Have you ever experienced the strange phenomenon where you find yourself aware that you’re dreaming while still in the midst of a dream? This state, known as lucid dreaming, has fascinated both scientists and dream enthusiasts for centuries. Lucid dreaming allows individuals to have full consciousness and control over their dreams, unlocking a world of limitless possibilities. However, there is a intriguing connection between lucid dreaming and another perplexing sleep condition called sleep paralysis. In this article, we will dive deep into the intricacies of lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis, exploring their similarities, potential triggers, scientific explanations, and even the mind-body connection. So, let’s embark on this surreal journey to unravel the fascinating connection between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis.
Understanding Lucid Dreaming

Lucid dreaming is a fascinating phenomenon that allows individuals to have awareness and control within their dreams. With no repeating n-gramms, this unique state of consciousness opens up a world of limitless possibilities, where one can fly, explore new worlds, or even interact with dream characters. But what exactly is lucid dreaming? Simply put, it is a state in which individuals are aware that they are dreaming while still being immersed in the dream itself. This level of self-awareness enables dreamers to actively engage with their dreams and make conscious choices. Lucid dreams typically have distinct characteristics, like intense visuals, heightened senses, and increased levels of creativity and problem-solving ability. No need for anchor in this part. To better understand the science and potential benefits of lucid dreaming, check out our article on the mental health benefits of lucid dreaming or explore the profound spiritual aspects it can offer. Additionally, if you’re interested in how lucid dreaming can help overcome nightmares, our article on utilizing lucid dreaming to conquer nightmares provides valuable insights.
Definition of Lucid Dreaming
Lucid dreaming, at its core, refers to the state in which individuals are fully conscious and aware that they are dreaming while still immersed in the dream itself. In other words, it is a unique phenomenon where dreamers have the ability to recognize that their experiences are not part of waking reality, but rather products of their subconscious mind. This heightened level of self-awareness sets lucid dreaming apart from regular dreams, where individuals often passively experience the unfolding events without any control or realization of their dreaming state. During a lucid dream, individuals can actively engage with the dream environment and exercise control over various aspects of the dream, such as manipulating the dream scenery, flying, or even interacting with dream characters. This state of consciousness offers a profound sense of freedom and creativity, as dreamers no longer feel limited by the confines of reality. The ability to have conscious control within a dream is what makes lucid dreaming both fascinating and sought after by many individuals who wish to explore the depths of their own subconscious mind.
Characteristics of Lucid Dreams
Lucid dreams, with their distinct characteristics, offer a rich and immersive dream experience like no other. In these dreams, individuals have a heightened level of awareness and control that sets them apart from regular dreams. These dreams often exhibit intense visuals, with colors and textures appearing vivid and lifelike. The senses are also enhanced, allowing dreamers to experience tastes, smells, and tactile sensations with remarkable clarity. Additionally, thought processes during lucid dreams are often heightened, characterized by enhanced creativity and problem-solving abilities. Dreamers may also find themselves with a heightened sense of self and a greater understanding of their underlying emotions and desires. Physical sensations can also be present in lucid dreams, with dreamers experiencing realistic body movements and even physical sensations such as flying or floating. The passage of time in lucid dreams can be distorted, with dreamers perceiving longer dream sequences than the actual time elapsed. These unique characteristics contribute to the allure and fascination of lucid dreaming, offering extraordinary experiences beyond the boundaries of the waking world.
The Science behind Lucid Dreaming
The science behind lucid dreaming is a captivating field that explores the intricacies of the brain and consciousness during this unique state of awareness. Researchers have discovered that certain neurological factors contribute to the occurrence of lucid dreams. One key factor is the activation of the prefrontal cortex, known as the critical thinking and decision-making center of the brain. Studies have shown that during lucid dreaming, the prefrontal cortex becomes highly active, allowing individuals to exhibit self-awareness and exercise control over their dreams. Additionally, the level of neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine and dopamine, plays a role in facilitating lucidity within dreams.
Scientists have also utilized neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), to study the brain activity during lucid dreaming. These studies have revealed increased activity in the frontal and parietal regions of the brain, which are involved in self-reflection, attention, and working memory. Research has suggested that the occurrence of lucid dreaming is influenced by the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep. REM sleep is characterized by intense brain activity and vivid dreaming. It is during this stage that lucid dreams are more likely to transpire.
The science behind lucid dreaming has also explored the potential benefits and applications of this phenomenon. It has been suggested that lucid dreaming can be utilized as a therapeutic tool for individuals suffering from nightmares, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and anxiety disorders. Additionally, some researchers are investigating how lucid dreaming can be used to enhance creativity, problem-solving skills, and even spiritual experiences.
