Nightmares can be a distressing experience for children, causing fear and anxiety during their sleep. As parents and caregivers, it is important to understand the causes and effects of nightmares in order to provide the necessary support and solutions. In this article, we will explore the various factors that can trigger nightmares in children, including anxiety, traumatic experiences, sleep disorders, and fear of imaginary monsters. Additionally, we will discuss the potential effects of nightmares on children and offer practical solutions to help them cope, such as creating a calm sleeping environment, establishing a bedtime routine, encouraging open communication, providing reassurance and comfort, teaching relaxation techniques, and limiting exposure to scary media. Knowing when to seek professional help will also be addressed. Join us as we delve into the realm of children’s nightmares, unraveling their mysteries and finding ways to ease their nocturnal fears.
What are Nightmares?

Nightmares can be vivid and disturbing dreams that occur during the REM (rapid eye movement) stage of sleep. They often evoke intense emotions such as fear, anxiety, or sadness, and can be accompanied by physical symptoms like sweating, rapid heartbeat, or crying. These dreams tend to be more common in children, as their imagination and emotional experiences are still developing. Nightmares usually involve threatening or dangerous situations, and often include elements of monsters, animals, or being chased. The content of nightmares can vary greatly from one child to another, but they generally reflect the child’s fears or anxieties. While nightmares are a normal part of the dream cycle, they can disrupt a child’s sleep patterns and cause significant distress. Understanding the nature of nightmares is crucial in order to address and alleviate their impact on children’s sleep quality and overall well-being.
Causes of Nightmares in Children
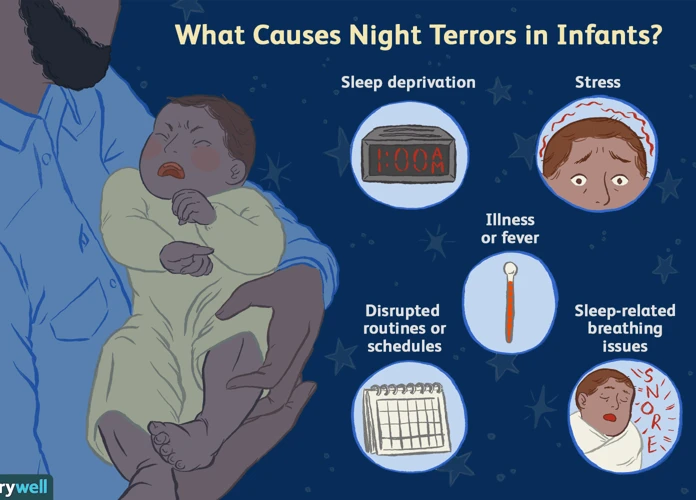
Nightmares in children can have various underlying causes. Understanding these causes is essential in order to address and mitigate the occurrence of nightmares. Some common triggers include:
– Anxiety and Stress: Children experiencing high levels of stress or anxiety, whether related to school, family issues, or social interactions, may be more prone to nightmares. Anxiety disorders can also contribute to the frequency and intensity of nightmares. (Learn more about the connection between nightmares and anxiety disorders here.)
– Traumatic Experiences: Children who have experienced a traumatic event, such as an accident or loss, may have nightmares as a result. These nightmares can be associated with reliving the traumatic experience or may simply reflect the child’s fear and distress.
– Sleep Disorders: Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome, can disrupt a child’s sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of nightmares. Addressing and managing these sleep disorders can help alleviate nightmares.
– Fear and Imaginary Monsters: Children’s vivid imagination, combined with fears of the dark or of imaginary creatures, can contribute to nightmares. Monsters, ghosts, or other fantastical elements may appear in their dreams, causing distress.
– Environmental Factors: Factors in a child’s environment, such as excessive noise, uncomfortable sleeping arrangements, or exposure to scary movies or stories, can also trigger nightmares. Creating a calm and safe sleeping environment is important for preventing nightmares and ensuring restful sleep.
By identifying and addressing these contributing factors, parents and caregivers can better support their children in coping with nightmares and promoting a healthier and more peaceful sleep experience. Additionally, exploring the symbolism of nightmares can provide further insights into their underlying causes and meaning. (Read more about exploring the symbolism of nightmares here.)
1. Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress are common triggers for nightmares in children. Just like adults, children can experience feelings of worry, fear, or unease, which can manifest in their dreams. Anxiety can stem from various sources, including separation anxiety, academic pressures, social interactions, or even changes in routine. Stressful events such as moving to a new school, parents divorcing, or the loss of a loved one can also contribute to heightened anxiety levels. These emotional disturbances can disrupt a child’s ability to relax and fall into a restful sleep, paving the way for nightmares to occur. It is essential for parents and caregivers to create a nurturing and supportive environment that helps alleviate anxiety and stress in children. By addressing underlying anxieties, such as through open communication and providing reassurance, it is possible to reduce the occurrence of nightmares linked to anxiety disorders.
2. Traumatic Experiences
Traumatic experiences can be a significant trigger for nightmares in children. These experiences may include events such as accidents, witnessing or being a victim of violence, natural disasters, or the loss of a loved one. When a child goes through a traumatic event, it can leave a lasting impact on their psyche, causing feelings of fear, anxiety, and distress. The memory and emotions associated with the trauma can manifest in nightmares during sleep, as the child’s subconscious tries to process and make sense of what they have experienced. These nightmares often involve reenactments of the traumatic event or may feature symbols and themes related to the incident. It is important for parents and caregivers to approach this sensitive topic with empathy and support. Providing a safe and nurturing environment for the child to express their feelings and emotions can greatly help in processing the traumatic experiences and reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Seeking professional help, such as therapy or counseling, may also be beneficial for children who have experienced trauma and continue to have persistent nightmares as a result (source).
3. Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares in children. One common sleep disorder that can lead to nightmares is called sleep apnea. This condition causes disruptions in breathing during sleep, which can result in fragmented sleep and increased arousal during the REM stage, where nightmares are most likely to occur. Another sleep disorder that may contribute to nightmares is restless leg syndrome (RLS), characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. RLS can disrupt sleep, leading to increased arousal and the potential for nightmares. Additionally, sleepwalking and night terrors, which are categorized as parasomnias, can also increase the likelihood of nightmares. These disorders involve abnormal behavioral or physiological events during sleep, causing distress and potential disruptions in sleep patterns. It’s important to recognize and address any underlying sleep disorders in children to help manage and reduce the frequency of nightmares. Seeking medical guidance and potentially undergoing a sleep study can aid in diagnosing and treating sleep disorders, promoting a healthier sleep environment for children.
4. Fear and Imaginary Monsters
Children’s imaginations are incredibly vibrant, and they often have a rich fantasy life. This imaginative world can sometimes lead to fear and the manifestation of imaginary monsters in their dreams. Fear of imaginary monsters is a common cause of nightmares in children. These monsters can take various forms, such as ghosts, zombies, or fantastical creatures. The fear of these imaginary beings is often rooted in children’s exposure to television shows, movies, books, or even stories told by peers. These external influences can fuel their imagination and create a sense of unease when it’s time for sleep. Additionally, developmental stages and cognitive leaps contribute to the creation of these imaginary monsters. As children begin to understand the concept of danger, their minds may invent creatures that represent this danger, leading to frightening dreams. It is important for parents to acknowledge and validate their child’s fears while providing reassurance and comfort. Open communication about their fears and helping them decipher between reality and imagination can alleviate their anxiety and reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
5. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can play a significant role in triggering nightmares in children. Here are some common environmental factors that can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares:
1. Exposure to Scary Media: Watching or reading content that is scary, violent, or unsettling before bedtime can stimulate a child’s imagination and lead to nightmares. It is important to limit their exposure to such media, including movies, TV shows, books, or video games that contain frightening or disturbing elements.
2. Sleep Environment: An uncomfortable or unfamiliar sleep environment can disrupt a child’s sleep and increase the likelihood of nightmares. Factors such as excessive noise, extreme temperatures, or sharing a bedroom with a sibling can contribute to disturbed sleep patterns and subsequent nightmares. Creating a calm and cozy sleep environment can help alleviate these factors.
3. Sleep Disruptions: Interruptions during sleep, such as frequent awakenings, loud noises, or bright lights, can disturb the natural sleep cycle and increase the chances of nightmares. Ensuring a quiet and peaceful sleep environment can minimize these disruptions and promote more restful sleep.
4. Sleep Routine Changes: Sudden changes in a child’s sleep routine, such as a new bedtime or inconsistent sleep schedule, can disrupt their sleep patterns and make them more prone to nightmares. Establishing a consistent bedtime routine can help provide a sense of security and stability, reducing the occurrence of nightmares.
