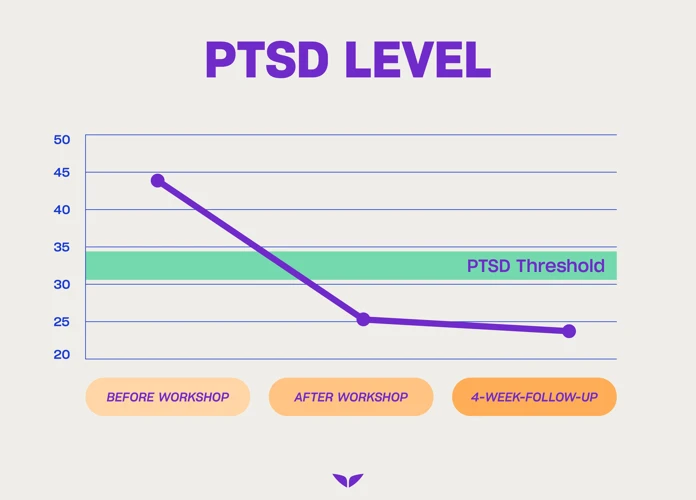
Have you ever wondered if dreams can have a profound impact on our emotional well-being? Specifically, can lucid dreaming serve as a tool for processing trauma and promoting healing? This article delves into the fascinating realm of dreaming and explores the potential link between lucid dreaming and emotional healing. We’ll examine the science behind dreams and trauma, introduce the concept of lucid dreaming, discuss its benefits and applications, and explore how it can help us process traumatic experiences. Additionally, we’ll share personal accounts of individuals who have successfully overcome trauma through lucid dreaming, as well as scientific studies that support this healing modality. Join us on this journey as we uncover the transformative potential of dreams in our emotional healing process.
The Science Behind Dreams and Trauma
The Science Behind Dreams and Trauma:
1. Understanding Dreams and Their Purpose: Dreams have fascinated humanity for centuries, prompting numerous theories and studies to unravel their mysteries. Scientists believe that dreaming serves several purposes, including memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and problem-solving. During sleep, our brains process memories and emotions, integrating them into our existing knowledge and experiences. This natural process aids in learning and psychological growth. Dreams often provide a symbolic representation of our thoughts, feelings, and desires, creating a rich inner world for exploration.
2. The Impact of Trauma on Dreams: Traumatic experiences can have a profound impact on our dreams. Individuals who have experienced trauma may frequently have distressing or vivid dreams related to their traumatic event. These dreams can be recurring and may cause sleep disturbances and anxiety. Additionally, trauma can affect the overall quality of sleep, leading to fragmented dreams and frequent awakenings. The emotional intensity of traumatic dreams reflects the deep emotional imprints left by the traumatic event, highlighting the need for effective healing methods.
Understanding the intricate relationship between dreams and trauma is crucial in exploring the potential of dreams, particularly lucid dreaming, in the healing process. Lucid dreaming, a state where individuals become aware that they are dreaming and can actively participate in and manipulate the dream, offers a unique opportunity for emotional healing and growth. By harnessing the power of lucid dreaming, individuals can actively engage with their dreams, allowing for profound self-exploration and processing of traumatic experiences. If you’re interested in learning more about different types of lucid dreams, including their potential role in overcoming nightmares and sleep disorders, you can check our informative article on ‘Understanding Types of Lucid Dreams‘.
1. Understanding Dreams and Their Purpose
Understanding Dreams and Their Purpose:
Dreams have long captivated the human imagination, and scientists have been unraveling their purpose and significance. One prevailing theory is that dreams serve as a mechanism for memory consolidation. During sleep, our brains process the events and information from the day, integrating them into existing neural networks to solidify memories. This process not only helps with memory recall but also aids in learning and problem-solving. Dreams also play a role in emotional regulation. They provide a safe space for us to process and release emotions, allowing us to explore complex feelings and experiences that we may be unable to consciously confront. Additionally, dreams can act as a form of problem-solving, as the brain continues to work on unresolved issues while we sleep. The mysterious nature of dreams and their ability to present symbolic imagery allows for deep exploration of our subconscious mind. Understanding the purpose of dreams provides a foundation for exploring how they can be utilized for emotional healing and personal growth. If you’re interested in learning more about the role of lucid dreaming in overcoming nightmares and sleep disorders, you can check our informative article on ‘The Role of Lucid Dreaming in Overcoming Nightmares and Sleep Disorders‘.
