Imagine a time long ago when the night sky was still a vast and mysterious expanse. Ancient civilizations across the globe were captivated by the celestial wonders above and sought to understand their significance. It was during this era that the intertwined disciplines of astronomy and astrology were born. However, the relationship between these two fields is far from straightforward. While astronomy focuses on the scientific study of celestial objects and phenomena, astrology delves into the belief that these celestial bodies have an influence on human affairs and personalities. Within this article, we will explore the link between astronomy and astrology in ancient times, uncovering the shared knowledge, cultural exchange, and the fascinating tools and discoveries that shaped these disciplines. So, join us as we venture back in time to unravel the mysterious connection between the stars and the human experience.
The Birth of Astronomy and Astrology
Ancient civilizations’ fascination with the skies laid the foundation for the birth of astronomy and astrology. These intertwined disciplines emerged as a way for early civilizations to make sense of the celestial realm and its potential impact on human life. The Sumerians, Egyptians, and Babylonians were among the first civilizations to invest significant efforts in observing the heavens. They built sophisticated structures like ziggurats and pyramids to study celestial movements. The Egyptians, for example, developed a calendar based on the annual flooding of the Nile, which required tracking the stars and the Sun’s movements. Similarly, the Babylonians meticulously recorded celestial events and developed complex mathematical systems to interpret them. The Greeks, particularly during the Hellenistic period, took a more philosophical approach to astrology and astronomy, seeking to understand the cosmos and humanity’s place within it. Influential philosophers like Plato and Aristotle pondered the relationship between the celestial and terrestrial realms, laying the groundwork for the development of astrology. These early observations and beliefs formed the bedrock for the rich traditions and practices that continued to evolve throughout history. (Link: /cosmic-beliefs-ancient-egypt/)
Ancient Civilizations’ Observation of the Skies
Ancient civilizations across the globe recognized the importance of observing the skies and studying celestial phenomena. The Sumerians, who inhabited Mesopotamia around 3500 BCE, were among the first to develop a complex system of astronomy. They meticulously tracked the movements of heavenly bodies and created elaborate sky maps. The Egyptians, known for their advanced knowledge of astronomy, constructed impressive monuments aligned with astronomical events. The Great Pyramids of Giza, for example, align with certain stars in the Orion constellation. Meanwhile, the Mayans of Central America developed a highly sophisticated calendar system based on their observations of celestial objects, such as the Sun and Venus. The Greeks, particularly during the Hellenistic period, embraced astronomy as a scientific discipline. Influential figures like Thales of Miletus and Pythagoras laid the foundation for Greek astronomy, exploring concepts such as celestial motion and the Earth’s position in the universe. The observation of the skies by these ancient civilizations paved the way for significant advancements in our understanding of the cosmos. (Link: /unveiling-ancient-astronomical-practices/)
The Influence of Constellations on Astrology
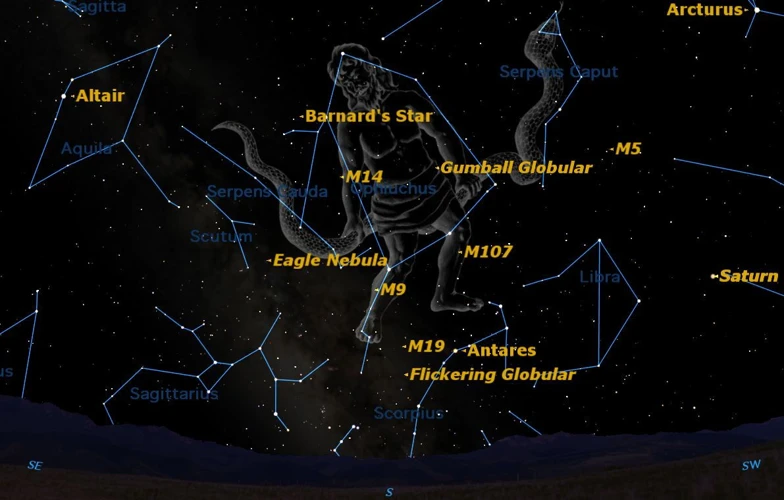
Constellations played a significant role in shaping astrological beliefs and practices. In ancient times, people observed patterns in the night sky and identified groups of stars that formed recognizable shapes or figures. These constellations became the foundation for astrological interpretations. Each constellation was associated with specific qualities and characteristics that were believed to influence individuals born under their celestial influence. For example, the constellation of Aries was associated with courage and assertiveness, while Taurus was linked to persistence and sensuality. As astrology developed, astrologers began to assign zodiac signs to specific constellations based on the Sun’s position during the time of a person’s birth. These zodiac signs became crucial in determining an individual’s personality traits and forecast their future. The influence of constellations on astrology further deepened during the Hellenistic period in ancient Greece, where philosophers like Aristotle and Plato delved into the symbolic meanings of celestial bodies and their relation to human existence. They believed that the alignment and movement of the planets and stars held profound significance for understanding human nature, destiny, and the interconnectedness of all things. This philosophical perspective continues to influence astrological practices today. (Link:/the-significance-of-astronomy-in-ancient-greek-philosophy/)
