Nightmares and sleep disorders have long been interconnected, perplexing researchers and sleep experts alike. From the haunting nature of nightmares to the disruptive impact of sleep disorders, understanding the connection between the two is crucial for ensuring healthy sleep patterns. In this detailed article, we delve deep into the world of nightmares and sleep disorders, exploring their definitions, causes, and effects on sleep. Additionally, we examine how nightmares can serve as symptoms of underlying sleep disorders and how these disorders can influence the content and recurrence of nightmares. Finally, we provide insights into the treatment options available for both nightmares and sleep disorders, aiming to shed light on this enigmatic relationship and offer guidance for those experiencing troubled dreams and disrupted sleep.
Understanding Nightmares

One of the most fascinating aspects of understanding nightmares is exploring their definition and causes. Nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that can evoke fear, anxiety, and a sense of helplessness in the individual experiencing them. They often involve threatening situations and can be accompanied by intense emotions such as terror or panic. The causes of nightmares can vary, with factors such as stress, trauma, medication side effects, and certain sleep disorders playing a role. It is crucial to explore the psychological meaning of nightmares and their connection to the subconscious mind and unresolved emotions. By shedding light on the intricate world of nightmares, we can gain insight into the impact they have on our sleep and overall well-being. To learn more about potential medications and treatments for nightmares, you can check out this resource. Additionally, for those interested in harnessing the power of dreams, the practice of lucid dreaming can be a powerful tool to conquer nightmares. Find out more about Lucid Dreaming as a tool to conquer nightmares here.
Definition of Nightmares
Nightmares can be defined as highly distressing dreams that occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep. These dreams often involve intense feelings of fear, terror, or anxiety, and they are vividly remembered upon waking. During a nightmare, individuals may experience a sense of danger, threat, or helplessness, making it difficult to differentiate between the dream world and reality. The content of nightmares can vary widely, ranging from being chased or attacked by unknown entities to experiencing traumatic events. They can be triggered by various factors, including stress, trauma, medication side effects, or even certain sleep disorders. Exploring the psychological meaning of nightmares can provide valuable insights into the subconscious mind and help individuals understand any unresolved emotions or traumatic experiences they may be dealing with. To delve deeper into the psychological meaning of nightmares, you can refer to this resource. Understanding the definition of nightmares is crucial in recognizing and addressing these unsettling dreams to promote better sleep and overall well-being.
Causes of Nightmares
Causes of Nightmares can be attributed to various factors that can provoke vivid and frightening dreams. Understanding these causes is essential in order to address and manage nightmares effectively. Here are some common factors that contribute to the occurrence of nightmares:
1. Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, increasing the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Emotionally challenging events, such as trauma, grief, or major life changes, can trigger nightmares as the mind processes and assimilates these intense emotions.
2. Trauma: Individuals who have experienced trauma, such as physical or emotional abuse, accidents, or natural disasters, may develop nightmares as a result of these distressing memories. The mind attempts to process and cope with the trauma through dreams, leading to recurrent nightmares.
3. Medication and Substance Abuse: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, blood pressure medications, and sleep aids, can cause nightmares as a side effect. Additionally, the use of substances like alcohol, nicotine, and recreational drugs can disrupt the sleep cycle and contribute to nightmare occurrences.
4. Sleep Disorders: Nightmares can be associated with sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, insomnia, and restless legs syndrome. These conditions affect the quality and duration of sleep, creating an environment conducive to nightmares.
5. Medical Conditions: Underlying medical conditions, such as fever, epilepsy, and psychiatric disorders, can also contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. These conditions may disrupt regular sleep patterns and increase the likelihood of experiencing distressing dreams.
6. Diet and Late-Night Eating: Consuming certain foods before bed, such as spicy or fatty foods, can trigger nightmares in some individuals. Additionally, eating late at night or going to bed on a full stomach can increase the risk of nightmares.
7. Sleep Deprivation: Lack of quality sleep and consistent sleep deprivation can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to an increased occurrence of nightmares. Fatigue and irregular sleep patterns can create an imbalance in brain activity during sleep, making nightmares more likely to occur.
