Do you often wake up in the middle of the night, drenched in sweat, feeling frightened and disoriented? You might be experiencing either a nightmare or a night terror. While these two terms are often used interchangeably, they actually refer to distinct types of sleep disturbances. In this article, we will delve into the world of nightmares and night terrors, exploring their definitions, causes, symptoms, and most importantly, the key differences between them. Understanding these differences is crucial to effectively managing and alleviating these distressing experiences, so read on to gain valuable insights into the fascinating realm of sleep disturbances.
What are Nightmares?

Nightmares are unsettling and vivid dreams that can cause intense fear, anxiety, or distress. These nocturnal experiences often occur during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, the stage of sleep associated with increased brain activity. Nightmare content can range from being chased or attacked to witnessing disturbing events or situations. While nightmares are a normal part of dream activity, recurring or frequent nightmares can negatively impact sleep quality and overall well-being. Common causes of nightmares include stress, trauma, certain medications, sleep deprivation, and even certain foods. Children may also experience nightmares as they navigate their emotions and develop coping mechanisms. To learn more about famous nightmares in history and literature, along with strategies to help children cope with nightmares, you can check out this article and this resource. If you’re looking for ways to overcome nightmares and improve your quality of sleep, you can find helpful tips in this guide.
Definition of Nightmares
Nightmares, in simple terms, are distressing and vivid dreams that often cause feelings of fear, anxiety, or terror. They occur during the REM stage of sleep, which is characterized by rapid eye movement and heightened brain activity. Unlike regular dreams, nightmares can be more intense, graphic, and emotionally disturbing. The content of nightmares varies greatly, but common themes include being chased, attacked, or experiencing life-threatening situations. These dreams can leave individuals feeling shaken, anxious, and even physically aroused upon waking. Nightmares can occur in both children and adults, but they are particularly prevalent in childhood. While an occasional nightmare is normal, frequent nightmares that consistently disrupt sleep and cause significant distress may require attention and management.
Causes of Nightmares
There are several factors that can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. Understanding these causes can help shed light on why nightmares happen and how to potentially reduce their frequency. Here are some common causes of nightmares:
- Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can easily trigger nightmares. When we’re anxious or overwhelmed, our brains are more prone to generating disturbing dream content during REM sleep.
- Trauma: People who have experienced trauma, such as physical or emotional abuse, may have an increased risk of nightmares. Traumatic events can deeply impact the subconscious mind, leading to nightmares as a manifestation of unresolved emotions and memories.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, blood pressure medications, and beta-blockers, have been known to cause nightmares as a side effect. It’s important to discuss any concerns or experiences with nightmares with a healthcare professional.
- Sleep Disorders: Nightmares can be associated with certain sleep disorders, including sleep apnea and insomnia. These conditions can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and contribute to nightmare occurrence.
- Substance Abuse: The use of substances like alcohol and drugs, especially before bedtime, can interfere with sleep patterns and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
- Food and Diet: Consuming certain foods, such as spicy or heavy meals, right before bedtime can disrupt digestion and potentially trigger nightmares. Additionally, caffeine and nicotine can interfere with sleep quality, leading to more frequent nightmares.
By identifying potential causes of nightmares, individuals can take proactive steps to address these underlying factors and potentially reduce the occurrence of unsettling dreams. Remember that consulting with a healthcare professional is always a wise choice when seeking guidance on managing nightmares and related sleep disturbances.
Symptoms of Nightmares
- Intense Emotions: When experiencing a nightmare, individuals may feel a wide range of intense emotions such as fear, anxiety, sadness, anger, or helplessness. These emotions can be so vivid that they linger upon waking, making it challenging to shake off the unsettling feelings.
- Vivid Imagery: Nightmares are characterized by vivid and realistic imagery. The dream scenarios can be terrifying and involve disturbing or threatening elements, such as being chased, attacked, or placed in life-threatening situations.