Astrology’s Role in Ancient Society
Astrology played a significant role in ancient society, permeating various aspects of daily life and shaping beliefs and practices. Ancient civilizations placed great importance on the alignment and positions of celestial bodies, believing that they held the key to understanding human behavior, destiny, and the course of events. Astrological beliefs were deeply intertwined with religion, politics, and personal decisions. People consulted astrologers for guidance on matters such as health, marriage, and agriculture. Kings and rulers often sought the advice of astrologers to determine the most auspicious times for battles or important decisions. Ancient societies also attributed personality traits and characteristics to different zodiac signs, which further influenced social dynamics and personal relationships. Temples dedicated to astrology were built, and astrological predictions and interpretations were inscribed on stone tablets and scrolls. Whether it was determining the right time to plant crops or choosing a suitable partner, astrology played a prominent role in shaping the beliefs and actions of individuals and communities in ancient times.
Astrological Beliefs and Practices
Astrology in ancient times was deeply rooted in the belief that celestial bodies and their positions at the time of a person’s birth influenced their traits, behaviors, and destiny. Astrologers believed that the movements of the planets and stars could provide insights into various aspects of life, including relationships, career paths, and health. Different civilizations developed their unique systems and practices. The Babylonians, for example, created intricate astrological charts known as horoscopes, which mapped out the positions of celestial objects at a specific moment in time and interpreted their significance. These horoscopes were often consulted for guidance and predictions. In ancient Egypt, astrology played a crucial role in the Pharaoh’s ruling and decision-making process. Priests believed that the pharaoh’s destiny was intertwined with the stars, and they used astrological knowledge to guide their actions. Astrological beliefs and practices varied across cultures and time periods, but the underlying concept of celestial influence on human life remained a central tenet. Understanding one’s astrological chart and consulting astrologers were integral to navigating life’s challenges and making informed decisions based on the interpretation of celestial alignments and their supposed impact on individual destinies.
Significance of Zodiac Signs in Astrology
The zodiac signs hold great significance in astrology, representing different personality traits and characteristics attributed to individuals based on their birth dates. There are 12 zodiac signs, each associated with a specific element (fire, earth, air, or water) and ruled by a corresponding celestial body. Aries, the first sign of the zodiac, is symbolized by the ram and is associated with qualities such as courage and assertiveness. Taurus, represented by the bull, is known for its stability and practicality. Gemini, symbolized by the twins, is characterized by curiosity and adaptability. Cancer, the crab, is associated with emotional sensitivity and nurturing tendencies. Leo, symbolized by the lion, is known for its creativity and leadership skills. Virgo, represented by the virgin, is detail-oriented and analytical. Libra, symbolized by the scales, is associated with balance and harmony. Scorpio, characterized by the scorpion, is intense and passionate. Sagittarius, represented by the archer, is known for its adventurous spirit and optimism. Capricorn, symbolized by the goat, is practical and ambitious. Aquarius, the water bearer, is associated with innovation and originality. Lastly, Pisces, represented by the fish, is known for its empathy and creativity. These zodiac signs serve as a way to categorize and interpret different aspects of an individual’s personality and life path, providing insights into compatibility, strengths, weaknesses, and life experiences. Whether one believes in the accuracy of astrology or not, the significance of zodiac signs in astrology is deeply ingrained in many cultures and continues to fascinate people around the world.
Astronomy and Astrology: Interconnected or Separated?