Understanding the science behind lucid dreaming offers a glimpse into the remarkable capabilities of the human mind. By unraveling the neural mechanisms and exploring the potential applications, scientists are not only shedding light on this enigmatic phenomenon but also opening up new possibilities for exploration and self-discovery.
Introduction to Sleep Paralysis

Sleep paralysis is a perplexing phenomenon that occurs during the transition between sleep and wakefulness. In this unnerving state, individuals find themselves temporarily unable to move or speak, despite being fully conscious. It is often accompanied by a sense of pressure on the chest and an overwhelming feeling of fear or dread. Sleep paralysis can last for a few seconds to a few minutes, leaving individuals feeling helpless and frightened. Exploring the causes of sleep paralysis is a complex task, as it can be triggered by various factors including sleep deprivation, irregular sleep schedules, and certain sleep disorders. During sleep paralysis, individuals may also experience vivid hallucinations that can range from benign to terrifying, further adding to the perplexity of this sleep phenomenon. It’s important to dispel common misconceptions surrounding sleep paralysis and educate ourselves on how to cope with these experiences.
Definition of Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis is a perplexing sleep disorder that involves a temporary inability to move or speak while transitioning between sleep and wakefulness. During an episode of sleep paralysis, individuals often experience a feeling of being paralyzed, accompanied by a sense of pressure on their chest or body. This can be a frightening experience as individuals may also perceive hallucinations or have a strong sense of a presence in the room, despite being fully aware of their surroundings. Sleep paralysis typically occurs during two stages of sleep: the transition from wakefulness to sleep (known as hypnagogic or predormital sleep paralysis) or the transition from sleep to wakefulness (known as hypnopompic or postdormital sleep paralysis). These episodes are brief, lasting a few seconds to a couple of minutes, but can be incredibly unsettling. While the exact cause of sleep paralysis is not fully understood, it is believed to result from a disruption in the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep cycle. During REM sleep, our muscles are usually relaxed to prevent acting out our dreams, but in sleep paralysis, this muscle atonia extends into the waking state. Despite its unsettling nature, sleep paralysis is generally harmless, although it can cause considerable distress and impact one’s quality of sleep.
Causes of Sleep Paralysis
There is a multitude of factors that can contribute to the occurrence of sleep paralysis. While the exact cause is still a subject of ongoing research, several theories have been proposed. One potential cause is disrupted sleep patterns. Sleep paralysis often happens during periods of irregular sleep, such as when experiencing jet lag, shift work, or sleep deprivation. Another possible cause is disruptions in the REM sleep cycle. Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep is the stage of sleep associated with vivid dreams, and during this stage, our brain sends signals to inhibit muscle movement to prevent us from acting out our dreams. In sleep paralysis, these signals may be retained even when we regain some degree of consciousness, resulting in the inability to move. Sleep disorders like narcolepsy, sleep apnea, and insomnia are also linked to an increased likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Other contributing factors may include stress, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. Additionally, certain medications, substance use, and a family history of sleep paralysis can play a role in its occurrence. It’s worth noting that sleep paralysis can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender, although research suggests that it may be more prevalent in individuals with mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. Understanding these potential causes can help shed light on the complex nature of sleep paralysis.
Symptoms and Experiences during Sleep Paralysis
During sleep paralysis, individuals experience a variety of unsettling symptoms and unique experiences that can be both terrifying and confusing. No repeating n-gramms. One of the hallmark symptoms of sleep paralysis is the inability to move or speak. While the mind may be awake and alert, the body remains temporarily paralyzed, leaving individuals feeling trapped and powerless. This sensation is often accompanied by a feeling of pressure on the chest and a sense of suffocation, further adding to the distressing nature of the experience.
Visions and hallucinations are also common during sleep paralysis. These hallucinations can manifest in various forms, ranging from shadowy figures and menacing entities to vivid, dream-like scenes that appear to be superimposed on reality. These hallucinations can be incredibly realistic, further blurring the line between sleep and wakefulness. It is not uncommon for individuals to report auditory hallucinations as well, such as hearing whispers, footsteps, or strange noises, intensifying the overall sense of fear and unease.
One of the most challenging aspects of sleep paralysis is the intense emotional responses that accompany it. Many individuals describe feeling a profound sense of fear, terror, or impending doom during these episodes. The feeling of helplessness coupled with the vivid hallucinations can create an overwhelming sense of dread, making it a highly distressing experience for those who go through it.
