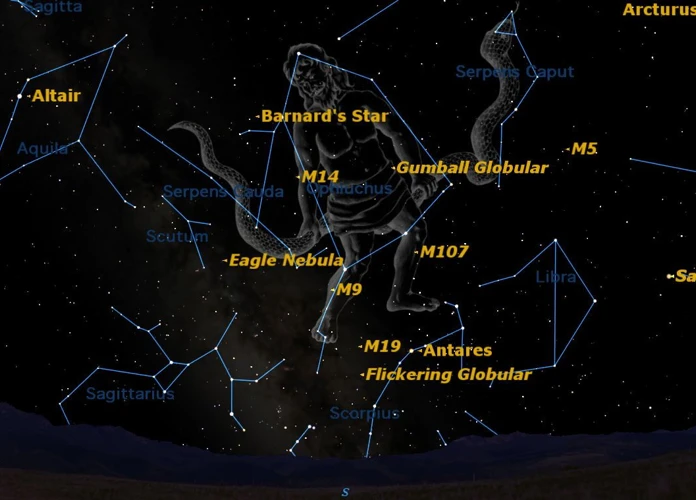
Ophiuchus, the celestial serpent bearer, sits quietly among the constellations, holding within its boundaries a wealth of astronomical wonders waiting to be discovered. This mystical region of the sky has captivated the minds of astronomers throughout history, leading to remarkable breakthroughs and significant contributions to our understanding of the cosmos. Join us on a journey through time as we explore the lives and achievements of the pioneering astronomers who dared to unravel the secrets hidden within the constellation of Ophiuchus. From Ptolemy to Johannes Kepler, Giovanni Domenico Cassini to William Herschel, these brilliant minds have left an indelible mark on the field of astronomy, forever changing the way we perceive the universe. Prepare to be enthralled by their tales of discovery and the profound impact they made on our understanding of the cosmos.
Ptolemy

Ptolemy, a Greek mathematician, astronomer, and geographer, lived during the 2nd century AD. His most significant contribution to the field of astronomy was his work “Almagest,” where he presented a comprehensive mathematical model of the universe.
Ptolemy’s model, known as the geocentric model, posited that the Earth was at the center of the universe, with all celestial bodies, including the planets, revolving around it in circular orbits. This model provided a framework for understanding the movements of celestial objects and was widely accepted for over a thousand years.
Within the constellation of Ophiuchus, Ptolemy made several key astronomical discoveries. One notable discovery was the identification of the star Rasalhague, also known as Alpha Ophiuchi. This bright star, located near the head of the serpent bearer, is one of the most prominent stars in the constellation.
Ptolemy also cataloged numerous other stars within Ophiuchus, including Epsilon Ophiuchi and Barnard’s Star. His meticulous observations and systematic cataloging of stars laid the groundwork for future astronomers to study and understand the celestial objects within Ophiuchus.
Ptolemy’s geocentric model, as presented in “Almagest,” had a profound impact on the field of astronomy. His work became the cornerstone of Western astronomy for centuries, shaping our understanding of the cosmos and influencing subsequent generations of astronomers.
While Ptolemy’s geocentric model has since been replaced by the heliocentric model proposed by Copernicus, his contributions to the field paved the way for further advancements in astronomical knowledge. The rigorous methodology and precision in his observations set a standard for scientific inquiry that continues to guide astronomers to this day.
Ptolemy’s work on Ophiuchus and other constellations laid the foundation for the ongoing exploration and understanding of the universe. By capturing the celestial wonders within Ophiuchus and documenting them for posterity, Ptolemy opened the doors to a deeper understanding of our place in the cosmos.
Note: For more information on star formation within Ophiuchus, check out our article on Unleashing Ophiuchus: Star Formation Analysis.
Life and Contributions
Ptolemy, also known as Claudius Ptolemaeus, was born in 90 AD in Alexandria, Egypt. He was a prolific scholar who excelled in various fields, including mathematics, astronomy, and geography. Ptolemy’s work had a lasting impact on astronomy, shaping our understanding of the cosmos for centuries.
Ptolemy’s most significant contribution was his mathematical model of the universe, presented in his influential book “Almagest.” This work synthesized the knowledge of his time, combining observations from earlier Greek astronomers with his own assessments.
In addition to his geocentric model, Ptolemy developed sophisticated techniques for predicting the positions of celestial bodies. He introduced the concept of epicycles, small circles within larger orbits, to explain the irregular movements of planets. These mathematical tools provided a framework for understanding and predicting the motions of the celestial spheres.