The relationship between astronomy and astrology in ancient times was complex and multifaceted. While they shared common roots in their study of the celestial realm, the two disciplines developed distinct focuses and methodologies. Astronomy, as a scientific pursuit, aimed to understand the movements and properties of celestial objects. Ancient astronomers meticulously observed and recorded celestial phenomena, allowing them to make predictions and track astronomical events. Their astronomical knowledge laid the groundwork for accurate calendars, navigation systems, and advancements in mathematics and physics. Astrology, on the other hand, delved into the belief that celestial bodies held influence over human affairs and personalities. Astrologers interpreted the positions and alignments of celestial bodies to make predictions about individual’s lives, relationships, and even political events. While astrology drew on astronomical observations, it also incorporated elements of mythology, symbolism, and divination. Despite their distinct approaches, there was undoubtedly a level of interconnectedness between astronomy and astrology. Ancient astronomers often acted as astrologers, using their astronomical knowledge to make astrological predictions. Additionally, the shared knowledge and cultural exchange between different ancient civilizations played a role in shaping both disciplines. Astronomy and astrology were intertwined in their early stages, and it was only during the Scientific Revolution that they began to separate and pursue distinct paths.
Shared Knowledge and Cultural Exchange
Shared knowledge and cultural exchange played a pivotal role in the development of astronomy and astrology in ancient times. As civilizations interacted and traded with one another, they also exchanged their astronomical and astrological practices, leading to the enrichment and cross-pollination of ideas. The ancient Greeks, for instance, absorbed and assimilated the astronomical knowledge of the Egyptians and Babylonians, adding their own philosophical interpretations. This exchange of knowledge resulted in the creation of significant astronomical texts, such as Ptolemy’s “Almagest,” which consolidated and synthesized the astronomical knowledge of the time. In India, the ancient Vedic texts integrated celestial observations into astrological practices, detailing the significance of planetary alignments and their influence on human life. Meanwhile, the Chinese developed their own unique system of astrology based on the observation of celestial phenomena and the zodiac animals. This exchange of ideas not only expanded the understanding of the cosmos but also enhanced astrological interpretations across cultures. It is through the collective knowledge and cultural exchange that ancient astronomers and astrologers were able to refine their practices and improve their understanding of the celestial world.
The Role of Ancient Astronomers and Astrologers
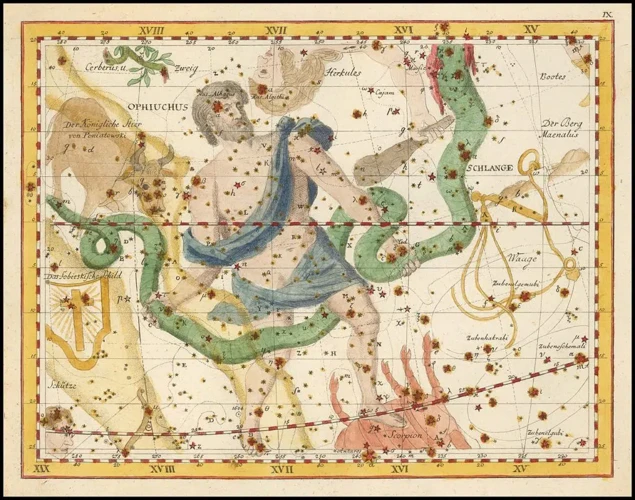
Ancient astronomers and astrologers played a crucial role in unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos and interpreting their significance for humanity. These esteemed individuals dedicated their lives to studying the skies, making observations, and drawing connections between celestial events and earthly affairs. In civilizations like ancient Greece, astronomers such as Hipparchus and Ptolemy made significant contributions to both fields. Hipparchus, often referred to as the “father of trigonometry,” meticulously cataloged the positions of over a thousand stars and developed a system to classify their brightness, known as magnitude. Ptolemy, on the other hand, built upon Hipparchus’s work and developed the geocentric model of the universe, which became the dominant cosmological theory of the time. He also penned the influential work known as the “Tetrabiblos,” which served as a cornerstone for astrology. Astrologers, like those in ancient Egyptian and Babylonian cultures, relied on these astronomical observations and calculations to create horoscopes and make predictions about various aspects of life, such as health, love, and success. These ancient astronomers and astrologers were highly respected figures, viewed as wise individuals with a deep understanding of the celestial realms and their impact on human existence. They passed down their knowledge through generations, leaving behind a valuable legacy that still fascinates and influences modern perceptions of the cosmos.