2. The Impact of Trauma on Dreams
2. The Impact of Trauma on Dreams:
– Distressing and Vivid Dreams: Traumatic experiences can leave a lasting impression on our subconscious mind, manifesting in our dreams. Many individuals who have gone through trauma often report experiencing distressing and vivid dreams related to their traumatic event. These dreams may contain intense emotions, graphic imagery, and a sense of reliving the traumatic experience. Such dreams can be emotionally challenging and contribute to problems with sleep and overall well-being.
– Recurring Themes and Symbols: Traumatic experiences can also give rise to recurring themes and symbols in dreams. These dreams may symbolically represent aspects of the traumatic event or emotions associated with it. For example, dreams of being chased, trapped, or attacked might symbolize a sense of powerlessness or vulnerability experienced during the trauma. These recurring patterns in dreams serve as a reflection of unresolved emotions and psychological distress.
– Sleep Disturbances and Anxiety: Trauma can significantly impact sleep quality, leading to sleep disturbances and heightened anxiety. Nightmares and intrusive thoughts related to the traumatic event can disrupt sleep, causing frequent awakenings and difficulty falling back asleep. This can result in sleep deprivation and further exacerbate emotional distress, creating a challenging cycle to break.
Understanding the impact of trauma on dreams is crucial in recognizing the role dreams play in processing and integrating traumatic experiences. Lucid dreaming, a state where individuals become aware that they are dreaming, offers a unique opportunity to actively engage with and reshape the content of dreams. For tips and techniques on inducing lucid dreaming to explore its potential benefits in the healing process, you can refer to our article on ‘Tips and Techniques to Induce Lucid Dreaming‘.
Lucid Dreaming: An Introduction

Lucid Dreaming: An Introduction:
1. What Is Lucid Dreaming? Lucid dreaming is a fascinating phenomenon where individuals become aware that they are dreaming while they are still in the dream state. This heightened awareness allows dreamers to have a sense of control and agency within their dreams. They can actively influence the dream’s narrative, manipulate the environment, and even interact with dream characters. Lucid dreaming can range from subtle moments of awareness to full lucidity, where the dreamer has complete knowledge of being in a dream state.
2. The Benefits and Applications of Lucid Dreaming: Lucid dreaming offers a wide array of benefits and applications beyond simple dream manipulation. For starters, it provides a platform for self-exploration and personal growth. By engaging in lucid dreams, individuals can delve into their subconscious, uncover deep-seated beliefs and desires, and gain valuable insights into their inner selves. Additionally, lucid dreaming can be a creative playground, allowing individuals to indulge in fantasy, artistic expression, and problem-solving. It can also serve as a source of inspiration, as ideas and solutions can be generated within the confines of a lucid dream. Lucid dreaming has shown promise in the fields of therapy and self-improvement, with its potential for overcoming nightmares, phobias, and even helping individuals practice and enhance real-life skills.
As we delve deeper into the realm of emotional healing, we’ll explore how lucid dreaming can be harnessed as a tool for processing trauma. Understanding the potential benefits and applications of lucid dreaming lays the foundation for utilizing this powerful tool in our healing journey. If you’re interested in learning some techniques for inducing lucid dreaming, check out our informative article on ‘Tips and Techniques to Induce Lucid Dreaming‘ for practical insights and methods to enhance your lucid dreaming experience.
1. What Is Lucid Dreaming?
What Is Lucid Dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is a remarkable phenomenon where individuals become aware that they are dreaming while still in the midst of the dream. In this state, the dreamer gains a level of consciousness and control over their dream experiences. They can actively recognize and navigate the dream world, essentially blurring the boundaries between reality and the dream realm. The term “lucid” refers to having clear awareness and perception. When someone is lucid dreaming, they are fully aware that they are in a dream state and can actively engage with the dream content, making decisions and influencing the dream’s direction.
During a lucid dream, the dreamer can harness their imagination and take on any role or scenario they desire. They may choose to fly, explore fantastical landscapes, interact with dream characters, or even delve deeper into their own subconscious mind. Lucid dreaming offers a unique and immersive experience, where individuals can tap into their creative abilities and explore the depths of their consciousness.
Lucid dreaming can occur spontaneously without any conscious effort, but it can also be induced through various techniques and practices. These techniques range from reality checks, where individuals question their waking state to determine if they are dreaming, to setting intentions before sleep or utilizing external stimuli such as light and sound to trigger lucidity. If you are interested in learning more about specific techniques for inducing lucid dreaming, you can refer to our comprehensive guide on ‘Tips and Techniques to Induce Lucid Dreaming‘. Lucid dreaming presents a world of possibilities for self-discovery, creativity, and personal growth.
