Imagine a world where you have complete control over your dreams, where you can fly through the sky, visit faraway lands, and live out your wildest fantasies. This is the realm of lucid dreaming, a phenomenon that has captivated the human imagination for centuries. But what happens when these dreams turn into a haunting experience known as sleep paralysis? In this article, we will unravel the mysterious connection between lucid dreams and sleep paralysis, exploring the ways in which these two states of consciousness intertwine and the scientific research that sheds light on their curious relationship. So fasten your seatbelts and get ready for a mind-bending exploration of the enigmatic realms of lucid dreams and sleep paralysis.
What are Lucid Dreams?

A lucid dream is a type of dream in which the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming while still in the dream state. This awareness enables the dreamer to have a sense of control and agency within the dream, as if they are an active participant rather than a passive observer. In a lucid dream, individuals can manipulate the dream environment, interact with dream characters, and even alter the course of the dream narrative. This unique state of consciousness opens up a world of possibilities, allowing individuals to explore their deepest desires, confront their fears, and engage in creative problem-solving. Lucid dreams can vary in intensity and clarity, with some individuals experiencing vivid and highly realistic dreams, while others may have a more hazy or fragmented experience. If you’re interested in delving deeper into the various types of lucid dreams, be sure to check out our article on exploring lucid dream types. Lucid dreaming has also been found to have numerous benefits that can improve waking life, such as enhancing creativity, improving problem-solving skills, and aiding in self-awareness and personal growth. To learn more about these benefits, take a look at our article on the benefits of lucid dreaming in improving waking life. If you’re interested in exploring techniques to induce lucid dreams, you may also want to explore the fascinating world of lucid dream induction devices, which use various methods to facilitate lucid dreaming. Find out more about these devices in our article on lucid dream induction devices.
What is Sleep Paralysis?

Sleep paralysis is a temporary condition that occurs during the transition between sleep and wakefulness. It is characterized by a state of complete muscle atonia, or paralysis, in which the individual is unable to move or speak. This can be an unsettling and frightening experience, as the person is typically awake and conscious but unable to control their body. Sleep paralysis often occurs when the person is drifting off to sleep or upon waking up from sleep. During sleep paralysis episodes, individuals may also experience hallucinations, which can be sensory or visual in nature. These hallucinations can range from feeling a presence in the room to seeing shadowy figures or supernatural entities. It’s important to note that sleep paralysis is a relatively common phenomenon and is not considered to be a medical condition or a sign of any underlying health issues. Episodes of sleep paralysis typically last for a few seconds to a couple of minutes, although they can feel much longer to the person experiencing them. While the exact cause of sleep paralysis is still not fully understood, it is believed to be associated with disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle and the REM (rapid eye movement) sleep stage.
The Link between Lucid Dreams and Sleep Paralysis
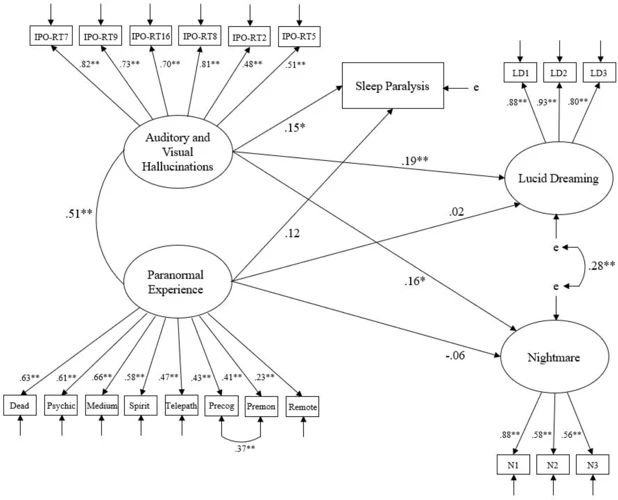
The link between lucid dreams and sleep paralysis lies in the overlapping states of consciousness that they share. While lucid dreaming occurs during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, sleep paralysis commonly occurs during the transition between sleep stages, particularly when waking up from REM sleep. These two phenomena can coexist, with individuals experiencing both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis in the same sleep cycle.
