Nightmares in Children: Causes and Solutions – Nightmares can be a frightening and distressing experience for children, causing significant disruptions to their sleep and overall well-being. It is important for parents and caregivers to understand the causes of nightmares and how to effectively address them. In this article, we will explore the various factors that contribute to nightmares in children, including anxiety, traumatic events, sleep disorders, and medications or illnesses. We will also delve into the effects of nightmares on children and provide helpful tips and strategies for preventing and addressing nightmares. By gaining knowledge and implementing appropriate solutions, parents can help their children overcome nightmares and enjoy a more peaceful and restful sleep.
Causes of Nightmares in Children

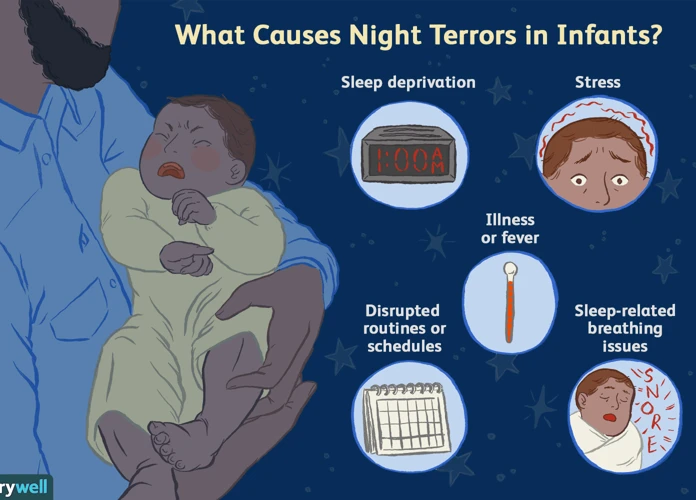
One of the main causes of nightmares in children is anxiety and stress. Children may experience feelings of worry, fear, or unease that can manifest in their dreams. These emotions can be triggered by various factors, such as school pressures, family conflicts, or changes in routine. Additionally, traumatic events can leave a lasting impact on a child’s mental and emotional well-being, leading to nightmares. These events may include accidents, natural disasters, or witnessing violence. Another possible cause is sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome, which can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and contribute to nightmares. Additionally, certain medications or illnesses can also impact a child’s dreams. For example, some medications used to treat ADHD or depression have been known to cause vivid dreams or nightmares. It is important for parents to be aware of these potential causes and take appropriate steps to address them.
1. Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and Stress can play a significant role in causing nightmares in children. Children may experience various sources of anxiety and stress, including academic pressures, social interactions, and family dynamics. These worries and concerns can manifest in their dreams, leading to nightmares. For example, a child who is anxious about an upcoming test or a stressful event at school may have nightmares about failing or being embarrassed. Additionally, conflicts within the family or changes in routine can also contribute to feelings of stress and anxiety in children, which may then be reflected in their dreams. It is important for parents to provide a supportive and nurturing environment for their children to help manage anxiety and stress levels. Creating a open line of communication with the child and addressing any underlying sources of stress can help reduce the occurrence of nightmares. Additionally, implementing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or guided imagery, can be beneficial in reducing anxiety and promoting more peaceful sleep. In some cases, if anxiety and stress persist or become overwhelming, it may be necessary to seek professional help to provide the child with the appropriate support and interventions.
2. Traumatic Events
Experiencing traumatic events can have a profound impact on a child’s mental and emotional well-being, often leading to nightmares. These events can range from accidents and natural disasters to witnessing or being a victim of violence. Trauma can disrupt a child’s sense of safety and security, leaving a lasting impression on their subconscious mind. Nightmares related to traumatic events may involve re-experiencing the event itself or elements associated with it. Children who have gone through traumatic experiences may have intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, or nightmares that reflect the distressing aspects of what they have witnessed or endured.