2. The Benefits and Applications of Lucid Dreaming
2. The Benefits and Applications of Lucid Dreaming:
Lucid dreaming offers a myriad of benefits and applications that can positively impact our well-being. Here are some significant advantages of practicing lucid dreaming:
A. Emotional Healing and Trauma Processing: Lucid dreaming provides a unique platform for individuals to confront and process their traumatic experiences within the safety of the dream world. By actively engaging in the dream, individuals can alter the dream narrative, reframe negative emotions, and find resolution or closure. This process can lead to emotional healing and a reduction in trauma-related symptoms.
B. Creative Exploration and Problem Solving: Lucid dreaming allows for imaginative exploration and problem-solving. In the lucid state, individuals can consciously manipulate their dreams, opening doors to new possibilities and creative insights. This can be helpful for artists, writers, and individuals seeking solutions to personal or professional challenges.
C. Overcoming Nightmares and Sleep Disorders: Lucid dreaming can provide relief for individuals who suffer from frequent nightmares or sleep disorders. By becoming aware that they are dreaming, individuals can take control of their dreams, transforming frightening or disturbing scenarios into more positive experiences. Lucid dreaming techniques can help alleviate the anxiety and sleep disturbances associated with nightmares and disorders like insomnia.
D. Self-Reflection and Personal Growth: Lucid dreaming offers opportunities for profound self-reflection and personal growth. By engaging with the dream world, individuals can gain insights into their subconscious desires, beliefs, and fears. This self-awareness can lead to personal development, increased self-confidence, and a deeper understanding of oneself.
E. Enhancing Skills and Performance: Lucid dreaming has been used as a tool for enhancing skills and performance in various areas. Athletes can practice specific movements or scenarios in their lucid dreams, improving muscle memory and overall performance. Likewise, individuals who want to improve their public speaking, artistic abilities, or any other skill can use lucid dreaming as a platform for practice and experimentation.
The benefits and applications of lucid dreaming are vast and continue to be explored by both researchers and individuals interested in harnessing the power of dreams. To learn more about techniques for inducing lucid dreaming and maximizing its potential, check out our comprehensive guide on ‘Tips and Techniques to Induce Lucid Dreaming‘. Let’s dive deeper into the healing potential of lucid dreams in the next section.
Lucid Dreaming and Emotional Healing

Lucid Dreaming and Emotional Healing:
1. The Healing Potential of Lucid Dreams: Lucid dreaming holds immense potential for emotional healing. In a lucid dream state, individuals have the ability to confront and process their trauma within the safe confines of their dream world. By recognizing that they are dreaming, individuals can actively engage with and reshape their dreams, allowing for a sense of control and empowerment. This active participation creates an opportunity to confront and overcome fears, anxieties, and unresolved emotions related to the trauma. Additionally, lucid dreaming provides a safe space for individuals to practice new coping mechanisms and explore alternative resolutions, promoting emotional healing and resilience.
2. How Dreams Help Us Process Trauma: Dreams play a vital role in processing trauma by integrating and reorganizing fragmented memories and emotions. During sleep, the brain engages in memory reactivation and consolidation processes, where it selectively strengthens and weakens neural connections related to emotional experiences. This reorganization helps individuals make sense of their trauma, process intense emotions, and form coherent narratives. Lucid dreaming amplifies this natural process by enabling individuals to actively engage with their traumatic memories and emotions, facilitating their integration and resolution. Through lucid dreaming, individuals can gain insights, achieve emotional catharsis, and eventually find closure.
3. Techniques for Inducing Lucid Dreaming: While some individuals naturally experience lucid dreams, others may require specific techniques to induce and enhance lucidity. Reality checks, such as questioning whether you are dreaming throughout the day, create a habit that carries over into dreams, triggering lucidity. Another technique is maintaining a dream journal, where you record your dreams upon waking. This practice enhances dream recall and encourages self-awareness within dreams. Additionally, incorporating mindfulness and meditation into your daily routine can increase overall self-awareness, promoting lucidity in dreams. If you’re interested in learning more about techniques to induce lucid dreaming, you can refer to our informative article on ‘Tips and Techniques to Induce Lucid Dreaming‘.
Lucid dreaming presents a unique pathway to emotional healing, allowing individuals to actively engage with their dreams and facilitate the processing of trauma. In the next section, we’ll explore personal accounts of individuals who have successfully utilized lucid dreaming for overcoming trauma, as well as scientific studies that shed light on the therapeutic potential of this practice.