Ptolemy’s contributions extended beyond theoretical models. He also compiled a comprehensive star catalog, known as the “Almagest Catalog,” which listed over a thousand stars with their positions, magnitudes, and classifications. This catalog became the standard reference for astronomers for centuries.
Ptolemy made significant advancements in the field of geography. His book “Geography” offered a detailed description of the known world, including maps and coordinates of various locations. Although some of his geographical calculations were flawed, his work laid the foundation for cartography and influenced future explorations.
The enduring legacy of Ptolemy’s contributions is evident in the impact he had on subsequent astronomers. His works were translated and studied extensively during the Islamic Golden Age, preserving and expanding upon his findings. Even in the Renaissance period, Ptolemy’s ideas continued to shape astronomical thought until the heliocentric model put forward by Copernicus revolutionized our understanding of the universe.
Ptolemy’s dedication to observation, mathematical precision, and systematic documentation set a benchmark for astronomical studies. His insights into the movements of celestial bodies within Ophiuchus and beyond not only enriched our understanding of the cosmos but also set the stage for future generations of astronomers to embark on further explorations.
For more information on the mythology and mysteries surrounding the Ophiuchus constellation, check out our guide Unveiling the Mysteries of Ophiuchus: A Guide to Mythology and the Constellation.
Key Discoveries in Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus, the serpent bearer, has been a source of fascination for astronomers throughout history. Within this constellation, several key discoveries have enhanced our understanding of the cosmos and expanded our knowledge of celestial objects.
1. Red Dwarf Stars: One notable discovery in Ophiuchus is the abundance of red dwarf stars. These small, cool, and dim stars have been found within the boundaries of the constellation. Red dwarfs, such as Proxima Centauri, are of particular interest to astronomers due to their potential for hosting exoplanets within their habitable zones.
2. Molecular Clouds: Ophiuchus is home to vast molecular clouds, such as the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex. These clouds are made up of gas and dust, acting as stellar nurseries where new stars and planetary systems are born. Scientists study these clouds to understand the processes of star formation and the birth of planetary systems.
3. Globular Cluster M14: In the southeastern region of Ophiuchus lies the breathtaking globular cluster known as M14. Comprised of hundreds of thousands of stars tightly bound by gravity, this cluster provides astronomers with valuable insights into stellar evolution and the dynamics of stellar populations.
4. Barnard’s Star: Named after the American astronomer E.E. Barnard, Barnard’s Star is a notable discovery within Ophiuchus. It is one of the closest known stars to the Sun and has the largest proper motion of any star visible to the naked eye. Captivating astronomers since its discovery, Barnard’s Star continues to be an intriguing subject of study.
5. Nebulae: Ophiuchus also boasts several stunning nebulae, including the Snake Nebula (B72) and the Dark Horse Nebula. These nebulae are regions of interstellar gas and dust, often illuminated by nearby stars. Their intricate structures and vibrant colors provide astronomers with visual wonders to behold and study.
The significant discoveries within Ophiuchus enhance our knowledge of various astrophysical phenomena, from stellar birth and evolution to the dynamics of galactic clusters. By delving into the hidden gems of the Ophiuchus constellation, astronomers continue to unravel the mysteries of the universe.
Note: For more information on hidden celestial gems within Ophiuchus, check out our article on Hidden Gems of Ophiuchus Constellation.
Impact on Astronomy
Impact on Astronomy:
1. Revolutionized Understanding: Ptolemy’s geocentric model revolutionized the understanding of the cosmos during his time. It provided a comprehensive framework for explaining the motions of celestial bodies and their positions in the sky. This model helped astronomers make accurate predictions for centuries.
2. Influence on Later Astronomers: Ptolemy’s work had a profound influence on later astronomers, particularly during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance. His detailed observations and mathematical calculations laid the foundation for advancements in astronomy and contributed to the development of new theories and models.
3. Pivotal in Astronomical Methods: Ptolemy’s meticulous approach to observation and cataloging of stars established a standard for astronomers that lasted for centuries. His emphasis on precision and accuracy set the stage for future scientific inquiry and the development of more advanced observation techniques.
4. Preservation of Ancient Knowledge: Ptolemy’s works, particularly “Almagest,” helped preserve the knowledge of ancient Greek astronomers. His writings acted as a bridge between the knowledge of the past and the scientific progress of the future, ensuring that important astronomical ideas and concepts were not lost to time.
5. Abandonment and Reevaluation: While Ptolemy’s geocentric model eventually gave way to the heliocentric model proposed by Copernicus, its impact on astronomy cannot be underestimated. The challenges presented by Ptolemy’s model encouraged critical thinking and scientific debate, ultimately leading to a more accurate understanding of the universe.