Tools Used by Ancient Astronomers and Astrologers
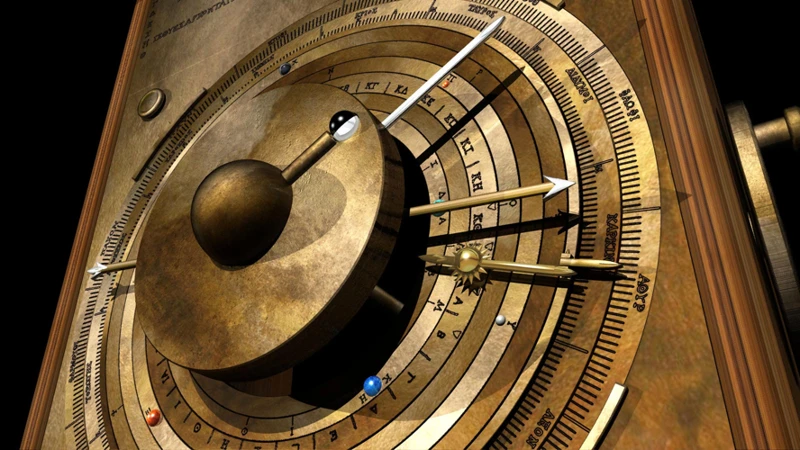

Ancient astronomers and astrologers employed a variety of tools to aid their observations and calculations. One crucial instrument used by these early scholars was the astrolabe, a handheld device that helped determine the positions of celestial objects. The astrolabe consisted of a rotating disk with marked coordinates and various pointers for measuring angles. It allowed astronomers to accurately determine the altitude and azimuth of celestial bodies. Another essential tool was the quadrant, which resembled a quarter of a circle. Astronomers used the quadrant to measure the altitude and coordinates of stars and planets. They would align one side of the quadrant with the horizon and use a plumb line to establish the correct position. Additionally, astronomers relied on observation towers and observatories to gain a higher vantage point for observing the night sky. These structures were strategically positioned to minimize obstructions and provided a clear view of the celestial objects. Alongside these instruments, ancient astrologers developed intricate charts and horoscopes to map the positions of planets and interpret their influences on individuals and events. These charts, often utilizing the zodiac system, allowed astrologers to make predictions and offer guidance based on celestial configurations. The tools and techniques employed by ancient astronomers and astrologers demonstrate their innovative thinking and dedication to unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos.
Observatories and Astronomical Instruments
Observatories and astronomical instruments played a crucial role in the advancement of ancient astronomy and astrology. These structures and tools were essential for precise celestial observations and helped ancient astronomers and astrologers make significant discoveries. One notable observatory was the observatory of Alexandria, constructed in the 3rd century BCE in Egypt. It featured instruments such as the armillary sphere, used to measure the positions of celestial bodies, and the astrolabe, a device for calculating the altitude of stars. In ancient Greece, the Antikythera mechanism was a groundbreaking mechanical device used for astronomical calculations, tracking celestial cycles and predicting astronomical events. Additionally, the Mayans in Mesoamerica built observatories, such as the Caracol in Chichen Itza, which had specifically designed windows and alignments for observing celestial phenomena. In China, the ancient astronomers developed instruments like the gnomon, used for measuring the angle and duration of sunlight, and the South Pointing Chariot, a mechanism that always indicated the south direction, aiding in accurate astronomical observations. These observatories and instruments demonstrate the ingenuity and dedication of ancient astronomers and their commitment to unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos.
Creation of Astrological Charts and Horoscopes
The creation of astrological charts and horoscopes was a fundamental aspect of astrology in ancient times. Astrologers believed that the positions and movements of celestial bodies at the time of a person’s birth could provide insights into their character, destiny, and even predict future events. To construct these charts, astrologers needed precise data about the positions of the planets, stars, and other celestial objects at specific moments. They used tools such as astrolabes and armillary spheres to measure the positions of heavenly bodies relative to the Earth. These measurements were then translated into symbolic representations, such as Zodiac signs and degrees, which were used to create the astrological charts. The charts were divided into twelve houses, each representing different aspects of life, such as love, career, and health. By interpreting the relationships between the planets, signs, and houses, astrologers could derive predictions and advice for individuals based on their unique birth charts. These intricate charts and horoscopes were meticulously crafted, requiring a deep understanding of astronomical principles and mathematical calculations. The creation of astrological charts and horoscopes represented the intersection of astronomy’s scientific observations and the mystical beliefs and practices of astrology.
