Have you ever experienced a nightmare after a particularly stressful day? It’s a perplexing phenomenon. In this article, we will delve deep into the connection between stress and nightmares, exploring the science behind stress, different types of nightmares, and the underlying mechanisms that link the two. We will also discuss the effects of stress on dream quality and provide practical techniques for managing stress-related nightmares. So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready for a fascinating journey into the realm of dreams and stress.
The Science Behind Stress
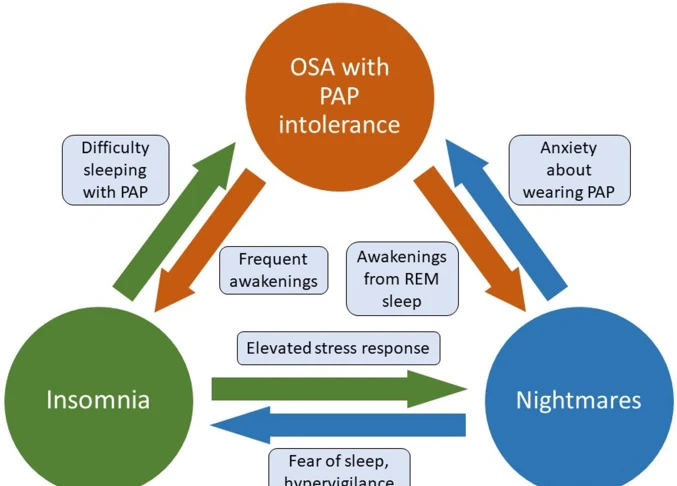
Stress is a complex biological and psychological response to challenging situations. When we encounter stressors, our body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol, as part of the fight-or-flight response. This physiological process prepares us to cope with immediate threats by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and alertness. Chronic stress, however, can have detrimental effects on our physical and mental well-being. The persistent activation of the stress response can lead to various health issues, including anxiety, depression, cardiovascular problems, and sleep disturbances like insomnia. In fact, research has shown a strong link between stress and sleep disorders, including nightmares. Stress can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and negatively impact the quality of our dreams. Understanding the science behind stress is crucial in investigating its connection to nightmares. By exploring the intricate mechanisms of stress, we can gain insights into how it influences our dream patterns and ultimately affects our overall sleep health.
To learn more about the impact of trauma on nightmares, click here. If you’re interested in the connection between medication and nightmares, you can find more information here.
Types of Nightmares

Nightmares can take on various forms and are often categorized based on their underlying causes. Some common types of nightmares include anxiety-related nightmares, trauma-induced nightmares, and stress-related nightmares. Anxiety-related nightmares are often linked to underlying anxiety disorders or high levels of stress. These nightmares are characterized by themes of helplessness, fear, and intense emotions. Trauma-induced nightmares, on the other hand, occur as a result of past traumatic experiences, such as abuse or accidents. These nightmares often involve vivid re-experiences of the traumatic event and can contribute to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Lastly, stress-related nightmares are specifically influenced by high levels of stress and can feature themes related to work, relationships, or personal fears. Understanding the different types of nightmares is crucial in addressing and managing their underlying causes. To learn more about sleep disorders and nightmares, you can visit here.
1. Anxiety-Related Nightmares
Anxiety-related nightmares are a specific type of nightmare that commonly occurs in individuals who struggle with anxiety disorders. These nightmares are characterized by vivid and distressing dreams that often center around themes of fear, danger, and insecurity. People experiencing anxiety-related nightmares may find themselves being chased, attacked, or trapped in dangerous situations within their dreams. These nightmares can be so vivid and intense that they often lead to feelings of panic and terror upon waking up.
The content of anxiety-related nightmares is closely tied to the individual’s underlying anxieties and fears. For example, someone with a fear of public speaking may have nightmares about embarrassing themselves in front of a large audience. Similarly, someone with social anxiety may frequently have nightmares about being judged or humiliated in social settings.
It’s important to note that anxiety-related nightmares can also be a result of other stressors in a person’s life, not just an anxiety disorder. High levels of daily stress, traumatic experiences, or significant life changes can also trigger these types of nightmares.
Managing anxiety-related nightmares typically involves addressing the underlying anxiety or stress. Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be effective in helping individuals identify and challenge the negative thought patterns and anxieties that contribute to their nightmares. Stress reduction techniques, such as relaxation exercises, mindfulness, and deep breathing, can also help alleviate anxiety and minimize the occurrence of these distressing dreams.