1. The Healing Potential of Lucid Dreams
1. The Healing Potential of Lucid Dreams:
Lucid dreaming holds tremendous potential for healing emotional wounds and promoting overall well-being. When individuals become aware that they are dreaming and can actively influence the dream content, they gain an opportunity to confront and address their traumas in a safe and controlled environment. This level of self-awareness within the dream state allows for a deeper exploration of the emotions and memories associated with the trauma.
During lucid dreams, individuals can engage in various therapeutic activities, such as visualization exercises, reimagining the traumatic event with a positive outcome, or confronting the source of their trauma from a place of empowerment. By actively participating in the dream scenario, individuals can rewrite the narrative surrounding their trauma, fostering feelings of resilience, control, and healing.
Lucid dreaming also offers a unique avenue for desensitization and emotional processing. Those suffering from phobias or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can use lucid dreaming as a platform to gradually expose themselves to their fears or triggers in a safe and controlled manner. This process allows for desensitization, reducing the emotional charge associated with these triggers in the waking world.
Lucid dreams can provide a sense of closure and resolution that may be elusive in waking life. By consciously engaging with the dream content, individuals can revisit unresolved emotions, address lingering questions or regrets, and find a sense of peace or acceptance. This transformative potential of lucid dreaming in emotional healing has garnered attention from psychologists and researchers.
It’s important to note that while lucid dreaming can be a powerful tool, it may not be suitable or effective for everyone. Those with severe trauma should approach lucid dreaming under the guidance of a trained therapist or expert in trauma therapy to ensure a safe and supportive healing process. Exploring the healing potential of lucid dreams can be a deeply personal and transformative journey, offering individuals a unique pathway to address and process their emotional wounds.
2. How Dreams Help Us Process Trauma
2. How Dreams Help Us Process Trauma:
Dreams play a significant role in processing and healing from trauma. Here are a few ways in which dreams aid in this transformative process:
a) Emotional Expression: Dreams provide a safe space for individuals to express and release intense emotions associated with trauma. During dreaming, the brain can construct scenarios that symbolically represent the emotional content of the traumatic event. This allows individuals to explore and confront their emotions in a controlled environment, facilitating emotional catharsis and reducing the emotional charge associated with the trauma.
b) Cognitive Reorganization: Dreams actively engage in cognitive reorganization, helping individuals make sense of their traumatic experiences. Through dream imagery, symbols, and narratives, the brain processes fragmented memories and constructs new associations, revealing different perspectives and insights. This cognitive reorganization can lead to a deeper understanding of the trauma, its impact, and potential pathways to healing.
c) Resolution and Integration: Dreams provide a natural platform for problem-solving and resolution. In the dream state, individuals may find creative solutions, resolutions, or alternative outcomes to traumatic events. This process can facilitate healing and promote a sense of closure, allowing individuals to move forward in their recovery journey.
d) Reestablishing Empowerment: Traumatic experiences can leave individuals feeling disempowered and helpless. Lucid dreaming can offer a sense of control and empowerment as individuals become active participants in their dreams. In a lucid dream, individuals can consciously navigate the dream environment, making choices and even rewriting the dream narrative. This sense of agency can be empowering and contribute to the healing process.
By actively engaging with dreams through lucid dreaming or simply reflecting on dream content, individuals can tap into the subconscious mind’s ability to process trauma. It’s important to note that while dreams offer a powerful avenue for healing, they are just one component of a comprehensive approach to trauma recovery. If you’re interested in learning techniques for inducing lucid dreaming and exploring its potential therapeutic applications, you can refer to our comprehensive guide on ‘Tips and Techniques to Induce Lucid Dreaming‘.
3. Techniques for Inducing Lucid Dreaming
3. Techniques for Inducing Lucid Dreaming:
Lucid dreaming can be a powerful tool for emotional healing and processing trauma. If you’re interested in exploring lucid dreaming further, there are several techniques you can try to increase your chances of having lucid dreams.
One technique is reality checks, which involve regularly questioning your waking state throughout the day. This helps train your mind to question reality, making it more likely to carry that habit into your dreams. Some common reality checks include looking at your hands and asking yourself if you’re dreaming, trying to push your finger through your palm, or looking at a clock or text and then looking away and back to see if it changes.
Another technique is keeping a dream journal. This involves writing down your dreams as soon as you wake up, ensuring that you capture as much detail as possible. By consistently recording your dreams, you’ll start to notice patterns and recurring themes, which can help trigger lucidity. Additionally, writing down your dreams cultivates a stronger connection to your dream world and improves dream recall.
