Welcome to the Mesmerizing World of Meteor Showers!
Have you ever looked up at the night sky and been captivated by the breathtaking display of shooting stars? These beautiful cosmic phenomena, known as meteor showers, have fascinated humanity for centuries. Each year, numerous meteor showers grace our skies, leaving us in awe of their splendor. In this article, we will delve into the wondrous world of meteor showers, exploring their different types, how they are formed, and how you can observe them. So, prepare to immerse yourself in the celestial wonders that await!
What are Meteor Showers?
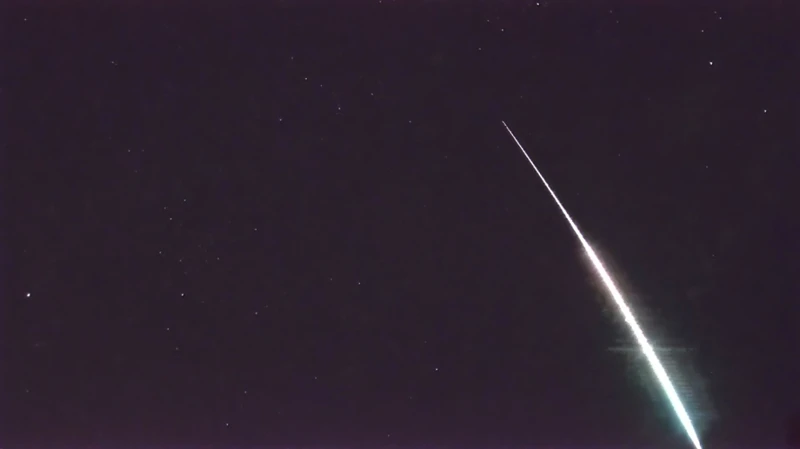

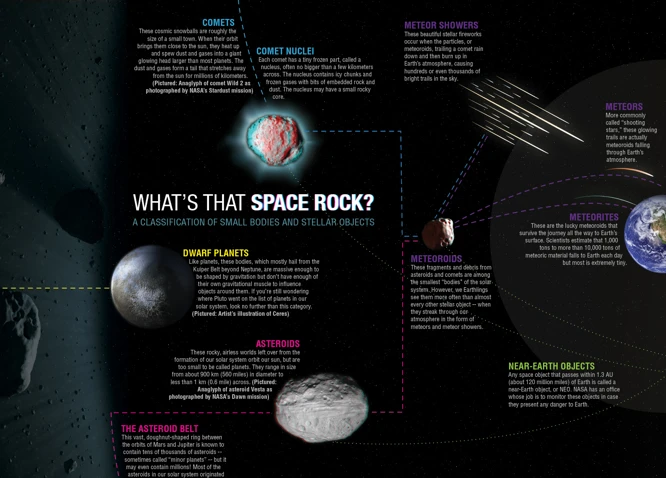
Meteor showers are mesmerizing celestial events that occur when Earth passes through the debris left behind by a comet or asteroid as it orbits the Sun. When these tiny fragments, typically no larger than a grain of sand, enter Earth’s atmosphere, they heat up and create bright streaks of light that we commonly refer to as shooting stars. These streaks of light are actually the ionized and glowing trails left behind by the debris. Meteor showers are named after the constellation from which they radiate, such as the Perseids, Geminids, Leonids, Quadrantids, and Orionids. Each meteor shower has its own unique characteristics, such as the number of meteors it produces per hour and the peak dates of activity. Some meteor showers, like the Perseids, are known for their abundance of bright and fast meteors, while others, like the Geminids, are known for their slower-moving meteors that often display vivid colors. Meteor showers have captured the imagination of people throughout history, with cultural significance and even inspiring famous historical events. To experience the magic of meteor showers, you can observe them with the naked eye or even try capturing their beauty through meteor shower photography. So, let’s embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of these celestial marvels!
Types of Meteor Showers

Meteor showers come in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics and celestial beauty. One of the most well-known meteor showers is the Perseids. Occurring in August each year, the Perseids are renowned for their high meteor counts and stunningly bright meteors. Next on the list is the Geminids, which lights up the December sky with its multi-colored meteors and slow-moving nature. Another meteor shower worth mentioning is the Leonids, which peaks in November and is famous for its occasional intense meteor storms. In January, we have the Quadrantids, known for its short-lived but vibrant meteors. Lastly, we have the Orionids, which offers a mesmerizing display of meteors radiating from the constellation Orion in October. Each of these meteor showers provides a unique spectacle for stargazers and photography enthusiasts alike. If you’re interested in capturing the beauty of meteor showers, you can learn more about meteor shower photography here. These celestial events hold cultural significance in various societies and have even left their mark in famous historical events. To explore more about the cultural significance of meteor showers, you can visit our article on meteor shower cultural significance here.