In addition to seeking professional help, individuals experiencing anxiety-related nightmares can also benefit from practicing good sleep hygiene. This includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a calming bedtime routine, and creating a sleep-friendly environment in the bedroom.
Anxiety-related nightmares are a manifestation of the anxiety and stress that individuals experience in their waking lives. By addressing and managing these underlying anxieties, it is possible to reduce the frequency and intensity of these distressing dreams, promoting a better night’s sleep and improved overall well-being.
2. Trauma-Induced Nightmares
Trauma-induced nightmares are a specific type of nightmare that occurs as a result of experiencing a traumatic event. Trauma can leave a lasting impact on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being, often manifesting in the form of vivid and distressing dreams. These nightmares are characterized by re-experiencing the traumatic event during sleep, which can be highly distressing and disruptive to sleep quality.
1. Content of Trauma-Induced Nightmares: The content of trauma-induced nightmares often reflects the traumatic event itself or elements associated with it. These nightmares can closely mirror the details of the trauma, causing the individual to relive the terrifying experience. They may involve intense emotions, graphic imagery, and a feeling of being trapped or powerless. The nightmare content can vary depending on the nature of the trauma, but it typically evokes fear, helplessness, and a sense of danger.
2. Psychological Impact: Trauma-induced nightmares can have a profound psychological impact on individuals. The recurrence of these nightmares can contribute to the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or exacerbate existing PTSD symptoms. Nightmares can serve as triggers, causing individuals to experience heightened anxiety, fear, and distress, even during waking hours. The emotional toll of trauma-induced nightmares can result in sleep disturbances, daytime fatigue, and difficulty functioning in daily life.
3. Treatment Approaches: Addressing trauma-induced nightmares often requires a comprehensive treatment approach. Therapeutic interventions such as trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT), Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), and exposure therapy have shown promising results in reducing the frequency and intensity of trauma-related nightmares. These approaches aim to help individuals process and heal from the trauma, ultimately reducing the impact on their sleep and overall well-being. Additionally, medication management may be considered in some cases, particularly if nightmares significantly interfere with daily functioning or pose mental health risks.
Understanding the unique characteristics and impact of trauma-induced nightmares is vital in providing appropriate support and interventions for individuals who have experienced trauma. These nightmares should be approached with sensitivity and a comprehensive perspective that recognizes the interconnectedness of trauma, sleep, and mental health.
3. Stress-Related Nightmares
Stress-related nightmares are a specific type of nightmares that occur as a result of heightened stress levels. These nightmares can be vivid, intense, and often disturbing, causing anxiety and distress upon awakening. Here are some key characteristics of stress-related nightmares:
1. Themes: Stress-related nightmares often revolve around themes that reflect the individual’s sources of stress. Common themes may include being chased, being trapped, failing in academic or professional endeavors, or experiencing conflicts in relationships.
2. Emotional Intensity: These nightmares are typically accompanied by strong emotions such as fear, anger, sadness, or helplessness. The emotional intensity may be so overwhelming that it can impact the individual’s ability to fall back asleep or lead to prolonged feelings of unease after waking up.
3. Recurrent Nature: Stress-related nightmares tend to recur over a period of time, especially during periods of heightened stress. The frequency of these nightmares may vary from person to person, but they often occur more frequently than typical dreams.
4. Physical Manifestations: When experiencing a stress-related nightmare, individuals may exhibit physical manifestations such as increased heart rate, sweating, or even sleep disturbances like thrashing or talking in sleep. These physical reactions are indicative of the body’s heightened stress response during the nightmare.
5. Cognitive Associations: Stress-related nightmares may also be associated with cognitive processes such as rumination, worry, or preoccupation with stressful events or situations. These cognitive factors can contribute to the intensity and persistence of stress-related nightmares.
It is important to note that while stress-related nightmares can be distressing, they can also serve as a reflection of the subconscious mind processing and attempting to cope with stressors in waking life. Recognizing and understanding the characteristics of stress-related nightmares can be a crucial step in effectively addressing and managing them.
Understanding the Link

To understand the link between stress and nightmares, we must explore the psychological and neurological factors at play. Psychologically, stress and nightmares are often interconnected through various associations. For example, individuals who experience high levels of stress may have a greater tendency to ruminate on negative thoughts and emotions, which can manifest in their dreams. Neurologically, stress can impact the brain regions involved in emotion regulation and sleep-wake cycles, leading to an increased likelihood of nightmares. Additionally, disrupted sleep patterns resulting from stress can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. Understanding the link between stress and nightmares requires a comprehensive examination of the psychological and neurological processes involved, highlighting the intricate relationship between our emotions, thoughts, and dream experiences.