5. Emotional Atmosphere: A tense or stressful emotional atmosphere at home can impact a child’s dreams. High levels of stress or unresolved conflicts within the family can contribute to anxiety and nightmares. Creating a positive and nurturing home environment can help alleviate these emotional triggers.
By identifying and addressing these environmental factors, parents and caregivers can create a sleep environment that promotes peaceful sleep and reduces the occurrence of nightmares in children.
Effects of Nightmares on Children

The effects of nightmares on children can be far-reaching and impact various aspects of their lives. Here are some key effects to be aware of:
1. Sleep Disturbances: Nightmares can disrupt a child’s sleep patterns, causing them to wake up frequently during the night. This can result in daytime sleepiness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating at school.
2. Anxiety and Fear: Experiencing disturbing dreams can lead to increased anxiety and fear in children. They may develop a fear of going to sleep or develop bedtime-related rituals in an attempt to avoid nightmares.
3. Emotional Distress: Nightmares can evoke intense emotions in children, such as sadness, anger, or confusion. These emotional responses can linger even after waking up, affecting their mood and overall well-being.
4. Impact on Mental Health: Long-term exposure to frequent nightmares can contribute to the development or exacerbation of anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
5. Disrupted Daily Functioning: The emotional and physical toll of nightmares can disrupt a child’s daily functioning. They may struggle with concentration, have difficulty participating in social activities, or experience a decline in academic performance.
6. Nighttime Rituals: To cope with nightmares, children may develop nighttime rituals or behaviors, such as avoiding certain foods or activities before bed, relying on nightlights, or seeking constant reassurance from their caregivers.
It is important to recognize the effects of nightmares on children and implement appropriate strategies to help them cope and overcome their impact.
Solutions to Help Children Deal with Nightmares

To help children deal with nightmares, there are several effective solutions that parents and caregivers can implement. Creating a calm and safe sleeping environment is crucial, ensuring that the child’s bedroom is free from any triggers or distractions that may contribute to nightmares. Establishing a consistent bedtime routine can also promote better sleep and reduce the likelihood of nightmares. Encouraging open communication with the child allows them to express their fears and concerns, providing an opportunity for reassurance and comfort. Teaching relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or visualization exercises, can help children manage anxiety and promote a sense of calm before bed. Limiting exposure to scary media, such as TV shows or movies, is important as it can instill fear and contribute to nightmares. By implementing these solutions, parents can help their children cope with nightmares and promote a peaceful and restful night’s sleep.
1. Create a Calm and Safe Sleeping Environment
To help children deal with nightmares, it is important to create a calm and safe sleeping environment. Here are some strategies to achieve this:
- Soothing colors and decor: Use soft, calming colors for the walls and bedding in your child’s bedroom. Avoid bright or stimulating colors, as they can contribute to a restless sleep. Opt for a night light that emits a gentle, warm glow to provide a sense of security.
- Comfortable bedding: Make sure your child’s mattress and pillows are comfortable and supportive. Consider using soft, breathable fabrics that promote a cozy sleep environment. Ensure that the room is at a comfortable temperature, neither too hot nor too cold.
- Noise reduction: Minimize any sources of noise that may disrupt your child’s sleep. Use white noise machines or fans to create a soothing background noise that can drown out other sounds. If there are external noises that cannot be controlled, consider using earplugs or a white noise app on a smartphone.
- Safe sleeping practices: Ensure that your child’s sleeping area is free from potential hazards. Remove any objects or furniture that could pose a safety risk. Keep cords from blinds or curtains out of reach, and ensure that the room is childproofed to prevent accidents.
- Establish a consistent bedtime routine: A predictable routine can signal to your child that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. This can include activities such as a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music. Consistency and repetition help create a sense of security and relaxation.
- Avoid stimulating activities before bed: Limit your child’s exposure to screens, such as television, video games, and electronic devices, in the hours leading up to bedtime. The blue light emitted by screens can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.
By implementing these strategies, you can create a calm and safe sleeping environment that promotes better sleep and reduces the likelihood of nightmares. Remember, consistency and comfort are key factors in establishing a peaceful bedtime routine for your child.