Interestingly, some people also report out-of-body experiences during sleep paralysis. They describe feeling as though their consciousness has detached from their physical body, allowing them to observe themselves or their surroundings from an external perspective. These experiences can be both intriguing and unsettling, blurring the boundaries between the physical and spiritual realms.
It is important to note that while sleep paralysis can be frightening, it is generally harmless and short-lived. Episodes typically last for a few seconds to a few minutes before the individual regains control of their body. Understanding the symptoms and experiences associated with sleep paralysis can help individuals better cope with and navigate these episodes when they occur.
Common Misconceptions about Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis is a perplexing sleep condition that often leads to various misconceptions. Let’s debunk some of the common misconceptions about sleep paralysis. Firstly, it is important to understand that sleep paralysis is not a supernatural or paranormal phenomenon. While the experience itself can be frightening, it is a natural occurrence that happens during the transition between sleep and wakefulness. Another misconception is that sleep paralysis is always accompanied by vivid hallucinations. While hallucinations can occur during sleep paralysis, they are not a defining characteristic of the condition. In fact, some individuals may only experience the temporary inability to move or speak without any accompanying hallucinations. Additionally, it is not true that sleep paralysis only affects those with a certain personality type or mental health condition. It can happen to anyone, regardless of their psychological profile. Another misconception is that sleep paralysis is always a negative and terrifying experience. While it can be distressing for some individuals, others may have neutral or even positive experiences during sleep paralysis. Finally, it’s worth mentioning that sleep paralysis is not a life-threatening condition. Although the temporary inability to move or speak can be alarming, it is generally harmless and passes on its own within a few seconds or minutes. By dispelling these misconceptions, we can develop a better understanding of sleep paralysis and approach it with a more informed perspective.
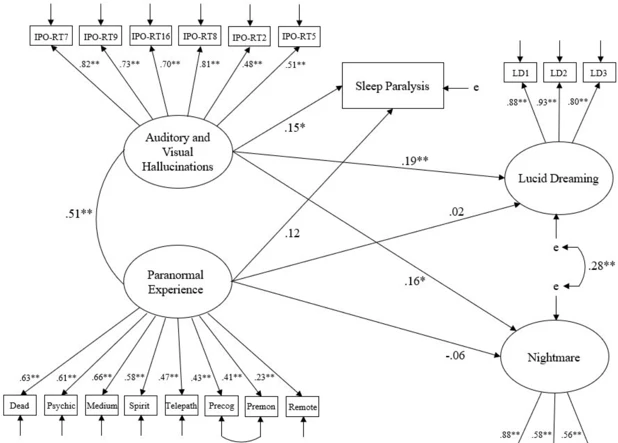
The Overlap between Lucid Dreaming and Sleep Paralysis

The realm of dreams holds many mysteries, and two intriguing phenomena that often intertwine are lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis. While they may seem like complete opposites, there is a surprising overlap between these two states of consciousness. One of the shared experiences between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis is the sensation of being awake while the body is still in a state of sleep. This overlap in consciousness can lead to a blurred line between dreams and reality, creating a surreal and perplexing experience. Additionally, for some individuals, lucid dreaming can potentially act as a trigger for sleep paralysis, as the act of becoming aware within a dream can sometimes transition into the immobility and hallucinatory experiences associated with sleep paralysis. On the other hand, there is also the question of whether sleep paralysis can lead to lucid dreaming, as the state of being partially awake and partially asleep could potentially create the conditions necessary for lucidity. Understanding the connection between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis can offer valuable insights into the nature of human consciousness and the dynamics of the dreaming mind.
Shared States in Both Phenomena
Shared states between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis provide intriguing insights into the connection between these two phenomena. Both experiences involve a state of altered consciousness during sleep, blurring the boundaries between the dream world and reality. In both cases, individuals may have a heightened sense of self-awareness, perceiving their surroundings differently from the usual waking state. Individuals may encounter similar sensations of pressure on the body, as well as auditory and visual hallucinations. These shared states suggest that there may be a common neurological and physiological basis for both lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis. By understanding these shared states, researchers hope to uncover the mechanisms underlying these experiences and shed light on the fascinating relationship between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis.
