overwhelming fear of social situations and a persistent concern of being judged by others. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) arises following a traumatic event and involves intrusive thoughts, nightmares, and flashbacks. Understanding these different anxiety disorders is essential in identifying symptoms and providing appropriate support and treatment for individuals who are experiencing anxiety-related sleep disturbances.
Common Sleep Disorders Associated with Anxiety
Common Sleep Disorders Associated with Anxiety:
– Insomnia: Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing poor quality sleep. Anxiety can play a significant role in the development and maintenance of insomnia. The racing thoughts and worries that accompany anxiety can make it difficult for individuals to quiet their minds and relax, leading to insomnia.
– Nighttime Panic Attacks: Anxiety can trigger nighttime panic attacks, which are sudden and intense episodes of fear or discomfort that occur during sleep. These panic attacks can jolt individuals awake, leaving them feeling panicked and unable to return to sleep.
– Sleep Apnea: Anxiety has been found to be associated with an increased risk of sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep. Anxiety can lead to muscle tension and heightened arousal, which can contribute to the development or exacerbation of sleep apnea.
– Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): RLS is a neurological disorder characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. Anxiety and stress can exacerbate symptoms of RLS, making it more difficult for individuals to relax and fall asleep.
– Narcolepsy: Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. Anxiety can worsen symptoms of narcolepsy, such as excessive daytime sleepiness and fragmented nighttime sleep.
It’s important to note that these sleep disorders can both contribute to and be worsened by anxiety. Understanding the relationship between anxiety and these sleep disorders is crucial in developing comprehensive treatment approaches that address both the anxiety and sleep disturbances.
The Role of Anxiety in Nightmares
Anxiety plays a pivotal role in the occurrence and intensity of nightmares. It is not uncommon for individuals with anxiety disorders to experience more frequent and intense nightmares compared to those without anxiety. The heightened emotional arousal associated with anxiety can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and lead to a greater likelihood of nightmares. Anxiety can also influence the content and themes of nightmares. For example, individuals with generalized anxiety disorder may have nightmares centered around themes of impending danger or worry, reflecting their persistent anxious thoughts and concerns. Additionally, anxiety-related nightmares often involve feelings of panic, fear, or being trapped, further exacerbating the distress experienced during sleep. It is important to note that nightmares can also contribute to the development or worsening of anxiety disorders, creating a vicious cycle where anxiety fuels nightmares, and nightmares perpetuate anxiety. Addressing anxiety through various therapeutic interventions can be instrumental in mitigating the frequency and intensity of nightmares and improving overall sleep quality. For more information on the benefits of therapy for anxiety and nightmares, check out our article on therapy for anxiety and nightmares.
How Nightmares and Anxiety Affect Sleep Quality

Nightmares and anxiety disrupt the delicate balance of sleep quality, leading to a variety of detrimental effects. The presence of nightmares can cause disturbed sleep patterns by interrupting the normal progression from lighter to deeper sleep stages. As a result, individuals may experience frequent awakenings throughout the night, preventing them from achieving a restful and rejuvenating sleep. This constant arousal can contribute to feelings of increased nighttime anxiety and a heightened state of alertness, further compromising the ability to relax and sleep deeply. The occurrence of recurring nightmares can lead to a specific type of sleep disorder known as insomnia, where an individual struggles to fall asleep or stay asleep. The intertwining relationship between nightmares and anxiety creates a challenging cycle that negatively impacts sleep quality and overall well-being.
