Nightmares can be a frightening and disruptive experience that leaves us feeling unsettled and anxious during sleep. These vivid and intense dreams often involve distressing themes and can be a symptom of underlying sleep disorders. Understanding the connection between nightmares and sleep disorders is crucial in order to address and manage these conditions effectively. In this article, we will delve into the definition of nightmares, explore the potential causes, and investigate the various types of sleep disorders that can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. We will discuss the impact of both nightmares on sleep disorders and vice versa. Lastly, we will provide strategies and treatments to help manage and reduce nightmares and improve overall sleep quality.
Understanding Nightmares

Understanding Nightmares: Nightmares are a common occurrence during sleep and can leave individuals feeling startled and distressed upon waking up. These vivid and often terrifying dreams typically involve themes of danger, fear, or helplessness. Nightmares can vary in intensity and duration, with some individuals experiencing them occasionally while others may have recurrent nightmares. The content of nightmares can be influenced by personal experiences, unresolved emotions, and external factors such as stress or trauma. It is important to note that nightmares are different from other sleep disorders, such as sleep paralysis, sleepwalking, or insomnia, although they may sometimes coexist or share similar causes. Understanding the factors that contribute to nightmares can help individuals find effective strategies for coping and managing their occurrence.
Definition of Nightmares
Nightmares are vivid, disturbing dreams that can cause intense fear, anxiety, or distress during sleep. They are characterized by their ability to wake up the individual, often with a rapid heart rate and a sense of panic. Nightmares usually occur during the REM (rapid eye movement) stage of sleep, which is when most of our dreaming takes place. During these dreams, the brain can generate highly detailed and immersive experiences that feel very real. While nightmares can vary in content and theme, they often involve scenarios that are threatening, disturbing, or traumatic. This can include being chased, falling, experiencing physical harm, or encountering supernatural elements. It’s important to differentiate nightmares from other sleep disorders like sleep paralysis, sleepwalking, or insomnia, as these conditions have distinct characteristics and causes. By understanding the definition of nightmares, individuals can gain insight into the nature of these experiences and seek appropriate strategies for managing and reducing their occurrence.
Common Themes in Nightmares
Common Themes in Nightmares: Nightmares can encompass a wide range of themes, often tapping into our deepest fears and anxieties. While individual experiences may vary, there are some common themes that tend to recur in nightmares. One prevalent theme is being chased or pursued, where individuals may find themselves running from an unknown or threatening entity. Another common theme is falling, which can evoke feelings of helplessness and loss of control. Some nightmares revolve around being trapped or unable to escape, creating a sense of confinement and terror. Another frequent theme is experiencing harm or danger to oneself or loved ones, which can instill a profound sense of fear and vulnerability. Nightmares can also involve unpleasant scenarios such as being attacked, witnessing disasters, or encountering supernatural beings. It is important to note that while these themes may be unsettling, they are a product of the mind and do not pose actual harm. Understanding the common themes in nightmares can provide insights into the subconscious fears and worries that individuals may be grappling with during their waking hours.
Potential Causes of Nightmares
- Stress and Trauma: Experiencing high levels of stress or going through a traumatic event can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. Stressful situations, such as work pressure, relationship difficulties, or financial issues, can manifest in nightmares as the mind processes and tries to cope with the emotional strain. Similarly, individuals who have experienced trauma, such as abuse, accidents, or war, may have nightmares as a means of reliving or processing the traumatic event (source).
- Medications and Substance Abuse: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, blood pressure medications, or medications for Parkinson’s disease, have been associated with an increased likelihood of experiencing nightmares as a side effect. Additionally, substance abuse, including alcohol, drugs, or withdrawal from these substances, can disrupt the sleep cycle and contribute to nightmares (source).
- Psychological Factors: Psychological conditions, such as anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, or other mental health disorders, can increase the risk of nightmares. These conditions often involve heightened emotional distress or unresolved psychological issues that may surface during sleep as nightmares (source).
