Nightmares in Children: Causes and Ways to Help
Nightmares can be a frightening and distressing experience for children, causing sleep disruptions and negative impacts on their emotional well-being. Understanding the causes behind nightmares is crucial in helping children cope with them effectively. This article explores the various factors that contribute to nightmares in children, including stress, traumatic experiences, sleep disorders, and the influence of imagination and media. Additionally, it discusses the potential effects of nightmares on children, such as emotional distress, sleep disturbances, and behavioral changes. This article provides useful strategies and techniques for parents and caregivers to assist children in managing and overcoming nightmares. Finally, it highlights the scenarios in which seeking professional help becomes necessary to address persistent nightmares and severe anxiety. By gaining insights into the causes of nightmares and implementing appropriate support, parents can alleviate their children’s distress and promote healthier sleep patterns.
Causes of Nightmares in Children

Nightmares in children can stem from various causes that contribute to their vivid and distressing dreams. 1. Stress and anxiety are common triggers for nightmares, as children often experience pressure from school, relationships, or family situations. 2. Traumatic experiences such as accidents, loss, or physical or emotional abuse can lead to the manifestation of nightmares. These distressing events often linger in a child’s subconscious, surfacing during sleep. 3. Sleep disorders like sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome can disrupt the sleep cycle, resulting in nightmares. Additionally, certain medications might also affect the content of dreams and contribute to nightmares. [Learn more about the effects of medications on dreams and nightmares]. 4. Imagination and media influence can play a role in the occurrence of nightmares. Children with vivid imaginations and exposure to frightening content, whether through books, movies, or games, may experience nightmares influenced by these stimuli. Exploring the diverse causes of nightmares in children helps parents and caregivers gain insight into their child’s experiences and enables them to support the child effectively in addressing and overcoming these unsettling dreams.
1. Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety are significant contributing factors to the occurrence of nightmares in children. When children experience high levels of stress or anxiety, it can disrupt their sleep patterns and lead to unsettling dreams. Stressors such as academic pressure, conflicts within the family, or social challenges can overwhelm a child, causing them to feel anxious and worried even during their sleep. These feelings often manifest as nightmares, reflecting their underlying fears and concerns. Additionally, anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder or separation anxiety disorder, can also increase the likelihood of nightmares in children. In some cases, nightmares can even be a reflection of the child’s subconscious attempt to process and cope with their stress or anxiety. Addressing stress and anxiety in children is crucial in minimizing the occurrence of nightmares. Providing a nurturing and supportive environment, teaching stress management techniques, and encouraging open communication can help alleviate the child’s anxiety. If the child’s anxiety persists or worsens, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor may be beneficial. Understanding the connection between stress, anxiety, and nightmares is essential in assisting children in managing their emotions and promoting more restful sleep. [Learn more about the role of trauma in nightmares and dream analysis].
2. Traumatic Experiences
Traumatic experiences can have a significant impact on children’s mental and emotional well-being, often leading to the occurrence of nightmares. These distressing events can range from accidents and injuries to the loss of a loved one, physical or emotional abuse, witnessing violence, or experiencing natural disasters. The traumatic memories and emotions associated with such events can linger in a child’s subconscious mind, resurfacing during sleep in the form of nightmares. Traumatic nightmares can be vivid and intense, replaying the distressing event or bringing forth related fears and anxieties. These nightmares can be particularly distressing for children, as they may experience a heightened sense of fear, helplessness, and vulnerability. Nightmares related to traumatic experiences are a natural response to processing and coping with the trauma. It is important for parents and caregivers to provide a safe and supportive environment for children to express their emotions and fears. Seeking professional help from therapists or counselors who specialize in trauma can be beneficial in helping children navigate and heal from these experiences. Additionally, understanding the potential connection between nightmares and sleep disorders like post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can aid in addressing and managing the impact of trauma on a child’s sleep patterns. [Learn more about the connection between nightmares and sleep disorders].
3. Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders can significantly contribute to the occurrence of nightmares in children. These disorders disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to restless and fragmented sleep, which can trigger vivid and intense dreams. One common sleep disorder associated with nightmares is sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, causing the child to wake up briefly, gasping for air. These abrupt awakenings can increase the likelihood of nightmares. Another sleep disorder that may contribute to nightmares is restless leg syndrome. This condition causes uncomfortable sensations in the legs, leading to an irresistible urge to move them. The frequent movements and disruptions in sleep can increase the occurrence of nightmares. It’s essential for parents to recognize the signs and symptoms of sleep disorders in their children, such as snoring, restless sleep, or excessive daytime sleepiness. Consulting a pediatrician or a sleep specialist can help diagnose and manage these sleep disorders, potentially decreasing the frequency and intensity of nightmares in children. Understanding the connection between sleep disorders and nightmares can guide parents and caregivers in seeking appropriate treatment and support for their children. [Unraveling the connection between nightmares and sleep disorders].
