Mystical practices have long captured the imagination of humanity, conjuring images of ancient rituals and ceremonies imbued with a sense of mystery and wonder. Across different cultures and throughout history, these practices have played a significant role in shaping beliefs, traditions, and spiritual experiences. From the cults of ancient Egypt to the mysteries of ancient Greece and the shamanic traditions of Native American cultures, mystical practices have pervaded human societies, offering a means of connecting with the divine, exploring the unknown, and seeking transcendence. In this article, we delve into the origins, techniques, and profound role that mystical practices have played in ancient rituals and ceremonies, unraveling the enigmatic allure that continues to captivate our collective consciousness.
The Origins of Mystical Practices

The origins of mystical practices can be traced back to the earliest civilizations, where humans sought to make sense of the inexplicable forces of the universe. Mysticism, a concept deeply rooted in spirituality and a direct connection to the divine, emerged as a way for individuals to explore the mysteries of existence beyond the limitations of the physical world. Ancient cultures were filled with beliefs and superstitions, intertwining mystical practices into their rituals and ceremonies. These practices often involved invoking the spiritual realm through rituals and sacrifices. Mystical beliefs shaped various aspects of ancient societies, from their religious and spiritual beliefs to their healing practices and even politics. The enigmatic role of mystics and seers in ancient politics is a testament to their influence and the perceived connection between the mystical and the earthly realms. Mystical symbols also played a significant role in ancient cultures, representing a myriad of meanings and interpretations that spanned across civilizations and cultures. The intricate relationship between mystical practices and the varied aspects of ancient societies is a subject of fascination and curiosity that continues to captivate our modern sensibilities.
The Concept of Mysticism
The concept of mysticism is deeply intertwined with the human quest for spiritual understanding and a connection to the divine. Mysticism refers to the belief in and experience of a direct, personal, and intimate union with a higher power, transcending the boundaries of traditional religious practices. It involves the exploration of the mystical dimensions of existence, seeking to achieve a deeper understanding of reality beyond what can be perceived by the five senses. Mystics, throughout history, have sought to elevate their consciousness and tap into the spiritual realm through various practices such as meditation, prayer, and contemplation. They often describe mystical experiences as a profound sense of unity with all things, an overwhelming feeling of love and compassion, and a heightened awareness of the interconnectedness of all life.
In ancient cultures, the concept of mysticism played a crucial role in shaping religious and spiritual beliefs. Ancient mystics sought communion with gods and goddesses, engaging in rituals and practices that aimed to establish a direct connection with the divine. They believed that through mystical experiences, they could gain insights into the nature of reality, receive guidance, and even access hidden knowledge. These mystical experiences often formed the foundation of religious and spiritual doctrines, influencing the rituals and ceremonies that were practiced within ancient societies.
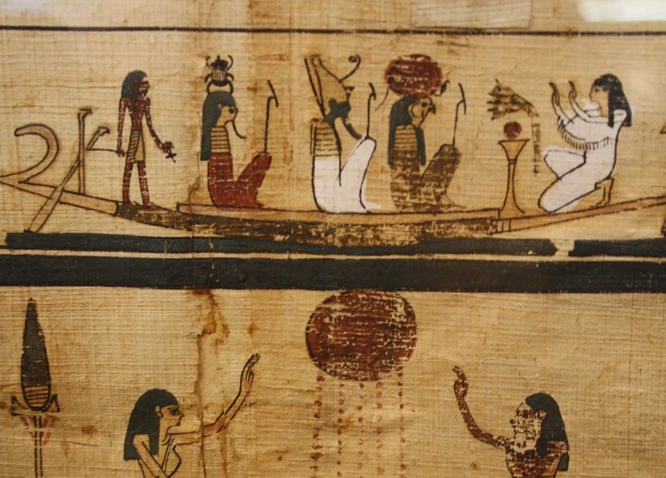
In ancient Egypt, for example, the priesthood played a central role in bridging the gap between the earthly and divine realms. The Egyptian pantheon of gods and goddesses provided the framework for their mystical practices, with rituals and ceremonies aimed at communing with these deities. The pharaohs themselves were considered to be divine, acting as intermediaries between the gods and the people. Ancient Egyptian mysticism encompassed a wide range of practices, including divination, dream interpretation, and the development of spiritual and magical texts.