- Physical Reactions: Nightmares can elicit physical reactions during sleep and upon waking. These reactions may include increased heart rate, sweating, rapid breathing, and even crying out or flailing in bed.
- Difficulty Returning to Sleep: The distress caused by nightmares often results in individuals having difficulty falling back asleep. The fear and anxiety from the dream can leave them feeling on edge, making it hard to relax and drift back into a peaceful slumber.
- Impaired Sleep Quality: Nightmares can disrupt the overall quality of sleep, leading to feelings of fatigue, grogginess, and irritability during the day. The emotional toll and the waking episodes can fragment sleep patterns, leaving individuals feeling unrested.
- Recurrent Themes: Some individuals may experience recurrent nightmare themes, where similar scenarios or content emerge repeatedly in their dreams. These recurring nightmares can be particularly distressing and may require further exploration and management.
What are Night Terrors?

Night terrors, also known as sleep terrors, are episodes of intense fear or terror that occur during sleep, usually in the first few hours after falling asleep. Unlike nightmares, night terrors are not dreams but rather brief periods of partial awakening from deep sleep. During a night terror, individuals may exhibit sudden screaming, thrashing, or exhibiting signs of extreme distress, often accompanied by rapid breathing and a racing heart. It can be alarming to witness someone experiencing a night terror, as they may appear awake but are not fully conscious or responsive. Night terrors are more common in children, especially between the ages of 3 and 8, and tend to decrease in frequency as they get older. The exact causes of night terrors are not fully understood but factors such as sleep deprivation, fever, stress, and certain medications can contribute to their occurrence.
Definition of Night Terrors
Night terrors, also known as sleep terrors, are a type of sleep disorder characterized by sudden and intense episodes of fear, panic, or terror during sleep. Unlike nightmares, which occur during REM sleep, night terrors typically happen during non-REM sleep, specifically during the transition from deep sleep to lighter stages of sleep. During a night terror episode, a person may suddenly sit up in bed, cry out, gasp, or thrash around, appearing to be in a state of extreme distress. However, they often have no recollection of the episode upon waking.
Causes of Night Terrors
Night terrors, also known as sleep terrors, are episodes of intense fear or terror that occur during sleep. These episodes can be characterized by screaming, thrashing, or even sleepwalking. The exact causes of night terrors are not fully understood, but there are several factors that may contribute to their occurrence. Extreme tiredness or insufficient sleep can increase the likelihood of experiencing night terrors. Additionally, factors such as fever, sleep deprivation, stress, and certain medications can trigger these episodes. Night terrors are more common in children, particularly between the ages of 3 and 8, but they can also occur in adults. It is believed that night terrors may be linked to an imbalance in the brain’s sleep patterns and the transition between different sleep stages. While the exact underlying causes may vary from person to person, addressing these potential triggers, ensuring a consistent sleep routine, and managing stress levels can help reduce the frequency and intensity of night terrors.
Symptoms of Night Terrors
- Terror-filled episodes: Night terrors are characterized by sudden bouts of intense fear or terror during sleep. These episodes can cause individuals to jolt upright in bed, scream, or thrash around involuntarily.
- Difficulty waking up: Unlike nightmares, people experiencing night terrors often remain in a deep sleep state and may be difficult to wake up or console during an episode.
- Lack of memory: Individuals who have night terrors typically have no recollection of the event upon waking up. This can be puzzling and disorienting for both the person experiencing the night terror and anyone witnessing it.
- Rapid breathing and increased heart rate: Night terrors can be accompanied by physical symptoms such as rapid breathing and a racing heart, adding to the overall sense of distress.
- Confusion and disorientation: Upon waking up from a night terror, individuals may experience confusion and disorientation. It may take some time for them to fully regain their awareness and understanding of their surroundings.
- Minimal response to comfort: While well-intentioned efforts to comfort someone during a night terror episode are important, it is common for the person to show minimal response to comforting gestures or attempts to soothe them.