Disturbed Sleep Patterns
Disturbed sleep patterns are a common consequence of experiencing nightmares. The unsettling nature of these dreams can jolt individuals out of deep sleep, causing frequent arousals throughout the night. This disruption in sleep architecture can prevent individuals from experiencing sufficient amounts of REM sleep (rapid eye movement), which is essential for the brain’s processing of emotions and memories. As a result, individuals may find themselves feeling fatigued and groggy during the day, impairing their cognitive function and overall well-being. The repeated interruptions to sleep caused by nightmares can also lead to a phenomenon known as sleep fragmentation, where the sleep cycle is consistently interrupted, preventing individuals from obtaining the restorative sleep they need. This can contribute to a constant state of sleep deprivation and exacerbate feelings of anxiety and stress. It is crucial to address these disturbed sleep patterns to ensure a more rejuvenating and restful night’s sleep. Strategies such as creating a conducive sleep environment, practicing relaxation techniques before bed, and seeking professional help are essential in combatting the negative impact of disturbed sleep patterns caused by nightmares.
Increased Nighttime Awakenings
Increased nighttime awakenings are a common consequence of experiencing nightmares. When a person has a nightmare, the intense emotions and fears can jolt them awake, interrupting their sleep cycle. These awakenings can be sudden and frequent, making it difficult for individuals to achieve a restful night’s sleep. The disruption of the sleep cycle can lead to feelings of fatigue and grogginess during the day. The fear of experiencing another nightmare can create anxiety around falling asleep, further contributing to the cycle of disturbed sleep. Individuals who experience increased nighttime awakenings may also have difficulty falling back asleep after waking up from a nightmare, prolonging the overall disruption to their sleep pattern. To address this issue, it is important to explore therapeutic approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, which can help individuals manage anxiety and develop coping strategies to minimize the impact of nightmares on their sleep. Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques and maintaining a consistent sleep hygiene routine can contribute to better sleep quality and reduce the frequency of nighttime awakenings.
Recurring Nightmares and Insomnia
Recurring nightmares can be a major contributor to insomnia, a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. When nightmares become a frequent occurrence, they can create a heightened level of anxiety and fear around going to sleep. As a result, individuals may develop a conditioned response, associating sleep with distressing dreams and anticipating their recurrence, which further disrupts the ability to fall asleep and maintain a restful sleep throughout the night. The fear of experiencing recurring nightmares can lead to bedtime anxiety and a reluctance to engage in sleep, creating a self-perpetuating cycle of sleeplessness. Insomnia caused by recurring nightmares can have a profound impact on one’s overall well-being, leading to daytime fatigue, impaired concentration, mood disturbances, and decreased productivity. Addressing the root causes of both the nightmares and the resulting insomnia is essential for improving sleep quality and breaking the cycle of sleep disruption. Techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy and relaxation methods can help individuals effectively manage and reduce the impact of recurring nightmares on their sleep and overall quality of life.
Treatment Approaches for Nightmares, Anxiety, and Sleep Disorders

When it comes to treating nightmares, anxiety, and sleep disorders, there are various approaches that can provide relief and improve overall well-being. One such approach is cognitive behavioral therapy, which aims to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with sleep disturbances. This therapy can help individuals develop coping mechanisms for managing anxiety and reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Another option is the use of medication, which can be prescribed to address specific sleep disorders or manage anxiety symptoms that contribute to nightmares. Additionally, incorporating relaxation techniques and sleep hygiene practices into one’s daily routine can promote a more peaceful and restorative sleep. These techniques may include deep breathing exercises, mindfulness meditation, and establishing a regular sleep schedule. Finding the right combination of treatments and tools tailored to individual needs is key to managing nightmares, anxiety, and sleep disorders effectively.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and effective treatment approach for addressing nightmares, anxiety, and sleep disorders. This therapeutic approach focuses on identifying and reshaping negative thoughts, beliefs, and behaviors that contribute to the development and maintenance of these issues. In the context of nightmares, CBT aims to help individuals reframe their interpretation and reaction to these distressing dreams. Through techniques such as imagery rehearsal therapy, individuals can actively change the content and outcome of their nightmares by mentally rehearsing alternative, more positive scenarios. CBT also addresses the underlying anxiety that fuels nightmares and sleep disorders by teaching relaxation techniques, stress management strategies, and sleep hygiene practices. By working with a trained therapist, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the root causes of their nightmares, develop coping skills, and gradually regain control over their sleep and overall well-being. CBT has been shown to have long-lasting effects and can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares, thus improving sleep quality and reducing anxiety levels. It is important to note that CBT may not be suitable for everyone, and individualized treatment plans should be discussed with a healthcare professional or therapist to determine the most appropriate approach.