During lucid dreaming, the dreamer is aware of their dream state and may have a certain level of control over the dream environment. However, there can be instances where the dreamer becomes aware of their physical body but remains in a state of paralysis, leading to sleep paralysis. This can be a frightening experience as the individual may feel a sense of helplessness and may also experience hallucinations or a feeling of pressure on the chest.
In some cases, sleep paralysis can act as a gateway to lucid dreaming. As individuals become aware of their inability to move during sleep paralysis, they may transition into a lucid dream, where they can actively engage and manipulate the dream content. This connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreams has led to speculation that the two states may be part of a continuous spectrum of consciousness during sleep.
It’s important to note that not everyone who experiences lucid dreams will also experience sleep paralysis, and vice versa. The occurrence and frequency of these phenomena can vary greatly among individuals, and while they may sometimes intersect, they can also happen independently.
To manage the experiences of both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis, individuals can develop mindfulness techniques and relaxation practices. These can help reduce fear and anxiety associated with sleep paralysis and potentially allow for a smoother transition into lucid dreaming. Additionally, maintaining a regular sleep schedule and practicing good sleep hygiene can contribute to overall better sleep quality and potentially reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
As we continue to explore the intricacies of sleep and consciousness, scientific research sheds light on the connection between lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the scientific studies that have investigated this relationship and the role of brain activity in both phenomena.
How Lucid Dreams can Lead to Sleep Paralysis

Lucid dreams can sometimes lead to the unsettling experience of sleep paralysis. Sleep paralysis occurs when a person is temporarily unable to move or speak, typically upon waking up or falling asleep. While in a state of sleep paralysis, individuals may also experience hallucinations, a sense of pressure on their chest, and a feeling of being watched or accompanied by a presence in the room. So, how do lucid dreams play a role in this phenomenon?
One possible explanation is that during a lucid dream, the brain is in a state of heightened awareness while the body remains in a state of sleep. This can create a discordance between the mind and body, leading to a transition from a lucid dream to a state of sleep paralysis. In other words, the brain wakes up, but the body remains “asleep,” resulting in the feeling of being immobilized.
Additionally, the intense focus and mental effort required to maintain lucidity in a dream can sometimes lead to a state of sleep deprivation. Sleep deprivation has been known to increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. The exhaustion caused by engaging in lucid dreams may contribute to the occurrence of sleep paralysis episodes.
Another factor that can lead to sleep paralysis during lucid dreaming is the fear or anxiety associated with the experience itself. While some individuals may find lucid dreaming exhilarating, others may feel overwhelmed or frightened by the intense and vivid nature of their dreams. This emotional response can trigger a stress response in the body, potentially leading to sleep paralysis.
It’s important to note that not everyone who experiences lucid dreams will also experience sleep paralysis. The occurrence of sleep paralysis during or after lucid dreaming is individual-specific and can depend on various factors such as sleep patterns, stress levels, and pre-existing sleep disorders. If you find yourself experiencing sleep paralysis frequently or it begins to interfere with your quality of sleep, it may be helpful to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying causes and explore potential solutions.
How Sleep Paralysis can Lead to Lucid Dreams

Sleep paralysis, a phenomenon characterized by temporary immobility and the inability to speak or move upon awakening or falling asleep, has been known to trigger lucid dreams in some individuals. When experiencing sleep paralysis, individuals find themselves in a state between being awake and asleep, where their mind is awake but their body remains in a state of paralysis. This unique state of consciousness can be accompanied by hallucinations, often of a frightening nature, which can create a sense of fear and unease. However, for some individuals, sleep paralysis can serve as a gateway to lucid dreaming. During sleep paralysis, the brain is in a highly activated state, with increased neural activity in areas associated with dreaming and vivid imagery. This heightened brain activity can transition into a lucid dream, where individuals become aware of their dream state and gain control over their actions and surroundings. It is during this overlap between sleep paralysis and the onset of a lucid dream that individuals can harness their awareness and transform a potentially unsettling experience into a fascinating lucid dream adventure. While not everyone who experiences sleep paralysis will have lucid dreams, this connection highlights the intricate relationship between these two fascinating states of consciousness.