Ancient Greek mysticism, on the other hand, revolved around the mystery cults, which were secretive religious groups that focused on the worship of specific deities such as Demeter, Dionysus, and Orpheus. These cults believed that through initiation ceremonies and rituals, individuals could attain spiritual purification, enlightenment, and a closer connection to the divine. The Eleusinian Mysteries, for instance, were a series of secretive rituals dedicated to the goddess Demeter and her daughter Persephone. Participants in these mysteries believed that by partaking in the rituals, they could gain insight into the mysteries of life, death, and the afterlife.
Native American cultures also had rich mystical traditions, often facilitated by shamans who acted as intermediaries between the people and the spirit world. Native American shamans practiced various forms of mysticism, including vision quests, sweat lodge ceremonies, and the use of sacred plants. These practices were aimed at achieving spiritual transformation, healing, and establishing harmony with nature and the spirit realm.
The concept of mysticism has left an indelible mark throughout human history, influencing ancient healing practices, the interpretation of mystical symbols, and even the political landscape of ancient societies. To this day, the quest for mystical experiences continues, as individuals seek a connection to something greater than themselves, transcendental insights, and a deeper understanding of the mysteries of existence.
[Link: The Influence of Mystical Beliefs on Ancient Healing Medicine](/the-influence-of-mystical-beliefs-on-ancient-healing-medicine/)
Ancient Beliefs and Superstitions
Ancient beliefs and superstitions were deeply intertwined with mystical practices, shaping the way people approached spirituality and the supernatural. These beliefs varied across civilizations, but common threads of mysticism can be found in many ancient cultures. One prominent aspect of ancient beliefs was the idea that the natural world was imbued with spiritual forces and entities. This notion gave rise to practices such as animism, where objects and elements of nature were believed to possess spirits or gods. The worship of deities and the pantheon of gods and goddesses was another widespread belief, with rituals and ceremonies conducted to appease and honor these divine beings. These ancient societies also held a profound belief in the power of rituals and ceremonies to influence the outcomes of their lives. These rituals involved intricate sequences of actions, recitations, and offerings that were performed to ensure everything from a successful harvest to protection from evil spirits. Superstitions were often closely linked to these rituals, with certain actions or objects believed to bring good luck or ward off misfortune. It was believed that failure to observe these rituals or the violation of taboos could lead to disastrous consequences. The interpretation of mystical symbols was another essential aspect of ancient beliefs and superstitions. Symbols such as the ankh in Egyptian culture or the yin and yang in Chinese philosophy carried deep spiritual meanings and were used in rituals and ceremonies to invoke the associated mystical forces. The blending of mystical practices with ancient beliefs and superstitions created a rich tapestry of spiritual experiences that shaped the lives of people in ancient times and left a lasting impact on their cultures. To learn more about the significance of mystical symbols in the interpretation of ancient cultures, and the enigmatic role of mystics and seers in ancient politics, continue reading.
Mystical Practices in Different Cultures

Throughout history, mystical practices have manifested in various forms across different cultures, each with its own unique traditions and beliefs. In ancient Egypt, rituals played a significant role in their mystical practices, with ceremonies dedicated to honoring the gods and goddesses, guiding the souls of the deceased, and ensuring prosperity in the afterlife. The ancient Greeks, on the other hand, delved into the mysterious world of Greek mysteries, secretive religious rites associated with deities and the quest for spiritual transformation and enlightenment. Native American cultures embraced shamanism, where shamans acted as spiritual intermediaries between the human and spirit worlds, performing rituals and healing practices to restore balance and harmony. These diverse cultural expressions of mystical practices reveal the deep-rooted human desire to connect with the spiritual realm and the profound impact it had on shaping ancient societies. Understanding the mystical practices of different cultures provides a glimpse into the rich tapestry of human spirituality and the universal quest for higher meaning.
Egyptian Rituals
Egyptian rituals were deeply intertwined with mysticism, reflecting the ancient Egyptians’ belief in the divine and their desire for spiritual connection. These rituals played a crucial role in their religious practices and were executed with meticulous precision. Here are some key aspects of Egyptian rituals:
– Offerings and Sacrifices: Egyptian rituals often involved the offering of food, drink, and various material items to the gods. These offerings were seen as a way to provide sustenance for the deities and establish a reciprocal relationship between humans and the divine. Animal sacrifices were also prevalent, with specific animals chosen for their symbolic significance.