It is important for parents and caregivers to create a supportive and understanding environment for children who have experienced trauma. Providing a safe space for them to express their feelings and fears can help alleviate the intensity of nightmares. Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor who specializes in trauma can also be beneficial in assisting children with processing and coping with their experiences. Addressing trauma effectively is crucial in promoting healing and reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
Note: These nightmares can occur as a result of trauma, but they can also be influenced by other factors. For example, certain medications used to treat trauma-related symptoms may have an impact on dreams. To learn more about the impact of medication on nightmares, you can read our article on medication and how it affects nightmares. Additionally, some individuals have found relief from nightmares through practices such as lucid dreaming, where they gain awareness and control within the dream state. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before pursuing alternative methods.
3. Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders can significantly contribute to the occurrence of nightmares in children. Here are some common sleep disorders that can have a direct impact on a child’s dream patterns:
Insomnia: Insomnia in children can lead to difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night. This can result in increased awakenings during the REM (rapid eye movement) sleep phase, which is when nightmares are more likely to occur.
Sleep Apnea: Sleep apnea is a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. It can disrupt the child’s sleep cycle and cause fragmented sleep, increasing the likelihood of nightmares. Children with sleep apnea may also experience restless sleep, gasping for air, or snoring loudly.
Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS): RLS causes uncomfortable sensations in the legs, often described as a “creepy-crawly” feeling. These sensations can make it difficult for children to fall asleep and lead to more disturbed sleep patterns, potentially triggering nightmares.
Night Terrors: Although different from nightmares, night terrors are a sleep disorder that can cause significant distress for both the child and their caregivers. Night terrors typically occur during the non-REM sleep phase and can involve intense fear, screaming, and physical movements. While children may not remember the content of their night terrors, they can still impact the quality of their sleep and contribute to the development of nightmares.
It is important for parents to be aware of these sleep disorders and seek medical attention if they suspect their child may be experiencing them. Addressing and managing these sleep disorders can not only improve the child’s sleep quality but also help reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
4. Medications or Illnesses
Certain medications or illnesses can contribute to nightmares in children. When a child is taking certain medications, it can affect their dream patterns and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Medications used to treat conditions like attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or depression have been known to impact the content and intensity of dreams, sometimes resulting in vivid or disturbing nightmares. It is important for parents to discuss any concerns or observations about their child’s dreams with their healthcare provider to determine if the medication may play a role.
In addition to medications, certain illnesses can also trigger nightmares in children. For example, high fever or infection can disrupt the sleep patterns and lead to vivid dreams or night terrors. It is important to monitor the child’s symptoms and seek medical attention if necessary.
To address the impact of medications or illnesses on nightmares, it is crucial to communicate with the child’s healthcare provider. They can provide guidance on potential alternatives or adjustments to medications, if appropriate, to help minimize the occurrence of nightmares. It is important to follow the prescribed medication regimen and not make any changes without consulting a healthcare professional.
Additionally, when a child is experiencing an illness, providing comfort and a calm sleeping environment can help alleviate anxiety and contribute to a more peaceful sleep. Ensuring a consistent bedtime routine and creating a soothing atmosphere can also be beneficial in reducing the likelihood of nightmares.
Effects of Nightmares on Children
The effects of nightmares on children can be far-reaching and impact various aspects of their lives. It is essential for parents and caregivers to recognize these effects to provide appropriate support and intervention.
1. Disturbed Sleep: Nightmares can disrupt a child’s sleep, leading to frequent awakenings throughout the night. As a result, children may feel exhausted, irritable, and have difficulty concentrating during the day.
2. Anxiety and Fear: Nightmares can induce feelings of anxiety and fear in children. They may develop a fear of going to sleep, anticipating the recurrence of nightmares. This fear can further exacerbate sleep disturbances and impact their overall quality of life.
3. Emotional Distress: Nightmares can evoke intense emotions in children, causing them to wake up feeling scared, sad, or disturbed. These emotional experiences can linger into their waking hours, affecting their mood, behavior, and overall well-being.
