Nightmares and trauma are two intertwining concepts that have captivated the interest of researchers, psychologists, and individuals alike. These experiences are deeply personal and can have a profound impact on one’s mental and emotional well-being. Many questions arise when considering the relationship between nightmares and trauma: What are nightmares? What is trauma? How are they linked? In this article, we will delve into the complexities of nightmares and trauma, exploring their connection and the effects they have on individuals. By understanding the intricacies of this relationship, we can begin to unravel the mysteries of these haunting experiences and explore potential strategies for healing and recovery.
1. What are nightmares?
Nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that can cause intense fear, anxiety, and distress. These dreams often occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, which is when most dreaming takes place. They are characterized by intense and realistic imagery, often involving threatening or traumatic situations. Nightmares can range from being relatively mild to extremely distressing, leading to a person waking up feeling panicked and disturbed. While nightmares are a common occurrence for many people, they can become a significant problem when they recur frequently or when they significantly disrupt sleep and daily functioning. To learn more about the psychological meaning behind nightmares, you can explore an article on exploring the psychological meaning of nightmares. It is also important to note that children may experience nightmares more frequently, and parents can refer to a helpful guide on nightmares in children. Additionally, there is a connection between nightmares and sleep disorders that can be further explored in an article on the nightmares-sleep disorders connection.
2. What is trauma?
Trauma refers to an emotional response to a distressing or disturbing event or experience that overwhelms an individual’s ability to cope. It can encompass a wide range of events, including but not limited to, physical or sexual abuse, accidents, natural disasters, witnessing acts of violence, or experiencing the death of a loved one. Traumatic events have a profound impact on a person’s psychological well-being, often leading to feelings of fear, helplessness, and horror. The effects of trauma can manifest in various ways, including intrusive thoughts, nightmares, flashbacks, and a heightened state of arousal. It is important to recognize that trauma is subjective, meaning that what may be traumatic for one person may not be for another. Individuals may also experience different levels of trauma and have varying responses to similar events. The impact of trauma on a person’s life can be long-lasting, affecting their mental health, relationships, and overall quality of life.
3. The relationship between nightmares and trauma
The relationship between nightmares and trauma is complex and interconnected. Nightmares can both be a symptom of trauma and serve as triggers for traumatic memories. Trauma refers to a distressing or disturbing event that exceeds an individual’s coping mechanisms, leaving a lasting impact on their psychological well-being. These traumatic experiences can range from incidents like accidents or natural disasters to more severe events such as abuse or violence. Nightmares, on the other hand, can be vivid and distressing dreams that often reflect past traumas or evoke intense emotions associated with the traumatic event. They can serve as a means for the brain to process and attempt to make sense of the traumatic experience. Ultimately, the relationship between nightmares and trauma highlights the profound impact that traumatic events can have on an individual’s subconscious mind, often manifesting in the form of recurrent and disturbing dreams.
3.1. Nightmares as a symptom of trauma
Nightmares can often serve as a prominent symptom of trauma. When individuals experience a traumatic event, such as physical or emotional abuse, combat exposure, or a natural disaster, it can leave a lasting impact on their psychological well-being. The distressing memories and emotions associated with the trauma can manifest in various ways, including through nightmares. These nightmares may involve reenactments of the traumatic event, causing individuals to relive the fear, pain, and helplessness they experienced. The vivid and realistic nature of these nightmares can be incredibly distressing and leave individuals feeling overwhelmed and anxious. They may also result in significant sleep disturbances, further exacerbating the emotional distress and impact on daily functioning. It’s important to note that not all nightmares are necessarily linked to trauma, as they can also be influenced by other factors such as stress or medications. However, when nightmares occur in the context of trauma, they can be a powerful indicator and signal the need for further assessment and support.
