Have you ever woken up in the middle of the night, breathing heavily and drenched in sweat, with vivid, unsettling images still lingering in your mind? Or perhaps you’ve experienced episodes where you suddenly sit up in bed, screaming and thrashing about, only to have no recollection of these events in the morning. These nighttime disturbances can be incredibly distressing and confusing, leaving you wondering if they were mere nightmares or something more sinister. In this article, we will unravel the mysteries of these unsettling experiences and help you understand the difference between nightmares and night terrors. By exploring the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention methods for both, you’ll gain valuable insights into effectively dealing with these nocturnal disturbances. So, prepare to uncover the secrets of the night and find solace in understanding the dynamics of your subconscious mind.
What are Nightmares?

Nightmares are unsettling and vivid dreams that occur during REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, which is the stage of sleep associated with increased brain activity and intense dreaming. These dreams often contain distressing or frightening themes, leaving the dreamer with a lingering sense of fear and unease upon waking. Nightmares can involve various scenarios such as being chased, falling, or being trapped in a life-threatening situation. They may also feature supernatural elements, monsters, or recurring traumatic events. It is important to note that nightmares are typically more common in children but can occur in adults as well. Nightmares can be triggered by a variety of factors including stress, anxiety, traumatic experiences, medications, or even certain foods and substances. They may serve as a reflection of our subconscious fears, unresolved conflicts, or as a way for the brain to process emotional or traumatic events. While nightmares can be distressing, they are a normal part of dreaming and rarely require medical intervention. However, if nightmares become frequent or significantly disrupt sleep and daily functioning, it may be beneficial to seek professional help to explore possible underlying causes and receive guidance on managing and interpreting these dreams. Dream analysis and therapy can also be helpful in understanding the deeper meanings and messages behind recurring nightmares. Additionally, certain medications can also affect dream patterns and may contribute to the occurrence of nightmares.
What are Night Terrors?

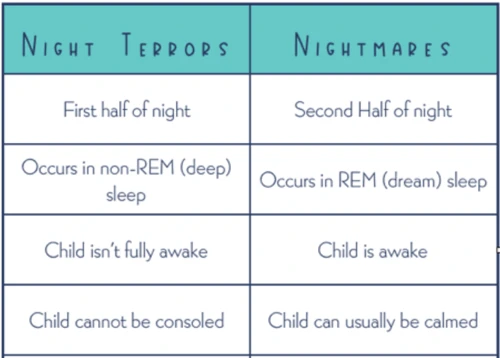
Night terrors, also known as sleep terrors, are episodes of intense fright that occur during sleep. Unlike nightmares, which happen during REM sleep, night terrors occur during deep non-REM sleep, usually in the first few hours after falling asleep. Night terrors are more common in children, particularly those aged between 3 and 7 years, but can also affect adults. During a night terror episode, the individual may suddenly sit up in bed, scream, and display signs of extreme fear, such as rapid breathing, increased heart rate, and sweating profusely. They may appear to be awake but are actually in a state of confusion and are often unresponsive to attempts to comfort them. It is important not to try to wake someone experiencing a night terror, as it can prolong the episode and increase their agitation. Night terrors typically last between 5 and 20 minutes, after which the person usually falls back asleep and has no memory of the episode in the morning. The exact causes of night terrors are not fully understood, but they may be triggered by factors such as sleep deprivation, stress, certain medications, or underlying sleep disorders. It is worth noting that night terrors differ from nightmares in that they are not associated with dreams or specific content. Certain medications can also contribute to the occurrence of night terrors, and discussions with a healthcare professional are recommended if medication use may be a contributing factor. Proper sleep hygiene, regular sleep schedules, and stress management techniques can help reduce the frequency and severity of night terrors. In severe cases or when night terrors significantly impact daily functioning, consulting a healthcare professional or sleep specialist may be beneficial in determining the underlying causes and exploring treatment options.
