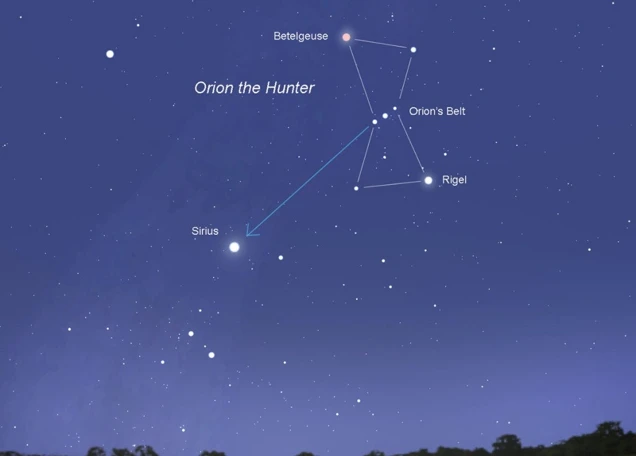
Orion’s Belt has captivated our imagination and curiosity for centuries, as it shines brightly in the night sky, forming a distinctive and easily recognizable pattern. But what is the story behind this celestial trio of stars? Delving into mythology from various cultures, we uncover tales of love, rivalry, and cosmic connections. From Greek and Egyptian mythology to Native American folklore, the stories surrounding Orion’s Belt offer a glimpse into the rich cultural tapestry woven around this enigmatic constellation. As we explore these legends and their significance, we begin to unravel the mystery and unravel the real significance behind Orion’s Belt.
Origin of Orion’s Belt
Legend has it that the origin of Orion’s Belt can be traced back to ancient mythology, where stories intertwine to create a tapestry of cosmic intrigue. In Greek mythology, Orion was a mighty hunter, born to the sea god Poseidon and the earth goddess Gaea (source). His birth was marked by extraordinary events, including his emergence from a bull’s hide and his ability to walk on water. But it was Orion’s quest for immortality that ultimately led to the formation of his famous belt. In Egyptian mythology, Orion was associated with the god Osiris, who symbolized resurrection and the afterlife (source). The ancient Egyptians believed that Orion’s Belt represented the three stars in the constellation – Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka – as the gods Isis, Osiris, and Horus respectively. As we delve deeper into the mythology surrounding Orion, we begin to unravel the threads of these captivating legends and their significance in shaping the lore of Orion’s Belt.
1.1 The Birth of Orion
In Greek mythology, the birth of Orion is shrouded in mystery and wonder. According to one legend, Orion was the son of the sea god Poseidon and the earth goddess Gaea. As the child of divine parentage, Orion was destined for greatness. However, his birth was no ordinary event. It is said that Orion emerged from a bull’s hide, which was buried in the ground by Poseidon. This unique and extraordinary birth marked his connection to the earth and the sea. With his immense strength and skill as a hunter, Orion quickly became renowned throughout the lands. His physical prowess and the stories of his heroic feats spread far and wide, solidifying his reputation as a formidable figure in Greek mythology. The tale of Orion’s birth sets the stage for the adventures and encounters that would shape his destiny and ultimately lead to the formation of his iconic belt of stars. To understand more about the celestial connections of Orion, it is essential to explore the stories that unfold in his mythology, including his legendary encounters with Artemis and his eternal rivalry with the Scorpion (source).
1.2 Orion’s Quest for Immortality
In the realm of Greek mythology, the story of Orion’s quest for immortality unfolds with both triumph and tragedy. As a renowned hunter, Orion caught the attention of the goddess Artemis, who admired his skills and valor. Orion, longing to be with Artemis forever, sought a way to obtain immortality. Various versions of the myth depict different paths he took in his pursuit. According to one tale, Orion traveled to the island of Chios, where he encountered the king’s daughter, Merope, who fell deeply in love with him. However, Orion’s affections remained solely for Artemis. Despite her love for Orion, Artemis could not grant him immortality as it went against the natural order of life and death. Determined, Orion sought the guidance of the blind seer, Tiresias, who directed him to the far east, where the rising sun could grant him eternal life. While the specific details of Orion’s journey vary, they ultimately converge on a tragic end. Betrayed by the gods, Orion perished, either from a scorpion’s sting or the wrath of Artemis herself. However, the gods, in recognition of his bravery and skill, placed Orion in the sky as a constellation, forever remembered as the great hunter. Thus, Orion’s quest for immortality serves as a poignant reminder of both the power and limitations of mortal beings.
