Have you ever woken up in the middle of the night, drenched in sweat, with your heart pounding in your chest? Were you just experiencing a nightmare or was it something more sinister like a night terror? Both nightmares and night terrors can leave us feeling shaken and afraid, but what exactly is the difference between the two? In this article, we will delve into the mysterious world of nightmares and night terrors, exploring their definitions, causes, effects, and most importantly, the key differences that set them apart. So grab a blanket and get ready to uncover the truth behind these nocturnal disturbances.
Understanding Nightmares

Nightmares are unsettling and vivid dreams that can evoke strong emotions and often wake us up from sleep. These nocturnal disturbances can range from mildly distressing to downright terrifying, leaving us with a lasting sense of unease. The definition of nightmares varies slightly from person to person, but they typically involve intense fear, anxiety, and a feeling of helplessness. Nightmares can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, trauma, medication, and even certain psychological disorders. While nightmares are more commonly associated with children, they can affect individuals of all ages. Understanding the root causes and effects of nightmares is crucial in learning how to cope with and overcome these nighttime terrors. To delve deeper into the connection between nightmares and trauma, click here. Additionally, to explore the impact of medication on nightmares, click here. Finally, to gain a better understanding of the psychology behind nightmares, click here.
Definition of Nightmares
Nightmares can be described as vivid and distressing dreams that occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep phase. The definition of nightmares varies, but they are typically characterized by intense emotions such as fear, anxiety, and terror. These dreams often involve disturbing scenarios or events that feel incredibly real and may lead to the person waking up suddenly. Nightmares are different from regular dreams in that they tend to leave a lasting impact on the individual and can be recalled with great detail upon awakening. The content of nightmares can vary greatly from person to person. While some individuals may experience recurring nightmares centered around specific themes or situations, others may have random and unpredictable nightmares. It is important to note that nightmares can occur at any age, although they are more common in children. By understanding the definition of nightmares, we can begin to explore their causes, effects, and strategies for coping with these unsettling dreams.
Causes of Nightmares
Nightmares can be triggered by various factors, and understanding the causes behind them is essential in finding ways to manage and alleviate these distressing dreams. One of the primary causes of nightmares is stress and anxiety. When we experience high levels of stress or anxiety, our minds can become overactive during sleep, leading to an increase in nightmares. Traumatic events also play a significant role in causing nightmares. People who have experienced a traumatic event may frequently have nightmares related to the trauma, as their subconscious mind processes and tries to make sense of the distressing event. Medications can also impact the occurrence of nightmares. Certain medications, such as antidepressants and beta-blockers, have been known to induce vivid dreams and nightmares as a side effect. Additionally, sleep disorders like sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome can contribute to the frequency of nightmares. Other factors include alcohol or drug abuse, sleep deprivation, and even certain foods like spicy or heavy meals eaten before bed. By identifying and addressing these underlying causes, individuals can take steps to reduce or eliminate nightmares and promote a more restful sleep.
Effects of Nightmares
The effects of nightmares can extend far beyond the fleeting fright experienced during sleep. Nightmares can have a profound impact on various aspects of our waking lives. One effect of nightmares is disrupted sleep patterns. The intense fear and distress experienced during a nightmare can lead to difficulties falling back asleep, resulting in sleep disturbances and insomnia. This lack of quality sleep can leave individuals feeling fatigued, irritable, and less focused the next day. Additionally, nightmares can have emotional effects such as increased anxiety, fear, and heightened stress levels. The vivid and distressing images experienced during nightmares can linger in our minds, causing feelings of unease and uneasiness even after waking up. This emotional impact can spill over into daily life, affecting relationships, work performance, and overall well-being. Nightmares have also been associated with an increased risk of developing psychological conditions such as depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The recurrence of nightmares can contribute to a cycle of fear and anxiety, making it important to address and manage them effectively. Coping strategies, such as keeping a dream journal, practicing relaxation techniques, and seeking therapy, can help mitigate the effects of nightmares and promote better sleep and emotional well-being.
