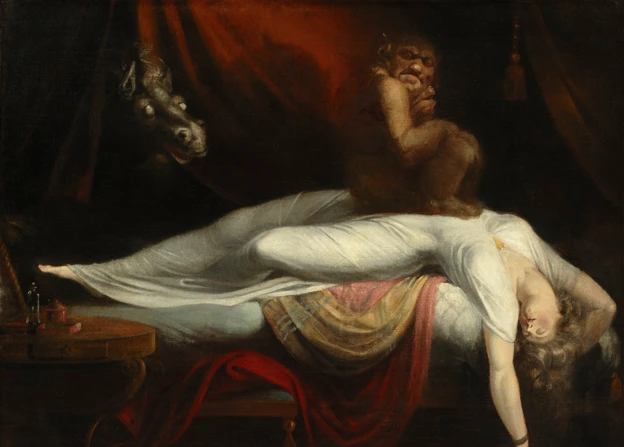
Have you ever woken up in the middle of the night, heart pounding, drenched in sweat, and feeling a profound sense of fear? If so, you’ve experienced the mysterious world of nightmares. These unsettling dreams can leave us feeling shaken, anxious, and even question our own sanity. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at nightmares, delving into their definition, common themes, and the various theories that attempt to explain their occurrence. We will explore the effects nightmares can have on our sleep quality, emotional well-being, and even their potential connection to traumatic experiences. Additionally, we will uncover different approaches to interpreting these vivid dreams, including the perspectives of renowned psychologists Freud and Carl Jung. Lastly, we will delve into coping strategies that can help alleviate the distress caused by nightmares. So, buckle up and prepare to explore the dark recesses of your mind as we unravel the mysteries of nightmares.
Understanding Nightmares

Nightmares are unsettling dreams characterized by intense fear, anxiety, and emotional distress. They often occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, which is when most dreaming occurs. Nightmares can be defined as vivid and disturbing dreams that evoke a sense of danger, terror, or helplessness. These dreams can feel incredibly real, leaving a lasting impression upon waking. While nightmares can vary from person to person, there are some common themes that frequently appear.
Nightmares can take on various forms, but certain themes tend to recur across different individuals. These themes include being chased or attacked, falling from great heights, experiencing natural disasters, encountering monsters or supernatural beings, and being trapped or unable to move. These recurring themes often tap into our deepest fears and anxieties, reflecting our subconscious thoughts and emotions.
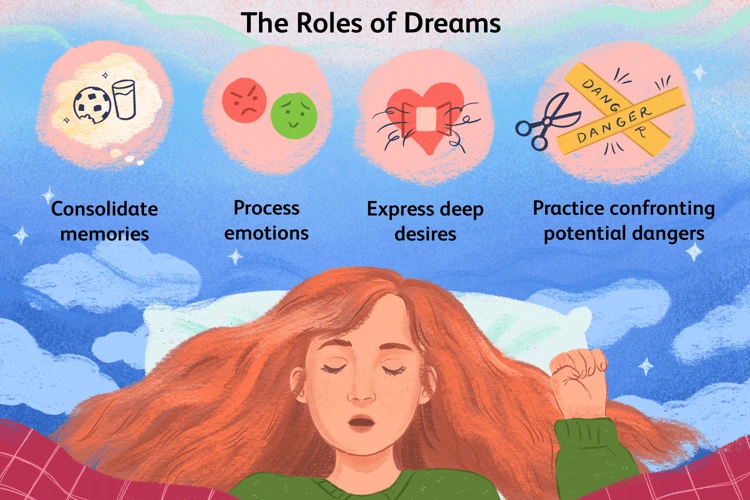
Psychologists have proposed several theories to explain the occurrence of nightmares. One prominent theory suggests that nightmares may serve as a way for the mind to process and cope with traumatic experiences or unresolved emotional conflicts. By replaying and reexperiencing these distressing events in the form of nightmares, the brain attempts to come to terms with the emotions associated with them. Another theory posits that nightmares may act as a mechanism for emotional regulation, allowing individuals to confront and release negative emotions that are often suppressed during waking hours.
Physiological factors can also contribute to the onset of nightmares. Research has shown a correlation between certain medications, such as antidepressants and beta-blockers, and an increased likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Substance abuse, withdrawal from drugs or alcohol, and sleep disorders like sleep apnea or narcolepsy have also been linked to the occurrence of nightmares. Additionally, physical illnesses, fever, and sleep deprivation can disrupt the sleep cycle and potentially lead to more frequent nightmares.