6. Continual Appreciation: Despite the advancement of modern astronomical theories, Ptolemy’s contributions are still appreciated today. His works are studied as historical landmarks in the development of astronomy, providing valuable insights into the evolution of our understanding of the cosmos.
Ptolemy’s impact on astronomy was multi-faceted. His geocentric model, observational techniques, and preservation of ancient knowledge paved the way for future breakthroughs and revolutions in the field. While his ideas may have been superseded by newer theories, his contributions remain instrumental in shaping our understanding of the universe.
Johannes Kepler
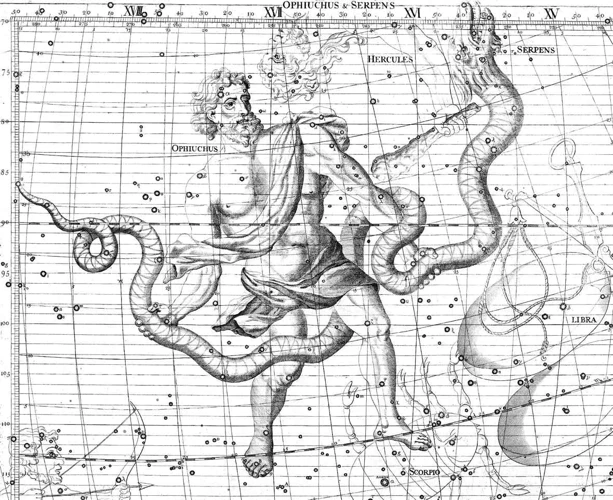
Johannes Kepler, a German astronomer and mathematician, lived from 1571 to 1630. His groundbreaking discoveries revolutionized our understanding of the solar system and laid the foundation for modern astronomy.
Kepler’s most significant contribution was his formulation of three laws of planetary motion, collectively known as Kepler’s Laws. These laws described the motion of planets around the Sun with unprecedented accuracy, debunking the prevailing notion of circular orbits and introducing the concept of ellipses.
Within the constellation of Ophiuchus, Kepler made observations of various celestial objects, furthering our understanding of the universe. Kepler’s observations of supernovae, such as the one that occurred in the year 1604 within Ophiuchus, challenged the notion that the heavens were unchanging and solidified his reputation as an astute observer.
In addition to his observations, Kepler also determined the orbital periods of several planets, including Mars, within Ophiuchus. His precise calculations were made possible by Tycho Brahe’s detailed observations, which Kepler inherited and used to derive his laws of planetary motion.
Kepler’s work had a profound impact on astronomy, providing further evidence for the heliocentric model proposed by Copernicus. His laws of planetary motion not only explained the movements of celestial objects but also paved the way for future astronomers to explore and understand the universe.
Kepler’s contributions to the field of astronomy brought profound changes to our understanding of the cosmos within Ophiuchus and beyond. His meticulous observations and mathematical calculations set a precedent for scientific investigation and continue to guide astronomers in their quest to unravel the mysteries of the universe.
Life and Contributions
Little is known about the specific details of Ptolemy’s life, adding to the enigma surrounding this influential figure. Ptolemy is believed to have been born around the year 90 AD in Egypt, which was under Roman rule at the time. His name, Claudius Ptolemaeus, suggests that he may have had Roman citizenship.
Ptolemy’s contributions to astronomy were vast and far-reaching. His most famous work, “Almagest,” is a comprehensive treatise that synthesized knowledge from earlier Greek astronomers, such as Hipparchus, and incorporated Ptolemy’s own observations and calculations. “Almagest” not only presented a detailed description of Ptolemy’s geocentric model of the universe but also cataloged and classified over a thousand stars.
In addition to his work on astronomy, Ptolemy also made significant contributions to the fields of geography and cartography. His book “Geography” provided a systematic approach to mapping the known world. Ptolemy’s maps, though imperfect due to the limitations of geographical knowledge at the time, laid the groundwork for future advancements in cartography.
Ptolemy’s achievements had a profound impact on the scientific and intellectual communities of his time and beyond. His geocentric model, with its mathematical precision and explanatory power, dominated astronomical thought until the Copernican revolution. Even then, Ptolemy’s work continued to be studied and referenced for its historical significance and contributions to scientific methodology.
Ptolemy’s truly groundbreaking contributions emerged from a time of great intellectual and cultural exchange in the ancient world. His work represents a synthesis of knowledge from diverse civilizations, including the Greeks, Egyptians, Babylonians, and Indians. The lasting legacy of Ptolemy’s ideas and methods is a testament to his brilliance as an astronomer and scientist.
Note: For a deeper dive into the mythology and symbolism of the Ophiuchus constellation, check out our article on Unveiling the Mysteries of Ophiuchus: A Guide to the Mythology of the Constellation.