4. Negative Impact on Mental Health: Persistent nightmares can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health issues in children, such as anxiety disorders or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It is important to address nightmares promptly to prevent the escalation of mental health concerns.
5. Impaired Cognitive Function: Lack of quality sleep due to nightmares can impair cognitive function and academic performance in children. They may have difficulty focusing, retaining information, and performing tasks that require attention and concentration.
6. Daytime Disturbances: The effects of nightmares can extend beyond the night. Children may experience daytime disturbances, including mood swings, irritability, and changes in behavior. They may also exhibit reluctance or resistance towards participating in activities they associate with the cause of their nightmares.
Understanding these effects emphasizes the need for effective strategies to address nightmares in children. By providing appropriate support and intervention, parents can help their children cope with the effects of nightmares and restore their overall well-being.
Signs and Symptoms of Nightmares

Children who experience nightmares may exhibit various signs and symptoms that indicate their distress. Frequent awakenings during the night are a common indication that a child is experiencing nightmares. They may wake up crying, sweating, or feeling scared, causing disruptions to their sleep patterns. Additionally, children who have nightmares may develop a fear of sleep. They may resist going to bed or exhibit anxiety or distress when it’s time to sleep. Difficulty falling asleep is another symptom to look out for. Children who have nightmares may struggle to fall asleep or experience restless and disturbed sleep patterns. Bedtime resistance is also common among children with nightmares. They may become resistant or hesitant to go to bed, expressing fear or reluctance. These signs and symptoms can be indicative of nightmares and should be addressed to ensure the child’s well-being and quality of sleep.
1. Frequent Awakenings
Frequent awakenings in children can be a sign of nightmares. When a child experiences frequent awakenings during the night, it disrupts their sleep pattern and can lead to excessive tiredness and irritability during the day. These awakenings are often accompanied by feelings of fear, anxiety, or distress, as the child may recall the content of their nightmares. It is important for parents to pay attention to these awakenings and provide reassurance and comfort to their child. Establishing a calming bedtime routine can help alleviate anxiety and promote a more restful sleep. Creating a sleep-friendly environment, such as a dimly lit and quiet bedroom, can also contribute to a better sleep quality and reduce the chances of frequent awakenings. If the frequency of awakenings persists or worsens over time, it may be beneficial to seek professional help to determine any underlying causes or to address any potential sleep disorders. It is essential to address frequent awakenings promptly to ensure that the child can achieve a healthy and restorative sleep.
2. Fear of Sleep
Children experiencing nightmares may develop a fear of sleep due to the unpleasant and scary experiences they have during the night. This fear can lead to avoidance behaviors and resistance towards bedtime. Here are some signs and symptoms that may indicate a fear of sleep in children:
- Nighttime Anxiety: Children may exhibit signs of anxiety and restlessness as bedtime approaches. They may express feelings of unease or fear about falling asleep, anticipating nightmares.
- Refusal to Sleep Alone: Children with a fear of sleep may demand constant companionship and resist sleeping alone. They may seek reassurance and comfort from a parent or sibling to ease their fears.
- Nighttime Waking: Children may experience frequent awakenings during the night due to their fear of sleep. These awakenings can disrupt their sleep patterns and contribute to ongoing sleep disturbances.
- Nighttime Rituals: Children may develop specific rituals or routines as part of their bedtime routine, such as checking under the bed or repeatedly asking for reassurance from their caregivers.
Addressing the fear of sleep in children is essential to help them overcome their nightmares and establish a healthier sleep routine. By creating a calm and comforting sleep environment, providing reassurance and support, and implementing relaxation techniques, parents can help their children gradually feel more secure and less fearful about going to sleep. It is crucial to establish open communication with the child, allowing them to express their fears and concerns, and actively listening to validate their emotions.
