Nightmares and anxiety disorders are two interconnected phenomena that can significantly impact an individual’s mental well-being. While nightmares are vivid and often disturbing dreams that can cause fear and unease, anxiety disorders manifest as excessive worry, fear, and anxiety that can interfere with daily life. Understanding the link between nightmares and anxiety disorders is crucial for identifying effective strategies to manage these conditions and improve overall mental health. In this article, we will delve into the definition and causes of nightmares, explore the different types of anxiety disorders and their symptoms, discuss the connection between nightmares and anxiety disorders, examine the effects of nightmares on anxiety disorders, and provide strategies for managing both nightmares and anxiety disorders.
Nightmares: Definition and Causes

Nightmares, defined as intensely vivid and distressing dreams, can often leave individuals feeling shaken and fearful upon waking. These dreams are typically filled with intense emotions and can involve threatening or uncomfortable situations. The causes of nightmares can vary, ranging from underlying psychological factors to external triggers. Some common causes include stress, anxiety, trauma, sleep disorders, certain medications, and substance abuse. In some cases, nightmares may be linked to past traumatic experiences, which can contribute to their recurring nature. Understanding the root causes of nightmares is essential in addressing and managing their impact on overall mental well-being. To explore the meanings and common themes behind nightmares, refer to our article on common themes in nightmares and their meanings.
1. Definition of Nightmares
Nightmares can be defined as vivid and disturbing dreams that evoke intense emotions such as fear, anxiety, or sadness. They typically occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, which is when dreaming is most common. These dreams are often filled with unsettling or threatening scenarios, and upon waking, individuals may experience a lingering sense of unease or discomfort. Nightmares can vary in intensity, frequency, and content from person to person. While occasional nightmares are considered a normal part of the dreaming process, recurring and distressing nightmares may indicate underlying psychological or emotional issues. To gain a deeper understanding of the role of past trauma in recurring nightmares, you can refer to our article on the role of past trauma in recurring nightmares. Exploring the meanings and causes of recurring nightmares can provide valuable insights into their impact on mental well-being. For more information on understanding recurring nightmares, please refer to our dedicated article on understanding recurring nightmares.
2. Common Causes of Nightmares
Common causes of nightmares can be attributed to a range of factors that affect an individual’s mental and emotional well-being. One significant contributor is stress, which can amplify the frequency and intensity of nightmares. High levels of stress, whether due to work, relationships, or personal circumstances, can create an overwhelming burden on the mind and lead to nightmares during sleep. Anxiety is another common cause, as individuals with anxiety disorders often experience heightened levels of fear and worry, which can manifest in their dreams as unsettling and distressing scenarios. Trauma, both recent and past, can also play a role in the occurrence of nightmares. Individuals who have experienced traumatic events may find themselves reliving these experiences in their sleep, causing nightmares to occur. Certain medications, such as antidepressants or sleep aids, can have side effects that include vivid dreams or nightmares. Substance abuse, including alcohol and drug use, can also disrupt the sleep cycle and contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. It is important to address and manage these underlying causes in order to reduce the frequency and impact of nightmares and improve overall sleep quality. For a deeper understanding of the connection between past trauma and recurring nightmares, refer to our article on the role of past trauma in recurring nightmares.
Anxiety Disorders: Types and Symptoms
Anxiety disorders encompass a range of conditions characterized by excessive and persistent feelings of fear, worry, and anxiety. These disorders can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life and overall well-being. Some of the most common types of anxiety disorders include Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Panic Disorder, Social Anxiety Disorder, and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). GAD is characterized by chronic worry and apprehension about various aspects of life, while Panic Disorder involves recurring panic attacks accompanied by intense physical symptoms. Social Anxiety Disorder is marked by a fear of social situations and interactions, leading to avoidance behavior. PTSD develops after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event and is characterized by intrusive memories, nightmares, and hyperarousal. Symptoms of anxiety disorders can vary but often include restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbances, and physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat and trembling. Proper identification and understanding of these anxiety disorders and their symptoms are crucial steps in seeking appropriate treatment and support.
