Have you ever experienced the puzzling phenomenon of recurring dreams? These are dreams that repeat themselves over and over again, leaving you wondering about their meaning and significance. As humans, we have always been fascinated by the mysteries of the subconscious mind and the power it holds over our dreams. In this article, we will explore the intriguing theories and explanations behind the occurrence of recurring dreams. From psychological interpretations to neuroscientific explanations, cultural and symbolic interpretations, and common themes, we will delve into the depths of the dream world to unlock the secrets behind these repetitive nocturnal journeys. So, let’s embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of recurring dreams and gain a deeper understanding of their possible meanings and implications.
What Are Recurring Dreams?
Recurring dreams are a unique phenomenon that occurs when a person experiences the same or similar dream repeatedly. These dreams may follow a specific pattern, involve similar themes, or feature recurring characters or settings. They can range from mundane to fantastical, and often leave the dreamer feeling perplexed and curious about their meaning. While the exact cause of recurring dreams is still not fully understood, there are several theories and explanations that attempt to shed light on this intriguing phenomenon. By examining these theories, we can gain a deeper insight into the nature and significance of recurring dreams. To explore further, you can check out our article on dream patterns and tips or dive into the exploration of subconscious messages in recurring dreams. Additionally, it is worth noting that recurring nightmares can have a potential impact on mental health, as discussed in our article on recurring nightmares and mental health.
Psychological Theories
Psychological theories provide insights into the occurrence of recurring dreams and offer interpretations rooted in the workings of the human mind. One prominent theory is the Freudian theory, proposed by Sigmund Freud, which suggests that recurring dreams stem from unresolved conflicts or repressed desires within the unconscious mind. These dreams may serve as a means of wish fulfillment or a way for the subconscious to express hidden emotions and desires. Another psychological theory is the Jungian theory, developed by Carl Jung, which focuses on the symbolic nature of recurring dreams. According to Jung, these dreams can be seen as a reflection of archetypes and collective unconscious elements, representing universal themes and experiences shared by all humanity. Additionally, the trauma theory explores how recurring dreams may be a result of past traumatic experiences, as the mind attempts to process and heal from the emotional impact of such events. These theories provide valuable perspectives on recurring dreams, highlighting the complexities of the human psyche and its influence on our dream experiences.
Freudian Theory
According to the Freudian theory of dream interpretation, recurring dreams can be attributed to unresolved conflicts and repressed desires within the unconscious mind. Sigmund Freud, the renowned psychoanalyst, believed that dreams play a crucial role in revealing hidden aspects of our psyche. He suggested that recurring dreams often stem from unconscious desires or unresolved childhood traumas that continue to influence our thoughts and behaviors.
Freud proposed that recurring dreams serve as a means for the unconscious mind to express repressed wishes or memories that have been deemed unacceptable or threatening by the conscious mind. These dreams serve as a form of wish fulfillment, allowing the individual to experience desires that they are unable to fulfill in waking life. Freud believed that the repetitive nature of these dreams indicated a persistent psychological conflict that needed to be resolved.
In Freudian theory, recurring dreams can also be seen as a manifestation of the ego’s defense mechanisms. The ego, which represents the conscious mind, employs various defense mechanisms to protect itself from anxiety and distress. Freud theorized that recurring dreams could serve as a way for the ego to maintain these defense mechanisms by disguising threatening or uncomfortable thoughts and emotions within the dream symbolism.
It is important to note that while the Freudian theory can provide insights into the nature of recurring dreams, it is just one of many theories that attempt to explain this phenomenon. Other psychological and scientific perspectives offer alternative explanations, which will be explored further in the subsequent sections of this article.
Jungian Theory
The Jungian theory, developed by Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung, offers a unique perspective on recurring dreams. According to Jung, recurring dreams can be seen as a manifestation of the collective unconscious, a reservoir of shared human experiences, symbols, and archetypes that exist within each individual. In Jung’s view, recurring dreams often contain symbols and themes that connect to universal human experiences rather than specific personal experiences. These symbols may have deep roots in our ancestral past and represent common themes, such as the hero’s journey, the shadow self, or the anima/animus (the masculine and feminine aspects of the psyche). Through recurring dreams, Jung believed that the unconscious is trying to communicate with us, bringing attention to unresolved conflicts or unacknowledged aspects of ourselves. By analyzing the symbols and themes present in recurring dreams, individuals can gain insight into their own personal development and confront hidden aspects of their psyche. This introspective exploration can lead to a deeper understanding of oneself and a greater sense of self-awareness. Understanding the Jungian theory in relation to recurring dreams opens up a pathway for individuals to explore the rich and symbolic depths of their own unconscious mind.