Emotional triggers play a significant role in the occurrence of nightmares. Stress, anxiety, and traumatic events can all contribute to the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Individuals who undergo significant life changes, such as the loss of a loved one, divorce, or job loss, may experience an increase in nightmares as these events can generate a great deal of emotional turmoil. Individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) often suffer from recurrent nightmares related to their traumatic experiences.
Definition of Nightmares
The definition of nightmares revolves around vivid and distressing dreams that often evoke a range of negative emotions, including fear, anxiety, and helplessness. Nightmares can be defined as intensely disturbing dreams that disrupt sleep and leave a lasting impression upon waking. These dreams usually occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, where most of our dreaming takes place. Nightmares are differentiated from regular dreams by their intense emotional content, often involving threatening or dangerous situations.
When experiencing a nightmare, individuals may feel a sense of terror or imminent danger. The content of nightmares can be diverse, ranging from being pursued or attacked by an unknown assailant to finding oneself in life-threatening situations. Some common themes in nightmares include falling from great heights, being chased by monsters, or being trapped in a claustrophobic space. Nightmares can also be influenced by personal experiences, fears, and anxieties.
It’s important to note that nightmares are different from other types of dreams. While dreams can be positive, neutral, or extraordinary, nightmares are specifically characterized by their negative emotional impact. They often disrupt sleep patterns and can lead to awakenings, leaving individuals with a sense of unease or distress. Understanding the definition of nightmares allows us to explore the causes, effects, and interpretation of these unsettling experiences.
Common Themes in Nightmares
Common themes in nightmares often reflect our deepest fears, anxieties, and subconscious emotions. While the specifics of nightmares vary from person to person, there are several recurring themes that tend to emerge. These themes include:
- Being chased or attacked: Many people experience nightmares of being pursued or attacked by unknown entities or even familiar individuals. These dreams can symbolize a sense of vulnerability, fear of being overwhelmed, or a need to confront and overcome threats in waking life. They may also represent unresolved conflicts or feelings of powerlessness.
- Falling from great heights: Falling nightmares are characterized by a sensation of plummeting or losing control. Such dreams can reflect feelings of insecurity, instability, or a fear of failure. They may indicate a lack of confidence or an apprehension about the unknown.
- Experiencing natural disasters: Nightmares involving earthquakes, floods, tornadoes, or other catastrophic events can signify a lack of control, a fear of change, or a sense of impending doom. These dreams may relate to anxieties about life’s uncertainties or recurring feelings of vulnerability.
- Encountering monsters or supernatural beings: Nightmares featuring monsters, ghosts, or other supernatural entities often tap into our primal fears and symbolize aspects of ourselves or repressed emotions. These dreams can represent hidden desires, unresolved conflicts, or feelings of guilt or shame.
- Being trapped or unable to move: Dreams of being trapped, paralyzed, or unable to move are common and can be highly distressing. These nightmares may reflect feelings of helplessness, stagnation, or a sense of being trapped in a situation or relationship. They can also relate to fears of failure or an inability to assert oneself.
It is important to note that while these themes are commonly reported, the interpretation of individual nightmares can vary significantly. Understanding the personal context, emotions, and experiences of the dreamer is crucial in deciphering the unique meaning behind their nightmares. Exploring the symbolism and underlying emotions can provide valuable insights into the individual’s subconscious mind and emotional state.
Psychological Theories
Psychologists have put forth several theories to explain the occurrence and significance of nightmares. These theories provide insight into the psychological aspects behind these unsettling dreams.
One prominent theory is Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic perspective. According to Freud, nightmares are symbolic representations of repressed desires, fears, or unresolved conflicts. He believed that the content of nightmares could be interpreted to gain insight into a person’s unconscious mind. Freud suggested that analyzing the symbols and themes present in nightmares could provide clues about the individual’s innermost thoughts and feelings.
Another influential theory is Carl Jung’s perspective. Jung believed that nightmares were not just a random occurrence but rather a way for the unconscious mind to communicate important messages to the conscious self. He proposed that nightmares often contained archetypal symbols, which are universal images representing collective human experiences. Jung emphasized the importance of exploring the meaning behind these symbols and their personal significance to the dreamer.
Dream analysis is a common technique used to interpret nightmares within the realm of psychology. This approach involves examining the various elements of the dream, such as characters, settings, and emotions, in order to uncover hidden meanings and connections to the dreamer’s waking life. By delving into the symbolism and personal associations behind these elements, dream analysis aims to shed light on the deeper psychological processes at play.