3.2. Trauma triggering nightmares
Trauma can have a profound impact on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being and can often trigger nightmares. When a person experiences a traumatic event, their brain and body can go into a heightened state of alertness, which can disrupt normal sleep patterns and lead to nightmares. The traumatic event may infiltrate their dreams, causing vivid and distressing imagery related to the trauma. These nightmares act as a way for the mind to process and attempt to make sense of the traumatic experience. The content of these nightmares can vary depending on the individual and the specific nature of the trauma. They may involve reenactments of the event, feelings of fear, helplessness, or even symbolic representations of the trauma. The intensity and frequency of these nightmares can vary, with some individuals experiencing them only occasionally and others experiencing them as a chronic and debilitating symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It’s important to note that trauma can also lead to other sleep disturbances such as insomnia. The relationship between trauma and nightmares is complex, and individuals who have experienced trauma may benefit from seeking professional help to address these issues and promote healing and recovery.
Effects of Nightmares on Trauma

Nightmares can have a significant impact on individuals who have experienced trauma, exacerbating their emotional distress and impeding their recovery process. Here are several ways in which nightmares can affect trauma:
- Nightmares and emotional distress: Nightmares can intensify feelings of anxiety, fear, and other negative emotions associated with trauma. Reliving traumatic events through nightmares can cause individuals to experience heightened emotional arousal and distress, making it difficult for them to find solace or relaxation during their waking hours.
- Impact on anxiety and fear: Nightmares can perpetuate and amplify feelings of anxiety and fear, leading to an increased sense of hypervigilance and unease in daily life. The vivid and distressing imagery experienced during nightmares can trigger a state of heightened alertness, making it challenging for individuals to feel safe and secure in their environment.
- Contribution to PTSD symptoms: Nightmares are a hallmark symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). They can exacerbate other PTSD symptoms, such as flashbacks and intrusive thoughts, by reactivating traumatic memories and emotions. This can create a cyclical pattern of distress, as nightmares can lead to increased symptom severity, which, in turn, can trigger more frequent and intense nightmares.
- The role of nightmares in memory processing: Nightmares may play a role in the processing and consolidation of traumatic memories. Research suggests that the content and themes of nightmares can reflect unresolved emotional conflicts and unprocessed traumatic experiences. By experiencing these vivid dreams, individuals may be unconsciously working through and attempting to make sense of traumatic events.
- Nightmares and sleep disturbance: Nightmares can significantly disrupt sleep patterns and impair overall sleep quality. The distressing nature of nightmares can cause individuals to awaken frequently during the night, leading to fragmented and unrestful sleep. This can contribute to sleep deprivation, daytime fatigue, and other sleep-related issues.
- Sleep quality and quantity: The presence of nightmares can lead to reduced overall sleep quality and quantity. Constantly experiencing distressing dreams can make it challenging for individuals to achieve restorative sleep, negatively impacting their physical and mental well-being.
- Insomnia and sleep disorders: Prolonged exposure to nightmares can contribute to the development of insomnia and other sleep disorders. Individuals may develop anxiety or fear surrounding sleep, leading to difficulties falling or staying asleep. This can further perpetuate a cycle of sleep deprivation and emotional distress.
The effects of nightmares on trauma are interconnected and can create significant challenges for individuals seeking to heal and recover from their traumatic experiences. Understanding these effects is crucial for developing effective strategies and interventions to address nightmares and their impact on trauma.
4. Nightmares and emotional distress
Nightmares not only disturb our sleep but also have a significant impact on our emotional well-being. The experience of intense fear, anxiety, and distress during a nightmare can leave a person feeling emotionally shaken long after waking up. These nightmares can evoke deep-seated emotions and triggers related to past traumatic experiences or unresolved issues. The emotional distress caused by nightmares can manifest in various ways, such as increased levels of anxiety, fear, and even mood disturbances. Individuals may find themselves feeling on edge, constantly on guard, or experiencing intense bouts of sadness or depression. The repetitive nature of nightmares can intensify these emotional responses, further exacerbating the distress. It is important to recognize the emotional toll that nightmares can have and seek appropriate support and strategies to cope with the associated emotional challenges.
