Have you ever woken up in the middle of the night, drenched in sweat, heart pounding, and filled with a sense of fear or dread? Nightmares, those vivid and distressing dreams that haunt our sleep, can have a profound impact on our mental health and overall well-being. Understanding the causes and effects of nightmares is crucial in order to address the toll they can take on our sleep quality and psychological state. In this article, we will delve into the definition of nightmares, explore common themes that occur within them, examine the connection between nightmares and sleep disruptions, and uncover the psychological impact they can have on anxiety, depression, and trauma. Additionally, we will discuss strategies and techniques for managing and reducing nightmares, ultimately aiming to improve sleep quality and promote overall mental health. So, join us as we unravel the mysteries of nightmares and discover the key to a peaceful night’s sleep.
Understanding Nightmares

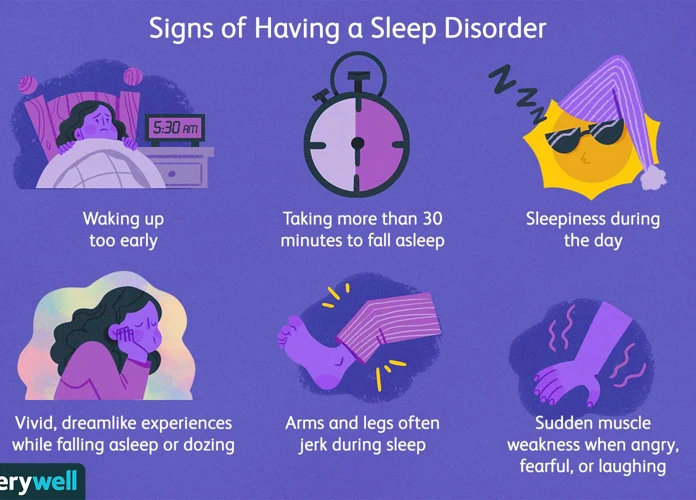
A deep dive into the realm of nightmares allows us to comprehend the intricate nature of these unsettling nighttime experiences. Nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that often leave a lingering impact upon waking. By definition, nightmares are intense and negative dream sequences that evoke feelings of fear, anxiety, and distress. Through the exploration of common themes present in nightmares, we gain insight into the fears and anxieties that may be hidden within our subconscious minds. These themes can vary widely, encompassing everything from falling, being chased, or experiencing harm to witnessing supernatural or paranormal phenomena. While nightmares may seem like a mere product of imagination, they often have underlying causes rooted in real-life experiences, emotions, and traumas. The understanding of these causes is fundamental in the process of addressing and managing nightmares effectively. By unraveling the mystery behind nightmares, we can take steps towards improving our sleep quality and nurturing our mental well-being. To understand the impacts of nightmares on sleep quality and mental health, we must first delve into the relationship between nightmares and sleep disruptions, as well as the effects of nightmares on sleep architecture. Stay tuned as we venture further into this fascinating world where dreams and reality converge.
Definition of Nightmares
Nightmares, in their simplest form, can be defined as intensely distressing dreams that provoke feelings of fear, anxiety, or terror. These types of dreams differ from regular dreams in their emotional intensity and the lasting impact they have upon waking. Nightmares are often characterized by a vivid and realistic quality, making them feel as if they are actually happening. The content of nightmares can vary widely, encompassing a range of themes that tap into our deepest fears and anxieties. Common scenarios include being chased or attacked by an unknown entity, experiencing a life-threatening situation, or witnessing the death of oneself or others. The intense emotions experienced during nightmares can manifest physically, causing increased heart rate, rapid breathing, sweating, and even waking from sleep. It is important to note that nightmares are more prevalent in certain populations, such as children and individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). By understanding the definition of nightmares and recognizing their distinct characteristics, we can begin to explore the underlying causes, explore effective coping strategies, and seek appropriate treatments to alleviate their impact on our mental well-being.
Please note that there are no relevant anchor texts within this paragraph.