3. Difficulty Falling Asleep
Difficulty Falling Asleep
Difficulty falling asleep is another common sign and symptom of nightmares in children. When children struggle to fall asleep, it can be an indication that they are experiencing anxiety or fear surrounding their upcoming dreams. The anticipation of having a nightmare can create a sense of unease and reluctance to go to bed. This can result in bedtime resistance, prolonged tossing and turning, and an overall difficulty in settling down for sleep. Additionally, difficulty falling asleep may also be related to other sleep disorders, such as insomnia or sleep apnea. These conditions can further exacerbate the occurrence of nightmares and make it harder for children to fall into a restful sleep. Parents should closely observe their child’s bedtime routine and if they consistently display difficulty falling asleep, it is essential to address the underlying causes. Implementing a soothing bedtime routine, creating a safe sleep environment, and managing anxiety and stress can all contribute to improving a child’s ability to fall asleep more easily.
4. Bedtime Resistance
Bedtime Resistance refers to a situation where a child consistently resists going to bed at their designated bedtime. This can be a common issue that parents face and may contribute to nightmares in children. There are several factors that can lead to bedtime resistance. One possible reason is the fear of experiencing nightmares itself. If a child has had a particularly distressing nightmare in the past, they may develop anxiety and resistance towards going to bed as a way to avoid those terrifying dreams. Another factor could be a lack of routine or structure in the child’s bedtime routine. Inconsistent bedtimes, lack of soothing nighttime rituals, or excessive stimulation before bed can make it difficult for a child to wind down and feel relaxed enough to fall asleep. Additionally, some children may exhibit bedtime resistance as a way to assert their independence or seek attention from their parents. They may resist bedtime as a form of protest or as a means of prolonging their awake time. To address bedtime resistance, it is important for parents to establish a consistent and soothing bedtime routine. This may include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or engaging in calming activities. Creating a calm and peaceful sleep environment can also help. Removing electronic devices from the bedroom, ensuring the room is dark and quiet, and providing comforting objects like a favorite stuffed animal can all contribute to a more positive sleep environment. Consistent and clear communication about bedtime expectations can also help alleviate bedtime resistance. By addressing and resolving bedtime resistance, parents can help their child establish healthier sleep habits and reduce the likelihood of nightmares.
Preventing Nightmares in Children

To prevent nightmares in children, there are several helpful strategies that parents and caregivers can implement. Creating a soothing bedtime routine can signal to the child that it is time to relax and prepare for sleep. This can include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or listening to calming music. Managing anxiety and stress is crucial, as reducing these factors can minimize the chances of nightmares occurring. Encouraging open communication and providing outlets for emotional expression can help children cope with their worries. Providing a safe and positive sleep environment involves ensuring the child’s bedroom is comfortable, quiet, and free from any potential triggers. Installing a nightlight or a comfort object, such as a stuffed animal, can provide a sense of security. It is also important to limit exposure to frightening content before bedtime, such as scary movies or books. By following these preventive measures, parents can help their children have a more peaceful and nightmare-free sleep.
1. Create a Soothing Bedtime Routine
Establishing a soothing bedtime routine is crucial in promoting quality sleep and reducing the likelihood of nightmares in children. Consistency is key when it comes to bedtime routines, as it helps signal to the child’s body and mind that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. Start by setting a regular bedtime and stick to it as much as possible. Create a calm and peaceful environment in the child’s bedroom, free from distractions and stimulating activities. Incorporate relaxing activities into the routine, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing gentle stretching exercises. Avoid activities that may increase excitement or anxiety, such as playing video games or watching stimulating TV shows. Limit the consumption of sugary snacks or drinks close to bedtime, as they can interfere with the child’s ability to fall asleep peacefully. Additionally, ensure that the room is cool, quiet, and comfortable, with appropriate bedding and pillows. By implementing a consistent and soothing bedtime routine, parents can help their child transition into a state of relaxation and optimize their chances of having a peaceful night’s sleep.
2. Manage Anxiety and Stress
Managing anxiety and stress plays a crucial role in preventing and addressing nightmares in children. Here are some effective strategies that can help parents and caregivers in this endeavor:
- Establish a Calming Bedtime Routine: Create a consistent bedtime routine that promotes relaxation and calmness. This can include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing deep breathing exercises.