4.1. Impact on anxiety and fear
Nightmares can have a significant impact on anxiety and fear levels. When individuals experience recurrent nightmares, they may develop heightened levels of anxiety and fear in their waking lives. The vivid and distressing nature of nightmares can leave a lasting impression, leading to persistent feelings of unease and apprehension. This can result in an overall increase in general anxiety levels, as well as specific fears that are related to the content of the nightmares. The fear response triggered during nightmares can be so intense that individuals may start to avoid certain situations or stimuli that remind them of the traumatic elements in their dreams. This avoidance behavior can further reinforce the fear and anxiety associated with the nightmares, potentially leading to the development of anxiety disorders. It is important for individuals experiencing these effects to seek professional help and address both the nightmares and the underlying trauma to alleviate anxiety and fear.
4.2. Contribution to PTSD symptoms
Nightmares can have a significant contribution to the symptoms experienced by individuals with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). PTSD is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. One of the core symptoms of PTSD is the re-experiencing of the traumatic event, which can manifest in the form of intrusive memories, flashbacks, and nightmares. Nightmares related to the traumatic event can be particularly distressing and can intensify the individual’s fear, anxiety, and emotional distress. These nightmares often depict aspects of the traumatic event, bringing back vivid and terrifying images and sensations. The recurrence of nightmares can further exacerbate the individual’s symptoms of hyperarousal, avoidance, and negative changes in mood and cognition. It is essential for individuals with PTSD to address and manage their nightmares as part of their overall treatment plan, aiming to alleviate the distress caused by these symptoms and promote healing and recovery.
5. The role of nightmares in memory processing
Nightmares not only have a significant impact on emotional well-being but also play a role in memory processing. During sleep, the brain actively consolidates and organizes memories, allowing them to be stored effectively. Research suggests that nightmares may serve as a mechanism for processing and integrating emotionally charged experiences and memories. When a person experiences a traumatic event, it can be challenging for the brain to make sense of and integrate the overwhelming emotions and information associated with it. Nightmares may act as a way for the brain to process and make sense of these fragmented memories by replaying and reevaluating the traumatic event within the dream state. This process allows for the integration of the event into long-term memory and may contribute to the individual’s ability to adapt and cope with the trauma. By exploring and examining the content and themes of nightmares, researchers and therapists can gain insights into an individual’s emotional state and the memories and experiences they are actively processing. This understanding can be valuable in the treatment and healing process for individuals struggling with nightmares and trauma-related experiences.
6. Nightmares and sleep disturbance
Nightmares have a significant impact on sleep disturbance and can disrupt both the quality and quantity of sleep. When individuals experience nightmares, they often wake up feeling anxious and frightened, making it difficult for them to fall back asleep. This leads to sleep fragmentation and a decrease in overall sleep duration. Additionally, the content of nightmares can be so vivid and emotionally intense that it can trigger physiological arousal, further disrupting sleep patterns. The resulting sleep disturbance can have a wide range of effects, including fatigue, daytime sleepiness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. It is important to address the impact of nightmares on sleep in order to improve overall well-being and promote healthy sleep habits.
6.1. Sleep quality and quantity
When it comes to the relationship between nightmares and trauma, one important aspect to consider is the impact on sleep quality and quantity. Nightmares can significantly disrupt both the quality and quantity of sleep that individuals experience. The distressing and vivid nature of nightmares can lead to frequent awakenings throughout the night, resulting in fragmented sleep patterns. As a result, individuals may find it difficult to fall back asleep, leading to reduced overall sleep duration. This lack of sleep can contribute to feelings of fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating during the day.
Nightmares can impact sleep quality by causing arousal responses during sleep. These arousal responses can be accompanied by physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, sweating, and rapid breathing, further disturbing the sleep cycle. As a consequence, individuals may experience a decreased overall quality of sleep, leading to feelings of unrest and fatigue upon awakening.
To address the impact of nightmares on sleep quality and quantity, it is essential to develop healthy sleep hygiene practices. These practices can include establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable and calming sleep environment, and engaging in relaxation techniques like deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation before bedtime. By implementing these strategies, individuals can promote a more restful night’s sleep, reducing the potential for nightmares and improving overall sleep quality and quantity.