Tips for Managing Lucid Dreams and Sleep Paralysis

Managing both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis can be challenging, but with the right techniques and strategies, it is possible to navigate these experiences in a positive and empowering way. Here are some tips to help you manage lucid dreams and sleep paralysis:
1. Reality Checks: Practice reality checks throughout the day to increase your self-awareness and improve your chances of becoming lucid in a dream. Reality checks involve questioning the nature of your reality, such as looking at your hands, trying to push your finger through your palm, or asking yourself if you are dreaming.
2. Keep a Dream Journal: Keep a journal by your bed to record your dreams as soon as you wake up. This will help you improve dream recall and identify recurring dream patterns or themes, which can be useful in inducing lucid dreams.
3. Meditation and Mindfulness: Incorporate meditation and mindfulness practices into your daily routine. These techniques can help improve your focus, reduce stress, and increase self-awareness, all of which can contribute to lucid dreaming and managing sleep paralysis.
4. Sleep Hygiene: Maintain good sleep hygiene by establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants close to bedtime. Quality sleep can contribute to more vivid dreams and better control over lucid dreams.
5. Relaxation Techniques: Before bed, engage in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery. These techniques can help calm your mind and body, making it easier to enter a state of lucid dreaming or manage sleep paralysis.
6. Manage Fear: If you experience sleep paralysis, it is common to feel fear or panic. Remind yourself that sleep paralysis is a natural occurrence and try to stay calm. Focus on regulating your breathing and reassuring yourself that the experience is temporary.
7. Seek Support: If you find that lucid dreaming or sleep paralysis is causing significant distress or interfering with your daily life, consider seeking support from a professional, such as a therapist or sleep specialist. They can provide guidance and strategies specific to your needs.
Remember, everyone’s experiences with lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis are unique, so it may take some experimentation to find the techniques that work best for you. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t achieve immediate results, as with practice and patience, you can learn to navigate these extraordinary states of consciousness.
Scientific Studies on the Connection
Scientific studies have shed light on the fascinating connection between lucid dreams and sleep paralysis, unraveling the complexities of these intertwined states of consciousness. Here are some key findings from research that has explored the connection:
1. REM Sleep and Lucid Dreams: One study published in the journal Sleep found a correlation between lucid dreaming and increased levels of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. REM sleep is a stage of sleep associated with vivid dreams, and it is believed that lucid dreams often occur during this phase. The study suggests that the ability to become lucid in dreams may be related to the brain’s ability to maintain a higher level of consciousness during REM sleep.
2. REM Sleep and Sleep Paralysis: Another study published in the journal Sleep Medicine discovered a link between sleep paralysis and disrupted REM sleep. Sleep paralysis is often associated with episodes of muscle paralysis that occur during the transition between sleep and wakefulness, and it was found that these episodes tended to happen during REM sleep. The study suggests that the inhibition of muscle movement during REM sleep may sometimes persist into wakefulness, leading to sleep paralysis.
3. Overlapping Brain States during Lucid Dreams and Sleep Paralysis: Research conducted at the University of Auckland used EEG measurements to examine the brain activity of individuals experiencing both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. The study found that there is a significant overlap in brain states between these two phenomena. This overlap suggests that lucid dreams and sleep paralysis may arise from similar neural mechanisms, highlighting their interconnected nature.