– Temple Ceremonies: Temples held immense importance in ancient Egyptian culture, serving as the focal point for religious and mystical practices. Rituals were performed by priests and priestesses within the temple sanctuaries, where they sought to commune with the gods and gain their favor. These ceremonies included purification rites, prayers, chanting, and the use of sacred objects and symbols.
– Mummification and Funeral Rituals: Death and the afterlife held great significance in Egyptian beliefs. Rituals surrounding death and burial were highly mystical and complex. The process of mummification ensured the preservation of the body for the soul’s journey to the afterlife. Elaborate funerary ceremonies with prayers, incantations, and rituals aimed to aid the deceased in their journey and secure their place in the afterlife.
– Divination and Dream Interpretation: Divination was a common practice in ancient Egypt, performed by priests and priestesses who acted as intermediaries between the earthly and divine realms. Methods of divination included interpreting dreams, reading omens, and using oracles. These practices were believed to provide insights into the future and guidance from the gods.
– Festival Celebrations: Festivals held great importance in Egyptian society and were celebrated with grandeur and enthusiasm. These events featured vibrant processions, music, dance, and elaborate rituals. Festivals were seen as a way to honor specific deities, strengthen communal bonds, and partake in the mystical energy that permeated the celebrations.
Egyptian rituals were deeply rooted in their mystical beliefs and served to establish a connection between the mortal and divine realms. The precise execution of these rituals was seen as imperative to maintain cosmic order and ensure the favor of the gods upon the land and its people.
Greek Mysteries
Greek Mysteries were secretive religious rituals that played a significant role in ancient Greek society. These mysterious and exclusive ceremonies were centered around the worship of various gods and goddesses, such as Demeter, Dionysus, and Orpheus. One of the most well-known Greek mysteries was the Eleusinian Mysteries. These rituals were held in Eleusis, a town near Athens, and were dedicated to the goddess Demeter and her daughter Persephone. Participants, known as initiates, would undergo a series of sacred rites including purification, fasting, and symbolic acts of rebirth. The purpose of the Eleusinian Mysteries was to achieve spiritual enlightenment and gain a deeper understanding of the cycles of life, death, and rebirth. The details of these ceremonies were shrouded in secrecy, and only those who were initiated were privy to the knowledge and experiences of the rituals. The Greek Mysteries were a source of great reverence and awe, providing a sacred space for individuals to connect with the divine and explore the mysteries of the cosmos. The influence of these practices extended beyond religious devotion, impacting areas such as philosophy and art, and leaving an indelible mark on Greek culture and spirituality.
Native American Shamanism
Native American Shamanism is a complex and profound mystical practice that has deep roots in the indigenous cultures of North America. Shamanism was integral to Native American societies, as the role of the shaman was to serve as a bridge between the physical and spiritual worlds, to heal the sick, provide guidance, and maintain balance within the community. The shaman would enter into altered states of consciousness through various means, such as drumming, dancing, or ingesting hallucinogenic plants like peyote or ayahuasca. Once in these altered states, the shaman would communicate with the spirits, ancestors, and animal guides, seeking their wisdom and guidance. Shamans often performed healing rituals, divination, and soul retrieval, believing that illness and imbalance were caused by spiritual disharmony. In addition to their healing abilities, shamans were also responsible for performing important community rituals and ceremonies, including those for hunting, fertility, and initiation. Native American Shamanism continues to be practiced today, keeping alive the rich spiritual traditions and sacred connections to the natural world that have been passed down for generations.
Tools and Techniques of Mystical Practices

Mystical practices were accompanied by a diverse array of tools and techniques that were employed to access spiritual realms and divine knowledge. Divination and oracles were common practices used to gain insight into the future or receive guidance from higher powers. These methods involved interpreting signs and symbols or consulting oracles through trance-like states. Additionally, ritualistic offerings and sacrifices were made to appease deities and evoke their favor. These offerings ranged from precious objects to animals and even human sacrifices in certain cultures. Another notable mystical practice was alchemy and hermeticism, which sought to transform base materials into something more refined and spiritual. Alchemy focused on the transformation of metals and the quest for the philosopher’s stone, an elusive substance believed to hold great mystical power. Hermeticism, influenced by Egyptian mythology, explored the mystical relationship between the divine and the human. These tools and techniques of mystical practices offered individuals a means to explore the mysteries of the universe and connect with higher realms of knowledge and power.