1.3 The Belt Formation
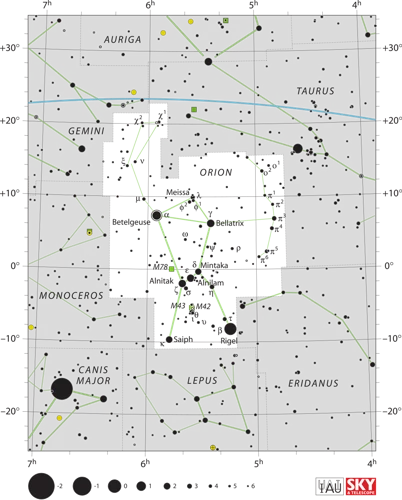
The Belt Formation refers to how Orion’s Belt came to be and the celestial mechanics behind its formation. According to mythology, the three stars in Orion’s Belt represent the fur belt worn by Orion the hunter. However, in astronomical terms, these stars are not physically connected or related. They merely appear aligned from our earthly vantage point.
In reality, the three stars in Orion’s Belt are vastly different in terms of distance and size. The easternmost star, Alnitak, is the most distant at approximately 800 light-years away from Earth. It is a massive blue supergiant, radiating intense ultraviolet light. The middle star, Alnilam, is closer at about 1,340 light-years away. It is also a blue supergiant, but larger and brighter than Alnitak. The westernmost star, Mintaka, is the closest at around 900 light-years away. It is a multiple-star system composed of several smaller stars orbiting each other.
The apparent alignment of these stars into a straight line is purely coincidental, as they are located at different distances and have no physical connection. This arrangement of stars is an example of an asterism, which is a recognizable pattern formed by stars that are not necessarily part of the same constellation or cluster. Orion’s Belt, with its distinctive line of stars, serves as a convenient navigational tool in the night sky due to its prominence and easy identification.
It is fascinating to explore how these seemingly unrelated stars in Orion’s Belt have captured the human imagination, forming a significant part of mythology and cultural narratives across different civilizations. The alignment of these stars is a reminder of the beauty and wonder of our vast universe, and our enduring fascination with the patterns and stories that we find among the stars.
Orion in Greek Mythology

In Greek mythology, Orion takes center stage as a prominent figure, entangled in tales of forbidden love and eternal rivalry. One of the most well-known stories involving Orion is his ill-fated love affair with the goddess Artemis. (source) Despite being warned by her brother Apollo not to pursue a relationship with a mortal, Artemis couldn’t resist the charm and bravery of Orion. Their love grew, but the gods frowned upon their union. In some versions of the myth, Orion’s demise is orchestrated by a scorpion sent by Gaia, the Earth goddess, to punish Artemis for this forbidden love. Orion and the scorpion engage in an eternal battle in the night sky, with each rising on opposite horizons as the other sets. This rivalry is said to explain the seasonal disappearance of Orion from the sky. These legends from Greek mythology intertwine with the celestial spectacle of Orion’s Belt, etching a poignant and captivating story for millennia to come.
2.1 Orion and Artemis: The Forbidden Love
In Greek mythology, the story of Orion and Artemis revolves around an intense and forbidden love that defied the boundaries of mortal and immortal. Artemis, the goddess of the hunt and the moon, was known for her strong and independent nature. Orion, a skilled hunter and powerful warrior, caught the attention of Artemis with his bravery and charm. They soon became inseparable companions, roaming the wilderness together and sharing a deep bond. However, their relationship faced a tumultuous obstacle as Zeus, the king of the gods, disapproved of their love. He feared that Orion’s mortal presence would distract Artemis from her divine duties. Consequently, Zeus devised a plan to separate the two lovers. One version of the myth tells how Apollo, Artemis’ brother, tricked Artemis into shooting Orion with an arrow, believing him to be a dangerous creature. Devastated by the loss of her beloved, Artemis placed Orion in the stars, forever immortalized as the constellation we now know as Orion. Their story serves as a poignant reminder of the power of love and the sacrifices it sometimes demands.