By identifying and addressing the underlying causes of nightmares, individuals can take steps to alleviate their frequency and intensity. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist to determine the specific factors contributing to nightmares and to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
The Impact of Nightmares on Sleep
Nightmares can have a profound impact on the quality and duration of sleep. Here are some key ways in which nightmares affect our sleep patterns:
1. Disrupted Sleep: When nightmares occur during the night, they can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, causing frequent awakenings. This can lead to fragmented and restless sleep, leaving individuals feeling tired and fatigued during the day.
2. Poor Sleep Quality: Nightmares can be incredibly vivid and emotionally intense, resulting in a heightened state of arousal. This can make it difficult to fall back asleep after experiencing a nightmare, impacting the overall quality of sleep.
3. Sleep Disturbances: The fear and anxiety triggered by nightmares can cause physiological responses, such as increased heart rate and sweating. These physical reactions can further disturb sleep, making it harder to enter deep, restorative stages of sleep.
4. Daytime Dysfunction: The impact of nightmares extends beyond the nighttime hours. The emotional distress and lack of restful sleep can lead to daytime symptoms, including difficulty concentrating, irritability, and decreased cognitive function.
5. Sleep Anxiety: For individuals who frequently experience nightmares, the fear of having another disturbing dream can create anxiety around sleep itself. This anxiety can further disrupt the ability to fall asleep and maintain a healthy sleep routine.
Understanding the impact of nightmares on sleep is crucial for identifying and addressing the underlying causes. By recognizing the negative effects of nightmares, individuals can seek appropriate treatment and strategies to promote better sleep and overall well-being.
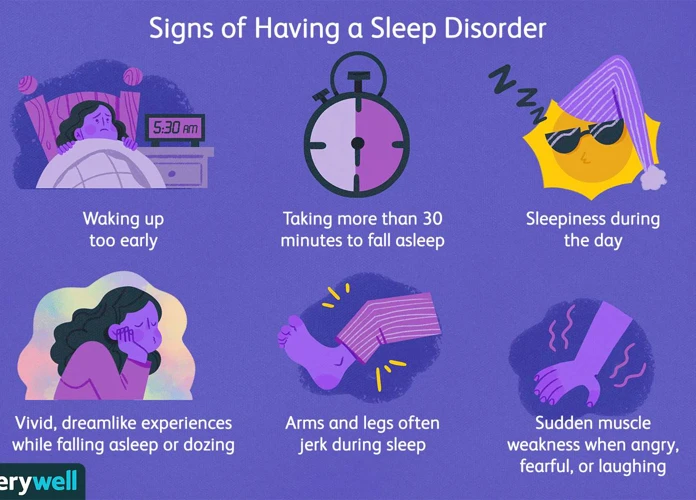
Types of Sleep Disorders

When it comes to sleep disorders, there are several types that can disrupt a person’s ability to get quality sleep. Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night. Narcolepsy, on the other hand, is a neurological disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden, uncontrollable episodes of sleep. Sleep apnea is a condition where breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep, leading to pauses in breathing and fragmented sleep. Restless Legs Syndrome is a disorder that triggers an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. Lastly, parasomnia encompasses a range of abnormal behaviors during sleep, such as sleepwalking and night terrors. Each type of sleep disorder can have various underlying causes and effects, and it is essential to understand them to provide appropriate treatment and improve sleep quality.
Insomnia
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to inadequate or poor-quality sleep. Individuals with insomnia often experience daytime fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. There are two main types of insomnia: acute and chronic. Acute insomnia is typically short-term and often caused by factors such as stress, jet lag, or a sudden change in sleep environment. Chronic insomnia, on the other hand, persists for a longer duration, typically lasting for at least three nights a week and lasting for a month or more. It can be caused by various underlying factors, including medical conditions, psychiatric disorders, medications, or lifestyle habits. To effectively manage insomnia, it is essential to address the underlying cause and implement healthy sleep practices. These may include creating a calm sleep environment, practicing relaxation techniques, sticking to a consistent sleep schedule, and avoiding stimulants before bedtime. For individuals struggling with chronic insomnia, seeking professional help from a healthcare provider or sleep specialist may be beneficial in identifying and treating the root cause.