- Encourage Open Communication: Establish a supportive and open environment where your child feels comfortable expressing their feelings and worries. Encourage them to talk about their anxieties and provide reassurance and validation.
- Teach Relaxation Techniques: Teach your child relaxation techniques that can help reduce anxiety and promote better sleep. This can include techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, or mindfulness exercises.
- Promote Physical Activity: Engage your child in regular physical activities, as exercise releases endorphins and helps reduce stress levels. Encourage them to participate in activities they enjoy, such as sports, dancing, or yoga.
- Teach Coping Skills: Help your child develop healthy coping mechanisms to deal with stress and anxiety. This can include teaching them problem-solving skills, positive self-talk, and practicing self-care activities.
- Seek Professional Help: If your child’s anxiety and stress levels are significantly affecting their daily life and causing persistent nightmares, it may be beneficial to seek the assistance of a mental health professional. They can provide specialized guidance and techniques to address and manage anxiety effectively.
By actively managing anxiety and stress, parents can create a calmer bedtime environment and help their children develop healthy coping mechanisms, thereby reducing the occurrence of nightmares.
3. Provide a Safe and Positive Sleep Environment
When it comes to addressing nightmares in children, providing a safe and positive sleep environment is of utmost importance. Creating a conducive sleeping space can help alleviate anxiety and promote better sleep quality. Firstly, ensure that the bedroom is safe by removing any potential hazards, such as sharp objects or loose wires. Keep the room well-lit to reduce the fear of darkness. Use nightlights or dim lighting to create a soothing atmosphere. Additionally, maintaining a positive sleep environment involves establishing consistent bedtime routines. This can include activities like reading a bedtime story, listening to calm music, or engaging in relaxation techniques. A comfortable and supportive mattress is also essential for a restful sleep. Keep the bedroom at a comfortable temperature and minimize noise disruptions. It is important to foster a sense of security and comfort for the child, ultimately reducing the likelihood of nightmares and promoting a peaceful sleep environment.
4. Encourage Emotional Expression
Encouraging emotional expression is crucial when addressing nightmares in children. By creating a safe and supportive environment, parents can help their children process and express their emotions in healthy ways. Here are some strategies to promote emotional expression:
- Listen actively: Give your child your undivided attention and actively listen when they want to talk about their nightmares or fears. Validate their feelings and reassure them that it is normal to have these emotions.
- Provide a creative outlet: Encourage your child to express their feelings through art, writing, or imaginative play. This can help them externalize their emotions and gain a sense of control over their nightmares.
- Use storytelling: Engage in storytelling activities where your child can create their own narratives around their nightmares. This can help them process their fears and empower them to find positive resolutions.
- Keep a dream journal: Encourage your child to keep a journal or draw pictures of their dreams. This can provide them with a sense of agency over their dreams and help them explore their emotions more deeply.
- Model healthy emotional expression: Be open about your own emotions and demonstrate how to express them in a constructive manner. This sets a positive example for your child to follow.
By actively encouraging emotional expression, parents can help their children gain a better understanding of their nightmares and provide them with the necessary tools to cope with and overcome their fears.
5. Limit Exposure to Frightening Content
To help prevent nightmares in children, it is important to limit their exposure to frightening content. This includes scary movies, TV shows, books, and video games that may contain violent or disturbing imagery. Exposing children to such content, especially close to bedtime, can stimulate their imagination and contribute to anxiety and fear, increasing the likelihood of nightmares. Instead, encourage children to engage in more calming and positive activities before sleep, such as reading books with uplifting stories, listening to soothing music, or engaging in quiet play. Creating a list of age-appropriate and non-threatening media options can help guide parents in selecting content that is less likely to trigger nightmares. Additionally, discussing the content of movies, shows, or books with children can help them process any potential fears or concerns and provide reassurance. By being mindful of the media children consume, parents can help create a more peaceful and reassuring bedtime environment, reducing the risk of nightmares.