Ancient Astronomical and Astrological Discoveries
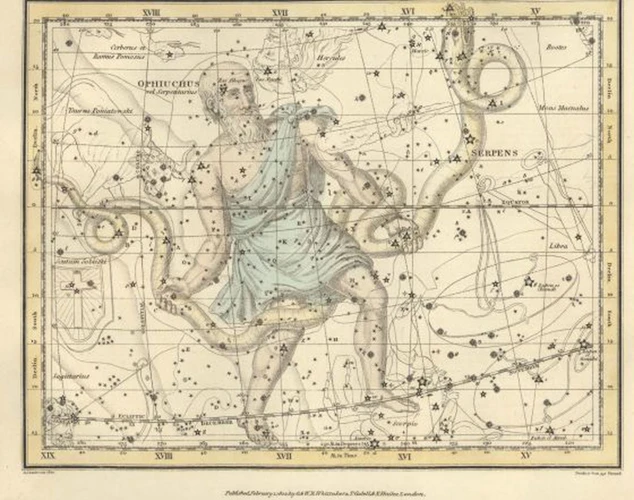
Ancient astronomers and astrologers made remarkable discoveries that shaped our understanding of the universe and its connection to human existence. One significant breakthrough was the unveiling of the precession of the equinoxes. This phenomenon, observed by ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians and Greeks, revealed that the Earth’s axis slowly shifts over time, resulting in a shift of the equinoxes along the ecliptic. This discovery had profound implications for astrology, as it necessitated adjustments to the zodiacal system that divided the sky into twelve equal signs. The Egyptians also made significant contributions to astrology, with their belief in the correlation between celestial events and earthly affairs. They developed a sophisticated system of cosmic beliefs that intertwined the movements of the stars, planets, and constellations with various aspects of life, including agriculture, politics, and the afterlife. Additionally, the ancient Greeks, particularly the astronomer and mathematician Ptolemy, advanced the geocentric model of the cosmos. According to this model, Earth was believed to be at the center of the universe, with celestial bodies orbiting around it. While this model was later disproved by the heliocentric model proposed by Copernicus, it still had a profound influence on astrology and continued to be widely accepted for centuries. The ancient astronomical and astrological discoveries made by these early civilizations laid the groundwork for future exploration and understanding of the cosmos, shaping both scientific and mystical interpretations of the heavens.
The Unveiling of the Precession of the Equinoxes
The unveiling of the precession of the equinoxes was a significant astronomical discovery in ancient times. This phenomenon refers to the gradual shifting of the Earth’s axis, causing the position of the vernal equinox to change slightly over time. The recognition of this celestial motion can be credited to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus in the 2nd century BCE. Through meticulous observations and calculations, Hipparchus noticed that the positions of the stars had shifted in relation to the equinoxes compared to earlier records. This realization challenged the prevailing belief that the stars were fixed in their positions. (1) Hipparchus’ groundbreaking work paved the way for a better understanding of the Earth’s motion and contributed to the development of future astronomical models. The discovery of the precession of the equinoxes also had implications for astrology as it meant that the zodiac constellations were not fixed in relation to the seasons as previously thought. (2) The precession added complexity to astrological interpretations and led to debates on the accurate interpretation of astrological charts. Although the discovery had significant implications, it took several centuries for the concept of precession to be fully understood and accepted by the wider astronomical and astrological communities.
Egyptian Contributions to Astrology
Egyptian civilization made significant contributions to the development of astrology. The ancient Egyptians had a deep connection with the celestial realm and believed that the movements of the stars and planets held great influence over human life. They developed a sophisticated system of astrology that incorporated both celestial observation and religious beliefs. One of the key contributions of the Egyptians was the development of the zodiac, which consisted of twelve astrological signs based on the twelve constellations that they observed along the ecliptic. Each sign was associated with different personality traits and characteristics, providing a framework for astrologers to interpret an individual’s destiny and personality. The Egyptians also believed that the position of the Sun, Moon, and planets at the time of a person’s birth could provide insights into their future and guide important life decisions. To aid in their astrological interpretations, the Egyptians developed intricate calendars and established observatories to accurately track celestial movements. Their knowledge and practices laid the foundation for astrological traditions that have endured to this day.
The Ptolemaic Model and Geocentrism
The Ptolemaic Model, developed by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the 2nd century CE, was a geocentric system that dominated astronomical thought for over a millennium. According to this model, the Earth was believed to be at the center of the universe, with the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars revolving around it in complex orbits. Ptolemy’s work, known as the “Almagest,” provided a comprehensive mathematical description of celestial motion based on observations and calculations. It accurately predicted the positions of celestial bodies and served as the basis for astrological calculations during ancient and medieval times.