Key Discoveries in Ophiuchus
1. Rasalhague: Ptolemy’s identification of Rasalhague, also known as Alpha Ophiuchi, was a significant discovery within the constellation of Ophiuchus. This bright star, located near the head of the serpent bearer, plays a crucial role in defining the constellation and serves as a reference point for astronomers studying the region.
2. Nebulae and Star Clusters: Ophiuchus is home to several notable nebulae and star clusters that have captivated astronomers throughout history. One such example is the Snake Nebula, a dark nebula that appears as a twisting, serpentine shape. This enigmatic feature intrigues scientists with its mysterious nature and provides an opportunity to study star formation processes.
3. Barnard’s Star: Ptolemy’s cataloging work within Ophiuchus included the identification of Barnard’s Star—a red dwarf that is one of the nearest known stars to our solar system. This discovery opened doors for future studies focusing on nearby stars and their potential exoplanetary systems.
4. Rho Ophiuchi Cloud Complex: The Rho Ophiuchi Cloud Complex, located within Ophiuchus, is a vast region of molecular gas and dust where new stars are actively forming. This complex hosts numerous bright and dark nebulae, such as the iconic blue reflection nebula IC 4603. Studies of this region have provided invaluable insights into stellar birth and evolution.
5. Variable Stars: Ophiuchus houses several intriguing variable stars, which are stars that exhibit periodic changes in their brightness. One notable example is the unique eclipsing binary star system Epsilon Ophiuchi, where two stars periodically pass in front of each other, causing variations in the overall brightness. The study of variable stars allows astronomers to delve into stellar physics, mass determinations, and other fundamental aspects of stellar evolution.
From the identification of prominent stars and cataloging of celestial objects to the exploration of star formation regions and the study of variable stars, the discoveries within Ophiuchus have contributed immensely to our understanding of the universe. These remarkable findings have shaped the course of astronomy, inspiring scientists to continue unraveling the mysteries of this mesmerizing constellation.
Note: If you’re interested in exploring the mythology surrounding the constellation of Ophiuchus, check out our article on Unveiling the Mysteries of Ophiuchus: A Guide to the Mythology of the Constellation.
Impact on Astronomy
The impact of Ptolemy’s work on astronomy cannot be overstated. His geocentric model, as presented in “Almagest,” shaped the field of astronomy for centuries and had profound implications for our understanding of the universe. Here are some key impacts of Ptolemy’s contributions:
- Foundation of Astronomical Observations: Ptolemy’s meticulous observations and cataloging of stars provided a foundation for future astronomers to study and understand celestial objects. His systematic approach to recording the positions and movements of stars served as a guide for astronomers throughout history.
- Advancement of Mathematical Tools: Ptolemy’s geocentric model required sophisticated mathematical calculations to accurately predict the movements of celestial bodies. This led to the development of new mathematical tools and techniques that were instrumental in the advancement of astronomy.
- Validation of Greek Cosmology: Ptolemy’s model aligned with the prevailing Greek cosmology that placed the Earth at the center of the universe. His work provided empirical evidence that supported the existing philosophical and religious beliefs of the time.
- Development of Epicycles: To explain the irregular motion of planets observed from Earth, Ptolemy introduced the concept of epicycles (smaller circles within larger circles). This mathematical device allowed for more accurate predictions of planetary positions and was a crucial development in the understanding of planetary motion.
- Influence on Islamic and Medieval European Astronomy: Ptolemy’s work was translated into Arabic during the Islamic Golden Age and became the foundation of astronomy in the Islamic world. Later, during the Middle Ages, his works were translated into Latin and had a significant influence on European astronomy, shaping scholarly understanding of the cosmos.
- Inspiration for Future Astronomers: Ptolemy’s dedication to careful observation and mathematical modeling inspired future generations of astronomers. His work served as a starting point for astronomers like Nicolas Copernicus, who would later challenge the geocentric model and propose the heliocentric model, revolutionizing our understanding of the solar system.
Ptolemy’s impact on astronomy extended beyond his own time, shaping the course of scientific inquiry for centuries to come. His contributions to observational techniques, mathematics, and cosmological theories provided a solid foundation upon which future astronomers built their understanding of the universe. The legacy of Ptolemy’s work continues to inspire and guide astronomers in their pursuit of knowledge about the cosmos.
Giovanni Domenico Cassini

Giovanni Domenico Cassini, an Italian-French astronomer, was born in 1625 in Perinaldo, Italy. Cassini’s contributions to the field of astronomy are numerous and varied, making him one of the most renowned astronomers of his time.