4. Imagination and Media Influence
Children’s vivid imagination and exposure to various forms of media can significantly influence the occurrence of nightmares. Here are a few key points to consider when exploring the connection between imagination, media, and nightmares:
Imagination:
– Children with active and imaginative minds may be more prone to nightmares. Their vivid imagination can create elaborate scenarios during sleep, sometimes leading to unsettling or frightening dreams.
– Fantasy play, storytelling, and imaginative games can stimulate a child’s mind, potentially influencing the content of their dreams.
– Overactive imagination, particularly when fueled by anxiety or fear, can contribute to the intensity and frequency of nightmares.
Media Influence:
– Books, television shows, movies, and video games can expose children to content that may be scary or distressing. Images, characters, or storylines from these sources can linger in a child’s mind, manifesting in nightmares.
– Not all media exposure leads to nightmares, but certain genres, such as horror or suspense, might increase the likelihood of unsettling dreams. Additionally, age-inappropriate content or exposure to media that a child is not yet emotionally ready for can contribute to nightmares.
– Paying attention to the types of media children consume and monitoring their exposure to frightening or disturbing content is important in reducing the risk of nightmares.
Managing Imagination and Media Influence:
– Encouraging creative outlets during waking hours, such as art, storytelling, or imaginative play, can help children channel their imagination in a positive way, potentially reducing the occurrence of nightmares.
– Setting boundaries and age-appropriate guidelines for media consumption can minimize exposure to content that may trigger nightmares.
– Engaging in open and honest conversations with children about their fears, discussing the difference between reality and fictional content, and providing comfort and reassurance can help alleviate any distress caused by imagination or media influence.
A child’s imagination and exposure to media can play a significant role in the occurrence of nightmares. Nurturing a child’s imagination while monitoring their media consumption allows parents and caregivers to create a healthy balance that supports positive dreaming experiences.
Impact of Nightmares on Children
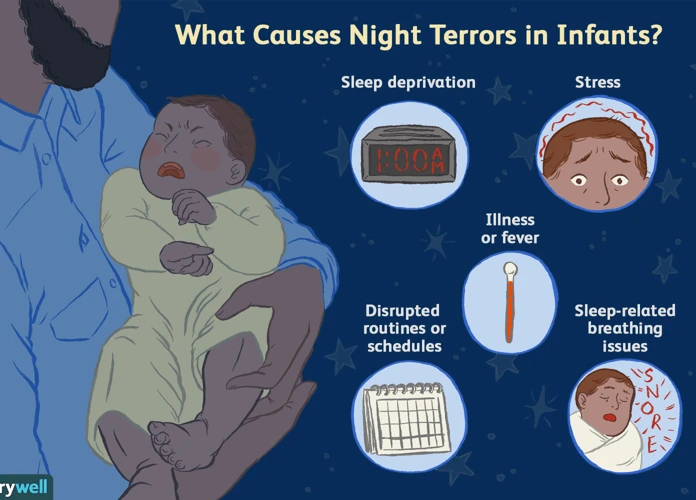
Nightmares can have a significant impact on children, affecting different aspects of their well-being. 1. Emotional distress is a common consequence of nightmares, as children may experience fear, anxiety, and a sense of helplessness after waking up from a terrifying dream. These intense emotions can linger throughout the day, impacting their mood and overall emotional stability. 2. Sleep disruptions are another consequence of nightmares, as they can lead to difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep. This can result in daytime sleepiness, decreased concentration, and poor academic performance. 3. Behavioral changes can occur as a result of nightmares, with children displaying clinginess, separation anxiety, or a fear of going to bed. They may also exhibit changes in their behavior such as aggression or withdrawal. Recognizing the impact of nightmares on children is crucial for parents and caregivers to provide the necessary support and interventions to help them navigate through and overcome the negative effects of these frightening dreams.