2.2 Orion and the Scorpion: Eternal Rivalry
In the realm of Greek mythology, the story of Orion and the Scorpion tells of an eternal rivalry between the two celestial beings. According to the legend, Orion, known for his unmatched hunting skills, crossed paths with the Scorpion, a fearsome creature sent by the jealous goddess Gaia to end his life. The reason behind their rivalry was rooted in a romantic twist. Orion had caught the eye of the moon goddess Artemis, who saw his strength and bravery as admirable qualities. Intrigued by him, she began spending time with Orion, much to the dismay of the Scorpion. Consumed by jealousy, the Scorpion attacked Orion, leading to a fierce battle between the two powerful beings (source). The battle was relentless, with each combatant displaying their formidable skills. Ultimately, Orion succumbed to the mighty sting of the Scorpion, and both the hunter and his rival were immortalized in the night sky as constellations. Orion became the constellation bearing his name, and the Scorpion was transformed into the constellation Scorpius. To this day, they remain locked in their celestial positions, forever locked in their eternal rivalry, with Orion’s Belt serving as a reminder of their legendary conflict.
Orion in Ancient Egyptian Mythology

In ancient Egyptian mythology, Orion held a significant place, intertwined with the celestial beliefs of the civilization. The Egyptians associated Orion with the god Osiris, the ruler of the afterlife and the embodiment of resurrection. The three stars of Orion’s Belt, Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka, represented the gods Isis, Osiris, and Horus, respectively. Osiris, just like Orion, symbolized rebirth and the cycle of life. The alignment of the three stars in Orion’s Belt held great symbolic importance in Egyptian culture, representing the divine connection between the earthly and celestial realms. The Egyptians believed that by observing Orion, they could gain insight into the mysteries of the afterlife and access the wisdom of Osiris (source). Orion’s presence in Egyptian mythology adds depth and significance to the cultural beliefs and reinforces the cosmic tapestry woven around the enigmatic constellation.
3.1 Osiris and Orion: The Celestial Connection
In the realm of ancient Egyptian mythology, a fascinating connection is forged between the god Osiris and the constellation of Orion. Osiris, revered as the god of the afterlife, fertility, and resurrection, is closely linked to the celestial hunter in the night sky. It is believed that Osiris represents the spiritual embodiment of Orion himself, symbolizing the cycle of life, death, and rebirth. The correlation between these two entities goes beyond mere symbolism, as the Osiris myth mirrors the narrative of Orion’s journey. Osiris was murdered by his jealous brother Set and dismembered, but was later resurrected by his wife Isis (source). Similarly, in the night sky, Orion appears to die in the west as it sets below the horizon, only to rise again in all its splendor in the east. This cosmic connection between Osiris and Orion reflects the ancient Egyptians’ belief in the eternal cycle of life and death, with the constellation serving as a celestial manifestation of Osiris’s enduring power and influence. As we explore the cultural tapestry spun around Orion’s Belt, we uncover the significance of this celestial connection and its profound impact on ancient Egyptian mythology and religious beliefs.