Cassini made significant discoveries within the constellation of Ophiuchus. One of his notable achievements was the observation and measurement of the Great Red Spot on Jupiter. This iconic storm, located in the atmosphere of the gas giant, has been a subject of fascination for astronomers for centuries. Cassini’s meticulous observations and measurements of the Great Red Spot provided valuable data for understanding the dynamics of Jupiter’s atmosphere.
In addition to studying Jupiter, Cassini also made important observations of Saturn. He discovered four of Saturn’s moons, including Iapetus, Rhea, Tethys, and Dione. Cassini’s discovery of these moons expanded our knowledge of Saturn’s moon system and contributed to our understanding of the dynamics of celestial objects within the Ophiuchus constellation.
Cassini’s most significant impact on astronomy, however, was his work in determining the scale of the solar system. Using a method called parallax, he accurately measured the distance between Earth and Mars. This measurement served as a crucial milestone in understanding the vast distances between celestial objects and paved the way for future astronomers to measure the scale of the universe.
Cassini’s observations and calculations of the orbit of the comet named after him, Comet Cassini, provided valuable insights into the nature of comets and their trajectories within the solar system.
Cassini’s work within the constellation of Ophiuchus and his overall contributions to astronomy laid the foundation for future advancements in the field. His meticulous observations and calculations set a standard for scientific inquiry and continue to inspire astronomers to this day.
Note: To learn more about the mythology and mysteries surrounding the Ophiuchus constellation, check out our article on Unveiling the Mysteries of Ophiuchus: A Guide to the Mythology of the Constellation.
Life and Contributions
Ptolemy, whose full name was Claudius Ptolemaeus, was born in the city of Ptolemais Hermiou in Egypt. Not much is known about his personal life, but his immense contributions to astronomy and geography have left a lasting legacy.
Ptolemy’s major contributions were in the field of astronomy, where he sought to understand the movements and positions of celestial bodies. His work “Almagest” was a groundbreaking treatise on astronomy, consisting of thirteen books that synthesized the knowledge of his time.
In addition to the geocentric model, Ptolemy developed the concept of “epicycles,” which were small circles traced by a planet’s motion around a larger circle along its orbital path. These epicycles helped explain the apparent retrograde motion observed in some planets, further refining his geocentric model.
Ptolemy’s understanding of mathematics was crucial to his astronomical research. He utilized trigonometry and geometry to calculate the positions and distances of the planets and stars, laying the foundation for precise measurements and predictions.
Outside of his astronomical pursuits, Ptolemy also made significant contributions to the field of geography. His work “Geographia” was a comprehensive compilation of geographical knowledge at the time, including maps and detailed descriptions of various regions.
Ptolemy’s geocentric model and his meticulous cataloging of stars and planets greatly influenced the work of later astronomers, including Copernicus and Kepler. His dedication to observation and mathematical precision set a high standard for scientific inquiry that continues to be respected and followed today.
Despite the advances made in astronomy since Ptolemy’s time, his work remains an integral part of the history of the field. His contributions paved the way for a new era of astronomical understanding and continue to inspire researchers to delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos.
Key Discoveries in Ophiuchus
The constellation of Ophiuchus has been a source of fascination for astronomers, leading to numerous key discoveries that have expanded our knowledge of the universe. Here are some of the notable findings within Ophiuchus:
1. Supernova Remnants: Ophiuchus is home to several remarkable supernova remnants, remnants of massive stars that have exploded. One such remnant is the famous Kepler’s Supernova Remnant, named after Johannes Kepler. This explosive event, observed by Kepler in 1604, provided crucial insights into the nature of supernovae and their role in enriching the cosmos with heavy elements.
2. Stellar Clusters: Ophiuchus hosts several open star clusters, dense groupings of stars that formed from the same molecular cloud. Messier 9 is one such cluster, located near the serpent bearer’s head. Stellar clusters like these offer astronomers valuable opportunities to study star formation, evolution, and stellar populations.
3. Dark Nebulae: Ophiuchus is adorned with intricate dark nebulae, dense clouds of gas and dust that obscure the light from background stars or glowing nebulae. One example is the Snake Nebula (Barnard 72), a winding structure that resembles a cosmic serpent in the night sky. The study of these dark nebulae provides insights into the processes of star formation and the interstellar medium.
4. Variable Stars: Ophiuchus is home to various variable stars, whose brightness changes over time. One noteworthy variable star is Epsilon Ophiuchi, a type of star known as an eclipsing binary. Epsilon Ophiuchi periodically eclipses its companion star, providing astronomers with valuable data on stellar properties and binary systems.