1. Perseids
The Perseids meteor shower is one of the most highly anticipated and popular meteor showers of the year. It occurs annually between late July and mid-August, peaking around August 11th to 13th. Named after the constellation Perseus, from which the meteors appear to radiate, the Perseids are known for their fast and bright meteors. With an average of 60-100 meteors per hour during its peak, the Perseids offer a spectacular celestial show.
The Perseids are associated with the comet Swift-Tuttle, which orbits the Sun once every 133 years. As Earth passes through the debris left behind by this comet, we witness the dazzling display of shooting stars. The meteors from the Perseids shower often leave persistent trails in the sky, making them a favorite among stargazers and astrophotographers.
To observe the Perseids, it is best to find a dark location away from city lights. Lie down or sit in a comfortable position and allow your eyes to adjust to the darkness. Look towards the northeastern sky, in the direction of the Perseus constellation. Patience is key, as it may take some time for your eyes to catch a glimpse of the elusive meteors. It is also worth noting that the Perseids are known for producing fireballs, which are extremely bright meteors that leave a lasting impression.
Throughout history, the Perseids have left a mark on various cultures and have been the subject of fascination. They have been mentioned in works of literature, art, and even played a role in famous historical events. Their ethereal beauty continues to inspire awe and wonder in people around the world. So, be sure not to miss the Perseids meteor shower, a celestial spectacle that will leave you in awe of the wonders of the universe.
2. Geminids
- Geminids: The Geminids meteor shower is one of the most highly anticipated and reliable meteor showers of the year. It peaks around mid-December, typically between the 13th and 14th of the month. The Geminids are named after the constellation Gemini, as they appear to radiate from this specific point in the sky. What sets the Geminids apart from other meteor showers is that they are not caused by a comet but by an asteroid called 3200 Phaethon. This makes them unique and fascinating. The Geminids are known for their slow-moving meteors that enter Earth’s atmosphere at a velocity of about 22 miles per second (35 kilometers per second). They also often produce bright fireballs, creating a captivating display for skywatchers.
3. Leonids
The Leonids meteor shower is a spectacular annual event that occurs in mid-November. Named after the constellation Leo, the Leonids are known for their incredibly fast and bright meteors. These meteors are remnants of the comet Tempel-Tuttle, which orbits the Sun and leaves behind a trail of debris. When Earth passes through this debris trail, the particles enter our atmosphere and create the stunning display of shooting stars we observe as the Leonids meteor shower. What makes the Leonids particularly noteworthy is their occasional outbursts. These outbursts occur when Earth encounters an especially dense part of the debris trail. In these years, the Leonids can produce hundreds or even thousands of meteors per hour, painting the night sky with a fiery spectacle. The most famous historical display of the Leonids occurred in 1833, when the meteor shower was so intense that it appeared as if the stars were falling from the sky. This event, known as the “Great Leonid Meteor Shower,” left a lasting impact on observers and has since become a subject of fascination. To witness the breathtaking beauty of the Leonids, find a dark location away from city lights and look towards the constellation Leo during the peak nights of activity. Whether you’re an avid stargazer or just beginning your journey into astronomy, the Leonids meteor shower is an event that is not to be missed. For more information on famous historical meteor showers, you can explore our article that delves deeper into their cultural significance.
4. Quadrantids
The Quadrantids meteor shower is an annual event that usually takes place in early January. Its name is derived from the obsolete constellation Quadrans Muralis, from which the meteors appear to radiate. With an average peak rate of around 120 meteors per hour, the Quadrantids are known for their brief but intense display of shooting stars. What makes this meteor shower unique is its origin. While most meteor showers are created by comets, the Quadrantids originate from the debris of an asteroid known as 2003 EH1. Despite being a potent meteor shower, the Quadrantids can be a bit challenging to observe. The peak period is quite narrow, lasting only a few hours, and it often occurs during cold winter nights. Nevertheless, dedicated skywatchers who brave the conditions are often rewarded with spectacular fireballs and bright meteors streaking across the sky. The Quadrantids have a fascinating history and have been observed for nearly two centuries. If you’re interested in exploring more about famous historical meteor showers, check out our article on their cultural significance.