Causes of Nightmares
Nightmares can be triggered by a variety of factors, and understanding these causes can help in managing and preventing their occurrence. One common cause of nightmares is stress and anxiety. When we are under significant stress, our minds may try to process and release these anxieties through dreams, resulting in nightmares. Traumatic experiences can also play a role in triggering nightmares, especially in individuals who have experienced post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These nightmares often replay the traumatic event and can be quite distressing. Certain medications, such as antidepressants, tranquilizers, or beta-blockers, have been known to affect dream patterns and potentially lead to nightmares. Additionally, consuming certain foods or substances before bed, such as alcohol, caffeine, or heavy meals, can disrupt sleep and increase the likelihood of nightmares. Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or restless legs syndrome, can also contribute to nightmares. It is important to note that nightmares can serve as a reflection of unresolved conflicts or emotional issues that may require attention and resolution. Seeking therapy or exploring techniques such as lucid dreaming can be helpful in managing and overcoming the causes of nightmares.
Causes of Night Terrors
Night terrors, also known as sleep terrors, are episodes characterized by sudden and intense fear or terror during sleep. Unlike nightmares, which occur during REM sleep, night terrors happen during non-REM sleep, specifically during the transition between deep sleep and waking up. The exact causes of night terrors are not fully understood, but several factors have been associated with their occurrence. Here are some potential causes:
1. Sleep Disruptions: Night terrors often arise due to disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle, such as irregular sleep patterns, lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation. When the body is unable to transition smoothly between sleep stages, it may trigger a night terror episode.
2. Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress, anxiety, or trauma can contribute to night terrors. These intense emotions can impact the brain’s ability to regulate sleep and arousal, leading to episodes of night terrors.
3. Genetics: A family history of night terrors can increase the likelihood of experiencing them. There may be certain genetic factors that make an individual more susceptible to night terror episodes.
4. Fever or Illness: Night terrors can be more common in children who have a fever or are experiencing an illness. The rise in body temperature and physical discomfort can disrupt normal sleep patterns and trigger night terrors.
5. Medications and Substances: Certain medications, such as antidepressants or sleep aids, may increase the risk of night terrors. Additionally, the use of substances like alcohol or recreational drugs can disrupt sleep and contribute to night terror episodes.
It’s important to note that each individual may have different triggers for night terrors, and identifying the specific cause can be challenging. Creating a conducive sleep environment, managing stress levels, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and avoiding substances that can disrupt sleep can help reduce the frequency and intensity of night terrors. If night terrors persist or significantly impact daily functioning, consulting a healthcare professional or sleep specialist may be beneficial to determine the underlying causes and explore appropriate treatment options.
Symptoms of Nightmares

The following are common symptoms associated with nightmares:
1. Intense emotions: Nightmares often evoke strong emotions such as fear, anxiety, or distress. The emotions experienced during a nightmare can be so intense that they may persist even after waking up.
2. Vivid and detailed dreams: Nightmares are characterized by incredibly vivid and detailed dream scenarios that feel incredibly realistic. These dreams can involve a wide range of elements, from being pursued by a menacing figure to being trapped in a life-threatening situation.
3. Recollection upon waking: Unlike night terrors where the person has little to no memory of the episode, individuals who experience nightmares can often recall the details of the dream upon waking. This recollection can contribute to the lingering fear or unease after the nightmare.
4. Sleep disturbances: Nightmares can disrupt sleep patterns, causing difficulty in falling back asleep after waking from a terrifying dream. This can result in fragmented or poor-quality sleep, leading to daytime fatigue and irritability.
5. Physical reactions: Nightmares can trigger physical responses such as increased heart rate, sweating, rapid breathing, and even sleepwalking in some cases. These physical reactions are often similar to those experienced during times of genuine fear or distress.
6. Frequency and duration: While nightmares can occur sporadically for some people, others may experience them on a regular basis. The duration of nightmares can also vary, with some lasting a few minutes while others may seem to go on for much longer.
It is important to remember that occasional nightmares are a normal part of sleep. However, if nightmares become frequent and significantly impact daily life, it may be beneficial to seek professional help to explore possible underlying causes and learn strategies to manage and reduce their occurrence.