6.2. Insomnia and sleep disorders
Insomnia and sleep disorders are common consequences of frequent nightmares and trauma. Nightmares can disrupt the quality and quantity of sleep, leading to difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep. This can result in chronic insomnia, characterized by persistent difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep. Insomnia can exacerbate emotional distress, making it harder for individuals to cope with the effects of trauma. Sleep disorders such as restless leg syndrome and sleep apnea can also co-occur with nightmares and trauma, further impacting sleep quality. These sleep disturbances can create a vicious cycle, where nightmares and trauma disrupt sleep, and poor sleep exacerbates the effects of nightmares and trauma. It is crucial to address these sleep issues as part of the healing process. Seeking professional help, such as therapy for trauma and nightmares, can be beneficial in managing insomnia and sleep disorders. Additionally, implementing good sleep hygiene practices, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a comfortable sleep environment, can help improve sleep quality and reduce the impact of nightmares and trauma on sleep.
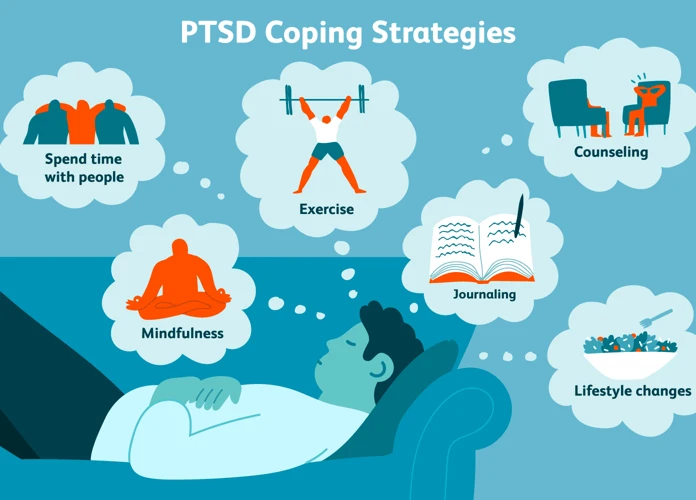
Addressing Nightmares and Trauma
When it comes to addressing nightmares and trauma, seeking professional help is often crucial. A mental health professional, such as a therapist or counselor, can provide valuable support and guidance in processing and healing from trauma and its associated nightmares. Therapy for trauma and nightmares can involve various approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR). Both of these therapeutic techniques aim to help individuals reprocess traumatic events and develop coping mechanisms for dealing with nightmares.
Cognitive-behavioral techniques can be particularly effective in addressing nightmares and trauma. These approaches involve identifying and challenging negative thought patterns, learning relaxation techniques, and implementing strategies for improving sleep hygiene. By working with a therapist, individuals can address the underlying causes of their nightmares and develop practical skills to manage and reduce their occurrence.
In addition to seeking professional help, there are also self-help strategies that individuals can employ to address nightmares and trauma. Relaxation and stress reduction techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or mindfulness, can help to calm the mind and ease anxiety associated with nightmares. Additionally, practicing good sleep hygiene, including maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities before bed, can contribute to better sleep quality and potentially reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
It is important to remember that addressing nightmares and trauma is a journey that may take time, patience, and the support of others. Every individual’s experience is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. However, by taking proactive steps and seeking appropriate assistance, it is possible to navigate the challenges of nightmares and trauma, promoting healing and restoring a sense of peace and well-being.
7. Seeking professional help
Seeking professional help is a crucial step in addressing nightmares and trauma. By consulting with a trained therapist or counselor, individuals can receive the guidance and support necessary for their healing journey. Therapy for trauma and nightmares often involves evidence-based treatments such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR). Through therapy, individuals are provided with a safe space to explore their experiences, process their emotions, and develop effective coping strategies. Additionally, therapists can help individuals identify and address any underlying issues or triggers contributing to their nightmares and trauma. It is important to remember that each person’s healing process is unique, and finding the right therapist who specializes in trauma can make a significant difference in their recovery.