5. Orionids
The Orionids meteor shower is an annual event that takes place between October and November. This meteor shower is named after the famous constellation Orion, as the meteors appear to originate from this point in the sky. The Orionids are remnants of Halley’s Comet, one of the most well-known comets in history. When Earth passes through the dust and debris left behind by Halley’s Comet, we are treated to a spectacular display of shooting stars. The Orionids are known for their fast and bright meteors, which often leave persistent trails in their wake. On average, the Orionids produce around 20 meteors per hour during its peak. However, this number can vary depending on the year and other factors. The peak activity usually occurs around October 20th or 21st. The best time to observe the Orionids is after midnight when the constellation Orion rises higher in the sky. Find a dark location away from city lights, lie back, and allow your eyes to adjust to the darkness. Be patient and enjoy the celestial fireworks as the Orionids grace the night sky. If you’re interested in learning more about other famous historical meteor showers, check out our article on famous historical meteor showers.
How are Meteor Showers Formed?
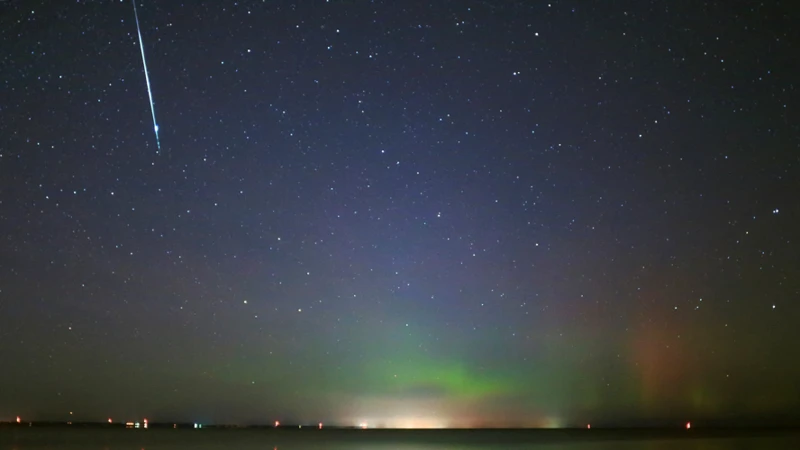

Meteor showers are formed when Earth’s orbit intersects the path of a comet or asteroid. As these celestial bodies orbit the Sun, they leave behind a trail of debris composed of rocky and icy particles. When Earth, on its own orbit around the Sun, passes through this debris field, the particles enter our planet’s atmosphere. The friction generated by the atmosphere rapidly heats up and vaporizes these particles, causing them to glow and produce the dazzling streaks of light we observe as meteor showers.
The parent comets or asteroids responsible for creating meteor showers follow elliptical paths around the Sun. As they approach the inner solar system, the Sun’s heat causes their icy surface to evaporate, releasing gas and dust particles along their path. These particles, in turn, spread out along the comet or asteroid’s orbit, forming a stream of debris. When Earth intersects this stream, a meteor shower occurs as our planet passes through the densest part of the debris trail. This is why meteor showers have specific dates and peak times each year, as Earth crosses the same point in its orbit.
The size and brightness of a meteor shower depend on various factors, including the size and density of the debris particles in the stream. Some comets and asteroids produce more active debris trails, leading to more intense and spectacular meteor showers. Additionally, the angle at which Earth intersects the debris stream can also influence the number and visibility of meteors during a meteor shower.
Understanding how meteor showers are formed enhances our appreciation for these celestial events and allows us to anticipate and enjoy their splendor to the fullest. So, grab a blanket, find a dark location, and prepare to witness the celestial spectacle of a meteor shower!
Observing Meteor Showers
Observing meteor showers is an exhilarating experience that allows us to witness the beauty of the cosmos firsthand. To make the most out of your meteor shower viewing, here are some essential tips to keep in mind.
- Find a Dark Location: Head to a location away from bright city lights to maximize your chances of spotting meteors. The darker the sky, the more visible the meteor shower will be.
- Check the Weather: Keep an eye on the weather forecast to ensure clear skies and optimal viewing conditions. Cloudy or rainy weather can hinder your chances of seeing the meteor shower.