1. Psychological Associations
1. Psychological Associations: The link between stress and nightmares is multifaceted, with several psychological mechanisms playing a role. One psychological association is the impact of negative emotions on dream content. When experiencing stress, negative emotions such as anxiety, fear, and sadness are heightened. These emotions can carry over into our dreams, manifesting as distressing and intense nightmares. Additionally, stress can lead to an increase in cognitive arousal, making our minds more active during sleep. This heightened mental activity can contribute to the occurrence of vivid and emotionally charged nightmares.
Another psychological association is the role of cognitive processes in shaping nightmare content. Stress can impact our thoughts and beliefs, leading to negative cognitive patterns such as rumination or catastrophic thinking. These cognitive processes can influence the themes and motifs that appear in our nightmares. For example, someone experiencing work-related stress may have nightmares about failure or being overwhelmed with tasks. The content of nightmares can reflect our subconscious worries, anxieties, and unresolved issues, highlighting the intricate relationship between stress and dream content.
Lastly, stress can disrupt our overall emotional regulation, making it challenging to process and cope with difficult emotions effectively. Nightmares can act as a mechanism for emotional release and processing. They provide an outlet for our unconscious mind to express and process intense emotions associated with stress. By exploring the psychological associations between stress and nightmares, we can gain a deeper understanding of how our emotional and cognitive states influence our dream experiences.
2. Neurological Impact
The neurological impact of stress on nightmares is a fascinating area of research. Stress can disrupt the normal functioning of the brain, particularly the regions responsible for emotion regulation and sleep-wake cycles. When we experience stress, the amygdala, which is involved in processing emotions, becomes hyperactive. This hyperactivity can lead to an increase in negative emotions and anxiety, which can subsequently intensify the content of our dreams, including nightmares. The prefrontal cortex, responsible for logical thinking and decision-making, may also be affected by stress. This can impair our ability to distinguish between dream and reality, causing nightmares to feel more vivid and immersive.
In addition to these effects, stress can disrupt the release of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, which play a crucial role in regulating mood and sleep. An imbalance in these neurotransmitters can contribute to the development of sleep disorders, including nightmares. Chronic stress can alter the brain’s reward system, leading to an increased sensitivity to negative experiences and, consequently, a higher likelihood of distressing dream content.
Understanding the neurological impact of stress on nightmares provides valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of this connection. By exploring how stress affects the brain and its various functions, researchers can develop targeted interventions and treatments to alleviate the frequency and intensity of stress-related nightmares.
3. Emotion Regulation
Emotion regulation plays a crucial role in the connection between stress and nightmares. When we experience stress, our ability to regulate our emotions can be impaired. This can result in heightened emotional reactivity and difficulty in managing distressing thoughts and feelings. Stressful events and emotions can carry over into our dream state, leading to the manifestation of nightmares.
One way in which emotion regulation impacts nightmares is through the relationship between stress and anxiety. Anxiety-related nightmares are common among individuals who struggle with excessive worry and nervousness. These nightmares often reflect the fears and concerns experienced during wakefulness. The inability to effectively regulate anxiety during the day can carry over into the sleep state, contributing to the occurrence of anxiety-related nightmares.
Another aspect of emotion regulation relevant to nightmares is post-traumatic stress. Trauma-induced nightmares are a hallmark symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Individuals who have experienced traumatic events often struggle with regulating the emotions associated with their trauma. This emotional dysregulation can intensify during sleep, leading to vivid and distressing nightmares that reenact elements of the traumatic event.
Additionally, stress-related nightmares can be influenced by negative mood states. Chronic stress can contribute to the development and maintenance of negative mood states, such as depression. These negative mood states can increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Depressed individuals may find it challenging to regulate their emotions, which can result in the generation of dream content that reflects their emotional difficulties.
Emotion regulation plays a significant role in the relationship between stress and nightmares. Difficulties in regulating anxiety, post-traumatic stress, and negative mood states can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. Understanding the mechanisms of emotion regulation can provide insights into how stress impacts dream content and the emotional experiences during sleep.