3.2 Orion as a Symbol of Resurrection
Orion’s association with resurrection is particularly emphasized in ancient Egyptian mythology, where the constellation is closely linked to the god Osiris. Osiris, the god of the afterlife and rebirth, was believed to have been dismembered by his brother Seth and later reassembled by his wife Isis. In this mythological narrative, Osiris embodies the concept of resurrection and eternal life. The three stars in Orion’s Belt, Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka, correspond to the gods Isis, Osiris, and Horus, respectively. This celestial alignment mirrors the belief that Orion’s Belt played a key role in guiding the souls of the deceased through the afterlife. Egyptians believed that if one’s soul passed through Orion’s Belt after death, it would reach Osiris and achieve rebirth, ensuring eternal existence. This symbolism of resurrection is further highlighted by the annual rising of Orion in the night sky, which coincided with the flooding of the Nile River, representing the cycle of renewal and rebirth in Egyptian culture. The association of Orion with resurrection serves as a powerful symbol of hope and the continuation of life, encapsulating the ancient Egyptians’ profound beliefs about the afterlife and the eternal nature of the soul.
Orion in Native American Mythology
In Native American mythology, Orion holds a prominent place, often referred to as “The Hunter.” Different tribes have their unique interpretations and stories associated with the constellation. For example, in the Lakota Sioux tradition, Orion’s Belt represents the spine of a sacred buffalo. The Lakota Sioux believe that the constellation serves as a guide for hunters and a symbol of strength and endurance. In the Blackfoot tribe, Orion is known as “Seven Brothers” and is associated with a group of seven stars, which includes Orion’s Belt. Each star represents one of the brothers, who journeyed across the sky to escape a grizzly bear. They transformed into stars to evade the bear’s relentless pursuit and serve as a reminder of bravery and unity. Through these captivating tales passed down through generations, we gain insight into the significance of Orion’s Belt within Native American culture, where it serves as a beacon of guidance, courage, and resilience.
4.1 The Hunter’s Belt in Native American Tribes
The Native American tribes have their own fascinating stories and interpretations surrounding Orion’s Belt, often referring to it as “The Hunter’s Belt.” For many tribes, the constellation of Orion, with its distinct belt of stars, holds significant cultural and spiritual symbolism. In some Native American legends, the three stars of Orion’s Belt are likened to the three warriors or hunters who are forever chasing the Great Bear in the sky. These hunters are believed to be pursuing the bear across the celestial plains, eternally locked in a cosmic chase (source). The Lakota Sioux tribe, for example, sees the three stars as representing three brothers who were transformed into stars after their selfless sacrifice to save their people from famine. According to their mythology, the brothers continue to guide and protect their tribe on their eternal journey through the night sky. Other tribes also associate the Belt with hunting and the changing seasons. The alignment of Orion’s Belt was often used as a celestial guide for hunting or marking the changing of the seasons, aiding them in navigating the physical world with the help of the celestial realm. The Native American interpretation of Orion’s Belt emphasizes the interconnectedness between the natural and spiritual worlds, reminding us of the significance of the stars and constellations in their cultural heritage.
4.2 The Influence of Orion’s Belt in Native American Culture
The Influence of Orion’s Belt in Native American Culture is a fascinating topic that highlights the significance of this celestial formation in the beliefs and traditions of various Native American tribes. Different tribes across North America have long observed and revered the stars, including the prominent constellation of Orion and its distinctive belt. In Native American mythology, Orion’s Belt is often associated with the figure of the Hunter, representing strength, bravery, and the pursuit of excellence in hunting and warfare.
Among the Lakota Sioux tribe, the three stars of Orion’s Belt are considered to be the footprints of the Great Buffalo, a sacred animal that symbolizes abundance and sustenance. The placement of these stars in the sky is believed to guide hunters to successful game and ensure a bountiful harvest.
In the Navajo culture, Orion’s Belt is known as the “Fire Drill,” representing a tool used to start fires. It is believed that the stars of the belt possess powerful fire-making abilities and provide protection against evil spirits. The alignment of Orion’s Belt with certain landmarks on Earth is also believed to hold spiritual significance for Navajo tribes, guiding them in ceremonies and rituals.
The impact of Orion’s Belt is not limited to these two tribes alone but extends to various other Native American cultures as well. The Hopi people, for instance, associate Orion’s Belt with the figure of the kachina spirit Soyoko, who is believed to bring rain and ensure fertility to their crops. The Pawnee tribe sees the belt as the backbone of the celestial bison, playing a crucial role in their creation stories and agricultural traditions.