4. The Impact of Sleep Disorders on Lucid Dreams and Sleep Paralysis: Studies have also explored the relationship between sleep disorders, such as insomnia or narcolepsy, and the occurrence of both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. Results indicate that individuals with certain sleep disorders may be more susceptible to experiencing these phenomena. For example, individuals with narcolepsy, a neurological disorder characterized by sudden daytime sleepiness, often report having vivid and lucid dreams, as well as episodes of sleep paralysis.
These scientific studies provide compelling evidence of the connection between lucid dreams and sleep paralysis, offering a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms that give rise to these intriguing experiences. Through further research and exploration, we can continue to unravel the mysteries of these states of consciousness and gain valuable insights into the workings of the human mind.
The Role of Brain Activity
The role of brain activity is crucial in understanding the connection between lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. To comprehend this relationship, we need to explore the different brain states associated with each phenomenon.
1. REM Sleep and Lucid Dreams: Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep is a stage of sleep characterized by heightened brain activity, vivid dreaming, and rapid eye movements. Lucid dreams often occur during REM sleep, when the brain is highly active and engaged in creating and experiencing dreams. During this stage, the prefrontal cortex, responsible for self-awareness and logical thinking, becomes more active, leading to the awareness and control experienced in lucid dreams.
2. REM Sleep and Sleep Paralysis: Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon that occurs during the transition between sleep and wakefulness when the brain is still in a state of REM sleep. It is characterized by temporary paralysis of the body, often accompanied by hallucinations and a sense of being trapped or unable to move. The heightened brain activity associated with REM sleep carries over into sleep paralysis, leading to increased sensory perceptions and intense hallucinations.
3. Overlapping Brain States during Lucid Dreams and Sleep Paralysis: Research suggests that there is an overlap in brain activity between lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. Both phenomena involve activation of the prefrontal cortex, which plays a significant role in self-awareness and conscious thought. This shared brain activity may explain why individuals who experience frequent lucid dreams are more prone to sleep paralysis episodes.
4. The Impact of Sleep Disorders on Lucid Dreams and Sleep Paralysis: Sleep disorders, such as insomnia or narcolepsy, can disrupt the normal sleep architecture and affect the occurrence of both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. Individuals with sleep disorders may experience more frequent or intense instances of both phenomena due to irregular sleep patterns and disrupted brain activity.
Understanding the role of brain activity in lucid dreams and sleep paralysis provides valuable insights into how these two states of consciousness are connected. By unraveling the intricacies of the brain’s functioning during these experiences, we can gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis.
1. REM Sleep and Lucid Dreams
REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep is a stage of sleep characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreaming. It is during REM sleep that lucid dreams are most likely to occur. Research has shown that lucid dreaming often takes place during the later stages of REM sleep, when brain activity is at its peak. During this stage, the frontal cortex of the brain, which is responsible for logic, self-awareness, and decision-making, becomes more active. This heightened activity allows individuals to realize that they are in a dream state and gain control over their dream experiences. Studies have also found that individuals who frequently experience lucid dreams tend to have shorter REM sleep latencies, meaning they enter REM sleep more quickly after falling asleep. This suggests that there may be a relationship between the speed at which one transitions into REM sleep and their propensity for lucid dreaming. The connection between REM sleep and lucid dreams highlights the intricate interplay between brain activity and conscious awareness during the dream state.
2. REM Sleep and Sleep Paralysis
During REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, which is one of the stages of the sleep cycle, the brain becomes highly active, similar to being awake. This stage is characterized by rapid eye movements, vivid dreams, and muscle paralysis, known as REM atonia. It is during this state that sleep paralysis can occur. Sleep paralysis is a temporary inability to move or speak while transitioning into or out of REM sleep. This phenomenon can be accompanied by hallucinations, a sense of pressure on the chest, and a feeling of being watched or a presence in the room. While sleep paralysis is typically brief and harmless, it can be a distressing experience for those who encounter it. The connection between REM sleep and sleep paralysis lies in the disruption of the normal transition between REM sleep and wakefulness. Normally, during REM sleep, the brain sends signals to inhibit voluntary muscle activity, causing temporary paralysis to prevent acting out dreams. However, when this process malfunctions, individuals may become consciously aware while their muscles remain immobilized, resulting in the experience of sleep paralysis. It’s worth noting that not all episodes of REM sleep correlate with sleep paralysis, but it is more likely to occur during these stages of the sleep cycle.