1. Emotional Distress
When children experience nightmares, it can result in significant emotional distress. Nightmares often elicit intense feelings of fear, anxiety, and sadness, causing a child to wake up feeling scared and unsettled. The vivid and realistic nature of these dreams can make it challenging for children to differentiate between the dream world and reality, further intensifying their emotional response. These distressing emotions can linger even after waking up, affecting a child’s overall mood and well-being. Children may experience difficulty in calming themselves down and may seek comfort and reassurance from their parents or caregivers. It is essential for adults to provide a safe and understanding environment for children to express their emotions and process the fear and anxiety associated with nightmares. Offering empathy, hugs, and soothing words can help alleviate the emotional distress caused by nightmares and ease a child’s transition back to a peaceful state of mind.
2. Sleep Disruptions
Sleep disruptions play a significant role in exacerbating nightmares in children. When a child doesn’t get enough quality sleep, their overall well-being can be affected, including their dreams. Here are some ways in which sleep disruptions can contribute to nightmares:
A. Irregular Sleep Schedule: Inconsistent bedtimes and wake-up times can disrupt the natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to fragmented sleep. This can increase the likelihood of nightmares as the child’s sleep patterns become disrupted.
B. Poor Sleep Environment: An uncomfortable sleep environment, such as excessive noise, uncomfortable bedding, or a room that is too hot or cold, can interfere with a child’s ability to fall asleep and stay asleep. This can lead to restless sleep and an increased chance of nightmares.
C. Sleep Disorders: Certain sleep disorders like sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome can disrupt a child’s sleep, making them more prone to nightmares. Addressing and treating these underlying sleep disorders can help reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
D. Disrupted Sleep Cycle: Disruptions in the different stages of sleep, particularly the REM (rapid eye movement) stage, can impact a child’s dreams. When the REM stage is interrupted or shortened, it can result in more intense and vivid dreaming, increasing the likelihood of nightmares.
To minimize sleep disruptions and promote better sleep quality, it is essential to establish a regular bedtime routine, create a comfortable sleep environment, and address any underlying sleep disorders. By ensuring that children get enough restful sleep, the frequency and intensity of nightmares can be effectively reduced.
3. Behavioral Changes
Nightmares in children can not only affect their emotional well-being and sleep patterns but also result in noticeable behavioral changes. These changes can manifest in a variety of ways, including:
1. Increased clinginess: Children may become more dependent on their parents or caregivers, seeking comfort and reassurance throughout the day. They may display clinginess or separation anxiety, fearing that something bad might happen.
2. Aggression and irritability: Nightmares can leave children feeling agitated and irritable during the day. They may exhibit increased aggression towards others, as they struggle to process and cope with the distressing feelings associated with their dreams.
3. Avoidance of sleep: Children who experience frequent nightmares may develop a fear of going to sleep. They may resist bedtime or exhibit signs of anxiety, such as requesting to sleep with a light on or in the presence of a parent.
4. Behavioural regression: Some children may exhibit regression in their behavior, reverting to behaviors they had previously outgrown. This could include bedwetting, thumb-sucking, or seeking excessive comfort and attention.
5. Difficulty concentrating: Nightmares can leave children feeling tired and emotionally drained, which can impact their ability to concentrate and focus. They may have difficulty paying attention in school or completing tasks.
6. Changes in appetite: Nightmares can disrupt a child’s appetite, leading to changes in eating habits. Some children may experience a decrease in appetite, while others may turn to food as a source of comfort, leading to an increase in emotional eating.
It is important for parents and caregivers to recognize these behavioral changes and understand that they are likely a result of the child’s distress from nightmares. By providing support, reassurance, and implementing strategies to address the underlying causes of nightmares, parents can help their children navigate through these behavioral challenges and restore a sense of normalcy to their daily lives.
Ways to Help Children Deal with Nightmares

When it comes to helping children deal with nightmares, there are several strategies that can provide comfort and reassurance. 1. Create a calm bedtime routine that promotes relaxation and a sense of security. This can include activities like reading a soothing story or engaging in calming activities before sleep. 2. Provide comfort and reassurance when a child wakes up from a nightmare. Offering hugs, cuddles, and soothing words can help alleviate fear and anxiety. 3. Encourage dream journaling as a way for children to express their feelings and thoughts about their nightmares. This can provide a sense of control and understanding. 4. Teach relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation to help children relax before bed and when they wake up from a nightmare. 5. Limit exposure to frightening content in books, movies, and games, as this can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. By implementing these strategies, parents can empower their children to navigate and cope with nightmares in a positive and supportive manner.
1. Create a Calm Bedtime Routine
Creating a calm bedtime routine is an essential step in helping children deal with nightmares and promoting better sleep quality. Here are some key strategies to incorporate into the routine:
1. Consistency: Establish a consistent bedtime schedule, ensuring that your child goes to bed and wakes up at the same time every day. This consistency helps regulate their body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep.