1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is a type of anxiety disorder characterized by persistent and excessive worry and anxiety about various aspects of daily life. Individuals with GAD often find it challenging to control their worrying thoughts, causing significant distress and impairment in their ability to function effectively. Some key symptoms of GAD include:
1. Excessive Worry: People with GAD may experience excessive worry about multiple areas of their life, such as work, finances, health, and relationships. The worry is often unrealistic and difficult to control, leading to a constant state of unease.
2. Restlessness and Irritability: Individuals with GAD may feel restless and on edge most of the time. They may have difficulty relaxing, experience muscle tension, and become easily irritable or agitated.
3. Physical Symptoms: GAD can also manifest in physical symptoms such as fatigue, difficulty sleeping, headaches, stomachaches, and muscle aches. These symptoms are often related to the chronic stress and anxious thoughts associated with GAD.
4. Difficulty Concentrating: GAD can impair one’s ability to concentrate and make decisions. The constant worrying and preoccupation with anxiety can make it challenging to focus on tasks or stay attentive.
5. Excessive Need for Reassurance: Individuals with GAD may seek reassurance from others excessively, constantly seeking affirmation and validation for their worries and fears.
It’s important to note that GAD is a chronic condition, and its symptoms can fluctuate in intensity over time. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is recommended to seek professional help for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
2. Panic Disorder
Panic Disorder is a type of anxiety disorder characterized by recurrent and unexpected panic attacks. These attacks are intense periods of fear and discomfort that are accompanied by physical symptoms such as heart palpitations, shortness of breath, sweating, trembling, and a sense of impending doom. Panic attacks can occur suddenly, without any identifiable trigger, and can last for several minutes to an hour. People with panic disorder often live in fear of experiencing another attack, which can lead to avoiding certain situations or places where they believe an attack might happen. This avoidance behavior can significantly disrupt their daily lives and lead to feelings of isolation and anxiety. Treatment for panic disorder may involve a combination of medication, therapy, and self-help strategies. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is often an effective approach, helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with panic attacks. Additionally, relaxation techniques and stress management strategies can aid in reducing the frequency and severity of panic attacks. It is crucial for individuals experiencing panic disorder to seek professional help to receive a comprehensive diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan.
3. Social Anxiety Disorder
Social Anxiety Disorder is a specific type of anxiety disorder characterized by an intense fear and discomfort in social situations. Individuals with this disorder may experience excessive worry and self-consciousness about being judged or embarrassed in front of others. They often have a strong desire to avoid social interactions, which can significantly impact their daily lives and relationships. Common symptoms of Social Anxiety Disorder include rapid heartbeat, trembling, sweating, nausea, and difficulty speaking. These symptoms can be debilitating and may lead to the avoidance of social events or situations altogether. People with Social Anxiety Disorder may also experience nightmares related to social scenarios and the fear of negative evaluation. These nightmares can further exacerbate their anxiety and contribute to a cycle of avoidance and distress. Understanding the connection between Social Anxiety Disorder and nightmares is essential in developing appropriate treatment strategies that address both the underlying anxiety and the resulting sleep disturbances. For more information on the various types of anxiety disorders, refer to our article on anxiety disorders and their symptoms.
4. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is an anxiety disorder that can develop after a person experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. Individuals with PTSD often experience persistent and intrusive nightmares related to the traumatic event. These nightmares can be distressing and vivid, causing the person to relive the trauma repeatedly. The content of these nightmares may mimic the details of the traumatic event, leading to heightened fear, anxiety, and physiological arousal upon waking. Individuals with PTSD may also experience night terrors, which are intense episodes of fear that occur during sleep. These nightmares and night terrors can significantly disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to the overall distress experienced by individuals with PTSD. It is important for individuals with PTSD to seek professional help to address both the underlying trauma and the associated nightmares. Therapy approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) can be effective in helping individuals manage and reduce the frequency and intensity of their nightmares. By addressing the root causes of PTSD and learning coping techniques for nightmares, individuals can work towards healing and improving their overall well-being. For more information on the role of past trauma in recurring nightmares, you can refer to our article on the role of past trauma in recurring nightmares.
