It’s common to experience unsettling dreams during sleep, but understanding the difference between nightmares and night terrors can help provide clarity and support. Nightmares are intense and vivid dreams that often evoke fear or anxiety, occurring during REM sleep. On the other hand, night terrors are characterized by sudden episodes of extreme terror, typically during non-REM sleep. Each type of sleep disturbance has its own causes, effects, and ways of coping. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, causes, effects, and distinguishing features of nightmares and night terrors. Additionally, we will explore tips and techniques for managing and preventing these disturbing sleep experiences. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of these phenomena and be equipped with strategies to mitigate their impact on your sleep quality and well-being.
Understanding Nightmares

Nightmares are intense and vivid dreams that can evoke fear, anxiety, and a range of other negative emotions. These distressing dreams usually occur during REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, the stage of sleep when most dreaming occurs. Nightmares often involve scenarios that are frightening or traumatic, such as being chased, falling, or experiencing a life-threatening situation. They can leave individuals feeling shaken, anxious, and even physically aroused upon waking up. Nightmares can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, trauma, sleep deprivation, certain medications, and even sleep disorders. In children, nightmares are a common occurrence, and they can often be coped with using techniques such as creating a comforting bedtime routine or providing reassurance. In adults, nightmares can sometimes be an indication of an underlying anxiety disorder or other mental health concerns, so seeking professional help may be necessary in such cases. Check out this link for tips on coping with nightmares in children, or this link for more information on the link between nightmares and anxiety disorders.
Definition of nightmares
Nightmares can be defined as intense, disturbing dreams that evoke strong negative emotions, such as fear, terror, or anxiety. These dreams are often vivid and can feel incredibly realistic, making it difficult to differentiate between the dream and reality. Nightmares usually occur during the REM (Rapid Eye Movement) stage of sleep, which is the phase associated with the most vivid dreaming. During a nightmare, individuals may experience a variety of frightening scenarios, such as being chased by a threatening figure, being trapped in a dangerous situation, or witnessing a traumatic event. It’s important to note that nightmares are more than just regular bad dreams – they often leave a lasting impression upon waking and can disrupt sleep patterns. While nightmares are common in children, affecting up to 50% of them at some point, adults can also experience them. If nightmares become frequent and are causing distress, it may be helpful to explore techniques for managing and preventing nightmares. For tips on coping with nightmares, check out this link.
Causes of nightmares
Nightmares can be caused by a variety of factors, both external and internal. One common cause of nightmares is prolonged stress and anxiety. When individuals are consistently exposed to stressors in their waking life, such as work pressure, relationship issues, or financial difficulties, it can manifest in their dreams as nightmares. Traumatic experiences, such as accidents, abuse, or witnessing violence, can also trigger nightmares. These intense and distressing events may be replayed in the dream state, causing emotional distress upon waking. Another factor that can contribute to nightmares is sleep deprivation or poor sleep quality. When the sleep cycle is disrupted or insufficient, it can disrupt the brain’s natural processing of emotions and memories, leading to vivid and disturbing dreams. Certain medications, such as antidepressants, beta-blockers, and some sleep aids, have also been linked to nightmares as a side effect. Additionally, substance abuse or withdrawal from drugs and alcohol can disrupt normal sleep patterns and contribute to nightmares. Mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and depression, are often associated with increased likelihood of experiencing nightmares. These underlying mental health issues can heighten emotional arousal during sleep, leading to more frequent and intense nightmares. It’s important to note that nightmares may have a complex combination of causes, and individual experiences can vary greatly. Identifying and addressing the underlying causes can play a crucial role in alleviating the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
Effects of nightmares
Nightmares can have significant effects on an individual’s overall well-being and daily functioning. The emotional impact of nightmares can be profound, causing fear, anxiety, and distress during both waking and sleeping hours. Recurrent nightmares may lead to sleep deprivation, as individuals may fear falling asleep and experiencing another distressing dream. This lack of quality sleep can result in daytime drowsiness, difficulty concentrating, and impaired cognitive function. Nightmares can disrupt a person’s mood, leading to increased irritability, mood swings, and a general sense of unease throughout the day. In some cases, nightmares can also trigger physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, and feelings of nausea or uneasiness upon waking up. Additionally, the fear and anxiety associated with nightmares can create a cycle of worry about sleep, contributing to the development or worsening of sleep disorders, such as insomnia. It is important to address the effects of nightmares and seek appropriate support and coping strategies to minimize their impact on daily life and overall mental well-being.