7.1. Therapy for trauma and nightmares
Therapy for trauma and nightmares plays a crucial role in helping individuals cope with and heal from their experiences. One widely used and effective therapy is trauma-focused therapy, which aims to address the underlying traumatic experiences that may be contributing to nightmares. This type of therapy typically involves techniques such as cognitive processing therapy (CPT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR). CPT focuses on changing negative thoughts and beliefs related to the trauma, while EMDR uses guided eye movements to help process and reframe traumatic memories. These therapies help individuals process their emotions, develop healthier coping mechanisms, and reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. In addition to trauma-focused therapy, other approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure therapy may also be used to address nightmares specifically. CBT focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns that contribute to nightmares, while exposure therapy gradually exposes individuals to the content of their nightmares in a safe and controlled manner. Through therapy, individuals can find support, validation, and guidance to navigate the complex terrain of trauma and nightmares, ultimately leading to healing and improved well-being.
7.2. Cognitive-behavioral techniques
Cognitive-behavioral techniques have proven to be effective in addressing nightmares and trauma. These therapeutic approaches focus on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to the development and maintenance of nightmares and trauma-related symptoms. One commonly used technique is cognitive restructuring, which involves examining and reframing distorted or unhelpful thoughts associated with the trauma. By challenging these thoughts and replacing them with more realistic and positive ones, individuals can begin to change their emotional responses and reduce the intensity of their nightmares. Another technique is exposure therapy, where individuals gradually confront their fears and traumatic memories in a controlled and therapeutic environment. This process allows for habituation, where the individual becomes less sensitive and reactive to the traumatic stimuli, ultimately reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Additionally, relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can help individuals manage the anxiety and distress associated with nightmares. These techniques promote relaxation, improve sleep quality, and provide individuals with a sense of control and empowerment over their nightmares and trauma-related symptoms. It is important to note that seeking guidance from a trained professional is recommended when implementing cognitive-behavioral techniques to address nightmares and trauma effectively.
8. Self-help strategies
When it comes to addressing nightmares and trauma, self-help strategies can be effective tools for managing and coping with these challenging experiences. One approach is to incorporate relaxation and stress reduction techniques into daily routines. These may include deep breathing exercises, meditation, or engaging in calming activities such as listening to soothing music or taking a warm bath. Another important aspect is practicing good sleep hygiene, which involves establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable and relaxing sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime. Additionally, keeping a dream journal can help individuals gain insights into their nightmares and identify any recurring patterns or themes. This can aid in exploring and processing the underlying emotions and experiences connected to the nightmares. By taking an active role in self-care and implementing these self-help strategies, individuals can empower themselves in their journey towards healing and recovery.
8.1. Relaxation and stress reduction techniques
Relaxation and stress reduction techniques can be effective strategies for addressing nightmares and trauma. By engaging in relaxation techniques, individuals can reduce the overall levels of stress and anxiety that contribute to the frequency and intensity of nightmares. One technique that can be helpful is deep breathing exercises, which involve taking slow, deep breaths and focusing on the sensations of the breath entering and leaving the body. This promotes relaxation and can help calm the mind before sleep. Another technique is progressive muscle relaxation, where individuals systematically tighten and relax different muscle groups to release tension and promote relaxation. Additionally, mindfulness meditation can be beneficial in reducing stress and improving overall well-being. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can develop an awareness of the present moment and cultivate a sense of calm and acceptance. Other techniques that may complement relaxation include guided imagery, aromatherapy, and yoga. It is important to note that not all techniques may work for everyone, so it may be helpful to try different methods and find what works best for each individual’s unique needs and preferences.
8.2. Sleep hygiene practices
When it comes to addressing nightmares and trauma, implementing good sleep hygiene practices can play a crucial role in promoting better sleep and reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Here are some essential sleep hygiene practices to consider:
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule: Establishing a regular sleep routine can help regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up at consistent times. Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Engaging in calming activities before bed can signal to your body and mind that it’s time to unwind and prepare for sleep. Consider incorporating activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation.