The Connection Between Nightmares and Anxiety Disorders

The connection between nightmares and anxiety disorders is intricate and multifaceted. Firstly, there exists a reciprocal relationship between the two, where anxiety can contribute to the occurrence and intensity of nightmares, while nightmares can also exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Anxiety has been found to influence dream content, often leading to more negative and fear-inducing dreams. This connection is particularly apparent in individuals with specific anxiety disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Nightmares can also serve as a symptom of anxiety disorders, acting as a subconscious manifestation of the individual’s anxious thoughts and fears. By understanding and addressing the relationship between nightmares and anxiety disorders, effective strategies can be developed to manage and alleviate the impact of both conditions on an individual’s well-being.
1. Reciprocal Relationship
1. Reciprocal Relationship: The relationship between nightmares and anxiety disorders is often reciprocal, meaning they can influence and amplify each other’s effects. On one hand, anxiety disorders can contribute to the occurrence and intensity of nightmares. Individuals experiencing high levels of anxiety may have an increased likelihood of experiencing nightmares due to the heightened emotional arousal and stress that accompanies their anxiety. Anxiety can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to more frequent awakenings during REM sleep, the stage when most vivid dreaming occurs. This disruption can further contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. The impact of anxiety on dream content can also play a role in the development of nightmares. Anxiety-related thoughts, fears, and concerns often infiltrate dream content, resulting in dreams that evoke distressing emotions. On the other hand, nightmares can fuel the symptoms of anxiety disorders. The fear and stress experienced during nightmares can persist upon awakening, triggering increased anxiety levels throughout the day. Nightmares can also reinforce existing fears and anxieties, creating a cycle of anxiety and nightmares that becomes difficult to break. It is important to understand this reciprocal relationship between nightmares and anxiety disorders in order to address and manage both conditions effectively.
2. Impact of Anxiety on Dream Content
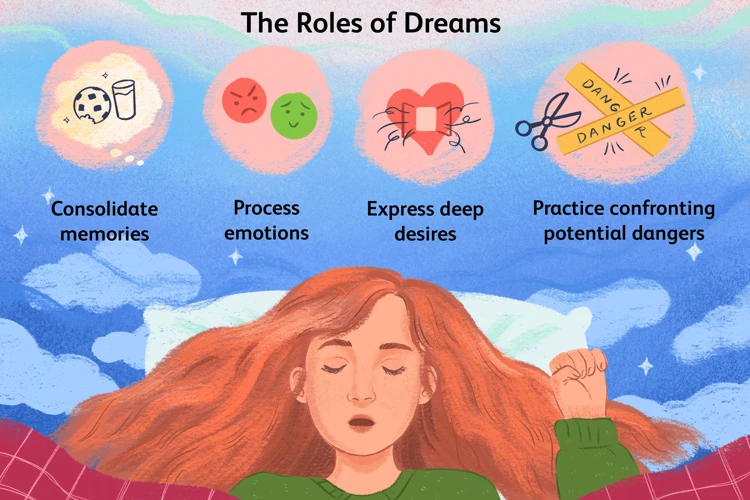
Anxiety can have a profound impact on the content of dreams, often leading to more frequent and intense nightmares. When individuals experience anxiety during their waking hours, it can seep into their subconscious mind during sleep, influencing the themes and emotions that arise in their dreams. Anxiety can manifest in various ways in dream content, such as feeling trapped, pursued, or overwhelmed. The dream scenarios may reflect real-life stressors and anxieties that the individual is facing, albeit in a symbolic or metaphorical manner. For instance, someone with social anxiety may have dreams involving embarrassing public situations or being judged by others. Similarly, individuals with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) may experience dreams centered around uncontrollable situations or catastrophic events. The impact of anxiety on dream content can create a feedback loop, as nightmares can further exacerbate anxiety levels, leading to a vicious cycle.