While psychological theories provide valuable insights into the nature of nightmares, it is important to note that the understanding and interpretation of these dreams can vary from person to person. The field of dream research continues to evolve, with ongoing efforts to unravel the complexities of the human mind and its relationship to the world of dreams.
Physiological Factors
Physiological factors can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares and influence their frequency and intensity. Medications can play a role in the development of nightmares. Some antidepressants and beta-blockers have been linked to an increased likelihood of experiencing nightmares. These medications can alter neurotransmitter levels and disrupt the sleep cycle, potentially leading to more vivid and disturbing dreams. Additionally, withdrawing from certain substances, such as alcohol or drugs, can trigger nightmares as the body adjusts to the absence of the substances.
Physical health conditions can also impact the occurrence of nightmares. Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea and narcolepsy, can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. These conditions can cause fragmented sleep and frequent awakenings, leading to more opportunities for nightmares to occur. Similarly, individuals with fever or illnesses that affect the central nervous system may experience an increase in nightmares as the body’s physiological processes are disrupted. It is important to address any underlying physical health issues that may be contributing to the occurrence of nightmares.
Sleep deprivation is another physiological factor that can contribute to nightmares. When the body does not get adequate rest, it can disrupt the normal sleep stages, including REM sleep where most dreaming occurs. This can lead to an increase in the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Establishing healthy sleep habits, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing sleep environment, can help reduce the occurrence of nightmares related to sleep deprivation.
Neurological conditions can also be associated with an increased likelihood of nightmares. Conditions such as epilepsy and migraines can disrupt brain activity and sleep patterns, potentially leading to the emergence of nightmares. Seeking appropriate medical treatment for these conditions can help manage and reduce nightmares.
Emotional Triggers
Emotional triggers play a significant role in the occurrence of nightmares. Stress is a common emotional trigger that can contribute to the frequency and intensity of nightmares. When we are under high levels of stress, our minds and bodies are in a state of heightened arousal, making it more likely for nightmares to occur. This can be due to work-related stress, relationship issues, financial difficulties, or other personal challenges. Similarly, anxiety can also be a potent emotional trigger for nightmares. Generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety, or specific phobias can create a constant undercurrent of fear and worry, which can manifest in the form of nightmares.
Experiencing traumatic events can have a profound impact on our mental and emotional well-being. Individuals who have experienced trauma, such as physical or sexual abuse, witnessing violence, or surviving a natural disaster, may be more prone to nightmares. These nightmares can serve as a way for the mind to process and integrate the traumatic experience, and they may occur repeatedly until the individual has fully processed and come to terms with the event. In some cases, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can develop, and nightmares can become a hallmark symptom of this condition. Nightmares associated with PTSD often replay specific aspects of the traumatic event, causing intense emotional distress and sleep disruption.
Another emotional trigger for nightmares is grief and loss. When we experience the death of a loved one, the grieving process can be overwhelming and complex. This emotional upheaval can seep into our dreams, resulting in nightmares that reflect the pain, sadness, and longing associated with the loss. Similarly, major life changes such as divorce or job loss can trigger a surge of emotions and uncertainty that may manifest in nightmares.
In some cases, pre-existing mental health conditions can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. Individuals with depression may experience an increase in nightmares due to the negative emotions and feelings of hopelessness that often accompany the condition. Certain anxiety disorders, such as panic disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), can also trigger nightmares as a result of the heightened anxiety and intrusive thoughts associated with these conditions. Additionally, individuals with a history of substance abuse or withdrawal may experience nightmares as their bodies and minds adjust to the absence of the substance.
The Effects of Nightmares
The effects of nightmares can extend beyond the realm of sleep, impacting various aspects of our well-being. One significant effect is the impact on sleep quality. Nightmares can disrupt the natural sleep cycle, causing frequent awakenings and difficulty falling back asleep. This can lead to feelings of fatigue, daytime drowsiness, and decreased overall sleep quality. In severe cases, chronic nightmares can contribute to the development of insomnia, further exacerbating sleep disturbances.
Another notable effect of nightmares is the emotional distress and anxiety they can evoke. The vivid and often terrifying nature of nightmares can leave individuals feeling unsettled, anxious, and fearful. Upon waking, it may take some time to shake off the residual emotions from the dream, impacting mood and overall emotional well-being during waking hours. Nightmares can also contribute to the development or worsening of anxiety disorders, leading to increased levels of stress and apprehension in daily life.