Divination and Oracles
Divination and oracles were crucial facets of mystical practices in ancient societies, acting as a means to gain insight and guidance from the spiritual realm. Divination encompassed various techniques and methods used to predict the future and uncover hidden knowledge. In ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Greece, and Rome, divination played a significant role in decision-making, offering a glimpse into the unknown and providing reassurance or warnings to individuals and communities.
One popular form of divination was astrology, which involved observing and interpreting the movements and positions of celestial bodies to make predictions about individuals and events. Astrologers believed that the alignment of the stars and planets could reveal cosmic messages and determine one’s destiny. This practice persisted through the ages and continues to influence astrology today.
Another well-known method was augury, practiced by the ancient Romans, where skilled priests, known as augurs, interpreted the flight patterns and behaviors of birds to gain insights into future outcomes. These priests believed that the behaviors of certain bird species held symbolic meanings and could provide answers to important questions.
The use of oracles also played a crucial role in divination. Oracles were revered individuals believed to possess the ability to communicate with the divine or spiritual entities. Seekers would present their questions or concerns to the oracle, who would then enter a trance-like state or receive messages through visions or dreams. The oracle’s responses were seen as divine guidance and often influenced significant decisions, such as the outcomes of battles or the establishment of new laws.
One renowned example of an oracle was the Oracle of Delphi in ancient Greece. The Pythia, the priestess of Apollo, would inhale mysterious vapors emitting from a fissure in the earth, which was believed to induce a prophetic state. People from all over sought the oracle’s advice, believing it to be a direct line of communication with the gods.
Divination and oracles were not only used to foresee the future but also to gain insights and clarity in the present. These practices allowed individuals and communities to navigate the uncertainties of life, make important decisions, and seek guidance from the spiritual realm. The role of divination and oracles in ancient societies demonstrates the profound desire of humans to connect with the mystical and transcendental forces that shape our existence.
Ritualistic Offerings and Sacrifices
Ritualistic offerings and sacrifices held immense significance in ancient mystical practices, serving as a means of communication and appeasement to the divine. These rituals involved the presentation of valuable objects, food, animals, or even human sacrifices as acts of devotion and supplication. The act of making offerings was grounded in the belief that by giving something of value, one could establish a harmonious relationship with the gods or spirits. The types of offerings varied across different cultures and traditions. In some cases, precious metals, gems, and other valuable materials were offered, symbolizing wealth and power. Food offerings, such as fruits, grains, and wine, represented sustenance and abundance. Animals, both domesticated and wild, were often sacrificed, symbolizing the ultimate surrender of life to the divine forces. The ritualistic process of offering and sacrificing carried immense symbolism, often accompanied by prayers, chants, and elaborate ceremonies conducted by priests or spiritual leaders. These rituals aimed to invoke blessings, protection, or favors from the divine, while also expressing gratitude and seeking forgiveness. The act of offering and sacrificing served not only as a manifestation of faith but also a way to maintain cosmic balance and ensure the well-being of the community. The practice of ritualistic offerings and sacrifices has evolved over time, with some elements transcending into modern religious ceremonies, though their exact form and significance may have altered. Nonetheless, the profound role they played in ancient mystical practices remains a testament to the deep spiritual connection between humans and the divine.
Alchemy and Hermeticism
Alchemy and Hermeticism are two mystical practices that have left an indelible mark on ancient rituals and ceremonies. Alchemy was a complex and secretive art that sought to transmute base metals into precious ones, such as gold, and discover the elixir of immortality. It originated in ancient Egypt and later found widespread popularity in Hellenistic and medieval Europe. Alchemists believed in the idea of the “Philosopher’s Stone,” a mythical substance that possessed transformative powers. They conducted experiments and rituals involving various substances and symbolic processes, aiming to uncover the hidden knowledge and spiritual wisdom embedded within matter. Alchemy emphasized the balance and harmony of opposing forces, such as the union of the sun (representing masculine energy) and the moon (representing feminine energy).