Symptoms of Night Terrors

Symptoms of night terrors can be extremely distressing for both the person experiencing them and those around them. Unlike nightmares, night terrors are characterized by intense episodes of fear and panic that occur during non-REM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, usually within the first few hours of falling asleep. These episodes can last anywhere from a few minutes to half an hour and can be accompanied by various symptoms, including:
1. Sudden awakening with a bloodcurdling scream or cry.
2. Rapid breathing and a racing heart.
3. Profuse sweating and trembling.
4. Dilated pupils and a look of extreme terror.
5. Difficulty in comforting or consoling the person.
6. Confusion and disorientation upon waking, often with no memory of the episode.
It’s important to note that individuals experiencing night terrors may appear awake, but they are actually still asleep and not fully conscious. They may sit up in bed, thrash around violently, or even attempt to flee from perceived threats. These symptoms can be alarming for both the individual and their loved ones. Night terrors are more common in children but can also occur in adults, especially those with a history of sleep disorders or psychological conditions. It is crucial to ensure the safety of the person experiencing night terrors by creating a safe sleep environment and removing any potential hazards. If night terrors persist or significantly affect their quality of life, seeking medical advice for further evaluation and guidance is recommended.
Treatment for Nightmares

Treatment for nightmares primarily involves addressing underlying factors that may be contributing to their occurrence and implementing strategies to reduce their frequency and impact. Here are several approaches that can be effective in managing nightmares:
1. Environmental modifications: Creating a calm and comfortable sleep environment can promote more restful sleep and potentially reduce the occurrence of nightmares. This can include ensuring a comfortable temperature, using soothing sounds or white noise, and keeping the bedroom free of distractions.
2. Stress reduction techniques: Since stress and anxiety can trigger nightmares, learning and implementing stress reduction techniques can be beneficial. This may include engaging in relaxation exercises like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga before bedtime.
3. Imagery Rehearsal Therapy (IRT): IRT is a therapeutic technique that involves rewriting the content of a nightmare to create a more positive or less distressing outcome. By visualizing a revised dream scenario repeatedly, the individual may achieve a sense of control and empowerment over their dreams, potentially reducing the occurrence of nightmares.
4. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): CBT-I is a type of therapy that focuses on improving sleep habits and addressing underlying thoughts and beliefs that may contribute to sleep disturbances, including nightmares. This therapy can help individuals develop healthier sleep patterns and manage stress and anxiety more effectively.
5. Medications: In cases where nightmares are particularly distressing or significantly affect daily functioning, medications may be prescribed. These may include antidepressants, anxiolytics, or medications specifically targeting sleep disorders. However, medications should only be used under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
It’s important to note that treatment approaches may vary depending on the individual and the underlying causes of their nightmares. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a mental health specialist can help tailor an appropriate treatment plan to address specific needs. Remember, consistency and patience are key when implementing treatment strategies, as it may take time to see significant improvements.
Treatment for Night Terrors
Treatment for night terrors primarily focuses on creating a safe sleep environment and minimizing any potential triggers. Since night terrors are believed to be related to sleep disruptions and are not typically associated with underlying psychological issues, medical intervention is usually not necessary. However, there are several measures that can be taken to help manage and reduce the occurrence of night terrors:
1. Establish a consistent sleep routine: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle and promotes better quality sleep. Set a fixed bedtime and wake-up time and follow it consistently, even on weekends.
2. Create a calm and soothing bedtime routine: Engage in relaxing activities before bed such as reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing deep breathing exercises. Establishing a peaceful and predictable routine helps signal to the body that it’s time to wind down and prepares it for restful sleep.
3. Ensure a comfortable sleep environment: Make sure the bedroom is conducive to a good night’s sleep. Keep the room cool, dark, and quiet. Use comfortable bedding and ensure proper ventilation.
4. Address underlying anxiety or stress: Since anxiety and stress can contribute to sleep disturbances, it’s important to identify and manage any underlying factors that may be triggering night terrors. Consider stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or counseling.
5. Implement safety measures: Since individuals experiencing night terrors may act out physically during episodes, it is crucial to ensure their safety. Clear the bedroom of any sharp or dangerous objects, and consider installing safety gates on stairs or securing windows to prevent potential accidents.
