When the sun sets and darkness falls, our minds venture into a world of dreams and nightmares. Strikingly vivid and often unsettling, nightmares can leave us feeling anxious, unsettled, and even terrified upon waking. It’s natural to wonder about the impact of these nighttime terrors on our mental health and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the deep-rooted psychological effects of nightmares, their intricate relationship with mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression, coping strategies to alleviate their distress, and proactive measures to prevent them from infiltrating our sleep. Whether you’ve experienced an occasional nightmare or are plagued by them regularly, this article aims to shed light on the importance of understanding and addressing this unsettling aspect of our subconscious minds.
What are Nightmares?

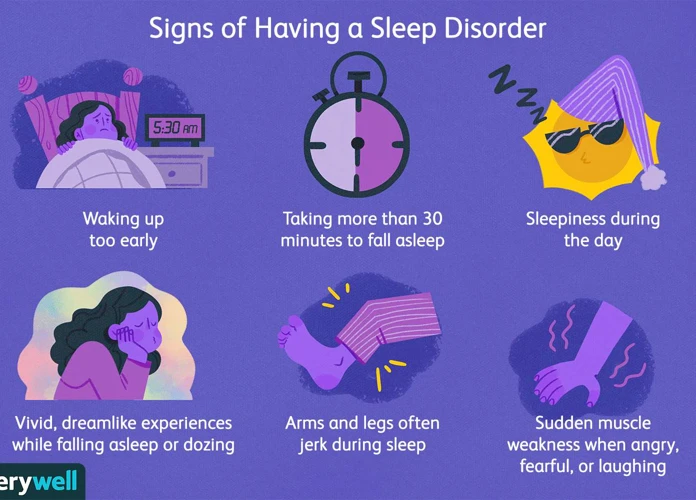
Nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that can cause intense emotions and fear upon waking. They often involve scenarios that are threatening, dangerous, or anxiety-inducing. These dreams can be so intense that they wake us up in the middle of the night, leaving us with a rapid heartbeat and a sense of dread. Nightmares are different from regular dreams because of their content and the level of distress they cause. Unlike regular dreams, nightmares can be easily remembered upon waking due to their emotional intensity. They can vary in frequency, with some individuals experiencing occasional nightmares, while others may have recurring nightmares that significantly impact their quality of sleep and overall well-being. Nightmares can originate from a variety of sources, including everyday stressors, traumatic experiences, medications, sleep disorders, or psychological disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Understanding the nature of nightmares is crucial in comprehending their impact on mental health and well-being. If you want to learn more about nightmares, you can check the article on Understanding Psychological Nightmares. Additionally, sleep disorders can also play a role in the occurrence of nightmares. To understand more about the relationship between sleep disorders and nightmares, you can read the article on the Role of Sleep Disorders in Nightmares. Addressing nightmares and improving sleep hygiene can play a significant role in preventing their occurrence. For insights and strategies on preventing nightmares by improving sleep, you can visit the article on Preventing Nightmares by Improving Sleep.
The Psychological Impact of Nightmares

Nightmares can have a profound impact on our psychological well-being, causing a range of negative effects that can affect our daily functioning and overall quality of life.
One of the primary psychological impacts of nightmares is the increase in anxiety and stress levels. The intense emotions experienced during nightmares can linger even after waking up, leaving us feeling on edge and anxious throughout the day. This heightened sense of anxiety can make it challenging to relax, concentrate, and engage in daily activities. The fear of having another nightmare can create a constant state of anticipation and nervousness, further exacerbating anxiety symptoms.
Nightmares can disrupt our sleep patterns, leading to sleep disturbances and inadequate rest. The vivid and distressing nature of nightmares can cause frequent awakenings during the night, making it difficult to have a restful sleep. As a result, individuals who experience recurring nightmares may suffer from chronic sleep deprivation and daytime fatigue, impacting their cognitive functioning, mood, and overall performance.
The emotional toll of nightmares extends beyond the momentary fright experienced during the dream. The lingering negative emotions, such as fear, sadness, anger, or helplessness, can persist long after waking up. This can contribute to a negative mood throughout the day, leading to irritability, sadness, and a lack of motivation. It may also impact interpersonal relationships, as the residual negative emotions can make it challenging to fully engage with others or enjoy daily activities.
Understanding the psychological impact of nightmares is crucial in recognizing the need to address and manage these distressing dreams effectively. By implementing appropriate coping strategies and seeking professional help when necessary, individuals can alleviate the negative psychological effects and improve their overall mental well-being.