Hermeticism, on the other hand, was a philosophical and spiritual tradition that originated in ancient Egypt and was further developed in the Hellenistic period. It was based on the teachings of the mythical figure Hermes Trismegistus, who was believed to be the author of the “Hermetic Corpus,” a collection of sacred texts. Hermeticism encompassed a wide range of mystical and metaphysical concepts, exploring the nature of the divine, the universe, and the relationship between the macrocosm and microcosm. It delved into the idea of the “As above, so below,” suggesting that there is a correspondence between the divine realm and the earthly realm. Hermetic practitioners engaged in ritualistic practices, meditation, and the study of esoteric texts to unlock hidden knowledge and achieve spiritual enlightenment.
Both alchemy and Hermeticism were closely intertwined, as alchemical experiments often incorporated Hermetic principles and symbolism. These mystical practices not only influenced the development of chemistry and the search for scientific knowledge but also had a profound impact on the spiritual and philosophical landscape of ancient societies. The pursuit of transmutation in alchemy symbolized the alchemist’s own spiritual transformation, while Hermeticism offered a path to understanding the mysteries of the universe and the divine. These practices continue to inspire fascination and intrigue, reminding us of humanity’s enduring quest for wisdom, enlightenment, and the divine mysteries that lie beyond the veil.
The Role of Mystical Practices in Ancient Ceremonies
Mystical practices played a pivotal role in ancient ceremonies, acting as a bridge between the physical and spiritual realms. One significant role was in initiation and rites of passage, marking important transitions and transformations in individuals’ lives. These rituals encompassed purification, guidance, and the acquisition of knowledge or abilities. Another role was in rituals for harvest and fertility, where mystical practices sought to ensure bountiful crops and prosperous seasons through interconnectedness with the natural world and divine forces. Additionally, mystical practices provided a means for communion with deities and spirits, allowing individuals to establish spiritual connections, seek guidance, and gain insight into the mysteries of the universe. Whether through divination, trance states, or ceremonies of invocation, ancient cultures placed great importance on mystical practices in their ceremonies, seeing them as essential for spiritual growth, communal cohesion, and the harmonious balance between the human and spiritual realms.
Initiation and Rites of Passage
Initiation and rites of passage were pivotal moments in ancient societies, marking the transition from one stage of life to another and symbolizing a profound transformation of an individual’s identity. These rituals often involved elaborate ceremonies and ritualistic practices, creating a sacred space where participants could undergo a spiritual awakening or acquire specific knowledge or skills. In many cultures, initiation rituals served as a means of entering adulthood, membership into a secret society, or even becoming a respected member of the community. One such example is the ancient Egyptian ritual of the “Opening of the Mouth,” which was performed on the deceased during the burial process to ensure the person’s ability to communicate in the afterlife. Similarly, in ancient Greece, young men underwent the initiation ceremony known as the “Rite of Passage” into adulthood. Native American cultures also placed great significance on initiation rites, with ceremonies marking the transition from adolescence to adulthood and granting individuals their roles within the community. These rituals often involved fasting, vision quests, and encounters with spirits or deities, allowing individuals to gain wisdom and guidance. The role of initiation and rites of passage in ancient societies emphasized the importance of personal growth, self-discovery, and communal bonds, serving as transformative experiences that connected individuals to the spiritual world and their cultural heritage.
Rituals for Harvest and Fertility
Rituals for Harvest and Fertility played a crucial role in ancient societies, as they were intimately connected to survival and abundance. These rituals were often performed to ensure a bountiful harvest and the fertility of both crops and livestock. In agricultural communities, a successful harvest was vital for the sustenance of the community, making these rituals of utmost importance. These rituals typically involved a combination of spiritual practices, communal gatherings, and offerings to divine entities associated with fertility and agriculture.
In ancient Egypt, for example, the festival of Wep Renpet celebrated the flooding of the Nile River, which brought fertile soil and ensured a prosperous harvest. Egyptians would perform ceremonies and offerings to Isis, the goddess of fertility, and Osiris, the god of agriculture. These rituals were aimed at appeasing these deities and seeking their blessings for a fruitful harvest.