In some cases, nightmares can be post-traumatic nightmares triggered by traumatic experiences. Individuals who have experienced significant trauma, such as military combat, sexual assault, or natural disasters, may face recurring nightmares that vividly replay the traumatic events. These nightmares can intensify feelings of fear, helplessness, and distress, making it difficult for individuals to recover from their trauma and potentially impacting their overall mental health.
The effects of nightmares are not limited to individual well-being; they can also impact interpersonal relationships. Partners and family members of individuals experiencing frequent nightmares may be affected by disrupted sleep and emotional distress. Understanding and supporting a loved one dealing with nightmares can be challenging but essential for their overall well-being and relationship dynamics.
Impact on Sleep Quality
Nightmares can have a significant impact on the quality of sleep. When nightmares occur, they can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to frequent awakenings throughout the night. This can result in fragmented sleep and a decreased amount of time spent in restorative REM sleep, which is crucial for mental and physical rejuvenation. As a result, individuals who experience nightmares may wake up feeling exhausted, irritable, and unrefreshed.
The powerful emotions and imagery associated with nightmares can linger even after waking up, making it difficult for individuals to fall back asleep. The adrenaline rush triggered by the intense fear or anxiety experienced during a nightmare can leave individuals feeling alert and on edge, further disrupting sleep. This can create a vicious cycle where the fear of experiencing another nightmare makes it challenging to relax and fall asleep, perpetuating sleep disturbances.
Chronic sleep disruptions caused by nightmares can have a detrimental impact on overall well-being. Sleep deprivation resulting from nightmares can lead to daytime sleepiness, decreased cognitive functioning, impaired concentration, and difficulties with memory recall. The emotional distress caused by nightmares can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health issues, such as anxiety and depression.
It is worth noting that nightmares are not necessarily indicative of a sleep disorder. While they can be distressing, occasional nightmares are a normal part of the dreaming process for many individuals. However, when nightmares become frequent and significantly impact sleep quality and overall functioning, it is essential to seek professional help for proper evaluation and management.
Emotional Distress and Anxiety
Emotional distress and anxiety are closely intertwined with the occurrence of nightmares. Nightmares can act as a reflection of our innermost fears and anxieties, amplifying emotional distress and potentially exacerbating underlying anxiety disorders. The intense emotions experienced during nightmares can leave individuals feeling unsettled, anxious, and even fearful of falling asleep. This fear of nightmares may lead to sleep disruptions and a decreased quality of sleep overall.
When individuals repeatedly experience nightmares, it can create a cycle of anxiety and sleep disturbance. The fear of having another terrifying dream can cause anticipatory anxiety, making it difficult to relax and fall asleep. This anxiety can further disrupt the sleep cycle, leading to a greater likelihood of nightmares occurring. Nightmares can trigger a heightened state of alertness and arousal, contributing to the development or exacerbation of anxiety disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Research has shown that individuals who experience frequent nightmares tend to have higher levels of general anxiety and increased sensitivity to daily stressors. Nightmares can serve as a manifestation of unresolved emotional conflicts or traumatic experiences, making it crucial to address and process these underlying issues to alleviate emotional distress and anxiety. Cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques, such as image rehearsal therapy, have been effective in reducing nightmare frequency and associated distress by addressing negative emotions and altering the content of nightmares.
It is important to note that not all dreams and nightmares are negative or anxiety-provoking. Positive dreams can provide relief from stress and induce feelings of happiness and contentment. Dreams can also serve as a source of creative inspiration and problem-solving, offering a different perspective on waking life challenges. However, when nightmares become frequent, excessively distressing, or significantly interfere with daily functioning, seeking professional help from a mental health provider is advisable to address the underlying emotional distress and anxiety.
Post-Traumatic Nightmares
Post-traumatic nightmares are a specific type of nightmare that occurs in individuals who have experienced a traumatic event. These nightmares are vivid and realistic, often replaying the traumatic event or incorporating elements of it.
One of the key characteristics of post-traumatic nightmares is their ability to cause significant distress and disrupt the individual’s ability to get a restful sleep. It is estimated that about 70-80% of individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) experience post-traumatic nightmares. These nightmares can lead to fear of falling asleep, anxiety surrounding sleep, and avoidance of situations or triggers that may remind the individual of the traumatic event.