1. Increased Anxiety and Stress
One of the primary psychological impacts of nightmares is the increased anxiety and stress they induce. When we experience a nightmare, our brains interpret the events and emotions as if they were real, triggering the body’s stress response. This response releases cortisol and adrenaline, leading to heightened arousal and anxiety. The intense fear and distress experienced during nightmares can linger even after waking up, making it challenging to relax and return to sleep. This heightened state of anxiety can persist throughout the day, negatively affecting overall well-being and mental health. Research has shown that individuals who frequently experience nightmares are more prone to generalized anxiety disorder and other anxiety-related conditions. The ongoing cycle of anxiety and stress caused by nightmares can disrupt daily functioning, impair concentration, increase irritability, and contribute to a decreased quality of life. Understanding the connection between nightmares and increased anxiety and stress is crucial in developing effective coping strategies and interventions to alleviate their impact on mental health.
2. Disrupted Sleep Patterns
Disrupted sleep patterns are a common consequence of nightmares. When we experience intense and distressing dreams, they can jolt us awake, interrupting our sleep cycles. This disruption can have significant effects on our overall sleep quality and duration. Sleep stages are important for various bodily functions, including memory consolidation, immune system functioning, and emotional regulation. Nightmares can prevent us from reaching deep and restorative sleep stages, such as REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, where most dreaming occurs. As a result, we may feel fatigued, groggy, and irritable the following day. The recurrent nature of nightmares can perpetuate a cycle of disrupted sleep, leading to chronic sleep deprivation. This, in turn, can have a negative impact on our mental health and well-being. To address disrupted sleep patterns caused by nightmares, establishing a bedtime routine that promotes relaxation and calmness is crucial. This may involve activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation before bed. Additionally, creating a comfortable sleep environment that is free from distractions, such as excessive noise or light, can help improve sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of nightmares. It’s important to prioritize sleep hygiene and make necessary adjustments to promote restful sleep and minimize the disruptions caused by nightmares.
3. Negative Mood and Emotions
Negative mood and emotions are common outcomes of experiencing nightmares. As we wake up from a distressing dream, the intense emotions and fear that accompanied it can persist, affecting our mood and overall emotional well-being throughout the day. The unsettling nature of nightmares can leave us feeling anxious, agitated, and on edge, making it harder to focus and engage in daily activities. These negative emotions can also contribute to irritability, decreased motivation, and a general sense of unease. Nightmares can evoke feelings of sadness, helplessness, and despair, leading to a negative outlook on life. The emotional impact of nightmares can be significant, affecting not only our mental health but also our relationships and overall quality of life. It is important to address and cope with these negative emotions to prevent them from escalating and having a long-term impact on our well-being. Strategies such as practicing relaxation techniques, seeking professional help, or engaging in therapeutic activities can be valuable in managing negative emotions associated with nightmares.
The Relationship Between Nightmares and Mental Health

Nightmares and mental health have a complex and intertwined relationship. The distressing nature of nightmares can have a significant impact on our psychological well-being. Understanding this relationship is crucial in addressing and managing mental health conditions that may arise or be exacerbated by nightmares. One mental health condition closely associated with nightmares is Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Individuals with PTSD often experience frequent and vivid nightmares related to their traumatic experiences. These nightmares can be distressing and may lead to further sleep disturbances and increased anxiety. Another mental health condition linked to nightmares is Anxiety Disorders. Individuals with anxiety disorders may have a higher likelihood of experiencing nightmares due to heightened levels of stress and anxiety. Nightmares can also contribute to the maintenance of anxiety disorders by reinforcing and intensifying existing fears and worries. Depression is another mental health condition associated with nightmares. Research has shown a bidirectional relationship between nightmares and depression, where nightmares can serve as both a symptom and a risk factor for the development or worsening of depressive symptoms. It’s important to note that not everyone who experiences nightmares will develop a mental health condition, but for those already struggling with their mental health, nightmares can be an additional burden. Seeking therapy and treatment for mental health conditions is crucial in addressing both the underlying issues and the impact of nightmares on overall well-being.