In the Greek tradition, the Thesmophoria festival was dedicated to Demeter, the goddess of agriculture. Women would gather and participate in ceremonies and rituals associated with fertility and the abundance of crops. These rituals often involved fasting, purification, and the symbolic burial of fertility symbols, such as phallic objects or seeds, to ensure the regeneration of life and a successful harvest.
Among the Native American cultures, rituals for harvest and fertility were deeply intertwined with their spiritual beliefs. For example, the Hopi tribe performed the Powamu ceremony, during which they offered prayers and performed dances to invoke the spirits of the land and ensure a prosperous harvest. Similarly, the Iroquois people celebrated the Green Corn Ceremony, a ritual that honored the corn mother and gave thanks for the first corn harvest of the season.
These rituals for harvest and fertility highlight the deep reverence ancient societies held for the cycles of nature and their dependence on the productivity of the land. They aimed to establish a harmonious relationship between humans and the divine forces that governed fertility and growth. Through these rituals, ancient communities sought to ensure the abundance of resources necessary for their survival, perpetuating their belief in the interconnectedness of all life and their role as stewards of the land.
Communion with Deities and Spirits
Communion with deities and spirits was a central aspect of mystical practices in ancient ceremonies. These rituals were dedicated to establishing a connection between the human and divine realms, allowing individuals to communicate with and receive guidance from powerful entities. Different cultures had their own unique methods of achieving this communion. In ancient Egypt, for example, priests and priestesses served as intermediaries between the people and the gods, performing rituals and offering sacrifices to invoke the presence and blessings of their deities. Egyptian pharaohs, considered divine themselves, also played a crucial role in these ceremonies, acting as a conduit for divine energy and communication.
In Greek mythology, the mysteries of Eleusis were an essential part of the communion with the deities. These secretive rituals, centered around the worship of Demeter and Persephone, provided initiates with the promise of a blessed afterlife and the opportunity to commune with the gods. The ceremonies involved theatrical performances, processions, and sacred rites conducted in the Eleusinian sanctuary near Athens. Participants believed that by engaging in these rituals, they would receive divine wisdom, enlightenment, and a closer connection to the divine realm.
Native American cultures, too, had their own mystical practices for communing with spirits. Shamans, revered as spiritual healers and intermediaries between the physical and spiritual realms, would enter trance-like states using techniques such as drumming, chanting, and the use of hallucinogenic substances. In these altered states of consciousness, shamans believed they could communicate with spirits, seek guidance, and receive messages to assist their communities in various aspects of life.
The communion with deities and spirits in mystical practices served to establish a bridge between the mortal and divine realms. These ceremonies provided individuals with a means to seek divine guidance, receive blessings, and tap into the spiritual energies believed to govern the world. Through these communal experiences, participants sought a deeper understanding of their place in the cosmos and a connection to forces greater than themselves.
Controversies Surrounding Mystical Practices
The world of mystical practices is not without its controversies, as the clash between science and mysticism continues to fuel debates and skepticism. The clash of science and mysticism arises from the differing approaches to understanding the nature of reality. While science relies on empirical evidence and rational explanations, mysticism delves into the realm of the spiritual and transcendent, often defying logical comprehension. Skeptics argue that mystical practices are mere superstitions or psychological phenomena, dismissing their spiritual significance. The perception of mystical practices in modern society can be polarizing, with some viewing them as antiquated beliefs or fraudulent practices, while others embrace them as pathways to personal enlightenment and connection to a higher power. The controversies surrounding mystical practices highlight the ongoing struggle to reconcile the realms of the unknown and the tangible, leaving us with enduring questions about the nature of existence, consciousness, and the boundaries of human understanding.
The Clash of Science and Mysticism
The Clash of Science and Mysticism has been a long-standing debate throughout history, as the realms of empirical evidence and mystical experiences collide. Science, with its emphasis on rationality, empiricism, and the observable world, often clashes with the intangible nature of mystical practices. Scientists have sought to explain the world through logical and systematic methods, focusing on measurable and repeatable experiments. Mysticism, on the other hand, delves into the realm of the transcendent and the spiritual, exploring the unseen forces that govern the universe.
