Understanding Nightmares

Definition of Nightmares
Causes of Nightmares
- Psychological factors: Emotions and experiences from our waking life can heavily influence our dreams. Stress, anxiety, trauma, and unresolved conflicts can all contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. These dreams may serve as a way for our subconscious mind to process and cope with challenging emotions or past events. Exploring the psychological impact of nightmares on mental health can provide valuable insights into how they are connected.
- Medications and substances: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, beta-blockers, and narcotics, have been known to cause nightmares as a side effect. Additionally, substances like alcohol or illicit drugs can disrupt the sleep cycle and lead to vivid and distressing dreams.
- Sleep disorders: Sleep disorders like sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, and narcolepsy can increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. These disorders can disrupt the normal sleep patterns, leading to fragmented and disrupted REM sleep, which is when most dreaming occurs.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors such as a noisy sleeping environment, extreme temperatures, or an uncomfortable sleeping arrangement can disrupt sleep and contribute to the occurrence of nightmares.
It is important to note that each individual’s experience with nightmares may be unique, and the specific causes can vary from person to person. Exploring common themes and symbols that frequently appear in nightmares can also provide valuable insights into the underlying psychological dynamics at play during these dreams.
Effects of Nightmares
Nightmares can have profound effects on our mental, emotional, and physical well-being. They can leave us feeling anxious, distressed, and even traumatized. Here are some of the common effects of nightmares:
- Emotional Disturbance: Nightmares often evoke intense emotions such as fear, terror, sadness, or anger. These emotional disturbances can linger even after waking up, impacting our mood and overall emotional state.
- Sleep Disruptions: Nightmares can disrupt our sleep patterns, causing frequent awakenings throughout the night. This can lead to difficulties in falling back asleep, resulting in disrupted sleep and daytime fatigue.
- Anxiety and Fear: Experiencing recurring nightmares can lead to increased anxiety and fear about going to sleep. This anxiety can create a vicious cycle, causing sleep disturbances and further exacerbating the occurrence of nightmares.
- Post-Traumatic Stress: Nightmares depicting traumatic events can trigger symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in individuals who have experienced trauma in the past. These nightmares can act as traumatic reminders, intensifying distress and affecting overall well-being.
- Impact on Daily Functioning: The distress caused by nightmares can spill over into our waking lives, making it difficult to concentrate, affecting productivity, and interfering with daily activities.
It is important to note that the effects of nightmares can vary from person to person. While some individuals may experience mild disruptions, others may face more significant psychological challenges. Understanding the common themes and symbols that appear in nightmares can help in uncovering deeper psychological meanings and potentially finding ways to mitigate their effects. Additionally, seeking professional help and exploring the psychological benefits of dream analysis can provide further insights and support in coping with the impact of nightmares.
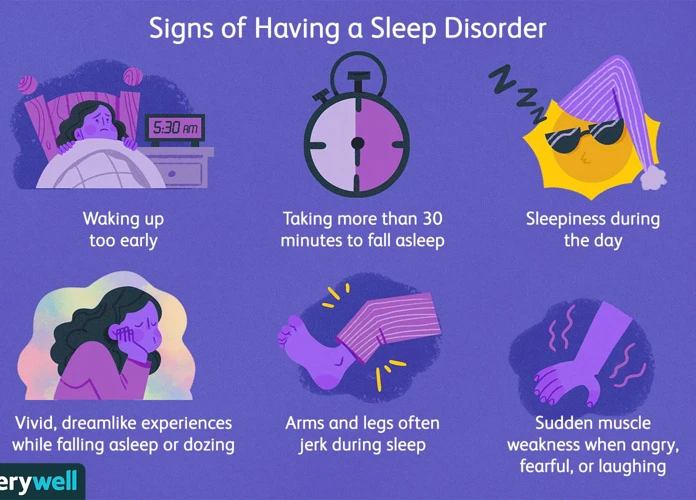
Types of Sleep Disorders
- Insomnia: Insomnia is a persistent difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, which can lead to inadequate sleep quantity or quality. It can be caused by various factors such as stress, anxiety, medical conditions, or lifestyle habits.