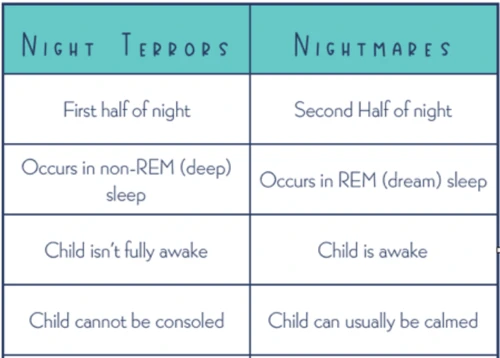
The Difference Between Nightmares and Night Terrors

While nightmares and night terrors may both disrupt our sleep, they are fundamentally different experiences. Nightmares are unsettling dreams that occur during REM sleep and can be recalled upon waking. On the other hand, night terrors are episodes of intense fear or agitation that occur during non-REM sleep, specifically during the transition from deep sleep to lighter stages of sleep. One of the key distinctions between the two is that nightmares often involve coherent storylines or themes, while night terrors are typically devoid of narrative and may result in sudden, piercing screams or physical thrashing. Additionally, individuals who experience nightmares can typically be comforted and may remember the details of their dream, while those who experience night terrors usually have no recollection of the event the next morning. Understanding these crucial differences is essential in identifying and managing these sleep disturbances effectively.
Key Similarities
- Both nightmares and night terrors are sleep disturbances: Despite their differences, nightmares and night terrors share the common characteristic of disrupting normal sleep patterns. They both occur during different stages of sleep and can leave the individual feeling distressed upon waking.
- Both can cause intense emotions: Whether it’s a nightmare or a night terror, both experiences can evoke intense emotions such as fear, anxiety, and panic. They can leave a lasting impression on the individual and affect their mood and well-being.
- Both can lead to physical symptoms: Nightmares and night terrors can manifest physical symptoms like increased heart rate, rapid breathing, sweating, and even sleepwalking in some cases. These physiological reactions are part of the body’s response to the emotional intensity experienced during these episodes.
- Both can be triggered by stress: Stress is a common trigger for both nightmares and night terrors. Whether it’s everyday stressors, traumatic events, or underlying mental health conditions, an increased level of stress can contribute to the occurrence of these sleep disturbances.
- Both can be managed and reduced: While nightmares and night terrors can be distressing, there are strategies to manage and reduce their frequency. From creating a soothing bedtime routine to addressing underlying stressors or seeking professional help, individuals can take proactive steps to cope with and alleviate these sleep disturbances.
Key Differences
One of the key differences between nightmares and night terrors lies in the intensity of the emotions experienced during the episodes. Nightmares are characterized by vivid and disturbing dreams that often evoke fear, anxiety, or other negative emotions. The dreamer is usually able to remember the content of the dream upon waking up. Night terrors, on the other hand, are episodes of intense fear or terror that occur during non-REM sleep. Unlike nightmares, night terrors are not accompanied by intricate dream sequences and are typically not remembered upon awakening.
Another important difference is the level of arousal and behavior exhibited during these episodes. During a nightmare, the individual may toss and turn, experience increased heart rate and breathing, and might even wake up from the dream. However, they are generally responsive and can be easily comforted. In contrast, individuals experiencing night terrors may sit up or even sleepwalk, appearing agitated and inconsolable. They may scream, thrash around, or display other physical manifestations of fear. Despite these apparent signs of distress, it’s important to note that individuals experiencing night terrors are often unaware of their surroundings and do not fully wake up during the episode.
The duration and timing of nightmares and night terrors also differ. Nightmares commonly occur during the REM stage of sleep, which typically happens in the latter part of the night or during early morning hours. They can last for several minutes, and the individual may have multiple nightmares throughout the night. On the other hand, night terrors occur during deep non-REM sleep, usually within the first few hours after falling asleep. They tend to be shorter in duration, lasting anywhere from a few seconds to a couple of minutes.