One area of contention between science and mysticism is the concept of causal relationships. Science relies on cause and effect relationships, seeking to understand the mechanisms behind natural phenomena. Mysticism, in contrast, often emphasizes a more holistic view of the world, where interconnectedness and the influence of the spiritual realm hold sway. The clash arises when scientific explanations struggle to account for mystical experiences that defy traditional cause and effect patterns.
Another point of contention revolves around the notion of verifiability. Science places great importance on the ability to verify and replicate experiments, ensuring the reliability of results. Mystical experiences, however, are highly subjective and personal, making them difficult to objectively measure or verify. This subjective nature has led some scientists to dismiss mystical practices as mere delusions or wishful thinking.
Yet, despite the clashes, there have been attempts to bridge the gap between science and mysticism. Quantum physics, for instance, has opened up new possibilities for understanding the universe beyond the confines of classical scientific approaches. It poses intriguing questions that resonate with mystical concepts, such as the interconnectedness of all things and the influence of consciousness on reality.
Ultimately, the clash between science and mysticism highlights the inherent tension between the need for empirical evidence and the allure of the intangible. Both realms have contributed to human knowledge and understanding in their own ways, and finding a harmonious middle ground can enrich our understanding of the mysteries of the universe.
| Points of Clash | Science | Mysticism |
|---|---|---|
| Causal Relationships | Relies on cause and effect relationships. | Emphasizes interconnectedness. |
| Verifiability | Relies on objective measurements and replicable experiments. | Experiences are subjective and difficult to measure objectively. |
| Bridging the Gap | Quantum physics poses questions that resonate with mystical concepts. | Many mystical practices are open to interpretation and personal experience. |
Perception of Mystical Practices in Modern Society
In modern society, the perception of mystical practices is multifaceted and varied. While some individuals view mysticism as a fascinating and valuable aspect of human spirituality, others regard it with skepticism or dismiss it as mere superstition. The perception of mystical practices largely depends on factors such as cultural background, religious beliefs, and personal experiences. The rise of science and rationality has influenced the perception of mysticism, with some viewing it as incompatible with empirical evidence and the principles of the scientific method. This clash between science and mysticism has led to debates and controversies surrounding the validity and efficacy of mystical practices. However, there are those who embrace mysticism as a means of personal exploration, self-discovery, and spiritual growth. They see it as a way to tap into the depths of consciousness, unlock hidden knowledge, and connect with something greater than themselves. The widespread popularity of practices like meditation, astrology, and energy healing in recent years indicates a growing acceptance and interest in mystical practices. In essence, the perception of mystical practices in modern society is a complex tapestry of belief systems, cultural attitudes, and individual experiences, reflecting the diversity and evolving nature of human spirituality.
The Enduring Legacy of Mystical Practices
The enduring legacy of mystical practices continues to resonate in our modern world, leaving a profound impact on various aspects of society. One area where this legacy is evident is in the realm of spirituality and personal growth. Many individuals today seek mystical practices as a means of self-exploration, inner healing, and enlightenment. Techniques such as meditation, dream analysis, and energy healing draw inspiration from ancient mystical traditions, offering individuals tools to connect with their higher selves and tap into the unseen realms of consciousness.
The enduring legacy of mystical practices is also reflected in the field of alternative and holistic therapies. From crystal healing to Reiki, these practices incorporate elements of ancient mysticism to promote overall well-being and harmony. The belief in the interconnectedness of mind, body, and spirit is deeply rooted in mystical traditions and has influenced the development of these healing modalities.
In addition to personal growth and healing, the enduring legacy of mystical practices can be seen in the arts and literature. Throughout history, artists and writers have been inspired by mystical concepts, incorporating themes of mysticism and spirituality into their works. From ancient religious texts to modern-day novels, mystical practices have served as a wellspring of inspiration, evoking a sense of wonder, transcendence, and exploration of the unknown.
The enduring legacy of mystical practices is manifested in the continued fascination and study of ancient cultures and their mystical rituals. Archaeologists and anthropologists delve into the remnants of ancient civilizations, uncovering artifacts and deciphering the symbols and practices associated with mysticism. This ongoing research not only sheds light on the rich tapestry of human history but also highlights the enduring curiosity and desire to understand the mystical practices that shaped ancient societies.