3. Overlapping Brain States during Lucid Dreams and Sleep Paralysis
The fascinating connection between lucid dreams and sleep paralysis lies in the overlapping brain states that occur during these experiences. Research has shown that both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis are associated with specific patterns of brain activity. During a lucid dream, the brain exhibits characteristics of both wakefulness and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. REM sleep is the stage of sleep where vivid dreaming occurs, and it is during this stage that the brain becomes highly active and resembles wakefulness in many aspects. Similarly, during sleep paralysis, the brain enters a state that is similar to REM sleep in terms of brain activity, while the body remains temporarily paralyzed. This overlap suggests that both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis may arise from a disruption in the normal transitions between sleep stages. Some studies have even shown that sleep paralysis can occur directly from a lucid dream state, with the dreamer transitioning from the immersive dream environment to a state of being awake but unable to move. This phenomenon, known as “dream-to-reality” sleep paralysis, highlights the intricate and complex relationship between these two intriguing states of consciousness.
4. The Impact of Sleep Disorders on Lucid Dreams and Sleep Paralysis
4. The Impact of Sleep Disorders on Lucid Dreams and Sleep Paralysis
Sleep disorders can have a significant impact on both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. Conditions such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and narcolepsy can disrupt normal sleep patterns and increase the likelihood of experiencing both phenomena.
Insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, can make it challenging to achieve the REM sleep stage where dreams, including lucid dreams, occur. As a result, individuals with insomnia may have fewer opportunities to experience lucid dreams.
Sleep apnea, a condition marked by interrupted breathing during sleep, can also interfere with the quality and duration of sleep. As a consequence, the occurrence of both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis may be affected. Sleep apnea tends to disturb the natural sleep cycle, potentially leading to fragmented sleep and an increased occurrence of sleep paralysis episodes.
Narcolepsy, a neurological disorder that disrupts sleep-wake cycles, can profoundly impact both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. People with narcolepsy often experience excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks, leading to fragmented nighttime sleep. This fragmented sleep can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis and can also influence the occurrence of lucid dreams.
It is worth noting that while sleep disorders may increase the likelihood of experiencing both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis, they are not exclusive factors. Healthy individuals without sleep disorders can also have lucid dreams and experience sleep paralysis under certain circumstances.
Understanding the relationship between sleep disorders and these phenomena can help individuals manage their sleep conditions and potentially reduce the frequency and intensity of both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. Seeking treatment for underlying sleep disorders and implementing healthy sleep habits, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a sleep-friendly environment, may contribute to a better overall sleep experience and potentially minimize the occurrence of sleep disturbances.
Methods to Induce Lucid Dreams without Sleep Paralysis

When it comes to inducing lucid dreams without the occurrence of sleep paralysis, there are several techniques that individuals can try. One popular method is reality testing. This involves regularly questioning and testing one’s reality throughout the day, which can carry over into the dream state. By consistently asking yourself, “Am I dreaming?” and performing reality checks, such as looking at a clock or trying to push your finger through your palm, you can increase your chances of becoming lucid in a dream. Another technique is the Wake Back to Bed (WBTB) method. With this method, you set an alarm to wake yourself up after a few hours of sleep and then go back to sleep with the intention of entering a lucid dream. This technique takes advantage of the fact that most lucid dreaming occurs during periods of REM sleep, which are more prevalent towards the end of the sleep cycle. Additionally, practicing meditation and mindfulness can help develop greater self-awareness and increase the likelihood of lucid dreaming. By training your mind to be more present and attentive, you may find it easier to recognize the dream state and become aware that you are dreaming. It’s important to note that not all methods work for everyone, and it may take some experimentation to find what works best for you. Patience, consistency, and maintaining a dream journal to track your progress can also be useful in your journey to induce lucid dreams without the presence of sleep paralysis.