Mnemonic induction of lucid dreams (MILD) is another popular technique. Before falling asleep, repeat a mantra to yourself, such as “I will have a lucid dream.” Visualize yourself becoming aware within a dream and imagine what you would do once you achieve lucidity. This technique helps program your subconscious mind to recognize when you’re dreaming, increasing the likelihood of having lucid dreams.
Other techniques include wake-back-to-bed (WBTB), where you set an alarm to wake up after a few hours of sleep and then go back to sleep while focused on lucid dreaming, and the use of supplements like galantamine or choline, which have been reported to increase the frequency and vividness of lucid dreams.
Remember, it can take time and practice to induce lucid dreaming consistently. Patience and persistence are key. If you’re interested in more tips and techniques for inducing lucid dreaming, you can check out our comprehensive guide on ‘Tips and Techniques to Induce Lucid Dreaming‘.
Personal Accounts and Research Studies

Personal Accounts and Research Studies:
1. Case Study: Overcoming Trauma Through Lucid Dreaming: One powerful example of the potential of lucid dreaming for emotional healing comes from a case study involving an individual who experienced severe trauma. This person actively engaged in lucid dreaming techniques as part of their therapeutic journey. Through lucid dreaming, they were able to confront and process their traumatic memories in a safe and controlled dream environment. By consciously facing their fears and emotions in the dream state, they gradually gained empowerment and a sense of control over their trauma. This case study highlights the transformative power of lucid dreaming as a tool for overcoming trauma and promoting emotional healing.
2. Scientific Studies on Lucid Dreaming and Trauma: The healing potential of lucid dreaming is not merely confined to personal anecdotes but is supported by scientific research as well. Studies have shown that practicing lucid dreaming techniques can lead to a reduction in nightmare frequency and intensity among individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Lucid dreaming allows individuals to actively change the dream narrative, providing an avenue for rewriting traumatic experiences and promoting psychological healing. Research also indicates that lucid dreaming enhances emotional regulation and helps individuals process distressing emotions related to trauma. These research findings consolidate the notion that lucid dreaming can be a valuable therapeutic tool for those seeking emotional healing.
Combining personal accounts and scientific studies strengthens our understanding of the potential of lucid dreaming for emotional healing. It offers validation to individuals who have experienced the transformative effects of lucid dreaming on their trauma recovery journey. The next section will provide practical tips for inducing lucid dreams and utilizing dream-related techniques for healing. If you’re interested in learning more about techniques to induce lucid dreaming, you can refer to our informative article on ‘Tips and Techniques to Induce Lucid Dreaming‘.
1. Case Study: Overcoming Trauma Through Lucid Dreaming
1. Case Study: Overcoming Trauma Through Lucid Dreaming:
One compelling case study showcasing the potential of lucid dreaming in overcoming trauma involved a woman named Emily. Emily had experienced a severe car accident that left her with deep emotional scars and recurring nightmares. Seeking a way to heal, she decided to explore lucid dreaming as a therapeutic tool.
Emily began practicing various techniques to induce lucid dreams, including reality checks, meditation, and visualization exercises before sleep. As she became more proficient in lucid dreaming, Emily started to confront her traumatic experiences within the dream state. With the awareness that she was dreaming, Emily gained a sense of control and empowerment that allowed her to navigate through her fears.
During a lucid dream, Emily confronted the vivid imagery associated with her car accident. Instead of feeling helpless, she actively reshaped the dream, recreating the scene with a positive outcome. By reliving the traumatic event in a safe dream environment, Emily was able to process her emotions and gradually reduce their intensity. With each lucid dream, she regained a sense of agency and gradually overcame the debilitating nightmares that had haunted her for years.
While this case study offers a powerful example of how lucid dreaming can aid in healing from trauma, it’s essential to note that individual results may vary. Lucid dreaming is a deeply personal experience, and it requires dedication, practice, and guidance to harness its full potential. However, the transformative possibilities it presents offer hope and a unique avenue for healing and growth for those struggling with trauma.
2. Scientific Studies on Lucid Dreaming and Trauma
2. Scientific Studies on Lucid Dreaming and Trauma:
Scientific research has begun to uncover the potential benefits of lucid dreaming in processing trauma and promoting emotional healing. Several studies have explored the connection between lucid dreaming and trauma, shedding light on its therapeutic applications:
– A study conducted by Zadra and colleagues in 2006 examined the use of lucid dreaming techniques in nightmare sufferers with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The participants underwent therapy focusing on lucid dreaming induction techniques, such as reality testing and visualization. The results showed a significant reduction in nightmare frequency and intensity, as well as improvements in overall sleep quality and PTSD symptoms.