2. Establish a Bedtime Routine
Establishing a consistent bedtime routine is an effective way to help children deal with nightmares. A structured routine before bed creates a sense of security and signals to the child that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. The routine can include activities such as bathing, brushing teeth, changing into pajamas, and reading a calming bedtime story. It’s important to choose activities that promote relaxation and avoid stimulating the child’s mind or body. For instance, engaging in high-energy play or allowing screen time before bed can interfere with the transition to sleep. Instead, opt for activities that encourage calmness, such as gentle stretching or listening to soothing music. Additionally, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, including a regular bedtime and wake-up time, helps regulate the child’s internal clock and promote better sleep patterns. By following a predictable bedtime routine, children can feel more secure and at ease, reducing the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
3. Encourage Open Communication
Encouraging open communication is essential when helping children deal with nightmares. Creating a safe and non-judgmental space for children to express their feelings allows them to process their experiences and fears. When a child has a nightmare, it is important to actively listen to their concerns and provide a supportive environment for them to share what they experienced. Validate their emotions and let them know that it is normal to feel scared or anxious after a nightmare. Engage in a conversation with the child, asking them to describe their dream and what they think may have triggered it. This can help uncover any underlying anxieties or stressors that may be contributing to the nightmares. Additionally, encourage the child to express any recurring themes or patterns they notice in their dreams. Regular communication about their dreams can help them gain insights into their own thoughts and emotions, promoting self-awareness and potentially reducing the frequency or intensity of the nightmares. Emphasize that they can always come to you or another trusted adult to talk about their dreams. By maintaining open lines of communication, you are providing valuable support to help children cope with their nightmares.
4. Provide Reassurance and Comfort
When a child wakes up from a nightmare, it is important to provide them with reassurance and comfort. Let them know that it was just a dream and that they are safe. Offering words of comfort and empathy can help alleviate their fears and anxieties. Sit with the child, hold their hand, and listen to their concerns. Assure them that you are there to protect and support them. It is important not to dismiss their feelings or belittle their fears, as this can invalidate their emotions. Instead, validate their experiences and offer understanding. Reassure them that nightmares are a normal part of growing up and that many children experience them. Encourage them to express their feelings and thoughts about the nightmare, as talking about it can help them process their emotions. Providing a sense of safety and security through your presence and kind words can help the child feel comforted and ease their distress.
5. Teach Relaxation Techniques
Teaching relaxation techniques to children can be an effective way to help them cope with nightmares and reduce their anxiety. Here are some techniques that you can incorporate into your child’s bedtime routine:
1. Deep Breathing: Encourage your child to take slow, deep breaths in through their nose and out through their mouth. This technique helps activate the body’s relaxation response.
2. Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Guide your child to tense and then relax each muscle group in their body, starting from their toes and working their way up to their head. This technique promotes relaxation and body awareness.
3. Visualization: Encourage your child to imagine a calm and peaceful place, such as a beach or a meadow. Help them visualize the details, such as the sound of waves or the smell of flowers.
4. Mindfulness: Teach your child to focus on the present moment by paying attention to their senses. You can guide them to notice the sensations of their breath, the sounds around them, or the feeling of their body against the bed.
5. Guided Imagery: Use gentle and soothing language to guide your child through a calming scenario, such as floating on a cloud or drifting on a calm boat on a lake.
By practicing these relaxation techniques regularly, your child can develop a sense of control over their emotions and learn to calm themselves when they experience nightmares. It is important to be patient and supportive as they learn these techniques, and to make them a consistent part of their daily routine.
6. Limit Exposure to Scary Media
Limiting exposure to scary media is an important step in helping children deal with nightmares. Scary movies, television shows, video games, and even books can contribute to the development or intensification of nightmares. The vivid and often graphic imagery in these media forms can trigger fear and anxiety in children, making it harder for them to differentiate between fantasy and reality. It’s essential for parents and caregivers to be mindful of the content their children are exposed to and set appropriate boundaries. Encourage them to engage in age-appropriate and non-threatening forms of entertainment. Instead of scary movies or shows, opt for educational programs, cartoons, or books that promote positive and imaginative storytelling. Additionally, creating a media-free zone in the bedroom can help promote a calm and peaceful sleeping environment, minimizing the chances of scary media content infiltrating their thoughts and dreams. By actively managing and monitoring their exposure to scary media, parents can reduce the likelihood of nightmares and help children feel more secure during sleep.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional help for your child’s nightmares is important to ensure their well-being and address any underlying issues. While most nightmares are a normal part of childhood and resolve on their own, there are instances where professional intervention may be necessary. Here are some indicators that indicate it may be time to seek professional help:
1. Frequent and Intense Nightmares: If your child experiences nightmares regularly and they are particularly intense or disruptive, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare professional. This is especially true if the nightmares persist for an extended period of time.