Effects of Stress on Dream Quality
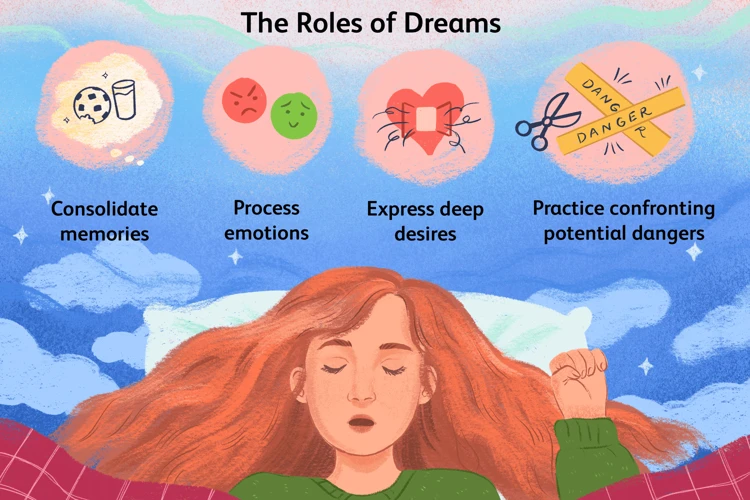
Stress has a profound impact on the quality of our dreams. Firstly, it often leads to an increase in nightmare frequency. As our bodies and minds are overwhelmed by stress, our subconscious may manifest these anxieties in the form of disturbing and vivid nightmares. Additionally, stress intensifies the content of our nightmares. The themes and events within these dreams may become more distressing and emotionally charged, causing heightened feelings of fear, helplessness, or even trauma. Lastly, stress disrupts our sleep patterns, which further exacerbates the negative effects on dream quality. When we are stressed, we may experience difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings throughout the night, or overall restless sleep. This fragmented sleep can limit the amount of time we spend in the REM (rapid eye movement) stage, when dreaming occurs, leading to a reduction in dream recall and potentially impacting the processing of emotional experiences during sleep. Thus, the effects of stress on dream quality are multi-faceted and can significantly impact our overall well-being.
1. Increased Nightmare Frequency
Increased nightmare frequency is a common consequence of stress. When we are under significant stress, our minds become more active during sleep, leading to heightened dream activity. This increased mental arousal can result in an uptick in nightmare frequency. Stress can cause our brains to produce more intense and vivid dreams, often filled with elements of fear, danger, or distress. These nightmares can be so vivid and realistic that they leave us feeling anxious and unsettled upon waking up. The exact reasons behind this increase in nightmare frequency during times of stress are not well understood, but it is believed to be related to the impact of stress on the brain’s emotional regulation and sleep patterns. Additionally, stress can interrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to fragmented and disrupted sleep, which further contributes to the occurrence of nightmares. Individuals experiencing heightened stress levels should not be surprised if they find themselves encountering an increased frequency of distressing nightmares.
2. Intensified Nightmares
Intensified nightmares are a common occurrence in individuals experiencing high levels of stress. These nightmares are characterized by vivid, intense, and emotionally charged dream content. During times of stress, the brain’s amygdala, responsible for processing emotions and fear responses, becomes hyperactive. This heightened activity can lead to the creation of more vivid and distressing dream scenarios.
In intensified nightmares, individuals may experience a wide range of intense emotions, such as fear, anxiety, and helplessness. The dream imagery may involve frightening or threatening situations, such as being chased, attacked, or trapped. These intense emotions and distressing scenarios can often lead to the individual waking up feeling fearful, startled, and emotionally drained.
It is important to note that intensified nightmares are not limited to specific themes and can vary greatly from person to person. For some individuals, stress-induced nightmares may involve reliving past traumas, while for others, they may revolve around everyday stressors or fears.
Intensified nightmares can have a significant impact on sleep quality and overall well-being. The heightened emotional arousal and intense dream experiences can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to sleep fragmentation and decreased sleep efficiency. Consequently, individuals may wake up feeling tired, anxious, and irritable, which can further exacerbate the effects of stress on their daily functioning.
To cope with intensified nightmares, it is crucial to address the underlying stress and find strategies to reduce its impact. Techniques like relaxation exercises, mindfulness meditation, and keeping a dream journal can help individuals manage stress levels and potentially alleviate the intensity of nightmares. Consulting with a healthcare professional or therapist who specializes in sleep disorders and trauma can also provide valuable guidance and support in managing intensified nightmares effectively.