- Sleep Apnea: Sleep apnea is a disorder characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep. It can range from mild to severe and can lead to excessive daytime sleepiness, snoring, and even serious health complications if left untreated.
- Restless Legs Syndrome: Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disorder that causes uncomfortable sensations in the legs, often accompanied by an irresistible urge to move them. RLS typically worsens at night, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep.
- Narcolepsy: Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden episodes of sleep attacks. People with narcolepsy often experience disrupted nighttime sleep and may also experience cataplexy, a sudden loss of muscle tone triggered by strong emotions.
- Parasomnias: Parasomnias refer to a group of abnormal behaviors or experiences that occur during sleep. These can include sleepwalking, sleep talking, nightmares, night terrors, and sleep-related eating disorders.
- Other Sleep Disorders: There are numerous other sleep disorders, including circadian rhythm disorders, sleep-related movement disorders, and sleep-related breathing disorders like nocturnal enuresis (bedwetting) and bruxism (teeth grinding).
Insomnia
is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non-restorative sleep, despite having the opportunity to sleep. It can result in a range of symptoms, including daytime fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and impaired functioning. Insomnia can be acute or chronic, and it can have various causes, including stress, anxiety, depression, medication side effects, or underlying medical conditions. Individuals with insomnia often find themselves lying awake in bed, unable to quiet their minds and achieve restful sleep. This sleep disorder can significantly impact both the quantity and quality of sleep, leading to a state of chronic sleep deprivation.
Insomnia’s relationship with nightmares is a complex and bidirectional one. Insomnia can contribute to the development or exacerbation of nightmares, as sleep disturbances and fragmented sleep can disrupt the normal sleep cycles, leading to an increase in REM sleep, which is closely associated with dreaming. The heightened emotional arousal and hyperarousal often experienced due to insomnia can also contribute to the intensity and frequency of nightmares. On the other hand, nightmares can also contribute to the maintenance of insomnia, as the fear of nightmares can create anxiety and apprehension around sleep, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep.
It is important to address and manage insomnia effectively to reduce the impact on overall sleep quality and to mitigate the potential occurrence of nightmares. Treatment options for insomnia include medical interventions, such as prescription sleep medications, as well as non-medical interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-i), relaxation techniques, and improving sleep hygiene practices. By addressing insomnia, individuals can better regulate their sleep patterns and reduce the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
Sleep Apnea
Restless Legs Syndrome
Narcolepsy
- Narcolepsy is a neurological sleep disorder characterized by extreme daytime sleepiness and sudden episodes of falling asleep. People with narcolepsy often experience excessive daytime sleepiness, regardless of how much sleep they get at night.
- The key symptom of narcolepsy is excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), which can result in recurrent episodes of falling asleep during daily activities, such as work or driving.
- Cataplexy is another common symptom of narcolepsy, characterized by sudden and temporary loss of muscle tone, usually triggered by strong emotions such as laughter or surprise. During a cataplexy episode, individuals may experience muscle weakness, slurred speech, or even total body collapse. These episodes can last from a few seconds to a few minutes.
- Some individuals with narcolepsy may also experience hallucinations and sleep paralysis. Hallucinations occur when a person sees or hears things that are not actually present, typically upon falling asleep or waking up. Sleep paralysis is a temporary inability to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up.
- The exact cause of narcolepsy is still not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. In some cases, narcolepsy may be triggered by a lack of a brain chemical called hypocretin, which helps regulate wakefulness and REM sleep.
- Treatment for narcolepsy involves a combination of behavioral and pharmacological interventions. Behavioral strategies include scheduled naps, maintaining regular sleep patterns, and avoiding triggers that induce sleepiness. Medications such as stimulants and antidepressants may also be prescribed to help manage excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy.
For more information about the psychological benefits of dream analysis, you can read our article on psychological benefits of dream analysis in understanding nightmares.
Parasomnias
Other Sleep Disorders
The Link Between Nightmares and Sleep Disorders

Nightmares as Symptoms of Sleep Disorders
- Insomnia: Individuals with insomnia often have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to fragmented and poor-quality sleep. As a result, they may experience an increase in nightmares and vivid dreams.