- Timing is Key: Research the peak dates and times of the meteor shower you plan to observe. Set your alarm and be patient, as meteor showers often have specific peak hours when activity is highest.
- Use Star Maps or Apps: Familiarize yourself with the night sky and the specific constellation radiating the meteor shower. Use star maps or mobile apps to help identify the constellations and locate the radiant point.
- Be Patient and Enjoy: Meteor showers can be unpredictable, and it may take some time before you spot your first meteor. Stay patient, relax, and enjoy the experience of gazing up at the starry sky.
By following these tips, you can enhance your meteor shower viewing experience and immerse yourself in the wonder of celestial phenomena. So, grab a blanket, find a comfortable spot, and get ready to witness nature’s very own light show above you.
1. Find a Dark Location
When it comes to observing meteor showers, finding a dark location is crucial for maximizing your viewing experience. Light pollution from cities and towns can significantly diminish the visibility of meteors. To escape the bright lights, consider traveling to a remote area away from urban centers. Look for a location that offers a clear and unobstructed view of the night sky. It could be a secluded spot in the countryside, a national park, or a hilltop away from city lights. Choosing a dark location will enhance your chances of spotting even the faintest meteors streaking across the sky. Additionally, try to plan your observation session during a moonless night, as a bright moon can also interfere with visibility. By finding the ideal dark location, you’ll create the perfect backdrop for witnessing the awe-inspiring beauty of meteor showers.
2. Check the Weather
When planning to observe a meteor shower, it is essential to check the weather conditions beforehand. Cloud cover, precipitation, and light pollution can all significantly impact your viewing experience. A clear and dark sky is crucial for optimal meteor observation. Clear skies will allow you to see the faintest meteors, while light pollution from cities can greatly diminish the number of visible meteors. Checking the weather forecast will help you determine if the sky will be clear or if there is a chance of cloud cover. Additionally, it’s beneficial to find a location away from artificial lights, such as streetlights or buildings, to minimize light pollution interference. If the weather conditions are unfavorable for the initial night you had planned to observe the meteor shower, don’t lose hope! Meteor showers often have a peak period that spans multiple nights, giving you another opportunity to witness the celestial spectacle. So, keep an eye on the weather forecast and be prepared to adjust your plans accordingly to make the most of your meteor shower viewing experience.
3. Timing is Key
Timeliness is crucial when it comes to observing meteor showers. Meteor showers have peak activity periods, which are typically spread over a few nights. To increase your chances of witnessing a spectacular meteor shower display, it is important to know when the shower is likely to be at its peak. Peak dates vary for each meteor shower, so it’s essential to stay updated with the latest information from reputable sources, such as astronomical societies or meteorological websites. Planning your meteor shower viewing around the peak dates will significantly enhance the number of meteors you’ll be able to see. Additionally, paying attention to the time of night is vital. Most meteor showers are best viewed after midnight when the radiant point is higher in the sky. This is because the Earth’s rotation positions you to face the direction in which the meteor shower radiant is located. If you’re in the northern hemisphere, facing northeast is usually a good direction to start with, while in the southern hemisphere, facing northwest is recommended. Remember, patience is key, as the number of meteors visible can vary throughout the night. So, make sure you plan your meteor shower observing session accordingly and be prepared to stay up late for a truly unforgettable celestial experience.
4. Use Star Maps or Apps
To enhance your meteor shower observing experience, it is highly recommended to utilize star maps or smartphone apps specifically designed for stargazing. These tools can assist you in identifying the constellations and their respective radiant points, making it easier to spot the meteors. Star maps are printed charts that plot the positions of stars and other celestial objects in the night sky. They typically indicate the location and timing of meteor showers, allowing you to focus your gaze towards the right direction. Some star maps even provide additional information, such as the estimated meteor activity rates during the peak of a specific meteor shower. On the other hand, smartphone apps offer a more interactive and convenient way to navigate the night sky. These apps use your device’s GPS and compass functionalities to create a real-time display of the stars and constellations above you. They often include features like augmented reality, allowing you to point your phone towards the sky and see labels and overlays of the stars and meteor shower radiant points. Popular stargazing apps include SkyView, Star Walk, and Stellarium. So, whether you prefer the traditional approach with a star map or the modern convenience of a smartphone app, utilizing these tools will greatly enhance your meteor shower viewing experience.