Common Themes in Nightmares
Nightmares can manifest in various forms, but there are several common themes that frequently occur across individuals. These themes often reflect underlying fears, anxieties, and emotional experiences. Here are some of the most prevalent themes found in nightmares:
1. Being Chased or Attacked: This is perhaps one of the most recurrent themes in nightmares. In these dreams, individuals often find themselves being pursued by unknown figures, monsters, or even animals. The feeling of being chased or attacked can evoke a sense of fear, vulnerability, and helplessness.
2. Falling or Failing: Dreams involving falling from great heights or failing to accomplish a task are also common. These nightmares can symbolize a fear of losing control, experiencing failure, or facing insecurities and self-doubt.
3. Lost or Trapped: Feeling lost or trapped in a nightmare can be a reflection of feeling stuck in a challenging situation in real life. Being unable to find a way out or escape can generate feelings of anxiety, entrapment, and frustration.
4. Death: Death-related dreams often evoke intense emotions. Dreaming about one’s own death or the death of loved ones can stem from the fear of loss, mortality, or unresolved grief.
5. Supernatural or Paranormal Phenomena: Nightmares involving supernatural entities, haunted places, or paranormal occurrences tap into our primal fears of the unknown. These dreams can be particularly unsettling and may indicate a fear of the supernatural or unresolved psychological issues.
6. Embarrassment or Public Humiliation: Dreams involving embarrassment, public humiliation, or being naked in public can reflect feelings of vulnerability, low self-esteem, or fear of judgment.
Understanding the common themes in nightmares helps shed light on the deep-rooted fears and anxieties that can manifest in our dreams. By analyzing these themes, individuals can gain valuable insights into their own subconscious thoughts and emotions, leading to a better understanding of their mental and emotional well-being. If you’re interested in exploring more about nightmares, you can check out our article on nightmares as trauma indicators.
Causes of Nightmares
Nightmares can have various underlying causes, ranging from psychological factors to physiological triggers. Let’s explore some of the common contributors to these unsettling dreams:
- Anxiety and Stress: Anxiety disorders and high levels of stress can significantly increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. The mind uses dreams as a way to process and address these overwhelming emotions, often resulting in vivid and distressing nightmares.
- Traumatic Experiences: Those who have experienced trauma, such as physical or emotional abuse, accidents, or military combat, are prone to experiencing nightmares. The brain attempts to process and make sense of the traumatic events through dreams, leading to recurring nightmares related to the trauma.
- Medications and Substances: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and blood pressure medications, can disrupt the sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of nightmares. Additionally, alcohol and substance abuse can also contribute to the occurrence of nightmares.
- Sleep Disorders: Nightmares are commonly associated with sleep disorders like sleep apnea, insomnia, and restless leg syndrome. The disordered sleep patterns and disruptions to the sleep cycle can trigger more frequent and intense nightmares.
- Food and Diet: Consuming certain foods and beverages close to bedtime, such as spicy foods, caffeine, and heavy meals, can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to nightmares. It is advisable to avoid these triggers before bedtime to reduce the likelihood of experiencing disturbing dreams.
Identifying and addressing the underlying causes of nightmares is essential in effectively managing and reducing their occurrence. Whether through therapy, medication adjustments, stress management techniques, or lifestyle changes, individuals can take proactive steps to alleviate the impact of nightmares on their sleep and overall well-being. To learn more about managing nightmares, you can refer to our article on managing nightmare medications.
The Relationship between Nightmares and Sleep Quality

The relationship between nightmares and sleep quality is complex and intertwined, with nightmares often leading to disruptions in our sleep patterns. When nightmares occur during sleep, they have the potential to jolt us awake, causing sleep disturbances and preventing us from obtaining the restorative sleep we need. Sleep disruptions caused by nightmares can result in fragmented sleep, making it difficult to reach deep, restful sleep stages. This can lead to daytime drowsiness, fatigue, and a general feeling of unrest. Nightmares can disrupt the delicate balance of sleep architecture, affecting the duration and quality of each sleep stage. Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, the stage where vivid dreaming occurs, is especially impacted by nightmares. As REM sleep is crucial for memory consolidation and emotional regulation, frequent nightmares can disrupt these essential cognitive processes. The detrimental effects of poor sleep quality on mental health are well-documented, and studies have shown that individuals who experience frequent nightmares are more likely to suffer from anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders. To gain a deeper understanding of the impact of nightmares on sleep quality and mental health, it is essential to explore the causes and effects of nightmares, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children. For more information on nightmares in children, including causes, effects, and coping strategies, check out our comprehensive guide here. By unraveling the intricate relationship between nightmares and sleep, we can begin to develop strategies for managing and reducing these unsettling dreams, ultimately improving both our sleep quality and overall mental well-being.