Addressing Nightmares in Children
When it comes to addressing nightmares in children, there are several strategies that parents and caregivers can employ. First and foremost, it is crucial to comfort and reassure the child after a nightmare, emphasizing that it was just a dream and not real. Encouraging the child to share and discuss their dreams can help them process any underlying emotions or fears. Teaching relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or visualization can also be beneficial in managing anxiety and promoting better sleep. Additionally, if nightmares persist or significantly impact the child’s well-being, it may be necessary to seek professional help from a child psychologist or counselor who specializes in sleep issues. Their expertise can provide valuable insights and interventions tailored to the child’s specific needs, facilitating the resolution of nightmares and promoting restful sleep.
1. Comfort and Reassure Your Child
When your child experiences a nightmare, it is crucial to provide comfort and reassurance to help them feel safe and secure. Here are a few strategies you can implement to accomplish this:
1. Create a Safe Environment: Ensure that your child’s bedroom is a comforting and relaxing space. Consider using a nightlight, comforting blankets, or a stuffed animal to help ease their anxieties.
2. Listen and Validate: When your child wakes up frightened from a nightmare, listen attentively to their concerns and validate their feelings. Let them know that it’s normal to have bad dreams sometimes, and that you are there to support them.
3. Offer Affection and Calming Techniques: Provide physical comfort by hugging or holding your child, reassuring them that they are safe. You can also teach them simple relaxation techniques like deep breathing or visualization exercises to help them calm down.
4. Encourage Reassurance Objects: If your child has a favorite toy or blanket, encourage them to keep it nearby during bedtime. Having a familiar object can provide a sense of security and comfort.
5. Establish a Bedtime Routine: Implement a consistent and soothing bedtime routine that includes activities like reading a book or engaging in calm activities. This can help your child feel more relaxed and prepared for sleep.
Remember, every child is unique, so find what works best for your child and adapt these strategies accordingly. By providing comfort and reassurance, you can help your child develop healthy coping mechanisms and create a positive association with sleep, reducing the occurrence of nightmares.
2. Encourage Dream Sharing
Encouraging dream sharing is a valuable strategy for addressing nightmares in children. When children share their dreams with a trusted adult, it provides them with an opportunity to express their feelings and emotions related to their nightmares. This process can help children gain a sense of control and understanding over their dreams, ultimately reducing the fear and anxiety associated with them. When discussing dreams, it is important for the adult to create a safe and non-judgmental environment, allowing the child to freely share their experiences. Parents and caregivers can engage in active listening, asking open-ended questions to encourage the child to elaborate on their dreams. Through this dialogue, the child may gain insights into the underlying factors contributing to their nightmares. Additionally, parents can offer comfort and reassurance, emphasizing that dreams are not real and helping the child reinterpret any scary or unsettling elements. This process of dream sharing not only helps children process their emotions but also strengthens the bond between the child and the adult.
3. Practice Relaxation Techniques
Practicing relaxation techniques can be a beneficial strategy for addressing nightmares in children. One effective technique is deep breathing exercises. Encourage your child to take slow, deep breaths in through their nose and out through their mouth. This simple act helps to relax the body and calm the mind. Another technique is progressive muscle relaxation, where the child focuses on tensing and then releasing each muscle group in their body, starting from their toes and working their way up to their head. This exercise promotes relaxation and reduces tension. Guided imagery is another valuable technique. Have your child close their eyes and imagine a peaceful, happy place, such as a beautiful beach or a serene forest. Encourage them to engage all their senses and really immerse themselves in the imagery. This can help distract from the distressing thoughts and feelings associated with nightmares. Additionally, incorporating mindfulness activities into your child’s daily routine can help reduce overall anxiety and promote relaxation. This can include simple practices such as mindful breathing, body scans, or guided meditation. By practicing these relaxation techniques regularly, your child can learn to manage stress and promote a sense of calm before bedtime, potentially reducing the occurrence of nightmares.