5. Exoplanet Discoveries: Over the years, several exoplanets have been discovered within the boundaries of Ophiuchus. These distant worlds orbit stars outside our solar system and offer insights into planetary formation and the potential for habitable environments beyond Earth.
The exploration of Ophiuchus has yielded a wealth of discoveries that have expanded our understanding of the universe. These findings continue to shape our knowledge of stellar evolution, star formation, and the complex workings of our cosmic neighborhood. Ophiuchus remains a captivating region of the sky, beckoning astronomers to uncover more of its hidden treasures.
Note: For a deeper exploration of the mythology surrounding Ophiuchus, check out our article on Unveiling the Mysteries of Ophiuchus: A Guide to the Mythology of the Constellation.
Impact on Astronomy
The impact of Ptolemy’s work on astronomy cannot be overstated. His geocentric model, as presented in “Almagest,” had a profound influence on the field for centuries. Here are some key aspects of Ptolemy’s impact on astronomy:
1. Framework for Understanding: Ptolemy’s model provided a comprehensive framework for understanding the movements of celestial bodies. It allowed astronomers to predict the positions of planets, stars, and other celestial objects with a remarkable level of accuracy using mathematical calculations. This laid the foundation for future astronomers to build upon.
2. Preservation of Knowledge: Ptolemy’s meticulous observations and cataloging of stars, including those within Ophiuchus, ensured their preservation for future generations. His work served as a valuable resource for later astronomers, allowing them to study and analyze the celestial objects within Ophiuchus and other constellations.
3. Influence on Future Astronomers: Ptolemy’s work inspired and influenced many astronomers who came after him. His geocentric model served as the basis for astronomical theory and calculations for centuries, shaping the way astronomers approached their studies and observations.
4. Continued Exploration: While Ptolemy’s model has been superseded by the heliocentric model, his contributions to astronomy paved the way for further exploration and understanding of the universe. His systematic approach to cataloging stars set the stage for future discoveries and observations, fueling the curiosity and passion of astronomers to continue exploring the wonders of Ophiuchus and beyond.
5. Historical Significance: Ptolemy’s work holds immense historical significance in the development of astronomy. His writings, including “Almagest,” were preserved and translated throughout the medieval period, ensuring their continued influence on the scientific community.
Ptolemy’s impact on astronomy is a testament to the power of his ideas and the lasting legacy of his work. His geocentric model shaped our understanding of the universe for centuries and continues to be studied and appreciated for its historical and scientific significance.
William Herschel
William Herschel, born Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel, was a German-born British astronomer and composer who lived during the 18th and 19th centuries. Herschel made significant contributions to both astronomy and music, but it was his astronomical achievements that earned him lasting recognition.
Herschel is most famously known for his discovery of the planet Uranus in 1781. Prior to this discovery, Herschel was an accomplished musician and composer, but his love for astronomy led him to build his own telescopes to explore the night sky.
Within the constellation of Ophiuchus, Herschel made important discoveries that expanded our understanding of the universe. One of his notable findings was the identification of the globular cluster known as M14. Located near the border of Ophiuchus and Serpens, this cluster contains thousands of tightly packed stars.
Additionally, Herschel discovered numerous binary star systems within Ophiuchus, including Xi Ophiuchi and Rho Ophiuchi. These pairs of stars orbiting around a common center of mass provided valuable insights into stellar evolution and dynamics.
Herschel’s systematic observation of the night sky led to the discovery of several nebulous objects within Ophiuchus. Notable examples include the reflection nebula IC 4605 and the dark nebulae Barnard 37 and Barnard 40.
William Herschel’s contributions to astronomy had a profound impact on the field. His discovery of Uranus not only expanded the known boundaries of the solar system but also played a crucial role in challenging the prevailing understanding of the cosmos at the time.
Herschel’s dedication to meticulous observation and exploration paved the way for future astronomers to delve deeper into the mysteries of space. His discoveries within Ophiuchus and beyond contributed to our understanding of stellar evolution, binary star systems, and the structure of the universe.
In addition to his specific findings, Herschel’s innovative use of larger telescopes and precise measurements inspired future generations of astronomers to push the boundaries of scientific inquiry. His influence on the field of astronomy continues to be felt to this day.
Note: For more information on the captivating hidden gems within the constellation of Ophiuchus, don’t miss our article on Hidden Gems of Ophiuchus: Exploring the Celestial Treasures.
Life and Contributions
Ptolemy, also known as Claudius Ptolemaeus, was born in Alexandria, Egypt, around 90 AD. He was a polymath who made significant contributions to various fields, including astronomy, mathematics, geography, and astrology.