The influence of Orion’s Belt in Native American culture is profound and multifaceted, intertwined with beliefs about navigation, hunting, spiritual guidance, and the cycles of nature. The celestial formation serves as a powerful symbol that connects indigenous communities to their ancestral traditions and the greater cosmos, fostering a deep reverence for the natural world and the interconnectedness of all things.
Significance of Orion’s Belt in Astronomy

In the realm of astronomy and stargazing, Orion’s Belt holds a significant place. Here are some key aspects highlighting the importance of Orion’s Belt in the field of astronomy:
1. Celestial Navigation: Orion’s Belt has long been used by navigators and explorers as a celestial reference point for finding one’s bearings. Due to its prominent position in the night sky and its straight alignment, it has served as a useful guide for sailors, travelers, and astronomers to orient themselves and locate other stars and constellations.
2. Stellar Distance Indicator: The stars that make up Orion’s Belt – Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka – are part of a larger stellar complex known as Orion’s Molecular Cloud Complex. This region is a stellar nursery, containing young, hot stars and stellar nurseries where new stars are born. By studying the properties and distances of the stars in this complex, astronomers have gained valuable insights into the processes of star formation and evolution.
3. Cosmological Studies: Orion’s Belt also plays a role in understanding the larger cosmos. By studying the intricate details of the stars within Orion’s Belt, scientists have been able to measure their temperatures, spectral types, and luminosities. This, in turn, helps in determining the life cycle of stars, their ages, and their contributions to the chemical enrichment of the universe.
4. Cultural Significance: Orion’s Belt has not only fascinated astronomers but also holds cultural and historical significance. Different cultures throughout history have incorporated this celestial feature into their mythologies, folklore, and societal beliefs. This interplay between astronomy and culture has shaped our understanding of the night sky, enriching our perception of the universe.
Whether it be as a navigational aid, a window into stellar evolution, or a symbol of cultural heritage, Orion’s Belt continues to captivate astronomers and stargazers alike. Its prominence in the night sky serves as a reminder of the profound connection between the cosmos and human civilization, both in scientific exploration and cultural storytelling.
The Mystery of Orion’s Belt

The mystery of Orion’s Belt continues to intrigue astronomers, conspiracy theorists, and stargazers alike. While many astronomers recognize Orion’s Belt as a prominent feature in the night sky, some raise questions about its possible extraterrestrial connections(source). Ancient astronaut theorists and believers in ancient civilizations’ advanced knowledge of the cosmos suggest that the alignment of Orion’s Belt with the pyramids of Giza is no mere coincidence. These theories propose that the pyramids were deliberately positioned to mimic the celestial arrangement, perhaps as a means of communication or as a reflection of extraterrestrial influence(source). Aside from extraterrestrial connections, Orion’s Belt has become a focal point of conspiracy theories, with some suggesting hidden messages, symbols, or even secret portals within its celestial formation. As the mysteries surrounding Orion’s Belt persist, each interpretation adds another layer to the celestial enigma, capturing the imagination of those who dare to peer into the unknown.
6.1 Alleged Extraterrestrial Connections
Alleged extraterrestrial connections to Orion’s Belt have long been a subject of fascination and speculation. Some conspiracy theories and ancient astronaut proponents believe that the arrangement of the three stars in Orion’s Belt is not a mere coincidence, but rather evidence of an advanced extraterrestrial civilization. They suggest that these stars could serve as markers or beacons for alien visitors, guiding them to our planet (source).
One theory proposes that the pyramids of Giza in Egypt were constructed to align with the stars of Orion’s Belt, implying a connection between ancient Egyptians and extraterrestrial beings. It is speculated that these magnificent structures were built under the influence and guidance of advanced alien technology (source).
Tales of encounters with extraterrestrial beings often mention a fascination with Orion’s Belt. These accounts recount individuals claiming to have been contacted or visited by beings who hail from the constellation of Orion. The belief is that these beings, with their advanced knowledge and technology, have a special connection to the stars in Orion’s Belt (source).