6. Supportive presence: If someone you know experiences night terrors, try staying nearby to ensure their safety without trying to wake them. Physical contact may provide comfort or a sense of grounding during the episode.
7. Consult a healthcare professional: If night terrors persist and significantly affect daily life or cause injuries, it may be helpful to consult a healthcare professional who specializes in sleep disorders. They can provide further guidance and recommend additional interventions, such as relaxation techniques or, in some cases, medication.
Remember, each individual’s experience with night terrors may vary, and it may take time to find the most effective strategies for managing them. Patience, consistency, and a supportive approach are key to navigating through night terrors and improving sleep quality.
Prevention of Nightmares

Prevention of nightmares involves adopting healthy sleep habits and managing potential triggers that can contribute to the occurrence of these distressing dreams. Here are some strategies to help prevent nightmares:
1. Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Establish a soothing bedtime routine that promotes relaxation and reduces stress before sleep. This can include activities such as taking a warm bath, listening to calming music, or practicing deep breathing exercises.
2. Manage Stress and Anxiety: Find healthy ways to manage stress and anxiety during the day. Engage in activities that help reduce stress levels, such as regular exercise, practicing mindfulness or meditation, or engaging in hobbies and interests.
3. Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Stick to a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep quality.
4. Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment: Make sure your sleep environment is comfortable, quiet, and dark. Use earplugs or a white noise machine to block out any disruptive sounds. Consider using blackout curtains or an eye mask to minimize light.
5. Avoid Stimulants and Substances: Limit the intake of stimulating substances close to bedtime. This includes avoiding caffeinated beverages, nicotine, and alcohol, as these can interfere with sleep patterns and potentially contribute to nightmares.
6. Be Mindful of Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, blood pressure medications, or even over-the-counter sleep aids, may have side effects that include vivid or disturbing dreams. Discuss with your healthcare provider if you suspect a medication may be causing nightmares.
7. Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bed: Eating a heavy meal before bedtime can disrupt digestion and potentially lead to nightmares. Opt for a light snack if needed, and allow time for digestion before lying down.
8. Manage Trauma and PTSD: If nightmares are linked to past trauma or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), seeking therapy or counseling can help address unresolved issues and develop coping mechanisms to reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
Remember, prevention strategies may require time and experimentation to find what works best for you. With consistent effort and a proactive approach, you can reduce the occurrence of nightmares and enjoy a more peaceful night’s sleep.
Prevention of Night Terrors

Prevention of night terrors primarily involves creating a sleep-friendly environment and adopting healthy sleep habits. Here are some strategies that can help minimize the occurrence of night terrors:
1. Stick to a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Establish a regular sleep routine by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This promotes a stable sleep pattern and reduces the likelihood of night terrors.
2. Create a Calm and Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in activities that promote relaxation before bed. This can include reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing deep breathing exercises. Avoid stimulating activities or screens close to bedtime, as these can disrupt sleep.
3. Ensure a Safe and Comfortable Sleep Environment: Make sure the bedroom is quiet, dark, and at a comfortable temperature. Use blackout curtains, earplugs, or white noise machines if necessary. Remove any potential hazards or distractions from the sleep environment.
4. Address Underlying Anxiety or Stress: Help children and adults manage stress and anxiety through techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or therapy. Encourage open communication to address any emotional issues that may be contributing to night terrors.
5. Implement a Gradual Wake-Up Approach: Gently wake the person experiencing night terrors about 15-30 minutes before the expected episode. This can disrupt the sleep cycle and help prevent the occurrence of night terrors.
6. Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid any potential triggers that may contribute to night terrors. These may include certain foods, medications, or sleep deprivation. Keeping a sleep diary can help track potential triggers.
7. Maintain a Supportive Environment: Offer emotional support and reassurance to individuals experiencing night terrors. Provide a sense of safety and comfort during episodes, if necessary, without forcibly waking them or trying to intervene.
Remember, prevention strategies for night terrors may vary depending on the individual and their specific triggers. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist for personalized guidance and treatment options if night terrors persist or significantly impact daily life.