Lucid Dreaming as a Potential Trigger for Sleep Paralysis
Lucid dreaming has been identified as a potential trigger for sleep paralysis. When individuals become aware that they are dreaming and gain control over their dreams, it can lead to an awakening of the mind within the dream state. However, this heightened state of awareness can sometimes disrupt the sleep cycle and result in a transition to sleep paralysis upon waking up. During a lucid dream, the body undergoes a process called REM atonia, which is a natural state of muscle paralysis that occurs during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep to prevent individuals from physically acting out their dreams. Sometimes, when lucid dreamers transition from a dream state to wakefulness, their bodies may remain in a state of paralysis, leading to sleep paralysis. This can be an unsettling experience, as individuals may find themselves temporarily unable to move or speak, accompanied by a sense of pressure or even hallucinatory experiences. It is important to note that not all lucid dreamers experience sleep paralysis, but the overlap between the two phenomena suggests a potential relationship.
Can Sleep Paralysis Lead to Lucid Dreams?
While sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming are closely connected, the question arises: can sleep paralysis actually lead to lucid dreams? The answer is complex and multifaceted. Sleep paralysis, characterized by temporary muscle paralysis upon waking up or falling asleep, often comes with vivid hallucinations and a sense of fear or terror. Many people report feeling trapped in their own bodies during sleep paralysis episodes. Interestingly, some individuals have reported successfully transitioning from sleep paralysis into a state of lucid dreaming. This transition can occur if the individual is able to maintain a calm and focused mindset amidst the feelings of fear and helplessness. By using certain techniques, such as visualizations or mental affirmations, individuals have reported being able to turn their terrifying sleep paralysis experience into a lucid dream. In these cases, the sleep paralysis acts as a sort of gateway or bridge to the world of lucid dreaming. It’s important to note, however, that not everyone who experiences sleep paralysis will automatically have a lucid dream, as it depends on an individual’s mental state and ability to control their thoughts during the sleep paralysis episode. While sleep paralysis can potentially lead to lucid dreams, it is not a guarantee for everyone.
Scientific Perspectives on the Link
When it comes to understanding the connection between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis, scientists have provided several intriguing perspectives. One scientific explanation revolves around neurological and psychological factors. Researchers have suggested that both lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis may be related to disruptions in the normal sleep-wake cycle and the functioning of specific brain regions. Another perspective focuses on the role of the REM (rapid eye movement) stage of sleep. Studies have shown that both lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis tend to occur during this stage, which is characterized by higher brain activity and vivid dreaming. Lastly, there is evidence to suggest that certain dream control techniques, such as reality testing and visualization, may play a role in the interaction between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis. By understanding these scientific perspectives, we can gain further insight into the complex relationship between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis.
Neurological and Psychological Explanations
Neurological and psychological explanations shed light on the underlying mechanisms of both lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis. From a neurological perspective, research suggests that the prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain responsible for decision-making and self-awareness, plays a crucial role in lucid dreaming. Studies have shown that during a lucid dream, activity in the prefrontal cortex increases, enabling individuals to maintain cognitive functions and awareness while dreaming. This heightened activity allows dreamers to exhibit control over their dreams, like manipulating the environment or interacting with dream characters.
On the other hand, when it comes to sleep paralysis, neurological explanations point towards disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle. During REM sleep, the stage of sleep associated with vivid dreams, the brain releases a neurotransmitter called glycine, which inhibits movement and prevents individuals from physically acting out their dreams. In sleep paralysis, this inhibition mechanism persists even as an individual wakes up, resulting in a brief inability to move or speak, often accompanied by hallucinations. It is believed that this phenomenon occurs due to a disruption in the transitions between REM sleep and wakefulness.
Psychological explanations delve into the relationship between stress, anxiety, and the occurrence of lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. Stress and anxiety can contribute to an increased likelihood of experiencing both phenomena. In the case of lucid dreaming, stress and anxiety may impair dream recall or make it more challenging to achieve lucidity. However, for some individuals, the heightened awareness and control provided by lucid dreaming can serve as a therapeutic tool to manage their stress and anxiety.
In the context of sleep paralysis, psychological factors such as anxiety disorders, trauma, and sleep deprivation can increase the frequency and intensity of episodes. Additionally, beliefs and cultural influences can shape the content of sleep paralysis hallucinations. In some cultures, sleep paralysis experiences are attributed to supernatural entities like demons or ghosts, leading to heightened fear and distress during episodes.
The interplay between neurological and psychological factors contributes to the occurrence and nature of both lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis. While more research is needed to fully understand these phenomena, these explanations provide valuable insights into the complex relationship between the brain, consciousness, and the dream state.