2. Impact on Day-to-Day Functioning: If your child’s nightmares are interfering with their overall mood, behavior, or daily activities, it could be a sign that professional assistance is needed. This could manifest as changes in appetite, difficulty concentrating, or increased anxiety during waking hours.
3. Sleep Disturbances: If your child is consistently having trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiences other sleep-related issues alongside their nightmares, it may be helpful to seek professional guidance. Sleep disorders such as sleep apnea or insomnia could be contributing factors.
4. Traumatic Experiences: If your child has experienced a traumatic event, such as the loss of a loved one or exposure to violence, and their nightmares persist or worsen, a mental health professional specializing in trauma may be able to provide the necessary support and therapy.
5. Unusual Symptoms or Behaviors: If your child displays any unusual symptoms or behaviors in addition to their nightmares, such as frequent night terrors, sleepwalking, or extreme fear of going to sleep, it is advisable to seek professional guidance.
Remember, every child is different, and what might be cause for concern for one child may not be for another. Trust your instincts as a parent, and if you feel that your child’s nightmares are significantly impacting their well-being, it is always best to reach out to a healthcare professional or a pediatrician. They can assess the situation and provide appropriate guidance or referrals to specialists, such as child psychologists or sleep medicine specialists, who can help your child in managing their nightmares effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nightmares can be a common occurrence in children and can stem from various causes such as anxiety, traumatic experiences, sleep disorders, fear, and environmental factors. These nightmares can have negative effects on children, leading to disrupted sleep, fear, and emotional distress. However, there are several solutions that can help children cope with nightmares. Creating a calm and safe sleeping environment, establishing a consistent bedtime routine, encouraging open communication, providing reassurance and comfort, teaching relaxation techniques, and limiting exposure to scary media can all contribute to alleviating the frequency and intensity of nightmares. It is important for parents and caregivers to recognize when professional help may be needed, such as when nightmares persist and significantly interfere with a child’s daily life. By understanding the causes and effects of nightmares and implementing appropriate solutions, we can support children in overcoming their nighttime fears and promoting better sleep quality. Remember, with patience, understanding, and a nurturing environment, children can conquer their nightmares and enjoy peaceful, restful nights.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What age group is most commonly affected by nightmares?
Nightmares are most commonly experienced by children between the ages of 3 and 12. During this stage of development, children’s imaginations are active, and they may struggle with fears and anxieties.
2. Are nightmares a sign of a more serious underlying condition?
While nightmares themselves are a normal part of sleep, frequent or recurring nightmares can sometimes indicate underlying issues such as anxiety disorders or trauma. If you are concerned about your child’s nightmares, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.
3. Can nightmares be prevented?
While it may not be possible to entirely prevent nightmares, there are steps that can be taken to reduce their occurrence. Creating a calming bedtime routine and providing a safe sleeping environment can help minimize nightmares in children.
4. How can I help my child if they wake up from a nightmare?
When your child wakes up from a nightmare, it’s important to provide comfort and reassurance. Stay with them until they feel calm, offer soothing words, and help them return to sleep if they wish.
5. Is there a connection between nightmares and sleep disorders?
Yes, nightmares can be associated with sleep disorders such as sleep apnea or insomnia. Addressing any underlying sleep issues can often help reduce the frequency of nightmares in children.
6. Can certain foods or beverages trigger nightmares?
While there is no conclusive evidence linking specific foods or beverages to nightmares, consuming caffeine or sugary treats close to bedtime may increase the likelihood of disrupted sleep and, consequently, nightmares.
7. Should I wake my child up during a nightmare?
It is generally advised not to wake your child up abruptly during a nightmare, as it may confuse and disorient them. Instead, try to provide a comforting presence and wait for them to naturally awaken or settle down.
8. Can talking about nightmares help alleviate them?
Encouraging open communication about nightmares can help children process their fears and anxieties. By discussing their nightmares in a supportive and non-judgmental manner, you can provide reassurance and assist them in finding coping strategies.
9. How long do nightmares typically last?
Nightmares can vary in duration, but they typically last for a few minutes. The emotional impact, however, may linger longer, causing distress and difficulty falling back asleep.
10. When should I seek professional help for my child’s nightmares?
If your child experiences frequent nightmares that significantly disrupt their sleep, cause excessive distress, or interfere with their daily functioning, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a pediatric psychologist specializing in sleep disorders.