Medication Options
When it comes to medication options for treating nightmares, anxiety, and sleep disorders, there are several possibilities to consider. It is important to note that medication should always be prescribed and monitored by a qualified healthcare professional, as they can assess individual needs and determine the most appropriate course of treatment. Below are some common medication options that may be considered:
1. Antidepressants: Certain antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), have been found to reduce the occurrence and intensity of nightmares. These medications work by modulating the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, which can help stabilize mood and improve sleep quality.
2. Anxiolytics: Anxiolytic medications, also known as anti-anxiety medications, are sometimes prescribed to manage anxiety-related sleep disturbances and nightmares. Benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine medications, such as lorazepam and zolpidem, may be used as short-term solutions to promote relaxation and induce sleep.
3. Alpha-1 Blockers: Alpha-1 blockers, typically used to treat high blood pressure, have also shown promise in reducing nightmares and improving sleep quality. Medications like prazosin work by blocking certain receptors in the brain, which can help alleviate anxiety symptoms and prevent frightening dream experiences.
4. Anticonvulsants: In some cases, anticonvulsant medications such as topiramate or gabapentin may be prescribed to manage nightmares and improve sleep continuity. While these medications are primarily used to treat seizures, they have been found to have a calming effect on the brain and may reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
It is important to remember that medication should be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes therapy, lifestyle changes, and other interventions. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most suitable medication and dosage for each individual’s specific needs and circumstances.
Relaxation Techniques and Sleep Hygiene
Relaxation techniques and sleep hygiene play a crucial role in managing nightmares, anxiety, and sleep disorders. Incorporating these practices into your daily routine can promote a sense of calmness and improve sleep quality. Some effective relaxation techniques include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and visualization. Deep breathing exercises involve taking slow, deep breaths, holding them for a few seconds, and then exhaling slowly. This technique helps activate the body’s relaxation response and reduces anxiety. Progressive muscle relaxation involves tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups in the body, helping to release tension and promote relaxation. Visualization techniques encourage creating and focusing on peaceful mental imagery to reduce anxiety and induce a sense of calmness.
In addition to relaxation techniques, adopting good sleep hygiene practices can also contribute to better sleep. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, ensuring a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities close to bedtime. Establishing a soothing bedtime routine can signal to the body that it’s time to relax and prepare for sleep. Avoiding caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol before bed is also important, as these substances can disrupt sleep patterns and exacerbate anxiety symptoms.
Creating a sleep-friendly environment is vital for promoting quality sleep. This involves keeping your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet, as well as investing in a comfortable mattress and pillows. Using relaxation techniques and practicing good sleep hygiene can help reduce anxiety, calm the mind, and create the optimal conditions for a restful night’s sleep.