1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition characterized by a range of symptoms that can occur after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Nightmares are a common feature of PTSD and can significantly impact the lives of those affected. Individuals with PTSD may experience recurring nightmares that recreate the traumatic event, causing them to relive the distressing emotions and sensory details associated with the trauma. These nightmares can be so vivid and intense that they disrupt sleep and contribute to further distress and anxiety. The content of the nightmares may vary, but they often involve themes related to the traumatic experience, such as danger, helplessness, or the threat of harm. Nightmares can act as triggers for other PTSD symptoms, including flashbacks, intrusive thoughts, and heightened anxiety. It is important for individuals with PTSD to seek appropriate treatment, such as therapy and medication, to address both the nightmares and the underlying trauma. By addressing the root cause of the nightmares, individuals can find relief and improve their overall mental health and well-being.
2. Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive and persistent anxiety and fear. These disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder, can have a complex relationship with nightmares. Individuals with anxiety disorders may experience frequent nightmares as a result of their heightened levels of anxiety and stress. Nightmares can act as triggers for anxiety, further exacerbating the symptoms of the disorder. The fear and distress caused by nightmares can contribute to a vicious cycle of anxiety and disrupted sleep patterns. Additionally, anxiety disorders can also increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares related to specific phobias or traumatic events. Conversely, nightmares themselves can contribute to the development or worsening of anxiety disorders, as they can lead to increased anticipatory anxiety and fear of sleep. It is important for individuals with anxiety disorders to seek professional help in order to address both the underlying anxiety as well as the impact of nightmares on their mental health and well-being. Treatment options may include therapy, medication, and the development of coping strategies.
3. Depression
Depression is a mental health condition characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest or pleasure in activities. While nightmares are commonly associated with anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), they can also have a significant impact on individuals with depression. Nightmares and depression can create a vicious cycle, where nightmares increase the likelihood of depressive symptoms, and depression can lead to an increase in the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Nightmares can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to poor quality sleep and daytime fatigue, which are common symptoms of depression. Additionally, the content of nightmares may align with the negative thoughts and emotions associated with depression, reinforcing feelings of sadness, guilt, or worthlessness. The combination of disturbed sleep and increased emotional distress can exacerbate depressive symptoms and make it even more challenging to cope with the condition. It’s important for individuals with depression to seek appropriate mental health support to address both the underlying condition and the impact of nightmares. Implementing strategies to manage depression, such as therapy, medication, and self-care practices, may also help alleviate the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Incorporating relaxation techniques and creating a peaceful sleep environment can contribute to improved sleep quality and reduced nighttime disturbances, consequently benefiting individuals with depression.
Coping Strategies for Nightmares
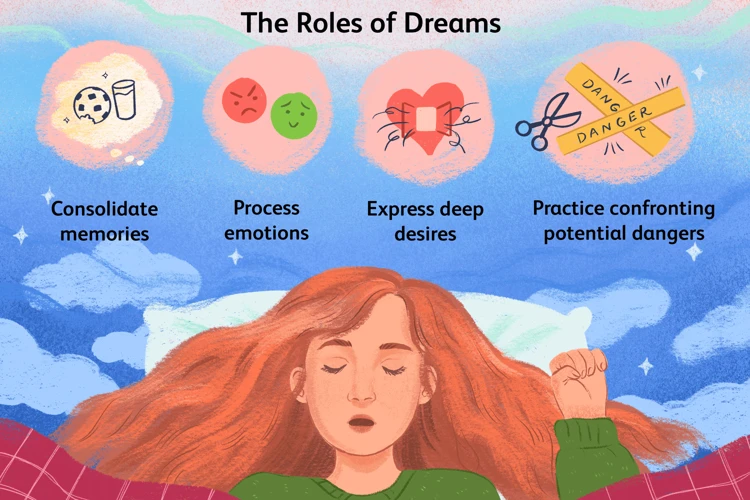
When nightmares disrupt our sleep and impact our mental well-being, it’s crucial to have effective coping strategies in place. Here are some strategies that can help alleviate the distress caused by nightmares:
1. Creating a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Establishing a calming routine before bed can signal to the mind and body that it’s time to unwind and prepare for sleep. This can include activities such as taking a warm bath, practicing deep breathing exercises, or engaging in relaxation techniques like listening to soft music or reading a book.
2. Keeping a Dream Journal: Keeping a journal next to your bed and jotting down your nightmares upon waking can provide an outlet for your emotions. It enables you to process the content of your dreams and potentially identify any recurring themes or triggers. Additionally, this can also serve as a tool for discussing your dreams with a therapist if necessary.
3. Seeking Professional Help: If nightmares persist and significantly impact your daily life, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor who specializes in dream analysis or trauma can be beneficial. They can help you explore the underlying causes of your nightmares and develop coping strategies tailored to your specific needs.
4. Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation techniques can help calm an overactive mind and promote relaxation before sleep. Engaging in mindfulness exercises, such as focusing on your breath or practicing body scan techniques, can help reduce anxiety and create a more peaceful mindset for bedtime.
Remember, finding the right coping strategies may require some trial and error. It’s essential to be patient with yourself and explore different techniques until you find what works best for you.
1. Creating a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
Creating a relaxing bedtime routine can be an effective strategy for coping with nightmares and improving sleep quality. Here are some steps you can take to establish a calming routine before bed:
1. Set a consistent bedtime: Establishing a regular sleep schedule helps regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up at the desired times.
2. Limit screen time: Avoid using electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, or laptops at least an hour before bed. The blue light emitted by these devices can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that promotes sleep.
3. Engage in relaxation techniques: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or meditation before bed. These techniques can help calm the mind, reduce anxiety, and promote a sense of relaxation.
4. Create a comfortable sleep environment: Make sure your bedroom is conducive to sleep. Keep the room cool, dark, and quiet. Use comfortable bedding and invest in a good quality mattress and pillows that support a restful sleep.
5. Establish a bedtime routine: Engage in relaxing activities before bed, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or listening to calming music. These activities can help signal to your brain that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
6. Avoid stimulating substances: Limit your intake of caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, as these substances can interfere with your sleep patterns and contribute to the occurrence of nightmares.
By incorporating these steps into your nightly routine, you can create a serene and soothing atmosphere that promotes better sleep and reduces the likelihood of nightmares. Remember, consistency is key when establishing a bedtime routine, so make an effort to follow this routine every night for optimal results.
2. Keeping a Dream Journal
Keeping a dream journal is an effective strategy for coping with nightmares and gaining insight into their underlying causes. By recording your dreams upon waking, you can capture the details, emotions, and themes of your nightmares. This practice helps you develop a better understanding of recurring patterns or triggers that may be contributing to the nightmares. To start a dream journal, keep a notebook and pen by your bed so you can conveniently jot down your dreams immediately upon awakening. When documenting your dreams, focus on key elements such as people, places, objects, and emotions. Describe the atmosphere and any sensations you experienced during the nightmare. It’s also helpful to note any events or stressors from the previous day that may have influenced the dream. Reviewing your dream journal periodically can reveal patterns or themes that may provide valuable insights into the underlying causes of your nightmares. For instance, you may notice that certain types of situations or emotions are consistently present in your nightmares, which can guide you in identifying potential triggers. Sharing your dream journal with a mental health professional can also be beneficial as they can provide guidance and help you make connections between your dreams and your mental well-being. Keeping a dream journal offers a proactive and empowering approach to managing and understanding nightmares on a deeper level.
3. Seeking Professional Help
When it comes to addressing nightmares and their impact on mental health, seeking professional help can be a valuable and effective approach. Mental health professionals, such as therapists and counselors, have the expertise and knowledge to provide guidance and support in managing and overcoming nightmares. They can help individuals explore the underlying causes of their nightmares, such as past trauma or unresolved emotions, and develop coping strategies tailored to their specific needs.
There are various therapeutic techniques that professionals may employ to address nightmares, including:
– Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a common approach used to treat nightmares. It focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and beliefs associated with nightmares. Through CBT, individuals can learn techniques to reframe their thoughts and reduce the emotional distress caused by nightmares.
– Exposure Therapy: This therapy involves gradually exposing individuals to the feared elements of their nightmares in a safe and controlled environment. By confronting their fears in a therapeutic setting, individuals can work towards desensitization and reduce the intensity of their nightmares.
– Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR is a specialized form of therapy often used to treat trauma-related nightmares. It involves guided eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation to help individuals process traumatic memories and reduce the distress associated with nightmares.
It’s important to note that seeking professional help is not a sign of weakness, but rather a proactive step towards improving mental health and well-being. Mental health professionals can provide a safe and nonjudgmental space for individuals to explore their nightmares, understand their deeper meanings, and develop effective coping strategies. If you are experiencing frequent or distressing nightmares that are impacting your daily life, consider reaching out to a mental health professional for support. They can assess your unique situation and recommend the most appropriate and beneficial treatment options to help you overcome your nightmares and improve your overall mental health.
4. Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation can be valuable tools for coping with nightmares and improving overall mental well-being. Practicing mindfulness involves being fully present in the moment, acknowledging and accepting our thoughts, feelings, and sensations without judgment. It allows us to cultivate a sense of calm and detachment from distressing thoughts and emotions. When applied to nightmares, mindfulness can help us develop resilience and a greater ability to manage the intense emotions that accompany these dreams. By practicing mindfulness before bed or during periods of wakefulness caused by nightmares, we can reduce anxiety and promote relaxation, making it easier to return to restful sleep.
Meditation, on the other hand, involves focusing the mind and achieving mental clarity and tranquility. By incorporating meditation into our daily routine, we can cultivate a sense of inner peace and balance, which can have a positive impact on our mental health and sleep quality. Meditation techniques such as guided imagery or body scan meditation can be especially helpful in managing nightmares, as they promote relaxation and provide a sense of control over our thoughts and emotions.
To incorporate mindfulness and meditation into your nighttime routine, you can try the following strategies:
1. Deep Breathing: Take slow, deep breaths in and out, focusing your attention on the sensation of the breath entering and leaving your body. This can help calm your mind and relax your body.
2. Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Starting from your toes and moving up to your head, tense and relax each muscle group in your body. This technique can help release physical tension and induce relaxation.
3. Visualization: Imagine yourself in a peaceful and relaxing environment, such as a beach or a forest. Engage your senses and visualize the sights, sounds, and smells of this serene place to create a sense of calm and tranquility.
4. Body Scan: Lie in bed and bring your attention to different parts of your body, starting from your toes and moving up to your head. Notice any sensations or tension in each area and consciously release any tension you find.
By incorporating these mindfulness and meditation techniques into your routine, you can promote a sense of peace, reduce anxiety, and create a more conducive environment for a restful night’s sleep. Remember, consistency is key, so try to practice these techniques regularly to experience their full benefits.
Preventing Nightmares
is an important aspect of maintaining good mental health and overall well-being. While nightmares can be distressing, there are proactive steps that can be taken to reduce their frequency and intensity. One effective strategy for preventing nightmares is managing stress and anxiety levels. High levels of stress and anxiety can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares, so finding healthy outlets for stress, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, or engaging in activities we enjoy, can help reduce the likelihood of experiencing distressing dreams. Another crucial step in preventing nightmares is addressing and processing any traumatic experiences one may have had. Traumatic events can often manifest in nightmares, so seeking therapy or counseling can assist in processing these experiences and reducing their impact on dream content. Developing and maintaining a consistent sleep routine can also be beneficial in preventing nightmares. Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle and promotes better overall sleep quality. Additionally, creating a calm and comfortable sleep environment, free from distractions and stimulating electronic devices, can contribute to a more restful sleep and decrease the likelihood of nightmares. It’s also important to avoid consuming alcohol or caffeine close to bedtime, as these substances can interfere with sleep patterns and potentially trigger nightmares. Making small lifestyle changes, such as implementing relaxation techniques before bed, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, can also help reduce stress levels and promote better sleep hygiene. By taking proactive measures to prevent nightmares, individuals can experience improved sleep quality and enhanced well-being.
1. Managing Stress and Anxiety
Managing stress and anxiety is crucial in preventing nightmares and promoting better sleep. Here are some strategies that can help individuals effectively manage stress and anxiety:
1. Engage in relaxation techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery can help reduce stress and anxiety levels before bed. These techniques can help calm the mind and prepare it for a restful sleep.
2. Exercise regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can have a positive impact on both mental and physical health. Exercise helps reduce stress and anxiety, promotes better sleep quality, and can contribute to an overall sense of well-being.
3. Establish a regular sleep routine: Creating a consistent sleep routine can signal to the body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. Establishing a regular bedtime and waking up at the same time every day can help regulate sleep patterns and reduce stress.
4. Practice stress management techniques: Find healthy ways to manage and cope with stress throughout the day. This could include activities such as journaling, talking to a trusted friend or therapist, engaging in hobbies, or practicing mindfulness and meditation.
5. Avoid stimulating activities before bed: Engaging in stimulating activities right before bed, such as watching intense television shows or using electronic devices, can increase stress levels and disrupt sleep. It’s best to create a calm and relaxing environment in the hours leading up to bedtime.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can effectively manage stress and anxiety, leading to a reduction in nightmares and an improvement in overall sleep quality.
2. Identifying and Addressing Traumatic Experiences
Identifying and addressing traumatic experiences is an essential step in preventing nightmares and promoting mental well-being. Trauma can have a profound impact on our mental health, leading to the development of nightmares and other psychological difficulties. Here are some key points to consider when it comes to identifying and addressing traumatic experiences:
1. Recognize the Signs: Traumatic experiences can range from a single event to ongoing situations of abuse or neglect. It’s crucial to recognize the signs of trauma, which may include intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, avoidance behaviors, hyperarousal, or emotional numbing. These symptoms can manifest in various ways and may differ from person to person.