Trauma Theory
Trauma Theory: According to the trauma theory, recurring dreams can be a manifestation of unresolved trauma or distressing experiences. When a person goes through a traumatic event, such as abuse, violence, or a significant loss, the impact of that experience can linger in their subconscious mind. These unresolved emotions and memories may resurface in the form of recurring dreams. The dreams act as a way for the individual’s mind to process and attempt to make sense of the traumatic event. In these dreams, the person may relive the traumatic event, often in a distorted or symbolic manner. The content and themes of the dreams may vary depending on the nature of the trauma. Some individuals may experience vivid flashbacks or nightmares, while others may have subtle recurring motifs or symbols that are associated with the traumatic event. It is important to note that recurring dreams related to trauma can be distressing and may indicate a need for therapeutic intervention and support. Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor trained in trauma processing can aid in understanding and working through the underlying unresolved emotions and experiences that are being expressed in the dreams.
Neuroscientific Explanations
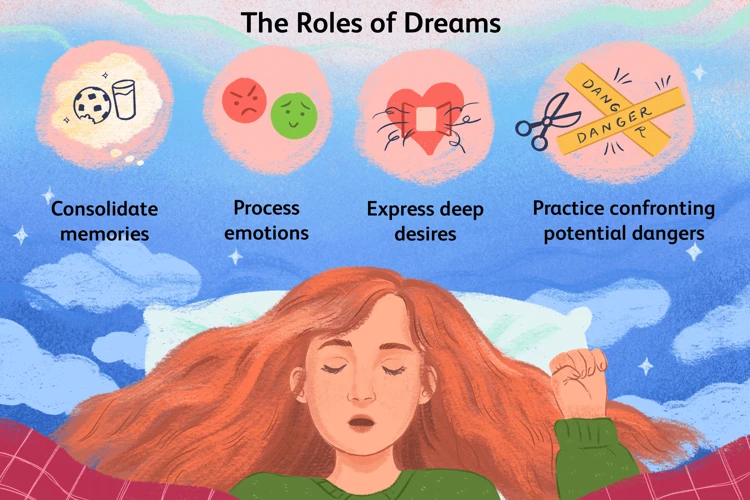
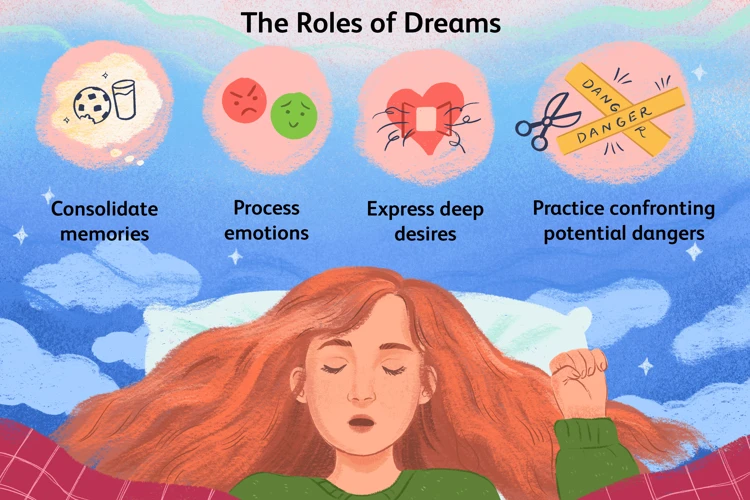
Neuroscientific explanations provide insights into the occurrence of recurring dreams by focusing on the intricate workings of the brain. One theory suggests that recurring dreams may be linked to memory consolidation, the process by which the brain strengthens and integrates new memories. During sleep, the brain replays and reactivates neural pathways associated with recent experiences, which could contribute to the repetition of certain dream content. Another explanation is the concept of emotional rehearsal, where recurring dreams serve as a way for the brain to process and regulate strong emotions or unresolved conflicts. This theory suggests that the repetition allows the dreamer to practice coping mechanisms and emotional responses in a safe environment. Additionally, studies on brain connectivity have revealed that certain brain regions involved in memory retrieval and emotional processing may exhibit increased activity during recurring dreams. These findings indicate that the neural networks involved in dream formation and replay might play a role in the occurrence of recurring dreams.