The content of post-traumatic nightmares can vary depending on the nature of the traumatic event. For example, a person who has experienced combat may have nightmares about being in the midst of a battle, while someone who has survived a car accident may have nightmares about the accident and its aftermath. These nightmares often contain vivid sensory details, intense emotions, and a strong feeling of helplessness or terror.
Post-traumatic nightmares can have a profound impact on an individual’s daily functioning and overall well-being. They can contribute to the development or exacerbation of symptoms associated with PTSD, such as hypervigilance, irritability, and flashbacks. In some cases, these nightmares can lead to a fear of sleep and insomnia, further worsening the individual’s emotional state and increasing the risk of other psychological and physical health issues.
It is essential for individuals experiencing post-traumatic nightmares to seek professional help. Therapeutic interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), have shown to be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of these nightmares. /the-impact-of-premonition-dreams-predicting-future/ These therapies aim to process and integrate the traumatic memories, allowing individuals to gain control over their nightmares and achieve a more restful sleep.
Interpreting Nightmares

Interpreting nightmares can provide valuable insights into our subconscious thoughts, emotions, and unresolved conflicts. Sigmund Freud, the father of psychoanalysis, believed that nightmares were a gateway to the unconscious mind and held hidden meanings. According to Freud, dreams, including nightmares, are symbolic representations of repressed desires and unresolved conflicts. He suggested that analyzing the symbols and imagery within a nightmare can help to uncover the latent content, or the hidden meaning behind the dream.
Carl Jung, a prominent psychologist and student of Freud, approached dream interpretation from a slightly different perspective. Jung believed that nightmares, like all dreams, were expressions of the collective unconscious and archetypal symbolism. According to Jung, the collective unconscious contains universal symbols and themes that are shared by all humans. He emphasized the importance of understanding the personal and cultural context of the dreamer to interpret the symbols and find their meaning.
When interpreting nightmares, it is important to consider the specific symbols and archetypes present in the dream. Symbolism can vary depending on the individual’s personal experiences and cultural background. For example, being chased or attacked in a nightmare can symbolize avoidance or confrontation of a problem or fear in waking life. Falling from great heights may represent a lack of control or insecurity. Presence of monsters or supernatural beings could symbolize inner fears or the struggle with one’s darker impulses. By analyzing these symbols and considering their personal significance, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their own fears, anxieties, and unresolved emotions.
It is important to note that dream interpretation is highly subjective and can vary from person to person. While some individuals may find meaning and insight through the interpretation of their nightmares, others may view them simply as a reflection of random brain activity during sleep. However, for those interested in delving deeper into the symbolism and potential significance of their nightmares, there are various resources available, including books, online forums, and dream analysis professionals, who can provide guidance and different perspectives.
Freudian Interpretation
Freudian Interpretation:
Sigmund Freud, the renowned psychoanalyst, believed that dreams, including nightmares, were windows into the unconscious mind. According to Freud, nightmares reflect repressed and unconscious desires, fears, and unresolved conflicts. He proposed that nightmares serve as a method of wish fulfillment, allowing individuals to satisfy their deepest, often taboo, desires in the realm of dreams.
In Freud’s view, nightmares were symbolic representations of underlying psychological issues. He emphasized the importance of analyzing the content of dreams, including the manifest (surface) and latent (hidden) content, to gain insight into the unconscious meaning. Freud identified various symbols and themes in dreams that he believed were indicative of specific desires or conflicts.
For example, he believed that dreams involving falling represented a desire for sexual release, while dreams featuring teeth falling out were related to anxieties about power and control. Additionally, Freud suggested that recurrent nightmares involving being chased or attacked could signify an unresolved childhood trauma or persistent feelings of guilt.
Freud’s interpretation of nightmares greatly influenced the field of psychology, although his theories have been met with both praise and criticism. While some psychologists still draw upon elements of Freud’s psychoanalytic approach to understand the symbolic meaning of dreams, others take a more scientifically based perspective, focusing on brain activity and neurobiological processes during sleep.
Understanding the mysteries of recurring dreams
Carl Jung’s Perspective
Carl Jung, a renowned Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst, had a unique perspective on dreams and nightmares. Jung believed that dreams, including nightmares, are a window into the unconscious mind and hold great significance for personal growth and self-discovery. According to Jung, dreams contain symbols and archetypes that represent universal patterns and themes. By analyzing these symbols and archetypes, individuals can gain insight into their subconscious and their journey towards individuation.