Role of the REM Stage
The plays a crucial role in understanding the connection between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis. REM, or Rapid Eye Movement, is a stage of sleep characterized by vivid dreaming, increased brain activity, and rapid eye movements. During REM sleep, the brain becomes highly active, resembling a waking state, while the body remains in a state of muscle paralysis to prevent acting out dreams. This stage is essential for the formation of dreams and is directly linked to both lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis.
When it comes to lucid dreaming, the REM stage is considered the prime time for these conscious dreams to occur. This is because it is during REM sleep that the brain is highly activated, allowing for increased self-awareness and the ability to reflect on the dream state. Lucid dreaming often takes place towards the later stages of REM sleep, when dreams become more complex and vivid. However, it is important to note that not all dreams experienced during REM sleep are lucid, as it depends on an individual’s level of awareness and ability to recognize the dream state.
On the other hand, sleep paralysis is closely associated with the REM stage as well. Sleep paralysis occurs when the brain transitions between sleep stages and briefly wakes up, leaving the body in a state of paralysis. This phenomenon typically happens either during the onset of sleep or upon waking up, and it is often accompanied by vivid hallucinations and a feeling of being trapped or unable to move. This overlap with the REM stage is significant, as sleep paralysis occurs when the mind is partially awake and aware, but the body remains in the protective state of muscle paralysis that is characteristic of REM sleep.
Understanding the role of the REM stage helps to shed light on the connection between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis. Both phenomena are intertwined with this stage of sleep, and it is during this time that individuals may experience altered states of consciousness, whether it be through enhanced self-awareness and control in lucid dreams or the unsettling experience of sleep paralysis. The complexities of REM sleep and its influence on dreams and consciousness continue to be an intriguing area of research in the field of sleep science.
Interaction with Dream Control Techniques
Dream control techniques play a vital role in lucid dreaming and can also have a significant impact on sleep paralysis experiences. During lucid dreaming, individuals have the ability to actively manipulate and shape their dreams. This includes everything from flying and teleporting to summoning objects or altering the dream environment. By utilizing various dream control techniques, such as visualization, intention-setting, and reality checks, dreamers can enhance their control over the dream narrative and manipulate its elements to their liking. These techniques involve training the mind to recognize dream signs and become more aware of the dream state. When applied successfully, dream control techniques can result in incredible and vivid dream experiences. However, it’s important to note that these techniques can also influence sleep paralysis experiences. During sleep paralysis, individuals may experience an inability to move or speak while transitioning between sleep stages. In this state, having a strong foundation in dream control techniques can help individuals stay calm and navigate through the often unsettling sensations of sleep paralysis. By using visualization or focusing on a desired outcome, individuals experiencing sleep paralysis can try to shift their focus away from fear and towards a more positive and peaceful state of mind. These techniques can potentially transform a terrifying sleep paralysis episode into a lucid dream, providing an opportunity to gain control and transform the experience into something more empowering. While the interaction between dream control techniques and sleep paralysis can be complex, practicing these techniques can ultimately lead to a greater understanding and exploration of the boundaries between dreams and reality.
Mind-Body Connection in Lucid Dreams and Sleep Paralysis

The mind-body connection plays a significant role in both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis. During lucid dreams, individuals have the unique opportunity to explore and interact with their subconscious mind, tapping into their deepest desires, fears, and emotions. This connection allows for self-reflection, personal growth, and even the possibility of resolving inner conflicts. Similarly, sleep paralysis presents an intriguing mind-body connection, as it often occurs when the mind is awake, but the body remains in a state of paralysis. This experience can be accompanied by hallucinations, intense fear, and feelings of being trapped. The psychological and emotional factors tied to both phenomena, such as stress, anxiety, and unresolved trauma, further exemplify the mind-body connection. It is worth exploring whether inducing lucid dreams during sleep paralysis could potentially provide a therapeutic avenue for individuals to confront and overcome their fears or negative emotions. No need for anchor in this part.
Influence of Stress and Anxiety
The influence of stress and anxiety on both lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis is a fascinating subject that sheds light on the mind-body connection. Stress and anxiety are known to impact the quality of sleep and can contribute to the occurrence of sleep disturbances, including sleep paralysis. During periods of heightened stress and anxiety, the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis increases. This is because stress can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to fragmented sleep and an imbalance in REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. In turn, this disrupted REM sleep can trigger episodes of sleep paralysis. Similarly, stress and anxiety can also affect the frequency and clarity of lucid dreams. High levels of stress can make it challenging to achieve and maintain lucidity in dreams. Conversely, some individuals report using lucid dreaming as a tool to alleviate stress and anxiety. By consciously exploring and reshaping dream experiences, individuals may find relief from stressors and gain a sense of empowerment. Researchers continue to investigate the intricate relationship between stress, anxiety, lucid dreaming, and sleep paralysis to uncover more insights into how these factors intersect and influence each other.