Managing Anxiety to Improve Sleep
Managing anxiety is essential for improving sleep quality and enjoying restful nights. There are several techniques and strategies that can help reduce anxiety levels and promote better sleep. One effective approach is to adopt stress reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation. These practices can calm the mind, relax the body, and reduce anxious thoughts before bedtime. Additionally, making anxiety-reducing lifestyle changes like incorporating regular exercise into the daily routine, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine and electronic screens before bed can have a positive impact on sleep. Seeking professional help is also an option for individuals struggling with severe anxiety that significantly affects their sleep. Therapists and counselors can provide guidance, support, and evidence-based treatments such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) that address anxiety and its impact on sleep. By actively managing anxiety, individuals can create a conducive environment for restful sleep, allowing them to wake up feeling refreshed and ready to face the day.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress reduction techniques play a crucial role in managing anxiety and improving sleep quality. When it comes to reducing stress, it’s important to find strategies that work best for you. Deep breathing exercises are a simple yet effective technique that can help calm the mind and relax the body. Focusing on your breath and taking slow, deep inhales and exhales can activate the body’s relaxation response, reducing stress levels. Another effective stress reduction technique is progressive muscle relaxation. This involves systematically tensing and then releasing each muscle group in the body, promoting a sense of relaxation and reducing muscle tension. Mindfulness meditation is another powerful tool that can help reduce stress. By bringing your attention to the present moment and accepting your thoughts and emotions without judgment, mindfulness can help you manage stress and anxiety more effectively. Regular exercise is yet another stress reduction technique that has numerous benefits. Engaging in physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters and stress relievers. Additionally, exercise can improve sleep quality and overall well-being. Lastly, engaging in hobbies or activities that bring you joy and relaxation can also help reduce stress. Whether it’s painting, reading, or gardening, finding activities that bring you a sense of fulfillment and enjoyment can act as a form of therapy and provide a much-needed break from the stressors of daily life. Incorporating these stress reduction techniques into your daily routine can have a significant positive impact on both your anxiety levels and your sleep quality.
Anxiety-Reducing Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly contribute to reducing anxiety levels and improving sleep quality. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to reduce anxiety and promote better sleep. Exercise helps release endorphins, which are natural mood-boosting chemicals in the brain. It also helps to reduce muscle tension and improve overall relaxation.
- Healthy Diet: Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet can have a positive impact on both anxiety and sleep. Avoiding excessive caffeine or alcohol intake, which can contribute to anxiety symptoms, is essential. Opting for whole foods, rich in vitamins and minerals, can help support a healthier mind and body.
- Stress Management Techniques: Incorporating stress management techniques into your daily routine can significantly reduce anxiety levels. Practices such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and mindfulness can promote a sense of calmness and relaxation. Additionally, engaging in activities that bring joy and pleasure, such as hobbies or spending time in nature, can help alleviate anxiety.
- Sleep Hygiene: Establishing healthy sleep habits can greatly improve both anxiety and sleep quality. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can help promote better sleep and reduce anxiety-related disturbances.
- Social Support: Building a strong support network of friends, family, or participating in support groups can provide emotional support during times of anxiety. Sharing experiences, receiving validation, and seeking guidance from others can help reduce anxiety levels and create a sense of belonging.
By incorporating these anxiety-reducing lifestyle changes into your daily routine, you can take proactive steps towards improving your overall well-being and achieving more restful sleep. Remember, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance on managing anxiety and sleep disorders.
Seeking Professional Help
– Consider reaching out to a licensed therapist or counselor specializing in sleep disorders and anxiety. They can provide you with valuable guidance and support in addressing your nightmares and the underlying issues causing them. Therapists may use various techniques, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), to help you understand and manage the anxiety that contributes to nightmares. CBT can help identify and challenge negative thought patterns, develop coping mechanisms, and promote better sleep habits. It may also involve exposure therapy, gradually exposing you to the themes or triggers of your nightmares in a safe and controlled environment to reduce their intensity over time.
– Consult a sleep specialist who can assess your sleep patterns and help identify any underlying sleep disorders that may contribute to your nightmares. They can conduct a thorough evaluation, including sleep studies, to diagnose conditions like sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, or insomnia. By addressing these underlying sleep disorders, you may experience a reduction in nightmares and an improvement in overall sleep quality.
– Psychiatric evaluation may be necessary in some cases, especially if the nightmares are accompanied by severe anxiety, depression, or other mental health concerns. A psychiatrist can provide an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate medication if necessary. Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), benzodiazepines, or alpha-blockers may be prescribed to target specific symptoms and alleviate anxiety-related nightmares. It’s important to note that medication should always be prescribed and monitored by a qualified medical professional.