Understanding Night Terrors

Night terrors are intense episodes of extreme fear and terror that occur during sleep, typically within the first few hours of falling asleep. Unlike nightmares, night terrors occur during non-REM sleep, specifically during the deep sleep stage. Individuals experiencing night terrors may display symptoms such as screaming, sweating, rapid breathing, and appearing visibly distressed. They might also engage in behaviors like sleepwalking or thrashing around. Night terrors can be deeply unsettling for both the person experiencing them and any witnesses. While the exact causes of night terrors are not fully understood, they can be triggered by factors such as sleep deprivation, stress, fever, or certain medications. It is important to note that night terrors are more common in children than adults, and they typically decrease in frequency as a child grows older. If you suspect you or your child is experiencing night terrors, it is advisable to consult a medical professional to rule out any underlying medical conditions and for guidance on managing these episodes effectively.
Definition of night terrors
Night terrors, also known as sleep terrors, are episodes of intense fear and terror that occur during sleep. Unlike nightmares, which happen during REM sleep, night terrors occur during non-REM sleep, specifically during the transition between deep sleep and lighter stages of sleep. These episodes can be incredibly alarming as individuals may appear to be screaming, thrashing, and exhibiting signs of extreme panic. However, despite their intense nature, night terrors are generally not remembered upon waking. The individual experiencing a night terror may appear to be awake but will have no recollection of the event. These episodes typically last for a few minutes and can happen multiple times in a single night. Night terrors are most commonly observed in children, particularly between the ages of 4 and 12, although they can occasionally occur in adults as well. It’s important to note that night terrors are not considered nightmares, as the experience is different both in terms of the sleep stage during which they occur and the level of consciousness and recollection.
Causes of night terrors
Night terrors, also known as sleep terrors, are episodes of extreme terror that can occur during non-REM sleep, specifically during the transition between deep sleep and waking. The exact causes of night terrors are not fully understood, but they are believed to be related to disruptions in the sleep cycle and over-arousal of the central nervous system. Some potential factors that may contribute to night terrors include:
1. Genetic predisposition: There is evidence to suggest that night terrors may run in families, indicating a genetic component to their occurrence.
2. Stress and anxiety: High levels of stress, anxiety, or emotional turmoil can trigger night terrors in susceptible individuals. This may be particularly true in individuals with certain anxiety disorders or those who have experienced trauma.
3. Sleep deprivation: Lack of adequate sleep or poor sleep quality can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of experiencing night terrors.
4. Fever: Night terrors can sometimes be associated with high fever, especially in children. The exact mechanism behind this association is not fully understood, but the temporary disruption to the sleep cycle caused by the fever may contribute to the occurrence of night terrors.
It is important to note that night terrors are different from nightmares in terms of their causes and characteristics. While nightmares are often triggered by specific events or emotions, night terrors seem to be more influenced by internal factors related to the sleep cycle and the nervous system. Understanding the potential causes of night terrors can help individuals and their healthcare providers identify strategies to minimize their occurrence and manage their impact on sleep quality and overall well-being.
Effects of night terrors
Night terrors can have significant effects on individuals who experience them and their loved ones. Some of the effects of night terrors include:
1. Disturbed Sleep: Night terrors can disrupt the sleep patterns of both the person experiencing them and anyone else sharing the same sleeping space. The episodes often occur within the first few hours of falling asleep and can last for several minutes. They can cause sleep fragmentation and lead to excessive daytime sleepiness.