- Sleep Apnea: Sleep apnea is characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep, leading to frequent awakenings throughout the night. These disruptions can trigger nightmares and cause individuals to wake up suddenly, gasping for air.
- Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): RLS causes uncomfortable sensations and an irresistible urge to move the legs, leading to difficulty falling asleep. The resulting sleep deprivation can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares.
- Narcolepsy: Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks. Individuals with narcolepsy may experience vivid and intense dreams during the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep stage, which can manifest as nightmares.
- Parasomnias: Parasomnias encompass a range of sleep disorders, including sleepwalking, sleep talking, and night terrors. Nightmares can be a component of these disorders, causing extreme fear and anxiety during sleep.
- Other Sleep Disorders: Various other sleep disorders, such as sleep-related eating disorder, sleep-related hallucinations, and sleep-related dissociative disorders, can also be accompanied by nightmares as part of their symptomatology.
Impact of Sleep Disorders on Nightmares
Furthermore, restless legs syndrome, a neurological disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, can lead to ongoing discomfort and frequent limb movements during sleep. These movements can disrupt the sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of nightmares. Narcolepsy, on the other hand, is a chronic sleep disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden episodes of sleep. The irregular sleep patterns associated with narcolepsy can result in vivid and intense dreams, including nightmares.
Additionally, parasomnias, a group of sleep disorders that involve abnormal behaviors during sleep, can also impact nightmares. Disorders such as sleepwalking, night terrors, or REM sleep behavior disorder can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and increase the chances of experiencing nightmares. Other sleep disorders, such as periodic limb movement disorder or circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders, can also contribute to the occurrence of nightmares.
Sleep disorders can have a significant impact on nightmares. The disruption in sleep patterns caused by insomnia, sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, narcolepsy, parasomnias, and other sleep disorders can increase the frequency, intensity, and emotional content of nightmares. Understanding the connection between sleep disorders and nightmares is crucial in addressing these issues and improving overall sleep quality and well-being.
How Nightmares Can Worsen Sleep Disorders
Nightmares have the potential to exacerbate existing sleep disorders and even contribute to the development of new ones. The distressing nature of nightmares can disrupt the continuity of sleep, leading to increased sleep fragmentation. Sleep fragmentation refers to the disruption of the sleep cycle, with frequent awakenings throughout the night. This can prevent individuals from experiencing the restorative sleep needed for optimal functioning and overall well-being.
Nightmares can also lead to a reduction in the quality of REM sleep, which is the sleep stage associated with vivid dreaming. When nightmares occur during REM sleep, it can disrupt the natural progression of sleep cycles and hinder the regenerative and restorative processes that typically occur during this stage. As a result, individuals may wake up feeling fatigued, irritable, and unrefreshed.
The negative emotions and high levels of arousal triggered by nightmares can aggravate symptoms of sleep disorders. For instance, individuals with insomnia may find it even more challenging to fall asleep or stay asleep after experiencing a distressing nightmare. Similarly, individuals with sleep apnea may experience heightened anxiety and stress due to the intense emotions provoked by nightmares, potentially worsening their sleep-related breathing issues.
In addition to exacerbating existing sleep disorders, nightmares can also contribute to the development of new sleep disorders. The fear and anxiety associated with repeated nightmares can create a conditioned response, leading to sleep-related phobias and anxiety disorders. These conditions can further disrupt someone’s ability to achieve restful sleep and exacerbate sleep disorders.
To summarize, nightmares can worsen sleep disorders through increased sleep fragmentation, reduced quality of REM sleep, aggravation of symptoms, and the potential development of new sleep disorders. It is essential to address both the nightmares and underlying sleep disorders to improve sleep quality and overall well-being.
Effects on Sleep Quality
Interrupted Sleep Patterns
Interrupted sleep patterns can also affect the different stages of sleep. Specifically, rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, which is the stage of sleep associated with dreaming, may be particularly disrupted. REM sleep is crucial for various aspects of cognitive function, emotional regulation, and memory consolidation. However, when sleep is frequently interrupted, individuals may experience a reduction in the overall amount and quality of REM sleep. This can further contribute to cognitive impairment, emotional disturbances, and a heightened susceptibility to stress.