2. Relaxation activities: Incorporate relaxing activities into the bedtime routine, such as reading a book, listening to soft music, or taking a warm bath. These activities help calm the mind and prepare the body for sleep.
3. No screens before bed: Avoid exposing your child to electronic devices, such as smartphones or tablets, before bedtime. The blue light emitted by these devices can interfere with the production of melatonin, the hormone responsible for inducing sleep.
4. Dim the lights: Create a soothing environment by dimming the lights in your child’s bedroom. This helps signal to their brain that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
5. Avoid stimulating foods and drinks: Limit the consumption of sugary or caffeinated foods and drinks close to bedtime, as these can disrupt sleep patterns and increase the likelihood of nightmares.
6. Comfortable sleep environment: Ensure that your child’s bedroom is cool, quiet, and comfortable. Use cozy bedding, a supportive mattress, and consider using white noise machines or soft music to create a tranquil atmosphere.
By incorporating these steps into a regular bedtime routine, parents can help create a calm and soothing environment that promotes better sleep and reduces the chances of nightmares occurring. Consistency and a peaceful atmosphere can significantly contribute to a child’s overall sleep quality and well-being.
2. Provide Comfort and Reassurance
Providing comfort and reassurance is a crucial step in helping children cope with nightmares. When a child wakes up from a nightmare, they may feel scared, anxious, or confused. It is important for parents and caregivers to create a supportive and nurturing environment. Offering comfort and reassurance helps the child feel safe and secure after a frightening dream.
When a child wakes up from a nightmare, acknowledge their feelings and let them know that it is okay to feel scared. Reassure them that nightmares are a normal part of life and that many children experience them too. Validate their emotions by saying something like, “I understand that you had a scary dream and it can be upsetting. But remember, it was just a dream, and I’m here to keep you safe.”
Physical comfort can also be incredibly comforting during this time. Hug your child or hold their hand to provide a sense of security. Offer to stay with them until they feel calm and ready to go back to sleep. Creating a cozy and calming sleep environment can also help alleviate their fears. Consider using a night light or playing soothing music to create a soothing atmosphere in their bedroom.
Encourage them to talk about their dream if they feel comfortable doing so. Sometimes, verbalizing their fears can help diminish their intensity. Listen attentively and validate their feelings throughout the conversation. Avoid dismissing their dreams as “just a dream” or belittling their experiences. Instead, show empathy and provide support.
In addition to immediate comfort, establishing a routine for the following nights can be beneficial. Reinforce the idea that their sleep environment is safe and that there are measures in place to prevent nightmares. This can include checking the room for any potential sources of fear before bedtime (such as monsters or shadows) and providing reassurance that there are no real dangers present.
By providing the necessary comfort and reassurance when a child wakes up from a nightmare, parents and caregivers can help ease their distress, build trust, and create a sense of security.
3. Encourage Dream Journaling
Encouraging dream journaling in children can be a helpful technique to not only provide them with an outlet for expressing their dreams but also to gain insights into their subconscious thoughts and emotions. Dream journaling involves keeping a notebook or journal by the child’s bedside where they can record their dreams immediately upon waking up. This practice helps in enhancing their dream recall and allows them to reflect on the content of their dreams later. By engaging in dream journaling, children develop a stronger connection with their inner thoughts and feelings, leading to a better understanding of their fears, hopes, and desires. It also promotes creativity and imagination as they express their dreams through writing or drawing. Parents can actively participate in this process by discussing the dreams with their child, asking open-ended questions, and providing a supportive environment for them to freely share their dreams. Encouraging children to engage in dream journaling not only aids in processing their dreams but can also serve as a valuable tool for identifying recurring patterns, themes, and emotions within their dreams. Over time, this practice can contribute to a deeper self-awareness and potentially provide clues for addressing any recurring nightmares or emotional concerns.
4. Teach Relaxation Techniques
Teaching relaxation techniques to children can be highly beneficial in helping them cope with nightmares and promote better sleep. Deep breathing exercises can be taught as a simple yet effective technique to calm the mind and body. Encourage your child to take slow, deep breaths, inhaling deeply through the nose and exhaling slowly through the mouth. Another technique is progressive muscle relaxation, where the child systematically tenses and relaxes different muscle groups. This can help them identify and release tension in their body, promoting relaxation. Mindfulness exercises can also be introduced, such as guided imagery or focusing on the present moment. Engaging in activities like gentle stretching or bedtime yoga can also aid in relaxation. Additionally, using calming sensory tools such as a weighted blanket or lavender-scented pillow can create a soothing environment for sleep. It is important to practice these relaxation techniques regularly with your child, both during the day and at bedtime, to make them a natural part of their routine. By incorporating these techniques, you can help your child develop effective coping mechanisms to manage nightmares and promote a sense of calmness before bedtime.