Memory Consolidation
Memory consolidation plays a crucial role in the occurrence of recurring dreams. It is a process in which the brain organizes and strengthens memories, transferring them from short-term memory to long-term memory storage. During sleep, the brain goes through different sleep stages, including rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, which is associated with vivid dreaming. Studies suggest that the brain is actively engaged in consolidating memories during REM sleep. This means that recurring dreams may be a result of the brain attempting to process and integrate specific experiences or memories that have not yet been fully stored or understood. The repetition in these dreams could stem from the brain’s persistent efforts to make sense of fragmented or unresolved memories. Recurring dreams might serve as a signal that certain memories or experiences hold greater significance and require additional attention for proper consolidation. It is important to note that memory consolidation is a complex and multifaceted process, and its exact relationship to recurring dreams is still a topic of ongoing research and exploration.
Emotional Rehearsal
Emotional rehearsal is an intriguing neuroscientific explanation for the occurrence of recurring dreams. According to this theory, our dreams serve as a way for our brains to practice and process emotions that we may struggle with in our waking lives. During sleep, our brain is free from the distractions and constraints of the conscious mind, allowing it to delve into deeper emotional territories. This emotional rehearsal can be especially prevalent in situations where we experience intense emotions such as fear, stress, or anxiety. By repeatedly reliving these emotions in our dreams, our brain may be attempting to process and regulate them, ultimately helping us cope better in real-life situations. The emotional intensity of recurring dreams can be incredibly vivid, leaving a lasting impact on our psyche. It is believed that this emotional rehearsal process is facilitated by the activation of certain brain regions involved in emotional memory, such as the amygdala and hippocampus. These areas play a crucial role in encoding and consolidating emotional experiences, which might explain why certain emotions tend to recur in our dreams. By analyzing the emotional content of recurring dreams, researchers can gain valuable insights into the unresolved emotional conflicts or challenges present in an individual’s waking life. This theory also suggests that by acknowledging, understanding, and addressing these emotions in our waking life, we may be able to reduce the frequency or intensity of recurring dreams.
Brain Connectivity
Brain connectivity plays a crucial role in understanding the occurrence of recurring dreams. Researchers have discovered that certain patterns of neural connectivity are associated with dream recall and the frequency of recurring dreams. The brain consists of various regions that communicate and exchange information through neural networks. These networks are responsible for processing and integrating different aspects of our experiences, thoughts, and emotions. When we sleep, our brain’s connectivity undergoes changes, particularly during the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep stage when most dreams occur. Studies have shown that during REM sleep, the brain’s prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for logical thinking and self-awareness, becomes less active, while other regions involved in memory, emotion, and sensory processing become more active. These shifts in brain connectivity may contribute to the vividness and emotional intensity often experienced in recurring dreams. Additionally, the connectivity between the hippocampus, involved in memory formation, and the cortex, responsible for higher-order cognitive processes, plays a crucial role in dream recall. Disturbances in this connectivity may be associated with increased dream fragmentation and the repetition of certain dream elements. While the precise mechanisms of brain connectivity in recurring dreams are still being explored, these findings highlight the intricate interplay between neural networks and the dreaming mind.
Cultural and Symbolic Interpretations

Cultural and symbolic interpretations of recurring dreams delve into the significance of these dreams within different cultural and spiritual contexts. One theory suggests that recurring dreams may be connected to archetypes and the collective unconscious, as proposed by psychologist Carl Jung. This theory suggests that certain symbols and themes that appear in these dreams may hold universal meaning and tap into shared human experiences. Another interpretation looks at the mythological significance of recurring dream themes, such as the hero’s journey or the symbolic representation of certain animals or objects. Additionally, recurring dreams can also carry spiritual or religious significance, with some believers viewing them as messages from a higher power or the subconscious mind trying to communicate deeper truths. Whether it is the exploration of archetypes, mythological connections, or spiritual interpretations, the cultural and symbolic analysis of recurring dreams provides a unique lens through which we can unravel the hidden meanings of these enigmatic nocturnal experiences.
Archetypes and Collective Unconscious
Archetypes and the collective unconscious are concepts introduced by renowned Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung. According to Jung, the collective unconscious is a part of the unconscious mind that is shared by all individuals, containing inherited and universal symbols, themes, and experiences. Archetypes, on the other hand, are the fundamental psychological patterns that exist within the collective unconscious. They represent common human experiences and emotions that are symbolically expressed in various cultures and mythologies.