Jung proposed that nightmares often arise when individuals are grappling with unresolved conflicts or repressed aspects of their personality. Through nightmares, the unconscious mind attempts to communicate these hidden aspects, urging the dreamer to confront and integrate them into their conscious life. Jung emphasized the importance of paying attention to recurring symbols in nightmares, as they can provide valuable clues about unconscious desires, fears, and unresolved issues.
One significant concept in Jungian dream analysis is the idea of the collective unconscious, which refers to the shared reservoir of knowledge and experiences that all humans inherit. Jung believed that certain archetypal symbols, such as the shadow, the anima/animus, and the wise old man/woman, frequently appear in dreams and nightmares to convey deeper psychological meanings. For example, encountering a menacing figure in a nightmare may represent the dreamer’s suppressed dark side or unresolved inner conflicts. By exploring these archetypal symbols and their associated emotions, individuals can gain a better understanding of their own psyche.
Jung’s perspective on nightmares emphasizes the transformative potential of these dreams – they provide an opportunity for self-reflection, personal growth, and integration of both the conscious and unconscious aspects of the self. Rather than being purely negative experiences, nightmares can be viewed as messages from the unconscious mind, guiding individuals towards wholeness and individuation. Understanding and interpreting the symbols and archetypes present in nightmares can be a powerful tool for self-discovery and psychological healing. So, next time you wake up from a terrifying nightmare, remember that it may be an invitation to explore the depths of your own psyche.
Symbols and Archetypes
In the realm of dream interpretation, symbols and archetypes play a crucial role in understanding the deeper meaning behind our nightmares. Symbols are objects, people, or situations that represent abstract ideas or emotions. These symbols can vary greatly from person to person, as they are often influenced by personal experiences, cultural background, and individual beliefs. Archetypes, on the other hand, are universal symbols that are present across different cultures and time periods. They are deeply ingrained in our collective unconscious and can hold powerful meanings.
When it comes to interpreting nightmares, analyzing the symbols that appear in our dreams can provide insights into our subconscious thoughts and emotions. For example, a common symbol in nightmares is falling, which can represent a lack of control or a fear of failure. This symbol may be indicative of feelings of insecurity or instability in waking life. Similarly, being chased or attacked in a nightmare can symbolize feelings of vulnerability, fear of confrontation, or a need to escape from a difficult situation.
It’s important to remember that symbols can have both personal and universal meanings. What a specific symbol represents to one person may differ from its general interpretation. For instance, spiders commonly appear in nightmares and can be a symbol of fear or anxiety. However, for someone with a love for spiders and an appreciation for their symbolism of creativity and patience, a spider in a dream may hold a different meaning.
Archetypal symbols can also manifest in nightmares. These symbols have been passed down through generations and are deeply rooted in our collective unconscious. For example, the image of a snake in a nightmare can represent transformation, rebirth, or temptation. This symbol is present in various mythologies and cultures, often associated with themes of power and transformation.
Interpreting symbols and archetypes in nightmares requires a deep understanding of the individual’s background, experiences, and beliefs. It is helpful to keep a dream journal to track recurring symbols and analyze their potential meanings over time. Discussing dreams with a therapist or joining a dream analysis group can also provide valuable insights into the symbolism within nightmares. By unraveling the hidden messages behind these symbols, we can gain a better understanding of our subconscious mind and the issues that may be influencing our waking lives.
Coping Strategies for Nightmares
Coping with nightmares can be challenging, but there are several strategies that individuals can employ to alleviate their distressing effects. Keeping a dream journal can be a powerful tool in understanding and processing nightmares. By recording the details of each nightmare upon awakening, individuals can gain insights into recurring patterns, symbols, and emotions that may be present. This process allows for a deeper exploration and interpretation of the subconscious mind, potentially leading to a greater understanding of the underlying issues contributing to the nightmares.
Another effective coping strategy for nightmares is the use of relaxation techniques. Meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help calm the mind and body before sleep, reducing the likelihood of nightmares. These practices promote a sense of inner peace and relaxation, making it easier to transition into a more serene dream state. Additionally, incorporating a bedtime routine that promotes relaxation, such as reading a book or taking a warm bath, can signal to the body that it is time to unwind and prepare for restful sleep.
Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor skilled in dream analysis can be beneficial for individuals struggling with persistent and distressing nightmares. A therapist can provide a safe space to explore the underlying emotions and experiences that may be contributing to the nightmares. They can also teach techniques such as lucid dreaming and imagery rehearsal therapy, which aim to change the content and outcome of nightmares. By actively engaging with the nightmares during the waking hours, individuals can gain a sense of control and empowerment over their dreams.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage nightmares, especially if they are a symptom of a larger sleep disorder or mental health condition. However, medication should always be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as it may have side effects and interactions with other medications.
Finally, nurturing a healthy sleep environment can also aid in reducing the occurrence of nightmares. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable and relaxing bedroom space, avoiding stimulating activities before bed, and limiting the consumption of caffeine and alcohol. Prioritizing self-care, practicing stress-reduction techniques, and engaging in activities that promote a positive mindset can also contribute to better overall sleep quality and diminish the frequency of nightmares.
Keeping a Dream Journal
One effective coping strategy for dealing with nightmares is keeping a dream journal. A dream journal is a dedicated notebook or electronic document where you record your dreams immediately upon waking up. This practice helps to capture the details and emotions of the dream while they are still fresh in your mind.
A dream journal can be an insightful tool for gaining a deeper understanding of your dreams and identifying patterns or recurring themes. When you consistently record your dreams, you may begin to notice connections between your dreams and your daily experiences or emotions. This self-reflection can provide valuable insights into your subconscious thoughts and feelings.
Recording your dreams in a dream journal also allows you to revisit and analyze them at a later time. By reviewing your past dreams, you may uncover hidden symbolism or meaning that was not immediately apparent. This process of reflection and analysis can provide a new perspective on your dreams and help you discover personal insights.
To keep a dream journal, start by keeping your journal and a pen or pencil beside your bed. As soon as you wake up, take a few moments to recall your dream and jot down any vivid details, emotions, or symbols that you remember. Don’t worry about capturing every single detail – focus on capturing the essence of the dream. You can also use sketches or drawings to represent certain elements of the dream.
It’s important to be consistent with your dream journaling practice. Make it a habit to record your dreams every morning, even if you don’t remember them well. Over time, this habit will train your brain to pay closer attention to your dreams and improve your dream recall abilities.
In addition to recording your dreams, you can also use your dream journal to set intentions for positive dreams. Before going to bed, write down affirmations or positive suggestions that you want to incorporate into your dreams. This can help shift the tone and content of your dreams towards more positive experiences.
Keeping a dream journal can be a fascinating and rewarding practice that enhances your self-awareness and helps you make sense of your nightmares. So, grab a journal and pen, and embark on the journey of exploring the depths of your dreams.
Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques can be highly effective in managing and reducing the frequency of nightmares. Implementing these techniques can help individuals achieve a state of calmness and reduce anxiety, making it easier to have a restful sleep. One popular relaxation technique is progressive muscle relaxation (PMR). This technique involves tensing and then relaxing each muscle group in the body, starting from the feet and working your way up to the head. By systematically releasing tension from the muscles, PMR can promote overall relaxation and alleviate physical and mental stress, ultimately reducing the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
Mindfulness meditation is another effective relaxation technique. By focusing on the present moment and cultivating a non-judgmental awareness of thoughts and sensations, mindfulness can help individuals develop a sense of calm and inner peace. Regular practice of mindfulness meditation has been shown to reduce stress, anxiety, and improve sleep quality. By incorporating mindfulness into your bedtime routine, you can create a peaceful and conducive environment for sleep, thereby decreasing the chances of nightmares.
Deep breathing exercises are simple yet powerful relaxation techniques that can be practiced anytime, anywhere. Deep breathing activates the body’s relaxation response, reducing physiological arousal and promoting a state of calmness. By taking slow, deep breaths through the nose and exhaling slowly through the mouth, you can decrease muscle tension, slow down the heart rate, and induce a sense of relaxation. Incorporating deep breathing exercises into your daily routine and using them before bedtime can help alleviate stress and reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
Aromatherapy, the use of essential oils, is another technique that can aid in relaxation and potentially reduce nightmares. Certain essential oils, such as lavender and chamomile, have calming properties that can promote relaxation and improve sleep quality. Diffusing these oils in the bedroom or using them in a warm bath before bedtime can create a soothing atmosphere and enhance relaxation. However, it’s important to note that some individuals may have sensitivities or allergies to certain essential oils, so it’s recommended to test them in small quantities before regular use.
Incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine can have a significant impact on reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Experiment with different techniques and find what works best for you. By indulging in relaxation before sleep, you create an environment that is conducive to peaceful and restful sleep, allowing you to wake up refreshed and nightmare-free.