- Sleep Disorders: Certain sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea and insomnia, can disrupt the sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Sleep apnea, a condition characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, can lead to fragmented sleep and more frequent awakenings, making individuals more prone to experiencing nightmares. Insomnia, which involves difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, can also disrupt the sleep cycle and contribute to nightmares as the brain tries to compensate during REM sleep (source).
- Environmental Triggers: Environmental factors can also play a role in the occurrence of nightmares. Sleeping in a noisy or uncomfortable environment, exposure to extreme temperatures, or disruptions in regular sleep patterns can all increase the likelihood of nightmares. Additionally, consuming stimulating substances close to bedtime, such as caffeine or heavy meals, can affect sleep quality and contribute to nightmare frequency.
Understanding Sleep Disorders
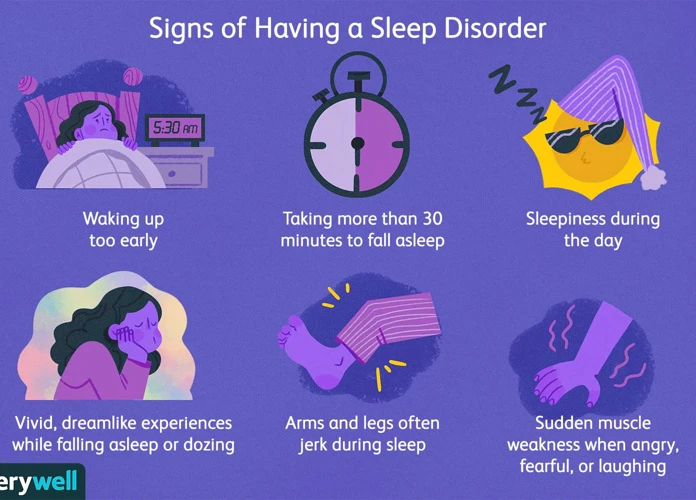
Understanding Sleep Disorders: Sleep disorders encompass a range of conditions that affect the quality and patterns of sleep. These disorders can have a significant impact on an individual’s overall well-being and daily functioning. Some common types of sleep disorders include insomnia, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, narcolepsy, and parasomnias. Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to daytime fatigue and impairment. Sleep apnea involves interrupted breathing during sleep, causing frequent awakenings and decreased oxygen levels. Restless leg syndrome causes an irresistible urge to move the legs, often leading to difficulty falling asleep. Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that results in excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks. Parasomnias include sleepwalking, sleep talking, and night terrors. These disorders can have various causes, including genetic factors, medical conditions, lifestyle factors, and certain medications. Understanding the different types of sleep disorders is essential in order to address and manage them effectively for improved sleep quality and overall health.
Definition of Sleep Disorders
Definition of Sleep Disorders: Sleep disorders are a group of conditions that affect the quality, duration, and overall pattern of sleep. They can interfere with a person’s ability to fall asleep, stay asleep, or achieve restful sleep. Sleep disorders can manifest in various ways, including difficulty falling asleep (insomnia), excessive daytime sleepiness (hypersomnia), abnormal behaviors during sleep (parasomnias), or disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders). These disorders can be categorized into primary sleep disorders, which are not directly caused by another medical condition, or secondary sleep disorders, which are a result of an underlying health issue or medication. It is important to note that sleep disorders can have a significant impact on an individual’s physical, mental, and emotional well-being, and prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential for improving sleep quality and overall quality of life.
Types of Sleep Disorders
There are several different types of sleep disorders that can significantly impact an individual’s sleep patterns and overall quality of rest. Each type of sleep disorder has its own distinct characteristics and symptoms. One common type of sleep disorder is insomnia, which is characterized by persistent difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Insomnia can be caused by various factors, including stress, anxiety, or certain medical conditions. Another type of sleep disorder is sleep apnea, a condition where a person’s breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep. This can lead to loud snoring, choking or gasping during sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness. Narcolepsy is another sleep disorder, characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden episodes of falling asleep during the day. People with narcolepsy may also experience muscle weakness or paralysis during moments of strong emotion, a condition known as cataplexy. Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) is a sleep disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. This can disrupt sleep and lead to restlessness and discomfort. Parasomnias are a group of sleep disorders that involve abnormal behaviors, movements, emotions, or perceptions during sleep. Examples of parasomnias include sleepwalking, sleep talking, and nightmares. By understanding the different types of sleep disorders, individuals can seek appropriate medical help and implement strategies to improve their sleep quality and overall well-being.