To illustrate this further, let’s consider an example. Imagine a person who frequently experiences nightmares due to a sleep disorder. Each time they have a nightmare, they wake up feeling anxious and unsettled, making it difficult for them to fall back asleep quickly. This pattern of interrupted sleep can occur multiple times throughout the night, leading to a fragmented and less restorative sleep experience. As a result, the individual may wake up feeling exhausted, groggy, and emotionally drained.
To mitigate the effects of interrupted sleep patterns, it is important to address both the underlying sleep disorder and the nightmares themselves. Seeking professional help, such as consulting with a sleep specialist or therapist, can provide valuable guidance and treatment options. Additionally, improving sleep hygiene practices, creating a relaxing sleep environment, and implementing relaxation techniques can all contribute to better sleep continuity and quality.
Interrupted sleep patterns are a significant consequence of nightmares and sleep disorders. They can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, particularly REM sleep, leading to daytime fatigue and difficulties in cognitive functioning. Understanding the impact of interrupted sleep patterns reinforces the importance of seeking appropriate treatment and adopting strategies to improve sleep hygiene. By addressing these disruptions, individuals can experience enhanced overall sleep quality and well-being.
Increased Sleep Fragmentation
One of the significant effects of nightmares on sleep quality is increased sleep fragmentation. Sleep fragmentation refers to the frequent interruptions or disruptions in the normal sleep pattern, resulting in fragmented and restless sleep. Nightmares can trigger heightened arousal during sleep, causing individuals to wake up abruptly throughout the night. This constant waking interrupts the natural sleep cycle, preventing the individual from experiencing sustained periods of restorative sleep. As a result, the overall sleep quality is compromised, leading to feelings of fatigue, daytime drowsiness, and difficulties in concentration and cognitive functioning.
This sleep fragmentation not only impacts the quantity of sleep but also the quality of different sleep stages. Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, which is the stage associated with vivid dreaming, is particularly affected by nightmares. Nightmares can disrupt the normal progression of REM sleep, leading to an imbalance in the sleep stages. REM sleep is essential for various physiological and cognitive processes, including memory consolidation and emotional regulation. When nightmares cause disruptions in REM sleep, it hinders the brain’s ability to undergo these crucial processes, potentially impacting memory, mood, and overall mental well-being.
The consequences of increased sleep fragmentation extend beyond the immediate effects of tiredness and difficulties in functioning. Prolonged disruption in sleep patterns can have more severe consequences for physical and mental health. Research has linked chronic sleep fragmentation to an increased risk of developing conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, obesity, diabetes, and mood disorders. Additionally, sleep fragmentation can perpetuate a vicious cycle, as it can further exacerbate the occurrence and severity of nightmares. The distressing nature of nightmares can create anxiety and fear around sleep, leading to heightened physiological arousal and increased likelihood of sleep disturbances. Addressing the issue of increased sleep fragmentation is crucial in managing both nightmares and sleep disorders.
Reduced Quality of REM Sleep
Managing Nightmares and Sleep Disorders
Seeking Professional Help
Improving Sleep Hygiene
Implementing Relaxation Techniques
Medications and Treatments
Conclusion
- The connection between nightmares and sleep disorders is a complex and intricate one
- Nightmares can be symptoms of sleep disorders, and the presence of sleep disorders can contribute to the occurrence and severity of nightmares
- The effects of nightmares and sleep disorders on sleep quality can be detrimental, leading to interrupted sleep patterns, increased sleep fragmentation, and reduced quality of REM sleep
- Managing nightmares and sleep disorders involves seeking professional help, improving sleep hygiene, implementing relaxation techniques, and considering medications and treatments
- It is crucial to address both nightmares and sleep disorders to improve overall well-being and quality of life
- By understanding the underlying causes and effects of nightmares and sleep disorders, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing and minimizing their impact
- Further research is needed to fully unravel the intricate relationship between nightmares and sleep disorders and to develop more effective treatments and interventions
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common themes and symbols in nightmares?