While these alleged extraterrestrial connections may pique the imagination and inspire wonder, it is important to note that they are purely speculative and lack scientific evidence. The mystery surrounding Orion’s Belt continues to captivate our collective imagination, leaving room for speculation, but ultimately it remains a topic that resides in the realm of mythology and conspiracy theories.
6.2 Orion’s Belt in Conspiracy Theories
Orion’s Belt, with its unmistakable three-star formation, has also found its way into various conspiracy theories that have intrigued and perplexed many. One such theory suggests that the alignment of Orion’s Belt with the Great Pyramids of Giza is not a mere coincidence, but evidence of extraterrestrial influence. Some theorists propose that the pyramids were built to mirror the alignment of the stars, acting as a cosmic gateway or landing site for alien beings (source). Others speculate that the arrangement of the three stars in Orion’s Belt holds a hidden message or a map to advanced extraterrestrial civilizations. Such theories have sparked debates and discussions, with believers arguing that ancient civilizations possessed knowledge and technology far beyond our understanding.
In addition to extraterrestrial theories, Orion’s Belt has also been linked to secret societies and occult symbolism. Some conspiracy theorists claim that the three stars represent the three pillars of Freemasonry: Wisdom, Strength, and Beauty (source). They suggest that secret societies have guarded esoteric knowledge associated with the constellation and that its presence in occult symbolism signifies an underlying influence on world events. These theories, although often controversial and lacking empirical evidence, continue to captivate the imagination of those who seek alternative explanations for the mysteries of the universe.
It is important to note that these conspiracy theories surrounding Orion’s Belt exist in the realm of speculation and conjecture. While they may provide an intriguing lens through which to view this celestial formation, it is essential to approach them with a critical mind and discernment. The allure of conspiracy theories lies in their ability to weave narratives that challenge conventional wisdom and offer alternative interpretations. Whether one chooses to embrace or debunk these theories, they undeniably add a layer of mystery and fascination to the enduring magic of Orion’s Belt.
The Cultural Impact of Orion’s Belt
The Cultural Impact of Orion’s Belt:
1. Art and Symbolism:
Orion’s Belt has long been a source of inspiration for artists and symbolists around the world. In ancient art, the constellation was often depicted in various forms, symbolizing strength, bravery, and the pursuit of higher knowledge. The three stars of Orion’s Belt have been incorporated into iconic works of art, such as paintings, sculptures, and even jewelry. Their alignment and prominence in the night sky have also influenced the creation of symbols and logos in contemporary culture.
2. Navigation and Exploration:
Throughout history, civilizations have relied on Orion’s Belt for navigation and exploration. Sailors traversing the seas used the constellation as a guide, orienting themselves based on its position in the night sky. The alignment of the three stars served as a reliable marker for determining direction, helping explorers and travelers navigate unknown territories. Orion’s Belt thus played a significant role in shaping the course of human exploration and discovery.
3. Myth and Folklore:
Orion’s Belt features prominently in various mythologies and folklores, each culture attributing different meanings and stories to the constellation. People have woven tales of valor, love, and cosmic battles around the three stars, passing down these narratives through generations. The cultural impact of Orion’s Belt can be seen in the widespread awareness and recognition of its symbolism across different societies.
4. Astronomy and Scientific Interest:
Orion’s Belt continues to capture the interest of astronomers and stargazers today. Its prominent position in the night sky makes it an easily identifiable point of reference for observing other celestial bodies. Scientists use the constellation as a calibration tool for telescopes and instruments, aiding in the study and understanding of distant stars and galaxies. The scientific community’s fascination with Orion’s Belt has sparked further exploration and research in the field of astronomy.
5. Astrology and Spirituality:
Orion’s Belt holds spiritual significance in various belief systems and astrological interpretations. In astrology, the constellation is often associated with strength, protection, and personal power. Astrologers believe that the alignment and positioning of the stars in Orion’s Belt can influence an individual’s character traits and destiny. Additionally, some spiritual traditions consider the three stars as portals or gateways to higher dimensions or realms.