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a neurological sleep disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. People with narcolepsy often experience excessive daytime sleepiness and may have sudden, uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep during the day. These episodes, called sleep attacks, can occur at any time and in any situation, making it difficult for individuals with narcolepsy to stay awake and alert. Another key symptom of narcolepsy is cataplexy, which is the sudden loss of muscle tone triggered by strong emotions such as laughter or surprise. This can result in temporary weakness or paralysis, causing the affected person to collapse. Narcolepsy can disrupt nighttime sleep, leading to fragmented and restless sleep patterns. The exact cause of narcolepsy is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. While there is no cure for narcolepsy, it can be managed with medications and lifestyle adjustments, such as establishing regular sleep schedules and incorporating strategic napping into daily routines. Seeking medical attention and diagnosis from a healthcare professional specializing in sleep disorders is crucial for managing narcolepsy and improving quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that can have a significant impact on an individual’s overall health and quality of sleep. It is characterized by periods of interrupted breathing during sleep, where the airway becomes partially or completely blocked, leading to temporary pauses in breathing. These pauses can last anywhere from a few seconds to a minute and can occur multiple times throughout the night, disrupting the normal sleep cycle. Individuals with sleep apnea often experience loud snoring, gasping or choking sensations, and daytime sleepiness due to the fragmented sleep. The two main types of sleep apnea are obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA). OSA occurs when the muscles in the throat relax and block the airway, while CSA is caused by a dysfunction in the brain’s respiratory control centers. Sleep apnea can significantly contribute to the development of other health issues such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes. Effective treatment options for sleep apnea include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and avoiding alcohol, and the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines, which help keep the airway open during sleep. Seeking medical attention and treatment for sleep apnea is crucial in improving both sleep quality and overall well-being.
Restless Legs Syndrome
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disorder characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, usually accompanied by uncomfortable sensations such as itching, tingling, or aching. These sensations typically worsen during periods of rest or inactivity, often leading to sleep disturbances. RLS can significantly impact a person’s ability to fall asleep and stay asleep, resulting in excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue. This disorder affects both men and women and is more prevalent in middle-aged and older individuals. While the exact cause of RLS is unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Treatment options for RLS range from lifestyle changes such as avoiding caffeine and nicotine to medications that help manage symptoms and improve sleep quality. Seeking medical attention is crucial for those experiencing RLS symptoms as proper diagnosis and treatment can greatly alleviate the discomfort and sleep disruption caused by this condition.
Parasomnia
Parasomnia is a sleep disorder that encompasses a wide range of abnormal behaviors and experiences during sleep. It is characterized by unwanted events or actions that occur while a person is asleep, often causing disruptions in sleep patterns and overall sleep quality. Some common examples of parasomnia include sleepwalking, night terrors, and sleep talking. Sleepwalking, also known as somnambulism, involves getting out of bed and walking or performing complex tasks while still asleep. Night terrors are intense episodes of fear, usually accompanied by screaming, thrashing, and a state of confusion. Sleep talking, also known as somniloquy, refers to talking during sleep without the person being aware of it. These parasomnias can be distressing for both the individual experiencing them and their sleep partners or family members. It is important to note that parasomnias can be triggered by various factors such as stress, sleep deprivation, certain medications, and underlying sleep disorders. Understanding and addressing the underlying causes of parasomnia is key to managing and minimizing its impact on sleep quality.
The Connection between Nightmares and Sleep Disorders
The connection between nightmares and sleep disorders is complex and multifaceted. Nightmares can often serve as symptoms of underlying sleep disorders, acting as harbingers of disrupted sleep. Sleep disorders such as insomnia, narcolepsy, sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, and parasomnia can all have a significant impact on the content and frequency of nightmares. Insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, can lead to heightened arousal and anxiety, triggering nightmares. Narcolepsy, a neurological disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles, can cause vivid and disturbing dreams. Sleep apnea, a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, can lead to fragmented sleep and an increased likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Restless legs syndrome, characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, can disrupt sleep and contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. Parasomnia, a category of sleep disorders that includes sleepwalking and night terrors, can also manifest as intense and vivid nightmares. Understanding the connection between nightmares and sleep disorders is crucial for addressing underlying sleep issues and improving overall sleep quality.