One of the main features of the Ptolemaic Model was the use of epicycles, which were small circles within larger circles. These epicycles were used to explain the irregular motions of planets, as they seemed to speed up, slow down, and even reverse their paths across the sky. The model involved a complex system of deferents and epicycles for each planet, allowing astronomers to account for these apparent discrepancies in planetary motion.
Geocentrism, as proposed by the Ptolemaic Model, aligned with the prevailing religious and philosophical beliefs of the time. Many ancient cultures saw Earth as the center of the universe, with celestial bodies and phenomena believed to revolve around and influence human life and events. This geocentric view of the universe persisted until the 16th century when the heliocentric model proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus challenged it.
Despite the eventual rejection of geocentrism in favor of heliocentrism, the Ptolemaic Model played a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the cosmos. It laid the foundation for scientific advancements in astronomy and the development of more accurate models of celestial motion. Its influence can still be seen in the astronomical terminology we use today, and it serves as a reminder of the human quest to unravel the mysteries of the universe.
Decline and Resurgence of Astrological Practices
The decline of astrological practices began with the advent of the scientific revolution in the 16th century. During this time, advancements in astronomy and the rise of the scientific method led to a separation between the disciplines of astronomy and astrology. Astrology was regarded as unscientific and dismissed by many scholars. The development of heliocentric models, such as the Copernican model proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus, challenged the geocentric principles on which astrology was based. As scientific knowledge progressed, astrology lost its credibility in the eyes of the scientific community.
However, despite this decline, astrology experienced a resurgence in popularity during the 20th and 21st centuries. This resurgence can be attributed to various factors. Firstly, the influence of popular culture, especially through social media, has contributed to astrology becoming more accessible and widespread. Celebrities openly discussing their zodiac signs and astrological readings have further fueled interest in astrology.
Additionally, the desire for self-discovery and personal guidance has propelled the renewed interest in astrology. In a modern world that can feel disconnected and complex, individuals turn to astrology as a means of seeking meaning, understanding themselves, and finding guidance in various aspects of life, including relationships, career choices, and personal development.
The development of technology has played a crucial role in astrology’s resurgence. Online astrology platforms and mobile applications provide easy access to horoscopes, birth charts, and personalized readings. These digital tools have made astrology more convenient and appealing to the masses.
While astrology’s resurgence has brought it back into popular culture, it is important to note that the scientific community continues to view astrology as a pseudoscience. Despite the lack of empirical evidence, astrology continues to maintain a significant following and has become ingrained in modern society.
The decline of astrological practices during the scientific revolution was a turning point in the separation of astronomy and astrology. However, astrology has experienced a resurgence in recent years due to the influence of popular culture, the desire for self-discovery, and technological advancements. Whether seen as a sincere belief system or a form of entertainment, astrology continues to intrigue and captivate individuals worldwide.
The Scientific Revolution and the Separation of Astronomy and Astrology
The Scientific Revolution in the 16th and 17th centuries marked a significant turning point in the relationship between astronomy and astrology. During this period, advancements in scientific reasoning and empirical observation challenged the traditional beliefs and practices of astrology. Prominent thinkers such as Nicolaus Copernicus, Galileo Galilei, and Johannes Kepler revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos through their observations and mathematical calculations. Copernicus’s heliocentric model replaced the geocentric worldview, shifting the focus away from Earth as the center of the universe. Galileo’s telescopic observations provided evidence against traditional astrological beliefs, such as the geocentric arrangement of celestial bodies. Kepler’s laws of planetary motion further solidified the scientific understanding of celestial mechanics. These breakthroughs led to a growing divide between astronomy and astrology, with astronomy gaining recognition as a legitimate scientific discipline and astrology being dismissed as pseudoscience. As the Scientific Revolution progressed, astrology gradually lost its influence on mainstream scientific thought, giving way to a more empirical and evidence-based approach to studying the cosmos. (Link: /unveiling-ancient-astronomical-practices/)
Astrology’s Modern Adaptations and Popularity
Astrology, with its ancient roots, has continued to adapt and evolve in modern times, captivating the interest of people around the world. While the scientific revolution of the 17th century led to the separation of astronomy and astrology, astrology never ceased to exist. In fact, it has experienced a resurgence in popularity in recent decades. One reason for its revival is the accessibility provided by advancements in technology. Astrological predictions and horoscopes are now readily available online, allowing individuals to easily access personalized readings based on their birth details. Social media platforms have also played a significant role in spreading astrological content, with countless astrology-related accounts and influencers sharing daily insights and interpretations.