2. Seek Professional Help: If you suspect that you have experienced a traumatic event, it is highly recommended to seek professional help. A therapist or counselor trained in trauma therapy can provide a safe and supportive environment to explore and process your experiences. They can help you identify and understand the impact of the trauma on your mental health.
3. Trauma-Focused Therapy: Trauma-focused therapies, such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) or Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT), can be effective in addressing traumatic experiences and reducing the occurrence of nightmares. These therapies aim to desensitize and reprocess traumatic memories, alleviate distressing emotions, and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
4. Support Systems: Building a strong support system is crucial in addressing and healing from trauma. Surrounding yourself with understanding and empathetic individuals can provide a safe space for sharing your experiences and receiving emotional support.
5. Self-Care and Coping Strategies: Engaging in self-care activities and implementing coping strategies can help manage the effects of trauma. This may include practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, journaling, or participating in creative outlets such as art or music therapy.
6. Gradual Exposure: Gradually exposing yourself to triggers and reminders of the traumatic event, under the guidance of a therapist, can help desensitize your response and reduce the intensity of nightmares.
Identifying and addressing traumatic experiences requires a compassionate and patient approach. It is essential to work at your own pace and prioritize self-care throughout the healing process. Remember, seeking professional help and guidance can provide valuable support on your journey towards healing and reducing the impact of nightmares on your mental health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nightmares can have a significant impact on our mental health and well-being. These vivid and disturbing dreams can lead to increased anxiety, disrupted sleep patterns, and negative mood and emotions. Moreover, nightmares have a strong relationship with various mental health conditions, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and depression. Fortunately, there are coping strategies that can help alleviate the distress caused by nightmares, such as creating a relaxing bedtime routine, keeping a dream journal, seeking professional help, and practicing mindfulness and meditation. Additionally, it’s important to take proactive measures to prevent nightmares, such as managing stress and anxiety and addressing any underlying traumatic experiences. By understanding the nature of nightmares and implementing these strategies, we can strive to improve our sleep quality, mental well-being, and overall quality of life. Remember, if nightmares persist or significantly impact your daily functioning, it’s always advisable to seek professional help.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can everyone experience nightmares?
Yes, nightmares can happen to anyone. However, some individuals may be more prone to experiencing nightmares due to factors such as stress, trauma, sleep disorders, or certain medications.
2. Are nightmares a sign of a mental health disorder?
Nightmares themselves are not considered a mental health disorder. However, they can be a symptom of an underlying condition such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, or depression.
3. Can nightmares be caused by medications?
Yes, certain medications, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and blood pressure medications, can potentially cause nightmares as a side effect. It’s important to discuss any disturbing dreams with your healthcare provider if you suspect it may be related to your medication.
4. How can nightmares affect sleep patterns?
Nightmares can disrupt sleep patterns by causing frequent awakenings during the night. These awakenings can lead to difficulty falling back asleep, resulting in fragmented and poor-quality sleep.
5. Can nightmares lead to physical symptoms?
Yes, nightmares can evoke physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, sweating, and feelings of anxiety or fear. These physiological responses can linger even after waking up from a nightmare and may affect daytime functioning.
6. Are there any coping strategies for dealing with nightmares?
Yes, there are several coping strategies that can help manage nightmares, including creating a relaxing bedtime routine, keeping a dream journal, seeking professional help, and practicing mindfulness and meditation techniques.
7. Can nightmares be a sign of unresolved trauma?
Yes, nightmares can be a manifestation of unresolved trauma. They may serve as a way for the subconscious mind to process and attempt to resolve traumatic experiences.
8. Can improving sleep hygiene help reduce nightmares?
Yes, practicing good sleep hygiene can contribute to reducing the frequency of nightmares. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities before bed.
9. Can recurring nightmares be a cause for concern?
Recurring nightmares can be a cause for concern, especially if they significantly affect sleep quality and overall well-being. It may be beneficial to seek professional help if recurring nightmares persist and interfere with daily functioning.
10. Can nightmares be prevented?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent nightmares, certain measures can be taken to reduce their occurrence. Managing stress and anxiety, addressing traumatic experiences, and adopting healthy sleep habits can all contribute to minimizing the likelihood of having nightmares.