– Another study by van den Bout and colleagues in 2010 investigated the impact of lucid dreaming therapy on individuals with chronic nightmares related to trauma. The participants received treatment involving lucid dreaming techniques, including guided imagery and rehearsal in lucid dreams. The findings revealed a decrease in nightmare frequency and distress, leading to improved sleep and a reduction in PTSD symptoms.
– A more recent study conducted by Malinowski and colleagues in 2017 explored the use of lucid dreaming in the treatment of recurrent nightmares in individuals with depression and anxiety disorders. The participants underwent cognitive behavioral therapy for nightmares combined with lucid dreaming techniques. The results showed a reduction in nightmare frequency, improved sleep quality, and a decrease in depression and anxiety symptoms.
These studies indicate that lucid dreaming can be a valuable therapeutic tool in addressing trauma-related nightmares and promoting emotional healing. By actively engaging with dreams, individuals can gain a sense of control and agency, allowing them to process and reshape their traumatic experiences. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind lucid dreaming’s therapeutic effects, these studies provide promising insights into its potential as an adjunctive treatment for trauma-related nightmares and emotional distress.
Tips for Lucid Dreaming and Emotional Healing
Tips for Lucid Dreaming and Emotional Healing:
1. Establishing a Dream Routine: Creating a consistent sleep schedule can enhance your ability to have lucid dreams. Aim for a regular bedtime and wake-up time, allowing for adequate sleep duration. Incorporating relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, before bed can promote a calm and receptive state of mind for lucid dreaming. By establishing a dream routine, you increase the likelihood of experiencing lucidity and emotional healing in your dreams.
2. Practicing Reality Checks and Dream Journaling: Reality checks are reality-testing exercises performed throughout the day to enhance self-awareness and the ability to recognize when you’re dreaming. Common reality checks include attempting to push a finger through your palm or checking the time multiple times. By regularly practicing these reality checks, you train your mind to question reality, increasing the chances of becoming lucid in a dream. Additionally, keeping a dream journal by your bedside and recording your dreams immediately upon waking helps strengthen dream recall and provides insights into recurring themes or symbols that may indicate unresolved emotional issues.
3. Utilizing Dream-Related Techniques for Healing: Lucid dreaming can be a powerful tool for emotional healing. Once you achieve lucidity in a dream, you can consciously work on resolving and processing trauma. Techniques such as visualization, inner dialogue, and emotional catharsis can be employed within the lucid dream state to confront and release deep-seated emotions associated with the traumatic event. Engaging in self-compassion and self-nurturing practices during lucid dreams can promote emotional healing and foster a sense of empowerment and resilience.
By incorporating these tips into your lucid dreaming practice, you can enhance your ability to engage with your dreams on a deeper level, facilitating emotional healing and growth. Remember, lucid dreaming is a skill that takes practice and patience, so be persistent in your efforts and allow yourself to explore the profound potential of your dream world.
1. Establishing a Dream Routine
1. Establishing a Dream Routine:
Creating a consistent dream routine is essential for maximizing the potential of lucid dreaming and emotional healing. Here are some key steps to incorporate into your dream routine:
a) Set a Regular Sleep Schedule: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule helps regulate your body’s internal clock and enhances the quality of your sleep. Aim for a consistent bedtime and wake-up time, even on weekends. This consistency promotes better dream recall and increases the likelihood of experiencing lucid dreams.
b) Create a Relaxing Bedtime Ritual: Establish a calming wind-down routine before bed to signal to your body and mind that it’s time to sleep. This can include activities like reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation. Avoid stimulating activities or electronic devices close to bedtime, as they can interfere with sleep.
c) Practice Reality Checks: Incorporate reality checks into your daily routine to enhance your self-awareness. Regularly question your reality by asking yourself if you are dreaming or awake. Perform simple reality checks, such as trying to push your finger through your palm or looking at a clock to see if the time changes unexpectedly. These reality checks can help you develop a habit of questioning reality, increasing the chances of becoming aware within your dreams.
d) Keep a Dream Journal: Keep a dream journal next to your bed and write down your dreams immediately upon waking up. Recording your dreams helps improve dream recall and allows you to identify recurring themes, symbols, or emotions. Pay attention to any patterns or connections between your dreams and your waking life. Reviewing your dream journal regularly can provide valuable insights into your subconscious mind and aid in emotional healing.
e) Affirmations and Visualizations: Before falling asleep, practice positive affirmations and visualizations related to lucid dreaming and emotional healing. Repeat affirmations such as “I am aware within my dreams” or “My dreams are a source of healing and growth.” Visualize yourself having vivid and lucid dreams, exploring them with confidence and gaining profound insights and emotional healing.