Common Experiences during Lucid Dreams and Sleep Paralysis

During lucid dreams and sleep paralysis, individuals often report various common experiences that can range from thrilling to terrifying. Let’s take a closer look at some of these experiences:
1. Sensations of Floating or Flying: Many individuals describe the sensation of weightlessness or the ability to fly during both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. This experience can be exhilarating and liberating, allowing individuals to explore the dream or sleep paralysis environment from a unique perspective.
2. Vivid Visuals and Sensory Perceptions: Lucid dreams and sleep paralysis can be characterized by exceptionally vivid visuals, as if one is fully immersed in a lifelike environment. Colors may appear brighter, textures may feel more tactile, and sounds may be more vivid and distinct. These enhanced sensory perceptions contribute to the immersive nature of both states.
3. Encounters with Dream Characters or Entities: In both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis, individuals may encounter various dream characters or entities. These can range from familiar individuals from one’s waking life to fantastical beings or even shadowy figures. The nature of these encounters can vary greatly, from friendly interactions to unsettling and threatening encounters.
4. Paralysis and Sensory Hallucinations: Sleep paralysis is characterized by a temporary loss of muscle movement while transitioning between sleep and wakefulness. During this state, individuals may experience vivid and sometimes disturbing sensory hallucinations. These hallucinations can manifest as visual, auditory, or tactile sensations, and often contribute to feelings of fear and helplessness.
5. Time Distortion: Time perception can be altered during both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. Seconds may feel like minutes, and minutes like hours. This distortion of time adds to the surreal and otherworldly nature of these experiences.
6. Intense Emotions: Lucid dreams and sleep paralysis can evoke a wide range of emotions. Excitement, joy, and awe may accompany positive lucid dream experiences, while fear, dread, and anxiety are common during sleep paralysis episodes. These intense emotions can linger even after waking up, creating a lasting impact on the individual’s mood and sense of well-being.
It is important to note that individual experiences can vary greatly, and not everyone will experience the same sensations or encounters during lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. These are just a few examples of the common experiences reported by individuals who have experienced these intriguing states of consciousness.
Understanding the Psychological and Spiritual Significance
Understanding the psychological and spiritual significance of lucid dreams and sleep paralysis can provide valuable insights into the human mind and consciousness. From a psychological perspective, lucid dreams can be seen as a window into the subconscious, revealing hidden desires, fears, and unresolved emotions. Through lucid dreaming, individuals can engage in self-exploration and introspection, gaining a deeper understanding of their own psyche. It can serve as a therapeutic tool, allowing individuals to confront and work through psychological issues in a safe and controlled environment. Lucid dreaming can also be a catalyst for personal growth and transformation, as individuals gain a greater sense of self-awareness and develop a stronger connection to their inner selves.
From a spiritual standpoint, lucid dreams are often viewed as a bridge between the physical and spiritual realms. Some believe that lucid dreaming provides a means for communication with higher beings, spirit guides, or deceased loved ones. It can be a source of spiritual guidance and enlightenment, offering profound mystical experiences and glimpses into the nature of existence. Lucid dreaming can also be used for spiritual practices such as dream yoga or astral projection, where individuals seek to explore higher dimensions of consciousness and expand their spiritual awareness.