The enduring legacy of mystical practices is evident in our contemporary world, influencing various domains such as spirituality, healing, art, literature, and academia. It serves as a testament to the timeless allure and universal appeal of mystical traditions, offering profound insights and lessons that continue to resonate with individuals and communities worldwide. Whether seeking personal growth, exploring artistic expression, or unraveling the secrets of the past, the enduring legacy of mystical practices invites us to transcend the boundaries of the known and embark on a journey of profound discovery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mystical practices have left an indelible mark on ancient rituals and ceremonies. They have been an integral part of numerous cultures, shaping beliefs, traditions, and spiritual experiences. From the Egyptians’ intricate rituals to the Greeks’ enigmatic mysteries and Native American shamanism, mystical practices have provided a means for humans to connect with the divine, explore the unknown, and seek transcendence. The tools and techniques utilized, such as divination, ritualistic offerings, and alchemy, have been foundational in these practices. Mystical rituals have played various roles in ancient ceremonies, including initiation and rites of passage, rituals for harvest and fertility, and communion with deities and spirits. While mystical practices have been met with controversy and skepticism, particularly in the clash between science and mysticism, their enduring legacy cannot be denied. They continue to hold allure and fascination in modern society, with individuals seeking spiritual experiences and connection with the mystical realm. The rich tapestry of history and the profound impact of mystical practices attest to their enduring significance in the human experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the definition of mysticism?
Mysticism is a spiritual practice or belief system that involves seeking a direct personal experience or union with the divine or transcendent reality.
2. How did mystical practices influence ancient healing medicine?
Mystical beliefs played a significant role in shaping ancient healing medicine, as many cultures believed that illnesses were caused by spiritual imbalances. Mystical practices such as divination and the use of herbs and rituals were employed to restore harmony and well-being.
3. What significance do mystical symbols hold in the interpretation of ancient cultures?
Mystical symbols held deep meaning and were used as powerful tools of communication in ancient cultures. They conveyed spiritual concepts, represented deities or cosmic forces, and could provide guidance or protection to individuals or communities.
4. How did mystics and seers influence ancient politics?
Mystics and seers were often sought after for their supposed ability to communicate with the divine and provide insight into future events. Ancient rulers and politicians would consult these individuals for guidance in decision-making, and their influence could shape political strategies and outcomes.
5. What techniques were commonly used in divination and oracles?
Divination and oracles were methods used to gain insight and seek guidance from the spiritual realm. Common techniques included interpreting patterns in natural phenomena, reading animal entrails, studying celestial bodies, or casting bones or stones to interpret messages from the divine.
6. Why were ritualistic offerings and sacrifices an integral part of mystical practices?
Ritualistic offerings and sacrifices were believed to appease and honor the gods or spirits, establishing a sacred connection and seeking their favor and blessings. They were seen as essential for ensuring the success of ancient rituals and ceremonies.
7. What is the relationship between alchemy and hermeticism in mystical practices?
Alchemy and hermeticism were closely intertwined mystical practices in ancient times. Both aimed to understand the nature of reality, the universe, and the spiritual realm. Alchemy focused on transforming matter and achieving spiritual purification, while hermeticism sought knowledge of higher truths and the unity of the divine.
8. How did mystical practices contribute to ancient initiation rites and rites of passage?
Mystical practices were often key components of ancient initiation rites and rites of passage. These practices were meant to facilitate the transition from one life stage to another, helping individuals connect with their spiritual selves, gain wisdom, and forge a deeper understanding of the world and their place in it.
9. What role did mystical practices play in rituals for harvest and fertility?
Mystical practices were deeply intertwined with rituals for harvest and fertility in ancient societies. These practices aimed to honor and invoke the deities or spirits associated with agricultural abundance and to ensure bountiful crops and successful reproduction.
10. How has the perception of mystical practices evolved in modern society?
In modern society, the perception of mystical practices varies greatly. While some individuals still embrace and practice mystical traditions, others view them with skepticism or dismiss them as mere superstition. However, there is a growing interest in ancient wisdom and spirituality, leading to a resurgence in the exploration and incorporation of mystical practices into contemporary lifestyles.