Nightmares and Sleep Disruptions
Nightmares have a profound impact on sleep, often leading to significant disruptions in our normal sleep patterns. When we experience a nightmare, it can jolt us awake, leaving us feeling startled, anxious, and with an increased heart rate. These sudden awakenings can disrupt the natural progression of sleep stages, particularly the REM (rapid eye movement) stage, which is when most dreaming occurs. Consequently, the cycle of sleep is interrupted, and it becomes more difficult to fall back asleep. The emotional distress caused by nightmares can also lead to difficulties in falling asleep, as the fear and anxiety linger even after waking up. This can result in insomnia, where individuals struggle to fall asleep or stay asleep, impacting the overall duration and quality of sleep. The disrupted sleep caused by nightmares can contribute to daytime drowsiness, fatigue, and impaired cognitive functioning. It can also lead to a vicious cycle, as the lack of quality sleep increases the likelihood of experiencing more nightmares. Addressing the sleep disruptions caused by nightmares is crucial in order to promote healthy sleep and overall well-being. Implementing strategies such as establishing a relaxing bedtime routine, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques can help mitigate the impact of nightmares on sleep quality.
Effects of Nightmares on Sleep Architecture
Nightmares have a significant impact on the architecture of our sleep. Sleep architecture refers to the different stages and patterns of sleep that our bodies go through during the night. Normal sleep is composed of several cycles, each consisting of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. However, the occurrence of nightmares can disrupt this delicate balance and alter the structure of our sleep.
One of the primary effects of nightmares on sleep architecture is an increase in nighttime awakenings. Nightmares often provoke intense emotions such as fear, anxiety, or distress, which can jolt us awake. These frequent awakenings disrupt the continuity of our sleep, leading to fragmented and restless nights. As a result, we may experience difficulties falling back asleep or maintaining a deep and restorative sleep.
Nightmares can prolong the duration of REM sleep, the stage of sleep where dreams usually occur. During REM sleep, our brain activity increases, and our eyes move rapidly. This stage is crucial for memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and overall cognitive functioning. However, when nightmares intrude upon our REM sleep, they can extend its duration, preventing us from entering the essential deep stages of non-REM sleep. This disruption in the balance between REM and NREM sleep can contribute to daytime sleepiness and fatigue.
Additionally, the emotional intensity of nightmares can lead to physiological arousal during sleep. This arousal can manifest as an increased heart rate, sweating, and rapid breathing. These physical responses to nightmares can further disrupt the quality of our sleep, making it more difficult to achieve the deep, restorative rest that is necessary for optimal mental and physical health.
The effects of nightmares on sleep architecture are multifaceted. Nightmares can lead to increased nighttime awakenings, prolonged REM sleep, and physiological arousal. These disruptions can result in poor sleep quality, diminished cognitive function, and impaired overall well-being. Understanding the impact of nightmares on sleep architecture is essential in developing strategies to improve sleep quality and minimize the negative consequences on our mental health.
How Sleep Quality Impacts Mental Health
How Sleep Quality Impacts Mental Health:
1. Increased Risk of Mental Health Disorders: Poor sleep quality has been linked to an increased risk of developing various mental health disorders. Lack of quality sleep can contribute to the development or exacerbation of conditions such as anxiety disorders, depression, bipolar disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Sleep disturbances can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to mood swings, emotional instability, and difficulties in managing stress.
2. Impaired Cognitive Functioning: Adequate sleep is crucial for optimal cognitive functioning. When sleep quality is compromised, cognitive processes such as attention, concentration, memory, and problem-solving abilities can be significantly impaired. This can result in difficulties with focus, decision-making, and learning new information. Additionally, sleep deprivation can hinder the brain’s ability to regulate emotions, leading to increased irritability and emotional reactivity.