It is important to note that the psychological and spiritual significance of lucid dreams and sleep paralysis may vary from person to person. While some individuals may find deep meaning and transformative experiences in these states, others may simply view them as fascinating phenomena without attaching any particular significance. Ultimately, the interpretation and understanding of these experiences are subjective and can be influenced by personal beliefs, cultural contexts, and individual experiences. Regardless of one’s perspective, the exploration of the psychological and spiritual aspects of lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis offers a rich and intriguing avenue for self-discovery and contemplation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the connection between lucid dreams and sleep paralysis is intriguing and complex. While both states of consciousness occur during the REM sleep stage, they can manifest in different ways and have distinct features. Lucid dreams offer individuals the ability to control and manipulate their dreams, providing a sense of empowerment and exploration. However, this heightened level of awareness can sometimes lead to sleep paralysis, a state where individuals are temporarily unable to move or speak while transitioning between sleep and wakefulness. Despite the potential for unsettling experiences, there are tips available for managing both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. These include maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, practicing relaxation techniques before bed, and seeking professional help if sleep disturbances persist. Scientific studies have shed light on the underlying brain activity during both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis, revealing overlapping patterns and brain states. It is important to note that these experiences can also be influenced by sleep disorders. If you are interested in inducing lucid dreams without the risk of sleep paralysis, various techniques can be explored, such as reality testing, meditation, and keeping a dream journal. It is fascinating to note the common experiences that individuals often report during lucid dreams and sleep paralysis, such as vivid visuals, auditory and tactile sensations, and encounters with supernatural entities. These experiences have psychological and spiritual significance for many, leading to questions about the nature of consciousness and the boundaries of the mind. In conclusion, the connection between lucid dreams and sleep paralysis invites further exploration and research, offering a glimpse into the mysterious realm of our subconscious minds.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can anyone learn to have lucid dreams?
Yes, virtually anyone can learn to have lucid dreams with practice and techniques that help increase self-awareness during sleep.
2. Are lucid dreams the same as vivid dreams?
No, lucid dreams and vivid dreams are not the same. Lucid dreams refer to dreams where the dreamer is aware they are dreaming, while vivid dreams simply involve dreams that are exceptionally clear and detailed.
3. Are there any risks or dangers associated with lucid dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is generally considered safe, but some individuals may experience sleep disturbances or become prone to sleep paralysis. It’s crucial to practice lucid dreaming techniques responsibly and prioritize overall sleep health.
4. Can lucid dreams be controlled at will?
With practice and experience, individuals can improve their ability to control and manipulate lucid dreams, but complete control over every aspect of the dream may not always be possible.
5. Is lucid dreaming the same as astral projection?
No, lucid dreaming and astral projection are distinct experiences. Lucid dreaming involves becoming aware within a dream, while astral projection refers to an out-of-body experience where one’s consciousness leaves the physical body.
6. How can sleep paralysis be managed during lucid dreams?
During a sleep paralysis episode in a lucid dream, it can help to stay calm, focus on positive thoughts, and try to gently move fingers or toes to break free from the paralysis. Developing a regular sleep schedule and reducing stress can also help manage sleep paralysis.
7. Can lucid dreams be used for problem-solving or personal growth?
Absolutely! Lucid dreams offer a unique opportunity to confront fears, explore desires, and engage in problem-solving scenarios. It can provide insights and personal growth when utilized effectively.
8. Are there any techniques to induce lucid dreaming without sleep paralysis?
Yes, there are various techniques to induce lucid dreaming without experiencing sleep paralysis, such as reality testing, mnemonic induction of lucid dreams (MILD), and wake-induced lucid dreaming (WILD). These techniques focus on increasing self-awareness during the dreaming process.
9. Can lucid dreaming improve creativity?
Yes, lucid dreaming has been linked to enhanced creativity. In a lucid dream, the dreamer can explore imaginative scenarios, create art, and engage in problem-solving exercises, which can have a positive impact on waking creativity.
10. Are there any spiritual or psychological implications of lucid dreaming?
Lucid dreaming can have profound psychological and spiritual implications. It can provide opportunities for self-reflection, personal growth, and exploration of the subconscious mind. Some individuals also view lucid dreaming as a spiritual practice for deepening their connection with the self and the universe.