How to Deal with Nightmares

Dealing with nightmares can be challenging, especially when they frequently disrupt your sleep and leave you feeling anxious or frightened. However, there are several strategies that can help you cope with and reduce the impact of nightmares. Firstly, creating a relaxing bedtime routine can promote better sleep quality and decrease the likelihood of nightmares. This routine may include activities like reading a calming book, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation, or taking a warm bath before bed. It is also important to ensure that your sleep environment is comfortable, dark, and free from distractions. Additionally, managing stress and anxiety levels during the day can have a positive impact on your sleep and reduce the frequency of nightmares. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing stress-management techniques, and seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist can all contribute to a healthier mental and emotional state. Another helpful strategy is to keep a dream journal. By writing down your dreams, you may start to identify patterns, themes, or triggers that contribute to your nightmares. This can aid in understanding the underlying emotional or psychological factors at play. If nightmares persist and significantly affect your well-being, it is important to seek professional help. Qualified therapists or counselors can provide guidance, support, and specific techniques, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for nightmares (CBT-N), which has been proven effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Remember that dealing with nightmares is a process, and finding the right approach may take time. Patience, self-care, and reaching out for professional assistance when needed are key elements to managing and overcoming nightmares.
How to Cope with Night Terrors

Coping with night terrors can be challenging, but there are strategies that can help ease their impact on your sleep and overall well-being. Here are some tips to cope with night terrors:
1. Establish a consistent sleep routine: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule can help regulate your sleep patterns and reduce the occurrence of night terrors. Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
2. Create a soothing bedtime environment: Make your bedroom a calm and relaxing space. Use soft lighting, comfortable bedding, and eliminate any potential triggers that may contribute to night terrors, such as loud noises or scary visuals.
3. Practice relaxation techniques: Before bed, engage in relaxation exercises such as deep breathing, meditation, or listening to calming music. These techniques can help reduce stress and promote a sense of tranquility as you prepare for sleep.
4. Avoid stimulants: Limit the consumption of caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, especially in the evening, as they can disrupt your sleep and contribute to night terrors.
5. Ensure safety during episodes: If you or a loved one experience night terrors that involve intense movement or potential harm, take precautions to prevent injuries. Remove any sharp or dangerous objects from the sleep environment and consider using protective padding or barriers if necessary.
6. Seek support from loved ones: Talk to your family and friends about your night terrors, as their understanding and support can alleviate some of the emotional distress associated with these episodes.
7. Consult a healthcare professional: If night terrors persist and significantly impact your quality of life, it may be beneficial to seek guidance from a healthcare professional. They can assess your situation, identify any underlying causes, and provide appropriate treatment options.
Remember, coping with night terrors can be a personal journey, and what works for one individual may not work for another. It may take time and patience to find the most effective coping strategies for yourself. Don’t hesitate to explore additional resources, such as support groups or therapy, for further assistance in managing night terrors and their potential underlying causes.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional help for nightmares or night terrors is crucial in ensuring proper support and treatment. Here are some indicators that might suggest it is time to reach out to a healthcare professional or sleep specialist:
1. Frequency and intensity: If nightmares or night terrors occur frequently, several times a week, and severely disrupt your sleep and overall well-being, it is advisable to seek professional help.
2. Sleep deprivation: If the frequency and intensity of nightmares or night terrors are causing significant sleep deprivation and affecting your ability to function during the day, professional guidance may be necessary.
3. Traumatic experiences: If nightmares are recurring and related to past traumatic experiences that continue to impact your daily life, seeking the help of a trauma specialist or therapist can be beneficial.
4. Safety concerns: Night terrors, which involve sudden and intense fear or panic, can sometimes lead to harmful behaviors such as sleepwalking or injuring oneself or others. If safety becomes a concern, immediate professional intervention is recommended.
5. Emotional distress: If nightmares or night terrors are causing extreme emotional distress, anxiety, or depression, seeking professional assistance can provide the necessary emotional support and coping strategies.
6. Impaired quality of life: When nightmares or night terrors start significantly affecting your relationships, work, or overall quality of life, it may be time to consult a healthcare professional who can assess and provide appropriate treatment.