Nightmares as Symptoms of Sleep Disorders
Nightmares can often serve as symptoms of underlying sleep disorders, providing important clues about an individual’s sleep health. One such sleep disorder is insomnia, where individuals have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to poor sleep quality. Insomnia can trigger nightmares due to the heightened anxiety and stress levels associated with insufficient sleep. Another sleep disorder linked to nightmares is narcolepsy, a condition characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks. People with narcolepsy often experience vivid and intense dreams during their rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, which can manifest as nightmares. Sleep apnea, a disorder characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, can also contribute to nightmares. The frequent awakenings and oxygen deprivation associated with sleep apnea disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to increased dream activity, including nightmares. Restless legs syndrome (RLS), a condition causing uncomfortable sensations and an irresistible urge to move the legs, can also result in nightmares due to the fragmented and disrupted sleep it causes. Lastly, parasomnias, a group of sleep disorders characterized by abnormal behaviors during sleep, may include nightmares as one of their symptoms. Understanding the relationship between nightmares and sleep disorders can help individuals recognize the potential underlying causes of their unsettling dreams and seek appropriate treatment.
Effects of Sleep Disorders on Dreaming
Sleep disorders can have profound effects on dreaming, altering the content and nature of our dreams. Let’s explore some of the specific effects that sleep disorders can have on our dream experiences:
1. Fragmented Dreams: Sleep disorders such as insomnia or sleep apnea can disrupt the normal sleep cycles, leading to fragmented sleep. This can result in fragmented dreams, where dream sequences may feel disjointed or incomplete. The lack of continuous and uninterrupted sleep can interrupt the natural flow of dreaming, making it difficult to engage in immersive dream experiences.
2. Vivid and Disturbing Dreams: Certain sleep disorders, like narcolepsy, can cause excessive daytime sleepiness and a disruption in the normal sleep-wake cycles. This can result in vivid and disturbing dreams that intrude into waking moments, blurring the line between dream and reality. The intense emotions generated by these dreams can be overwhelming and impact the overall well-being of individuals.
3. Absence of Dreams: In some cases, sleep disorders such as sleep apnea or medications used to treat sleep-related issues can cause a complete absence of dreaming. This can be attributed to the disruptions in sleep cycles and the inability to reach the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep stage, which is associated with dreaming. The absence of dreams can have implications for cognitive processes and emotional well-being.
4. Increased Frequency of Nightmares: Certain sleep disorders can contribute to an increase in the frequency and intensity of nightmares. For example, individuals with sleep apnea may experience oxygen deprivation during sleep, which can lead to more frequent and unsettling nightmares. Similarly, those with restless legs syndrome or parasomnia may have disrupted sleep patterns that trigger nightmares.
It is important to note that the effects of sleep disorders on dreaming can vary from person to person. Understanding these effects can help individuals recognize the role that sleep disorders play in their dream experiences and seek appropriate treatment to improve both their sleep quality and dream content.
Recurring Nightmares and Sleep Disorders
Recurring nightmares can be closely linked to the presence of underlying sleep disorders. These types of nightmares are characterized by their repetitive nature, often depicting similar themes or situations that reoccur over extended periods. Sleep disorders such as insomnia, narcolepsy, sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, and parasomnia can contribute to the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares. Insomnia, a common sleep disorder, can disrupt the sleep cycle and lead to heightened dream recall, making recurring nightmares more likely. Narcolepsy, on the other hand, causes excessive daytime sleepiness, which can result in fragmented and disrupted sleep patterns, potentially triggering recurring nightmares during periods of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Sleep apnea, characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, can also impact the quality of sleep and contribute to the occurrence of recurring nightmares. Restless legs syndrome, a neurological condition characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, can cause sleep disturbances, leading to an increased likelihood of recurring nightmares as well. Finally, parasomnia disorders such as sleepwalking or night terrors can also be associated with recurring nightmares. It is important to address and treat these underlying sleep disorders to alleviate the frequency and distress caused by recurring nightmares. Seeking medical advice and exploring treatment options can help break the cycle of recurring nightmares and improve overall sleep quality.
Treating Nightmares and Sleep Disorders
When it comes to addressing nightmares and sleep disorders, a variety of treatment options are available. The approach to treatment may vary depending on the specific sleep disorder or underlying cause of nightmares. Here are some common methods used to treat nightmares and sleep disorders:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely used therapeutic technique that has shown effectiveness in treating nightmares. It involves identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with sleep disturbances. CBT can help individuals develop coping mechanisms and reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
2. Medications: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage sleep disorders and alleviate nightmares. Medications such as antidepressants, alpha-blockers, and benzodiazepines can be used to regulate sleep patterns and reduce the occurrence of nightmares. However, it is important to consult with a medical professional before starting any medication.