Common Symptoms of Sleep Disorders
Common Symptoms of Sleep Disorders: Sleep disorders can manifest in various ways, and individuals experiencing these conditions may exhibit a range of symptoms. Some common symptoms of sleep disorders include:
1. Difficulty falling asleep: Insomnia and certain sleep disorders may lead to trouble initiating sleep, causing individuals to lay awake in bed for extended periods before finally falling asleep.
2. Frequent awakenings: Interrupted sleep can be a symptom of sleep disorders, where individuals wake up multiple times throughout the night, making it difficult to achieve a restful night’s sleep.
3. Excessive daytime sleepiness: Feeling excessively tired and lacking energy during the day, regardless of the amount of sleep obtained at night, is a common symptom of sleep disorders such as sleep apnea or narcolepsy.
4. Irregular sleep patterns: Sleep disorders can disrupt normal sleep patterns, causing individuals to experience irregular sleep cycles, leading to unpredictable periods of wakefulness and sleep.
5. Difficulty staying asleep: Individuals with sleep disorders often struggle to stay asleep throughout the night, frequently waking up and finding it challenging to get back to sleep.
6. Restless movements during sleep: Conditions like restless leg syndrome or periodic limb movement disorder can cause involuntary and disruptive movements during sleep, leading to restless nights and fatigue during the day.
7. Night sweats: Some sleep disorders, including sleep apnea, can cause night sweats and excessive sweating during sleep, leading to disruptions and discomfort.
8. Difficulty breathing during sleep: Sleep disorders such as sleep apnea can result in episodes of interrupted breathing or shallow breathing during sleep, often accompanied by snoring or gasping for air.
9. Changes in mood or behavior: Sleep disorders can impact emotions and behavior, leading to irritability, mood swings, anxiety, or depression.
10. Impaired concentration and memory: Lack of quality sleep due to sleep disorders can result in difficulties with concentration, memory recall, and cognitive function during waking hours.
It is important to note that these symptoms can vary depending on the specific sleep disorder an individual may be experiencing. If these symptoms persist or significantly impact daily functioning, it is essential to seek medical evaluation and treatment from a healthcare professional.
The Connection Between Nightmares and Sleep Disorders
The connection between nightmares and sleep disorders is a complex and intricate relationship. Research has shown that there is a significant overlap between the two, with sleep disorders often contributing to the occurrence of nightmares, and nightmares exacerbating the symptoms of sleep disorders. For example, individuals with sleep disorders such as insomnia, sleep apnea, or restless leg syndrome may experience more frequent nightmares as a result of fragmented sleep or physiological disturbances. On the other hand, the presence of nightmares can disrupt sleep continuity, leading to poor sleep quality and exacerbating the symptoms of sleep disorders. This bidirectional relationship highlights the importance of addressing both nightmares and sleep disorders concurrently in order to improve overall sleep health and quality of life. By effectively managing sleep disorders and implementing strategies to reduce nightmares, individuals can achieve better sleep and alleviate the psychological distress associated with both conditions.
Research on Nightmares and Sleep Disorders
Research on Nightmares and Sleep Disorders: Extensive research has been conducted to understand the relationship between nightmares and sleep disorders. Studies have shown that there is a bidirectional connection between the two, with each influencing the other’s frequency and severity. One study found that individuals with sleep disorders, such as insomnia or sleep apnea, are more likely to experience nightmares compared to those without these disorders. Another research study discovered that nightmares can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to the development of sleep disorders. Additionally, research has shown that nightmares can have detrimental effects on overall sleep quality, leading to daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and impaired cognitive function. Studies have indicated that addressing and treating sleep disorders can significantly reduce the occurrence and intensity of nightmares. This highlights the importance of identifying and treating underlying sleep disorders to manage and alleviate nightmares effectively. Thus, continued research in this field is essential to discover innovative treatments and interventions that can improve sleep quality and reduce the frequency of nightmares in individuals suffering from sleep disorders.