5. Limit Exposure to Frightening Content
When dealing with nightmares in children, it is essential to limit their exposure to frightening content. By controlling what children see, read, or watch, parents can help create a safer and more positive environment for their child’s mental well-being. Here are some practical strategies to consider:
Avoiding Graphic or Violent Media: Monitor the type of media your child consumes, including television shows, movies, video games, and books. Opt for age-appropriate and wholesome content that doesn’t contain scary or violent themes.
Establishing Screen Time Guidelines: Set clear boundaries on screen time and ensure that your child’s exposure to electronic devices is controlled. Excessive screen time, especially before bedtime, can contribute to nightmares. Encourage alternative activities such as reading, outdoor play, or creative pursuits.
Engaging in Open Communication: Talk to your child about their fears and concerns. Encourage them to share any distressing content they may have encountered, such as scary stories from classmates or disturbing images online. Providing a safe space for discussion can help alleviate their anxieties.
Involving Age-Appropriate Content: Be mindful of the age recommendations for various media. Ensure that the content your child engages with aligns with their developmental stage and emotional maturity. This approach helps prevent exposure to topics that may be too overwhelming for them.
Modeling Healthy Media Consumption: Be a positive role model by monitoring your own media consumption habits. Limit your exposure to frightening or distressing content, especially in the presence of your child. This practice helps create a calm and secure atmosphere at home.
Encouraging Pre-Bedtime Relaxation: Establish a relaxing pre-bedtime routine that avoids any stimulating or scary content. Engage in activities like reading a calming book, listening to soothing music, or practicing deep breathing exercises. These activities promote a sense of calm and reduce the chances of nightmares occurring during sleep.
By implementing these strategies, parents can actively protect their children from unnecessary exposure to frightening content and ultimately help reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
When to Seek Professional Help
Recognizing when to seek professional help is crucial in providing appropriate support for children experiencing persistent nightmares and severe anxiety. Here are some indicators that may signal the need for professional intervention: 1. Persistent nightmares that continue to occur frequently and disrupt the child’s sleep and daily functioning. If nightmares persist despite attempts to address them, consulting a healthcare professional or pediatrician is advisable. 2. Severe anxiety and fear accompanying nightmares, where the child experiences extreme distress, intense emotions, and overwhelming fear that impacts their overall well-being. In such cases, a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or therapist, can help the child work through their emotions and develop coping strategies. 3. Disruptions in daily functioning caused by nightmares, such as increased difficulty focusing at school, refusing to sleep alone, or displaying significant behavioral changes. Seeking professional guidance can assist in identifying the underlying causes and developing interventions to alleviate these challenges. Remember, professional help is available and can provide valuable support to both children and their families in navigating the complexities of nightmares and associated issues.
1. Persistent Nightmares
Persistent nightmares in children can have a significant impact on their overall well-being and daily functioning. 1. Persistent nightmares refer to recurring and frequent nightmares that persist over an extended period. These nightmares can cause immense distress and anxiety for the child, affecting their ability to get a restful night’s sleep. It is important to note that occasional nightmares are a normal part of childhood, but when they become persistent, it may indicate an underlying issue that needs to be addressed. Parents should pay attention to the frequency and intensity of their child’s nightmares. If a child experiences persistent nightmares, it may be an indication of an unresolved trauma, stress, or emotional disturbance that requires professional intervention. A child who is continually plagued by nightmares may exhibit symptoms of fear, anxiety, and sleep disturbances during the day. Parents should seek help from a healthcare professional or mental health expert if their child is experiencing persistent nightmares, as it may require specialized intervention and therapy. By addressing the root cause of the nightmares, parents can help their child find relief and improve their overall well-being.