5. Be Patient and Enjoy
Patience is key when observing meteor showers. It’s important to remember that meteor showers are natural phenomena and can be unpredictable. While some meteor showers have a predicted peak date, the exact timing and intensity of the meteor activity may vary. It’s essential to be patient and give yourself enough time to fully experience the event. Find a comfortable spot to sit or lie down, away from bright lights, and give your eyes time to adjust to the darkness. Allow yourself to become fully immersed in the beauty of the night sky. Sometimes, the meteors may appear in clusters or lulls, so it’s crucial to stay focused and watch attentively. Relax, breathe in the cool night air, and let the magic of the meteor shower unfold before your eyes. Remember that meteor showers are not just about counting the number of shooting stars you see but about appreciating the wonder and awe of the universe. So, be patient, have a sense of wonder, and enjoy the celestial spectacle as it unfolds above you.
Conclusion
In conclusion, meteor showers are awe-inspiring celestial events that grace our night skies and fill us with wonder. We have explored the different types of meteor showers, including the Perseids, Geminids, Leonids, Quadrantids, and Orionids, each with its own unique characteristics and peak dates of activity. Meteor showers occur when Earth passes through the debris left behind by comets or asteroids, resulting in the beautiful display of shooting stars. Observing meteor showers can be a magical experience, and we have discussed some tips, such as finding a dark location, checking the weather, and using star maps or apps to enhance our viewing experience. It is important to remember that patience is key when observing meteor showers, as they may have moments of high activity followed by lulls. So, as you gaze up at the night sky and witness the celestial spectacle, take a moment to marvel at the vastness of our universe and the wonders it has to offer. Whether you are a seasoned stargazer or a budding astronomer, meteor showers will continue to inspire and captivate us for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What causes a meteor shower?
Meteor showers are caused by Earth passing through the trail of debris left behind by a comet or asteroid as it orbits the Sun. When these tiny fragments enter Earth’s atmosphere, they burn up and create the streaks of light we see as shooting stars.
2. How often do meteor showers occur?
Meteor showers occur throughout the year, with different showers peaking at different times. Some showers have an annual occurrence, while others have irregular or periodic occurrences. The frequency of meteor showers can range from just a few meteors per hour to hundreds or even thousands per hour during a peak event.
3. Can I see a meteor shower from any location?
Yes, meteor showers can be observed from anywhere on Earth, although the visibility may vary depending on factors such as light pollution and weather conditions. Finding a dark location away from city lights will provide the optimal viewing experience.
4. Do meteor showers pose any danger to Earth?
Meteor showers pose no direct danger to Earth. The small particles that create meteor showers burn up completely in the atmosphere and do not reach the surface. Occasionally, larger debris may survive the atmospheric entry and land as meteorites, but this is rare.
5. How long do meteor showers last?
Meteor showers can have varying durations, lasting from a few days to several weeks. The peak activity, when the most meteors can be observed per hour, usually occurs over a night or two.
6. Are all meteor showers visible to the naked eye?
Most meteor showers are visible to the naked eye, as they produce bright streaks of light that can be seen without the aid of telescopes or binoculars. However, some showers may have fainter meteors that require dark skies and keen observation to spot.
7. Can I photograph a meteor shower?
Absolutely! Capturing meteor showers through photography can be a rewarding experience. You will need a camera with manual settings, a sturdy tripod, and a wide-angle lens. Adjusting the camera settings and using long exposure techniques can help capture the fleeting beauty of meteors. Check out our guide on meteor shower photography for more tips!
8. What is the cultural significance of meteor showers?
Meteor showers have fascinated and inspired humans throughout history. They have been depicted in artwork, mentioned in ancient myths and legends, and are often seen as magical or spiritual events. Different cultures have attributed various meanings and interpretations to meteor showers, adding to their cultural significance. Learn more about the cultural significance of meteor showers.
9. Are there any famous historical meteor showers?
Yes, there are several famous historical meteor showers that have left a mark on human history. The Leonid meteor shower of 1833, known as the “Great Meteor Storm,” is one such example, where the sky was filled with thousands of meteors per hour, creating a stunning spectacle for onlookers. Explore more about famous historical meteor showers and their impact.
10. Can meteor showers be heard?
No, meteor showers cannot be heard. The streaks of light, or meteors, are caused by the combustion of the debris in the Earth’s atmosphere. As sound requires a medium to travel, such as air or water, and meteor showers occur high up in the atmosphere, they do not generate any sound waves that can be heard by humans.