Impact of Sleep Disorders on Nightmares
Impact of Sleep Disorders on Nightmares:
Sleep disorders can have a significant impact on the occurrence and intensity of nightmares. Let’s explore some of the ways sleep disorders can influence nightmares:
1. Insomnia: Insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, can contribute to an increase in nightmares. The fragmented and disrupted sleep patterns that individuals with insomnia experience can disrupt the normal sleep cycles, leading to an imbalance in REM sleep, which is strongly associated with dreaming and nightmares.
2. Sleep Apnea: Sleep apnea, a sleep disorder characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, can also impact nightmares. The repeated awakenings and compromised sleep quality associated with sleep apnea can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and have a negative influence on dream patterns, potentially increasing the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
3. Narcolepsy: Narcolepsy, a neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden bouts of sleep, can also impact nightmares. Individuals with narcolepsy often experience disruptions in REM sleep, which can lead to vivid dreams and nightmares.
4. Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): RLS, a condition characterized by the irresistible urge to move the legs, especially during periods of rest or sleep, can also contribute to nightmares. The discomfort and disruptive sensations experienced by individuals with RLS can lead to sleep disturbances and potentially trigger nightmares.
5. Parasomnias: Parasomnias, a group of sleep disorders that involve abnormal behaviors, movements, or experiences during sleep, such as sleepwalking or night terrors, can also coexist with nightmares. These sleep disorders can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of experiencing distressing dreams.
It is important to note that the impact of sleep disorders on nightmares can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience a direct correlation between their sleep disorder and nightmares, while others may not. Seeking medical evaluation and treatment for sleep disorders can help alleviate their impact on nightmares and improve overall sleep quality.
Impact of Nightmares on Sleep Disorders
The impact of nightmares on sleep disorders can be significant, exacerbating the symptoms and disrupting the overall quality of sleep. Here are some ways in which nightmares can affect different sleep disorders:
1. Insomnia: Nightmares can worsen insomnia symptoms by causing sleep disturbances and making it difficult for individuals to fall back asleep. The distressing content of nightmares can also lead to increased anxiety and arousal, further perpetuating insomnia.
2. Sleep Apnea: For individuals with sleep apnea, nightmares can contribute to sleep fragmentation. The fear and anxiety triggered by nightmares can lead to awakenings and disrupt the continuous breathing patterns, further compromising the quality of sleep in those already dealing with interrupted breathing during the night.
3. Narcolepsy: Nightmares can be a common symptom for individuals with narcolepsy. These unsettling dreams can occur during both daytime naps and nighttime sleep. Nightmares may contribute to increased daytime sleepiness and emotional distress, further impacting the already disrupted sleep-wake cycle in narcolepsy.
4. Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): Nightmares can worsen the symptoms of RLS by causing further sleep disturbances. Individuals with RLS often struggle with the sensation of discomfort in their legs, and the emotional distress caused by nightmares can heighten the urge to move the legs, making it challenging to achieve restful sleep.
5. Periodic Limb Movement Disorder (PLMD): Nightmares can trigger involuntary leg movements in individuals with PLMD, leading to fragmented sleep and increased sleep disruptions. The emotional arousal associated with nightmares can contribute to the frequency and intensity of limb movements during sleep.
It is worth mentioning that while nightmares can contribute to sleep disorders, they can also be a result or symptom of underlying sleep disturbances. Understanding this bidirectional relationship is essential for developing comprehensive treatment plans that target both the nightmares and the underlying sleep disorder. Proper diagnosis and management of both nightmares and sleep disorders play a crucial role in improving sleep quality and overall well-being.