Remember that establishing a dream routine requires consistency and patience. It may take time for your mind and body to adapt to the new habits. However, with perseverance and dedication, you can create the optimal conditions for lucid dreaming and emotional healing.
2. Practicing Reality Checks and Dream Journaling
2. Practicing Reality Checks and Dream Journaling:
Engaging in reality checks and maintaining a dream journal are essential practices for enhancing lucid dreaming and promoting emotional healing. Reality checks involve regularly questioning your waking reality to determine whether you are dreaming or awake. By developing the habit of performing reality checks throughout the day, you increase your chances of carrying out these checks while dreaming. This can lead to a realization that you are in a dream and trigger lucidity.
Reality checks can take various forms, such as:
1. Hand Test – Observe your hands closely and question if they appear normal or distorted. In dreams, hands often appear strange or distorted, prompting lucidity.
2. Digital Watch Test – Glance at a digital watch or clock, look away, and then look back to see if the time has changed. In dreams, time tends to behave erratically, and the digits on the watch may change or blur.
3. Breathing Test – Pinch your nose and try to breathe through it. If you can breathe normally while pinching your nose, it indicates that you are in a dream. In reality, you wouldn’t be able to breathe with your nostrils blocked.
Dream journaling is another valuable practice. Keep a journal by your bedside and record your dreams immediately upon waking up. Write down as many details as possible, including emotions, sensations, and any significant events or symbols. Regularly recording your dreams helps improve dream recall and aids in identifying recurring themes or patterns. It also provides a valuable resource for exploring the emotional aspects of your dreams and tracking changes over time.
Consider using the following strategies to enhance dream journaling:
1. Consistency – Make it a habit to write in your dream journal every morning, even if you only remember fragments of a dream. The act of regularly engaging with your dreams strengthens the dream recall capacity.
2. Reflective Analysis – Take time to review and analyze your dream journal entries. Notice recurring symbols, emotions, or themes that may hint at unresolved trauma or emotional patterns requiring attention.
By practicing reality checks and maintaining a dream journal, you develop a deeper awareness of your dreams and increase the likelihood of experiencing lucid dreams. These techniques serve as invaluable tools for emotional healing, allowing you to actively engage with the dream space and process trauma within a safe and controlled environment.
3. Utilizing Dream-Related Techniques for Healing
3. Utilizing Dream-Related Techniques for Healing:
Dream-related techniques can be powerful tools for healing and processing trauma within the realm of lucid dreaming. These techniques allow individuals to actively engage with their dreams and harness their potential for emotional growth. Here are some effective strategies for utilizing dream-related techniques for healing:
a) Dream Rehearsal: In this technique, individuals consciously rehearse a dream scenario in which they confront and overcome traumatic experiences. By practicing this scenario in a lucid dream, individuals can reframe their traumatic memories and build confidence in their ability to cope with challenging situations. This technique not only empowers the dreamer but also facilitates a sense of resolution and healing.
b) Emotional Release: Lucid dreams can provide a safe space for emotional release. During a lucid dream, individuals can consciously process their emotions and release pent-up feelings associated with trauma. This process allows for emotional catharsis, providing a sense of relief and renewal. Keeping a dream journal to record and reflect upon the emotions experienced in lucid dreams can further support the healing process.
c) Imagery Rehearsal Therapy: This technique involves creating a new narrative or script for the traumatic dream. Individuals can rewrite the dream’s storyline, introducing positive outcomes, resolution, and healing. By rehearsing this new script in lucid dreams, the dreamer can gradually reshape their experience of the traumatic event, promoting a sense of empowerment and resilience.
d) Guided Visualization: Utilizing visualization techniques during lucid dreaming can be beneficial for emotional healing. By envisioning soothing and calming scenes, individuals can create a sense of safety and security within the dream. This practice helps to counteract the distressing aspects of traumatic dreams and promotes emotional healing and relaxation.
e) Integration and Reflection: After a lucid dream, taking the time to reflect on and integrate the dream experience is essential for healing. Engaging in introspection, journaling, or discussing the dream with a trusted individual can help process and make sense of the emotions, symbols, and themes encountered in the dream. This reflective process enhances self-awareness and facilitates the integration of healing insights into waking life.
By applying these dream-related techniques for healing, individuals can tap into the transformative power of lucid dreaming and promote emotional well-being. Remember, each person’s healing journey is unique, and it may take time and practice to develop proficiency in utilizing these techniques effectively.