2. Extreme Fear and Panic: During a night terror episode, individuals may display intense fear, panic, and agitation. They may scream, cry, and appear to be in a state of extreme distress. These behaviors can be distressing not only for the person experiencing the night terror but also for family members or caregivers who witness it.
3. Difficulty in Awakening: Unlike nightmares, individuals experiencing night terrors are often difficult to wake up and may be disoriented or confused if they do wake up. They may have no memory or only a partial memory of the episode, which can leave them feeling unsettled.
4. Impact on Daily Functioning: The disrupted sleep and emotional impact of night terrors can lead to daytime difficulties. Fatigue, irritability, and difficulties concentrating or focusing on tasks are common consequences. In severe cases, individuals may experience impaired social and occupational functioning due to the persistent sleep disturbances.
5. Psychological Impact: Night terrors can cause significant psychological distress, leading to anxiety about going to sleep or fear of having another episode in the future. The fear of sleep-related disturbances can create a cycle of sleep anxiety, which further disrupts sleep and exacerbates the occurrence of night terrors.
It’s important to note that the effects of night terrors can vary from person to person. While some individuals may experience occasional episodes with minimal impact, others may have frequent and severe episodes that significantly affect their quality of life. Seeking professional guidance and support can be beneficial in managing the effects of night terrors and improving overall sleep health.
Distinguishing Nightmares from Night Terrors

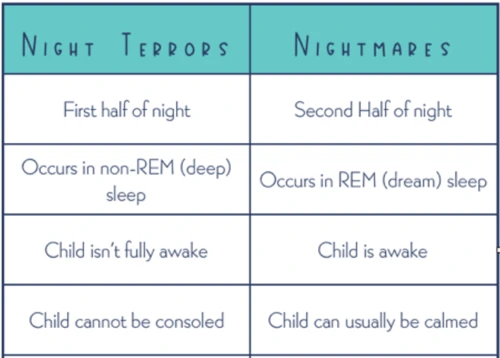
Distinguishing nightmares from night terrors can be perplexing, as both sleep disturbances can cause intense fear and disrupt a peaceful night’s rest. However, there are subtle differences that can help identify which one is occurring. Nightmares generally occur during REM sleep and are often vividly recalled upon waking. They can be triggered by specific events, such as a stressful day or exposure to scary media. Symptoms of nightmares include feelings of fear, anxiety, and a rapid heartbeat. In contrast, night terrors primarily occur during non-REM sleep and are characterized by sudden awakenings with a sense of intense terror and confusion. Unlike nightmares, night terrors are usually not remembered and may involve physical movements or even sleepwalking. This distinction suggests that nightmares occur during a lighter stage of sleep, while night terrors occur during a deeper stage. Understanding these differences can help in effectively managing and seeking appropriate treatment for each sleep disturbance.
Symptoms of nightmares
Symptoms of nightmares can vary from person to person, but there are some common experiences that individuals may have when dealing with nightmares. Here are some symptoms to look out for:
- Intense fear or anxiety: Nightmares often elicit strong emotions, leaving individuals feeling scared, anxious, or distressed upon waking up. The emotions experienced during a nightmare can be so intense that they linger even after the dream has ended.
- Vivid and detailed dreams: Nightmares are characterized by their detailed and realistic nature. The images, sounds, and sensations experienced during a nightmare can feel extremely vivid and lifelike, making the dream feel all the more real and terrifying.
- Feeling trapped or helpless: Many nightmares involve scenarios where individuals feel trapped, threatened, or unable to escape from a dangerous situation. This feeling of helplessness can contribute to the overall distress experienced during the nightmare.
- Physical reactions: Nightmares can also trigger physical reactions in the body. These can include rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, or even screaming or sleep talking. These physical reactions are often a result of the intense fear or anxiety experienced during the nightmare.