Managing Nightmares and Sleep Disorders
Managing Nightmares and Sleep Disorders: Finding ways to effectively manage nightmares and sleep disorders is essential for improving overall sleep quality and reducing the impact of these conditions on daily life. Treatment options for sleep disorders vary depending on the specific disorder, and may include medical interventions, therapy, or lifestyle changes. For example, individuals with insomnia may find relief through cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), while those with sleep apnea may benefit from continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. Implementing healthy sleep habits, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and creating a sleep-conducive environment, can help regulate sleep patterns and mitigate the occurrence of nightmares. It can be beneficial to develop strategies to reduce stress and anxiety throughout the day, as these emotions can contribute to sleep disturbances and nightmares. These strategies may include exercise, relaxation techniques, and engaging in enjoyable activities before bedtime. By addressing both the underlying sleep disorder and implementing effective coping mechanisms, individuals can work towards better sleep and a reduction in nightmares, leading to improved overall well-being.
Treatments for Sleep Disorders
Treatments for Sleep Disorders:
Treating sleep disorders involves a combination of lifestyle changes, therapy, and, in some cases, medications. Here are some commonly used treatments for sleep disorders:
1. Sleep Hygiene: Establishing healthy sleep habits is often the first step in treating sleep disorders. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing sleep environment, avoiding stimulants before bedtime, and practicing relaxation techniques.
2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of therapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to sleep disturbances. It helps individuals develop healthier sleep habits and cope with stress and anxiety that may interfere with sleep.
3. Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to treat specific sleep disorders. For example, melatonin supplements can help regulate sleep-wake cycles in individuals with circadian rhythm sleep disorders. Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed for individuals with insomnia or sleep disorders related to mental health conditions.
4. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): CPAP therapy is a common treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. It involves wearing a mask over the nose or mouth during sleep, which delivers a continuous flow of air to keep the airway open.
5. Alternative Therapies: Some individuals find relief from sleep disorders through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, yoga, or herbal remedies. While the effectiveness of these therapies may vary, they can be worth exploring under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
It is important to work with a healthcare provider or sleep specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your specific sleep disorder. They can provide personalized recommendations and monitor your progress to ensure that the chosen treatments are effective and safe.
Strategies to Reduce Nightmares
Strategies to Reduce Nightmares: If you’re experiencing frequent nightmares, there are several strategies that can help reduce their occurrence and intensity. One effective technique is called imagery rehearsal therapy. This involves mentally rehearsing a new, positive ending to the nightmare before going to sleep. By visualizing a different outcome, you can train your brain to respond differently to the dream and potentially decrease the frequency of the nightmare. Another strategy is to create a relaxing bedtime routine. Engaging in activities like taking a warm bath, practicing deep breathing exercises, or listening to calming music before bed can promote a sense of relaxation and reduce the likelihood of having nightmares. It’s also essential to create a sleep-friendly environment. Ensure that your bedroom is quiet, dark, and at a comfortable temperature. Avoid stimulating activities before bed, such as watching intense movies or engaging in stressful conversations. Additionally, managing stress through techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, or journaling can help alleviate anxiety and reduce the likelihood of nightmares. Finally, it is important to establish a consistent sleep schedule. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day can regulate your sleep patterns, decreasing the occurrence of nightmares. Implementing these strategies and finding what works best for you can significantly improve your sleep quality and reduce nightmares’ impact on your overall well-being.
Healthy Sleep Habits
Healthy Sleep Habits: Cultivating healthy sleep habits is essential for improving sleep quality and reducing the occurrence of nightmares and sleep disorders. Here are some recommended habits that can promote a restful and peaceful night’s sleep:
1. Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Establishing a regular sleep schedule helps regulate the body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep. Aim to go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends.
2. Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in relaxing activities before bed to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This could include reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation.
3. Create a Sleep-friendly Environment: Ensure that your sleep environment is comfortable, quiet, and dark. Use earplugs, eye masks, or white noise machines if necessary to minimize external disruptions.