Remember, professional help can come in the form of psychologists, therapists, sleep specialists, or psychiatrists who specialize in sleep disorders. They can evaluate your individual situation, provide a diagnosis if necessary, and recommend tailored treatments or therapies to help alleviate the distress caused by nightmares or night terrors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between nightmares and night terrors is crucial in effectively addressing these unsettling nighttime experiences. Nightmares are vivid and distressing dreams that occur during REM sleep and can be triggered by various factors such as stress, anxiety, and trauma. They serve as a reflection of our subconscious fears and unresolved conflicts. On the other hand, night terrors are episodes of intense fear and panic that occur during deep sleep, causing the person to sit up, scream, or thrash around. Night terrors are more common in children and can be associated with sleep disorders or underlying medical conditions.
When it comes to treatment for nightmares, various approaches can help manage and minimize their occurrence. These include maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and addressing any underlying stress or anxiety through therapy or stress-reduction techniques. The use of medications for nightmares is generally not recommended, but in certain cases, they may be prescribed under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
For night terrors, the focus lies more on creating a safe sleep environment and preventing potential injury during episodes. It is important to ensure that the person experiencing night terrors is safe and cannot harm themselves during the episode. Establishing a calming bedtime routine and reducing any stressors can also help alleviate night terrors. Seeking professional help may be necessary if night terrors significantly impact the person’s quality of life or if they are accompanied by other sleep disorders.
Remember, both nightmares and night terrors are common experiences that can be managed and understood with the right tools and support. By implementing preventative measures, seeking professional help when necessary, and practicing self-care techniques, it is possible to minimize the impact of these nocturnal disturbances and promote restful sleep.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the main difference between nightmares and night terrors?
The main difference between nightmares and night terrors lies in the stage of sleep in which they occur. Nightmares happen during REM sleep, while night terrors occur during deep non-REM sleep.
2. Are nightmares a sign of a psychological disorder?
Not necessarily. Nightmares are a common occurrence and might simply be a reflection of everyday stress, anxiety, or certain life events. However, frequent and severe nightmares could be associated with underlying psychological conditions that should be evaluated by a professional.
3. Can nightmares be influenced by what we eat?
Yes, certain foods like spicy meals, caffeine, and heavy or late-night meals can potentially contribute to nightmares. It’s a good idea to monitor your diet and see if there is a correlation between what you eat and the occurrence of nightmares.
4. Can children outgrow nightmares?
Most children do outgrow nightmares as they develop better coping mechanisms and their imaginations mature. However, if nightmares persist and significantly affect the child’s well-being, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and guidance.
5. Are there any medications that can help with nightmares?
In some cases, medications such as certain antidepressants or medications used to treat anxiety disorders may be prescribed to alleviate nightmares. However, the use of medication should always be discussed with a healthcare professional to weigh the benefits and potential side effects.
6. Can lucid dreaming be used to overcome nightmares?
Yes, lucid dreaming techniques can be employed to gain control over the dream and change the outcome, potentially turning a nightmare into a more positive experience. However, mastering lucid dreaming requires practice and dedication.
7. Can trauma play a role in the occurrence of nightmares?
Yes, trauma can often trigger nightmares. Traumatic experiences can leave a lasting impact on the subconscious mind and manifest in dreams as a way for the brain to process and cope with the emotional aftermath of the trauma.
8. Can night terrors be dangerous?
Night terrors themselves are not physically dangerous. However, during a night terror episode, the person may exhibit intense fear, scream, and thrash about, which can be alarming for anyone witnessing it. It’s important to create a safe sleep environment and ensure the person doesn’t harm themselves during the episode.
9. Can sleep disorders like sleep apnea contribute to nightmares?
Yes, certain sleep disorders, including sleep apnea, have been linked to an increased likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Treating the underlying sleep disorder may help alleviate the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
10. Should you wake up someone having a night terror?
No, it is generally advised not to wake up someone experiencing a night terror. Trying to wake them might increase their disorientation and confusion. Instead, ensure their safety by gently guiding them back to bed or providing a reassuring presence until the episode subsides.