Common themes and symbols in nightmares can vary greatly depending on the individual’s experiences and personal beliefs. However, some recurring themes include being chased, falling, being trapped, or experiencing harm or danger. Symbols such as snakes, spiders, or dark and eerie settings are also commonly encountered in nightmares.
Can nightmares be a sign of mental health issues?
Yes, frequent nightmares or recurring nightmares can sometimes be indicative of underlying mental health issues such as anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or depression. If nightmares significantly disrupt sleep or cause distress during waking hours, it may be helpful to consult a mental health professional for further evaluation.
How do sleep disorders contribute to nightmares?
Sleep disorders can contribute to nightmares in several ways. For example, sleep apnea and other forms of disrupted breathing during sleep can lead to poor sleep quality, which can increase the likelihood of nightmares. Similarly, sleep deprivation caused by insomnia or restless legs syndrome can disrupt normal sleep patterns and increase the occurrence of nightmares.
Are nightmares more common in children or adults?
Nightmares are more common in children than in adults. This can be attributed to various factors such as the development of the imagination, the processing of emotions, and the fear of the unknown. However, nightmares can still occur in adults, particularly during periods of increased stress or trauma.
What are some techniques for managing nightmares?
Techniques for managing nightmares include improving sleep hygiene, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises before bed, and avoiding certain substances like caffeine or alcohol that can disrupt sleep. In some cases, therapy or counseling may be recommended to address underlying issues that contribute to nightmares.
Can medication help with nightmares?
In certain cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage nightmares. This can include medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or prazosin, which have been found to reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares, particularly in individuals with PTSD.
Can nightmares be prevented?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent nightmares, certain strategies can help reduce their occurrence. This includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, avoiding stimulating activities or screens before bed, and managing stress levels. Additionally, addressing any underlying sleep disorders or mental health issues can also help minimize the frequency of nightmares.
How do nightmares impact sleep quality?
Nightmares can significantly disrupt sleep quality by causing frequent awakenings throughout the night. This can lead to fragmented sleep and a reduction in the amount of restorative REM sleep, which is crucial for overall sleep quality and cognitive function. The intense emotions and fear experienced during nightmares can also make it difficult to fall back asleep, further impacting sleep continuity.
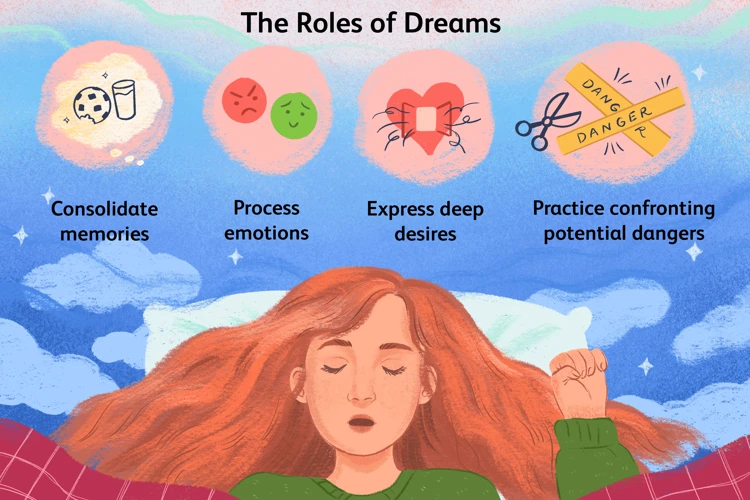
Do nightmares have any evolutionary purpose?
Some researchers believe that nightmares may serve an evolutionary purpose by helping us prepare for potential threats or dangers. The intense emotions and vivid imagery experienced during nightmares may simulate real-life situations, allowing us to practice coping mechanisms or develop heightened vigilance. However, more research is needed to fully understand the evolutionary significance of nightmares.
When should professional help be sought for nightmares?
Professional help should be sought for nightmares if they significantly interfere with daily functioning, cause severe distress or anxiety, or are accompanied by other symptoms such as insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, or mood disturbances. A healthcare professional or mental health specialist can provide appropriate evaluation and determine the best course of treatment.