In the context of recurring dreams, the presence of archetypes and the collective unconscious suggests that certain dream elements have a broader and deeper significance beyond the individual dreamer. The repetition of specific symbols or themes in recurring dreams may access archetypal content within the collective unconscious. For example, encountering a wise old man or woman in a recurring dream may tap into the archetype of the “wise elder” or “sage.”
These archetypal figures and symbols in recurring dreams often carry profound meaning and can serve as guides or messengers for the dreamer. They may represent aspects of the dreamer’s own psyche or provide insights into universal aspects of the human experience. Exploring the archetypal dimensions of recurring dreams can lead to a greater understanding of oneself and the larger collective of humanity.
It is important to note that archetypes and their interpretations can vary across cultures and individuals. While some symbols may have collective meanings, personal experiences and cultural backgrounds can influence the interpretation of archetypal symbols in recurring dreams. The exploration of archetypes and the collective unconscious in recurring dreams can be a fascinating journey of self-discovery and connection with the deeper layers of the human psyche.
Mythological Significance
Mythological significance plays a fascinating role in understanding recurring dreams. Many symbols and themes found in recurring dreams are deeply rooted in ancient mythologies and collective cultural narratives. In mythologies from various cultures around the world, certain archetypal figures and events reoccur in stories, representing universal human experiences and psychological states. These archetypes, such as the hero, the trickster, or the wise old man/woman, often appear in recurring dreams, offering insights into our own personal narratives and the challenges we face in life.
For example, the symbol of a dragon, which frequently appears in recurring dreams, often represents hidden fears and desires that need to be addressed. In mythologies, dragons are often seen as powerful and dangerous creatures that must be either conquered or reconciled with. In recurring dreams, encountering a dragon may be symbolic of facing and overcoming our own inner demons or obstacles.
Additionally, recurring dreams may feature mythological creatures or gods/goddesses from specific cultural traditions, reflecting the influence of these myths on the dreamer’s psyche. These dreams can provide opportunities for exploring our cultural heritage, connecting with ancestral wisdom, or tapping into collective unconscious knowledge. In some cases, recurring dreams featuring mythological symbols may also be interpreted as spiritual encounters or messages from the divine.
Understanding the mythological significance in recurring dreams requires a deep exploration of cultural narratives and symbolism. By studying the myths and legends that resonate with our own recurring dream themes, we can gain valuable insights into our subconscious and its connection to the collective human experience.
Spiritual and Religious Significance
The occurrence of recurring dreams can also hold spiritual and religious significance for individuals. In many spiritual and religious traditions, dreams are considered a pathway to higher consciousness or divine communication. People who have recurring dreams with spiritual or religious themes often interpret them as messages from a higher power or as spiritual guidance. These dreams may involve encounters with spiritual figures, prophetic visions, or symbolic representations of spiritual concepts. For example, in Christianity, recurring dreams of angels or Jesus may be seen as messages of divine protection or guidance. In Hinduism, recurring dreams featuring gods or goddesses may be seen as invitations for deeper devotion or reminders of one’s spiritual path. Interpretations of these dreams may vary based on an individual’s faith, beliefs, and personal experiences. The spiritual and religious significance of recurring dreams can serve as a source of inspiration, reflection, and deeper connection to one’s inner self and higher powers. It is important for individuals to explore the meaning of these dreams in the context of their own spiritual or religious beliefs, seeking guidance from trusted mentors, religious leaders, or spiritual communities.
Interpretation and Personal Meanings

Interpretation plays a crucial role in understanding the personal meanings behind recurring dreams. Since dreams are highly subjective and unique to individuals, there is no one-size-fits-all interpretation. Instead, it is important to consider the context, emotions, and personal experiences associated with the dream. One approach to interpreting recurring dreams is through symbolism. Symbols and metaphors in dreams can hold deep personal significance and may represent emotions, fears, desires, or unresolved issues in our waking lives. Analyzing the symbolism and connections between recurring dream elements can provide insights into our subconscious thoughts and emotions.
Another aspect of interpretation is exploring the emotions and feelings experienced during recurring dreams. Emotions can serve as valuable clues to uncover the personal meanings behind the dreams. For example, recurring dreams that evoke fear or anxiety may indicate unresolved fears or stressors in our waking lives. Similarly, recurring dreams that evoke joy or excitement may reflect hidden desires or aspirations.