2. Severe Anxiety and Fear
Severe anxiety and fear can significantly impact a child’s experience of nightmares. When a child is dealing with intense levels of anxiety and fear, it can increase the frequency and intensity of their nightmares. These feelings of anxiety and fear can stem from various sources, including traumatic events, phobias, or ongoing stressful situations. Nightmares related to anxiety and fear often involve themes of being chased, attacked, or trapped, reflecting the child’s underlying emotional challenges. These nightmares not only cause distress during sleep but can also lead to persistent worry and fear during wakeful hours. It’s essential for parents and caregivers to provide support and reassurance to children experiencing severe anxiety and fear. Implementing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or guided imagery, can help alleviate anxiety before bedtime and promote a sense of calm. Additionally, creating a safe and nurturing environment where the child feels comfortable expressing their fears can also aid in reducing anxiety-related nightmares. Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor may be necessary for children experiencing severe anxiety and fear that significantly disrupts their daily functioning. By addressing the underlying anxiety, parents can assist their children in managing and reducing the occurrence of these distressing nightmares.
3. Disrupted Daily Functioning
Disrupted daily functioning can be a significant consequence of frequent nightmares in children. When nightmares occur regularly and disturb a child’s sleep, it can lead to fatigue and daytime sleepiness. This can affect their ability to concentrate and perform well in school. The emotional distress caused by nightmares can also impact a child’s overall mood and behavior, leading to irritability, mood swings, and difficulty managing their emotions. Frequent nightmares may cause anxiety and fearfulness, making children hesitant or fearful of going to bed. This can disrupt their bedtime routine and make it challenging for them to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night. Consequently, the lack of quality sleep can further contribute to difficulties in functioning during the day, such as decreased academic performance, impaired social interactions, and reduced overall productivity. It is essential for parents to recognize these disruptions and take appropriate steps to address their child’s nightmares to restore their daily functioning and well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nightmares in children can have a significant impact on their emotional well-being and overall sleep quality. It is crucial for parents and caregivers to understand the causes behind nightmares to provide effective support. By addressing stress and anxiety, addressing traumatic experiences, managing sleep disorders, and moderating exposure to frightening content, parents can help alleviate the occurrence of nightmares in children. Creating a calm bedtime routine, providing comfort and reassurance, encouraging dream journaling, and teaching relaxation techniques are valuable strategies in assisting children in dealing with nightmares. However, in cases of persistent nightmares, severe anxiety, and disrupted daily functioning, seeking professional help becomes necessary to ensure the child receives appropriate care and intervention. Overall, with the right guidance and support, parents can play a vital role in helping their children navigate and conquer their nightmares, promoting a healthier and more restful sleep experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do children have nightmares?
Children have nightmares due to various factors, including stress, anxiety, traumatic experiences, sleep disorders, and exposure to frightening stimuli from media or their imagination.
2. Are nightmares a normal part of childhood?
Yes, nightmares are considered a normal part of childhood development. They are a way for children to process emotions and experiences, but they can be distressing for them.
3. How can stress and anxiety contribute to nightmares?
Stress and anxiety activate the body’s fight-or-flight response, which can lead to heightened brain activity during sleep. This increased brain activity can result in vivid and frightening dreams or nightmares.
4. Can trauma cause nightmares in children?
Yes, traumatic experiences such as accidents, abuse, or loss can trigger nightmares in children. These dreams might be a way for children to process and cope with the emotions associated with the trauma.
5. Do sleep disorders play a role in nightmares?
Yes, sleep disorders like sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome can disrupt the sleep cycle, leading to nightmares. Additionally, certain medications used to treat sleep disorders can also influence the content of dreams and contribute to nightmares.
6. What impact can nightmares have on children?
Nightmares can have several impacts on children, including emotional distress, sleep disruptions, and behavioral changes. They may feel scared, anxious, and find it challenging to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night.
7. How can a calm bedtime routine help children deal with nightmares?
A calm bedtime routine creates a relaxing environment that helps children unwind before sleep. Establishing a consistent routine with activities like reading, gentle music, or relaxation exercises can promote better sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of nightmares.
8. Why is dream journaling helpful in managing nightmares?
Dream journaling allows children to express and analyze their dreams. By writing down their dreams, they can gain insights into recurring patterns or themes in their nightmares. This process can help them process their emotions and find ways to cope with their fears.
9. How do relaxation techniques assist children in coping with nightmares?
Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, visualization, or progressive muscle relaxation can help children calm their minds and bodies before bed. These techniques can reduce anxiety levels and promote a sense of peace, making it easier for children to fall asleep peacefully.
10. When should parents seek professional help for a child’s nightmares?
It’s important to seek professional help if a child experiences persistent nightmares that significantly disrupt their sleep or daily functioning. Additionally, if a child shows severe anxiety, fear, or trauma-related symptoms, a mental health professional can provide specialized support and guidance.