3. Nightmares as a Symptom of Anxiety Disorders
Nightmares can serve as a symptom of anxiety disorders, providing insight into the underlying emotional distress experienced by individuals. Anxiety disorders manifest as persistent worry, fear, and anxiety that can significantly impact daily functioning. When individuals are plagued by anxiety disorders, it can result in an increased vulnerability to experiencing nightmares. Nightmares may act as a manifestation of the intense fear and distress associated with anxiety disorders, reflecting the individual’s internal struggles and emotional turmoil. These nightmares often contain themes that mirror the individual’s fears and anxieties, exacerbating their sense of helplessness and unease. The occurrence of nightmares as a symptom of anxiety disorders signifies the deep-rooted impact of anxiety on an individual’s psychological well-being. It is vital to acknowledge and address these nightmares as part of the comprehensive treatment approach for anxiety disorders. By targeting the underlying anxiety, individuals can reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares, ultimately improving their overall mental health and quality of life.
Effects of Nightmares on Anxiety Disorders
Nightmares can have significant effects on individuals who already suffer from anxiety disorders. These distressing dreams can heighten anxiety levels, leading to increased stress and emotional turmoil. The impact of nightmares on anxiety disorders can result in a vicious cycle, where anxiety triggers nightmares, and nightmares, in turn, exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Additionally, nightmares can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to sleep deprivation and impaired functioning during the day. Sleep disruption further contributes to heightened anxiety and can negatively impact an individual’s overall quality of life. Managing and addressing nightmares is crucial in alleviating the effects they have on anxiety disorders and restoring a sense of mental well-being.
1. Heightened Anxiety and Stress Levels
Heightened anxiety and stress levels are significant effects of nightmares on anxiety disorders. When individuals experience frequent nightmares, it can lead to a continual state of heightened anxiety and stress throughout the day. The intense emotions and distressing content of nightmares can trigger a cascade of physiological and psychological responses, such as increased heart rate, sweating, and a sense of fear or unease. This state of heightened arousal can persist even after waking, causing individuals to feel on edge and anxious. The continuous disruption of sleep due to nightmares can also contribute to chronic fatigue and further exacerbate feelings of anxiety and stress. This persistent anxiety and stress can then feed back into the cycle of nightmares, creating a vicious cycle that perpetuates both the anxiety disorder and the occurrence of nightmares. It is crucial to address and manage these heightened anxiety and stress levels to break this cycle and improve overall well-being.
2. Sleep Disruption and Impaired Functioning
Sleep disruption and impaired functioning are significant effects of nightmares on individuals with anxiety disorders. Nightmares can lead to restless nights, frequent awakenings, and difficulty falling back asleep, disrupting the overall quality of sleep. This can result in daytime fatigue, drowsiness, and a lack of concentration or focus, impairing an individual’s cognitive functioning and ability to perform daily tasks. The ongoing cycle of sleep disturbance caused by nightmares can further exacerbate anxiety symptoms, creating a vicious cycle. As a result, individuals may experience heightened anxiety levels during the day, leading to increased stress and reduced overall functioning. Additionally, the sleep deprivation caused by nightmares can negatively impact mood regulation, making individuals more susceptible to experiencing irritability, mood swings, and emotional instability. Taking steps to address and manage nightmares is crucial in alleviating sleep disruption and minimizing impaired functioning for individuals with anxiety disorders. This can involve seeking professional help, incorporating relaxation techniques, and implementing cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
Managing Nightmares and Anxiety Disorders
Managing nightmares and anxiety disorders requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the psychological and physiological aspects of these conditions. Seeking professional help is crucial in effectively managing nightmares and anxiety disorders. Therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can be particularly beneficial in helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety and nightmares. Additionally, relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation, can help reduce anxiety and promote better sleep. Creating a soothing bedtime routine, ensuring a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene can also contribute to improved sleep quality and reduced nightmares. It’s important to remember that managing nightmares and anxiety disorders may require patience and persistence, but with the right support and strategies, individuals can find relief and improve their overall well-being.