Exploring the Subconscious in Both States
In both lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis, there is a unique opportunity to delve into the depths of the subconscious mind. When lucid dreaming, individuals have the ability to consciously explore their own thoughts, emotions, and memories within the dream state. They can embark on a journey of self-discovery, gaining insights into their deepest desires, fears, and unresolved issues. Lucid dreaming provides a platform for introspection and self-reflection, allowing individuals to confront and work through personal challenges. Similarly, during sleep paralysis, the mind is in a state between wakefulness and sleep, giving rise to vivid hallucinations and intense sensory experiences. These hallucinations are often influenced by one’s subconscious thoughts and emotions. Individuals may encounter symbolic representations of their fears, traumas, or unresolved psychological conflicts. This overlap between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis highlights the profound connection between the conscious and subconscious mind. By exploring the subconscious in both states, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of themselves and potentially resolve underlying psychological issues. It is an opportunity for personal growth, healing, and self-integration.
Possibility of Inducing Lucid Dreams during Sleep Paralysis
The phenomenon of sleep paralysis, characterized by a temporary inability to move or speak while transitioning between sleep and wakefulness, may offer a unique opportunity for inducing lucid dreams. During sleep paralysis, the mind remains fully awake while the body remains in a paralyzed state, creating a perfect environment for conscious dream exploration. Sleep paralysis can serve as a natural launchpad into lucid dreaming, as individuals can utilize their heightened awareness to transition from the paralyzed state into a lucid dream.
There are various techniques that one can employ to induce lucid dreams during sleep paralysis. One method is to maintain a calm and relaxed state of mind. By not succumbing to fear or panic during sleep paralysis, individuals can create the optimal mental environment for lucidity. Another technique is to visualize and imagine their desired dream scenario, effectively steering their consciousness towards a lucid dream. This process involves focusing on specific details, such as the sights, sounds, and sensations one wishes to experience.
The use of reality checks can be beneficial during sleep paralysis to confirm whether one is dreaming or awake. Reality checks involve testing the boundaries of the dream world, such as trying to float or pass through objects. If individuals find that these reality checks produce the expected results, they can confirm their lucid dreaming state and begin to actively engage with the dream environment.
It is important to note that attempting to induce lucid dreams during sleep paralysis may require practice and experimentation. Not every attempt will be successful, as the transition from sleep paralysis to lucid dreaming can be delicate and nuanced. However, with perseverance and a deep understanding of one’s own sleep patterns and experiences, it is possible to increase the likelihood of inducing lucid dreams during sleep paralysis.
As with any practice involving altered states of consciousness, it is vital to approach lucid dreaming during sleep paralysis with caution and prioritize one’s mental and emotional well-being. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, managing stress levels, and seeking guidance from experienced practitioners can contribute to a safe and fulfilling lucid dreaming experience.
The fascinating phenomenon of sleep paralysis can serve as a gateway to inducing lucid dreams. By leveraging the heightened awareness and the unique state of consciousness experienced during sleep paralysis, individuals can explore and engage with their dreams in a deeply conscious and intentional manner. With the right techniques and a respectful approach, the possibility of inducing lucid dreams during sleep paralysis can provide an extraordinary avenue for personal growth and self-discovery.
Practical Applications and Techniques
When it comes to practical applications and techniques for lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis, there are various approaches that individuals can explore. No repeating n-gramms! First and foremost, using lucid dreaming to overcome sleep paralysis can be an effective strategy. By realizing the dream state and gaining control, individuals can transform a potentially frightening experience into an opportunity for exploration and empowerment. Another approach is harnessing sleep paralysis for lucid dream induction. By remaining calm and mentally focused during sleep paralysis episodes, dreamers can transition directly into a lucid dream state. Additionally, the therapeutic potential of lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis in treating sleep disorders is being increasingly recognized. Techniques like relaxation exercises, meditation, and keeping a dream journal can all play a part in enhancing both lucid dreaming and sleep quality. No need for anchor in this part. By leveraging these practical applications and techniques, individuals can unlock new dimensions of consciousness and gain a deeper understanding of the dream world.