3. Increased Sensitivity to Stress: Sleep deprivation can make individuals more vulnerable to the effects of stress. When sleep quality is poor, the body’s stress response is heightened, leading to increased levels of stress hormones such as cortisol. This can lead to difficulties in coping with stressors, increased feelings of overwhelm, and a reduced ability to regulate emotions effectively.
4. Weakened Immune System: Sleep plays a vital role in supporting the immune system’s function. During sleep, the body repairs and restores itself, including enhancing immune system functioning. When sleep quality is compromised, the immune system may become weakened, making individuals more susceptible to infections, illnesses, and chronic health conditions.
5. Decreased Overall Well-being: Ultimately, poor sleep quality can have a detrimental impact on overall well-being and quality of life. The combination of physical and mental health consequences can lead to chronic fatigue, decreased motivation, decreased productivity, reduced enjoyment of activities, and a general decline in quality of life.
Understanding the intricate relationship between sleep quality and mental health emphasizes the importance of addressing and improving sleep disturbances, such as nightmares. By prioritizing and enhancing sleep quality, individuals can take proactive steps towards nurturing their mental health and overall well-being.
The Psychological Impact of Nightmares
Nightmares not only disrupt our sleep but also have a profound psychological impact on our well-being. One of the primary psychological effects of nightmares is their association with heightened levels of anxiety. The intense fear and distress experienced during a nightmare can carry over into our waking lives, leading to a constant state of unease and worry. Nightmares have been linked to an increased risk of developing depression. The repetitive and distressing nature of these dreams can contribute to feelings of hopelessness and sadness. In some cases, nightmares can even serve as indicators of past trauma, as they often contain vivid and distressing content related to the event. These traumatic nightmares can trigger flashbacks and intrusive thoughts, exacerbating the psychological impact of the trauma. Understanding the psychological consequences of nightmares is crucial in order to address their potential toll on mental health. By exploring therapeutic approaches, coping strategies, and lifestyle changes, we can effectively manage and reduce the psychological impact of nightmares, promoting better sleep and overall psychological well-being.
Nightmares and Anxiety
Nightmares and anxiety are closely intertwined, with nightmares often exacerbating feelings of anxiety and vice versa. People who experience frequent nightmares may find themselves caught in a cycle of heightened anxiety, as nightmares can elicit intense fear and unease during sleep. Upon waking, these feelings can persist, leading to increased levels of anxiety throughout the day. Nightmares can trigger various symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and a sense of impending doom. The fear and distress experienced during nightmares can also contribute to the development or worsening of anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Individuals who already have anxiety disorders may be more prone to experiencing nightmares. The relationship between nightmares and anxiety is complex and bidirectional, with each influencing and amplifying the other. Taking steps to address and reduce nightmares can not only improve sleep quality but also alleviate anxiety symptoms and promote overall mental well-being. If you want to learn more about managing anxiety related to nightmares, you can refer to our comprehensive guide on coping strategies for nightmares.
Nightmares and Depression
Nightmares and depression are intimately intertwined, creating a complex interplay between the two. Depression, a mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest or pleasure in activities, can both contribute to and be exacerbated by nightmares. Individuals experiencing depression may find themselves more prone to experiencing nightmares, as the negative emotions and distress associated with depression can manifest in their dreams. These nightmares often revolve around themes of despair, loss, and helplessness, mirroring the deep-seated emotions felt in waking life. On the flip side, nightmares can also contribute to the development or worsening of depressive symptoms. The distressing nature of nightmares can disrupt sleep, leading to sleep deprivation and fatigue, which are known contributors to depressive feelings. The content of nightmares can evoke intense emotional responses, further exacerbating depressive symptoms. This cyclical relationship between nightmares and depression creates a challenging cycle to break, but seeking appropriate treatment and support from mental health professionals can provide relief. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or dream journaling can help individuals better understand and process the emotions and experiences behind their nightmares, ultimately aiding in the management of both the nightmares themselves and the accompanying depressive symptoms.