It is crucial to approach dream interpretation with an open mind and a willingness to introspect. Keeping a dream journal can be a helpful tool in recording and analyzing recurring dreams over time. By examining patterns, common themes, and emotional triggers, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their own unique dream world and the personal meanings embedded within.
Ultimately, the interpretation and personal meanings of recurring dreams are deeply subjective and personal. It is important to trust your intuition and explore the connections between your dreams and your waking life experiences. Seeking the guidance of a professional dream therapist or psychologist can also offer valuable insights and support in deciphering the personal meanings behind recurring dreams.
Common Themes in Recurring Dreams

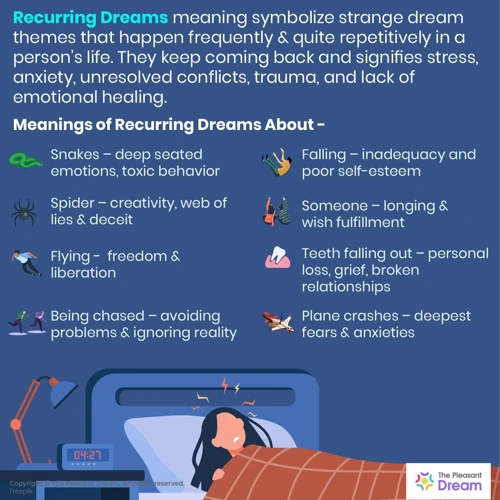
Common themes in recurring dreams are fascinating and often leave us pondering their significance. These themes can vary greatly from person to person, but there are a few that seem to be widespread. One common recurring dream theme is the sensation of falling from great heights. This dream can evoke a sense of fear or anxiety and may be connected to feelings of insecurity or loss of control in waking life. Another common theme is being chased or pursued, which can signify a desire to escape from something or someone in our waking lives that is causing stress or pressure. Another puzzling recurring dream theme is teeth falling out. This dream can be unsettling, as it may symbolize a loss of power, confidence, or self-esteem. Lastly, many individuals experience recurring dreams of being unprepared for an exam or presentation, which could be an indicator of feeling unready to face challenges or feel competent in certain areas of life. The interpretation of these themes can vary, and the personal context and emotions surrounding these dreams are essential in understanding their meaning and potential impact.
Falling from Heights
The recurring theme of falling from heights in dreams is quite common and can evoke a sense of fear and unease. Many individuals have experienced dreams where they find themselves plummeting from tall buildings, cliffs, or airplanes. While the experience of falling can be distressing, the meaning behind it is subjective and can vary from person to person.
One possible interpretation of falling dreams is a representation of a lack of control or instability in one’s waking life. It could signify feelings of powerlessness or a fear of losing control over a particular situation. These dreams might occur during times of stress, anxiety, or when faced with major life changes. The sensation of free-falling serves as a metaphor for the loss of stability or the fear of failure.
Alternatively, falling dreams may also be linked to a fear of letting go or a reluctance to confront certain emotions or situations. They could signify a subconscious resistance to change or an avoidance of taking risks. The act of falling can symbolize a need for release or surrender in order to overcome emotional or psychological obstacles.
It’s important to note that the interpretation of falling dreams is highly individualized. While some may relate these dreams to a sense of vulnerability, others may find them exhilarating or liberating. Analyzing the context, emotions, and personal experiences associated with these recurring dreams can provide a deeper understanding of their significance on an individual level.
To explore more about common themes in recurring dreams, you can read our article on dream patterns and tips which also discusses falling from heights in more detail.
Being Chased or Pursued
Being chased or pursued is a common theme in recurring dreams that often evokes a sense of fear, panic, and vulnerability. In these dreams, the dreamer may find themselves in a variety of situations where they are being chased by an unknown entity or a familiar person. The pursuer can take on different forms, such as a stranger, an animal, or even a supernatural being. The intensity of the chase can vary, with some dreams involving a leisurely pursuit and others escalating into a high-speed chase. While the exact meaning of being chased or pursued in dreams may vary from person to person, there are some common interpretations that have been proposed.
One psychological interpretation suggests that being chased or pursued in dreams may reflect feelings of anxiety, stress, or a sense of being overwhelmed in waking life. It could represent unresolved conflicts or problems that the dreamer is trying to escape from. The pursuer may symbolize the pressures and demands that the dreamer is experiencing, and the act of being chased may indicate a need to confront and address these issues.