1. Seeking Professional Help
1. Seeking Professional Help:
When dealing with nightmares and anxiety disorders, it is important to consider seeking professional help. Mental health professionals, such as therapists, psychologists, or psychiatrists, have the expertise and knowledge to provide appropriate guidance and support. They can help individuals explore the underlying causes of their nightmares and anxiety disorders, as well as develop effective treatment strategies.
A professional can conduct a thorough assessment to make an accurate diagnosis and recommend the most suitable treatment options. They may suggest therapy sessions, which can be done on an individual basis or in a group setting, depending on the individual’s needs and preferences. Therapy can help individuals gain insight into their fears and anxieties, understand patterns in their thinking, and develop coping mechanisms to manage both nightmares and anxiety disorders effectively.
Additionally, seeking professional help can also involve medication management. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to alleviate severe anxiety symptoms or to stabilize sleep patterns disrupted by nightmares. A qualified medical professional can closely monitor the individual’s response to medication and make any necessary adjustments.
Remember, seeking professional help is a proactive step towards finding lasting relief from nightmares and anxiety disorders. It allows for personalized guidance based on individual circumstances, ensuring a comprehensive approach to mental well-being.
2. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and effective treatment approach for managing nightmares and anxiety disorders. This therapeutic technique focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety and distress. CBT aims to restructure cognitive distortions and develop healthier coping mechanisms. In the context of nightmares, CBT can help individuals gain control over their dreams and reduce the distress associated with them. There are several key components of CBT that make it effective in addressing nightmares and anxiety disorders:
1. Cognitive Restructuring: This involves identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs associated with nightmares and anxiety. The therapist helps individuals recognize distorted thinking patterns and replace them with more realistic and positive thoughts. By reframing negative interpretations, individuals can reduce anxiety and promote a sense of control over their dream experiences.
2. Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy is often used in conjunction with CBT to help individuals confront and gradually reduce their fear and anxiety related to nightmares. This may involve creating a safe environment to engage with feared dream scenarios or using virtual reality technology to simulate anxiety-provoking situations. Through repeated exposure, individuals can desensitize themselves to the distressing elements of their nightmares.
3. Relaxation Techniques: CBT incorporates various relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery. These techniques help individuals manage stress, reduce anxiety levels, and promote better sleep hygiene. By practicing relaxation techniques regularly, individuals can enhance their ability to self-soothe and reduce the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
4. Sleep Hygiene Education: CBT also emphasizes the importance of maintaining good sleep hygiene practices. This includes establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, avoiding stimulants before bedtime, and implementing relaxation techniques as part of a bedtime routine. Improving sleep hygiene can contribute to a more restful sleep and minimize the occurrence of nightmares and anxiety symptoms.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers effective strategies for individuals experiencing nightmares and anxiety disorders. It provides practical tools to address the underlying causes of distress and empowers individuals to regain control over their thoughts, emotions, and dream experiences. CBT can be conducted individually or in a group setting, based on the individual’s preferences and the recommendations of a mental health professional.
3. Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques are valuable tools in managing both nightmares and anxiety disorders. These techniques aim to promote a sense of calm and relaxation, reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares while also alleviating symptoms of anxiety. Here are some effective relaxation techniques to consider:
1. Deep Breathing: Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing or belly breathing, can help activate the body’s relaxation response. By focusing on slow, deep breaths, individuals can lower their heart rate, reduce muscle tension, and promote feelings of relaxation.
2. Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This technique involves systematically tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups in the body. By consciously releasing tension in each muscle group, individuals can experience a deep sense of relaxation and relieve physical and mental stress.
3. Mindfulness Meditation: Mindfulness meditation focuses on being fully present in the moment, observing one’s thoughts and sensations without judgment. Regular practice of mindfulness meditation can enhance self-awareness and reduce anxiety, ultimately leading to improved sleep quality.