- Disrupted sleep: Nightmares can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, causing individuals to wake up frequently throughout the night. This can lead to feelings of sleep deprivation, fatigue, and a general disruption of sleep quality.
- Impaired daily functioning: The impact of nightmares can extend beyond the sleep itself. The fear, anxiety, and lack of sleep caused by nightmares can affect an individual’s daily functioning, leaving them feeling tired, irritable, and less able to concentrate or perform daily tasks effectively.
If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent and distressing nightmares that significantly interfere with daily life, it may be helpful to seek professional help to address any underlying causes or develop strategies to manage and cope with the nightmares.
Symptoms of night terrors
Night terrors are characterized by a distinct set of symptoms, which can be highly alarming for both the individual experiencing them and those around them. Some key symptoms of night terrors include:
- Intense fear or terror: During a night terror episode, the affected person may experience an overwhelming sense of fear or terror, often to an extreme degree. This fear is usually accompanied by a sense of imminent danger or impending doom.
- Loud screaming or shouting: Unlike nightmares, where individuals may have muffled cries or murmurs, night terrors often involve loud screaming or shouting that can be extremely unsettling for others in the vicinity.
- Physical agitation: During a night terror episode, the individual may exhibit physical signs of agitation, such as thrashing, kicking, or flailing their arms. They may appear to be in a state of panic or distress.
- Rapid heart rate and breathing: Night terrors can cause an increase in heart rate and breathing, as the individual’s body reacts to the intense fear they are experiencing.
- Sweating and flushed appearance: Sweating and a flushed appearance are common during night terrors. The intense fear and physical agitation can lead to an increase in body temperature.
- Difficulty or impossibility to become fully awakened: One distinguishing feature of night terrors is the difficulty or even impossibility of fully awakening the person experiencing them. They may be unresponsive to attempts to wake them up and often have no memory of the episode upon waking up in the morning.
It is important to note that night terrors primarily occur during non-REM sleep, specifically during the transition from deep sleep to lighter stages of sleep. Understanding these symptoms is crucial in distinguishing night terrors from other sleep disturbances and seeking appropriate support and management strategies.
Differences in REM sleep patterns
Differences in REM Sleep Patterns:
– Duration: One of the key differences between nightmares and night terrors lies in the duration of REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep. Nightmares typically occur during REM sleep, which accounts for about 20-25% of the sleep cycle. REM sleep is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreaming. In contrast, night terrors predominantly occur during non-REM sleep, specifically during the transition from deep sleep to lighter stages of sleep. Non-REM sleep is divided into several stages, including Stage N1, N2, and N3 (also known as slow-wave sleep), with REM sleep occurring later in the sleep cycle.
– Physiological Responses: Nightmares and night terrors differ in the physiological responses exhibited by individuals during these sleep disturbances. During nightmares, individuals may exhibit physical signs of distress such as increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and, in some cases, even sleep talking or sleepwalking. These physiological responses are reflective of the vivid and emotionally charged nature of nightmares. In contrast, during night terrors, individuals may experience extreme autonomic arousal, including a rapid heart rate, sweating, and dilated pupils. They may also display behaviors such as screaming, thrashing, or even sleepwalking. These physical responses can be very intense, often leading to a temporary state of confusion or disorientation upon awakening.
– Recall and Awareness: Another notable difference is the level of recall and awareness individuals have of their experiences during nightmares and night terrors. People who have nightmares often have clear and detailed memories of the dream content upon waking up. They can remember the storyline, emotions, and specific details of the dream, which may contribute to the lingering anxiety or fear. In contrast, individuals who experience night terrors typically have little to no recollection of the events that occurred. They may wake up feeling scared or agitated but struggle to remember the specific details of their experience. This lack of recall can make it challenging for individuals to understand or process what happened during the night terror episode.
Understanding these differences in REM sleep patterns between nightmares and night terrors can help individuals and healthcare professionals gain insights into these sleep disturbances and develop appropriate coping strategies and interventions.