Another interpretation focuses on the symbolism of the pursuer itself. It could represent an aspect of the dreamer’s own personality or characteristics that they are trying to distance themselves from. For example, the pursuer may embody feelings of anger, insecurity, or past trauma that the dreamer is trying to avoid or suppress. By confronting and understanding the pursuer, the dreamer may gain insight into their own inner struggles and work towards personal growth and resolution.
In some cases, being chased or pursued in dreams may stem from a deep-rooted fear or traumatic experience. These dreams can serve as a way for the subconscious mind to process and integrate past events or fears. By repeatedly experiencing the chase scenario, the dreamer may gradually desensitize themselves to the fear or find ways to cope with it.
It is important to note that while recurring dreams of being chased or pursued can be unsettling, they can also present an opportunity for self-reflection, growth, and problem-solving. Keeping a dream journal can be helpful in identifying patterns, triggers, and emotions associated with these dreams. Exploring techniques such as lucid dreaming or therapy can also assist in gaining a deeper understanding of the underlying meanings and working towards resolving any unresolved issues that may be manifesting in these dreams.
Teeth Falling Out
The dream of teeth falling out is a common and often unsettling recurring theme. In this dream, the dreamer may suddenly find themselves with loose or crumbling teeth, or even have their teeth completely fall out. This dream imagery can evoke feelings of vulnerability, loss, and powerlessness. While the exact meaning of teeth falling out dreams may vary from person to person, there are several interpretations that are commonly associated with this dream theme.
One psychological interpretation suggests that dreaming of teeth falling out may reflect underlying anxieties about self-image and self-esteem. Teeth are an important part of our appearance and are associated with our ability to communicate and express ourselves. The loss or deterioration of teeth in a dream may symbolize a fear of losing attractiveness, confidence, or the ability to effectively convey one’s thoughts and emotions.
Another interpretation relates teeth falling out dreams to feelings of powerlessness or loss of control in waking life. Teeth are strong and essential for biting, chewing, and speaking. Losing them in a dream could represent a sense of powerlessness or difficulty in asserting oneself in certain situations. It may signify a fear of being unable to defend oneself, express opinions, or stand up to others.
Some cultural and symbolic interpretations propose that teeth falling out dreams may symbolize significant life transitions or personal growth. Just as children lose their baby teeth to make room for permanent ones, dreaming of teeth falling out could represent a transitional period in the dreamer’s life. It may symbolize the shedding of old ways, beliefs, or relationships to make way for new experiences and personal transformation.
It’s important to note that the meaning of teeth falling out dreams can vary depending on the individual’s personal experiences, beliefs, and cultural background. To gain a better understanding of the personal significance of these dreams, keeping a dream journal and reflecting on the emotions and events surrounding the dream can be helpful. Exploring the specific emotions and events associated with teeth falling out dreams can provide valuable insights into one’s subconscious thoughts, fears, and desires.
Unprepared for an Exam or Presentation
The dream of being unprepared for an exam or presentation is a common theme that many people experience in their recurring dreams. This type of dream often evokes feelings of anxiety, stress, and a sense of being overwhelmed. In these dreams, individuals often find themselves in a situation where they are about to take an exam or give a presentation, but they are completely unprepared. They may have forgotten to study, misplaced their notes, or find themselves in a completely unfamiliar subject matter. These dreams can be particularly distressing, as the fear of failure and the pressure to perform well can intensify in the dream state.
Psychologically, the dream of being unprepared for an exam or presentation can symbolize feelings of inadequacy or a fear of judgment. It may reflect a fear of being evaluated or measured up to certain standards. These dreams can also be a manifestation of imposter syndrome, where individuals doubt their abilities and fear being exposed as a fraud.
Additionally, this type of dream can be linked to real-life situations that evoke similar emotions of being unprepared or overwhelmed. It could be a reflection of stress or pressure from work or school, where individuals may feel that they are not adequately equipped to handle the demands being placed upon them. It may also represent a fear of making mistakes or being criticized by others.
Understanding the personal context and emotions associated with the dream is crucial in interpreting its meaning. Reflecting on the specific circumstances and underlying emotions can provide valuable insights into areas of one’s life where they may feel unprepared or insecure. By addressing these issues and taking steps to build confidence and preparedness in relevant areas, individuals may find that the frequency of these dreams decreases over time.