3. Relaxation Techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques before bedtime can help promote a more restful sleep and reduce the occurrence of nightmares. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can help calm the mind and body, creating a conducive environment for a peaceful sleep.
4. Sleep Hygiene: Maintaining good sleep hygiene is essential for managing sleep disorders and reducing nightmares. This includes adhering to a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime, and limiting the consumption of caffeine and alcohol.
5. Addressing Underlying Issues: For individuals experiencing nightmares due to underlying psychological or emotional issues, addressing and resolving these issues through therapy or counseling can be beneficial. By working through unresolved trauma, stress, or anxiety, the frequency and intensity of nightmares can often be significantly reduced.
It is important to remember that treatment approaches may vary depending on the individual and their specific needs. Consulting with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist is recommended to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for addressing nightmares and sleep disorders. By addressing the root causes and implementing effective treatment strategies, individuals can experience improved sleep quality and a reduction in troubling nightmares.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the connection between nightmares and sleep disorders is essential for promoting healthy sleep and overall well-being. Nightmares, with their vivid and disturbing nature, can be indicative of underlying sleep disorders and can significantly impact the quality of sleep. By recognizing nightmares as potential symptoms of sleep disorders, individuals can seek appropriate medical attention and treatment to address the root causes. Sleep disorders, such as insomnia, narcolepsy, sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, and parasomnia, can all contribute to the occurrence of nightmares and disrupt the sleep cycle. It is crucial to identify and address these disorders to alleviate the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Treatment options for nightmares and sleep disorders range from medication to therapy, depending on the specific condition and individual needs. Exploring psychological meaning and practicing techniques like lucid dreaming can also provide valuable insights and tools for managing nightmares. By prioritizing sleep health and seeking professional guidance when necessary, individuals can work towards achieving restful nights and peaceful dreams.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are some common triggers for nightmares?
Nightmares can be triggered by various factors such as stress, anxiety, trauma, medications, sleep deprivation, and even certain foods or substances like alcohol or caffeine.
2. Can nightmares be a symptom of an underlying sleep disorder?
Yes, nightmares can be a symptom of sleep disorders like sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, or narcolepsy. It is important to address any ongoing sleep issues and consult a healthcare professional if you experience frequent nightmares.
3. Can recurring nightmares be a sign of a deeper psychological issue?
Recurring nightmares can sometimes be a sign of unresolved psychological issues or trauma. These dreams can reflect underlying anxieties, fears, or emotions that need to be addressed with the help of therapy or counseling.
4. How can nightmares impact overall sleep quality?
Nightmares can disrupt sleep cycles and lead to poor sleep quality. They can cause sleep fragmentation, frequent awakenings, and difficulty falling back to sleep, resulting in daytime fatigue and decreased cognitive function.
5. Are there any natural remedies or lifestyle changes that can help reduce nightmares?
Yes, making certain lifestyle changes can potentially reduce nightmares. These include managing stress levels, establishing a regular sleep routine, creating a relaxing bedtime environment, and avoiding stimulating activities or substances close to bedtime.
6. Can medications contribute to the occurrence of nightmares?
Yes, certain medications like antidepressants, antipsychotics, and some blood pressure medications can increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares as a side effect. If you suspect your medication is causing nightmares, it is important to consult your doctor.
7. Is there a link between sleep disorders and nightmares?
Yes, sleep disorders can often coexist with nightmares. Conditions like sleep apnea, narcolepsy, and insomnia can disrupt sleep cycles and increase the occurrence of nightmares.
8. Can lucid dreaming techniques help in managing nightmares?
Yes, practicing lucid dreaming techniques can be beneficial in managing nightmares. Becoming aware that you are dreaming during a nightmare can provide an opportunity to take control of the dream and alter its course or confront your fears.
9. How can treating an underlying sleep disorder help alleviate nightmares?
Treating the underlying sleep disorder can help improve sleep quality and reduce the occurrence of nightmares. By addressing sleep issues, the overall sleep architecture becomes more stable, leading to a decrease in disruptive dreams.
10. When should I seek professional help for recurring nightmares?
If recurring nightmares consistently disrupt your sleep, cause distress or affect your daily functioning, it is recommended to seek professional help. A healthcare provider or sleep specialist can assist in identifying the underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatment options.