3. Disturbed Sleep Patterns
Disturbed sleep patterns are a common consequence of stress-related nightmares. When we experience nightmares, especially those induced by stress, our sleep can be frequently disrupted throughout the night. The content and intensity of these nightmares can be so vivid and unsettling that they jolt us awake, leaving us feeling anxious, fearful, and unable to fall back asleep easily. This repetitive cycle of nightmares and sleep disturbances can have a significant impact on the overall quality of our sleep. As a result, we may wake up feeling tired, groggy, and irritable, which can further contribute to daytime fatigue and reduced cognitive function. The lack of restorative sleep can have negative effects on our physical and mental well-being, leading to decreased productivity and overall quality of life. To break this cycle of disturbed sleep patterns caused by stress-related nightmares, it is essential to address the underlying stressors and implement effective stress management techniques. By reducing stress and promoting relaxation before bedtime, we can improve our sleep quality and minimize the occurrence of nightmares, allowing for a more restful and rejuvenating sleep experience.
Managing Stress-Related Nightmares
Managing stress-related nightmares is crucial to improve the quality of sleep and overall well-being. There are various effective strategies that can help individuals cope with these distressing dreams. Firstly, stress reduction techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga can help reduce overall stress levels and promote relaxation. These techniques can be practiced before bedtime to create a calm and peaceful state of mind. Additionally, maintaining good sleep hygiene practices such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine and electronic devices before bed can contribute to better sleep quality and reduce the occurrence of nightmares. Finally, therapy and cognitive techniques, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help individuals address underlying stressors and learn effective coping mechanisms to manage stress and anxiety. Seeking professional help from therapists or sleep specialists can provide valuable guidance and support in managing stress-related nightmares. By implementing these strategies, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving a more restful and nightmare-free sleep.
1. Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress reduction techniques play a vital role in managing stress-related nightmares and promoting overall well-being. There are various strategies that individuals can incorporate into their daily lives to help alleviate stress. One effective technique is practicing relaxation exercises. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can help calm the mind and body, reducing stress levels. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as yoga, jogging, or dancing, is another powerful stress management tool. Exercise releases endorphins, which act as natural mood lifters and stress reducers. Additionally, finding healthy outlets for stress, such as engaging in creative activities like painting, writing, or playing a musical instrument, can provide a cathartic release and promote emotional well-being. Building a strong support system is also crucial for stress reduction. Talking to trusted friends, family, or a therapist can help alleviate stress by providing emotional support and perspective. Incorporating stress management techniques into one’s daily routine, such as meditation or mindfulness practices, can cultivate a sense of calm and resilience in the face of stress. By implementing these stress reduction techniques, individuals can reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares caused by stress and improve their overall sleep quality.
2. Sleep Hygiene Practices
Implementing good sleep hygiene practices can be a valuable tool in managing stress-related nightmares and improving overall sleep quality. Here are some tips to consider:
1. Establish a consistent sleep schedule: Aim to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, including weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock and enhances the quality of your sleep.
2. Create a comfortable sleep environment: Make sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet to promote optimal sleep conditions. Consider using earplugs, eye masks, or white noise machines to block out any disturbances.
3. Avoid electronic devices before bed: The blue light emitted by screens can interfere with your sleep-wake cycle. Try to limit or eliminate the use of electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and computers, at least one hour before bedtime.
4. Establish a pre-bedtime routine: Engage in relaxing activities before sleep, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing meditation. This signals to your body that it’s time to unwind and prepares you for a restful night’s sleep.
5. Avoid stimulants and heavy meals: Limit caffeine intake, especially in the afternoon and evening, as it can interfere with falling asleep. Additionally, avoid large, heavy meals close to bedtime as digestion can disrupt sleep.
6. Exercise regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can promote better sleep. However, try to avoid intense workouts too close to bedtime as they can increase alertness and make it harder to fall asleep.
7. Manage stress: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or journaling. By reducing overall stress levels, you can improve your ability to relax and sleep peacefully.
By adopting these sleep hygiene practices, you can create a conducive sleep environment and establish a healthy sleep routine. These habits can help regulate your sleep patterns, reduce the occurrence of stress-related nightmares, and promote a more restful night’s sleep.
3. Therapy and Cognitive Techniques
When it comes to managing stress-related nightmares, therapy and cognitive techniques play a crucial role. Here are three effective approaches:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely used therapeutic approach that aims to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. In the context of nightmares, CBT techniques can help individuals challenge and reframe their distressing dream content. This may involve keeping a dream journal, practicing relaxation exercises before sleep, and engaging in imagery rehearsal therapy, where the individual imagines a new, positive ending to their nightmares. CBT can also target underlying anxiety and stress that contribute to nightmares, providing individuals with coping strategies to reduce overall psychological distress and improve sleep quality.