Using Lucid Dreaming to Overcome Sleep Paralysis
Lucid dreaming offers a potential avenue for individuals to address and overcome the unsettling experiences of sleep paralysis. While both lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis may share similarities in terms of altered states of consciousness, they can also provide a unique opportunity for intervention. When confronted with sleep paralysis, individuals can try to shift their focus towards the concept of lucid dreaming. By embracing the idea that they are in a dream-like state, they can harness their cognitive abilities to gain control over the experience.
During a sleep paralysis episode, it can be helpful to remind oneself that it is simply a dream, and that the sensations and hallucinations being experienced are not real or permanent. This understanding is critical in separating the fear and anxiety associated with sleep paralysis from the actual physical reality. With focused intention, individuals can try to engage in reality checks, such as attempting to move a body part or using breathing techniques to calm themselves. These techniques can signal to the brain that the individual is conscious and in control, potentially breaking free from the paralysis.
In the realm of lucid dreaming, dream control techniques, such as visualization and positive affirmations, can be employed to navigate the sleep paralysis experience. By actively visualizing a desired dream scene or engaging in positive self-talk, individuals can shift their focus away from the negative aspects of sleep paralysis and create a more favorable dream scenario. This approach can potentially transform the fear and distress of sleep paralysis into a more positive and empowering experience.
It is important to note that using lucid dreaming to overcome sleep paralysis may require practice and patience. Developing the skill of lucid dreaming and mastering dream control techniques takes time and dedication. However, for individuals who experience recurrent sleep paralysis episodes, the potential benefits of finding solace and empowerment through lucid dreaming can make the journey worthwhile.
In addition to using lucid dreaming as a tool to overcome sleep paralysis, it is essential to address any underlying factors that may contribute to the occurrence of sleep paralysis. This may involve implementing healthy sleep habits, reducing stress levels, and seeking professional guidance if sleep paralysis becomes a persistent issue.
Using lucid dreaming to overcome sleep paralysis offers a proactive approach to transform a distressing experience into a more positive and controllable one. By tapping into the power of lucid dreaming, individuals can take charge of their dream states and potentially mitigate the impact of sleep paralysis on their overall well-being.
Harnessing Sleep Paralysis for Lucid Dream Induction
Harnessing Sleep Paralysis for Lucid Dream Induction is a technique utilized by some experienced lucid dreamers to deliberately enter a lucid dreaming state. While sleep paralysis can be a frightening experience, some individuals have learned to embrace it as a gateway to lucid dreaming. During sleep paralysis, the body is temporarily immobilized, but the mind remains awake. This liminal state creates an opportunity to transition directly into a lucid dream.
One approach to harnessing sleep paralysis for lucid dream induction is to maintain a calm and relaxed mindset during the episode. Instead of fighting against the sensation of being unable to move, one can attempt to embrace it and let go of any fear or anxiety. By remaining calm, the mind can remain focused and clear, increasing the chances of transitioning into a lucid dreaming state.
Another technique is to visualize a desired dream scenario during the sleep paralysis episode. By mentally picturing oneself in a lucid dream and engaging the imagination, it becomes possible to enter the desired dream landscape. This visualization technique can help bridge the gap between the state of sleep paralysis and the fully immersive experience of a lucid dream.
It is important to note that attempting to induce lucid dreaming through sleep paralysis may not be suitable for everyone. It requires a thorough understanding of sleep paralysis and a willingness to explore these altered states of consciousness. It is always recommended to prioritize safety and well-being when experimenting with any sleep-related practices.
By harnessing sleep paralysis for lucid dream induction, individuals can transform what was once a potentially distressing experience into a doorway to extraordinary dream adventures. It offers an alternative method for entering lucid dreaming states and can be an exciting avenue for those interested in exploring the depths of their subconscious minds.
Therapeutic Potential for Sleep Disorders
The therapeutic potential of lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis extends beyond mere exploration and understanding of the mind. It has shown promise in assisting individuals who struggle with various sleep disorders. For those experiencing recurrent nightmares or night terrors, lucid dreaming can be utilized as a powerful tool to confront and overcome these distressing experiences. By becoming aware within the dream state, individuals can actively alter the course of their dreams, transforming nightmares into more positive and empowering scenarios. This process, known as lucid dream therapy, has proven to be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares, providing relief and improving overall sleep quality.
Individuals suffering from insomnia may also benefit from the therapeutic potential of lucid dreaming. By engaging in lucid dream exercises and techniques, individuals can explore and address the underlying causes of their sleep disturbances. Lucid dreaming allows them to delve into their subconscious, potentially unearthing unresolved psychological issues or traumas that contribute to their sleep difficulties. Through increased self-awareness and understanding, individuals can work towards resolving these issues, leading to improved sleep patterns and overall well-being.