- Create a sleep-friendly environment: Make sure your bedroom promotes a peaceful and comfortable atmosphere. Keep the room dark, quiet, and cool. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine to block out any disruptive stimuli.
- Avoid stimulating substances and activities: Refrain from consuming caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, especially close to bedtime. These substances can interfere with sleep quality and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Additionally, limit screen time and exposure to bright lights before bed, as they can disrupt your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Regular exercise can have a positive impact on sleep quality and overall well-being. However, try to avoid intense physical activity too close to bedtime, as it can make it harder to wind down and fall asleep.
- Create a comfortable sleep environment: Invest in a supportive mattress, pillows, and bedding that are tailored to your preferences. A comfortable sleep environment can contribute to better sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
- Manage stress and anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can contribute to sleep disturbances and nightmares. Explore relaxation techniques and stress management strategies, such as journaling, practicing mindfulness, or seeking support from a therapist or counselor.
By incorporating these sleep hygiene practices into your daily routine, you can create a sleep environment that promotes restful sleep and helps mitigate the effects of nightmares and trauma.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the link between nightmares and trauma is undeniable. Nightmares can serve as a symptom of trauma, as they may be a manifestation of repressed emotions or unresolved experiences. Trauma, on the other hand, can also trigger nightmares, as the brain tries to process and make sense of the traumatic event. The effects of nightmares on trauma should not be underestimated. They can contribute to emotional distress, amplifying feelings of anxiety and fear, and even intensify symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Furthermore, nightmares can disrupt sleep, leading to sleep disturbances and insomnia, which can further exacerbate the negative impact on mental well-being. It is crucial for individuals experiencing nightmares and trauma to seek professional help. Therapy, particularly trauma-focused therapy, can provide effective strategies for addressing both nightmares and the underlying trauma. Cognitive-behavioral techniques can also be beneficial in managing and reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Additionally, incorporating self-help strategies such as relaxation techniques and maintaining good sleep hygiene practices can aid in alleviating the impact of nightmares on trauma. With the right support and strategies in place, individuals can work towards healing, processing trauma, and finding relief from the distressing nightmares that haunt them.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can nightmares be a sign of underlying psychological issues?
Yes, nightmares can sometimes be a manifestation of underlying psychological issues such as anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or depression.
2. What are some common themes or content in nightmares?
Nightmares often involve themes such as being chased or attacked, experiencing a threat to one’s safety or well-being, or reliving past traumatic events.
3. Can medication contribute to the occurrence of nightmares?
Yes, certain medications, such as antidepressants, can potentially increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares as a side effect.
4. Are nightmares more common in children or adults?
Nightmares are more common in children, particularly during periods of developmental milestones or when they are exposed to stressful situations.
5. How can nightmares impact overall sleep quality?
Nightmares can disrupt normal sleep patterns, leading to fragmented and disturbed sleep, ultimately resulting in decreased overall sleep quality.
6. Do nightmares have any long-term effects?
Recurring nightmares can contribute to psychological distress and sleep disturbances, potentially impairing overall mental and physical well-being in the long run.
7. Can trauma-related nightmares be treated?
Yes, trauma-related nightmares can be effectively treated through various therapeutic approaches, including trauma-focused therapy and cognitive-behavioral techniques.
8. Are there any self-help strategies to alleviate nightmares?
Yes, self-help strategies such as relaxation techniques, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and creating a relaxing sleep environment can help reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
9. Can writing in a dream journal be beneficial for understanding nightmares?
Keeping a dream journal can be beneficial as it allows individuals to explore the symbolism and underlying meaning of their nightmares, helping gain insights into their emotional experiences.
10. When should professional help be sought for recurring nightmares?
If recurring nightmares significantly impact daily functioning, overall well-being, or are associated with symptoms of trauma-related disorders, seeking professional help from a therapist or mental health professional is recommended.