Conclusion
Conclusion:
In conclusion, dreams have long been a subject of fascination and intrigue, and their potential for healing and emotional processing is gaining attention. The science behind dreams and trauma reveals that dreams serve valuable purposes, such as memory consolidation and emotional regulation. Trauma can significantly influence our dream experiences, leading to distressing and recurring dreams related to the traumatic event. However, lucid dreaming offers a promising avenue for emotional healing and growth. By becoming aware and active participants in their dreams, individuals can engage with and process their traumatic experiences in a safe and controlled environment.
Through personal accounts and scientific studies, it is evident that lucid dreaming can have a profound impact on individuals’ ability to overcome trauma. Techniques for inducing lucid dreaming, such as establishing a dream routine, practicing reality checks, and dream journaling, can enhance the likelihood of having lucid dreams. Utilizing dream-related techniques for healing, such as visualization and re-scripting, provides individuals with powerful tools for processing and integrating their traumatic experiences.
While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind the healing potential of lucid dreaming, the stories of individuals who have successfully utilized this practice to overcome trauma are inspiring. Lucid dreaming offers a unique opportunity to navigate the inner landscape of dreams and tap into the innate healing capacities of the mind.
Incorporating lucid dreaming into therapeutic approaches for trauma recovery holds great promise and can complement traditional therapeutic interventions. As scholars and researchers continue to explore the complex intersection between dreams, trauma, and healing, the transformative potential of lucid dreaming is being recognized and embraced.
In harnessing the power of our dreams, we unlock a realm of unconscious wisdom and healing that can help us navigate and process the challenges we face in life. Whether it’s processing trauma, overcoming nightmares, or simply gaining a deeper understanding of ourselves, dreams offer a gateway to self-discovery and emotional healing. So, let us embrace the world of dreams, explore the possibilities of lucid dreaming, and embark on a remarkable journey of self-discovery and transformation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can dreams really help us process trauma?
Yes, dreams can play a significant role in processing trauma. During sleep, our brains work to integrate and make sense of our experiences, including traumatic ones. Dreams provide a safe space for our minds to explore and express emotions linked to the trauma, ultimately assisting us in the healing process.
2. What is the difference between lucid dreaming and regular dreaming?
In regular dreaming, we are unaware that we are dreaming and typically experience the dream passively. In contrast, lucid dreaming involves becoming aware that we are dreaming while the dream is occurring. This awareness allows us to actively participate in and even control the dream’s content.
3. Are lucid dreams always positive and enjoyable?
No, lucid dreams can vary in nature just like regular dreams. While some lucid dreams can be positive and enjoyable, others may still carry emotional intensity, especially when processing trauma. Lucid dreaming provides an opportunity for self-exploration and growth, which can include confronting and working through challenging emotions.
4. Can anyone learn to have lucid dreams?
Yes, with practice and dedication, most individuals can learn to have lucid dreams. Various techniques and strategies, such as reality checks, dream journaling, and visualization exercises, can increase the likelihood of experiencing lucid dreams.
5. Is lucid dreaming a form of therapy?
While not a formal therapy in itself, lucid dreaming can be used as a complementary tool for emotional healing. It allows individuals to engage with and gain insights from their dreams, facilitating self-reflection and aiding in the processing of traumatic experiences.
6. Can lucid dreaming be used to overcome nightmares?
Yes, lucid dreaming can be an effective method for overcoming nightmares. By becoming lucid within a nightmare, individuals can actively change the dream’s narrative or confront the source of fear, transforming the experience into a more positive or manageable one.
7. Are there any risks associated with lucid dreaming?
For most people, lucid dreaming is a safe practice. However, it’s important to prioritize sleep hygiene and ensure a healthy sleep routine. It’s also essential to approach lucid dreaming with a balanced mindset and seek support from professionals if intense emotions arise during the dream process.
8. Can lucid dreaming replace traditional therapy for trauma?
No, lucid dreaming should not replace traditional therapy for trauma. While lucid dreaming can be a valuable tool, it is best used in conjunction with professional therapy to ensure comprehensive and long-lasting healing.
9. How long does it take to learn lucid dreaming?
The time it takes to learn lucid dreaming can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience lucid dreaming relatively quickly after practicing techniques, while others may require more time and patience. Consistency and persistence are key to developing the skill.
10. Can lucid dreaming have benefits beyond trauma processing?
Absolutely! Lucid dreaming has a wide range of potential benefits beyond trauma processing. It can be used for creative inspiration, personal growth, problem-solving, and enhancing self-awareness. It offers a unique and immersive experience that can be explored in various ways.