Ptolemy’s most influential work, “Almagest,” brought together the knowledge of ancient Greek astronomy and provided a comprehensive description of the cosmos. In this monumental treatise, he elaborated on the geocentric model, which became the prevailing theory of the universe for centuries.
Apart from astronomy, Ptolemy also made notable contributions to the field of geography. His work “Geographia” introduced a system of longitude and latitude, creating a foundation for cartography that would be followed for more than a millennium.
Ptolemy’s impact extended beyond his theoretical writings. He developed various instruments, such as the astrolabe and the equatorium, to aid in astronomical observations and calculations. His methods and tools greatly influenced the practice of astronomy and the accuracy of measurements for centuries to come.
In addition to his scientific endeavors, Ptolemy was a prominent figure in astrology. He wrote “Tetrabiblos,” a treatise on astrological theory, which became a fundamental text in the field. Ptolemy’s work on astrology influenced the development of horoscopic astrology and its integration into various cultures throughout history.
Ptolemy’s comprehensive understanding of the natural world, his mathematical calculations, and his meticulous observations formed the basis for much of the astronomical knowledge in the ancient and medieval world. His works were translated and studied throughout the Islamic and European civilizations, preserving and expanding upon his contributions.
Despite the passage of time and the advancement of scientific knowledge, Ptolemy’s work remains essential to the history of astronomy. His dedication to systematic observation, precise calculations, and detailed documentation set the standard for future astronomers and scientists. Ptolemy’s legacy lives on, a testament to his brilliance and the lasting impact of his contributions.
Key Discoveries in Ophiuchus
The constellation of Ophiuchus has been a focal point for astronomers throughout history, yielding numerous key discoveries that have expanded our knowledge of the cosmos. From the identification of new stars to the exploration of star clusters and nebulae, Ophiuchus has provided a rich tapestry of celestial wonders to be unraveled.
One notable discovery within Ophiuchus is the Serpens Nebula, located near the head of the serpent bearer. This nebula is composed of two distinct regions, Serpens Main and Serpens South, and has been the subject of extensive study. Astronomers have used various observatories and instruments to investigate the Serpens Nebula, revealing insights into star formation, protostars, and young stellar objects.
Another fascinating discovery within Ophiuchus is the Barnard’s Star, a red dwarf located in the vicinity of the Serpens Nebula. Barnard’s Star is notable for its high proper motion, meaning it moves relatively quickly across the sky. This discovery was significant as it provided evidence of nearby stars moving relative to the Sun, further expanding our understanding of the universe’s dynamics.
Additionally, Ophiuchus is home to the Rho Ophiuchi Complex, a dark cloud and stellar nursery. This complex is filled with dense dust and gas, harboring the potential for new star formation. Astronomers have studied this region extensively, uncovering the intricacies of how stars are born and the processes that drive their evolution.
One of the most intriguing discoveries within Ophiuchus is the Kepler’s Supernova Remnant. In 1604, Johannes Kepler observed a supernova explosion in this constellation, marking the last observed supernova within the Milky Way galaxy. The remnants of this ancient cosmic event serve as a reminder of the explosive nature of stellar evolution and have provided valuable insights into the life cycles of massive stars.
These key discoveries within Ophiuchus illustrate the ongoing quest for knowledge and exploration in the field of astronomy. By studying the celestial wonders within this constellation, astronomers have deepened our understanding of star formation, stellar evolution, and the dynamics of our universe.
Note: To learn more about the mythology and fascinating stories behind Ophiuchus, check out our article on Unveiling the Mysteries of Ophiuchus: A Guide to the Mythology of the Constellation.
Impact on Astronomy
The impact of Ptolemy’s work on astronomy cannot be overstated. His geocentric model, as outlined in “Almagest,” shaped the field of astronomy for centuries. It provided a framework for understanding the movements of celestial bodies, allowing astronomers to predict the positions of planets, stars, and other objects in the sky with remarkable accuracy.
Ptolemy’s meticulous cataloging of stars in Ophiuchus and other constellations laid the groundwork for future astronomers to study and explore the universe. His precise observations and systematic approach set a standard for scientific inquiry, emphasizing the importance of accuracy and detail in astronomical observations.
The geocentric model proposed by Ptolemy remained the prevailing view of the universe for over a thousand years. It was widely accepted until the heliocentric model, introduced by Copernicus in the 16th century, challenged the notion that the Earth was at the center of the cosmos.
Despite the eventual shift to the heliocentric model, Ptolemy’s work on Ophiuchus and other constellations still holds significance in the field of astronomy. His contributions set the stage for further advancements in our understanding of the universe and propelled the study of celestial objects within Ophiuchus and beyond.