Coping with Nightmares

Coping with nightmares can be challenging, but there are techniques and strategies that can help alleviate their impact and frequency. Firstly, it’s important to establish a relaxing bedtime routine that promotes good sleep hygiene. This can include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation exercises. Creating a calm and peaceful sleep environment, free from distractions and stimulating devices, can also contribute to a better night’s sleep. If nightmares persist, keeping a dream journal can be beneficial as it allows for reflection and helps identify any recurring themes or triggers. Seeking support from a therapist or counselor who specializes in sleep disorders or trauma can also provide helpful coping mechanisms. Additionally, there are specific techniques, such as imagery rehearsal therapy, which involves rewriting the script of a recurring nightmare to create a more positive outcome. Taking steps to manage stress, practice self-care, and engage in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, can further assist in reducing the occurrence and impact of nightmares.
Tips for preventing nightmares
Here are some helpful tips that can assist in preventing nightmares and improving overall sleep quality:
1. Maintain a consistent sleep schedule: Establishing a regular sleep routine can help regulate your body’s internal clock and promote better sleep. Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
2. Create a calm and comfortable sleep environment: Make your bedroom a peaceful sanctuary conducive to sleep. Ensure that your room is dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature.
3. Manage stress levels: High levels of stress can contribute to increased nightmares. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga. Find healthy ways to cope with stress throughout the day.
4. Avoid stimulating substances: Avoid consuming stimulating substances like caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol close to bedtime, as they can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to nightmares.
5. Limit screen time before bed: The blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Avoid using smartphones, tablets, or computers at least an hour before bedtime.
6. Practice relaxation techniques: Incorporate relaxation techniques into your bedtime routine, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or listening to soothing music. These activities can help calm the mind and prepare for a restful night’s sleep.
7. Be mindful of bedtime snacks: Avoid heavy or spicy foods, as well as excessive fluid intake before bed, as they can lead to indigestion or discomfort during sleep, potentially triggering nightmares.
8. Consider therapy or counseling: If nightmares persist and significantly impact your daily life, seeking therapy or counseling can help address the underlying causes and provide guidance on managing them effectively.
By implementing these preventive tips, you can create a sleep-friendly environment and minimize the occurrence of nightmares, promoting restful and rejuvenating sleep.
Techniques for managing nightmares
There are several effective techniques that can help manage nightmares and minimize their frequency and impact. These techniques aim to address the underlying causes of nightmares and create a more peaceful sleep environment. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Maintain a regular sleep schedule: Establishing a consistent sleep routine can help regulate sleep patterns and reduce the occurrence of nightmares. Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day to promote better sleep quality.
2. Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Engage in calming activities before bed to promote relaxation. This can include reading a book, practicing deep breathing or meditation, or taking a warm bath. Relaxing activities help to ease stress and anxiety before sleep, potentially reducing the likelihood of nightmares.
3. Manage stress levels: Stress and anxiety can contribute to the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Explore stress-management techniques such as exercising regularly, practicing mindfulness, or seeking therapy or counseling to address and reduce overall stress levels.
4. Create a sleep-friendly environment: Make your bedroom a peaceful and comfortable space that promotes restful sleep. Ensure the room is dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature. Consider using a white noise machine or earplugs to block out disruptive sounds.
5. Avoid certain foods and substances before bed: Some individuals find that consuming certain foods or substances before bedtime can trigger nightmares. Limit or avoid the intake of caffeine, alcohol, and heavy meals close to bedtime.
6. Keep a dream journal: Recording your dreams in a journal can help identify patterns or triggers. This can provide insight into recurring themes and allow for further exploration or discussion with a healthcare professional if needed.
7. Seek professional help if necessary: If nightmares persist and significantly disrupt sleep or daily life, it may be beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional. They can help identify any underlying causes and recommend appropriate interventions or therapies.
By implementing these techniques, individuals can take an active role in managing their nightmares and promoting better sleep quality. Remember, finding the most effective strategies may require some trial and error, so be patient and persistent in exploring what works best for you.