Understanding Night Terrors

Night terrors, often misunderstood and shrouded in mystery, are a type of sleep disorder characterized by episodes of intense fear and distress during sleep. These episodes, also known as sleep terrors, are different from nightmares in several ways. The definition of night terrors involves sudden awakenings accompanied by screaming, thrashing, and a sense of sheer panic. Unlike nightmares, where the dreamer can often recall the details of their dream, those experiencing night terrors usually have no memory of the event upon awakening. Night terrors are most common in children, especially between the ages of 3 and 8, but can also occur in adults. The causes of night terrors are not entirely clear, but they are believed to be triggered by factors such as sleep deprivation, stress, fever, and certain medications. These episodes can have a profound effect on those who experience them, leading to disrupted sleep patterns, daytime fatigue, and heightened anxiety. Understanding the nature of night terrors is crucial in seeking appropriate treatment and support for those affected.
Definition of Night Terrors
Night terrors, also known as sleep terrors, are a distinct sleep disorder characterized by sudden episodes of extreme fear that occur during deep non-REM sleep. Unlike nightmares, which are vivid and often remembered upon waking, night terrors leave individuals with little to no recollection of the experience. These episodes typically happen in the first few hours of sleep and can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes. During a night terror, a person may exhibit intense physical symptoms such as screaming, thrashing, and appearing wide-eyed with a look of sheer terror. However, despite these alarming behaviors, it’s important to note that individuals experiencing night terrors are not awake and are often unresponsive to attempts of comfort or reassurance. Night terrors are most commonly experienced by children aged 3 to 8, but they can also occur in adults. It’s crucial to differentiate night terrors from nightmares, as they are distinct in terms of their characteristics, duration, and lack of recall upon waking.
Causes of Night Terrors
Night terrors, also known as sleep terrors, are a phenomenon that can cause extreme fear and terror during sleep. The causes of night terrors can vary and are often multifactorial. Here are some common factors that can contribute to the occurrence of night terrors:
1. Genetics: There seems to be a genetic component to night terrors, as they tend to run in families. If one or both parents experience night terrors, there is a higher likelihood that their children may also have them.
2. Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can trigger night terrors. These can be related to various factors such as work, school, personal relationships, or traumatic events.
3. Disrupted Sleep: Sleep disruptions, such as irregular sleep patterns, inadequate sleep duration, or sleep deprivation, can increase the likelihood of experiencing night terrors. These disruptions can interfere with the normal sleep cycle and lead to disturbances in sleep stages.
4. Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as fever, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, and certain neurological disorders, have been found to be associated with night terrors.
5. Medications: Some medications, such as certain antidepressants, sedatives, and antipsychotics, have been known to trigger night terrors in some individuals.
It’s important to note that the exact mechanisms and causes of night terrors are not fully understood. Each individual may have unique triggers and underlying factors contributing to their experience of night terrors. Consulting with a medical professional or sleep specialist can help identify and address specific causes in order to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Effects of Night Terrors
Night terrors can have profound effects on both the individual experiencing them and the people around them. The effects of night terrors can be quite distressing and disruptive. For the person experiencing them, night terrors can lead to intense fear and panic, often accompanied by physical symptoms such as rapid breathing, sweating, and an increased heart rate. These episodes can be so intense that the individual may even scream or thrash around in their sleep. Upon waking, they may not remember the details of the episode, adding to their confusion and disorientation. Night terrors can also disrupt the quality of sleep, leading to excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue. Additionally, the frequency and intensity of night terrors can cause significant distress, anxiety, and fear of going to sleep. It is not uncommon for individuals with night terrors to develop sleep-related anxiety disorders. The effects of night terrors extend beyond the person experiencing them. Family members or roommates may also be impacted by witnessing these episodes, which can be alarming and distressing. The disrupted sleep patterns can strain relationships, causing tension and fatigue among family members. It is essential to seek proper diagnosis and treatment for night terrors to alleviate the emotional and physical toll they can have on individuals and their loved ones.