– Seeking professional help can also involve alternative therapies such as acupuncture, relaxation techniques, or hypnosis. While the effectiveness of these approaches may vary, some individuals find them helpful in managing anxiety and promoting relaxation, which can improve sleep quality and reduce the frequency or intensity of nightmares.
Remember, seeking professional help is a proactive step towards addressing your nightmares, anxiety, and sleep disorders. Professionals trained in these areas have the knowledge and expertise to create tailored treatment plans to suit your unique needs and goals. Don’t hesitate to reach out and explore the available resources to regain control over your sleep and overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between nightmares, anxiety, and sleep disorders highlights the profound impact that these phenomena have on our overall well-being. Nightmares disrupt our sleep, leading to disturbed patterns, increased nighttime awakenings, and even insomnia. These sleep disturbances further contribute to anxiety and perpetuate the cycle of nightmares. However, there is hope for those who struggle with these issues. Treatment approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy, medication options, and relaxation techniques can provide relief and improve sleep quality. Managing anxiety through stress reduction techniques, lifestyle changes, and seeking professional help can also contribute to better sleep. By addressing both the underlying anxiety and sleep disorders, individuals can regain control over their sleep and find a sense of peace and tranquility. It is important to remember that each person’s journey is unique, and what works for one individual may not work for another. With determination and a comprehensive approach, it is possible to minimize the impact of nightmares and anxiety on sleep, leading to a more restful and rejuvenating slumber.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can nightmares be a symptom of an anxiety disorder?
Yes, nightmares can be a symptom of an anxiety disorder. Anxiety can manifest in various ways, and one of them is through vivid and disturbing nightmares. These nightmares often reflect the fears and worries that individuals with anxiety experience during their waking hours.
2. What types of sleep disorders are commonly associated with anxiety?
There are several sleep disorders commonly associated with anxiety, including insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless legs syndrome. These disorders can disrupt sleep quality and contribute to the development of anxiety symptoms.
3. How does anxiety contribute to the occurrence of nightmares?
Anxiety can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares by heightening emotional arousal during sleep. When anxiety levels are high, the brain remains more active during sleep, leading to more vivid and intense dreams, including nightmares.
4. Do nightmares only occur during REM sleep?
No, nightmares can occur during both REM (rapid eye movement) and non-REM sleep. However, nightmares that are more memorable and vivid usually happen during REM sleep, which is the stage of sleep associated with dreaming.
5. Is there a link between nightmares and insomnia?
Yes, there is a link between nightmares and insomnia. Recurring nightmares can disrupt sleep, leading to difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep, which are common symptoms of insomnia.
6. What is cognitive behavioral therapy for nightmares?
Cognitive behavioral therapy for nightmares (CBT-N) is a therapeutic approach that helps individuals manage and reduce the frequency and intensity of their nightmares. It involves techniques such as image rehearsal therapy, cognitive restructuring, and relaxation exercises.
7. Can medication help reduce nightmares and anxiety?
Medication can be prescribed to help reduce nightmares and anxiety in some cases. Certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can be effective in managing anxiety and reducing the occurrence of nightmares.
8. What are some relaxation techniques that can improve sleep for individuals with anxiety?
Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, and guided imagery can help individuals with anxiety relax their minds and bodies, promoting better sleep quality.
9. Are there any lifestyle changes that can alleviate anxiety and improve sleep?
Yes, adopting certain lifestyle changes can help alleviate anxiety and improve sleep. These changes include regular exercise, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding stimulants before bedtime, creating a calming sleep environment, and practicing healthy stress management techniques.
10. When should someone consider seeking professional help for their nightmares and anxiety?
If nightmares and anxiety are significantly interfering with daily functioning, causing distress, or persisting for an extended period, it may be beneficial to seek professional help. Mental health professionals can provide guidance and specialized treatments to address these issues effectively.