Preventing or Managing Recurring Dreams
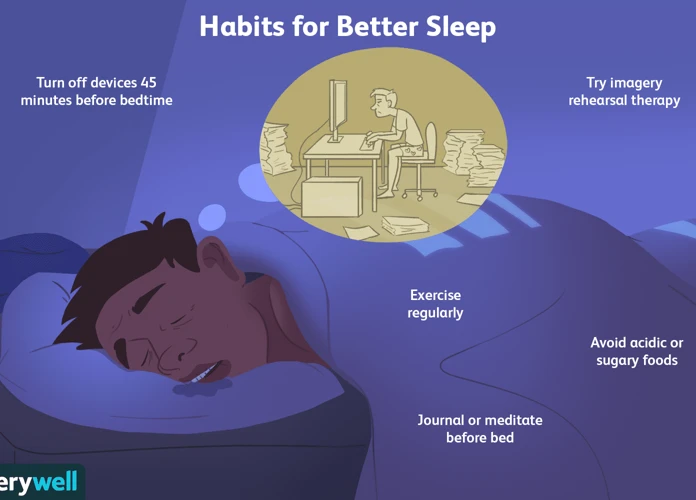
If you find yourself wanting to prevent or manage recurring dreams, there are several strategies you can try. One effective technique is dream journaling, where you write down your dreams in a journal immediately upon waking up. This can help you identify patterns, symbols, and emotions that may be associated with your recurring dreams. Another approach is to practice lucid dreaming techniques, which involve becoming aware that you are dreaming while still in the dream state. This awareness can give you the ability to alter the course of your dream and potentially break the cycle of recurrence. Additionally, focusing on stress reduction and practicing self-care can contribute to a better quality of sleep and potentially minimize the occurrence of recurring dreams. By implementing these methods, you can take an active role in managing and even finding resolution for your recurring dreams.
Dream Journaling
Dream journaling is a powerful technique that can help individuals gain insight into their recurring dreams and uncover patterns or recurring themes. Dream journaling involves keeping a dedicated notebook or digital document by your bedside to write down your dreams as soon as you wake up, while the memories are still fresh. It is important to record as many details as possible, including emotions, colors, people, objects, and any other significant elements that stood out in the dream. By consistently recording your dreams over time, you may start to notice recurring symbols, situations, or emotions that appear across multiple dreams. This process can provide valuable clues and understanding into the meaning behind your recurring dreams. Additionally, dream journaling can also serve as a form of self-reflection and self-expression, allowing you to explore your subconscious thoughts and desires. You may even discover hidden connections between your dreams and waking life experiences. To enhance the effectiveness of dream journaling, it is recommended to establish a regular sleep routine, create a peaceful sleep environment, and practice relaxation techniques before bed. By incorporating dream journaling into your daily routine, you can gain a deeper understanding of your recurring dreams and unlock the messages they hold.
Lucid Dreaming Techniques
Lucid dreaming is an intriguing practice that involves becoming aware that you are dreaming while you are still in the dream state. It allows the dreamer to gain control over their dreams, making it possible to manipulate the dream environment and storyline. For those experiencing recurring dreams, learning and practicing lucid dreaming techniques can offer a way to actively engage with and potentially alter the content of the dreams. Here are some popular techniques that can help induce lucid dreaming:
1. Reality Testing: This technique involves regularly questioning your reality throughout the day. By habitually asking yourself, “Am I dreaming?” and performing reality checks such as trying to push your finger through your palm or looking at the time, you can train your brain to become more aware of the distinction between waking life and the dream world.
2. Dream Journaling: Keeping a dream journal by your bedside and recording your dreams immediately upon awakening can enhance your dream recall and self-awareness. By reviewing your dream journal regularly, you may begin to notice common themes or patterns in your recurring dreams, which can serve as triggers for lucidity.
3. Mnemonic Induction of Lucid Dreams (MILD): This technique involves setting an intention to have a lucid dream while you fall back asleep. Before going to bed, repeat a phrase or affirmation to yourself, such as “I will have a lucid dream tonight.” Visualize yourself becoming aware within a dream, and hold onto that intention as you drift off to sleep.
4. Wake-Back-to-Bed (WBTB): This technique involves setting an alarm to wake up after several hours of sleep and then going back to bed with the intention of inducing a lucid dream. During the brief wakeful period, engage in activities that promote wakefulness, such as reading about lucid dreaming or visualizing yourself in a lucid dream. This technique takes advantage of the increased likelihood of entering a dream state during the REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep cycle.
5. Reality-Testing Apps: There are numerous smartphone apps available that can assist in lucid dreaming. These apps often use various methods such as reality-check reminders throughout the day or playing subtle audio cues during sleep to help induce lucidity.