Nightmares as Trauma Indicators
Nightmares have been recognized as powerful indicators of past trauma and can serve as a window into the unconscious mind. When individuals experience traumatic events, such as physical or sexual abuse, accidents, or acts of violence, the distressing memories and emotions associated with these events can manifest in nightmares. Nightmares related to trauma can be vivid, intense, and recurring, often replaying the traumatic event or elements of it. The content of these nightmares may involve the individual being trapped, pursued, or experiencing a sense of helplessness. The emotional impact can be overwhelming, leading to heightened levels of anxiety, fear, and even panic upon awakening. These nightmares can act as a form of re-experiencing the trauma, preventing the individual from processing and moving forward. Thus, nightmares serve as important indicators of unresolved trauma and can be a signal for the need for therapy or professional intervention to address the underlying psychological wounds. By recognizing and addressing nightmares as trauma indicators, appropriate support and treatment can be provided to help individuals heal and regain control over their mental health. To learn more about trauma and nightmares, you can explore our article on “Exploring Nightmares and Trauma“.
Managing and Reducing Nightmares
When it comes to managing and reducing nightmares, there are various approaches and coping strategies that can be helpful in promoting better sleep and alleviating the distressing impact of nightmares. Making lifestyle changes plays a crucial role in establishing a foundation for quality sleep. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment. Additionally, implementing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation or deep breathing exercises can help calm the mind before sleep. Therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) or imagery rehearsal therapy (IRT), have shown promising results in reducing nightmare frequency and severity. These evidence-based therapies aim to reframe negative thought patterns and control the content of dreams. Finally, incorporating specific coping strategies like journaling, expressing emotions through art or writing, and seeking support from loved ones or a mental health professional can provide an outlet for processing and reducing the psychological impact of nightmares. By combining these strategies, individuals can actively work towards managing and reducing nightmares to promote better sleep and overall well-being.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Sleep
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve sleep quality and reduce the incidence of nightmares. One crucial aspect is establishing a consistent sleep routine. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate the body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine can also signal the brain that it’s time to wind down. This may involve activities such as taking a warm bath, practicing deep breathing exercises, or reading a book. Additionally, it’s important to create a sleep-friendly environment. A comfortable and supportive mattress, pillows, and bedding can enhance sleep comfort. Keeping the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet can also promote optimal sleep conditions. Another lifestyle change to consider is managing stress levels. High levels of stress and anxiety can increase the likelihood of nightmares. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or journaling before bed can help calm the mind and prepare it for restful sleep. It’s essential to be mindful of dietary habits that can impact sleep. Avoiding stimulating substances like caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol close to bedtime can help prevent sleep disturbances. Lastly, regular exercise during the day can contribute to better sleep quality at night. Engaging in physical activity can promote feelings of tiredness and improve overall sleep satisfaction. By incorporating these lifestyle changes, individuals can create an optimal sleep environment and pave the way for a more peaceful and restorative night’s sleep.
Therapeutic Approaches
Therapeutic approaches offer valuable tools and strategies for managing and reducing nightmares. Individuals who experience frequent or distressing nightmares may benefit from seeking professional help to address the underlying causes and find effective solutions. Here are some therapeutic approaches that can be explored:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): CBT-I is a structured form of therapy that focuses on correcting negative thought patterns and behaviors related to sleep. It can help individuals develop healthier sleep habits, identify and challenge negative beliefs about sleep, and reduce anxiety or stress that may contribute to nightmares.
2. Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP): ERP is a type of therapy commonly used in the treatment of anxiety disorders, but it can also be applied to nightmares. It involves gradually exposing oneself to thoughts, images, or situations that trigger nightmares while refraining from engaging in the usual response, such as fear or avoidance. This approach can help desensitize individuals to the content of their nightmares and reduce their power to provoke distress.
3. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR is a therapy primarily used to treat post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) but has also shown promise in addressing nightmares related to trauma. It involves using eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation to process and reframe traumatic memories, reducing their impact on sleep.
4. Imagery Rehearsal Therapy (IRT): IRT is a technique specifically designed to target nightmares. It involves mentally rehearsing alternative endings or outcomes to recurring nightmares, replacing the negative content with more positive or neutral imagery. By repeatedly practicing these new endings, individuals may experience a reduction in the frequency and intensity of their nightmares.