4. Guided Imagery: Guided imagery involves creating mental images that evoke a sense of calm and peacefulness. This technique can be done through the use of guided audio recordings or visualizing serene environments. It can be an effective way to redirect the mind’s focus away from anxious thoughts and promote relaxation.
5. Yoga and Tai Chi: These mind-body practices combine physical movements, breath control, and meditation. Engaging in yoga or tai chi regularly can enhance relaxation, improve sleep quality, and reduce anxiety symptoms.
It is important to note that while relaxation techniques can be beneficial, they may not work for everyone. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or therapist to determine which relaxation techniques are best suited to your individual needs and preferences. Regular practice and persistence are key to experiencing the full benefits of relaxation techniques in managing nightmares and anxiety disorders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the connection between nightmares and anxiety disorders is undeniable. Nightmares can both be a symptom of anxiety disorders and exacerbate anxiety symptoms, creating a vicious cycle. The reciprocal relationship between nightmares and anxiety means that addressing one can positively impact the other. Heightened anxiety and stress levels caused by nightmares can significantly impact an individual’s daily functioning and overall well-being. Sleep disruption, often caused by frequent nightmares, can further contribute to anxiety symptoms and impair daily functioning. However, there are strategies available to manage both nightmares and anxiety disorders effectively. Seeking professional help, such as therapy or counseling, can provide valuable support and guidance. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has shown effectiveness in both reducing nightmares and managing anxiety disorders. Additionally, relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and meditation, can help individuals alleviate anxiety and improve sleep quality. By understanding the complex relationship between nightmares and anxiety disorders and implementing appropriate management strategies, individuals can take steps towards better mental health and improved overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can everyone experience nightmares?
No, not everyone experiences nightmares. Nightmares are more common in children, but they can occur in adults as well. Certain factors such as stress, trauma, and anxiety disorders can increase the likelihood of having nightmares.
2. Are nightmares and night terrors the same thing?
No, nightmares and night terrors are not the same thing. Nightmares are vivid dreams that cause fear and unease, whereas night terrors are episodes of intense fear or terror that occur during sleep, often accompanied by physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat and sweating.
3. Can anxiety disorders cause nightmares?
Yes, anxiety disorders can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. Excessive worry and stress associated with anxiety disorders can disrupt sleep and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
4. How can certain medications affect the frequency of nightmares?
Some medications, such as certain antidepressants and blood pressure medications, have been known to cause nightmares as a side effect. It is essential to discuss any changes in dream patterns with a healthcare provider if you suspect your medication may be contributing to nightmares.
5. Are nightmares a symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)?
Yes, nightmares are a common symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Individuals with PTSD may experience recurring nightmares related to their traumatic experiences, which can contribute to sleep disturbances and overall distress.
6. Can nightmares be a sign of an underlying sleep disorder?
Yes, frequent nightmares can be a sign of an underlying sleep disorder such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to properly diagnose and address any sleep disorders that may be contributing to nightmares.
7. Can recurring nightmares be a result of unresolved emotional issues?
Yes, recurring nightmares can sometimes be a manifestation of unresolved emotional issues. Trauma, grief, or other unresolved psychological conflicts can resurface in the form of recurring nightmares. Seeking therapy or counseling can help address and process these underlying emotional issues.
8. How can I reduce the frequency of nightmares?
There are several techniques you can try to reduce the frequency of nightmares. These include practicing relaxation techniques before bed, establishing a consistent sleep routine, managing stress and anxiety levels through therapy or meditation, and creating a calm and comfortable sleep environment.
9. Can lucid dreaming techniques help with nightmares?
Yes, some individuals have found that practicing lucid dreaming techniques can help them gain control over their nightmares. Lucid dreaming involves becoming aware that you are dreaming while in the dream, which allows you to consciously influence the dream’s outcome.
10. When should I seek professional help for nightmares?
If nightmares are causing significant distress, disrupting daily life, or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it is advisable to seek professional help. A healthcare provider or mental health professional can assess your situation, provide appropriate guidance, and explore treatment options.