Astrology has adapted to contemporary interests and concerns. Modern astrology has incorporated psychological and self-help elements, intertwining personality traits and life guidance. It has become a tool for self-reflection, personal growth, and understanding relationships. Additionally, the emphasis on spirituality in today’s society has contributed to astrology’s increased popularity, as people seek a sense of meaning and guidance beyond scientific explanations.
Although astrology is not considered a science, its enduring popularity suggests that it fulfills a human need for connection, meaning, and self-discovery. Whether individuals wholeheartedly believe in the power of the stars or view astrology as a source of entertainment, its modern adaptations and widespread popularity continue to shape and influence many lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the link between astronomy and astrology in ancient times is a fascinating and complex subject. While astronomy focused on the scientific study of celestial objects and their motions, astrology delved into the belief that these celestial bodies influenced human affairs and personalities. Ancient civilizations across the world observed the skies, developing sophisticated tools and techniques to track and interpret celestial phenomena. The exchange of knowledge among different cultures played a crucial role in the development of both disciplines. However, as scientific advancements and the age of reason emerged, astronomy and astrology gradually diverged. The scientific revolution brought about a clear separation between the two, prioritizing empirical evidence over astrological beliefs. Despite this separation, astrology continues to have a significant influence in contemporary society, with modern adaptations and interpretations. Today, astrology remains a popular practice for many, providing insights and guidance into personal and collective experiences. The ancient roots of astronomy and astrology remind us of our enduring fascination with the cosmos and our ongoing quest to understand our place within it.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How did ancient civilizations observe and study the skies?
Ancient civilizations observed the skies through naked-eye observations, without the aid of telescopes. They built structures like ziggurats, pyramids, and stone circles to track celestial movements and used their observations to develop calendars and predict seasonal events.
2. Were ancient astronomers aware of the connection between celestial bodies and human life?
Ancient astronomers believed in the connection between celestial bodies and human life. Astrology, a practice closely associated with astronomy, suggested that the positions and movements of celestial bodies could influence personalities, events, and human affairs.
3. What was the role of astrology in ancient society?
Astrology played a significant role in ancient society. It was used to offer guidance on personal matters, predict future events, aid in decision-making, and even determine favorable times for significant actions such as marriage or starting a venture.
4. How did ancient astronomers and astrologers share knowledge?
Ancient astronomers and astrologers shared knowledge through cultural exchange, trading of astronomical observations, and the spread of ideas through ancient trade routes. Scholars from different civilizations would meet, exchanging knowledge and contributing to the advancement of these fields.
5. What tools did ancient astronomers use to study the skies?
Ancient astronomers used various tools, such as astrolabes, armillary spheres, and celestial globes, to measure and track celestial bodies’ positions. They also developed observational techniques and mathematical calculations to make precise observations and predictions.
6. How were astrological charts and horoscopes created in ancient times?
Astrologers in ancient times created astrological charts and horoscopes by mapping the positions of celestial bodies at the time of an individual’s birth. These charts were then interpreted to provide insights into the person’s personality traits, future events, and potential challenges they may encounter.
7. What was the significance of zodiac signs in ancient astrology?
Zodiac signs played a vital role in ancient astrology. These signs represent specific constellations that the Sun passes through over the course of a year. Each zodiac sign was associated with certain characteristics and traits that were believed to influence individuals born under them.
8. What astronomical discoveries impacted ancient astrology?
The unveiling of the precession of the equinoxes, a gradual shift in the Earth’s axis, had a profound impact on ancient astrology. It led to changes in the zodiac system and influenced the interpretation of astrological charts and predictions.
9. How did the scientific revolution separate astronomy and astrology?
The scientific revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries brought forth a new era of scientific inquiry. During this time, astronomy began to focus purely on the scientific study of celestial objects and phenomena, moving away from the belief-based practices of astrology.
10. Is astrology still popular and relevant today?
Astrology has remained popular and relevant to this day. While it may not be universally accepted within the scientific community, many individuals still consult astrologers and find value in the insights astrology provides through horoscopes, personality assessments, and guidance on various aspects of life.