Coping with Night Terrors
Coping with night terrors can be challenging, as they are intense and often frightening episodes that occur during non-REM sleep. Unlike nightmares, which are vivid dreams, night terrors cause a sudden awakening accompanied by extreme fear and a sense of terror. While night terrors are more common in children, adults can also experience them. When it comes to managing night terrors, it’s important to focus on creating a safe sleep environment and implementing strategies to reduce stress and anxiety. Establishing a consistent bedtime routine can help promote better sleep hygiene and minimize the occurrence of night terrors. It may also be helpful to avoid triggers such as sleep deprivation and excessive caffeine consumption. Additionally, reassuring and providing comfort to the person experiencing night terrors during the episode can help them feel more secure. For more tips on preventing night terrors, check out this link. Remember, in severe cases or when night terrors significantly impact daily life, seeking guidance from a healthcare professional may be beneficial.
Tips for preventing night terrors
– Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Establishing a regular sleep routine can be beneficial in preventing night terrors. Make sure to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, including weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep quality, reducing the likelihood of night terrors.
– Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in relaxing activities before bed to create a calm environment. This can include reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation. By winding down before sleep, you can promote a more peaceful and restful night’s sleep.
– Ensure a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Make your bedroom conducive to sleep by keeping it cool, dark, and quiet. Use blackout curtains or a sleep mask to block out any unwanted light, and consider using earplugs or white noise machines to drown out any noise disturbances. A comfortable mattress and pillows can also contribute to a more comfortable sleep environment.
– Limit Stimulants and Caffeine: Avoid consuming stimulants and caffeine close to bedtime, as they can interfere with sleep. Stimulants, such as nicotine and certain medications, can disrupt your sleep patterns and potentially trigger night terrors. Opt for decaffeinated beverages or herbal teas instead.
– Address Underlying Stress or Anxiety: Night terrors can sometimes be linked to stress or anxiety. If you find that stress or anxiety is contributing to your night terrors, consider seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor. They can help you develop coping strategies to manage stress and anxiety, which may help alleviate night terrors.
– Practice Relaxation Techniques: Engaging in relaxation techniques before bedtime can help reduce the likelihood of night terrors. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery can help calm your mind and body, promoting a more peaceful sleep.
Remember, while these tips may be helpful in preventing night terrors, it’s important to consult with a medical professional if you or a loved one is experiencing frequent or severe night terrors. They can provide further guidance and support tailored to your specific needs.
Techniques for managing night terrors
Techniques for managing night terrors can help individuals cope with these distressing episodes and reduce their impact on sleep quality and overall well-being. Here are some strategies that may be effective:
1. Maintain a consistent sleep schedule: Establish a regular sleep routine by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day. This helps regulate sleep patterns and can minimize the occurrence of night terrors.
2. Create a calming bedtime environment: Make the bedroom a relaxing and comfortable space for sleep. Use soothing colors, eliminate distractions, and consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as aromatherapy or a white noise machine.
3. Practice relaxation techniques: Engaging in relaxation exercises before bed can help reduce stress and promote a more peaceful sleep. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery can be beneficial.
4. Address underlying stress or anxiety: Night terrors can sometimes be triggered by stress or anxiety. Identifying and managing these underlying issues through therapy, stress reduction techniques, or lifestyle changes may help alleviate night terrors.
5. Ensure safety during episodes: While it’s important not to interrupt someone experiencing a night terror, it’s essential to ensure their safety. Remove any potential hazards from the immediate environment and consider installing safety measures such as padding sharp corners or securing windows and doors.
6. Sleep hygiene practices: Establishing good sleep hygiene habits can contribute to better overall sleep quality. This includes avoiding caffeine or stimulating activities close to bedtime, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and engaging in regular physical exercise.