Additionally, Ptolemy’s emphasis on accurate measurements and systematic observations planted the seeds for the development of modern astronomical techniques. His meticulous approach to cataloging stars, along with his mathematical calculations, established a foundation upon which later astronomers would build their own discoveries and theories.
Ptolemy’s impact on astronomy can be seen in the way his work influenced subsequent generations of astronomers. His geocentric model, along with his observations of celestial objects in Ophiuchus and other constellations, helped shape our understanding of the universe and set the stage for the remarkable advancements that have followed in the field of astronomy.
Note: To delve deeper into the mythology of the Ophiuchus constellation, check out our guide on Unveiling the Mysteries of Ophiuchus: A Guide to the Mythology of the Constellation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the constellation of Ophiuchus has been a source of fascination and inspiration for astronomers throughout history. We have explored the lives and contributions of four pioneering astronomers who made significant discoveries within Ophiuchus.
Ptolemy, with his geocentric model and meticulous cataloging of stars, set the stage for future astronomers to study and understand the celestial objects within Ophiuchus. Johannes Kepler’s laws of planetary motion revolutionized our understanding of planetary orbits and laid the foundation for Isaac Newton’s laws of motion. Giovanni Domenico Cassini’s observations of Saturn and its moons provided crucial insights into the dynamics of the solar system. Lastly, William Herschel’s discovery of Uranus expanded our knowledge of the outer reaches of our solar system.
These astronomers had a profound impact on the field of astronomy, shaping the way we perceive and interpret the universe. Their efforts have led to advancements in our understanding of star formation, planetary motion, and the structure of the cosmos.
But the exploration of Ophiuchus doesn’t end here. There are still countless discoveries waiting to be made within this vast constellation. Whether it’s uncovering the mysteries of mythology associated with Ophiuchus or delving deeper into the hidden gems it holds, there is always more to learn and explore.
As humanity continues to gaze at the stars, we can only imagine what future astronomers will discover within the boundaries of Ophiuchus. The legacy of these pioneering astronomers serves as a reminder of the infinite wonders that await us in the night sky, inspiring future generations to continue seeking knowledge and pushing the boundaries of our understanding.
Note: If you want to learn more about the hidden gems within the Ophiuchus constellation, be sure to check out our article on Hidden Gems of Ophiuchus: Exploring the Unseen Treasures.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can you observe Ophiuchus with the naked eye?
Yes, Ophiuchus is a constellation that can be seen with the naked eye. It is located in the northern hemisphere and is best observed during the summer months.
2. What is the mythological origin of the constellation Ophiuchus?
Ophiuchus represents the serpent bearer in Greek mythology. It is associated with Asclepius, the god of medicine and healing, who is often depicted holding a serpent.
3. Are there any notable deep-sky objects within Ophiuchus?
Yes, there are several notable deep-sky objects within Ophiuchus. One of the most famous is the globular cluster Messier 10, which is a dense cluster of stars located near the serpent bearer’s left knee.
4. Did Ptolemy make any other significant contributions to astronomy?
Absolutely! Ptolemy’s work extended far beyond his observations within Ophiuchus. He is also known for his development of a comprehensive catalog of stars, his study of planetary motion, and his contribution to the understanding of optics.
5. How did Ptolemy’s geocentric model impact the field of astronomy?
Ptolemy’s geocentric model was the prevailing theory of the universe for over a thousand years. It provided a framework for understanding the movements of celestial bodies and influenced astronomical thought and observation until the Copernican revolution.
6. What other constellations neighbor Ophiuchus?
Ophiuchus is surrounded by several notable constellations, including Scorpius, Serpens, Hercules, and Aquila. These constellations add to the richness and interconnectedness of the night sky.
7. Is there any ongoing research within Ophiuchus?
Yes, Ophiuchus continues to be a subject of study for astronomers. Some current research focuses on star formation within the constellation and the search for exoplanets in the region.
8. Can Ophiuchus be seen from both the northern and southern hemispheres?
While the constellation is more visible from the northern hemisphere, parts of Ophiuchus can also be observed from the southern hemisphere. Its position in the sky varies depending on the observer’s location.
9. How did Ptolemy’s catalog of stars within Ophiuchus contribute to future astronomical discoveries?
Ptolemy’s meticulous cataloging of stars within Ophiuchus provided a valuable resource for future astronomers. It allowed for the identification and study of specific stars, contributing to our understanding of stellar evolution and the composition of the universe.
10. Can you see the constellation Ophiuchus from urban areas with light pollution?
While light pollution can make it more challenging to observe fainter stars and objects within Ophiuchus, some of the brighter stars and clusters can still be seen even in urban areas. However, for the best viewing experience, it is recommended to find a location with minimal light pollution.