Conclusion
- Nightmares are a fascinating and often unsettling aspect of our dream world. These vivid and disturbing dreams can leave a lasting impact on our emotional well-being and sleep quality.
- Understanding nightmares involves exploring their definition, common themes, and the various psychological and physiological factors that contribute to their occurrence.
- Common themes in nightmares include being chased or attacked, falling from great heights, encountering monsters or supernatural beings, and feeling trapped or unable to move.
- Psychological theories propose that nightmares serve as a means for the mind to process traumatic experiences or unresolved emotional conflicts. They may also act as a mechanism for emotional regulation.
- Physiological factors such as medication, substance abuse, sleep disorders, physical illnesses, fever, and sleep deprivation can all contribute to the onset of nightmares.
- Emotional triggers, such as stress, anxiety, and traumatic events, can also increase the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
- Interpreting nightmares can be approached from various perspectives, including the Freudian interpretation and Carl Jung’s perspective of symbols and archetypes. These interpretations provide insights into the subconscious mind.
- To cope with nightmares, individuals can keep a dream journal and practice relaxation techniques to alleviate emotional distress and anxiety associated with these dreams.
- In conclusion, nightmares are a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that can reveal much about our subconscious mind. By understanding the causes, effects, and interpretations of nightmares, we can gain valuable insights into our emotions, experiences, and inner selves. Exploring the mysteries of our dream world can open up new avenues of self-discovery and personal growth.
Continue your exploration of the realm of dreams by exploring the intriguing concept of prophetic dreams.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can nightmares have physical effects on the body?
Nightmares can indeed have physical effects on the body. During a nightmare, the body can experience increased heart rate, rapid breathing, sweating, and even physical movements or vocalizations.
2. Are there any ways to prevent nightmares?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent nightmares, there are certain strategies that can help decrease their occurrence. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, practicing relaxation techniques before bed, and creating a calming sleep environment can all contribute to reducing the frequency of nightmares.
3. Can nightmares be a sign of an underlying mental health condition?
Nightmares can be a symptom of various mental health conditions, such as anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or depression. If nightmares are frequent, distressing, and interfering with daily life, it may be beneficial to consult a mental health professional for proper evaluation and support.
4. Do children experience nightmares more frequently than adults?
Yes, nightmares are more common in children than in adults. This is partly due to the fact that children’s imaginations are more active, and they may have difficulty distinguishing between dreams and reality. Nightmares tend to decrease as children grow older.
5. Can medication help in reducing the frequency of nightmares?
In some cases, medication can be prescribed to help reduce the occurrence of nightmares. Certain medications, such as low-dose antidepressants or drugs that regulate sleep cycles, have been shown to have a positive effect on reducing nightmares. However, medication should always be prescribed and monitored by a medical professional.
6. Are there cultural differences in the interpretation of nightmares?
Yes, cultural differences can influence the interpretation of nightmares. Different cultures may attribute different meanings to specific symbols or events that occur in a nightmare. It’s important to consider cultural context when analyzing and interpreting the content of dreams and nightmares.
7. Can recurring nightmares be a sign of unresolved trauma?
Recurring nightmares can be a sign of unresolved trauma. When traumatic events are not processed or understood fully, they can manifest in the form of repetitive nightmares. Seeking therapy or counseling can help individuals address and work through these unresolved traumas.
8. Can lucid dreaming techniques be used to control nightmares?
Yes, lucid dreaming techniques can be used to gain control over nightmares. Lucid dreaming involves becoming aware that you are dreaming while still in the dream itself. With practice, individuals can learn to manipulate and change the dream scenario, effectively transforming a nightmare into a more positive or neutral experience.
9. Do nightmares have any evolutionary purpose?
There are several theories regarding the evolutionary purpose of nightmares. One theory suggests that nightmares acted as a form of rehearsal for dangerous or threatening situations, allowing our ancestors to mentally prepare for real-life dangers. Another theory proposes that nightmares served as a mechanism for learning, helping humans to better understand and avoid potential threats in their environment.
10. Can chronic sleep deprivation contribute to more frequent nightmares?
Yes, chronic sleep deprivation can contribute to more frequent nightmares. When the body and mind are not well-rested, the sleep cycle can be disrupted, leading to increased dream activity and the potential for more nightmares. Prioritizing healthy sleep habits and ensuring an adequate amount of restful sleep can help reduce the occurrence of nightmares.