As we can see, the cultural impact of Orion’s Belt is far-reaching and diverse. Its influence is seen in various artistic expressions, navigational practices, mythologies, scientific endeavors, and spiritual beliefs. This celestial trio of stars continues to ignite our imagination, connecting us to the vastness of the cosmos and reminding us of the intricate interplay between human culture and the celestial realm.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mythology behind Orion’s Belt is a testament to the enduring power of human imagination and storytelling. Across cultures and civilizations, the constellation of Orion has sparked tales of love, rivalry, cosmic connections, and resurrection. From Greek mythology, where Orion’s forbidden love and eternal rivalry with a scorpion unfolded, to Egyptian mythology, where Orion symbolized resurrection and the celestial connection between Osiris and Horus, and even in Native American folklore, where the hunter’s belt held significance in various tribes, Orion’s Belt has left an indelible mark on our collective consciousness (source). In the realm of astronomy, Orion’s Belt serves as a guidepost for stargazers and a gateway to exploring the wonders of the universe. Beyond mythology and astronomy, Orion’s Belt has also found its place in popular culture, inspiring artists, writers, and even conspiracy theories. Whether gazing up at the night sky or unraveling the mysteries that surround it, the mythological significance and cultural impact of Orion’s Belt continue to captivate our curiosity and fuel our fascination with the wonders of the cosmos.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the significance of Orion’s Belt in astronomy?
Orion’s Belt is significant in astronomy as it serves as a guide for stargazers and astronomers to locate other celestial objects. By drawing a line through the three stars of the belt, one can easily find other prominent constellations and stars in the night sky.
2. Is Orion’s Belt visible from both hemispheres?
Yes, Orion’s Belt is visible from both the northern and southern hemispheres. However, its position in the sky may vary depending on the observer’s location, as well as the time of year.
3. How far away is Orion’s Belt from Earth?
Orion’s Belt is located approximately 1,400 light-years away from Earth. This means that the light we see from the stars in the belt today actually left their surfaces 1,400 years ago.
4. Are the stars in Orion’s Belt actually close to each other?
Although the stars in Orion’s Belt appear close together from our vantage point on Earth, they are not physically close to each other. Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka are actually located at different distances from Earth and are not gravitationally bound.
5. Are there other constellations associated with Orion?
Yes, there are several constellations associated with Orion in mythology and astronomy. These include the Pleiades, which are often depicted as Orion’s hunting dogs, as well as Taurus the Bull and Canis Major, the constellation of Orion’s faithful hunting companion.
6. What is the historical significance of Orion’s Belt in different cultures?
Orion’s Belt holds great historical and cultural significance in different civilizations. In ancient Egypt, it represented the gods Isis, Osiris, and Horus, while in Native American tribes, it held various interpretations tied to hunting and seasonal changes.
7. Can you see Orion’s Belt during any specific time of the year?
Orion’s Belt is visible during different seasons depending on the viewer’s location. In the northern hemisphere, it is most easily seen during the winter months. In the southern hemisphere, it is visible during the summer months.
8. Are there any interesting theories or conspiracies associated with Orion’s Belt?
Yes, there are several intriguing theories and conspiracies surrounding Orion’s Belt. Some speculate that the alignment of the pyramids in Egypt mirrors the alignment of the stars in Orion’s Belt, suggesting a connection between ancient civilizations and extraterrestrial beings.
9. Are there any famous myths or legends featuring Orion’s Belt?
A famous myth featuring Orion’s Belt is the story of Orion and Artemis, where Orion’s pursuit of the goddess Artemis leads to tragic consequences. Another popular legend involves Orion’s eternal rivalry with the Scorpion, resulting in their placement on opposite sides of the sky.
10. How can I find Orion’s Belt in the night sky?
To find Orion’s Belt, look for three bright stars in a straight line, close to each other. These stars form the distinctive belt of the Orion constellation. The best time to spot Orion’s Belt is during the winter months in the northern hemisphere.