It’s important to note that learning to lucid dream takes time and practice. While these techniques can be effective, they may not yield immediate results. With patience and perseverance, however, individuals experiencing recurring dreams may find these techniques to be valuable tools in gaining control over their dream experiences and exploring the depths of their subconscious minds.
Stress Reduction and Self-Care
Stress reduction and self-care play a crucial role in managing and preventing recurring dreams. When we are under significant stress, our dreams can intensify and become more frequent, including recurring dreams. By incorporating stress reduction techniques and practicing self-care, we can create a more conducive environment for peaceful sleep and reduce the occurrence of recurring dreams.
Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Relaxation techniques: Engage in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation. These techniques can help calm the mind and reduce overall stress levels, promoting more restful sleep.
2. Establish a bedtime routine: Create a soothing routine before bed to signal to your brain that it’s time to unwind and relax. This can include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing gentle stretching.
3. Improve sleep hygiene: Optimize your sleep environment by keeping your bedroom dark, quiet, and comfortable. Disconnect from electronic devices before bed to promote better sleep quality.
4. Engage in regular physical activity: Regular exercise helps reduce stress and anxiety, enhances mood, and improves overall sleep quality. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.
5. Practice self-care: Take time for self-care activities that bring you joy and relaxation. This can include hobbies, spending time with loved ones, engaging in creative outlets, or practicing mindfulness.
6. Manage stress levels: Identify sources of stress in your life and develop healthy coping mechanisms to manage them effectively. This may involve seeking support from friends, family, or professional counselors.
Remember that everyone’s experience with recurring dreams is unique, and it may take time to find the strategies that work best for you. By prioritizing stress reduction and self-care, you can create a more balanced and peaceful mindset that will positively impact your dream experiences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recurring dreams continue to captivate and intrigue us with their enigmatic nature. Throughout this article, we have explored various theories and explanations behind the occurrence of these repetitive dreams. From psychological theories such as Freudian and Jungian interpretations, to neuroscientific explanations including memory consolidation and emotional rehearsal, and even cultural and symbolic interpretations that delve into archetypes and mythological significance, we have gained a deeper understanding of the possible meanings and implications of recurring dreams. It is important to remember that while these theories offer valuable insights, the interpretation of recurring dreams is a highly personal and subjective experience. Ultimately, it is up to the individual to explore their own dreams and find their own personal meanings within them. Whether they serve as messages from the subconscious mind, reflections of past traumas, or simply a way for our brains to sort through memories and emotions, recurring dreams will continue to spark curiosity and wonder in our quest for self-discovery and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are recurring dreams common?
Yes, recurring dreams are relatively common. Many people report having recurring dreams at some point in their lives.
2. Can recurring dreams have personal meanings?
Absolutely! Recurring dreams often hold personal significance and can be influenced by a person’s life experiences, emotions, and subconscious thoughts.
3. Do recurring dreams always have the same storyline?
No, recurring dreams may have variations in their storyline or details. While some may be nearly identical each time, others may have slight alterations or different outcomes.
4. Can recurring dreams be interpreted differently by different individuals?
Yes, the interpretation of recurring dreams can vary from person to person. Dreams are highly subjective, and their meanings can be influenced by individual beliefs, experiences, and cultural background.
5. Can recurring dreams be a sign of unresolved issues?
Yes, recurring dreams are often associated with unresolved issues or unresolved emotions that the dreamer may be grappling with in their waking life.
6. Are recurring dreams only specific to certain age groups?
No, recurring dreams can happen to individuals of all age groups, from children to adults. However, the themes and content of recurring dreams may vary based on one’s age and life experiences.
7. Can recurring dreams be influenced by external factors?
Yes, external factors such as stress, significant life events, or trauma can influence the occurrence and content of recurring dreams.
8. Can recurring dreams be a form of self-reflection?
Absolutely! Recurring dreams can serve as a way for the subconscious mind to process emotions, conflicts, and thoughts, offering the dreamer an opportunity for self-reflection and introspection.
9. Are recurring dreams always negative or scary?
No, while some recurring dreams may be unsettling or scary, others can be neutral or even positive. The emotional tone of recurring dreams can vary greatly.
10. Can recurring dreams be overcome or stopped?
With self-awareness, understanding, and sometimes professional guidance, recurring dreams can be addressed and potentially resolved. Techniques such as dream journaling, lucid dreaming, and stress reduction strategies can help manage and reduce the frequency of recurring dreams.