2. Exposure Therapy: This technique involves gradually exposing oneself to the triggering elements of their nightmares in a safe and controlled manner. By repeatedly confronting the fear-inducing aspects of the dreams, individuals can desensitize themselves and reduce the emotional intensity associated with the nightmares. This can be facilitated through virtual reality simulations, guided imagery, or in vivo exposure exercises. Exposure therapy can help individuals regain a sense of control over their dreams and reduce the frequency and intensity of stress-related nightmares.
3. Mindfulness-Based Techniques: Mindfulness practices involve focusing attention on the present moment, accepting thoughts and emotions without judgment, and cultivating a sense of awareness and relaxation. Mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can be beneficial in managing stress-related nightmares. By incorporating mindfulness into their daily routine, individuals can develop greater emotional regulation and resilience, which can positively impact their dream patterns. Mindfulness-based therapies may also address underlying stressors and promote overall well-being, contributing to a reduction in nightmares.
Remember, therapy and cognitive techniques should be implemented under the guidance of a qualified mental health professional. Every individual’s experience with nightmares is unique, and a personalized approach is essential for effective management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the connection between stress and nightmares is a fascinating subject that highlights the intricate relationship between our mental and physical well-being. Stress can significantly impact our dream patterns, leading to an increase in nightmare frequency and intensity. Understanding the science behind stress is crucial in unraveling this connection. Psychological associations, neurological impact, and emotion regulation all play a role in linking stress to nightmares. However, it’s important to note that not all nightmares are stress-related, as anxiety and trauma can also contribute to their occurrence. Managing stress-related nightmares requires a multi-faceted approach, including stress reduction techniques, sleep hygiene practices, and therapy. By implementing these strategies and addressing the root causes of stress, individuals can improve their sleep quality and mitigate the negative effects of nightmares. So, take a proactive approach to managing stress, and remember, a good night’s sleep is within reach.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can stress cause nightmares?
Yes, stress can lead to an increase in nightmares. When we experience high levels of stress, our brain may incorporate stressful thoughts and emotions into our dreams, resulting in more frequent or vivid nightmares.
2. What are some common triggers for stress-related nightmares?
Triggers for stress-related nightmares can vary from person to person. However, common triggers may include traumatic experiences, significant life changes, work-related stress, relationship conflicts, or financial difficulties.
3. Are nightmares a sign of a mental health disorder?
While nightmares can be a symptom of certain mental health disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or anxiety disorders, experiencing occasional nightmares is generally considered normal. However, frequent or disturbing nightmares that significantly affect sleep quality should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
4. Does poor sleep quality contribute to stress-related nightmares?
Yes, poor sleep quality can contribute to stress-related nightmares. When we don’t get enough restful sleep, our stress levels can increase, making us more susceptible to nightmares. It becomes a vicious cycle, with nightmares disrupting sleep and sleep disturbances heightening stress levels.
5. Are there any natural remedies to reduce stress-related nightmares?
While natural remedies may not eliminate stress-related nightmares completely, practices such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce overall stress levels, potentially leading to a decrease in nightmares.
6. Can medication help in managing stress-related nightmares?
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage the symptoms of stress-related nightmares. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can evaluate your specific situation and recommend appropriate treatment options, as medication is not suitable or necessary for everyone.
7. How does journaling help with stress-related nightmares?
Journaling can be a helpful tool for managing stress and nightmares. By writing down your thoughts and emotions before bed, you can potentially release any pent-up stress or worries, allowing for a more peaceful sleep. Additionally, journaling can provide insights into patterns or triggers that may be contributing to your nightmares.
8. Can therapy be beneficial for individuals experiencing stress-related nightmares?
Yes, therapy can be beneficial for individuals experiencing stress-related nightmares. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic techniques can help identify and address underlying sources of stress, develop coping mechanisms, and provide support in managing nightmares and improving overall sleep quality.
9. Are there specific foods that can aggravate stress-related nightmares?
While the effect of specific foods on nightmares is not well-documented, consuming heavy or spicy meals close to bedtime may disrupt sleep, potentially increasing the likelihood of nightmares. It is generally recommended to have a light, balanced meal and avoid consuming caffeine or alcohol close to bedtime.
10. Should I be concerned if I experience stress-related nightmares occasionally?
Experiencing occasional stress-related nightmares is generally considered normal. However, if nightmares begin to occur frequently or severely impact your daily life, it may be beneficial to seek advice from a healthcare professional who can provide guidance and support in managing stress and improving sleep quality.