4. Avoid Stimulants: Limit the consumption of stimulating substances such as caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, especially before bedtime. These substances can interfere with the natural sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of sleep disturbances.
5. Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity during the day can help promote better sleep at night. However, avoid exercising too close to bedtime as it may have a stimulating effect on the body.
6. Manage Stress: Find healthy ways to manage and reduce stress, as high levels of stress can contribute to sleep difficulties and nightmares. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, mindfulness, or talking to a therapist.
7. Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Choose a comfortable mattress, supportive pillow, and breathable bedding to optimize your sleep comfort. Keep your bedroom cool, well-ventilated, and free from distractions.
By incorporating these healthy sleep habits into your daily routine, you can create a conducive environment for restful sleep and minimize the occurrence of nightmares and sleep disorders. Remember that good sleep hygiene is an ongoing practice that requires consistency and commitment for long-term benefits.
Conclusion
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the connection between nightmares and sleep disorders is a complex and intricate one. It is important to understand that nightmares can be a symptom of underlying sleep disorders, such as insomnia or sleep apnea. Additionally, the occurrence of nightmares can also worsen sleep disorders by causing disruptions in sleep patterns. The impact of nightmares and sleep disorders on an individual’s overall well-being cannot be underestimated, as they can lead to chronic fatigue, impaired cognitive function, and increased anxiety levels.
Managing nightmares and sleep disorders requires a multi-faceted approach. Treatment options for sleep disorders can include medications, therapy, and lifestyle changes aimed at improving sleep quality. Strategies to reduce nightmares involve identifying and addressing any underlying issues or traumas, developing relaxation techniques, and practicing good sleep hygiene. Implementing healthy sleep habits, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and creating a conducive sleep environment, can also significantly improve sleep quality and reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
Seeking professional help from healthcare providers such as sleep specialists or therapists can provide invaluable support and guidance in managing nightmares and sleep disorders. It is essential to prioritize and prioritize sleep, as adequate and restful sleep plays a vital role in overall physical and mental health.
By understanding the connection between nightmares and sleep disorders and employing appropriate management strategies, individuals can gain control over their sleep patterns and experience a significant improvement in their overall quality of life. Remember, it is crucial to address any concerns related to nightmares or sleep disorders with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of nightmares?
Nightmares can have a profound impact on our overall well-being. They can disrupt sleep patterns, cause daytime fatigue, and contribute to increased anxiety and stress levels.
Are nightmares a symptom of a sleep disorder?
While nightmares can occur on their own, they can also be a symptom of underlying sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, insomnia, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
What are some common themes in nightmares?
Nightmares often involve themes of being chased, falling, being trapped, or experiencing a life-threatening situation. Other common themes include loss, failure, and supernatural occurrences.
Can medication cause nightmares?
Yes, certain medications such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and blood pressure medications have been reported to cause nightmares as a side effect.
Can children have nightmares?
Yes, nightmares are common in children, especially during developmental stages. They can be triggered by fears, imagination, or exposure to certain movies or stories.
Is there a connection between nightmares and trauma?
Yes, nightmares can be a common symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in individuals who have experienced traumatic events. These nightmares can be vivid and recurring, often replicating the traumatic experiences.
Can nightmares be influenced by sleep deprivation?
Yes, sleep deprivation can increase the frequency and intensity of nightmares. A lack of quality sleep can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of experiencing vivid and disturbing dreams.
Can certain foods or drinks trigger nightmares?
There is limited scientific evidence linking specific foods or drinks to nightmares. However, consuming heavy or spicy meals close to bedtime, as well as excessive alcohol consumption, may increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
Are nightmares always negative experiences?
No, nightmares are typically distressing, but they can also provide an opportunity for emotional processing and exploration of subconscious fears and anxieties.
Can therapy help in managing nightmares?
Yes, therapy approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for nightmares (CBT-I) and exposure therapy can be effective in managing and reducing the frequency of nightmares.