7. Consult a healthcare professional: If night terrors persist and significantly impact daily life, it may be beneficial to seek guidance from a healthcare professional. They can offer further evaluation, diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Remember, each person’s experience with night terrors may be unique, so finding the most effective management techniques may require some trial and error. Patience and persistence are key in finding the strategies that work best for managing night terrors and promoting restful, undisturbed sleep.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between nightmares and night terrors is crucial for effectively managing and coping with these sleep disturbances. Nightmares are intense and vivid dreams that often evoke fear or anxiety during REM sleep. They can be triggered by various factors such as stress, trauma, and sleep disorders. On the other hand, night terrors are sudden episodes of extreme terror that occur during non-REM sleep. Night terrors are more common in children and are often outgrown as they mature. However, adults can also experience night terrors, which may be linked to underlying sleep disorders or psychological factors.
It is important to recognize the symptoms of both nightmares and night terrors, as they can vary significantly. Nightmares are typically easier to remember and may cause feelings of distress upon waking up. Night terrors, on the other hand, are characterized by sudden episodes of extreme fright, often accompanied by confusion, screaming, and physical agitation. Understanding the differences in REM sleep patterns between nightmares and night terrors can also provide valuable insights into these sleep disturbances.
Managing nightmares involves preventive measures such as establishing a calming bedtime routine, reducing stress, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment. Techniques like imagery rehearsal therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy can also be effective in managing recurring nightmares. Similarly, prevention and management of night terrors often involve maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, addressing any underlying sleep disorders, and providing a safe sleep environment for individuals experiencing night terrors.
In summary, nightmares and night terrors are distinct sleep disturbances with their own causes, effects, and management strategies. It is important to seek professional help if these sleep disturbances significantly impact overall well-being, persist over an extended period, or occur frequently. With appropriate understanding, support, and coping techniques, individuals can navigate the challenges of nightmares and night terrors, improving the quality of their sleep and overall mental health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between nightmares and night terrors?
The main difference between nightmares and night terrors is the stage of sleep in which they occur. Nightmares happen during REM sleep, while night terrors occur during non-REM sleep.
Are nightmares more common in children or adults?
Nightmares are more common in children, particularly between the ages of 3 and 6. However, adults can also experience nightmares, especially if they have underlying anxiety or trauma.
What causes nightmares?
Nightmares can be caused by various factors, including stress, anxiety, trauma, medications, and sleep disorders. Experiencing a significant life event or having a disrupted sleep schedule can also contribute to nightmares.
Can nightmares be a symptom of an anxiety disorder?
Yes, recurring nightmares can be a symptom of an anxiety disorder. Nightmares can reflect and amplify the fears and worries associated with anxiety disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
What are the effects of nightmares on sleep quality?
Nightmares can disrupt normal sleep patterns and lead to fragmented sleep, resulting in decreased sleep quality and increased daytime fatigue. They can also cause anxiety about going to sleep, which perpetuates a cycle of poor sleep.
How can nightmares be prevented?
To prevent nightmares, it can be helpful to establish a regular sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, manage stress levels, avoid stimulating activities close to bedtime, and create a sleep-conducive environment.
What can I do to manage nightmares when they occur?
When experiencing a nightmare, it can be helpful to practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation. Writing down the dream, talking about it with a trusted person, or seeking professional help through therapy can also aid in managing nightmares.
Do night terrors have any long-term effects?
In most cases, night terrors do not have long-term effects and are considered harmless. However, they can cause distress for both the individual experiencing them and their family members. If night terrors persist or significantly impact daily functioning, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare professional.
Is it possible to prevent night terrors?
Preventing night terrors can be challenging, as they often occur spontaneously. However, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, ensuring a quiet and calm sleep environment, and reducing any sources of anxiety or stress can potentially help minimize the occurrence of night terrors.
Is there a link between nightmares and anxiety disorders?
Yes, a link between nightmares and anxiety disorders exists. Nightmares can be more prevalent in individuals with anxiety disorders, and experiencing nightmares can also contribute to the development or worsening of anxiety symptoms.