5. Medication: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage nightmares, especially if they are related to underlying mental health conditions. Medications such as prazosin, an alpha-blocker, have been found to be effective in reducing nightmare frequency and intensity. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate medication and dosage.
It’s worth noting that therapeutic approaches should be individualized, taking into account the specific needs and preferences of each person. A combination of different approaches or tailoring them to each individual’s circumstances may yield the best results. Working with a qualified therapist or healthcare provider can help guide the therapeutic process and maximize the chances of success in managing nightmares effectively.
Coping Strategies for Nightmares
Coping Strategies for Nightmares can provide valuable tools for individuals seeking to manage and alleviate the distressing effects of these nighttime experiences. It is important to note that coping strategies may vary in effectiveness from person to person, so it may be necessary to try different approaches to find what works best for you. Here are some strategies that can be helpful:
1. Establish a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Creating a soothing and consistent bedtime routine can help signal to your body and mind that it is time to unwind and prepare for sleep. Incorporate relaxing activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing deep breathing exercises.
2. Create a Safe Sleep Environment: Ensure that your sleep environment is comfortable, quiet, and conducive to relaxation. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine to minimize external distractions that may contribute to nightmares.
3. Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Aim to establish a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day. This can help regulate your body’s internal clock and promote more restful sleep.
4. Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Engaging in mindfulness exercises, such as meditation or progressive muscle relaxation, can help reduce anxiety and promote a sense of calm before sleep. These techniques can assist in managing stress and potentially decrease the occurrence of nightmares.
5. Keep a Dream Journal: Keeping a dream journal can be a helpful tool for understanding patterns and themes within your nightmares. By recording your dreams upon waking, you may identify triggers or recurring symbols that can provide insight into your subconscious thoughts and emotions.
6. Seek Support from a Therapist: If nightmares persist and significantly impact your quality of life, it may be beneficial to seek support from a mental health professional. Therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for nightmares (CBT-I) or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) can be effective in managing and reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
Remember, coping strategies are unique to each individual, and it may take time to find the strategies that work best for you. Patience and persistence are key in overcoming the challenges posed by nightmares.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of nightmares on sleep quality and mental health is undeniable. Nightmares can disrupt our sleep, leading to fragmented and restless nights. This, in turn, can result in daytime fatigue, irritability, and difficulties in concentration and cognitive functioning. The effects of nightmares on sleep architecture are significant, as they can disturb both REM and non-REM sleep stages, impairing the restorative functions of sleep. Furthermore, nightmares have a profound psychological impact. They are closely associated with anxiety and can exacerbate symptoms of anxiety disorders. Additionally, nightmares are linked to depression, with studies showing a bidirectional relationship between the two. Nightmares also serve as indicators of trauma, as they often reflect and reenact distressing or traumatic experiences.
Managing and reducing nightmares is crucial for improving sleep quality and promoting mental well-being. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a regular sleep routine, practicing relaxation techniques before bedtime, and creating a peaceful sleep environment, can contribute to better sleep and reduced nightmare frequency. Therapeutic approaches, including cognitive-behavioral therapy for nightmares (CBT-N), imagery rehearsal therapy (IRT), and medication options, may be effective in addressing chronic or severe nightmares. Additionally, coping strategies such as journaling, talking about the nightmares with a therapist or support network, and engaging in stress-reduction activities can help individuals navigate the emotional impact of nightmares.
In essence, understanding nightmares, their causes, and their impact on sleep quality and mental health empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing and reducing their occurrence. By prioritizing sleep hygiene, seeking therapy when needed, and implementing coping strategies, individuals can reclaim peaceful nights and cultivate overall well-being. So, let us strive to conquer the realm of nightmares and embrace the restorative power of restful sleep for a healthier mind and body.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between nightmares and night terrors?
Nightmares and night terrors are both types of sleep disturbances, but they have distinct differences. Nightmares occur during REM (rapid eye movement) sleep and are vivid, disturbing dreams that can be remembered upon waking. Night terrors, on the other hand, occur during deep non-REM sleep and often involve sudden screams, intense fear, and physical movements. Unlike nightmares, night terrors are typically not remembered.