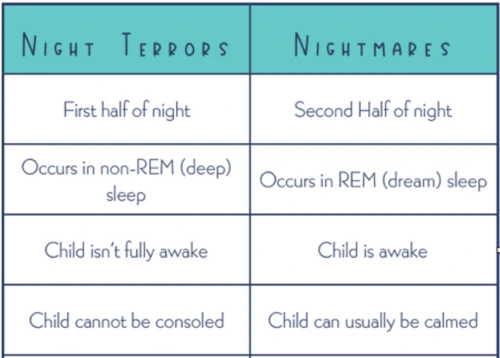
Differences Between Nightmares and Night Terrors
When it comes to nightmares and night terrors, there are several key differences that set them apart. First and foremost, the symptoms and duration of these nighttime disturbances differ significantly. Nightmares usually occur during REM sleep and can be remembered upon waking up. They often involve vivid imagery, fear, and anxiety. Night terrors, on the other hand, occur during non-REM sleep and are typically not remembered or only recalled partially. They are characterized by intense bouts of fear, screaming, and thrashing, which can last for several minutes. Another notable difference lies in the emotional response elicited by these episodes. Nightmares evoke a strong emotional response, often leaving the person feeling disturbed and anxious even after waking up. Night terrors, however, typically result in confusion and disorientation upon awakening, with little to no recollection of the specific incident. Additionally, age groups affected differ between nightmares and night terrors. Nightmares are more common in children, while night terrors are more prevalent in young children and can diminish or disappear as they grow older. Lastly, the treatment and coping strategies for nightmares and night terrors also differ. Nightmares can often be managed through techniques such as relaxation exercises, creating a peaceful sleep environment, and addressing any underlying psychological factors. Night terrors, on the other hand, may require more specialized treatment approaches, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule and minimizing any potential triggers. Understanding these differences can help individuals and their loved ones navigate these nighttime disturbances more effectively.
Symptoms and Duration
Symptoms and Duration
Nightmares and night terrors differ in terms of their symptoms and duration. When it comes to nightmares, individuals often experience a range of unsettling symptoms. These can include intense fear, anxiety, sweating, rapid heartbeat, and even physical reactions like screaming or sleepwalking. The duration of nightmares can vary as well, lasting anywhere from a few minutes to up to an hour. They typically occur during REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, which is the stage of sleep associated with vivid dreaming.
Night terrors, on the other hand, present with distinct symptoms that set them apart from nightmares. During a night terror episode, individuals may exhibit behaviors such as sitting up in bed, screaming, flailing their limbs, or appearing to be in a state of extreme distress. Unlike nightmares, night terrors occur during deep sleep and individuals may have no recollection of the event upon awakening. These episodes are usually much shorter in duration, lasting anywhere from a few seconds to a few minutes.
The symptoms and duration of nightmares and night terrors differ significantly. Nightmares are characterized by intense fear, anxiety, and physical reactions, and they occur during REM sleep. They can last from a few minutes to an hour. Night terrors, on the other hand, involve behaviors such as screaming and flailing that occur during deep sleep. They are typically shorter in duration, lasting only a few seconds to a few minutes. Understanding these distinctions can help individuals and their loved ones navigate the challenges of these sleep disturbances.
Emotional Response
When it comes to the emotional response, there is a notable difference between nightmares and night terrors. Nightmares often evoke a range of intense emotions such as fear, anxiety, and helplessness. These emotions can linger even after waking up, leaving individuals feeling unsettled and on edge. The vivid and realistic nature of nightmares makes it hard to distinguish between the dream and reality, intensifying the emotional impact. On the other hand, night terrors elicit extreme fear and distress, but unlike nightmares, individuals experiencing night terrors may not have a clear recollection of what caused their intense emotions. This can leave them feeling confused and disoriented upon waking up. The emotional response to night terrors is often described as a sudden and overwhelming surge of terror, sometimes accompanied by physical symptoms like rapid breathing and a racing heart. While both nightmares and night terrors can provoke intense emotions, nightmares tend to have a more lingering effect, while night terrors are characterized by a more abrupt and intense emotional response.
Age Groups Affected
Age plays a crucial role in determining who is most susceptible to nightmares and night terrors. Let’s take a closer look at how different age groups are affected by these nocturnal disturbances:
1. Infants and Toddlers: Nightmares and night terrors are common in infants and toddlers, typically between the ages of 1 and 4. At this stage, children are still developing their language skills, making it challenging for them to express their fears and anxieties. Night terrors, characterized by sudden episodes of intense fear and screaming, are more prevalent in this age group.
2. Children and Adolescents: Nightmares continue to be relatively common in children and adolescents, but they often have different themes compared to younger age groups. Children may experience nightmares related to school, social situations, or specific fears such as monsters or being separated from their parents. As they grow older, nightmares may be triggered by stressors such as exams, peer pressure, or personal insecurities.
3. Adults: While nightmares may occur at any age, they tend to decrease in frequency as individuals transition into adulthood. However, adults who have experienced trauma or are dealing with high levels of stress may still experience nightmares. In some cases, these nightmares may be indicative of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or other psychological conditions.
4. Older Adults: As individuals enter their later years, nightmares become less common. However, sleep disturbances such as nightmares can be a side effect of certain medications or underlying health conditions. Older adults may also experience night terrors or sleepwalking episodes, which can be attributed to factors such as poor sleep quality or neurological changes.