Lastly, the frequency of occurrence sets nightmares and night terrors apart. Nightmares are more common and can happen occasionally or frequently, depending on various factors such as stress levels, lifestyle, and emotional well-being. Night terrors, on the other hand, are relatively rare and typically occur sporadically, usually during childhood. Most people outgrow night terrors by adolescence, while nightmares may persist into adulthood if underlying causes are not addressed.
By understanding these key differences between nightmares and night terrors, individuals and their loved ones can gain insights into the nature of these experiences. This knowledge can help in seeking appropriate management strategies and support, ultimately leading to improved sleep and overall well-being.
How to Deal with Nightmares and Night Terrors
Dealing with nightmares and night terrors can be challenging, but there are strategies to manage and minimize their impact on your sleep and well-being. When it comes to nightmares, it can be helpful to create a calm and soothing environment in your bedroom, establish a relaxing bedtime routine, and practice stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing or meditation before sleep. Additionally, keeping a dream journal and exploring any underlying emotions or triggers can provide insights into the causes of your nightmares. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can also be beneficial in addressing recurrent nightmares. When it comes to night terrors, it is important to prioritize safety by creating a safe sleep environment, removing any potentially dangerous objects, and ensuring that sleep surfaces are secure. It is generally advised not to wake someone experiencing a night terror, as it can prolong the episode. Instead, gently guiding them back to bed and providing reassurance can be helpful. If night terrors persist or significantly impact sleep quality, seeking professional guidance and evaluation may be beneficial. Remember, everyone’s experience with nightmares and night terrors is unique, so finding the right approach that works for you is key.
Managing Nightmares
Managing Nightmares: Coping with nightmares can be challenging, but there are strategies and techniques that can help alleviate their impact on your sleep and daily life. Here are some effective ways to manage nightmares:
1. Establish a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Create a soothing routine before bed to promote relaxation and prepare your mind for sleep. This may include activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation.
2. Create a Peaceful Sleep Environment: Ensure that your bedroom is a calm and comfortable space that promotes sleep. Keep the room dark, quiet, and at a cool temperature. You can use earplugs, eye masks, or white noise machines to drown out any external disturbances that may trigger nightmares.
3. Avoid Stimulants and Heavy Meals: Certain substances like caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol can interfere with your sleep patterns and contribute to nightmares. Avoid consuming these stimulants close to bedtime. Additionally, heavy or spicy meals before bed may lead to indigestion, which can disrupt sleep and increase the likelihood of nightmares.
4. Practice Stress Reduction Techniques: Since stress is a common trigger for nightmares, incorporating stress reduction techniques into your daily routine can be beneficial. This may include engaging in regular exercise, practicing mindfulness or yoga, or seeking therapy or counseling to address underlying stressors.
5. Keep a Dream Journal: Keeping a dream journal can help you track patterns and identify potential triggers for your nightmares. Write down your dreams immediately upon waking, paying attention to the emotions, themes, and events that stood out. This can provide insights that may aid in understanding and managing your nightmares.
6. Talk to a Healthcare Professional: If your nightmares persist and significantly impact your sleep and well-being, consider seeking help from a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance, recommend therapeutic techniques or medications if necessary, and address any underlying psychological or medical conditions contributing to your nightmares.
Remember, managing nightmares takes time and patience. It is important to prioritize self-care, practice stress management, and create a sleep-friendly environment to promote restful nights and minimize the occurrence of distressing nightmares.
Managing Night Terrors
Managing Night Terrors: Managing night terrors requires a different approach compared to nightmares due to the nature of these episodes. Here are some strategies that can help:
1. Create a safe sleep environment: Ensure that the sleeping area is free from any potential hazards that could cause injury during a night terror episode. Remove sharp objects, secure furniture, and use safety gates if needed.
2. Stick to a consistent sleep routine: Establishing a regular bedtime routine can help regulate sleep patterns and minimize the occurrence of night terrors. Consistency is key, so aim for a set time and follow the same rituals each night, such as reading a book or taking a warm bath before bed.