Another intriguing application of lucid dreaming in sleep disorder therapy lies in its potential to address sleep-related phobias, such as sleep paralysis itself. With the ability to maintain lucidity during sleep paralysis episodes, individuals can change their perception of the experience, transforming it from a terrifying ordeal into a controlled and empowering encounter. By doing so, the fear and anxiety associated with sleep paralysis can be diminished, allowing individuals to approach future episodes with a greater sense of calm and control.
It is worth noting that while the therapeutic potential of lucid dreaming for sleep disorders is promising, it should be approached with caution. It is important to seek guidance from trained professionals experienced in dream therapy techniques. They can provide the necessary support and guidance to ensure the safe and effective use of lucid dreaming in addressing sleep disorders.
The therapeutic potential of lucid dreaming in treating sleep disorders like nightmares, insomnia, and sleep-related phobias holds great promise. By harnessing the power of conscious awareness within dreams, individuals can confront and overcome these sleep disturbances, leading to improved sleep quality, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the connection between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis is a complex and intriguing topic that continues to be studied by scientists and explored by dream enthusiasts. While both phenomena have distinct characteristics and experiences, there is a clear overlap between them. Lucid dreaming offers individuals the ability to become aware and control their dreams, while sleep paralysis can sometimes serve as a gateway to lucid dreaming. The scientific perspectives on this link suggest neurological and psychological explanations, highlighting the role of the REM stage in both phenomena. Furthermore, the mind-body connection plays a significant role, with stress, anxiety, and the exploration of the subconscious being key factors in both states. The practical applications and techniques discussed in this article showcase the potential therapeutic benefits of utilizing lucid dreaming to overcome sleep paralysis and harnessing sleep paralysis as a method to induce lucid dreams. Overall, the connection between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis offers a fascinating glimpse into the depths of human consciousness and the boundless capabilities of the mind during sleep. Whether you’re intrigued by the science behind it or seeking ways to enhance your dream experiences, understanding this connection can lead to exciting possibilities in the exploration of your own inner worlds.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of lucid dreaming?
Lucid dreaming holds great significance as it allows individuals to consciously explore and interact with their dreams. It offers opportunities for self-discovery, creativity, and personal growth.
Can anyone learn to lucid dream?
Yes, anyone can learn to lucid dream. With dedication, practice, and the use of various techniques such as reality checks and dream journals, individuals can increase their chances of having lucid dreams.
Are there any potential risks or drawbacks of lucid dreaming?
While lucid dreaming is generally considered safe, some individuals may experience sleep disturbances or find it difficult to differentiate between dreams and reality upon waking up. It’s important to maintain a healthy sleep schedule and seek professional guidance if needed.
What causes sleep paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is often caused by a disruption in the transition between sleep stages, specifically the rapid eye movement (REM) stage. It can be triggered by sleep deprivation, irregular sleep patterns, stress, and certain sleep disorders.
Can sleep paralysis be prevented?
Though it can be challenging to prevent sleep paralysis entirely, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, reducing stress levels, and practicing good sleep hygiene can help minimize the occurrence of sleep paralysis episodes.
What should I do if I experience sleep paralysis?
If you experience sleep paralysis, it’s important to stay calm and remind yourself that it’s a temporary and harmless condition. Focus on controlling your breathing and try to wiggle your fingers or toes to signal your body to fully awaken.
What are the common misconceptions about sleep paralysis?
Some common misconceptions about sleep paralysis include thinking it is a supernatural or paranormal phenomenon, or mistaking it for a medical emergency. Understanding the science behind sleep paralysis can help dispel these misconceptions.
Can lucid dreaming induce sleep paralysis?
While there is a close connection between lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis, it’s rare for lucid dreaming to directly induce sleep paralysis. However, maintaining a balance between lucid dreaming practices and promoting healthy sleep patterns can help prevent sleep paralysis episodes.
How can the mind and body be influenced during lucid dreams and sleep paralysis?
Both lucid dreams and sleep paralysis have the potential to influence the mind and body. In lucid dreams, individuals can actively control and shape their dream experiences, while sleep paralysis can elicit vivid hallucinations and sensations, leading to intense emotional reactions.
Are there therapeutic applications for lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis?
Yes, both lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis have shown potential therapeutic applications. Lucid dreaming can be utilized for psychological healing, self-exploration, and overcoming nightmares. Sleep paralysis, when understood and addressed, can provide insights into one’s fears and anxieties, leading to personal growth and improved well-being.