It is important to note that while nightmares and night terrors are more prevalent in certain age groups, they can occur in individuals of any age. Understanding the age-related patterns can help identify appropriate coping strategies and treatment options for those affected.
Treatment and Coping Strategies
When it comes to the treatment and coping strategies for nightmares and night terrors, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. However, there are several techniques that individuals can try to reduce the frequency and intensity of these unsettling experiences. One popular method is called Image Rehearsal Therapy (IRT). This technique involves identifying the main theme or content of the nightmare and then consciously rewriting the dream in a more positive and empowering way. By rehearsing the new dream scenario mentally, individuals can gradually desensitize themselves to the original nightmare and potentially reduce its occurrence.
Another effective strategy is relaxation techniques. Engaging in activities such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or meditation before bedtime can help individuals relax their minds and bodies, promoting a more peaceful sleep environment. Creating a calming bedtime routine, incorporating activities like reading a book or taking a warm bath, can also aid in reducing stress and anxiety levels before sleep, potentially decreasing the likelihood of nightmares or night terrors.
In some cases, seeking professional help may be necessary, especially if nightmares or night terrors significantly impact daily life and cause distress. Therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) can be beneficial for individuals struggling with trauma-related nightmares. Medications may also be prescribed in certain situations, but it is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks with a healthcare provider.
Finding effective treatment and coping strategies for nightmares and night terrors may take time and experimentation. It is essential to remain patient, persistent, and open to trying different techniques until a method that works best for each individual is discovered. Remember, addressing the underlying causes, managing stress levels, and prioritizing self-care can contribute to a more peaceful and restorative sleep.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between nightmares and night terrors is essential in addressing these nocturnal disturbances effectively. While both can be distressing and disruptive to a good night’s sleep, there are key distinctions to consider. Nightmares are vivid and often frightful dreams that elicit strong emotions like fear and anxiety. They can be triggered by various factors such as stress, trauma, and medication. On the other hand, night terrors are intense episodes of terror that typically occur during non-REM sleep, causing individuals to wake up in a state of extreme fright. Night terrors are more common in children and can be associated with sleep disorders. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the emotional response, age groups affected, and treatment options for each condition is crucial for finding the appropriate coping strategies. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if nightmares or night terrors persist and significantly disrupt daily life. By gaining a deeper understanding of these nocturnal disturbances, we can work towards achieving restful, peaceful nights and overcoming the fear that may haunt our dreams.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the scientific term for nightmares?
The scientific term for nightmares is “nocturnal dysphoria.” It refers to the experience of negative and distressing dreams during sleep.
Can nightmares be caused by trauma?
Yes, nightmares can be caused by trauma. Traumatic experiences can trigger the brain to process and replay distressing memories during sleep, resulting in nightmares.
Are nightmares more common in children or adults?
Nightmares are more common in children, especially during their early years. However, they can also affect adults, particularly those who have experienced trauma or have certain psychological conditions.
Can medication have an impact on nightmares?
Yes, certain medications can impact the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Some drugs, such as antidepressants or medications that affect the central nervous system, may increase the likelihood of experiencing vivid dreams or nightmares.
How do nightmares differ from night terrors?
Nightmares are vivid and distressing dreams that occur during REM sleep, whereas night terrors are episodes of intense fear or terror that happen during non-REM sleep. Night terrors typically involve physical symptoms and a sense of confusion upon waking up.
Are nightmares a sign of a mental health condition?
Nightmares can be a symptom of certain mental health conditions, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or anxiety disorders. However, occasional nightmares are generally considered a normal part of the dream cycle.
Can nightmares be prevented?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent nightmares, there are strategies that can help reduce the likelihood of experiencing them. These include practicing stress-reduction techniques, maintaining a consistent sleep routine, and creating a comfortable sleep environment.
Do nightmares serve any purpose?
Some theories suggest that nightmares may serve a protective function by allowing the brain to rehearse and prepare for potential threatening situations. They may also provide an opportunity for emotional processing and catharsis.
Can recurring nightmares be treated?
Yes, recurring nightmares can be treated. Therapy techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), image rehearsal therapy (IRT), and medication management can be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares.
When should I seek professional help for nightmares or night terrors?
If nightmares or night terrors are significantly impacting your daily life, causing distress, or disrupting your sleep on a regular basis, it is advisable to seek professional help from a healthcare provider or mental health specialist.