3. Reduce stress and anxiety: Night terrors can be triggered by stress and anxiety, so it’s important to manage these factors during waking hours. Encourage relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or gentle stretching before bedtime.
4. Offer reassurance during an episode: When a night terror occurs, it’s essential not to try to wake the person experiencing it. Instead, calmly ensure their safety by gently guiding them away from any potential danger. Avoid trying to reason with them or engage in conversation, as this may prolong the episode.
5. Keep a sleep diary: Keeping track of night terror episodes can help identify any patterns or triggers. Note down the time of occurrence, duration, and any known factors that may have contributed to the episode. This information can be valuable when seeking professional assistance if the night terrors persist or worsen.
6. Seek professional help if needed: If night terrors significantly disrupt sleep or cause distress, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate any underlying conditions or factors contributing to the night terrors and recommend appropriate treatments or interventions.
Remember, managing night terrors requires patience and understanding. Providing a safe and supportive environment, along with consistent routines, can help minimize their impact on both the individual experiencing them and their loved ones.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between nightmares and night terrors is crucial for effectively managing and alleviating these distressing sleep disturbances. While nightmares are unsettling dreams that can cause fear and anxiety, night terrors are episodes of extreme panic and terror during sleep. Both can disrupt sleep quality and impact overall well-being. Nightmares are often related to stress, trauma, or certain medications, while night terrors are more commonly associated with sleep disorders and disruptions in sleep patterns. To manage nightmares, it can be helpful to create a calming bedtime routine, practice relaxation techniques, and address any underlying emotional or psychological factors. On the other hand, managing night terrors may involve maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a safe sleeping environment, and seeking professional guidance if necessary. Remember, if you or someone you know experiences regular or severe nightmares or night terrors, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance. By gaining a deeper understanding of these sleep disturbances and implementing appropriate strategies, you can strive for better sleep and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the main difference between nightmares and night terrors?
Nightmares are vivid dreams that cause fear or distress during REM sleep, while night terrors are sudden episodes of extreme fear or terror that occur during non-REM sleep.
2. Can nightmares be a sign of an underlying psychological condition?
Yes, recurring nightmares can be associated with various psychological conditions such as anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and depression.
3. Are nightmares more common in children or adults?
Nightmares are more commonly reported in children, with an estimated 50-85% of children experiencing at least one nightmare before the age of 12. However, they can occur in adults as well.
4. How do nightmares affect sleep quality?
Nightmares can disrupt sleep, leading to difficulties falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, and feelings of unrest upon waking. This can result in poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue.
5. Can medications contribute to the occurrence of nightmares?
Yes, certain medications such as antidepressants, beta-blockers, and some sleep aids have been known to increase the frequency or intensity of nightmares.
6. Is there any way to prevent nightmares?
While it is not always possible to prevent nightmares entirely, practicing good sleep hygiene, managing stress, and avoiding triggers such as late-night snacks, caffeine, and alcohol before bed can help reduce their occurrence.
7. Should you wake someone up from a nightmare or night terror?
In the case of a nightmare, gently waking someone up and providing reassurance can be helpful. However, it is generally advised not to forcefully wake someone experiencing a night terror, as it may prolong their distress.
8. Can a traumatic event trigger nightmares or night terrors?
Yes, a traumatic event can trigger both nightmares and night terrors, especially in individuals with PTSD or other anxiety-related disorders.
9. How long do nightmares and night terrors typically last?
Nightmares usually occur during REM sleep and may last anywhere from a few minutes to half an hour. Night terrors, on the other hand, can occur during non-REM sleep and typically last for a few minutes.
10. When should someone seek professional help for nightmares or night terrors?
If nightmares or night terrors persist, significantly impact daily life, or are accompanied by other symptoms such as insomnia or high levels of anxiety, it is advisable to seek professional help from a healthcare provider or sleep specialist.