Can nightmares be caused by medications?
Yes, certain medications can potentially trigger nightmares as a side effect. Medications such as antidepressants, beta blockers, and some sleep medications have been known to cause vivid dreams and nightmares. If you suspect that your medication may be contributing to your nightmares, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider to explore alternative options.
Are nightmares more common in children?
Nightmares are more common in children than in adults. This can be attributed to the fact that children have more active imaginations and are still developing coping mechanisms. Nightmares in children can be caused by a variety of factors, including fear, stress, or significant life events. It’s crucial to provide support and reassurance to children who experience nightmares.
Can recurring nightmares be a sign of an underlying mental health condition?
Recurring nightmares can sometimes be an indication of an underlying mental health condition, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, or depression. It’s important to consider the frequency, intensity, and impact of recurring nightmares and consult with a healthcare professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
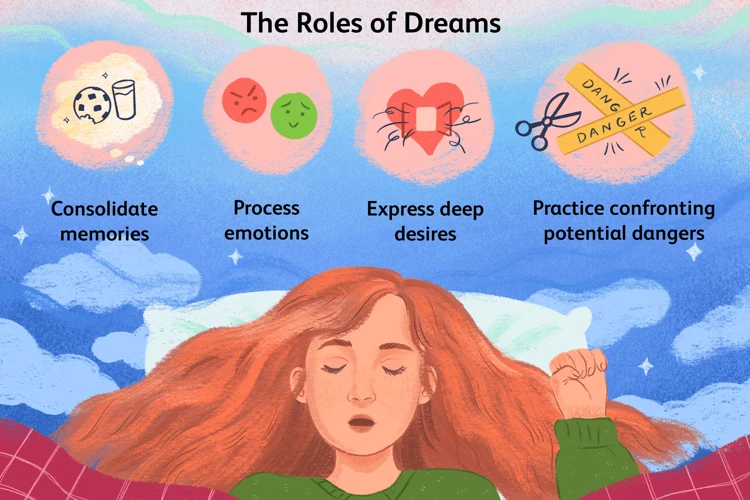
Do nightmares serve any purpose?
While nightmares can be distressing, they may serve a purpose in our psychological well-being. Some experts suggest that nightmares act as a form of emotional processing, allowing us to confront and process fears or unresolved emotions in a safe environment. Nightmares can also serve as warning signs or indicators of potential stressors or traumas in our lives, prompting us to address them and seek necessary support.
What are some coping strategies for nightmares?
There are several coping strategies that can help manage nightmares. These include creating a relaxing bedtime routine, practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation before sleep, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities before bed. It can also be helpful to keep a dream journal and discuss your dreams with a therapist or support group to gain deeper insights and develop strategies for managing nightmares.
Can lucid dreaming techniques help control nightmares?
Lucid dreaming, the experience of being aware that you are dreaming while still in the dream state, can potentially be used as a technique to control nightmares. With practice, individuals can learn to recognize when they are having a nightmare and consciously alter the dream narrative or wake themselves up. However, mastering lucid dreaming techniques may take time and effort.
Can nightmares be a symptom of trauma?
Yes, nightmares can be a symptom of trauma. Those who have experienced traumatic events may often experience nightmares that are reminiscent of the trauma they endured. These nightmares can contribute to the emotional distress associated with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It is important for individuals who have experienced trauma to seek professional help to address the nightmares and underlying trauma.
Do nightmares always reflect real-life fears?
No, nightmares do not always reflect real-life fears. While some nightmares may be influenced by real-life fears, others may be a manifestation of subconscious emotions, anxieties, or stressors. Nightmares can be influenced by various factors, including personal experiences, cultural influences, and individual perceptions.
How can poor sleep quality affect mental health?
Poor sleep quality can have a significant impact on mental health. Sleep disruptions, such as those caused by nightmares, can lead to daytime fatigue, irritability, difficulties in concentration, and impaired cognitive function. Chronic sleep deprivation can also increase the risk of developing mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. It is crucial to prioritize quality sleep to support optimal mental well-being.