4. Seek Professional Help if Needed
: If your child continues to experience persistent and distressing nightmares despite your efforts to address them, it may be necessary to seek professional help. A pediatrician or a child psychologist with experience in sleep disorders can provide valuable guidance and assistance. They can assess your child’s overall sleep patterns, explore potential underlying causes, and recommend appropriate interventions. This may involve conducting further evaluations, such as sleep studies, to gather more information about your child’s sleep quality and patterns. The professional can also teach your child coping techniques, such as relaxation exercises or imagery rehearsal therapy, which can help them manage and overcome their nightmares. They may also suggest therapy or counseling sessions to address any underlying emotional issues contributing to the nightmares. Remember, seeking professional help is not a sign of weakness, but rather a proactive step towards ensuring your child’s well-being and helping them achieve restful and peaceful nights.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nightmares in children can be a common and distressing phenomenon that can significantly impact their sleep quality and overall well-being. By understanding the various causes of nightmares, such as anxiety, traumatic events, sleep disorders, and medications or illnesses, parents and caregivers can take proactive steps to prevent and address these nightmares effectively. Creating a soothing bedtime routine, managing anxiety and stress, providing a safe sleep environment, encouraging emotional expression, and limiting exposure to frightening content are all effective strategies for preventing nightmares in children. Additionally, addressing nightmares involves comforting and reassuring the child, encouraging dream sharing, practicing relaxation techniques, and seeking professional help if necessary. By implementing these preventive and addressing strategies, parents can help their children overcome nightmares and achieve a more peaceful and restful sleep. It is essential to remember that patience, understanding, and support are crucial in helping children navigate and overcome their nightmares successfully.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can nightmares in children be a sign of anxiety?
Yes, nightmares can often be a manifestation of anxiety in children. Anxiety can trigger intense emotions that may carry over into their dreams, causing frightening or distressing nightmares.
2. Are nightmares in children a result of trauma?
Yes, nightmares can be a common symptom of trauma in children. Traumatic events, such as accidents or witnessing violence, can impact a child’s mental well-being and lead to recurring nightmares.
3. Are sleep disorders a common cause of nightmares in children?
Yes, sleep disorders like sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome can disrupt a child’s sleep and contribute to nightmares. These conditions interfere with the normal sleep cycle, leading to vivid or disturbing dreams.
4. Can medications or illnesses cause nightmares in children?
Yes, certain medications used to treat conditions like ADHD or depression have been known to cause vivid dreams or nightmares in children. Additionally, illnesses that affect the central nervous system or cause fever may also contribute to nightmares.
5. How can nightmares affect a child’s well-being?
Nightmares can have a significant impact on a child’s well-being. They can lead to disrupted sleep, fear of going to bed, and difficulty falling asleep, which can result in daytime fatigue, irritability, and increased anxiety levels.
6. What are some signs that a child is experiencing nightmares frequently?
Frequent awakenings during the night, reluctance or fear of going to sleep, difficulty falling asleep, and bedtime resistance are common signs that a child may be experiencing nightmares on a regular basis.
7. How can parents create a soothing bedtime routine to prevent nightmares?
Parents can establish a consistent and calming bedtime routine by incorporating activities like reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques before bed. This can help promote a sense of relaxation and ease any anxious feelings that may contribute to nightmares.
8. Is it helpful for children to share their dreams with their parents or caregivers?
Yes, encouraging children to share their dreams with parents or caregivers can help them process any fears or anxieties associated with their nightmares. It also provides an opportunity for parents to reassure and comfort their child.
9. Are there relaxation techniques that can help children cope with nightmares?
Yes, relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery can be helpful in managing anxiety and promoting a sense of calm before bedtime, reducing the likelihood of nightmares.
10. When should parents consider seeking professional help for their child’s nightmares?
If nightmares persist over an extended period, significantly interfere with the child’s sleep quality and daily functioning, or if the child demonstrates increased anxiety or other emotional distress, it may be beneficial for parents to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or child psychologist.